Case Report Modified and Grafted Coronectomy: A New Technique and a Case Report with Two-Year Followup
|
|
|
- Luke Stafford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
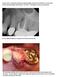
1 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID , 7 pages Case Report Modified and Grafted Coronectomy: A New Technique and a Case Report with Two-Year Followup Michael Leizerovitz and Olga Leizerovitz UCLA School of Dentistry, Le Conte Avenue, Los Angeles, CA , USA Correspondence should be addressed to Michael Leizerovitz; travel.surgery@hotmail.com Received 24 December 2012; Accepted 25 February 2013 Academic Editors: N. Brezniak, M. De Bruyne, and K. H. Zawawi Copyright 2013 M. Leizerovitz and O. Leizerovitz. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Purpose. A standard coronectomy (intentional partial odontectomy) is recommended for mandibular third molar (MTM) extraction cases with a high risk of inferior alveolar nerve injury (IANI). However, complications such as inadvertent intraoperative root removal, post-op root migration, second molar (MSM) periodontal defects and others do exist. This report presents a new technique, the Modified and Grafted Coronectomy (MGC), describes the measures to prevent or minimize the known drawbacks of the standard coronectomy, and reviews the literature for comparison with three other IANI-prevention techniques. Materials and Methods. MGC was performed on two MTMs with nerve involvement and severe periodontal pockets on the distal of MSM. Modifications were: stabilizing the root stump to prevent intraoperative movement, creation of a large intrabony space for bone graft material, and grafting for periodontal healing while minimizing the possibility of post-op root migration. Results. Excellent overall periodontal improvement, with probing depths reduced to 3-4 mm. Panoramic radiograph displayed remarkable bone regeneration. No residual root migration was evident at the two year follow up. Conclusion. MGCmaybeagoodalternative, especially in cases with periodontal defects on the distal of MSM. It may also help to minimize inadvertent intraoperative root removal and postoperative root migration. 1. Introduction The removal of impacted mandibular third molar (MTM) in close proximity to the mandibular canal has proven to be problematic. One of the more severe risks is inferior alveolar nerve injury (IANI). The prevalence of this type of nerve injury in the twenty-four prospective studies reviewed varies between a minimum of 0% [1, 2] andamaximumof8.4% [3]. The need to prevent these kinds of injuries is especially important since current treatment modalities of neurosensory deficit management (four surgical and two nonsurgical [4]) show only limited improvement in sensation. According to studies, complete recovery is uncommon with all types of available treatments [4, 5]. Coronectomy is the oldest and the best researched of the IANI-risk reducing procedures [6 19]. First described in 1984 [14], it has been extensively reviewed in multiple articles and retrospective studies, has been examined in eight prospective trials (Table 1),and has been now listed as a standard treatment option for surgical management of third molars by AAOMS ParCare 2012 in USA [20]. Despite those facts, coronectomy has not yet been accepted by the majority of the oral surgery community. In the regular coronectomy, the aspect of the third molar root/s in the closest proximity to the inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) is intentionally retained. The clear benefit of a successful coronectomy is the avoidance of IANI. The disadvantages of this technique include deep periodontal pockets on the distal of the second molars (similar to those after extractions in comparable circumstances), root migration with the possible need of a second procedure, dry sockets, local postoperative infections, postoperative pain and inadvertent root removal, or root walk-out during surgery which may increase the risk of IANI (also known as a failed coronectomy) [6, 7, 17, 21, 22]. Deep pockets and other periodontal damages have been previously reported on the distal of the second molar teeth
2 2 Case Reports in Dentistry Reference Author Article [6] Pogreletal. [7] Rentonetal. Coronectomy: a technique to protect the inferior alveolar nerve A randomised controlled clinical trial to compare the incidence of injury to the inferior alveolar nerve as a result of coronectomy and removal of mandibular third molars [8] Pogrel Anupdateoncoronectomy [9] Leung and Cheung [10] Hatanoetal. [11] Dolanmaz et al. [12] Cilasun et al. [13] Leung and Cheung Safety of coronectomy versus excision of wisdom teeth: a randomized controlled trial Clinical evaluations of coronectomy (intentional partial odontectomy) for mandibular third molars using dental computed tomography: a case-control study A preferable technique for protecting the inferior alveolar nerve: coronectomy Coronectomy in patients with high risk of inferior alveolar nerve injury diagnosedbycomputedtomography Coronectomy of the lower third molar is safe within the first 3 years Table 1: Published prospective trials. Published in journal Br J Oral Maxillofac Oral Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod Year published n subjects n teeth Study design Not available Randomized controlled trial Randomized controlled trial Case control study after third molar removal [23 26]. The measurements used in these studies were attachment levels, pocket depth and/or alveolar bone height. Shallower pocket depths postoperatively have been obtained through the debridement of the distal root of the second molar [27, 28]. Grafting following extraction has also minimized the development of second molar periodontal defects in the high-risk group (age 26 years., preexisting attachment loss 3 mm, and mesioangular or horizontal impaction) [29, 30] and in the younger patients group (ages years) [31]. However, coronectomy in conjunction with grafting and distal root surface of the second molar debridement and demineralization has not been previously reported. This paper provides a description of a case of a Modified and Grafted Coronectomy (MGC), developed by the authors. The goals of the technique are to decrease the incidence of intraoperative root walkout, to minimize the potential and/or preexisting periodontal pockets distal to the second molar similartothe Preservationofperiodontalhealthofadjacent teeth Specific Therapeutic Goal of ParCare 2012 [20], and to decrease the risk of delayed root migration with the possible need for a second surgical procedure, all while preserving the excellent IANI-prevention record of a standard coronectomy. The reduction in pocket depth may also prevent or minimize the need for future periodontal interventions. The following case has met the goals described herein. 2. Clinical Report A 37-year-old female, a smoker for the past 15 years but otherwise in good general health, was repeatedly referred for extractions of her MTM due to severe localized periodontal disease at the distal of the mandibular second molar (MSM) teeth. She stated that over the last four years she had consulted five oral surgeons who each suggested third molar extraction. Thepatientwasalsoadvisedthatshewouldhaveahigher than normal chance of bilateral permanent paresthesia. She reported that her periodontist warned her about the deterioratingperiodontalhealthofbothofherlowersecondmolar teeth. She also reported occasional pressure and intermittent pain associated with the lower right third molar. At her consultation appointment, the patient presented with a panoramic radiograph and multiple dental treatment plans, all of which included extraction of the MTMs. A new panoramic radiograph was taken (Figure 1)which confirmed bilateral complete bony, horizontally impacted MTMs, Pell and Gregory s [32] class 2C on the lower right and 3C on the lower left with the roots in intimate radiographic proximity to the IAN bundle. The periodontal ligament space appeared sclerotic. The distal of the right MSM was tender to palpation and slightly swollen, which the patient stated had been bothersome for the last few weeks. Immediately prior to the surgical procedure, the periodontal probing depths were
