Osseous allografts have been
|
|
|
- Vincent Young
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Periodontol November 2016 Fresh-Frozen Bone Allografts in Maxillary Alveolar Augmentation: Analysis of Complications, Adverse Outcomes, and Implant Survival Daniel Deluiz,* Luciano Oliveira, Paul Fletcher, Fábio R. Pires, Marcus A. Nunes, i and Eduardo M.B. Tinoco* Background: Success of any bone augmentation procedure is dependent on several factors. Because complications occur in some cases, the aims of this study are to analyze adverse events associated with placement of fresh-frozen bone allografts (FFBAs) during alveolar ridge augmentation and to assess 1-year survival of dental implants placed in reconstructed sites. Methods: Fifty-eight consecutive patients (15 males and 43 females, aged 38 to 76 years; mean age: years) requiring maxillary bone reconstruction prior to implant placement were enrolled in this study. A total of 268 implants was subsequently placed in sites reconstructed with FFBAs. There were 22 posterior grafted sites, 19 anterior, and 17 full-arch sites. After a 4- to 6-month integration period, all patients received an implant-supported fixed prostheses. Complications occurring during treatment and the 12-month follow-up period were recorded and evaluated. Results: Thirteen of 58 (22.41%) patients experienced some kind of complication in the receptor site. Infection occurred in six (10.34%) individuals, dehiscence in five (8.62%), and mucosal perforation in seven (12.07%). Adverse outcomes categorized as partial and total graft loss occurred in four (6.90%) and three (5.17%) patients, respectively. Implant failure rate was 16 (5.97%) of the 268 fixtures placed in 12 (20.70%) of 58 patients. Conclusions: Infection and suture dehiscence are significantly correlated with graft loss in a maxillary FFBA augmentation. Patients with full-arch grafting reconstructions lost significantly more implants. Early diagnosis and prompt management of adverse events seem to be of great importance in prevention of total graft loss. J Periodontol 2016;87: KEY WORDS Allografts; alveolar ridge augmentation; bone transplantation; graft survival; postoperative complications; wound healing. * Department of Periodontology, State University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Department of Implantology, Pontifícal Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Department of Periodontology, College of Dental Medicine, Columbia University, New York, NY. Department of Oral Pathology, State University of Rio de Janeiro. i Department of Statistics, Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte, Natal, Brazil. Osseous allografts have been widely used as a bone substitute during dental implant surgery. Depending on processing methods used, grafting materials with distinct characteristics have been developed. 1-5 The most common are: 1) freeze-dried bone allograft (FDBA); 2) demineralized FDBA; and 3) fresh-frozen bone allograft (FFBA). Each form has a precise clinical application and all are well-documented in the literature. 2,6,7 FFBA is a widely used substitute for autologous bone in large reconstructions when block grafts are indicated. 7-9 Numerous studies have shown both clinical evidence of alveolar ridge augmentation and histologic evidence of bone regeneration with use of this material. 7,9-15 While the osseous autograft has distinctive properties that make it the gold standard among grafting materials, 16 FFBA is available in unlimited supply and does not require a secondary harvesting site. Elimination of potential for secondary complications at a donor site represents a major benefit of its application Success of any bone augmentation procedure depends on factors ranging from accurate preoperative planning to a complete patient health evaluation as well as a thorough preoperative clinical assessment and proper surgical technique. doi: /jop
2 Outcomes of Fresh-Frozen Allografts in Alveolar Augmentation Volume 87 Number 11 In the case of block reconstructions, special attention must be paid to proper shaping and fixation of grafts. Tension-free closure of flaps is imperative as is an appropriate post-surgical medication therapy and rigorous follow-up. A well-adapted provisional prosthesis (fixed or removable) with no excessive occlusal pressure is also of paramount importance for ideal graft maturation Studies evaluating short-term receptor site outcomes of autografts and FDBA block ridge augmentation reported relatively low complication rates; 7,8,11,12,20,21,24-26 however, complications did occur. Most often, loss of soft tissue integrity at the receptor site led to loss of graft material, and contamination during the surgical procedure or inability of the patient to keep the surgical site clean led to local infection. 12,20,23,27-29 However, these complications did not necessarily lead to total failure of the grafting procedure. 20,27 To the best of the authors knowledge, no studies found in the literature assess prevalence of complications, defined as: 1) infection; 2) dehiscence or mucosal perforation; or 3) adverse outcomes, defined as partial or total graft loss or implant failure, after use of FFBA for maxillary augmentation. Aims of the present study are to analyze: 1) complications and subsequent adverse outcomes associated with use of FFBA in maxillary alveolar ridge onlay block graft augmentation and 2) 1-year survival of dental implants placed in these reconstructed sites. MATERIALS AND METHODS Fifty-eight consecutive patients (15 males and 43 females, aged 38 to 76 years; mean age: years) requiring maxillary bone block reconstruction prior to implant placement at the Department of Implantology at the Pontifical Catholic University in Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, were enrolled in this study from July 2010 to June Exclusion criteria were: 1) smoking; 2) systemic diseases; 3) patients currently or previously taking oral or intravenous bisphosphonates; and 4) patients irradiated in the past 5 years. A total of 268 implants was placed in reconstructed sites. Grafted sites were classified as posterior (n = 22), anterior (n = 19), and full-arch (n = 17). The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Pedro