M axillary sinus augmentation
|
|
|
- Hillary Phelps
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 406 SINUS IN RELATION TO COMPLICATIONS IN LATERAL WINDOW SINUS AUGMENTATION CHAN AND WANG Sinus Pathology and Anatomy in Relation to Complications in Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Hsun-Liang Chan, DDS,* and Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MS, PhD M axillary sinus augmentation via a lateral window approach (SALW) is an effective procedure to gain bone height for implant placement in an atrophic posterior maxilla. 1,2 This technique was first published by Boyne and James 3 in According to them, a bony window was made on the lateral sinus wall and a space was created between the Schneiderian membrane and the sinus walls, where a grafting material was placed. One key advantage of this approach is gaining direct access to the sinus. However, despite the high success rate, do occur. 4 The most frequently encountered surgical complication is perforation of the Schneiderian membrane. 5 Other include massive bleeding, infection, implant displacement into the sinus, etc. 1 More than often these are related to the sinus anatomy and preexisting antral pathologies. Knowledge about common sinus diseases and variations in sinus anatomy would greatly reduce the occurrence of these. Therefore, this article aimed at reviewing antral diseases and anatomy that might predispose to surgical in SALW. A treatment *Resident, Graduate Periodontics, School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI. Professor and Director, Graduate Periodontics, School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI. Reprint requests and correspondence to: Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MS, PhD, 1011 North University Avenue, Ann Arbor, MI , Phone: (734) , Fax: (734) , homlay@umich.edu ISSN /11/ Implant Dentistry Volume 20 Number 6 Copyright 2011 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins DOI: /ID.0b013e f79 Antral pathoses and anatomical variations increase the risk of surgical during a lateral window sinus augmentation procedure. Therefore, an understanding of maxillary sinus diseases and anatomies is imperative. In the first part of this article, common sinus diseases will be reviewed, which include acute/chronic rhinosinusitis, mucoceles, pseudocysts, retention cysts, and odontogenic diseases of the maxillary sinus. In addition, a treatment strategy will be proposed toward the management of proposal aiming at managing antral diseases was introduced. In addition, the management of these surgical was discussed. MAXILLARY SINUS DISEASES One of the main functions of the maxillary sinus is to humidify and filter the air inhaled in the nose. It is achieved by a layer of specialized respiratory epithelium, classified as ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. 6 The main components of this epithelial layer are basal cells, goblet cells, and ciliated cells. 7 Basal cells own the ability to proliferate and differentiate into the other 2 cell types. Goblet cells are secretory cells that produce mucin. The ciliated cells are columnar epithelial cells that possess cilia. They function by moving the mucin toward the ostium, an opening connecting the maxillary sinus to the middle meatus in the nasal cavity. Blockage of this pathway could lead to accumulation of mucin and antral these antral diseases. In the second part, anatomical variations of the maxillary sinus, for example, the septum and artery that is in approximation to the osteotomy site will be discussed. Knowledge of diagnosing and managing sinus pathoses and anatomies could assist surgeons in reducing the incidence of sinus augmentation. (Implant Dent 2011;20: ) Key Words: maxillary sinus, sinus pathology, sinus anatomy, sinus augmentation, dental implants pressure in the sinus, eventually giving rising to symptoms, such as palpation pain around infraorbital region and headache. Many of the sinus diseases and some resulting from SALW are associated with the inability of the maxillary sinus to drain mucin. Sinus diseases and abnormities are prevalent (40%) in patients scheduled for sinus lift procedures and the presence of those conditions is significantly correlated with a history of indicative symptoms. 8 In addition, their presence might increase the difficulties in performing the surgery and the risk of developing postoperative As a result, maxillary sinus diseases should be recognized and managed with care before a sinus augmentation procedure. Many of them could be identified via a thorough medical and dental history evaluation, with a special focus on any signs and symptoms that might suggest a concern in the sinus. 8 A careful
2 IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 20, NUMBER Table 1. Common Maxillary Sinus Diseases and Their Managements for SALW Diagnosis Disease Clinical Symptoms Radiographic Findings Etiology Histological Findings Management ARS CRS Duration up to 4 wk Anterior or posterior mucopurulent drainage Nasal congestion Facial pain/pressure Decreased sense of smell Duration longer than 8 12 wk Anterior or posterior mucopurulent drainage Nasal congestion Facial pain/pressure Decreased sense of smell Opacification or air-fluid level Bacterial/viral/fungal infection Infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages Thickening of the sinus lining more or less in even width Pseudocyst Usually none Prevalence: 1.5% 10% Dome-shaped radiopacity Commonly located on the floor of the sinus Retention cyst Mucocele Usually none Very rare, more commonly found in frontal sinuses May include headache, diplopia, visual impairment, and/or nasal obstruction Mostly too small to be detected Commonly found around ostium Initial stage: cloudy sinus cavity Later stage: thinner sinus wall Mainly inflammation from low-grade infection or allergy Focal accumulation of inflammatory exudate Blockage and dilatation of ducts of the seromucinous glands Blockage of ostium due to trauma or other diseases Infiltration of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages No epithelial lining Exudates accumulation Inflammatory infiltration With epithelial lining Mucin accumulation With epithelial lining (typical respiratory epithelium or squamous metaplasia) ENT consultation ENT consultation: with symptoms or thick membrane 1/3 sinus height Otherwise, proceed with SALW ENT consultation: with symptoms or closer to medial wall Otherwise, enucleation via lateral window Proceed with SALW ENT consultation dental and periodontal examination especially for those teeth that are in the vicinity of the sinus should be executed to rule out any odontogenic lesions. Common sinus diseases that might interfere with the performance of SALW include acute/chronic rhinosinusitis, sinusitis of odontogenic origin, odontogenic cysts, pseudocysts, mucoceles, and retention cysts. The clinical and radiographic features of each of them was discussed in below and summarized in Table 1. Rhinosinusitis The term rhinosinusitis has replaced sinusitis because of the close interrelationship between the 2 diseases. 12 Rhinosinusitis is defined as inflammation of the nose and paranasal sinuses. 13 Acute rhinosinusitis (ARS) is usually infectious and lasts up to 4 weeks, whereas chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is more inflammatory and has a minimal duration of either 8 or 12 weeks. 12 Apart from their differences in the duration and pathogenesis, symptoms associated with the 2 diseases are similar. More than 2 of the following symptoms are required to establish the diagnosis for both ARS and CRS: (1) anterior or posterior mucopurulent drainage, (2) nasal congestion, (3) facial/pain pressure, and (4) decreased sense of smell. 