3 Case Reports in Dentistry Figure 1: Preoperative panoramic radiograph. The direction of the initial cuts is marked. measured at 13 mm on the distal of right MSM and 8 mm on the distal of left MSM. The patient was given the options and risks of observation, extractions with grafting, and Modified Grafted Coronectomy. The patient chose to have bilateral MGC performed. The treatment plan was reviewed and her consent was obtained. Due to the presence of infection, she was placed on oral Clindamycin 150 mg, 40 tablets, QID, and 0.12% chlorhexidine mouth rinse twice a day beginning two days prior to the procedure. The surgery was performed with i.v. sedation and local anesthesia. A lower right full thickness distally released envelope flap was reflected. No lingual retraction was used. A bony window was created for access. An initial vertical cut with a #703 cross cut fissure carbide FG bur, 2.1 mm diameter was made above the CEJ and oriented at a 20 angle to the distal root of the second molar, to facilitate coronal fragment removal. The cut was completed at 3/4 of the tooth diameter to avoid cutting into the lingual wall and/or IAN and to avert possible lingual nerve injury or IANI. The crown was broken off, without excessive apical pressure. After the removal of the first fragment, rest seats were created in the root portion at each of the subsequent steps. These were used to apply gentle apical pressure on the distal section with the sharp end of a Molt 9A periosteal elevator while grinding, cutting, and fracturing off the coronal fragments. This action stabilized the root portion, dampened the vibration, and helped to prevent inadvertent movement and therefore pressure of the remaining root against the IAN. Next, a #10 round carbide HP bur, 2.7 mm diameter was used to grind away the distoocclusal section of the remaining stump above the IAN, well below the bone crest level (Figure 2(a)). Due to insufficient clearance between the third molar stump and the second molar root, an additional cut was performed on the mesial portion of the remaining tooth, at 3/4 of the diameter and it was fractured off with a Schmeckebier #81 straight elevator (Figure 2(b)). A sufficient clearance to the second molar was confirmed with a radiograph (Figure 2(c)). The distal root of the second molar was detoxified and prepared for the bone graft by ultrasonic scaling and by a treatment with a 25% solution of citric acid for five minutes. A resorbable hydroxyapatite (HA) graft was placed into the bleeding site and no membrane was used. The flap was advanced for full coverage of the graft and primary closure and then sutured with 4-0 Vicryl sutures. The 3 (a) (b) (c) Figure 2: Lower right MTM: (a) after amputation of the crown, rotary instruments were used to reduce the distoocclusal section of the remaining stump; (b) after an additional cut and sectioning of the mesial portion of the tooth; (c) sufficient clearance to the second molar confirmed. surgery on left MTM was carried out in a similar fashion. This side was somewhat more difficult due to less available space mesiodistally and significant resorption of the distal root of left second molar. (Figures 3(b) and 3(c)). Serial progress periapical radiographs were taken. The patient was seen for a follow-up visit at six days postoperatively. The surgical sites appeared to be healing within normal limits. The absence of paresthesia in the IAN and lingual nerve distribution was assessed by the patient s subjective report of normal sensation with sharp, blunt, and light touch. A follow-up panoramic radiograph was obtained (Figure 4). Instructions were given for the patient to return for reassessment and radiographs every six months for the first
4 4 Case Reports in Dentistry (a) Figure 4: Six days postoperatively. Please note that the bone graft is radiolucent at this stage. (b) Figure 5: A 23-month follow-up with excellent healing. (c) Figure 3: Lower left MTM: (a) after amputation of the crown; (b) after reducing the distoocclusal section of the remaining stump; (c) after an additional cut and removal of the mesial portion of the tooth, to create sufficient clearance to the second molar. two years, and once more after the third year. The patient was advised, if there are no problems found during the first three years, to return only if she experiences any unusual symptoms. The patient and the referring dentist were advised to exercise special care with the grafted sites for the first six to nine months following treatment by not traumatizing them needlessly and to allow the graft to mature. This included no periodontal pocket charting, scaling on the distal of the second molars, and/or manipulating with any hard objects by the patient. According to the manufacturer, the grafted area becomes radiopaque in comparison to the surrounding bone indicating that the resorbable HA graft has matured. 3. Results At the two-year follow-up the patient stated the areas felt fine with no sensitivity around the second molars. Periodontal examination revealed decreased periodontal pocket depths, down to three and four mm. Panoramic radiograph was obtained (Figure 5), displaying good bone fill with excellent periodontal improvement overall. No residual root migration was evident. 4. Discussion Regular coronectomy is the best studied alternative to the extraction of teeth, which are at a high risk for IANI, as determined by radiographic signs [6, 7, 10, 17, 33 37]. It has now been accepted in USA as a standard and is no longer a controversial treatment option at Third Molar Multidisciplinary Conference in Washington, DC, on October 19, 2010, and AAOMS ParCare 2012 [20, 38]. There are several technique variations to perform a standard coronectomy procedure [6, 7, 9, 10, 14, 16, 17]. While nerve damage is avoided in a successful standard coronectomy, other complications can arise. IANI was the most serious complication which occurred during some failed coronectomies, where the remaining root was inadvertently mobilized during surgery. This mandated the surgeons to proceed with the extraction of the entire root in 4 38% of the cases [7 9, 17], also resulting in temporary IANI, with an incidence of % [7, 8]. Other known complications are deep periodontal pockets on the distal of the second molar, delayed postoperative root migration with the possible need of a second procedure, postoperative pain, dry socket, and infection [7 9, 21, 22].