Ernesto University Hospital, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (CEP-HUPE, 2762/2010). Eligible patients gave written informed consent prior to participation. A diagnosis of severe alveolar ridge atrophy and indication for use of an FFBA block for bone reconstruction were determined by cone-beam computed tomography (CT). The surgical plan and number and size of bone blocks were determined using linear measurements on CT scans. FFBAs were provided by the Musculoskeletal Tissue Bank of the National Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics (INTO, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). Grafts used were fragments of corticocancellous proximal tibia (n = 53), iliac crest (n = 3), and femur (n = 2). Surgical Protocol Prior to surgery, bone grafts were thawed in sterile saline for 30 minutes. Patients were asked to rinse with chlorhexidine (CHX) mouthwash 0.2% for 60 seconds. Antisepsis of the skin was accomplished using iodopovidone 10%. Local anesthetic and lidocaine 2% with epinephrine 1:100,000 were administered and a crestal incision placed over the length of the edentulous segment. Mesial and distal releasing incisions were also placed to improve surgical access, and a full-thickness mucoperiosteal flap was elevated to expose the recipient site. The alveolar ridge was perforated to increase vascularization of the grafts from recipient bone marrow. Allografts were sculpted to precisely fit defects and were secured with two titanium screws to ensure mechanical stability. No adjunctive particulate graft was used. The flap was undermined with a periosteal incision to release tension, and primary wound closure was achieved with 4-0 silk sutures. Patients were medicated with 500 mg azithromycin once daily for 3 days as an antibiotic therapy, and non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) were recommended every 6 hours as needed for postoperative pain control. CHX 0.12% mouthrinse was prescribed twice a day for 15 days as a topic antiseptic. Sutures were removed 7 to 14 days after surgery. Clinical appointments at 7, 14, 30, 60, 90, and 120 days postsurgery were scheduled to evaluate any possible complications. After a healing period of 4 to 6 months, a new CT scan was taken to evaluate amount of bone augmentation and select the number and size of implants to be placed. The implant placement procedures followed the same routine: locoregional anesthesia with lidocaine 2% and epinephrine 1:100,000 were used, and a fullthickness mucoperiosteal flap was elevated to expose grafted areas. Screws used to fix blocks were removed. Implants were placed using implant system drills according to specifications of the manufacturer. Flaps were repositioned and closed with 4-0 silk sutures. Patients were medicated with azithromycin, NSAIDs, and CHX 0.12% mouthrinse following the same protocol used for grafting surgeries. Sutures were removed 7 days after the procedure. Implants were left submerged during healing. Second-stage surgery and initiation of prosthetic therapy occurred 4 months after fixture placement. All patients received implant-supported fixed prostheses. I-Cat Image Sciences International, Hatfield, PA. 1262
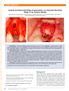
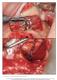
3 J Periodontol November 2016 Deluiz, Oliveira, Fletcher, Pires, Nunes, Tinoco dehiscence parameter. Adverse outcomes were partial or total graft loss (Fig. 1D) and implant failure. In cases where a partial or total graft loss occurred, a sample of removed material was sent for histologic analysis according to standard protocol (Fig. 2). Slides were examined and results were reported descriptively but were not used in any further assessments. Evidence of a relationship between occurrence of a complication and an adverse outcome was sought. Statistical independent variables were infection, dehiscence, and mucosal perforation, while dependent variables were partial graft loss, total graft loss, and implant failure. Likewise, an assessment was made as to whether there was a relationship between location of grafting site in the arch and Figure 1. occurrence of a complication A) Suture dehiscence. B) Infection. C) Mucosal perforation. D) Total graft loss. or adverse outcome. Statistical independent variables in this instance were grafting sites, which were categorized as anterior, posterior, and full-arch, while dependent variables were complications and adverse outcomes that occurred. The Fisher exact test was used to explore these two relationships. Hypotheses were: 1) there was no association among variables (H0) or 2) there was an association between variables (HA). Consequently, if test results are significant, it could be said there is a statistical relationship among dependent and independent variables. Figure 2. Sample of removed material sent for histologic analysis. The total follow-up period after loading implants was 12 months. Complications and adverse outcomes were recorded and assessed. Complications observed were: 1) suture dehiscence; 2) clinical signs of infection; and 3) mucosal perforation (Figs. 1A through 1C). Mucosal perforation was characterized as a soft tissue loss of integrity exposing any part of the graft after incision line complete healing, differing from the RESULTS Fifty-eight patients with 92 atrophic alveolar ridges were treated in the study. Distribution of complications and adverse outcomes were analyzed using the individual as a unit. Complications recorded were: 1) infection in six (10.34%) patients; 2) dehiscence in five (8.62%); and 3) mucosal perforation in seven (12.07%). Adverse outcomes as partial and total graft loss occurred in four (6.90%) and three (5.17%) patients, respectively. Sixteen (5.97%) of 268 implants, placed in 12 of 58 (20.70%) patients, failed. Infected sites showed significant statistical correlation with partial and total graft loss compared with sites without infection. Suture dehiscence also showed a statistically significant correlation with partial and total graft loss. Only one partial graft loss and one total graft loss were recorded in sites demonstrating mucosal 1263