13 In addition, CRS may be diagnosed with objective methods, for example, a rhinoscopic or radiographic examination with a preference for computed tomography (CT). CRS can be further categorized into 3 subtypes with distinct but overlapping clinical characteristics: CRS without nasal polyposis, CRS with nasal polyposis, and allergic fungal rhinosinusitis. 13 Radiographically, ARS might present with an airfluid interface and CRS is associated with thickening of the sinus lining and radiopacity in the sinus. 14 Odontogenic Sinus Diseases Maxillary sinusitis of odontogenic origin account for approximately one tenth of total maxillary sinus diseases. 15 Common dental diseases that can cause sinusitis include periapical infection, periodontal disease, and perforation of the antral mucosa during tooth extraction. Other dental-related maxillary diseases are odontogenic cysts, for example, the radicular and dentigerous cyst. 16 These earlier mentioned diseases might serve as a reservoir for microbes, which might contaminate the grafting material and dental implants resulting in treatment failure if left untreated. As a result, before planning a SALW, a thorough dental examination is required to rule out the earlier mentioned diseases. Pseudocyst, Retention Cyst, and Mucocele A pseudocyst, as the name implies, is not a true cyst (without epithelium lining) while a retention cyst is. 17,18 A pseudocyst is believed to be an accumulation of inflammatory exudates between the bony wall and periosteum. A retention cyst is formed when mucin is allowed to accumulate in a dilated seromucous duct that is blocked. Radiographically, a pseudocyst is characterized by its domeshaped radiopaque structure and is commonly found on the floor of the maxillary sinus. The prevalence of pseudocysts ranges from 7.3% 19 to 14% 20 on radiographs. On the other hand, a retention cyst is not readily seen on the x-ray because it is too small and if found, it is often around the ostium. Under normal conditions, both lesions are usually asymptomatic and require no treatment. However, when a SALW is planned, a pseudocyst might complicate procedures and risk the development of surgical. A mucocele, on the contrary, is invasive in nature. The pressure generated from the fluid in the mucocele
3 408 SINUS IN RELATION TO COMPLICATIONS IN LATERAL WINDOW SINUS AUGMENTATION CHAN AND WANG may resorb the bony walls of the sinus. It is also much larger in size and may fill the entire sinus thus creating sinus symptoms. The blockage of the ostium is believed to be responsible for this pathosis. 18 Fig. 1. A proposed treatment strategy for common antral diseases before SALW. Fig. 2. A proposed treatment strategy for common antral diseases during and after SALW. Management of Maxillary Sinus Diseases A proposed treatment strategy is summarized in Figures 1 and 2 for patients who are diagnosed with maxillary sinus diseases and at the same time planned for SALW. From a medicolegal and preventive standpoint, dental surgeons should collaborate closely with an otorhinolaryngologist in managing maxillary sinus diseases. The general goal is to alleviate sinusrelated symptoms, eliminate the lesion and regain sinus membrane health before sinus augmentation. The procedures to achieve this goal may include a nonsurgical or a surgical approach or a combination of both. More specifically, a mucocele should be removed first because of its aggressive nature and large size. If diagnosed during the sinus augmentation surgery, the pathologic tissue can be removed with a Caudwll-Luc procedure and the augmentation procedure is aborted. 21 CRS should be referred, when it is symptomatic or if the sinus membrane thickness is greater than one third of the height of the sinus. For maxillary sinus diseases of odontogenic origin, the lesion should resolve itself after dental procedures, which might include endodontic therapy, periodontal treatment, and extraction. 22 The retention cyst is often small, symptomless, and near the ostium. Therefore, no specific treatment is warranted. The management of the pseudocyst is somewhat controversial and different approaches have been reported in several case reports. 19,21,23,24 Sinus augmentation was performed with the presence of a pseudocyst in 2 cases. 23 One case developed an abscess postoperatively and was controlled by antibiotics, after which the implants had been followed for 7 months without further. In another study, 19 8 cases with a pseudocyst were treated with a standard SALW. acute sinusitis and membrane perforation occurred in one and 2 cases, respectively. The authors concluded that a sinus lift procedure can be performed safely even when a pseudocyst is present; however, in cases of unclear diagnosis or if the cyst is large, further evaluation is recommended. On the other hand, Lin et al 24 suggested removing the pseudocyst routinely before SALW. In their case report, a 5 mm round window was created on the lateral wall of the sinus, from where the cyst was enucleated. The SALW was performed 3 months after the removal of the cyst. The authors claimed that this procedure allowed for elimination of the cyst and shortening of treatment time (a Caldwell-Luc procedure or an endoscopic surgery for cyst removal normally requires 6 months healing). The pseudocyst should be removed before sinus augmentation because of the following reasons. First, histopathologic examination can be performed to rule out any possible malignancy. Second, the healed sinus membrane after elimination of the cyst would be healthier, and thus facilitate the sinus elevation procedure. Third, the long-term effect of the pseudocyst on the grafting material and implants are not known. Whether the enucleation procedure is referred depends on
4 IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 20, NUMBER Table 2. Summary of Articles Studying the Prevalence, Size, Location, and Orientation of Maxillary Septa N (Subjects) Methods Dental Status Septum Definition Prevalence/Sinus Location Direction Size (mm) Ulm et al Cadavers Edentulous 2.5 mm 31.7 Premolars: 73.3; 1st molar: 19.9; 2nd molar: 6.6 Krennmair 165 Clinical et al 27 examination and CT Both NA Clinical: 27.7; CT: 16; dentate: 13.2; edentulous: 26.8 Kim et al CT Edentulous 2.5 mm Total: 26.5; edentulous: 31.8; dentate: 22.6 Shibli et al Panoramic radiographs NA 7.9 NA NA 6.8 (clinical), 8.1 (CT) 2nd premolar: 25.4; 1st and 2nd molars: 50.8; 3rd molar: 23.7 Edentulous NA 21.6 NA NA NA Neugebauer et al CBCT Both NA st molar: 31.6; 2nd molar : 27.6; 2nd premolar: 17.1 Rosano 30 Cadavers Edentulous 3 mm nd premolar-1st molar: et al 30 30; 1st-2nd molar: 40; distal to 3rd molar: 30 Park et al CT Edentulous NA st and 2nd premolar: 22.5; 1st and 2nd molar: 45.9; 3rd molar: 31.5 CT, computed tomography; CBCT, cone-beam computed tomography. NA Medial-lateral: 74.7; anterior-posterior: 25.3 Medial-lateral: 30; anterior-posterior: 70 Medial-lateral: 96.3; anterior-posterior: (lateral), 3.55 (middle), 5.46 (medial) 7.3 (mesiodistal); 11.7 (anterior-posterior) the presence of symptoms and the location of the cyst. When the cyst is symptomatic or is medially located, an endoscopic surgery might be indicated and therefore should be referred to an otorhinolaryngologist. Intraoperatively, the outcome of sinus augmentation is influenced by several factors, such as the presence of a membrane perforation, size of the perforation, presence of unexpected infection, and the ability to clean the infection. The presence of pus/exudate requires a debridement procedure and if the debridement could not be completed, the sinus augmentation should be aborted. If the size of the perforation is larger than 10 mm, the procedure generally should be terminated too. ly, decongestant medications and antibiotics should be prescribed and the patients should be informed about the possibility of having higher incidence of developing. VARIATIONS IN THE ANATOMY COULD PREDISPOSE TO COMPLICATIONS Sinus Septum and Membrane Perforation The internal structures of the maxillary sinus have been described a hundred years ago. 25 It was not until the introduction of the SALW did these internal anatomies regain attention, and in particular, the septum. Articles related to the maxillary sinus septum are summarized in Table 2. A septum is a bony projection with various sizes, locations, and orientations, most commonly arising from the floor of the maxillary sinus. The prevalence of the septum ranges from 16% to 33.3%, depending on ethnicity, methods used to identify a septum and the dentate status, etc The septum has been found more commonly in edentulous than dentate status because of the presence of the secondary septum. 