Comparison of implant primary stability between maxillary edentulous ridges receiving intramembranous origin block grafts
|
|
|
- Teresa Dalton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi: /medoral Comparison of implant primary stability between maxillary edentulous ridges receiving intramembranous origin block grafts Alberto Monje 1, Florencio Monje 2, Fernando Suárez 1, Raúl González-García 2, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol 2, Agustín García-Nogales 3, Pablo Galindo-Moreno 4, Hom-Lay Wang 1 1 D.D.S. D.D.S. D.D.S., M.S., PhD. Graduate Periodontics, Department of Periodontics and Oral Medicine, University of Michigan School of Dentistry, Ann Arbor, MI, USA 2 MD, PhD. MD, PhD. MD. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon, CICOM, Center of Implantology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Badajoz, Spain 3 PhD. Department of Mathematics, University of Extremadura, Badajoz, Spain 4 D.D.S., PhD Professor of Oral Surgery, Department of Oral Surgery, University of Granada, Granada, Spain Correspondence: Calle Juan Miró s/n, local Badajoz Spain amonjec@umich.edu Received: 19/08/2012 Accepted: 14/11/2012 Monje A, Monje F, Suárez F, González-García R, Villanueva-Alcojol L, García-Nogales A, Galindo-Moreno P, Wang HL. Comparison of implant primary stability between maxillary edentulous ridges receiving intramembranous origin block grafts. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal May 1;18 (3):e Article Number: Medicina Oral S. L. C.I.F. B pissn eissn: medicina@medicinaoral.com Indexed in: Science Citation Index Expanded Journal Citation Reports Index Medicus, MEDLINE, PubMed Scopus, Embase and Emcare Indice Médico Español Abstract Purpose: The purposes of the present study were: to compare the resonance frequency analysis (RFA) values of implant placed in either ramus or calvaria block grafts; and to determine if implant diameter influences RFA implant stability quotient (ISQ) value. Material and Methods: This was a retrospective study that included 16 consecutives healthy patients treated with autogenous onlay block grafts for horizontal bone reconstruction in maxilla. Ten ramus and ten calvaria block graft treated patients were selected and compared. Results: Totally, 59 implants were placed, 35 (59.3%) were placed on the calvaria bone grafts and the remaining 24 (40.7%) were on the ramus bone graft. Of all the implants studied, 13 (22%), 35 (59.3%), and 11 (18.6%) were 10 mm, 11.5 mm and 13 mm in length respectively. Regarding the diameter, 4 (7%) were 3.3 mm, 3 (5%) were 3.5 mm, 20 (34%) were 3.7 mm and 32 (54%) were 4 mm. Mean ISQ value obtained by RFA was ± 6.08, being ± 6 and ± 6.06 for the calvaria and ramus treated group respectively. No significant differences were noted between the two groups (p= 0.154). Implants were pooled and divided by their diameter. Mean ISQ value obtained for 3.3 mm was 80 ± 5.09, while for 4.0 mm was 72.5 ± Again, no significant differences were found among the groups (p= 0.138). Conclusion: For RFA ISQ value, the bone graft origins (calvaria or ramus) or implant diameters did not influence the outcome. Key Words: Bone augmentation, dental implant, resonance frequency analysis, implant stability. e449
2 Introduction The term osseointegration is defined as the close contact between bone and implant material in histological observations and, in clinical terms, as the ankylosis of the implant in bone (1), the absence of mobility represents the primary clinical manifestation of osseointegration. For that, a noninvasive quantitative method for measuring the implant stability was sought out. In 1996, resonance frequency analysis (RFA) was developed and used implant stability quotient (ISQ) as a quantitative unit to assess implant stability (2). It has been reported that RFA ISQ value ranged form 57 to 82 after 1 year of loading (3). Maxillary bone resorption often results in a ridge that is inadequate for ideal implant placement (4). In order to overcome these challenges, different bone-grafting procedures and materials have been proposed and used in attempts to provide enough height and width for proper implant placement. Many procedures such as sinus lifting (5) or guided bone regeneration (GBR) (6) have been shown to be predictable for bone augmentation. However, autogenous bone block grafting is still considered the gold standard in extensive reconstruction of the maxilla (7). Creping substitution is known as the process of bone remodeling, where new bone replaces the necrotic bone, being a longer process in cortical bone (8). Intraoral autogenous grafts have several benefits as well as limitations. It has less amount of bone resorption after healing when compared to endochondral oriented bones (9). In addition, the graft harvesting can be performed in the same surgery and under local anesthesia (10). However, morbidity of their donor site and amount of availability represent the main disadvantages. On the contrary, calvararium is a useful donor site that provides a large amount of intramembranous bone to rebuild the atrophic posterior maxilla. Adding bone substitutes such as particular bone around the autogenous graft to fill the gaps is often performed when doing a big block graft to serve as a scaffold for space maintenance and filler. Generally speaking membrane is not needed when doing the block graft since block can provide the coverage by itself (11,12). However, a collagen absorbable membrane, covering the graft may be suggested, due to its biologic advantages such as the higher stimulation of DNA synthesis over non-resorbables membranes (13). It has been suggested that the stiffness of the bone might influence RFA (14), hence the purpose of the present study was to compare the