4 Outcomes of Fresh-Frozen Allografts in Alveolar Augmentation Volume 87 Number 11 Table 1. Prevalence of Adverse Outcomes According to Complications Partial Graft Loss Total Graft Loss Implant Failure (individual as unit) Complication Occurrence n (%) Yes (%) No (%) P Value Yes (%) No (%) P Value Yes (%) No (%) P Value Infection Yes 6 (10.34) 2 (3.44) 4 (6.89) 0.04* 3 (5.17) 3 (5.17) <0.001* 4 (6.89) 2 (3.44) 0.59 No 52 (89.66) 2 (3.44) 50 (86.20) 0 (0) 52 (89.65) 42 (72.41) 10 (17.24) Dehiscence Yes 5 (8.62) 2 (3.44) 3 (5.17) 0.03* 2 (3.44) 3 (5.17) 0.02* 3 (5.17) 2 (3.44) 0.27 No 53 (91.38) 2 (3.44) 51 (87.93) 1 (1.72) 52 (89.65) 43 (74.13) 10 (17.24) Mucosal perforation Yes 7 (12.07) 1 (1.72) 6 (10.34) (1.72) 6 (10.34) (10.34) 1 (1.72) >0.99 No 51 (87.93) 3 (5.17) 48 (82.75) 2 (3.44) 49 (84.48) 40 (68.96) 11 (18.96) Total 58 (100.00) 4 (6.90) 54 (93.10) 3 (5.17) 55 (94.82) 46 (79.31) 12 (20.68) * P <0.05. Table 2. Prevalence of Adverse Outcomes (partial graft loss, total graft loss, and implant failure) According to Grafted Sites Partial Graft Loss Total Graft Loss Implant Failure (individual as unit) Site n (%) Yes (%) No (%) Yes (%) No (%) Yes (%) No (%) Anterior 19 (32.75) 2 (3.44) 17 (29.31) 0 (0) 19 (32.75) 4 (6.89) 15 (25.86) Posterior 22 (37.93) 1 (1.72) 21 (36.20) 2 (3.44) 20 (34.48) 1 (1.72) 21 (36.20) Full-arch 17 (29.31) 1 (1.72) 16 (27.58) 1 (1.72) 16 (27.58) 7 (12.06) 10 (17.24) Total 58 (100.00) 4 (6.89) 54 (93.10) 3 (5.17) 55 (94.82) 46 (79.31) 12 (20.68) Significance * * P <0.05. perforation. This was not statistically significant when compared with sites without mucosal perforation (Table 1). Association between presence of a complication and implant failure was not statistically significant, suggesting it is not possible to determine a direct relationship among infection and implant failure, dehiscence, and implant failure, or mucosal perforation and implant failure (Table 1). Results show (Table 2) implant failure was more prevalent in full-arch grafted patients than in anterior or posterior ridge reconstructions. Twelve of 58 (20.68%) patients lost at least one implant and seven (12.06%) of these had received full-arch bone grafting. It was not possible to find a correlation between prevalence of complications and the reconstructed sites (Table 3). Histologic samples from fragments removed in partial and total graft loss were merely descriptive, showing severe inflammatory infiltrate as expected. In samples where bone loss occurred after initial graft incorporation, acute inflammatory cells were visible close to newly-formed bone (Fig. 3). DISCUSSION Currently, several different biomaterials and surgical techniques are available to augment extremely resorbed alveolar ridges. 25,30 Autologous onlay block grafting is one of the methods most often used to reconstruct large defects. 20,31 In contrast to particulate grafts, block grafts are self-contained and can provide space while maintaining stability, and when properly adapted, require no additional materials. 31 Onlay grafts have been evaluated in a large number of publications and are considered a reliable technique. 7,27,32 This study used FFBA blocks for ridge augmentation. While there are reports in the literature of 1264
5 J Periodontol November 2016 Deluiz, Oliveira, Fletcher, Pires, Nunes, Tinoco Table 3. Prevalence of Complication (infection, dehiscence, and mucosal perforation) According to Grafted Sites Infection Dehiscence Mucosal Perforation Site n (%) Yes (%) No (%) Yes (%) No (%) Yes (%) No (%) Anterior 19 (32.75) 1 (1.72) 18 (31.03) 0 (0) 19 (32.75) 1 (1.72) 18 (31.03) Posterior 22 (37.93) 2 (3.44) 20 (34.48) 3 (5.17) 19 (32.75) 2 (3.44) 20 (34.48) Full-arch 17 (29.31) 3 (5.17) 14 (24.13) 2 (3.44) 15 (25.86) 4 (6.89) 13 (22.41) Total 58 (100.00) 6 (10.34) 52 (89.65) 5 (8.62) 53 (91.38) 7 (12.07) 51 (87.93) Significance transmission of infectious diseases as a result of contaminated bone allograft transplantation, 33,34 modern processing techniques have proven to be extremely effective in preventing transmission of disease Because risk of a graft being infected with human immunodeficiency virus is less than 1 in 8 million, 35,36 FFBA grafts are currently considered safe from both an immunologic and virologic standpoint. 38,39 In the current study, 13 of 58 (22.41%) patients experienced at least one complication assessed in the receptor site during follow-up. In five of the 13 cases, local infection was combined with another adverse event. Although, to the best of the authors knowledge, reports specifically evaluating FFBA are not found in the dental literature, these data corroborate studies evaluating complications using all types of allogenic and autogenous block grafts. 27,40 Proper care of a graft that has become exposed can prevent development of further complications. To avoid additional soft tissue damage and further wound margin retraction, debridement is performed without raising a flap. Using a bur under abundant irrigation, superficial layers of necrotic bone are removed until the vital bleeding part of the graft is exposed. The graft is concurrently recontoured to allow surrounding soft tissue to migrate over it. In the experience of the current authors, and as reported by Chaushu et al., 27 if an exposed but decontaminated allograft is recessed within the confines of the wound edges, it will take 4 to 6 weeks for soft tissue to heal over it. An oral broad-spectrum antibiotic (amoxicillin or azithromycin) is prescribed for 5 to 7 days. The patient s oral hygiene is carefully monitored in an effort to preserve the graft, and cleaning of the wound is accomplished with topical CHX 2%. Results suggested infection and dehiscence of the incision line could be directly related to both partial and total graft loss. As stated in other studies, 12,20,21,27,41 open flap surgery to correct these Figure 3. Histologic samples removed after the initial graft incorporation showing acute inflammatory cells close to newly formed bone. (Hematoxylin and eosin stain; original magnification 100 (A) and 400 (B).) problems was avoided when possible and interceptive therapy consisted of: 1) debridement; 2) antibiotic therapy; 3) local CHX application; and 4) conscientious oral hygiene. It must be emphasized that early diagnosis and prompt treatment in cases of infection and suture dehiscence is of paramount importance to prevent total graft loss. 1265