27 It was hypothesized that after tooth loss, a selective bony resorption of the sinus floor resulted in areas of protrusion and depression. The protrusive bony spike formed the secondary septum, in comparison with the primary septum, which was formed along with the development of the maxillary sinus. This theory was further supported by the fact that a primary septum is higher in size and may split a sinus into 2 compartments, whereas a secondary septum is considerably shorter. The septum was most commonly found at the molar area, 26,28 30 where a sinus augmentation procedure is commonly performed. The height of the septum varies greatly among studies, ranging from to 11.7 mm. 28 A septum can be found more commonly in a mediolateral direction, partially separating the sinus into an anterior and posterior compartment, 28,29 although a septum in the transverse and sagittal directions could also be found. To summarize, a septum, varying in size, location, and orientation is commonly present in the maxillary sinus. Its presence may increase the risk of a sinus membrane perforation during the surgery. A membrane perforation is the most commonly encountered complication. 1 The mean prevalence of sinus perforation during sinus elevation procedures is 19.5%, with a range of 0% to 58.3%. 1 The highest perforation rate is associated with single tooth replacement. 27 It might be possible that the limited access had significantly increased the perforation rate. Whether membrane perforation incurs more postoperative and higher implant failure rate is debatable. Barone et al 33 found that the use of an onlay graft and/or smoking and not the membrane perforation is associated with higher postoperative infection rate. Becker et al 34 also suggested that with proper treatment, a perforation of the membrane did not elevate the risk for implant loss, infection, or displacement of grafting material. Schwartz-Arad et al 5 concluded that a membrane perforation significantly increased postoperative but it did not result in more implant failures. On the other hand, Cho-Lee et al 35 found that the implant survival rate was lower (81%) when surgical, membrane exposure or postoperative sinusitis occurred, compared with no (97.6%).
5 410 SINUS IN RELATION TO COMPLICATIONS IN LATERAL WINDOW SINUS AUGMENTATION CHAN AND WANG Table 3. Summary on Managements of Sinus Membrane Perforation Management by the Size of the Perforation References Total No. of Augmentations Total No. of Implants Perforation Rate Implant Placement Timing Perforation Size (mm) Shlomi et al Staged No. of perforations 20 Repair technique DFDLB sheet 0 rate 90 (NSS from NP group) Ardekian et al Simultaneous No. of perforations Repair technique Collagen membrane 5.7 (0 in NP group) 94.4 (NSS from NP group) rate Becker et al Both No. of perforations Repair technique rate Collagen membrane Collagen membrane suture 4.8 (1 in NP group) 98 (NSS from NP group) Discontinue the procedure Hernandez-Alfaro Simultaneous No. of perforations et al 37 Repair technique Suturing, or resorbable collagen membrane Lamellar bone resorbable collagen membrane Lamellar bone, lamellar bone buccal fat pad, or bone block graft rate NSS, not statistically significant; NP, nonperforation; DFDLB, demineralized freeze dried human lamina bone. Regardless of the controversies in the potential effect of membrane perforation on postoperative and implant failure, this intraoperative complication absolutely increase surgical difficulty and lengthen surgical time. It is, therefore, preferable to prevent the occurrence of a membrane perforation. Of equal importance is the management of a perforation once identified during the procedure. Management of Sinus Membrane Perforation Table 3 summarized methods used to repair a membrane perforation of different sizes. A perforation 5 mm is generally repaired with a collagen membrane alone or sutures. 34,36,37 A perforation size between 5 and 10 mm might be treated with a collagen membrane alone, 36 in combination with sutures 34 or lamina bone harvested from the lateral wall after osteotomy. 37 It might be corrected with a demineralized freeze-dried human lamellar bone sheet. 38 Attempts were made to repair a larger perforation ( 10 mm), including a demineralized freeze-dried human lamellar bone sheet, 38 lamina bone alone, combined with buccal fad pad, or the use of a block graft. 37 On the contrary, it was suggested to abandon the surgery. 34 From these clinical evidences, small to medium perforations might be repaired, after which the augmentation procedure could be completed without jeopardizing implant survival rate. However, when a large perforation occurs, the surgery should be terminated because lower implant survival rate was found in cases with a 10 mm perforation and a repair was attempted. 37 Distributions of Blood Vessels and Massive Hemorrhage Accidently injuring the blood vessels in the maxillary sinus might cause massive hemorrhage during an augmentation surgery. Therefore, it is important to understand the distributions and variations of these arteries. The artery that is located on the lateral wall where an osteotomy will be performed is especially important. It is the anastomosis of the posterior superior alveolar artery and infraorbital artery. In cadaver studies, this anastomosis could always be found 39,40 ; however, from CT images only 50% to 60% could be identified Its location in relation to the alveolar crest was on average 11.25, , , 42 and 19 mm. 39 Because of its location, it was estimated that 20% of normally positioned lateral window osteotomies might come across this artery, potentially causing major bleeding. 41 The use of a piezoelectric machine for osteotomy might preserve the integrity of this artery because it only cuts hard tissue. 43 With regard to its relationship with the lateral sinus bony wall, it was found to be intraosseous 39,41 or partially intraosseous. 40,42 If it is located between the interior side of the bony wall and the Schneiderian membrane (partially intraosseous), care should also be taken not to tear it when ele-
6 IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 20, NUMBER vating the membrane. The diameter of this artery was 1 mm in 55.3%, 1 to 2 mm in 40.4%, and 2 to 3 mm in 4.3% of cases. 40 When a large diameter blood vessel (3 mm) is encountered, it may be wise to ligate it to prevent massive bleeding. 44 Location of the Ostium and Sinus Obliteration The ostium is located 40 mm above the antral floor. 45 A case was reported for a patient who complained about frequent headache, sinus congestion, and discharge after a sinus augmentation procedure. 46 CT revealed that the grafting material occupied 80% of the maxillary sinus and was just below the ostium. It was possible that the grafting material had blocked the normal fluid movement in the maxillary sinus and symptoms developed. Therefore, maxillary sinus should not be overpacked. Migration of the Implant Displacement of implant into sinus was reported sporadically in the literature. 47,48 the incidence of this complication is currently unknown and believed to be rare. The timing of its occurrence varies from several days after implant placement, 49 at abutment connection surgery, 50 or even several years after function. 