5 Case Reports in Dentistry 5 These drawbacks could be a possible motivation for the recent emergence of additional IANI-risk reducing procedures: staged removal (the removal of a portion of the crown, creating space for the root to erupt away from the IAN, with subsequent removal of the remainder of the root) [39], pericoronal ostectomy (the removal of the overlying bone to allow for the tooth to erupt away from the IAN) [21], and orthodontic extractions (active orthodontic movement of the tooth away from the IAN) [40, 41]. Pericoronal ostectomy and orthodontic extraction allow for bone formation on the distalofthesecondmolarwhichoccursduetotheocclusal extrusion as the MTM moves away from the IAN [21, 41]. While it is obvious that preservation of periodontal health, regenerating bone and preventing or reducing the further need of periodontal surgery at the distal of the lower second molar, is an important advantage for the patients [20], a standard coronectomy procedure lacks this benefit. With only one recorded case of permanent IANI in its history [17], there is an abundance of evidence that coronectomy has had great success in avoiding IANI. While performing the standard coronectomy since 1995, we have experiencedbothitsianiavoidancebenefitsaswellasall its negative side effects. In an effort to overcome these, we attempted various modifications to the different steps of the original technique. Ultimately, the technique used in the case reported above appears to have the most encouraging outcome. In it we introduced a series of amendments to the standard coronectomy procedure and called it a Modified and Grafted Coronectomy. As with the standard coronectomy, MGC involves the removal of the crown and part of the root/s of an impacted MTM in cases with a high risk of IANI. This modified procedure introduces steps to prevent the complication of inadvertent intraoperative root loosening. It accomplishes this by stabilizing the radicular fragment during cutting as well as when separating the coronal section off, thus overall decreasing the risk of nerve injury. Yet as another modification, to reduce or prevent periodontal pockets on the distal of the second molar, the technique calls for the creation of periodontal scaffolding, which is achieved through grafting, thus the name Modified and Grafted Coronectomy. Scaling and debridement [27, 28] as well as root surface demineralization [42 44] with either citric acid or tetracyclineofthedistalofthesecondmolarwerethenecessary elements for the reattachment success in all our cases. Of the graft materials we used, only resorbable HA (with or without use of resorbable collagen membrane) or cortical allograft with the membrane gave us satisfactory results. In our experience with grafting, it is important to create a larger vertical space to allow for bone regeneration. According to Hatano even if appropriate trimming 2 to 3mmbelowthealveolarcrestisdone,bonecoverageonthe resected surface is sometimes delayed because of significant root migration [10]. Combining grafting with the creation of a larger space resulted in a bulkier graft, which worked well in this case. The resulting periodontal healing is very encouraging (Figure5), as well as the absence of root migrationwhichinturnavertsthepossiblenecessityofasecond surgicalproceduretoremovetherootfragment.thefindings inthispaperappeartobepromisingwithoutthesideeffects of the standard coronectomy procedure. MGC appears to be an alternate technique that could be considered for nearly all coronectomy cases of vertical, mesioangular, or horizontal impactions and especially in the cases which have preexisting periodontal lesions or are expected to have large postsurgical defects. A possible additional benefit is the potential prevention for the need of further pocket reduction surgery on the distal of the lower second molar, minimizing the need of subsequent treatments and visits. Possible considerations of the technique are the additional costs of the graft and the time required to perform the procedure. Further modifications and enhancements could include the use of different graft materials and/or the use of a membrane. Additional research with a large of patients and randomized prospective studies are needed to verify the outcome. While more research is absolutely necessary, this new technique and/or just some of its steps appears to offer a viable alternative for a coronectomy practitioner, helpful in obtaining superior results in addition to the existing IANIrisk reduction procedures. Acknowledgments The authors would like to thank Earl G. Freymiller, D.M.D., M.D., for the editorial guidance; Shankar Iyer, D.D.S., M.D.S., for structural guidance; the late John A. Yagiela, D.D.S, Ph.D., for help with research; Julia Cherney R.D.H., M.S., for editorial assistance. References [1] G. W. Bell, Use of dental panoramic tomographs to predict the relation between mandibular third molar teeth and the inferior alveolar nerve. Radiological and surgical findings, and clinical outcome, British Oral and Maxillofacial ery, vol. 42, no. 1, pp , [2] R.J.Middlehurst,G.R.Barker,andJ.P.Rood, Postoperative morbidity with mandibular third molar surgery: a comparison of two techniques, Oral and Maxillofacial ery, vol. 46, no. 6, pp , [3] V. Lopes, R. Mumenya, C. Feinmann, and M. Harris, Third molar surgery: an audit of the indications for surgery, postoperative complaints and patient satisfaction, British Oral and Maxillofacial ery,vol.33,no.1,pp.33 35,1995. [4]Y.Y.Leung,P.P.L.Fung,andL.K.Cheung, Treatment modalities of neurosensory deficit after lower third molar surgery: a systematic review, Oral and Maxillofacial ery, vol. 70, no. 4, pp , [5] A. Alantar, M. H. Roisin-Chausson, Y. Commissionat et al., Retention of third molar roots to prevent damage to the inferior alveolar nerve, Oral ery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and,vol.80,no.2,p.126,1995. [6] M. A. Pogrel, J. S. Lee, and D. F. Muff, Coronectomy: a technique to protect the inferior alveolar nerve, Oral and Maxillofacial ery,vol.62,no.12,pp ,2004.