ISQ values of intramembranous origin block grafts, either ramus or calvarium, for horizontal bone augmentation in the maxilla. Additionally, the influence of implant diameter upon ISQ value was also evaluated. Material and Methods Sixteen partially edentulous consecutive health patients requiring extensive horizontal bone reconstruction in the maxilla were included in this study. An overall of 20 onlay block grafts were placed. These were harvested either from the ramus (10) or the calvaria (10). Written consent of each subject was signed prior to treatment. -Surgical protocol Ramus block graft Under local anesthesia with intravenous sedation, an incision was performed in the posterior mandible following the external oblique line of the mandible. A full-thickness flap was reflected exposing the lateral aspect of the ramus. Rectangular-shape grafts were harvested. At the recipient site, a mid-crestal incision was performed with intrasulcular and vertical releasing incisions on the adjacent teeth. A full-thickness flap was reflected to expose the recipient area. Ramus block grafts were adapted to the recipient sites and anchored to the alveolar residual bone by two 1.5mm diameter titanium fixation screws (Level One 1.5 Neuro, KLS Martin LP, FL, USA). After achieving stability of the graft, sharp edges of the graft were smoothened using a fissure bur. - Calvaria block graft Under general anesthesia with local anesthesia, an incision was performed in the parietal area, parallel to the cranial major axis. Rectangular-shape grafts of the calvaria were marked with a fissure bur and harvested using very gently chisels. A full-thickness flap was reflected to expose the recipient area. Calvaria block grafts were adapted to the recipient sites and anchored to the alveolar residual bone by two 1.5mm diameter titanium fixation screws (Level One 1.5 Neuro, KLS Martin LP, FL, USA). After achieving stability of the graft, sharp edges of the graft were smoothened using a fissure bur. -Resonance frequency analysis The technique of RFA measurement followed manufacturer s recommendations. Basically, a small, precision-crafted metal rod was screwed into the implant side thread. Then, the handheld probe was placed close to the rod first at the midfacial side and the ISQ value, ranging from 1 to 100, was generated and recorded. Immediately after implant placement, implant stability was measured with using Ostell Mentor (Integration Diagnostics AB, Göteborg, Sweden). The Smartpeg (Integration Diagnostics AB, Göteborg, Sweden) was attached to the implant with 4-5 Ncm of torque. Two measurements were taken and the averages were calculated to reduce measurements errors. -Statistics Statistical package SPSS 13.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and StatSoft, Inc. (2006) STATISTICA (data analysis software system), version 7.1. were used to analyze the data. Descriptive statistical analysis for continuous and categorical variables was performed. Student s t-test for unpaired samples was used to analyze the influence of implant diameter in primary stability measured by RFA. P value 0.05 was considered statistically significant. e450
3 Results A total of 20 onlay block grafts were placed in the maxilla. These were harvested either from the ramus (10) or the calvarial (10) depending of the amount of graft needed (calvarial > ramus). On them, an overall of 59 implants were placed, being 35 (59.3%) of them placed on calvaria bone grafts (Table 1) and 24 (40.7%) on ramus bone graft (Table 2). Mean age of the patients included in the study was 43.8 years old, with a 3:7 male: female distribution. All implants were stable and no mobility was present at the time of prosthesis delivery (4 to 6 months after implant placement). -Implant length and diameter Of all the implants studied, 13 (22%), 35 (59.3%), and 11 (18.6%) were 10 mm, 11.5 mm and 13 mm in length respectively. Regarding the diameter, 4 (7%) were 3.3 mm, 3 (5%), 20 (34%) and 32 (54%) 3.3 mm, 3.5 mm, 3.7 mm and 4 mm, respectively (Fig. 1). -RFA between both groups Mean ISQ value was ± 6.08, being ± 6 for the calvaria group and ± 6.06 for the ramus group (Fig. 2). Median ISQ value obtained was 73 for both groups. No significant differences were observed between both groups (p= 0.154) following the application of the Student s t-test for unpaired data. RFA between implant diameters Implants were pooled and divided by their diameter. Mean ISQ value obtained for 3.3 mm (the narrowest implant diameter group) was 80 ± 5.09, while for 4.0 mm (the widest implant diameter group) was 72.5 ± Mean ISQ values for 3.5 mm and 3.7 mm implants were ± 4.04 and ± 7.19, respectively (Fig. 3). Median ISQ values found were 81 for 3.3 mm, 73 for 3.5 mm, 72 for 3.7 mm and 74 for 4 mm implants. Again, no significant differences were found among any groups (p= 0.138). However, there is a trend of higher ISQ val- Table 1. Distribution of the onlay grafts harvested from the calvaria. Implants Mean ISQ Onlay graft no. Age Sex Edentulism Recipient site (N) value 1 22 M P Anterior M P Anterior F P Anterior/posterior F P Anterior/posterior F P Anterior/posterior F P Anterior/posterior F P Anterior/posterior F P Anterior/posterior F P Anterior/posterior F P Anterior/posterior 4 79 Table 2. Distribution of the onlay grafts harvested from the ramus. Onlay graft no. Age Sex Edentulism Recipient site Implants (N) Mean ISQ value F P Anterior M P Anterior M P Anterior M P Posterior F P Anterior/posterior M P Anterior F P Posterior F P Posterior F P Anterior F P Anterior 1 69 e451