6 Outcomes of Fresh-Frozen Allografts in Alveolar Augmentation Volume 87 Number 11 Absence of a statistical correlation between occurrences of mucosal perforation and partial or total graft loss (P = 0.41 and P = 0.32, respectively) suggests progression of problems after graft exposure can be limited by use of a precise interceptive therapy and close follow-up of the grafted areas. Within the limitations of this 1-year follow-up study which used FFBA for ridge augmentation in the maxilla, statistical correlation between implant failure and the complications evaluated was not found. This result is in accordance with results of previous studies evaluating use of block autografts and allografts. 20,27,41 Additionally, no correlation was found between location of a grafted site in the arch and presence of a specific complication, although full-arch grafted cases were found to be more prone to implant failure. While most complications led to some degree of graft impairment, outcome of the final treatment was not jeopardized as all patients in this study received a final implant-supported fixed prosthesis after the healing period of the fixture. Histologic samples of fragments of lost grafts showed a severe inflammatory infiltrate. In samples where the complication occurred after initial graft incorporation, particles of newly formed bone could be seen close to areas with acute inflammation. CONCLUSIONS Withinlimitationsofsamplesizeandthe1-yearfollowup, infection and suture dehiscence demonstrated significant statistical correlation with graft loss in a maxillary alveolar ridge onlay block FFBA graft augmentation. Patients with full-arch grafting reconstructions lost significantly more implants. Early diagnosis and prompt management of adverse events seem to be of great importance in prevention of total graft loss. Future studies, including larger number of individuals and longer follow-up periods, are necessary to allow further conclusions. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Dr. Deluiz would like to thank Dr. Paul C. Schiller, Dr. Gianluca D Ippolito, and Dr. Gaëtan Delcroix from the Department of Orthopedics, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami, Florida, for the support and for the Sandwich PhD period in their department. The authors would like to thank Ms. Andrea Bonnin from the Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center of the Bruce W. Carter Miami Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Miami, Florida, and Mr. Diego Armengol from the Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, for assistance provided. Dr. Deluiz received a scholarship from the Brazilian funding agency Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (Distrito Federal, Brazil). The authors report no conflicts of interest related to this study. REFERENCES 1. Wei L, Miron RJ, Shi B, Zhang Y. Osteoinductive and osteopromotive variability among different demineralized bone allografts. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2015; 17: Committee on Research, Science and Therapy of the American Academy of Periodontology. Tissue banking of bone allografts used in periodontal regeneration. J Periodontol 2001;72: Judas F, Figueiredo MH, Cabrita AM, Proencxa A. Incorporation of impacted morselized bone allografts in rabbits. Transplant Proc 2005;37: Kluger R, Bouhon W, Freudenberger H, Kröner A, Engel A, Hoffmann O. Removal of the surface layers of human cortical bone allografts restores in vitro osteoclast function reduced by processing and frozen storage. Bone 2003;32: Piattelli A, Scarano A, Corigliano M, Piattelli M. Comparison of bone regeneration with the use of mineralized and demineralized freeze-dried bone allografts: A histological and histochemical study in man. Biomaterials 1996;17: Spin-Neto R, Stavropoulos A, Dias Pereira LA, Marcantonio E Jr., Wenzel A. Fate of autologous and fresh-frozen allogeneic block bone grafts used for ridge augmentation. A CBCT-based analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res 2013;24: Monje A, Pikos MA, Chan HL, et al. On the feasibility of utilizing allogeneic bone blocks for atrophic maxillary augmentation. Biomed Res Int 2014;2014: Novell J, Novell-Costa F, Ivorra C, Fariñas O, Munilla A, Martinez C. Five-year results of implants inserted into freeze-dried block allografts. Implant Dent 2012; 21: Pereira E, Messias A, Dias R, Judas F, Salvoni A, Guerra F. Horizontal resorption of fresh-frozen corticocancellous bone blocks in the reconstruction of the atrophic maxilla at 5 months. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2015;17(Suppl. 2):e444-e Contar CM, Sarot JR, da Costa MB, et al. Fresh-frozen bone allografts in maxillary ridge augmentation: Histologic analysis. J Oral Implantol 2011;37: D Aloja C, D Aloja E, Santi E, Franchini M. The use of fresh-frozen bone in oral surgery: A clinical study of 14 consecutive cases. Blood Transfus 2011;9: Barone A, Varanini P, Orlando B, Tonelli P, Covani U. Deep-frozen allogeneic onlay bone grafts for reconstruction of atrophic maxillary alveolar ridges: A preliminary study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009;67: Lumetti S, Consolo U, Galli C, et al. Fresh-frozen bone blocks for horizontal ridge augmentation in the upper maxilla: 6-month outcomes of a randomized controlled trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2014;16: Deluiz D, Oliveira LS, Pires FR, Tinoco EM. Timedependent changes in fresh-frozen bone block grafts: Tomographic, histologic, and histomorphometric findings. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2015;17: Contar CM, Sarot JR, Bordini J Jr., Galvão GH, Nicolau GV, Machado MA. Maxillary ridge augmentation with fresh-frozen bone allografts. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009;67:
7 J Periodontol November 2016 Deluiz, Oliveira, Fletcher, Pires, Nunes, Tinoco 16. Laurencin C, Khan Y, El-Amin SF. Bone graft substitutes. Expert Rev Med Devices 2006;3: Spin-Neto R, Landazuri Del Barrio RA, Pereira LA, Marcantonio RA, Marcantonio E, Marcantonio E Jr. Clinical similarities and histological diversity comparing fresh frozen onlay bone blocks allografts and autografts in human maxillary reconstruction. Clin ImplantDentRelatRes2013;15: Deatherage J. Bone materials available for alveolar grafting. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 2010;22: , v. 19. Silva FM, Cortez AL, Moreira RW, Mazzonetto R. Complications of intraoral donor site for bone grafting prior to implant placement. Implant Dent 2006;15: Chiapasco M, Zaniboni M. Failures in jaw reconstructive surgery with autogenous onlay bone grafts for pre-implant purposes: Incidence, prevention and management of complications. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 2011;23:1-15, v. 21. Schwartz-Arad D, Levin L. Intraoral autogenous block onlay bone grafting for extensive reconstruction of atrophic maxillary alveolar ridges. J Periodontol 2005;76: Felice P, Pistilli R, Lizio G, Pellegrino G, Nisii A, Marchetti C. Inlay versus onlay iliac bone grafting in atrophic posterior mandible: A prospective controlled clinical trial for the comparison of two techniques. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2009;11(Suppl. 1):e69-e Chiapasco M, Casentini P, Zaniboni M. Bone augmentation procedures in implant dentistry. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2009;24(Suppl.): Cordaro L, Amadé DS, Cordaro M. Clinical results of alveolar ridge augmentation with mandibular block bone grafts in partially edentulous patients prior to implant placement. Clin Oral Implants Res 2002;13: Milinkovic I, Cordaro L. Are there specific indications for the different alveolar bone augmentation procedures for implant placement? A systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2014;43: Spin-Neto R, Stavropoulos A, Coletti FL, Pereira LA, Marcantonio E Jr., Wenzel A. Remodeling of cortical and corticocancellous fresh-frozen allogeneic block bone grafts A radiographic and histomorphometric comparison to autologous bone grafts. Clin Oral Implants Res 2015;26: Chaushu G, Mardinger O, Peleg M, Ghelfan O, Nissan J. Analysis of complications following augmentation with cancellous block allografts. J Periodontol 2010;81: Antoun H, Sitbon JM, Martinez H, Missika P. A prospective randomized study comparing two techniques of bone augmentation: Onlay graft alone or associated with a membrane. Clin Oral Implants Res 2001;12: Peleg M, Sawatari Y, Marx RN, et al. Use of corticocancellous allogeneic bone blocks for augmentation of alveolar bone defects. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2010;25: Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Felice P, Karatzopoulos G, Worthington HV, Coulthard P. The efficacy of horizontal and vertical bone augmentation procedures for dental implants A Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Oral Implantology 2009;2: Waasdorp J, Reynolds MA. Allogeneic bone onlay grafts for alveolar ridge augmentation: A systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2010;25: McAllister BS, Haghighat K. Bone augmentation techniques. J Periodontol 2007;78: Simonds RJ, Holmberg SD, Hurwitz RL, et al. Transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from a seronegative organ and tissue donor. N Engl J Med 1992;326: Tomford WW. Transmission of disease through transplantation of musculoskeletal allografts. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1995;77: Joyce MJ. Safety and FDA regulations for musculoskeletal allografts: Perspective of an orthopaedic surgeon. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2005;435: Holtzclaw D, Toscano N, Eisenlohr L, Callan D. The safety of bone allografts used in dentistry: A review. J Am Dent Assoc 2008;139: Goldberg VM, Stevenson S. Natural history of autografts and allografts. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1987;225: Buckley SC, Stockley I, Hamer AJ, Kerry RM. Irradiated allograft bone for acetabular revision surgery. Results at a mean of five years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2005;87: D Aloja E, Santi E, Aprili G, Franchini M. Fresh frozen homologous bone in oral surgery: Case reports. Cell Tissue Bank 2008;9: Maestre-Ferrín L, Boronat-López A, Peñarrocha-Diago M, Peñarrocha-Diago M. Augmentation procedures for deficient edentulous ridges, using onlay autologous grafts: An update. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2009; 14:e402-e Macedo LG, Mazzucchelli-Cosmo LA, Macedo NL, Monteiro AS, Sendyk WR. Fresh-frozen human bone allograft in vertical ridge augmentation: Clinical and tomographic evaluation of bone formation and resorption. Cell Tissue Bank 2012;13: Correspondence: Dr. Daniel Deluiz, Boulevard 28 de Setembro, andar - sala 10, Rio de Janeiro, RJ - CEP , Brazil. d.deluiz@implanto-puc. org. Submitted March 11, 2016; accepted for publication June 1,
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
B one volume is an important
 304 RECONSTRUCTION OF ALVEOLAR BONE RIDGE IN IMPLANTOLOGY ARAÚJO ET AL Block Allograft for Reconstruction of Alveolar Bone Ridge in Implantology: A Systematic Review Pryscyla P. T. Araújo, DDS, MS,* Kerlison
304 RECONSTRUCTION OF ALVEOLAR BONE RIDGE IN IMPLANTOLOGY ARAÚJO ET AL Block Allograft for Reconstruction of Alveolar Bone Ridge in Implantology: A Systematic Review Pryscyla P. T. Araújo, DDS, MS,* Kerlison
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using the Allograft Bone Shell Technique
 Mogammad Thabit Peck CASE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1755 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using the Allograft Bone Shell Technique Mogammad Thabit Peck ABSTRACT Background: The loss of teeth, whether
Mogammad Thabit Peck CASE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1755 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using the Allograft Bone Shell Technique Mogammad Thabit Peck ABSTRACT Background: The loss of teeth, whether
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla
 CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Posterior mandible and vertical augmentation
 CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Vertical Augmentation
 Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft
 Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation. Sanju P. Jose
 Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
More than bone regeneration. A total solution.