6 6 Case Reports in Dentistry [7] T. Renton, M. Hankins, C. Sproate, and M. McGurk, A randomised controlled clinical trial to compare the incidence of injury to the inferior alveolar nerve as a result of coronectomy and removal of mandibular third molars, British Oral and Maxillofacial ery,vol.43,no.1,pp.7 12,2005. [8] M. A. Pogrel, An update on coronectomy, Oral and Maxillofacial ery,vol.67,no.8,pp ,2009. [9] Y.Y.LeungandL.K.Cheung, Safetyofcoronectomyversus excision of wisdom teeth: a randomized controlled trial, Oral ery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontology,vol.108,no.6,pp ,2009. [10] Y. Hatano, K. Kurita, Y. Kuroiwa, H. Yuasa, and E. Ariji, clinical evaluations of coronectomy (intentional partial odontectomy) for mandibular third molars using dental computed tomography: a case-control study, Oral and Maxillofacial ery,vol.67,no.9,pp ,2009. [11] D. Dolanmaz, G. Yildirim, K. Isik, K. Kucuk, and A. Ozturk, A preferable technique for protecting the inferior alveolar nerve: coronectomy, JournalofOralandMaxillofacialery,vol.67, no. 6, pp , [12] U. Cilasun, T. Yildirim, E. Guzeldemir, and Z. O. Pektas, Coronectomy in patients with high risk of inferior alveolar nerve injury diagnosed by computed tomography, Oral and Maxillofacial ery, vol. 69, no. 6, pp , [13]Y.Y.LeungandL.K.Cheung, Coronectomyofthelower third molar is safe within the first 3 years, J Oral and Maxillofacial ery,vol.70,no.7,pp ,2012. [14] J. Ecuyer and J. Debien, ical deductions, Actualites Odonto-Stomatologiques,vol.38,no.148,pp ,1984. [15] K. Knutsson, L. Lysell, and M. Rohlin, Postoperative status after partial removal of the mandibular third molar, Swedish Dental Journal,vol.13,no.1-2,pp.15 22,1989. [16] G. L. Freedman, Intentional partial odontectomy: review of cases, JournalofOralandMaxillofacialery,vol.55,no.5, pp , [17] B. C. O Riordan, Coronectomy (intentional partial odontectomy of lower third molars), Oral ery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontology,vol.98,no.3,pp , [18] L. A. Assael, Coronectomy: a time to ponder or a time to act? JournalofOralandMaxillofacialery,vol.62,no.12,pp , [19] A. Garcia-Garcia, Is coronectomy really preferable to extraction? [7], British Oral and Maxillofacial ery,vol. 44, no. 1, p. 75, [20] S. E. Lieblich, M. A. Kleiman, and J. Zak MJ, Parameters of care: clinical practice. Guidelines for oral and maxillofacial surgery. (AAOMS ParCare 2012), JournalofOralandMaxillofacial ery, vol. 70, e50, [21] L. Tolstunov, B. Javid, L. Keyes, and A. Nattestad, Pericoronal ostectomy: an alternative surgical technique for management of mandibular third molars in close proximity to the inferior alveolar nerve, JournalofOralandMaxillofacialery,vol. 69,no.7,pp ,2011. [22] G. A. Bonetti, In reply, JournalofOralandMaxillofacial ery,vol.66,no.6,p.1317,2008. [23] T. A. Quee, D. Gosselin, E. P. Millar, and J. W. Stamm, ical removal of the fully impacted mandibular third molar. The influence of flap design and alveolar bone height on the periodontal status of the second molar, Periodontology, vol. 56, no. 10, pp , [24] C. F. Kugelberg, U. Ahlström,S.Ericson,A.Hugoson,and H. Thilander, The influence of anatomical, pathophysiological and other factors on periodontal healing after impacted lower third molar surgery. A multiple regression analysis, Clinical Periodontology,vol.18,no.1,pp.37 43,1991. [25]K.Y.Peng,Y.C.Tseng,E.C.Shen,S.C.Chiu,E.Fu,andY. W. Huang, Mandibular second molar periodontal status after third molar extraction, Periodontology, vol. 72, no. 12, pp , [26] W.K.Kwok,J.K.S.Liu,E.C.M.Lo,E.F.Corbet,andW.K. Leung, Residual periodontal defects distal to the mandibular second molar 6-36 months after impacted third molar extraction: a retrospective cross-sectional study of young adults, Clinical Periodontology, vol. 29, no. 11, pp , [27] W.K.Leung,E.F.Corbet,W.K.Kwok,E.C.M.Lo,andJ.K. S. Liu, A regimen of systematic periodontal care after removal of impacted mandibular third molars manages periodontal pockets associated with the mandibular second molars, Journal of Clinical Periodontology,vol.32,no.7,pp ,2005. [28] O. Pons-Vicente, E. Valmaseda-Castellón, L. Berini-Aytés, and C. Gay-Escoda, Effect on pocket depth and attachment level of manual versus ultrasonic scaling of lower second molars following lower third molar extraction: a randomized controlled trial, Oral ery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontology,vol.107,no.3,pp.e11 e19,2009. [29] T. B. Dodson, Management of mandibular third molar extraction sites to prevent periodontal defects, Oral and Maxillofacial ery,vol.62,no.10,pp ,2004. [30] T. B. Dodson, Third molar socket grafting: is there an indication? JournalofOralandMaxillofacialery,vol.64,p.7, [31] G.Sammartino,M.Tia,G.Marenzi,A.EspeditoDiLauro,E. D Agostino, and P. P. Claudio, Use of autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in periodontal defect treatment after extraction of impacted mandibular third molars, JournalofOraland Maxillofacial ery, vol. 63, no. 6, pp , [32] G.J.PellandB.T.Gregory, Impactedmandibularthirdmolars. Classification and modified techniques for removal, Dental Digest, vol. 39, p. 330, [33] G. Howe and H. G. Poyton, Prevention of damage to the inferior dental nerve during the extraction of mandibular third molars, British Dental Journal, vol. 109, pp , [34] J. P. Rood and B. A. A. Nooraldeen Shehab, The radiological prediction of inferior alveolar nerve injury during third molar surgery, British Oral and Maxillofacial ery, vol. 28, no. 1, pp , [35] B. F. Blaeser, M. A. August, R. B. Donoff, L. B. Kaban, and T. B. Dodson, Panoramic radiographic risk factors for inferior alveolar nerve injury after third molar extraction, Oral and Maxillofacial ery,vol.61,no.4,pp ,2003. [36] M. Sedaghatfar, M. A. August, and T. B. Dodson, Panoramic radiographic findings as predictors of inferior alveolar nerve exposure following third molar extraction, JournalofOraland Maxillofacial ery,vol.63,no.1,pp.3 7,2005. [37] Y. Y. Leung and L. K. Cheung, Correlation of radiographic signs, inferior dental nerve exposure, and deficit in third molar surgery, JournalofOralandMaxillofacialery, vol. 69, no. 7, pp , 2011.
7 Case Reports in Dentistry 7 [38]T.B.Dodson,I.D.Cheifetz,W.J.Nelson,andL.K.Rafetto, Summary of the proceeding of the third molar multidisciplinary conference, JournalofOralandMaxillofacialery, vol. 70, no. 9, supplement 1, pp. S66 S69, [39] L. Landi, P. F. Manicone, S. Piccinelli, A. Raia, and R. Raia, A novel surgical approach to impacted mandibular third molars to reduce the risk of paresthesia: a case series, JournalofOral and Maxillofacial ery, vol. 68, no. 5, pp , [40]A.Hirsch,S.Shteiman,B.D.Boyan,andZ.Schwartz, Use of orthodontic treatment as an aid to third molar extraction: a method for prevention of mandibular nerve injury and improved periodontal status, Periodontology,vol.74, no. 6, pp , [41] G. A. Bonetti, M. Bendandi, L. Laino, V. Checchi, and L. Checchi, Orthodontic extraction: riskless extraction of impacted lower third molars close to the mandibular canal, OralandMaxillofacialery,vol.65,no.12,pp , [42] A. M. Polson and M. P. Proye, Effect of root surface alterations on periodontal healing. II. Citric acid treatment of the denuded root, Clinical Periodontology, vol. 9, no. 6, pp , [43] B. Shetty, A. Dinesh, and H. Seshan, Comparitive effects of tetracyclines and citric acid on dentin root surface of periodontally involved human teeth: a scanning electron microscope study, Indian Society of Periodontology, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 8 15, [44]A.Polson,K.Gutierrez,B.Frantzetal., Dentinattachment after treatment with either citric acid or tetracycline, Journal of Dental Research,vol.86,p.2966,2007.