4 7% 5% Implant diameter (mm) % 34% Fig. 1. Implant distribution by diameter. Fig. 2. Plot for mean implant stability quotient (ISQ) values from calvaria and ramus groups. ue for narrower implants. Nonetheless, it is noteworthy that 3.3 mm and 3.5 mm groups have small sample size (4 and 3 implants, respectively) in comparison with the other two groups analyzed. Hence, precautions should be exercised when interpreting the results of this study. Discussion Primary implant stability plays the most important role in the success of osseointegration (16). However, bone resorption/remodeling of the maxilla after tooth loss often result in a residual ridge where primary stability can e452
5 ISQ A B C D DIAMETER (cualit) Mean Mean±0,95 Conf. Interval Fig. 3. Plot for mean implant stability quotient (ISQ) values for implant diameters analyzed. A. 3.3 mm, B. 3.5 mm, C. 3.7 mm and D. 4.0 mm. not be obtained (4). In these cases, bone-grafting procedures are often required in order to place implants in proper 3 dimensional positions. Autogenous block graft remains to be the gold standard for bone augmentation. The sites for harvesting the autogenous bone graft can be obtained either from intraoral such as ramus and chin or extraoral such as calvaria or iliac crest. While iliac crest belongs to endochondral origin bone, the other three mentioned are grafts of intramembranous origin. At this moment, there is no study that compares the implant stability outcome between these 2 distinct intramembraneous origin autogenous bone. Henceforth, the aim of study was to assess the ISQ on implants placed upon either ramus or calvaria bone blocks. A quantitative measurement of implant stability, such as RFA, is essential prior to implant restoration. Stability is defined as a measure of the difficulty of displacing an object or system from equilibrium (17). Thus, implant stability could be considered as the absence of mobility, and this has been considered as the clinical meaning of the histologic term osseointegration. Many methods have been proposed to assess initial osseointegration (18). However, most of them are no longer available due to their invasiveness and inaccuracy (18). RFA used ISQ as a quantitative unit to assess implant stability has become a main tool these days for assessing implant stability (2). It is dependent of 3 main factors: (1) the stiffness of the implant fixture and its interface with the surrounding tissues, (2) the design of the transducer and (3) the total effective length above the bone level (19). It uses a small L-shape transducer that is tightened to the implant by a screw. This transducer comprises 2 piezoceramic elements, one vibrating by a sinusoidal sign (5 to 15 Hz) while the other serves as a receptor (20). It has been reported that RFA ISQ value ranged form 57 to 82 after 1 year of loading (3). Hence, values < 50 may be an assumption of potential risk of failure (20). Results obtained from this study showed there was no significant difference on RFA ISQ value between implant placed on ramus and calvaria bone block. This suggests that intramembranous bone after healing, regardless of their locations, matures and converts in host bone. Additionally, both locations show to have the same ability to support implant placement. Intramembranous bone heals with thicker trabeculae and lower connectivity than endochondral origin bone (9). Hence, they show less resorption and higher revascularization when compared to endochondral origin bone (21). These reasons may explain the good behavior supporting implants providing them of high mechanical stability in order to achieve secondary implant stability. The present study shows that when they were incorporated into host bone in the attempt to support implant placement/stability, they behave similar (p= 0.154). The correlation between implant diameter and RFA ISQ value was conducted and result demonstrated there was no correlation (p=138). This implies that as long as implant is integrated into bone no mater what diameter is, the reading remain to be similar. Since the RFA is used to detect implant stability, the finding does not surprise to us. In this study, we did not examine the influence of implant length upon RFA ISQ value since early studies have clearly demonstrated that as long as implant is integrated no matter what length is the value remained to be the same (15). Hence, no attempt was done in this experiment to look into this relationship. Even though, e453
6 this is the first study that examined the correlation between implant diameters of implants placed in ridges grafted by autogenous block grafts and ISQ. Nonetheless, two studies looked at relationship between implant width and ISQ values, and both found that ISQ values were not influenced by the implant diameter (22,23) as observed in our study. Interestingly, implant width has been reported a major factor (more than length) to support prosthetic load (15). This is due to the role that plays the width of the coronal aspect of the implant in concentrating higher loads (15). It has been shown that increasing 0.5 mm in implant width provides 10%-15% more implant surface (15). Subsequently, it may be due to the greater bone-to-implant interface that achieves higher degree of osseointegration. Hence, it was assumed that wider implants provide higher ISQ values. However, our results and others contradict this assumption (22,23). Conclusion RFA shows to be a reliable and noninvasive technique to foresee short-term implant stability in values over 70 for implants supported by bone block grafts. Furthermore, the origin of the intramembranous bone graft used for horizontal bone augmentation in the maxilla did not influence the outcome of ISQ values (p=0.154). In addition, no correlation was established between implant diameter and ISQ value (p= 0.138). References 1. Albrektsson T, Zarb GA. Current interpretations of the osseointegrated response: clinical significance. Int J Prosthodont. 