 More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material- A case Report
 A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 07 Page July 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
Keywords: Biomechanics, Biostatistics, Maxilla, Maxillary sinus, Sinus floor augmentation.
 Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:58-63 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.2.58 Peri-implant bone length changes and survival rates of implants penetrating the
Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:58-63 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.2.58 Peri-implant bone length changes and survival rates of implants penetrating the
Oral Health and Dentistry
 Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION
 original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
ß-tricalcium phosphate used with onlay graft for horizontal bone augmentation yielded preferable result: a case report
 ß-tricalcium phosphate used with onlay graft for horizontal bone augmentation yielded preferable result: a case report Yaqian Chen, Qingqing Wu, Yi Man State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, West China
ß-tricalcium phosphate used with onlay graft for horizontal bone augmentation yielded preferable result: a case report Yaqian Chen, Qingqing Wu, Yi Man State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, West China
Years of research and advancement in
 Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Localized Maxillary Ridge Augmentation Using Onlay Technique with a Xenograft Block for Dental Implant Placement A Case Series
 Localized Maxillary Ridge Augmentation Using Onlay Technique with a Xenograft Block for Dental Implant Placement A Case Series Hassan Maghaireh - BDS, MFDS RCSEd, MSc Implants Head of the International
Localized Maxillary Ridge Augmentation Using Onlay Technique with a Xenograft Block for Dental Implant Placement A Case Series Hassan Maghaireh - BDS, MFDS RCSEd, MSc Implants Head of the International
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Immediate Implant Placement Along With Guided Bone Regeneration In Mandibular Anterior Region A Case Report.
 IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft
 Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Sinus Augmentation Studies Methods and Definition
 FDA approved indications for Infuse Bone Graft in the Maxillofacial Skeleton Alveolar Ridge Augmentation (Buccal Wall Defects) in the Maxilla Maxillary Sinus Floor augmentation Sinus Augmentation Studies
FDA approved indications for Infuse Bone Graft in the Maxillofacial Skeleton Alveolar Ridge Augmentation (Buccal Wall Defects) in the Maxilla Maxillary Sinus Floor augmentation Sinus Augmentation Studies
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus.
 Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus. Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Rees J, Karasoulos D, Felice P, Alissa R, Worthington HV, Coulthard P. Cochrane Database
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus. Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Rees J, Karasoulos D, Felice P, Alissa R, Worthington HV, Coulthard P. Cochrane Database
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report
 Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Procedure Manual and Catalog
 Procedure Manual and Catalog TM Why SynthoGraft? SynthoGraft offers a unique structure which provides stability, while its micro-porosity allows for rapid vascularization and subsequent resorption. Although
Procedure Manual and Catalog TM Why SynthoGraft? SynthoGraft offers a unique structure which provides stability, while its micro-porosity allows for rapid vascularization and subsequent resorption. Although
Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging
 Bone Grafting: Essential Indications and Techniques in Implant Dentistry Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging and sometimes unpredictable. Candidates for implant therapy must have
Bone Grafting: Essential Indications and Techniques in Implant Dentistry Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging and sometimes unpredictable. Candidates for implant therapy must have
The Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique. Jia-Hui Fu* and Hom-Lay Wang*
 CASE REPORT The Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique Jia-Hui Fu* and Hom-Lay Wang* Introduction: Horizontal ridge width reduction after tooth extraction is a common clinical scenario. As such, when implant-supported
CASE REPORT The Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique Jia-Hui Fu* and Hom-Lay Wang* Introduction: Horizontal ridge width reduction after tooth extraction is a common clinical scenario. As such, when implant-supported
Ridge Split Procedure
 Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Implants- immediate restoration of postextraction edentation both esthetically and functionally
 Implants- immediate restoration of postextraction edentation both esthetically and functionally Otilia Stana (Gag), LileIoana Elena, Freiman Paul, Mugur Popescu, Elisei Gabriela, Sebesan Voicu, Vincze
Implants- immediate restoration of postextraction edentation both esthetically and functionally Otilia Stana (Gag), LileIoana Elena, Freiman Paul, Mugur Popescu, Elisei Gabriela, Sebesan Voicu, Vincze
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
4. What about age? There is no age limit. After puberty, anyone can get dental implants.
 Dental Implants 1. What are Osseointegrated implants? Osseointegrated implants are a new generation of dental implants in Rio de Janeiro, introduced in the 1960 s, they come in different shapes and sizes.
Dental Implants 1. What are Osseointegrated implants? Osseointegrated implants are a new generation of dental implants in Rio de Janeiro, introduced in the 1960 s, they come in different shapes and sizes.