8 Advances in Preventive Medicine The Scientific World Journal Case Reports in Dentistry International Dentistry Scientifica Pain Research and Treatment International Biomaterials Environmental and Public Health Submit your manuscripts at Oral Implants Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Advances in Oral Oncology Anesthesiology Research and Practice Orthopedics Drug Delivery Dental ery BioMed Research International International Oral Diseases Endocrinology Radiology Research and Practice
A Preferable Technique for Protecting the Inferior Alveolar Nerve: Coronectomy
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 7:13-138, 9 A Preferable Technique for Protecting the Inferior Alveolar Nerve: Coronectomy Dogan Dolanmaz, DDS, PhD,* Gulsun Yildirim, DDS, PhD, Kubilay Isik, DDS, PhD, Korhan Kucuk,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 7:13-138, 9 A Preferable Technique for Protecting the Inferior Alveolar Nerve: Coronectomy Dogan Dolanmaz, DDS, PhD,* Gulsun Yildirim, DDS, PhD, Kubilay Isik, DDS, PhD, Korhan Kucuk,
CORONECTOMY OF MANDIBULAR WISDOM TEETH: A CASE SERIES AND BRIEF REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 26 DENTAL STUDENTS RESEARCH CORONECTOMY OF MANDIBULAR WISDOM TEETH: A CASE SERIES AND BRIEF REVIEW OF LITERATURE Rasha Alafaleg1 1 SAN DANETH 1 Bachelor of Dental Surgery, University of Health Sciences,
26 DENTAL STUDENTS RESEARCH CORONECTOMY OF MANDIBULAR WISDOM TEETH: A CASE SERIES AND BRIEF REVIEW OF LITERATURE Rasha Alafaleg1 1 SAN DANETH 1 Bachelor of Dental Surgery, University of Health Sciences,
Coronectomy a Cognizance Technique Nescient to Oral Surgeons: Translational Paradigms
 REVIEW ARTICLE Coronectomy a Cognizance Technique Nescient to Oral 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1015 Surgeons: Translational Paradigms Coronectomy a Cognizance Technique Nescient to Oral Surgeons: Translational
REVIEW ARTICLE Coronectomy a Cognizance Technique Nescient to Oral 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1015 Surgeons: Translational Paradigms Coronectomy a Cognizance Technique Nescient to Oral Surgeons: Translational
Staged Removal of Horizontally Impacted Third Molars to Reduce Risk of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Injury
 CASE REPORTS J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:442-446, 2010 Staged Removal of Horizontally Impacted Third Molars to Reduce Risk of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Injury Luca Landi, DDS,* Paolo Francesco Manicone, DDS,
CASE REPORTS J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:442-446, 2010 Staged Removal of Horizontally Impacted Third Molars to Reduce Risk of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Injury Luca Landi, DDS,* Paolo Francesco Manicone, DDS,
Coronectomy of Third Molar: A Reduced Risk Technique for Inferior Alveolar Nerve Damage
 Chkoura Ahmed El Wady Wafae and Taleb Bouchra Coronectomy of Third Molar: A Reduced Risk Technique for Inferior Alveolar Nerve Damage Abstract: Causing damage to the inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) when
Chkoura Ahmed El Wady Wafae and Taleb Bouchra Coronectomy of Third Molar: A Reduced Risk Technique for Inferior Alveolar Nerve Damage Abstract: Causing damage to the inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) when
Panoramic Radiographic Findings as Predictors of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Exposure Following Third Molar Extraction
 CLINICAL ARTICLES Panoramic Radiographic Findings as Predictors of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Exposure Following Third Molar Extraction Michael Sedaghatfar, BS, DMD,* Meredith A. August, DMD, MD, and Thomas
CLINICAL ARTICLES Panoramic Radiographic Findings as Predictors of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Exposure Following Third Molar Extraction Michael Sedaghatfar, BS, DMD,* Meredith A. August, DMD, MD, and Thomas
Coronectomy of impacted mandibular third molars: A meta-analysis and systematic review of the literature
 Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 016 Jul 1;1 (4):e50513. Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.1074 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.1074 of impacted mandibular
Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 016 Jul 1;1 (4):e50513. Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.1074 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.1074 of impacted mandibular
Evaluation of Outcome Following Coronectomy for the Management of Mandibular Third Molars in Close Proximity to Inferior Alveolar Nerve
 DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/20991.8273 Dentistry Section Original Article Evaluation of Outcome Following Coronectomy for the Management of Mandibular Third Molars in Close Proximity to Inferior Alveolar Nerve
DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/20991.8273 Dentistry Section Original Article Evaluation of Outcome Following Coronectomy for the Management of Mandibular Third Molars in Close Proximity to Inferior Alveolar Nerve
Nabil Khzam, 1 Adam Fell, 2 Anthony Fisher, 3 Paul Kim, 4 Usman A. Khan, 5 and Mahmoud M. Bakr Introduction
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 3847615, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3847615 Case Report A New Multi-Ingredient Recipe for the Treatment of Localized Advanced Periodontal Disease
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 3847615, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3847615 Case Report A New Multi-Ingredient Recipe for the Treatment of Localized Advanced Periodontal Disease
Coronectomy (intentional partial odontectomy of lower third molars)
 Vol. 98 No. 3 September 2004 ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY Editor: James R. Hupp Coronectomy (intentional partial odontectomy of lower third molars) Brian C. O Riordan, BDS (NUI), FDSRCS (Eng), FFDRCSI,
Vol. 98 No. 3 September 2004 ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY Editor: James R. Hupp Coronectomy (intentional partial odontectomy of lower third molars) Brian C. O Riordan, BDS (NUI), FDSRCS (Eng), FFDRCSI,
Coronectomy versus surgical removal of the lower third molars with a high risk of injury to the inferior alveolar nerve. A bibliographical review
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.20432 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.20432 Coronectomy versus surgical removal of the lower third molars with a high risk
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.20432 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.20432 Coronectomy versus surgical removal of the lower third molars with a high risk
Subject: Removal of Teeth Guideline #: Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/06/2018
 DDental Policy Dental Subject: Removal of Teeth Guideline #: 07-101 Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/06/2018 Description This document addresses the removal of teeth, erupted
DDental Policy Dental Subject: Removal of Teeth Guideline #: 07-101 Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/06/2018 Description This document addresses the removal of teeth, erupted
Relation between the complex diagnostics and the complications of the wisdom-tooth surgery
 Relation between the complex diagnostics and the complications of the wisdom-tooth surgery Changes of the "surgical profile" at the Dental Surgery Department of the Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Clinic,
Relation between the complex diagnostics and the complications of the wisdom-tooth surgery Changes of the "surgical profile" at the Dental Surgery Department of the Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Clinic,
Functional Sensory Recovery After Trigeminal Nerve Repair
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:60-65, 2007 Functional Sensory Recovery After Trigeminal Nerve Repair Srinivas M. Susarla, BA,* Leonard B. Kaban, DMD, MD, R. Bruce Donoff, DMD, MD, and Thomas B. Dodson, DMD,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:60-65, 2007 Functional Sensory Recovery After Trigeminal Nerve Repair Srinivas M. Susarla, BA,* Leonard B. Kaban, DMD, MD, R. Bruce Donoff, DMD, MD, and Thomas B. Dodson, DMD,
Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 902861, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/902861 Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis S. Venkata
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 902861, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/902861 Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis S. Venkata
SELEC T ED R E A D I NGS ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY THE ART AND SCIENCE OF CORONECTOMY
 SELEC T ED R E A D I NGS IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY THE ART AND SCIENCE OF CORONECTOMY Kyriaki C. Marti, DMD, MD, PhD Christos A. Skouteris, DMD, PhD Volume 22, Number 2 April, 2014 INTRODUCTION
SELEC T ED R E A D I NGS IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY THE ART AND SCIENCE OF CORONECTOMY Kyriaki C. Marti, DMD, MD, PhD Christos A. Skouteris, DMD, PhD Volume 22, Number 2 April, 2014 INTRODUCTION
Coronectomy as a surgical approach to impacted mandibular third molars: a systematic review
 Martin et al. Head & Face Medicine (2015) 11:9 DOI 10.1186/s13005-015-0068-7 HEAD & FACE MEDICINE REVIEW Open Access Coronectomy as a surgical approach to impacted mandibular third molars: a systematic