1993;6: Meredith N, Alleyne D, Cawley P. Quantitative determination of the stability of the implant-tissue interface using resonance frequency analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1996;7: Balleri P, Cozzolino A, Ghelli L, Momicchioli G, Varriale A. Stability measurements of osseointegrated implants using Osstell in partially edentulous jaws after 1 year of loading: a pilot study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2002;4: Pietrokovski J, Massler M. Alveolar ridge resorption following tooth extraction. J Prosthet Dent. 1967;17: Wallace SS, Froum SJ. Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants. A systematic review. Ann Periodontol. 2003;8: Hammerle CH, Jung RE, Feloutzis A. A systematic review of the survival of implants in bone sites augmented with barrier membranes (guided bone regeneration) in partially edentulous patients. J Clin Periodontol. 2002;29 Suppl3: Tessier P, Kawamoto H, Matthews D, Posnick J, Raulo Y, Tulasne JF, et al. Autogenous bone grafts and bone substitutes--tools and techniques: I. A 20,000-case experience in maxillofacial and craniofacial surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116 Suppl5:6S-24S. 8. Burchardt H. The biology of bone graft repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;174: Zins JE, Whitaker LA. Membranous versus endochondral bone: implications for craniofacial reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1983;72: Schwartz-Arad D, Levin L. Intraoral autogenous block onlay bone grafting for extensive reconstruction of atrophic maxillary alveolar ridges. J Periodontol. 2005;76: Proussaefs P, Lozada J. The use of intraorally harvested autogenous block grafts for vertical alveolar ridge augmentation: a human study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2005;25: Triplett RG, Schow SR. Autologous bone grafts and endosseous implants: complementary techniques. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996;54: Marinucci L, Lilli C, Baroni T, Becchetti E, Belcastro S, Balducci C, et al. In vitro comparison of bioabsorbable and non-resorbable membranes in bone regeneration. J Periodontol. 2001;72: Zix J, Kessler-Liechti G, Mericske-Stern R. Stability measurements of 1-stage implants in the maxilla by means of resonance frequency analysis: a pilot study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2005;20: Capek L, Simunek A, Slezak R, Dzan L. Influence of the orientation of the Osstell transducer during measurement of dental implant stability using resonance frequency analysis: a numerical approach. Med Eng Phys. 2009;31: Sennerby L, Roos J. Surgical determinants of clinical success of osseointegrated oral implants: a review of the literature. Int J Prosthodont. 1998;11: Sennerby L, Meredith N. Implant stability measurements using resonance frequency analysis: biological and biomechanical aspects and clinical implications. Periodontol ;47: Huang HM, Lee SY, Yeh CY, Lin CT. Resonance frequency assessment of dental implant stability with various bone qualities: a numerical approach. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002;13: Chan HL, El-Kholy K, Fu JH, Galindo-Moreno P, Wang HL. Implant primary stability determined by resonance frequency analysis in surgically created defects: a pilot cadaver study. Implant Dent. 2010;19: Atsumi M, Park SH, Wang HL. Methods used to assess implant stability: current status. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2007;22: Vinci R, Rebaudi A, Cappare P, Gherlone E. Microcomputed and histologic evaluation of calvarial bone grafts: a pilot study in humans. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2011;31:e Pattijn V, Van Lierde C, Van der Perre G, Naert I, Vander Sloten J. The resonance frequencies and mode shapes of dental implants: Rigid body behaviour versus bending behaviour. A numerical approach. J Biomech. 2006;39: Gonzalez-Garcia R, Monje F, Moreno-Garcia C. Predictability of the resonance frequency analysis in the survival of dental implants placed in the anterior non-atrophied edentulous mandible. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011;16:e Acknowledgements The authors want to thanks FEDICOM Foundation (Foundation for the study of Implantology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery), Badajoz, Spain for financial support. Also, they want to thank to Ms. Purificación Barragán, Center of Implantology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (CICOM), Badajoz, Spain, for her valuable helping in order to collect and organize the data included in this study. Agustín García-Nogales has been partially supported by the spanish Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología under the project MTM and the Junta de Extremadura(Autonomous Government of Extremadura) under the project GR Disclaimer The authors do not have any financial interests, either directly or indirectly, in the products or information listed in the paper. e454
Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla
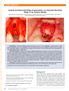 CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
P rimary or mechanical implant
 IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 0, NUMBER 0 2013 1 Effect of Location on Primary Stability and Healing of Dental Implants Alberto Monje, DDS,* Fernando Suarez, DDS,* Carlos Andrés Garaicoa, DDS, Florencio Monje,
IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 0, NUMBER 0 2013 1 Effect of Location on Primary Stability and Healing of Dental Implants Alberto Monje, DDS,* Fernando Suarez, DDS,* Carlos Andrés Garaicoa, DDS, Florencio Monje,
e153 Resident, Department of Periodontics and Oral Medicine, University of Michigan School of Dentistry, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA.