Deep-Frozen Allogeneic Onlay Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Atrophic Maxillary Alveolar Ridges: A Preliminary Study
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:1300-1306, 2009 Deep-Frozen Allogeneic Onlay Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Atrophic Maxillary Alveolar Ridges: A Preliminary Study Antonio Barone, DDS, PhD, MSc,* Paolo Varanini,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:1300-1306, 2009 Deep-Frozen Allogeneic Onlay Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Atrophic Maxillary Alveolar Ridges: A Preliminary Study Antonio Barone, DDS, PhD, MSc,* Paolo Varanini,
Anarrow alveolar ridge is a challenging situation that
 CASE LETTER Minimally Invasive Approaches to Optimize Block Grafting: A Case Report Gilberto Sammartino, MD, DDS 1 * Giuseppe Pantaleo, DDS 1 Paolo Nuzzolo, DDS 1 Massimo Amato, MD, DDS 2 Francesco Riccitiello,
CASE LETTER Minimally Invasive Approaches to Optimize Block Grafting: A Case Report Gilberto Sammartino, MD, DDS 1 * Giuseppe Pantaleo, DDS 1 Paolo Nuzzolo, DDS 1 Massimo Amato, MD, DDS 2 Francesco Riccitiello,
One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A Case Series
 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2012 14/3:62-68 One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A
Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2012 14/3:62-68 One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
Maxillary Ridge Augmentation With Fresh-Frozen Bone Allografts
 DENTAL IMPLANTS J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:1280-1285, 2009 Maxillary Ridge Augmentation With Fresh-Frozen Bone Allografts Cintia Mussi Milani Contar, DDS, MS,* João Rodrigo Sarot, DDS, MS, Jayme Bordini,
DENTAL IMPLANTS J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:1280-1285, 2009 Maxillary Ridge Augmentation With Fresh-Frozen Bone Allografts Cintia Mussi Milani Contar, DDS, MS,* João Rodrigo Sarot, DDS, MS, Jayme Bordini,
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up
 Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
hard tissue maxgraft cortico Surgical guide botiss biomaterials innovative efficient atraumatic Prefabricated allogenic bone plate
 bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials maxgraft cortico Prefabricated allogenic bone plate Surgical guide innovative efficient hard tissue atraumatic 1 Content maxgraft cortico Surgical guide 1.
bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials maxgraft cortico Prefabricated allogenic bone plate Surgical guide innovative efficient hard tissue atraumatic 1 Content maxgraft cortico Surgical guide 1.
Socket Treatment. Procedure Guide
 Socket Treatment Procedure Guide www.implantdirect.com 888.649.6425 Extraction Healing and Ridge Resorption The Why Working with patients to educate them on the benefits of bone maintenance post extraction
Socket Treatment Procedure Guide www.implantdirect.com 888.649.6425 Extraction Healing and Ridge Resorption The Why Working with patients to educate them on the benefits of bone maintenance post extraction
Sandwich osteotomy of the atrophic posterior mandible prior to implant placement
 CASE REPORT Sandwich osteotomy of the atrophic posterior mandible prior to implant placement Luan Mavriqi 1, Egresa Baca 2 & Ariona Demiraj 3 1 Departament of Periodontology, Albanian University and Private
CASE REPORT Sandwich osteotomy of the atrophic posterior mandible prior to implant placement Luan Mavriqi 1, Egresa Baca 2 & Ariona Demiraj 3 1 Departament of Periodontology, Albanian University and Private
Long-term success for osteointegrated
 CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
Alveolar Ridge Preservation:
 Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
SHELL TECHNIQUE WITH ALLOGENIC CORTICAL STRUTS
 bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials maxgraft cortico SHELL TECHNIQUE WITH ALLOGENIC CORTICAL STRUTS Surgical guide innovative efficient hard tissue atraumatic 1 Content maxgraft cortico Surgical
bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials maxgraft cortico SHELL TECHNIQUE WITH ALLOGENIC CORTICAL STRUTS Surgical guide innovative efficient hard tissue atraumatic 1 Content maxgraft cortico Surgical
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Benefits of CBCT in Implant Planning
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
IMPLANTS. Guideline Number: DCG Effective Date: January 1, 2018
 IMPLANTS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG007.04 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1 COVERAGE RATIONALE...1
IMPLANTS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG007.04 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1 COVERAGE RATIONALE...1
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
Initially, implant dentistry was focused on
 CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
In 1977, Lew1 developed a passive
 CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
Revisions for CDT 2016
 Revisions for CDT 2016 This document was developed from preliminary actions of the Code Maintenance Committee (CMC). This document has been compared to the CMC meeting notes and the ASCII file. This document
Revisions for CDT 2016 This document was developed from preliminary actions of the Code Maintenance Committee (CMC). This document has been compared to the CMC meeting notes and the ASCII file. This document
Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
 227 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 4, 227-232, 2003 Case report Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
227 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 4, 227-232, 2003 Case report Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
Minimal invasive horizontal ridge augmentation using subperiosteal tunneling technique
 Kim et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2016) 38:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-016-0087-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Minimal invasive horizontal
Kim et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2016) 38:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-016-0087-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Minimal invasive horizontal
Case Report Treatment of an Erratic Extraction Socket for Implant Therapy in a Patient with Chronic Periodontitis
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 1746961, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1746961 Case Report Treatment of an Erratic Extraction Socket for Implant Therapy in a Patient with Chronic
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 1746961, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1746961 Case Report Treatment of an Erratic Extraction Socket for Implant Therapy in a Patient with Chronic