Martin et al. Head & Face Medicine (2015) 11:9 DOI 10.1186/s13005-015-0068-7 HEAD & FACE MEDICINE REVIEW Open Access Coronectomy as a surgical approach to impacted mandibular third molars: a systematic
Complex Exodontia. Jone Kim, DDS, MS
 Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
The relative risk of neurosensory deficit following removal of mandibular third molar teeth: the influence of radiography and surgical technique
 The relative risk of neurosensory deficit following removal of mandibular third molar teeth: the influence of radiography and surgical technique W. P. Smith, FDSRCS (Eng), FRCSEd, FRCS (Eng), Northamptonshire,
The relative risk of neurosensory deficit following removal of mandibular third molar teeth: the influence of radiography and surgical technique W. P. Smith, FDSRCS (Eng), FRCSEd, FRCS (Eng), Northamptonshire,
Case Report Treatment of Two Canals in All Mandibular Incisor Teeth in the Same Patient
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 893980, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/893980 Case Report Treatment of Two Canals in All Mandibular Incisor Teeth in the Same Patient Vandana B. Kokane, Swapnil
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 893980, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/893980 Case Report Treatment of Two Canals in All Mandibular Incisor Teeth in the Same Patient Vandana B. Kokane, Swapnil
SECTION XVI. EssentialSmile Ped 111, ST, INN, Pediatric Dental SCHEDULE OF BENEFITS
 SECTION XVI. EssentialSmile Ped 111, ST, INN, Pediatric Dental SCHEDULE OF BENEFITS COST-SHARING PEDIATRIC DENTAL CARE ESSENTIAL HEALTH BENEFIT Deductible One (1) Member under age 19 Two (2) or more Members
SECTION XVI. EssentialSmile Ped 111, ST, INN, Pediatric Dental SCHEDULE OF BENEFITS COST-SHARING PEDIATRIC DENTAL CARE ESSENTIAL HEALTH BENEFIT Deductible One (1) Member under age 19 Two (2) or more Members
LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES
 LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES The following is a complete list of those dental Services which will be considered for payment by Constitution Life Insurance Company after the expiration of any applicable
LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES The following is a complete list of those dental Services which will be considered for payment by Constitution Life Insurance Company after the expiration of any applicable
Introduction. Report of a Case BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN
 10.1515/bjdm-2016-0008 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Tooth Multi-Sectioning with the Use of Magnification, for Extraction of a Deeply Impacted Lower Second Molar
10.1515/bjdm-2016-0008 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Tooth Multi-Sectioning with the Use of Magnification, for Extraction of a Deeply Impacted Lower Second Molar
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1
 PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH
 FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
Surgical removal of wisdom teeth
 Oral surgery/dr.hazem Lecture #8 Rand Herzallah Surgical removal of wisdom teeth Wisdom teeth extraction is harder than the extraction of any other teeth; because of: 1) The anatomical location of the
Oral surgery/dr.hazem Lecture #8 Rand Herzallah Surgical removal of wisdom teeth Wisdom teeth extraction is harder than the extraction of any other teeth; because of: 1) The anatomical location of the
Senior Dental Insurance Scheduled Allowance
 Senior Dental Insurance Scheduled Allowance LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES The following is a complete list of those dental services which will be considered for payment by The American Progressive Life
Senior Dental Insurance Scheduled Allowance LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES The following is a complete list of those dental services which will be considered for payment by The American Progressive Life
Surgical Uprighting Is a Successful Procedure for Management of Impacted Mandibular Second Molars
 DENTOALVEOLAR SURGERY Surgical Uprighting Is a Successful Procedure for Management of Impacted Mandibular Second Molars Bonnie L. Padwa, DMD, MD,* Rushil R. Dang, BDS, DMD,y and Cory M. Resnick, DMD, MDz
DENTOALVEOLAR SURGERY Surgical Uprighting Is a Successful Procedure for Management of Impacted Mandibular Second Molars Bonnie L. Padwa, DMD, MD,* Rushil R. Dang, BDS, DMD,y and Cory M. Resnick, DMD, MDz
Radiographic assessment of lower third molar prior to surgery: A report of four cases
 Radiographic assessment of lower third molar prior to surgery: A report of four cases V Sreenivas Prasad Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman,
Radiographic assessment of lower third molar prior to surgery: A report of four cases V Sreenivas Prasad Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman,
SECTION XVI. EssentialSmile Ped 111, ST, INN, Pediatric Dental Schedule of Benefits
 COST-SHARING SECTION XVI. EssentialSmile Ped 111, ST, INN, Pediatric Dental Schedule of Benefits Members can search for a Network Provider at www.solsticecare.com/provider-search.aspx Member Services:
COST-SHARING SECTION XVI. EssentialSmile Ped 111, ST, INN, Pediatric Dental Schedule of Benefits Members can search for a Network Provider at www.solsticecare.com/provider-search.aspx Member Services:
The extraction of an impacted mandibular. Reliability of panoramic radiography in evaluating the topographic relationship
 ABSTRACT Reliability of panoramic radiography in evaluating the topographic relationship between the mandibular canal and impacted third molars GIUSEPPE MONACO, D.M.D.; MARCO MONTEVECCHI, D.M.D.; GIULIO
ABSTRACT Reliability of panoramic radiography in evaluating the topographic relationship between the mandibular canal and impacted third molars GIUSEPPE MONACO, D.M.D.; MARCO MONTEVECCHI, D.M.D.; GIULIO
Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask
 Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure with serious potential complications and should only be performed by a trained veterinarian.
Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure with serious potential complications and should only be performed by a trained veterinarian.
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the. Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System
 Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
CDT CODE** DOCUMENTATION GUIDELINES COVERAGE GUIDELINES* Restorative D2929-D2390 D2542-D2544 D2642-D2644 D2662-D2664 D2710-D2799 D2930 D2960-D2962
 DENTAL AND ORAL SURGERY CLAIM DOCUMENTATION GUIDELINES Each benefits plan defines which services are covered, excluded and subject to dollar caps or other limits. Members and their dentists will need to
DENTAL AND ORAL SURGERY CLAIM DOCUMENTATION GUIDELINES Each benefits plan defines which services are covered, excluded and subject to dollar caps or other limits. Members and their dentists will need to
Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports
 0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
Principles of endodontic surgery
 Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Alveolar Ridge Preservation:
 Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Fee Schedule Detail Procedure Procedure Description Code Fee
 Fee Schedule Detail Procedure Procedure Description Code Fee D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT $ 32.29 D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION-PROBLEM FOCUSED $ 53.02 D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL
Fee Schedule Detail Procedure Procedure Description Code Fee D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT $ 32.29 D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION-PROBLEM FOCUSED $ 53.02 D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL
SURGICAL EXTRACTION OF IMPACTED TEETH
 UnitedHealthcare Dental Clinical Policy SURGICAL EXTRACTION OF IMPACTED TEETH Policy Number: DCP006.03 Effective Date: December 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
UnitedHealthcare Dental Clinical Policy SURGICAL EXTRACTION OF IMPACTED TEETH Policy Number: DCP006.03 Effective Date: December 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS
 INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
EssentialSmile Ped 221 Schedule of Benefits
 EssentialSmile Ped 221 Schedule of Benefits P.O. Box 19199 Plantation, FL 33318 Telephone: 877-760-2247 Fax: 954-370-1701 www.mysolstice.net Members can search for a Network Provider at www.solsticecare.com/provider-search.aspx
EssentialSmile Ped 221 Schedule of Benefits P.O. Box 19199 Plantation, FL 33318 Telephone: 877-760-2247 Fax: 954-370-1701 www.mysolstice.net Members can search for a Network Provider at www.solsticecare.com/provider-search.aspx
EssentialSmile Ped 221 Schedule of Benefits
 EssentialSmile Ped 221 Schedule of Benefits P.O. Box 9 Plantation, FL 33318 Telephone: 877 760 2247 Fax: 954 370 1701 www.mysolstice.net Members can search for a Network Provider atwww.solsticecare.com/provider
EssentialSmile Ped 221 Schedule of Benefits P.O. Box 9 Plantation, FL 33318 Telephone: 877 760 2247 Fax: 954 370 1701 www.mysolstice.net Members can search for a Network Provider atwww.solsticecare.com/provider
3-Dimensional Imaging for Lower Third Molars: Is There an Implication for Surgical Removal?