 e153 Comparison of Microstructures Between Block Grafts from the Mandibular Ramus and Calvarium for Horizontal Bone Augmentation of the Maxilla: A Case Series Study Alberto Monje, DDS 1 /Florencio Monje,
e153 Comparison of Microstructures Between Block Grafts from the Mandibular Ramus and Calvarium for Horizontal Bone Augmentation of the Maxilla: A Case Series Study Alberto Monje, DDS 1 /Florencio Monje,
Predictability of the resonance frequency analysis in the survival of dental implants placed in the anterior non-atrophied edentulous mandible
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.16982 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.16982 Predictability of the resonance frequency analysis in the survival of dental
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.16982 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.16982 Predictability of the resonance frequency analysis in the survival of dental
Horizontal Bone Augmentation using Autogenous Block Grafts and Particulate
 Horizontal Bone Augmentation using Autogenous Block Grafts and Particulate Xenograft in the Severe Atrophic Maxillary Anterior Ridges: A Cone-beam Computed tomography Case Series Alberto Monje (corresponding
Horizontal Bone Augmentation using Autogenous Block Grafts and Particulate Xenograft in the Severe Atrophic Maxillary Anterior Ridges: A Cone-beam Computed tomography Case Series Alberto Monje (corresponding
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Ridge resorption resulting from tooth loss often
 CLINICAL Horizontal Bone Augmentation Using Autogenous Block Grafts and Particulate Xenograft in the Severe Atrophic Maxillary Anterior Ridges: A Cone-Beam Computerized Tomography Case Series Alberto Monje,
CLINICAL Horizontal Bone Augmentation Using Autogenous Block Grafts and Particulate Xenograft in the Severe Atrophic Maxillary Anterior Ridges: A Cone-Beam Computerized Tomography Case Series Alberto Monje,
Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Key Words: bone graft, mandibular ramus, iliac crest, horizontal bone augmentation, block graft
 CLINICAL Horizontal Bone Augmentation Using Autogenous Block Grafts and Particulate Xenograft in the Severe Atrophic Maxillary Anterior Ridges: A Cone-Beam Computerized Tomography Case Series Alberto Monje,
CLINICAL Horizontal Bone Augmentation Using Autogenous Block Grafts and Particulate Xenograft in the Severe Atrophic Maxillary Anterior Ridges: A Cone-Beam Computerized Tomography Case Series Alberto Monje,
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Posterior mandible and vertical augmentation
 CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Annals of Dental Research
 P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
Long-term success for osteointegrated
 CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
Osseointegrated implants are a very reliable means
 Tridimensional Reconstruction of Knife-Edge Edentulous Maxillae by Sinus Elevation, Onlay Grafts, and Sagittal Osteotomy of the Anterior Maxilla: Preliminary Surgical and Prosthetic Results Matteo Chiapasco,
Tridimensional Reconstruction of Knife-Edge Edentulous Maxillae by Sinus Elevation, Onlay Grafts, and Sagittal Osteotomy of the Anterior Maxilla: Preliminary Surgical and Prosthetic Results Matteo Chiapasco,
Oral Health and Dentistry
 Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up
 Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
Case study 2. A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant
 Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Hiron Andreaza da Cunha, MS 1 /Carlos Eduardo Francischone, DMD 2 /Hugo Nary Filho, DDS 3 / Rubelisa Cândido Gomes de Oliveira, BDS 4
 A Comparison Between Cutting Torque and Resonance Frequency in the Assessment of Primary Stability and Final Torque Capacity of and TiUnite Single-Tooth Implants Under Immediate Loading Hiron Andreaza
A Comparison Between Cutting Torque and Resonance Frequency in the Assessment of Primary Stability and Final Torque Capacity of and TiUnite Single-Tooth Implants Under Immediate Loading Hiron Andreaza
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Envelope approach for onlay bone grafting: Preliminary surgical and prosthetic results
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.16.e45 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.16.e45 : Preliminary surgical and prosthetic results Federico Hernández-Alfaro
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.16.e45 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.16.e45 : Preliminary surgical and prosthetic results Federico Hernández-Alfaro
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban
 Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
TOPICS. T O P I C S Day 1. Implant Locations. Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla. Anatomy and risk factors Option 1: Short implants
 T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE
 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT. simultaneous implant placement and is an alternative Summer s osteotome both clinical use as well as the
 BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT AUTHORS: Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD*, João Carlos Paixão** ABSTRACT: Bone spreading technique (BST) is horizontal augmentation with minimal trauma for simultaneous
BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT AUTHORS: Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD*, João Carlos Paixão** ABSTRACT: Bone spreading technique (BST) is horizontal augmentation with minimal trauma for simultaneous
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft
 Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
In 1981, Dr. Albrektsson, a member of
 Osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability in the maxilla: part II case report with 2-year follow-up Drs. Ann Marie Hofbauer and Salah Huwais offer another case study
Osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability in the maxilla: part II case report with 2-year follow-up Drs. Ann Marie Hofbauer and Salah Huwais offer another case study
DEVELOPMENT OF PREDICTABLE STABILITY TEST FOR ASSESSMENT OF OPTIMUM LOADING TIME IN DENTAL IMPLANT
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI:10.4047/jkap.2008.46.6.628 DEVELOPMENT OF PREDICTABLE STABILITY TEST FOR ASSESSMENT OF OPTIMUM LOADING TIME IN DENTAL IMPLANT Seong-Kyun Kim 1, DDS, PhD, Seong-Joo Heo 2, DDS, PhD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI:10.4047/jkap.2008.46.6.628 DEVELOPMENT OF PREDICTABLE STABILITY TEST FOR ASSESSMENT OF OPTIMUM LOADING TIME IN DENTAL IMPLANT Seong-Kyun Kim 1, DDS, PhD, Seong-Joo Heo 2, DDS, PhD,
Resonance frequency analysis-reliability in third generation instruments: Osstell mentor
 Journal section: Periodontology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17861 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17861 Resonance frequency analysis-reliability in third generation instruments:
Journal section: Periodontology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17861 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17861 Resonance frequency analysis-reliability in third generation instruments:
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Volume changes of autogenous bone grafts after alveolar ridge augmentation of atrophic maxillae and mandibles
 Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009; 38: 1059 1065 doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2009.06.024, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com Clinical Paper Pre-Implant Surgery Volume changes of autogenous bone
Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009; 38: 1059 1065 doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2009.06.024, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com Clinical Paper Pre-Implant Surgery Volume changes of autogenous bone
Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material- A case Report
 A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
Moderately to severely resorbed edentulous
 The Zygomatic Implant: Preliminary Data on Treatment of Severely Resorbed Maxillae. A Clinical Report Edmond Bedrossian, DDS, FACD, FACOMS 1 /Lambert Stumpel III, DDS 2 / Michael Beckely, DDS 3 /Thomas
The Zygomatic Implant: Preliminary Data on Treatment of Severely Resorbed Maxillae. A Clinical Report Edmond Bedrossian, DDS, FACD, FACOMS 1 /Lambert Stumpel III, DDS 2 / Michael Beckely, DDS 3 /Thomas
Intramembranous autogenous bone graft is the gold
 CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
Years of research and advancement in
 Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
 227 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 4, 227-232, 2003 Case report Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
227 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 4, 227-232, 2003 Case report Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft
 The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
10 Years of XiVE Implantology Unlimited
 10 Years of XiVE Implantology Unlimited Implantology Unlimited is obligate for XiVE and every limit gives always a push to surrender new challenges: Primary stability in low bone quality? No problem with
10 Years of XiVE Implantology Unlimited Implantology Unlimited is obligate for XiVE and every limit gives always a push to surrender new challenges: Primary stability in low bone quality? No problem with
The Brånemark osseointegration method, using titanium dental implants (fixtures)
 Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Maxillary Sinus Lateral Wall Thickness and Their Morphologic Patterns in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla
 Maxillary Sinus Lateral Wall Thickness and Their Morphologic Patterns in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla Alberto Monje, D.D.S.*, Andrés Catena PhD Florencio Monje, MD, PhD, Raúl Gonzalez-García MD, PhD,
Maxillary Sinus Lateral Wall Thickness and Their Morphologic Patterns in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla Alberto Monje, D.D.S.*, Andrés Catena PhD Florencio Monje, MD, PhD, Raúl Gonzalez-García MD, PhD,
The Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique. Jia-Hui Fu* and Hom-Lay Wang*
 CASE REPORT The Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique Jia-Hui Fu* and Hom-Lay Wang* Introduction: Horizontal ridge width reduction after tooth extraction is a common clinical scenario. As such, when implant-supported
CASE REPORT The Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique Jia-Hui Fu* and Hom-Lay Wang* Introduction: Horizontal ridge width reduction after tooth extraction is a common clinical scenario. As such, when implant-supported
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Comprehensive Dental Implantology
 Comprehensive Dental Implantology Surgical Course Presented by: Dr Chan Siew Luen BDS (Singapore) MDS Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (HK) FAMS (Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery) CPE TBC 3 Modules covering topics
Comprehensive Dental Implantology Surgical Course Presented by: Dr Chan Siew Luen BDS (Singapore) MDS Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (HK) FAMS (Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery) CPE TBC 3 Modules covering topics
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
Deep-Frozen Allogeneic Onlay Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Atrophic Maxillary Alveolar Ridges: A Preliminary Study
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:1300-1306, 2009 Deep-Frozen Allogeneic Onlay Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Atrophic Maxillary Alveolar Ridges: A Preliminary Study Antonio Barone, DDS, PhD, MSc,* Paolo Varanini,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:1300-1306, 2009 Deep-Frozen Allogeneic Onlay Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Atrophic Maxillary Alveolar Ridges: A Preliminary Study Antonio Barone, DDS, PhD, MSc,* Paolo Varanini,