51 The exact cause is not clear; however, 3 essential conditions must be present for this unfortunate incident to occur, these are a lack of osseointegration, membrane perforation, and a pushing force on the implant toward sinus. It is generally agreed that once the displacement is diagnosed, the implant should be removed as early as possible. Three main rescue therapies have been discussed and the treatment protocol has been developed, which comprises of intraoral approach (modified Caldwell-Luc procedure), functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS), and the combination of both. 47 According to their protocol, an intraoral approach is chosen when no symptoms of sinusitis are present and the ostium is patent, whereas a FESS is selected when there is obstruction of maxillary ostium without oroantral communications. The FESS is combined with an intraoral approach when sinusitis, obstruction of the ostium, and oroantral communications are all present. A high success rate (26 of 27 patients recovered completely) following this protocol suggests that this is an effective approach. Nevertheless, the best way is probably to prevent this complication from happening. Because of rare occurrence, it was difficult to identify the risk factors. Possible predisposing factors include inadequate residual ridge height, poor bone quality, and simultaneous implant placement with sinus augmentation. CONCLUSIONS The occurrence of surgical during SALW is most likely related to the presence of maxillary sinus pathoses and anatomical variations. Management strategies for antral diseases before, during and after the augmentation procedure were proposed. In addition, maxillary sinus anatomies, in particular the maxillary septum, ostium, and artery in the vicinity of the osteotomy site and their clinical significance were discussed. Correct diagnosis and management of sinus diseases and the knowledge of sinus anatomies could greatly reduce the incidence of surgical. DISCLOSURE The authors claim to have no financial interest in any company or any of the products mentioned in this article. REFERENCES 1. Pjetursson BE, Tan WC, Zwahlen M, et al. A systematic review of the success of sinus floor elevation and survival of implants inserted in combination with sinus floor elevation. J Clin Periodontol. 2008; 35: Wallace SS, Froum SJ. Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants. A systematic review. Ann Periodontol. 2003;8: Boyne PJ, James RA. Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone. J Oral Surg. 1980;38: Katranji A, Fotek P, Wang HL. Sinus augmentation : Etiology and treatment. Implant Dent. 2008;17: Schwartz-Arad D, Herzberg R, Dolev E. The prevalence of surgical of the sinus graft procedure and their impact on implant survival. J Periodontol. 2004;75: Bell GW, Joshi BB, Macleod RI. Maxillary sinus disease: Diagnosis and treatment. Br Dent J. 2011;210: Mogensen C, Tos M. Quantitative histology of the maxillary sinus. Rhinology. 1977;15: Beaumont C, Zafiropoulos GG, Rohmann K, et al. Prevalence of maxillary sinus disease and abnormalities in patients scheduled for sinus lift procedures. J Periodontol. 2005;76: Manor Y, Mardinger O, Bietlitum I, et al. Late signs and symptoms of maxillary sinusitis after sinus augmentation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;110:e1-e Anavi Y, Allon DM, Avishai G, et al. Complications of maxillary sinus augmentations in a selective series of patients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;106: Timmenga NM, Raghoebar GM, Boering G, et al. Maxillary sinus function after sinus lifts for the insertion of dental implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997;55: ; discussion Meltzer EO, Hamilos DL, Hadley JA, et al. Rhinosinusitis: Establishing definitions for clinical research and patient care. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114: Dykewicz MS, Hamilos DL. Rhinitis and sinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:S103-S Van Dis ML, Miles DA. Disorders of the maxillary sinus. Dent Clin North Am. 1994;38: Brook I. Sinusitis of odontogenic origin. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; 135: Thunthy KH. Diseases of the maxillary sinus. Gen Dent. 1998;46: ; quiz Gardner DG. Pseudocysts and retention cysts of the maxillary sinus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1984;58: Gardner DG, Gullane PJ. Mucoceles of the maxillary sinus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1986;62: Mardinger O, Manor I, Mijiritsky E, et al. Maxillary sinus augmentation in the presence of antral pseudocyst: A clinical approach. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007;103: MacDonald-Jankowski DS. Mucosal antral cysts observed within a London inner-city population. Clin Radiol. 1994;49: Garg AK, Mugnolo GM, Sasken H. Maxillary antral mucocele and its relevance for maxillary sinus augmentation grafting: A
7 412 SINUS IN RELATION TO COMPLICATIONS IN LATERAL WINDOW SINUS AUGMENTATION CHAN AND WANG case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000;15: Mehra P, Murad H. Maxillary sinus disease of odontogenic origin. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2004;37: Kara IM, Kucuk D, Polat S. Experience of maxillary sinus floor augmentation in the presence of antral pseudocysts. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68: Lin Y, Hu X, Metzmacher AR, et al. Maxillary sinus augmentation following removal of a maxillary sinus pseudocyst after a shortened healing period. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68: Underwood AS. An inquiry into the anatomy and pathology of the maxillary sinus. J Anat Physiol. 1910;44: Kim MJ, Jung UW, Kim CS, et al. Maxillary sinus septa: Prevalence, height, location, and morphology. A reformatted computed tomography scan analysis. J Periodontol. 2006;77: Krennmair G, Krainhofner M, Schmid-Schwap M, et al. Maxillary sinus lift for single implant-supported restorations: A clinical study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2007;22: Neugebauer J, Ritter L, Mischkowski RA, et al. Evaluation of maxillary sinus anatomy by cone-beam CT prior to sinus floor elevation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010;25: Park YB, Jeon HS, Shim JS, et al. Analysis of the anatomy of the maxillary sinus septum using three-dimensional computed tomography. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011:69; Rosano G, Taschieri S, Gaudy JF, et al. Maxillary sinus septa: A cadaveric study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68: Shibli JA, Faveri M, Ferrari DS, et al. Prevalence of maxillary sinus septa in 1024 subjects with edentulous upper jaws: A retrospective study. J Oral Implantol. 2007;33: Ulm CW, Solar P, Krennmair G, et al. Incidence and suggested surgical management of septa in sinus-lift procedures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1995;10: Barone A, Santini S, Sbordone L, et al. A clinical study of the outcomes and associated with maxillary sinus augmentation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2006;21: Becker ST, Terheyden H, Steinriede A, et al. Prospective observation of 41 perforations of the Schneiderian membrane during sinus floor elevation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008;19: Cho-Lee GY, Naval-Gias L, Castrejon-Castrejon S, et al. A 12-year retrospective analytic study of the implant survival rate in 177 consecutive maxillary sinus augmentation procedures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010;25: Ardekian L, Oved-Peleg E, Mactei EE, et al. The clinical significance of sinus membrane perforation during augmentation of the maxillary sinus. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;64: Hernandez-Alfaro F, Torradeflot MM, Marti C. Prevalence and management of Schneiderian membrane perforations during sinus-lift procedures. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008;19: Shlomi B, Horowitz I, Kahn A, et al. The effect of sinus membrane perforation and repair with Lambone on the outcome of maxillary sinus floor augmentation: A radiographic assessment. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004;19: Solar P, Geyerhofer U, Traxler H, et al. Blood supply to the maxillary sinus relevant to sinus floor elevation procedures. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1999;10: Rosano G, Taschieri S, Gaudy JF, et al. Maxillary sinus vascular anatomy and its relation to sinus lift surgery. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;22: Elian N, Wallace S, Cho SC, et al. Distribution of the maxillary artery as it relates to sinus floor augmentation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2005;20: Guncu GN, Yildirim YD, Wang HL, et al. Location of posterior superior alveolar artery and evaluation of maxillary sinus anatomy with computerized tomography: A clinical study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22: Toscano NJ, Holtzclaw D, Rosen PS. The effect of piezoelectric use on open sinus lift perforation: A retrospective evaluation of 56 consecutively treated cases from private practices. J Periodontol. 2010;81: Testori T, Rosano G, Taschieri S, et al. Ligation of an unusually large vessel during maxillary sinus floor augmentation. A case report. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2010; 3: May M, Sobol SM, Korzec K. The location of the maxillary os and its importance to the endoscopic sinus surgeon. Laryngoscope. 1990;100: Maksoud MA. Complications after maxillary sinus augmentation: A case report. Implant Dent. 2001;10: Chiapasco M, Felisati G, Maccari A, et al. The management of following displacement of oral implants in the paranasal sinuses: A multicenter clinical report and proposed treatment protocols. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;38: Ridaura-Ruiz L, Figueiredo R, Guinot-Moya R, et al. Accidental displacement of dental implants into the maxillary sinus: A report of nine cases. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2009;11(suppl 1):e38- e Lubbe DE, Aniruth S, Peck T, et al. Endoscopic transnasal removal of migrated dental implants. Br Dent J. 2008; 204: Kluppel LE, Santos SE, Olate S, et al. Implant migration into maxillary sinus: Description of two asymptomatic cases. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;14: Iida S, Tanaka N, Kogo M, et al. Migration of a dental implant into the maxillary sinus. A case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;29:
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
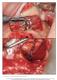 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation
 42 Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation LvingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Jang-yeol Lee, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park, Sang-chull
42 Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation LvingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Jang-yeol Lee, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park, Sang-chull
Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane
 10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1077 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane BC Deepthi, Shilpa Shetty, CL Satish Babu, P Rohit, DM Mallikarjuna,
10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1077 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane BC Deepthi, Shilpa Shetty, CL Satish Babu, P Rohit, DM Mallikarjuna,
Evaluation of the Posterior Superior Alveolar Artery Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2016; 81: 606-610 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.899221 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.04.22 Accepted: 2016.05.11 Published: 2016.12.19 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2016; 81: 606-610 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.899221 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.04.22 Accepted: 2016.05.11 Published: 2016.12.19 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Location of Posterosuperior Alveolar Artery and Correlation with Maxillary Sinus Anatomy
 e60 Location of Posterosuperior Alveolar Artery and Correlation with Maxillary Sinus Anatomy 1 Department of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology and Imaging, School of Dentistry, Lebanese University, Beirut,
e60 Location of Posterosuperior Alveolar Artery and Correlation with Maxillary Sinus Anatomy 1 Department of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology and Imaging, School of Dentistry, Lebanese University, Beirut,
The study of the alveolar antral artery canal in using cone beam computed tomography C Mung San Aung 1, Soontra Panmekiat 2, Atiphan Pimkhaokham 3
 Original Article pissn, eissn 0125-5614 M Dent J 2017; 37 (1) : 63-69 The study of the alveolar antral artery canal in using cone beam computed tomography C Mung San Aung 1, Soontra Panmekiat 2, Atiphan
Original Article pissn, eissn 0125-5614 M Dent J 2017; 37 (1) : 63-69 The study of the alveolar antral artery canal in using cone beam computed tomography C Mung San Aung 1, Soontra Panmekiat 2, Atiphan
Evaluation of maxillary sinus septa: a retrospective clinical study with cone beam computerized tomography (CBCT)
 Art. 5781 PM 7200 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5306-5314 Evaluation of maxillary sinus septa: a retrospective clinical study with cone beam computerized tomography
Art. 5781 PM 7200 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5306-5314 Evaluation of maxillary sinus septa: a retrospective clinical study with cone beam computerized tomography
One in four sinus lift procedures can be
 11 Volume 5, Issue 1: Summer 2017 Inspyred: The alternative EAO voice Handling perforations of the sinus membrane A new approach using advanced platelet-rich fi brin (A-PRF) One in four sinus lift procedures
11 Volume 5, Issue 1: Summer 2017 Inspyred: The alternative EAO voice Handling perforations of the sinus membrane A new approach using advanced platelet-rich fi brin (A-PRF) One in four sinus lift procedures
Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Following Removal of a Maxillary Sinus Pseudocyst After a Shortened Healing Period
 DENTAL IMPLANTS J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:2856-2860, 2010 Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Following Removal of a Maxillary Sinus Pseudocyst After a Shortened Healing Period Ye Lin, MD,* Xiulian Hu, DMD, Arnulf-Reimar
DENTAL IMPLANTS J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:2856-2860, 2010 Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Following Removal of a Maxillary Sinus Pseudocyst After a Shortened Healing Period Ye Lin, MD,* Xiulian Hu, DMD, Arnulf-Reimar
Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla
 IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
Clinical progress of teeth and implant displaced into the maxillary sinus: retrospective clinical study
 Oral Biology Research, 2017; December 31, 41(4):207-214 Copyright c 2017, Oral Biology Research Institute DOI: 10.21851/obr.41.04.201712.207 Original Article ORAL BIOLOGY RESEARCH Clinical progress of
Oral Biology Research, 2017; December 31, 41(4):207-214 Copyright c 2017, Oral Biology Research Institute DOI: 10.21851/obr.41.04.201712.207 Original Article ORAL BIOLOGY RESEARCH Clinical progress of
Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material- A case Report
 A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers
 Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2013)107-112 Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers Mohammad A. Abd-alla BDS, MSc., Ph.D. (1) Abdul-Jabbar J. Mahdi BDS, MSc., Ph.D.
Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2013)107-112 Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers Mohammad A. Abd-alla BDS, MSc., Ph.D. (1) Abdul-Jabbar J. Mahdi BDS, MSc., Ph.D.