botiss dental bone & tissue regeneration biomaterials mucoderm 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Ridge Augmentation. Selection of Applicable Abstracts and Posters. Using Titanium-Reinforced PTFE Membranes
 Ridge Augmentation Selection of Applicable Abstracts and Posters Using Titanium-Reinforced PTFE Membranes Gultekin BA, Cansiz E, Borahan MO. Clinical and 3-Dimensional Radiographic Evaluation of Autogenous
Ridge Augmentation Selection of Applicable Abstracts and Posters Using Titanium-Reinforced PTFE Membranes Gultekin BA, Cansiz E, Borahan MO. Clinical and 3-Dimensional Radiographic Evaluation of Autogenous
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Case report: Replacement of failing 2 stage implants by basal implants and conventional bridgework
 Case report: Replacement of failing 2 stage implants by basal implants and conventional bridgework Authors Dr. Aleksandar Lazarov Solunska Str. 3 BG-1000 Sofia Bulgaria Email: alex.lazarov@yahoo.co.uk
Case report: Replacement of failing 2 stage implants by basal implants and conventional bridgework Authors Dr. Aleksandar Lazarov Solunska Str. 3 BG-1000 Sofia Bulgaria Email: alex.lazarov@yahoo.co.uk
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
The success of implant-supported dental prostheses is
 CASE LETTER Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft-Tissue Augmentation of Small Defects: Two Case Reports With 5-Year Follow-Up Jorge Saade, DDS, MD 1, PhD 1 Bruno Salles Sotto-Maior, DDS, MD, PhD 2 * Carlos
CASE LETTER Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft-Tissue Augmentation of Small Defects: Two Case Reports With 5-Year Follow-Up Jorge Saade, DDS, MD 1, PhD 1 Bruno Salles Sotto-Maior, DDS, MD, PhD 2 * Carlos
Comprehensive Dental Implantology
 Comprehensive Dental Implantology Surgical Course Presented by: Dr Chan Siew Luen BDS (Singapore) MDS Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (HK) FAMS (Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery) CPE TBC 3 Modules covering topics
Comprehensive Dental Implantology Surgical Course Presented by: Dr Chan Siew Luen BDS (Singapore) MDS Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (HK) FAMS (Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery) CPE TBC 3 Modules covering topics
Exclusion Criteria. Subjects were excluded if they were smokers and if they had residual mandible height after
 Stability of Implants Placed in Augmented Posterior Mandible after Alveolar Osteotomy Using Resorbable Nonceramic Hydroxyapatite or Intraoral Autogenous Bone: 12-Month Follow-Up Alexandre M. Dottore, DDS;*
Stability of Implants Placed in Augmented Posterior Mandible after Alveolar Osteotomy Using Resorbable Nonceramic Hydroxyapatite or Intraoral Autogenous Bone: 12-Month Follow-Up Alexandre M. Dottore, DDS;*
The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting
 44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study
 26 News No.26 January 2011 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study Make it Simple 2 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone
26 News No.26 January 2011 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study Make it Simple 2 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone
Evaluation of custom made xenogenic bone grafts in mandibular alveolar ridge augmentation versus particulate bone graft with titanium mesh
 Original Article Evaluation of custom made xenogenic bone grafts in mandibular alveolar ridge augmentation versus particulate bone graft with titanium mesh Mohammed S. Abuelnaga, Nader N. Elbokle, Mohammed
Original Article Evaluation of custom made xenogenic bone grafts in mandibular alveolar ridge augmentation versus particulate bone graft with titanium mesh Mohammed S. Abuelnaga, Nader N. Elbokle, Mohammed
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the. Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System
 Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Bone augmentation with maxgraft
 Patient information bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with maxgraft established safe X100 natural Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the jaw bone loss
Patient information bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with maxgraft established safe X100 natural Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the jaw bone loss
Dr. Michael A. Pikos
 Dr. Michael A. Pikos Dr. Pikos is originally from Campbell, Ohio. He attended The Ohio State University where he graduated Summa Cum Laude and Phi Beta Kappa. He also graduated with honors from The Ohio
Dr. Michael A. Pikos Dr. Pikos is originally from Campbell, Ohio. He attended The Ohio State University where he graduated Summa Cum Laude and Phi Beta Kappa. He also graduated with honors from The Ohio
Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic. Review
 Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic Review A dissertation submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry (Oral and
Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic Review A dissertation submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry (Oral and
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation
 Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
Osseointegrated dental implants have been used for
 Use of Distraction Osteogenesis for Repositioning of an Osseointegrated Implant: A Case Report Gustavo Mendonça, DDS, MS 1 /Daniela Baccelli Silveira Mendonça, DDS 2 / Alfredo Júlio Fernandes Neto, DDS,
Use of Distraction Osteogenesis for Repositioning of an Osseointegrated Implant: A Case Report Gustavo Mendonça, DDS, MS 1 /Daniela Baccelli Silveira Mendonça, DDS 2 / Alfredo Júlio Fernandes Neto, DDS,
Sandwich bone graft for vertical augmentation of the posterior maxillary region: a case report with 9-year follow-up
 Tanaka et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:20 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0063-9 International Journal of Implant Dentistry CASE REPORT Sandwich bone graft for vertical augmentation of
Tanaka et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:20 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0063-9 International Journal of Implant Dentistry CASE REPORT Sandwich bone graft for vertical augmentation of
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
Intramembranous autogenous bone graft is the gold
 CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
MASTERS SERIES 2010 ACCELERATED IMPLANT DENTISTRY EDUCATION. San Francisco April-September Miami March-August CREDIT HOURS
 MASTERS SERIES 2010 Level II Implant Continuum Advanced Continuum Miami March-August 2010 San Francisco April-September 2010 ACCELERATED IMPLANT DENTISTRY EDUCATION 120 CREDIT HOURS Arun K. Garg, D.M.D.
MASTERS SERIES 2010 Level II Implant Continuum Advanced Continuum Miami March-August 2010 San Francisco April-September 2010 ACCELERATED IMPLANT DENTISTRY EDUCATION 120 CREDIT HOURS Arun K. Garg, D.M.D.