Augmentation in Two Stages of Atrophic Alveolar Bone Prior to Dental Rehabilitation: A Case Report
 Augmentation in Two Stages of Atrophic Alveolar Bone Prior to Dental Rehabilitation: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The aim of this report is to describe a significantly deficient case of alveolar bone that
Augmentation in Two Stages of Atrophic Alveolar Bone Prior to Dental Rehabilitation: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The aim of this report is to describe a significantly deficient case of alveolar bone that
Revisions for CDT 2016
 Revisions for CDT 2016 This document was developed from preliminary actions of the Code Maintenance Committee (CMC). This document has been compared to the CMC meeting notes and the ASCII file. This document
Revisions for CDT 2016 This document was developed from preliminary actions of the Code Maintenance Committee (CMC). This document has been compared to the CMC meeting notes and the ASCII file. This document
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94
 ( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
BONE SPREADER TECHNIQUE: APRELIMINARY 3-YEAR STUDY Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, MSc, PhD; Francisley Avila Souza, DDS, MSc
 RESEARCH BONE SPREADER TECHNIQUE: APRELIMINARY 3-YEAR STUDY Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, MSc, PhD; Francisley Avila Souza, DDS, MSc The purpose of this study was to observe the clinical outcome of bone
RESEARCH BONE SPREADER TECHNIQUE: APRELIMINARY 3-YEAR STUDY Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, MSc, PhD; Francisley Avila Souza, DDS, MSc The purpose of this study was to observe the clinical outcome of bone
The use of endosseous implants is currently a routine
 Evaluation of 31 Zygomatic Implants and 74 Regular Dental Implants Used in 16 Patients for Prosthetic Reconstruction of the Atrophic Maxilla with Cross-Arch Fixed Bridges Jonas P. Becktor, DDS;* Sten Isaksson,
Evaluation of 31 Zygomatic Implants and 74 Regular Dental Implants Used in 16 Patients for Prosthetic Reconstruction of the Atrophic Maxilla with Cross-Arch Fixed Bridges Jonas P. Becktor, DDS;* Sten Isaksson,
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Intraoral and extraoral autologous bone block graft techniques: A review of the recent literature
 International Journal of Contemporary Dental and Medical Reviews (2016), Article ID 030316, 5 Pages REVIEW ARTICLE Intraoral and extraoral autologous bone block graft techniques: A review of the recent
International Journal of Contemporary Dental and Medical Reviews (2016), Article ID 030316, 5 Pages REVIEW ARTICLE Intraoral and extraoral autologous bone block graft techniques: A review of the recent
Dental Research Journal
 Dental Research Journal Original Article The effect of shape, length and diameter of implants on primary stability based on resonance frequency analysis Hamidreza Barikani, Shadab Rashtak, Soolmaz Akbari,
Dental Research Journal Original Article The effect of shape, length and diameter of implants on primary stability based on resonance frequency analysis Hamidreza Barikani, Shadab Rashtak, Soolmaz Akbari,
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
/TLv/ A classification of the edentulous jaws. Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery. iiiii!iii!iii! ] BASAL
![/TLv/ A classification of the edentulous jaws. Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery. iiiii!iii!iii! ] BASAL /TLv/ A classification of the edentulous jaws. Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery. iiiii!iii!iii! ] BASAL](/thumbs/72/66558540.jpg) Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery A classification of the edentulous jaws J. I. awood ~ and R. A. Howell 2 ~Maxillofacial Unit, Royal Infirmary, hester, UK, 2Liverpool Dental Hospital, Liverpool, UK J. L awood
Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery A classification of the edentulous jaws J. I. awood ~ and R. A. Howell 2 ~Maxillofacial Unit, Royal Infirmary, hester, UK, 2Liverpool Dental Hospital, Liverpool, UK J. L awood
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 07 Page July 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Endosseous cylindric implants are well accepted
 Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
Bone grafts are widely used in the reconstruction of
 RESEARCH Cone Beam Computerized Tomography Measurement of Alveolar Ridge at Posterior Mandible for Implant Graft Estimation Wenjian Zhang, DDS, MS, PhD 1 * Justin Tullis, BS 2 Robin Weltman, DDS, MS 3
RESEARCH Cone Beam Computerized Tomography Measurement of Alveolar Ridge at Posterior Mandible for Implant Graft Estimation Wenjian Zhang, DDS, MS, PhD 1 * Justin Tullis, BS 2 Robin Weltman, DDS, MS 3
Ridge Split Procedure
 Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Local Intraoral Autologous Bone Harvesting for Dental Implant Treatment: Alternative Sources and Criteria of Choice. Private Practice, Rome, Italy 2
 REVIEW Local Intraoral Autologous Bone Harvesting for Dental Implant Treatment: Alternative Sources and Criteria of Choice Federico Brugnami, 1 Alfonso Caiazzo 2 and Cataldo Leone 3 1 Private Practice,
REVIEW Local Intraoral Autologous Bone Harvesting for Dental Implant Treatment: Alternative Sources and Criteria of Choice Federico Brugnami, 1 Alfonso Caiazzo 2 and Cataldo Leone 3 1 Private Practice,
A comparative study on the initial stability of different implants placed above the bone level using resonance frequency analysis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2011.3.4.190 A comparative study on the initial stability of different implants placed above the bone level using resonance frequency analysis In-Ho Kang,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2011.3.4.190 A comparative study on the initial stability of different implants placed above the bone level using resonance frequency analysis In-Ho Kang,
Osstell ISQ. The objective way to measure implant stability.