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery
 An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery Huda Moutaz Asmael, B.D.S. (1) Thair Abdul Lateef, B.D.S., H.D.D., F.I.B.M.S. (2) ABSTRACT
An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery Huda Moutaz Asmael, B.D.S. (1) Thair Abdul Lateef, B.D.S., H.D.D., F.I.B.M.S. (2) ABSTRACT
Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation. Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics
 A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics Boyne, 1980 Maxillary Sinus Augmentations Maxillary sinus augmentation,
A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics Boyne, 1980 Maxillary Sinus Augmentations Maxillary sinus augmentation,
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan
 Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Differential diagnosis of antral pseudocyst, surgical ciliated cyst, and mucocele of the maxillary sinus
 Page 1 of 6 Pathology Differential diagnosis of antral pseudocyst, surgical ciliated cyst, and mucocele of the maxillary sinus RZ Araujo 1*, RS Gomez 1*, WH Castro 1, LF Lehman 1 Abstract Introduction
Page 1 of 6 Pathology Differential diagnosis of antral pseudocyst, surgical ciliated cyst, and mucocele of the maxillary sinus RZ Araujo 1*, RS Gomez 1*, WH Castro 1, LF Lehman 1 Abstract Introduction
Migration of foreign bodies
 CASE LETTER Atraumatic Removal of an Asymptomatic Migrated Dental Implant Into the Maxillary Sinus: A Case Report Spiros Tsodoulos, DDS, MD, PhD Irene Karabouta, DDS, MD, PhD* Margarita Voulgaropoulou,
CASE LETTER Atraumatic Removal of an Asymptomatic Migrated Dental Implant Into the Maxillary Sinus: A Case Report Spiros Tsodoulos, DDS, MD, PhD Irene Karabouta, DDS, MD, PhD* Margarita Voulgaropoulou,
Healing pattern of the mucous membrane after tooth extraction in the maxillary sinus
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:23-29 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.1.23 Healing pattern of the mucous membrane after tooth extraction in the maxillary sinus Ji-Young Yoo, Sung-Hee Pi, Yun-Sang
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:23-29 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.1.23 Healing pattern of the mucous membrane after tooth extraction in the maxillary sinus Ji-Young Yoo, Sung-Hee Pi, Yun-Sang
The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting
 44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
Antral computerized tomography pre-operative evaluation: relationship between mucosal thickening and maxillary sinus function
 Guy Carmeli Zvi Artzi Avital Kozlovsky Yoram Segev Roee Landsberg Antral computerized tomography pre-operative evaluation: relationship between mucosal thickening and maxillary sinus function Authors affiliations:
Guy Carmeli Zvi Artzi Avital Kozlovsky Yoram Segev Roee Landsberg Antral computerized tomography pre-operative evaluation: relationship between mucosal thickening and maxillary sinus function Authors affiliations:
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Since the proximity of the maxillary sinus may result
 Incidence, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Sinus Graft Infection After Sinus Floor Elevation: A Clinical Study Istvan A. Urban, DMD, MD 1 /Heiner Nagursky, PhD 2 / Christopher Church, MD, MS 3 /Jaime L. Lozada,
Incidence, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Sinus Graft Infection After Sinus Floor Elevation: A Clinical Study Istvan A. Urban, DMD, MD 1 /Heiner Nagursky, PhD 2 / Christopher Church, MD, MS 3 /Jaime L. Lozada,
Incidence of Odontogenic Sinusitis Experience in a Tertiary Care Centre
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/130 Incidence of Odontogenic Sinusitis Experience in a Tertiary Care Centre B G Prakash 1, Suhasini Biyyapu 2 1 Professor, Department of ENT, JSS Medical College,
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/130 Incidence of Odontogenic Sinusitis Experience in a Tertiary Care Centre B G Prakash 1, Suhasini Biyyapu 2 1 Professor, Department of ENT, JSS Medical College,
Prevalence, Height, and Location of Antral Septa in Iranian Patients Undergoing Maxillary Sinus Lift
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article Prevalence, Height, and Location of Antral Septa in Iranian Patients Undergoing Maxillary Sinus Lift Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 Amir Reza Babaloo
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article Prevalence, Height, and Location of Antral Septa in Iranian Patients Undergoing Maxillary Sinus Lift Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 Amir Reza Babaloo
Maxillary Sinus Lateral Wall Thickness and Their Morphologic Patterns in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla
 Maxillary Sinus Lateral Wall Thickness and Their Morphologic Patterns in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla Alberto Monje, D.D.S.*, Andrés Catena PhD Florencio Monje, MD, PhD, Raúl Gonzalez-García MD, PhD,
Maxillary Sinus Lateral Wall Thickness and Their Morphologic Patterns in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla Alberto Monje, D.D.S.*, Andrés Catena PhD Florencio Monje, MD, PhD, Raúl Gonzalez-García MD, PhD,
Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter. Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July Volume 2
 Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION
 original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
Nasal floor elevation combined with dental implant placement
 1 Nasal floor elevation combined with dental implant placement Ziv Mazor, DMD * Adi Lorean, DMD ** Eitan Mijiritsky Liran Levin, DMD * Private Practice, Ra anana, Israel ** Private Practice, Tiberius,
1 Nasal floor elevation combined with dental implant placement Ziv Mazor, DMD * Adi Lorean, DMD ** Eitan Mijiritsky Liran Levin, DMD * Private Practice, Ra anana, Israel ** Private Practice, Tiberius,
Intramembranous autogenous bone graft is the gold
 CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
Review Article The Prevalence of Concha Bullosa and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship to Maxillary Sinusitis by Volumetric Tomography
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
Crestal endoscopic approach for evaluating sinus membrane elevation technique
 Elian and Barakat International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2018) 4:15 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-018-0126-6 International Journal of Implant Dentistry TECHNICAL ADVANCES ARTICLE Crestal endoscopic
Elian and Barakat International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2018) 4:15 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-018-0126-6 International Journal of Implant Dentistry TECHNICAL ADVANCES ARTICLE Crestal endoscopic
International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
The study of arterial anastomoses in the region of the alveolar process and the anterior maxilla wall in foetuses
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 2, pp. 65 69 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The study of arterial anastomoses in the region of the alveolar process
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 2, pp. 65 69 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The study of arterial anastomoses in the region of the alveolar process
Title endoscope. Kitamura, Akira; Zeredo, Jorge L. Implant dentistry, 19(1), pp.16-20; Issue Date
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Migrated maxillary implant removed endoscope. Kitamura, Akira; Zeredo, Jorge L Citation Implant dentistry, 19(1), pp.16-20; Issue Date 2010-02 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/24593
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Migrated maxillary implant removed endoscope. Kitamura, Akira; Zeredo, Jorge L Citation Implant dentistry, 19(1), pp.16-20; Issue Date 2010-02 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/24593
The change of maxillary sinus ostium in diameter following Sinus floor elevation surgery using Cone beam computered tomography
 74 The change of maxillary sinus ostium in diameter following Sinus floor elevation surgery using Cone beam computered tomography LivingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Ho-yeol
74 The change of maxillary sinus ostium in diameter following Sinus floor elevation surgery using Cone beam computered tomography LivingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Ho-yeol
Cone beam computed tomography investigation of the antral artery anastomosis in a population of Central Italy
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 75, No. 2, pp. 149 153 DOI: 10.5603/FM.a2015.0095 Copyright 2016 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Cone beam computed tomography investigation
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 75, No. 2, pp. 149 153 DOI: 10.5603/FM.a2015.0095 Copyright 2016 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Cone beam computed tomography investigation