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69:1867-1872, 2011 3-Dimensional Imaging for Lower Third Molars: Is There an Implication for Surgical Removal? Gerold Eyrich, MD, DMD,* Burkhardt Seifert, PhD, Felix Matthews, MD,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69:1867-1872, 2011 3-Dimensional Imaging for Lower Third Molars: Is There an Implication for Surgical Removal? Gerold Eyrich, MD, DMD,* Burkhardt Seifert, PhD, Felix Matthews, MD,
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Patient information leaflet about Lower Wisdom Teeth (3 rd Molars)
 Patient information leaflet about Lower Wisdom Teeth (3 rd Molars) This leaflet is designed to give you more information about what the issues are with wisdom teeth, what treatment options may be given,
Patient information leaflet about Lower Wisdom Teeth (3 rd Molars) This leaflet is designed to give you more information about what the issues are with wisdom teeth, what treatment options may be given,
2018 Dental Code Set For dates of service from 1/1/ /31/2018
 D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
2018 Dental Code Set
 D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
extraction and describe the evolution of LN sensitivity as well as the prognosis of LN damage based on preoperative data.
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 64:42-47, 26 Frequency and Evolution of Lingual Nerve Lesions Following Lower Third Molar Extraction Elena Queral-Godoy, DDS,* Rui Figueiredo, DDS, Eduard Valmaseda-Castellón, DDS,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 64:42-47, 26 Frequency and Evolution of Lingual Nerve Lesions Following Lower Third Molar Extraction Elena Queral-Godoy, DDS,* Rui Figueiredo, DDS, Eduard Valmaseda-Castellón, DDS,
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Analysis and evaluation of relative positions of mandibular third molar and mandibular canal impacts
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/.525/jkaoms.24.4.6.278 pissn 2234-755 eissn 2234-593 Analysis and evaluation of relative positions of mandibular third molar and mandibular canal impacts Hang-Gul Kim,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/.525/jkaoms.24.4.6.278 pissn 2234-755 eissn 2234-593 Analysis and evaluation of relative positions of mandibular third molar and mandibular canal impacts Hang-Gul Kim,
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
Case Report Management of a Severely Submerged Primary Molar: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 796242, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/796242 Case Report Management of a Severely Submerged Primary Molar: A Case Report Iman Parisay, 1 Fatemeh
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 796242, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/796242 Case Report Management of a Severely Submerged Primary Molar: A Case Report Iman Parisay, 1 Fatemeh
DENTAL EXTRACTIONS MADE EASIER. Brook A. Niemiec, DVM
 DENTAL EXTRACTIONS MADE EASIER Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Diplomate, European Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry San Diego Vet Dental
DENTAL EXTRACTIONS MADE EASIER Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Diplomate, European Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry San Diego Vet Dental
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Clinical Perspectives
 Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Age as a Risk Factor for Third Molar Surgery Complications
 BASIC AND PATIENT-ORIENTED RESEARCH Age as a Risk Factor for Third Molar Surgery Complications Sung-Kiang Chuang, DMD, MD, DMSc,* David H. Perrott, DDS, MD, MBA, Srinivas M. Susarla, BA, and Thomas B.
BASIC AND PATIENT-ORIENTED RESEARCH Age as a Risk Factor for Third Molar Surgery Complications Sung-Kiang Chuang, DMD, MD, DMSc,* David H. Perrott, DDS, MD, MBA, Srinivas M. Susarla, BA, and Thomas B.
Case Report Esthetic Root Coverage with Double Papillary Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 509319, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/509319 Case Report Esthetic Root Coverage with Double Papillary Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft: A Case Report
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 509319, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/509319 Case Report Esthetic Root Coverage with Double Papillary Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft: A Case Report
Research Article Assessment of Nerve Injuries after Surgical Removal of Mandibular Third Molar: A Prospective Study
 Asian Journal of Neuroscience Volume 2013, Article ID 291926, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/291926 Research Article Assessment of Nerve Injuries after Surgical Removal of Mandibular Third Molar:
Asian Journal of Neuroscience Volume 2013, Article ID 291926, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/291926 Research Article Assessment of Nerve Injuries after Surgical Removal of Mandibular Third Molar:
Newport News Public Schools Summary Schedule of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan
 Newport News Public Schools Summary of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan Services In-Network Out-of-Network PPO Premier All Other Diagnostic & Preventive Oral Exams & Teeth Cleanings Fluoride Applications
Newport News Public Schools Summary of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan Services In-Network Out-of-Network PPO Premier All Other Diagnostic & Preventive Oral Exams & Teeth Cleanings Fluoride Applications
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 505676, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/505676 Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 505676, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/505676 Case Report Endodontic Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary First Premolars with Three Roots Using CBCT: A Case Report
Buccal approach in surgical removal of lingually embedded teeth: a report of 2 cases
 Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Case report Buccal approach in surgical removal of lingually embedded teeth: a report of 2 cases Thatsanai Tangmankongworakoon 1, Nattamet Wongsirichat 2 1 Lad Yao
Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Case report Buccal approach in surgical removal of lingually embedded teeth: a report of 2 cases Thatsanai Tangmankongworakoon 1, Nattamet Wongsirichat 2 1 Lad Yao
Pre op Failed endodontic treatment with sinus involvement.
 Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases
 Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
HDS PROCEDURE CODE GUIDELINES
 D0100 - D0999 Clinical Oral Evaluations D0120 - D0180 The codes in this section have been revised to recognize the cognitive skills necessary for patient evaluation. The collection and recording of some
D0100 - D0999 Clinical Oral Evaluations D0120 - D0180 The codes in this section have been revised to recognize the cognitive skills necessary for patient evaluation. The collection and recording of some
Schedule of Benefits (GR-9N S )
 Schedule of Benefits (GR-9N S-01-001-01) Employer: Group Policy Number: BNSF Railway Company GP-727796 Issue Date: January 1, 2016 Effective Date: January 1, 2016 Schedule: 1A Cert Base: 1 For: DMO - All
Schedule of Benefits (GR-9N S-01-001-01) Employer: Group Policy Number: BNSF Railway Company GP-727796 Issue Date: January 1, 2016 Effective Date: January 1, 2016 Schedule: 1A Cert Base: 1 For: DMO - All
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
Schedule of Benefits (GR-9N S )
 Schedule of Benefits (GR-9N S-01-001-01) Employer: Group Policy Number: Roman Catholic Diocese Of Dallas GP-870560-WI Issue Date: February 9, 2015 Effective Date: January 1, 2015 Schedule: 7A Cert Base:
Schedule of Benefits (GR-9N S-01-001-01) Employer: Group Policy Number: Roman Catholic Diocese Of Dallas GP-870560-WI Issue Date: February 9, 2015 Effective Date: January 1, 2015 Schedule: 7A Cert Base:
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries
 The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
Postprint.
 http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper published in Dento-Maxillo-Facial Radiology. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections
http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper published in Dento-Maxillo-Facial Radiology. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter. Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July Volume 2
 Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Gingivectomy, excision gingival, each quadrant Gingivoplasty, each quadrant
 Dental in Nature Oral Surgery Effective CDT D3410 surgery - anterior D3421 surgery bicuspid (first root) D3425 surgery molar (first root) D3426 D3427 surgery (each additional root) Periradicular surgery
Dental in Nature Oral Surgery Effective CDT D3410 surgery - anterior D3421 surgery bicuspid (first root) D3425 surgery molar (first root) D3426 D3427 surgery (each additional root) Periradicular surgery
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
Management of osseous defects in aggressive periodontitis: A report of four cases using different techniques
 www.edoriumjournals.com case series OPEN ACCESS Management of osseous defects in aggressive periodontitis: A report of four cases using different techniques Sangeeta Singh, Parul Sharma ABSTRACT Introduction:
www.edoriumjournals.com case series OPEN ACCESS Management of osseous defects in aggressive periodontitis: A report of four cases using different techniques Sangeeta Singh, Parul Sharma ABSTRACT Introduction:
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery. Dr.maryam khosravi
 Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION UTILIZING PLATELET RICH FIBRIN IN COMBINATION WITH DEMINERALIZED FREEZE-DRIED BONE ALLOGRAFT A CASE REPORT
 ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION UTILIZING PLATELET RICH FIBRIN IN COMBINATION WITH DEMINERALIZED FREEZE-DRIED BONE ALLOGRAFT A CASE REPORT * Mishal Piyush Shah 1 and Sheela Kumar Gujjari 2 1 Department of
ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION UTILIZING PLATELET RICH FIBRIN IN COMBINATION WITH DEMINERALIZED FREEZE-DRIED BONE ALLOGRAFT A CASE REPORT * Mishal Piyush Shah 1 and Sheela Kumar Gujjari 2 1 Department of
Case Report Orthodontic Treatment of a Mandibular Incisor Extraction Case with Invisalign
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 657657, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/657657 Case Report Orthodontic Treatment of a Mandibular Incisor Extraction Case with Invisalign Khalid H. Zawawi Department
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 657657, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/657657 Case Report Orthodontic Treatment of a Mandibular Incisor Extraction Case with Invisalign Khalid H. Zawawi Department
Malpractice claims related to tooth extractions. Koskela, Sanna
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Malpractice claims related to tooth extractions Koskela, Sanna 2017-03 Koskela, S, Suomalainen, A, Apajalahti, S & Venta, I 2017, ' Malpractice claims related to tooth extractions
https://helda.helsinki.fi Malpractice claims related to tooth extractions Koskela, Sanna 2017-03 Koskela, S, Suomalainen, A, Apajalahti, S & Venta, I 2017, ' Malpractice claims related to tooth extractions
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
FEE SCHEDULE. Complete Dental Plan is a discount plan offered and administered by our organization at:
 FEE SCHEDULE Complete Dental Plan is a discount plan offered and administered by our organization at: 7801 CORAL WAY SUITE # 106, MIAMI, FL 33144 (786) 326-6873 F (305) 6979785 COMPLETE DENTAL PLAN HIGHLIGHTS
FEE SCHEDULE Complete Dental Plan is a discount plan offered and administered by our organization at: 7801 CORAL WAY SUITE # 106, MIAMI, FL 33144 (786) 326-6873 F (305) 6979785 COMPLETE DENTAL PLAN HIGHLIGHTS
Immediate Implant Placement Along With Guided Bone Regeneration In Mandibular Anterior Region A Case Report.
 IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
Comparison of panoramic radiography with cone beam CT in predicting the relationship of the mandibular third molar roots to the alveolar canal
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2013; 43: 105-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.2.105 Comparison of panoramic radiography with cone beam CT in predicting the relationship of the mandibular third molar
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2013; 43: 105-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.2.105 Comparison of panoramic radiography with cone beam CT in predicting the relationship of the mandibular third molar
RETIREE DENTAL PLAN. RETIREE DENTAL PLAN FEE SCHEDULE Page 1 of 8
 D0120 periodic oral evaluation $ 30.50 D0140 limited oral evaluation problem focused $ 30.50 D0150 comprehensive oral evaluation - new or established patient $ 30.50 D0160 detailed and extensive oral evaluation
D0120 periodic oral evaluation $ 30.50 D0140 limited oral evaluation problem focused $ 30.50 D0150 comprehensive oral evaluation - new or established patient $ 30.50 D0160 detailed and extensive oral evaluation
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12 Accepted on:22/05/12
 SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
Elevators. elevators:- There are three major components of the elevator are:-
 Elevators Elevators:- Are exo-levers, instrument designed to elevate or luxate the teeth or roots from their bony socket in close or surgical method of extraction to force a tooth or root along the line
Elevators Elevators:- Are exo-levers, instrument designed to elevate or luxate the teeth or roots from their bony socket in close or surgical method of extraction to force a tooth or root along the line
BRITISH BIOMEDICAL BULLETIN
 Journal Home Page www.bbbulletin.org BRITISH BIOMEDICAL BULLETIN Case Report Hemisection- A Baton for Extracting Teeth Savita S, R S Senthil Rajan, Ambica *, Krishna Kripal, Poorna Prakash and Sachidananda
Journal Home Page www.bbbulletin.org BRITISH BIOMEDICAL BULLETIN Case Report Hemisection- A Baton for Extracting Teeth Savita S, R S Senthil Rajan, Ambica *, Krishna Kripal, Poorna Prakash and Sachidananda
The Dental Microscope. Index. Acceptance of Microscope endodontic 17. Broken Instruments endodontic 26. Depth of Field managing 170
 257 Acceptance of Microscope endodontic 17 Index Broken Instruments endodontic 26 Depth of Field managing 170 Efficiency maximizing 243-245 Endodontics access debridement 40 access opening 28 anatomic
257 Acceptance of Microscope endodontic 17 Index Broken Instruments endodontic 26 Depth of Field managing 170 Efficiency maximizing 243-245 Endodontics access debridement 40 access opening 28 anatomic
Techniques of local anesthesia in the mandible
 Techniques of local anesthesia in the mandible The technique of choice for anesthesia of the mandible is the block injection and this is attributed to the absence of the advantages which are present in
Techniques of local anesthesia in the mandible The technique of choice for anesthesia of the mandible is the block injection and this is attributed to the absence of the advantages which are present in