 Osstell ISQ. The objective way to measure implant stability. www.osstell.com Three reasons why you need Osstell ISQ. Dr Tiziano Testori, Private Practice, Como, Italy: I use the Osstell meter as a quality-assurance
Osstell ISQ. The objective way to measure implant stability. www.osstell.com Three reasons why you need Osstell ISQ. Dr Tiziano Testori, Private Practice, Como, Italy: I use the Osstell meter as a quality-assurance
Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic. Review
 Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic Review A dissertation submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry (Oral and
Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic Review A dissertation submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry (Oral and
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla
 IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
POSSIBILITIES OF PROSTHETIC IMPLANT REHABILITATION USING VARIOUS BONE GRAFTING MATERIALS
 POSSIBILITIES OF PROSTHETIC IMPLANT REHABILITATION USING VARIOUS BONE GRAFTING MATERIALS Calin Tataru 1, Doriana Agop Forna 2, Norina Consuela Forna 1, 1. Department of Implantology, Removable Dentures,
POSSIBILITIES OF PROSTHETIC IMPLANT REHABILITATION USING VARIOUS BONE GRAFTING MATERIALS Calin Tataru 1, Doriana Agop Forna 2, Norina Consuela Forna 1, 1. Department of Implantology, Removable Dentures,
Vertical and horizontal alveolar ridge augmentation
 CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
Minimal invasive horizontal ridge augmentation using subperiosteal tunneling technique
 Kim et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2016) 38:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-016-0087-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Minimal invasive horizontal
Kim et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2016) 38:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-016-0087-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Minimal invasive horizontal
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft
 Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
 Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Atieh MA, Ibrahim HM, Atieh AH. J Periodontol. 2010 Oct;81(10):1350-66. BACKGROUND: Platform
Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Atieh MA, Ibrahim HM, Atieh AH. J Periodontol. 2010 Oct;81(10):1350-66. BACKGROUND: Platform
03 Best combination for thin ridge
 MILAkit TM BonEx kit TM 03 Best combination for thin ridge Joel A. Gonzales RDA Product Specialist Email: Cell: joelg@megagenus.com (480) 440-3927 Thor MEGAGEN Implant 28 29 Why Thor? 1. Simple & Strong
MILAkit TM BonEx kit TM 03 Best combination for thin ridge Joel A. Gonzales RDA Product Specialist Email: Cell: joelg@megagenus.com (480) 440-3927 Thor MEGAGEN Implant 28 29 Why Thor? 1. Simple & Strong
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Keywords: Biomechanics, Biostatistics, Maxilla, Maxillary sinus, Sinus floor augmentation.
 Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:58-63 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.2.58 Peri-implant bone length changes and survival rates of implants penetrating the
Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:58-63 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.2.58 Peri-implant bone length changes and survival rates of implants penetrating the
Predictable Synthetic Bone Grafting Procedures for Implant Reconstruction: Part Two
 CLINICAL ARTICLE IJCID Predictable Synthetic Bone Grafting Procedures for Implant Reconstruction: Part Two Predictable Synthetic Bone Grafting Procedures for Implant Reconstruction: Part Two 1 Scott D
CLINICAL ARTICLE IJCID Predictable Synthetic Bone Grafting Procedures for Implant Reconstruction: Part Two Predictable Synthetic Bone Grafting Procedures for Implant Reconstruction: Part Two 1 Scott D
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
Vertical Augmentation
 Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Outcomes of Calvarial Bone Grafting for Alveolar Ridge Reconstruction
 Outcomes of Calvarial Bone Grafting for Alveolar Ridge Reconstruction Rajesh Gutta, BDS, MS 1 /Peter D. Waite, MPH, DDS, MD 2 Purpose: This article describes a series of patients who underwent calvarial
Outcomes of Calvarial Bone Grafting for Alveolar Ridge Reconstruction Rajesh Gutta, BDS, MS 1 /Peter D. Waite, MPH, DDS, MD 2 Purpose: This article describes a series of patients who underwent calvarial
GUIDED BONE & TISSUE REGENERATION 2-DAY MASTERCLASS (CHOOSE LONDON OR PARIS) DR. ISABELLA ROCCHIETTA & DR. DAVID NISAND
 GUIDED BONE & TISSUE REGENERATION DR. ISABELLA ROCCHIETTA & DR. DAVID NISAND 2-DAY MASTERCLASS (CHOOSE LONDON OR PARIS) This hands-on course will be delivered in small group workshops and will equip the
GUIDED BONE & TISSUE REGENERATION DR. ISABELLA ROCCHIETTA & DR. DAVID NISAND 2-DAY MASTERCLASS (CHOOSE LONDON OR PARIS) This hands-on course will be delivered in small group workshops and will equip the
Identification of Stability Changes for Immediately Placed Dental Implants
 Identification of Stability Changes for Immediately Placed Dental Implants Jason D. West, DDS, MS 1 /Thomas W. Oates, DMD, PhD 2 Purpose: To evaluate the changes in stability of immediately placed implants
Identification of Stability Changes for Immediately Placed Dental Implants Jason D. West, DDS, MS 1 /Thomas W. Oates, DMD, PhD 2 Purpose: To evaluate the changes in stability of immediately placed implants
Young-Jin Park, DDS,* and Sung-Am Cho, DDS, MS, PhD
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