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re. Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T
 Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Reconstruction of large oroantral defects using a pedicled buccal fat pad
 Yang et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-018-0144-6 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery CASE REPORT Open Access Reconstruction
Yang et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-018-0144-6 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery CASE REPORT Open Access Reconstruction
I. Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2012.38.2.71 pissn 22347550 eissn 22345930 Study on the position of the posterior superior alveolar artery in relation to the performance of the maxillary
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2012.38.2.71 pissn 22347550 eissn 22345930 Study on the position of the posterior superior alveolar artery in relation to the performance of the maxillary
Treatment of dental implant displacement into the maxillary sinus
 An et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:35 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0133-1 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery REVIEW Open Access Treatment of dental implant displacement
An et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:35 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0133-1 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery REVIEW Open Access Treatment of dental implant displacement
ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan July 1, 2012 ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/51/
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan July 1, 2012 ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/51/
Three-Dimensional Evaluation of Implant Positioning in the Maxillary Sinus Septum: A Retrospective Study
 CLINICAL RESEARCH e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.894403 Received: 2015.04.18 Accepted: 2015.05.25 Published: 2015.09.08 Three-Dimensional Evaluation of Implant Positioning in the Maxillary Sinus Septum:
CLINICAL RESEARCH e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.894403 Received: 2015.04.18 Accepted: 2015.05.25 Published: 2015.09.08 Three-Dimensional Evaluation of Implant Positioning in the Maxillary Sinus Septum:
The Nose and Sinuses. Ophir Ilan, MD, PhD Department of Otolaryngology/Head&Neck surgery Hadassah University Hospital
 The Nose and Sinuses Ophir Ilan, MD, PhD Department of Otolaryngology/Head&Neck surgery Hadassah University Hospital Nasal Mucociliary System Function of the Nasal Mucosa warming and humidifying the
The Nose and Sinuses Ophir Ilan, MD, PhD Department of Otolaryngology/Head&Neck surgery Hadassah University Hospital Nasal Mucociliary System Function of the Nasal Mucosa warming and humidifying the
Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3.
 DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
Keywords: Biomechanics, Biostatistics, Maxilla, Maxillary sinus, Sinus floor augmentation.
 Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:58-63 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.2.58 Peri-implant bone length changes and survival rates of implants penetrating the
Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:58-63 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.2.58 Peri-implant bone length changes and survival rates of implants penetrating the
Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases
 Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases Pages with reference to book, From 15 To 17 Alper Alkan, Osman Etoz ( Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Erciyes University, Faculty of
Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases Pages with reference to book, From 15 To 17 Alper Alkan, Osman Etoz ( Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Erciyes University, Faculty of
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift
 Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Chronic Sinusitis. Acute Sinusitis. Sinusitis. Anatomy of the Paranasal Sinuses. Sinusitis. Medical Topics - Sinusitis
 1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING
 RHINOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING Exposure to clinical rhinology is provided in each of the four ORL years over the course of several rotations in a graduated approach. MEE General Otolaryngology
RHINOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING Exposure to clinical rhinology is provided in each of the four ORL years over the course of several rotations in a graduated approach. MEE General Otolaryngology
complications (Zitzmann and Schaerer,
 Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
Oral Health and Dentistry
 Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
PLACEMENT OF DENTAL IMPANT IN POSTERIOR MAXILLARY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRAFT: A CASE REPORT
 CSE REPORT PLCEMENT OF DENTL IMPNT IN POSTERIOR MXILLRY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRFT: CSE REPORT S.P.S Sooch 1, Puja 2, Seema ggarwal 3 (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print:
CSE REPORT PLCEMENT OF DENTL IMPNT IN POSTERIOR MXILLRY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRFT: CSE REPORT S.P.S Sooch 1, Puja 2, Seema ggarwal 3 (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print:
Title. Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu. CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5. Issue Date
 Title Bilateral hypoplasia of the maxillary sinus : swelli Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5 Issue Date 2017-04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/68826
Title Bilateral hypoplasia of the maxillary sinus : swelli Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5 Issue Date 2017-04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/68826
PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours)
 PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours) First Semester (9 Credit Hours) OSRG 701 Oral Surgery I 1 OSRG 791 Oral Surgery Clinics I 2 OSRG 706 Applied Surgical Anatomy 1 OSRG 707 Pain and Anxiety Control 1
PhD in Oral Surgery (50 Credit Hours) First Semester (9 Credit Hours) OSRG 701 Oral Surgery I 1 OSRG 791 Oral Surgery Clinics I 2 OSRG 706 Applied Surgical Anatomy 1 OSRG 707 Pain and Anxiety Control 1
Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case Report?
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation: Review of Anatomy and Lateral Sinus Lift Technique
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. 2016), PP 29-33 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation: Review
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. 2016), PP 29-33 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation: Review
ISSN: Volume 4 Issue CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS Sunita Singh Sonia Chhabra Pansi Gupta Priya Malik Pt B.D. Sharma PGIMS, Rohtak, Haryana
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 CHOLESTEROL GRANULOMA: AN UNCOMMON CLINICAL ENTITY OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS Sunita Singh Sonia Chhabra Pansi Gupta Priya Malik Pt B.D. Sharma PGIMS, Rohtak, Haryana
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Implant placement in the posterior maxilla may be a
 An Analysis of Frequency, Morphology, and Locations of Maxillary Sinus Septa Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Michael M. Bornstein, Prof Dr Med Dent 1 /Carol Seiffert, Dr Med Dent 2 / Laura Maestre-Ferrín,
An Analysis of Frequency, Morphology, and Locations of Maxillary Sinus Septa Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Michael M. Bornstein, Prof Dr Med Dent 1 /Carol Seiffert, Dr Med Dent 2 / Laura Maestre-Ferrín,
Assessing the Anatomical Variations of Lingual Foramen and its Bony Canals with CBCT
 International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 2307-4531 (Print & Online) http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 2307-4531 (Print & Online) http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla,
 Staged Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Crestal Core Elevation (CCE) Procedure: A Review of the Technique Michael, DDS Abstract In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla, trephined cores measuring
Staged Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Crestal Core Elevation (CCE) Procedure: A Review of the Technique Michael, DDS Abstract In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla, trephined cores measuring
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Benefits of CBCT in Implant Planning
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
Crestal Window Sinus Lift, minimally invasive, predictable, and systematic approach to sinus grafting.
 Crestal Window Sinus Lift, minimally invasive, predictable, and systematic approach to sinus grafting. Samuel Lee, DDS*, Grace Kang-Lee, DDS, Kwang-Bum Park, DDS, MS, PhD, Thomas Han, DDS, MS Abstract
Crestal Window Sinus Lift, minimally invasive, predictable, and systematic approach to sinus grafting. Samuel Lee, DDS*, Grace Kang-Lee, DDS, Kwang-Bum Park, DDS, MS, PhD, Thomas Han, DDS, MS Abstract
Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant Planning: A Clinical Study
 JCDP Original Research Reliability of OPG and CBCT 10.5005/jp-journals-00000-0000 in Presurgical Implant Planning Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant
JCDP Original Research Reliability of OPG and CBCT 10.5005/jp-journals-00000-0000 in Presurgical Implant Planning Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation
 Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Faculty of Dental Medicine, Medical University of Varna
 CASE REPORTS A CLINICAL CASE OF PERFORATION OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS MEMBRANE DURING SINUS LIFT SURGERY AND A PROPOSED METHODOLOGY FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF SUBSEQUENT COMPLICATIONS Elitsa Djongova 1, Tihomir
CASE REPORTS A CLINICAL CASE OF PERFORATION OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS MEMBRANE DURING SINUS LIFT SURGERY AND A PROPOSED METHODOLOGY FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF SUBSEQUENT COMPLICATIONS Elitsa Djongova 1, Tihomir
Bilateral Diplopia and Abducent Nerve Palsy Secondary to Odontogenic Sinusitis: An Unusual Presentation
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Bilateral Diplopia and Abducent Nerve Palsy Secondary to Odontogenic Sinusitis: An Unusual Presentation Samer Malas, MD* Hiba Al-Reefy, MB, BCh,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Bilateral Diplopia and Abducent Nerve Palsy Secondary to Odontogenic Sinusitis: An Unusual Presentation Samer Malas, MD* Hiba Al-Reefy, MB, BCh,
Sinus elevation with short implant
 Sinus elevation with short implant Authors: Prof. Dr Mauro Marincola, Prof. Dr Dr Rolf Ewers, Prof. Giorgio Lombardo (University of Verona) & Prof. Miguel Simancas Pallares (University of Cartagena), Austria/Italy/Colombia
Sinus elevation with short implant Authors: Prof. Dr Mauro Marincola, Prof. Dr Dr Rolf Ewers, Prof. Giorgio Lombardo (University of Verona) & Prof. Miguel Simancas Pallares (University of Cartagena), Austria/Italy/Colombia
Transnasal endoscopy Evaluation and treatment method for patients with sinus lift and dental implants indications
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 5, No. 19, July - September 2015 ORIGINAL STUDY Transnasal endoscopy Evaluation and treatment method for patients with sinus lift and dental implants indications Anca
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 5, No. 19, July - September 2015 ORIGINAL STUDY Transnasal endoscopy Evaluation and treatment method for patients with sinus lift and dental implants indications Anca
A CASE REPORT OF ORO ANTAL FISTULA TREATED WITH A COMBINATION TECHNIQUE OF BUCCAL ADVANCEMENT FLAP AND BUCCAL FAT PAD
 Case Report: A CASE REPORT OF ORO ANTAL FISTULA TREATED WITH A COMBINATION TECHNIQUE OF BUCCAL ADVANCEMENT FLAP AND BUCCAL FAT PAD 1 Dr Gopal Sharma, 2 Dr Jaya Mukherjee, 3 Dr Bhagyashree Purandare 1Head
Case Report: A CASE REPORT OF ORO ANTAL FISTULA TREATED WITH A COMBINATION TECHNIQUE OF BUCCAL ADVANCEMENT FLAP AND BUCCAL FAT PAD 1 Dr Gopal Sharma, 2 Dr Jaya Mukherjee, 3 Dr Bhagyashree Purandare 1Head
Mucocele of paranasal sinuses
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
Implant surgery of the edentulous premaxilla
 Evaluation of Maxillary Incisive Canal Characteristics Related to Dental Implant Treatment With Computerized Tomography: A Clinical Multicenter Study Tolga F. Tözüm,* Güliz N. Güncü,* Yağmur D. Yıldırım,*
Evaluation of Maxillary Incisive Canal Characteristics Related to Dental Implant Treatment With Computerized Tomography: A Clinical Multicenter Study Tolga F. Tözüm,* Güliz N. Güncü,* Yağmur D. Yıldırım,*
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu
 2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
T he cortical bone of the maxillary
 KIM ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 26, NUMBER 3 2017 351 Sinus Membrane Elevation by the Crestal Approach Using a Novel Drilling System Young-Kyun Kim, DDS, PhD,* Ji-Young Lee, DDS, Jin-Woo Park, DDS,
KIM ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 26, NUMBER 3 2017 351 Sinus Membrane Elevation by the Crestal Approach Using a Novel Drilling System Young-Kyun Kim, DDS, PhD,* Ji-Young Lee, DDS, Jin-Woo Park, DDS,
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488 Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP - SINUS CT 76380 Guideline
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488 Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP - SINUS CT 76380 Guideline
Rhinosinusitis. John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD
 Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS. Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel GTO I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E
 GTO THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel R E G E N E R A T I O N S C I E N C E I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E A unique biotechnology
GTO THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel R E G E N E R A T I O N S C I E N C E I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E A unique biotechnology
Surgical ciliated cyst of the maxilla: pathology of the maxillary sinus
 Archives of Orofacial Sciences The Journal of the School of Dental Sciences, USM Case Report Arch Orofac Sci (2017), 12(2): 105-109. Surgical ciliated cyst of the maxilla: pathology of the maxillary sinus
Archives of Orofacial Sciences The Journal of the School of Dental Sciences, USM Case Report Arch Orofac Sci (2017), 12(2): 105-109. Surgical ciliated cyst of the maxilla: pathology of the maxillary sinus
Differential application of a repair technique for large perforations of the Schneiderian membrane: case report
 Vol. 31 No. 3, December 2012 Differential application of a repair technique for large perforations of the Schneiderian membrane: case report In-Seong Jeon, Min-Suk Heo 1, Kyu-Ho Yoon 2, Kwang-Heung Han
Vol. 31 No. 3, December 2012 Differential application of a repair technique for large perforations of the Schneiderian membrane: case report In-Seong Jeon, Min-Suk Heo 1, Kyu-Ho Yoon 2, Kwang-Heung Han
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Complex Exodontia. Jone Kim, DDS, MS
 Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
