MINIMUM INTERVENTION DENTISTRY ESSENTIAL CONCEPTS
|
|
|
- Esther Sullivan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MINIMUM INTERVENTION DENTISTRY ESSENTIAL CONCEPTS Martin J Tyas BDS, PhD, DDSc, GradDipHlthSc, FADM, FICD, FRACDS, FPFA, FADI Professor and Head, Restorative Dentistry Melbourne Dental School The University of Melbourne Australia Martin J Tyas (1)(
2 SUMMARY overview of Minimum Intervention (MI) definition of MI elements of MI dental caries caries risk assessment prevention remineralisation (medical) techniques operative (surgical) techniques management of defective restorations Martin J Tyas (2)(
3 DEFINITION OF MI an approach to the management of dental caries with the aim of minimising the loss of tooth structure by disease or by iatrogenic intervention Martin J Tyas (3)(
4 Int Dent J 2000;50: Martin J Tyas (4)(
5 CONSENSUS STATEMENT (2007) General Assembly of the World Congress of Minimally Invasive Dentistry Members of the Western, Central, and Eastern (US) Caries Management by Risk Assessment (CAMBRA) Coalitions ADEA Cariology Special Interest Group recognize the 2002 FDI Policy Statement as the current clinical standard for caries management Tyas, Anusavice, Frencken & Mount. Int Dent J 2000;50: Martin J Tyas (5)(
6 ELEMENTS OF MINIMUM INTERVENTION the dentist as a physician (requires a knowledge of the factors associated with the development of caries) individualised assessment of caries risk appropriate preventive strategies remineralisation/arrest of non-cavitated lesions the dentist as a surgeon (requires a knowledge of the caries lesion) minimum surgical intervention of cavitated lesions appropriate maintenance of existing restorations Martin J Tyas (6)(
7 ELEMENTS OF MINIMUM INTERVENTION the dentist as a physician (requires a knowledge of the factors associated with the development of caries) individualised assessment of caries risk appropriate preventive strategies remineralisation/arrest of non-cavitated lesions the dentist as a surgeon (requires a knowledge of the caries lesion) minimum surgical intervention of cavitated lesions appropriate maintenance of existing restorations Martin J Tyas (7)(
8 MULTIFACTORIAL NATURE OF CARIES local factors saliva (quality; quantity) diet carbohydrate intake frequency of exposure to acids exposure to fluoride plaque accumulation and retention modifying factors dental history medical history lifestyle socio-economic status compliance Martin J Tyas (8)(
9 TRAFFIC LIGHT RISK ASSESSMENT MODEL traffic light system colours convey levels of risk already used in dentistry, health education, food labelling allocates a threshold value for each risk category for caries, 16 criteria in five categories Martin J Tyas (9)(
10 GC (JAPAN) TRAFFIC LIGHT SYSTEM saliva five criteria diet # of CHO exposures/day # of acid exposures/day fluoride exposure past and current plaque three criteria modifying factors five criteria Martin J Tyas (10( 10)
11 SALIVA AND DENTAL CARIES Martin J Tyas (11( 11)
12 SALIVA COMPOSITION 99% water bicarbonate (buffers to ph ) inorganic ions (e.g, calcium, phosphate for remineralisation) enzymes: amylase, lipase, proteases, nuclease mucins (lubrication; clear bacteria) antibacterials (e.g., IgA, enzymes) Martin J Tyas (12( 12)
13 FUNCTIONS OF SALIVA lubrication taste (by dissolving ions) health of oral mucosa (promotes wound healing) assists digestion dilutes/clears material (e.g., carbohydrate) buffers plaque and dietary acid reservoir for calcium and phosphate Martin J Tyas (13( 13)
14 ASSESSMENT OF SALIVA (FIVE CRITERIA) unstimulated minor salivary gland function viscosity ph stimulated flow rate buffering capacity GC Saliva Test kit Martin J Tyas (14( 14)
15 MINOR SALIVARY GLAND FUNCTION evert lower lip dry with gauze measure time for droplets to appear at minor salivary gland orifices single ply tissue may help > 60 s s < 30 s Martin J Tyas (15( 15)
16 Ngo & Gaffney Martin J Tyas (16( 16)
17 VISCOSITY open mouth; check for pooling of saliva lift tongue to palate; check for appearance and shiny film on floor of mouth web test: normal = mm Thick, ropy, frothy, extended web test No visible pooling; a little sticky Watery with pooling; shiny thin film Martin J Tyas (17( 17)
18 Ngo & Gaffney Martin J Tyas (18( 18)
19 RED OR YELLOW LIGHT! causes of defective function severe dehydration medication hormonal imbalance salivary gland pathology Martin J Tyas (19( 19)
20 ph dribble into container insert ph paper read after 10 s < > 6.8 Martin J Tyas (20( 20)
21 FLOW RATE chew on paraffin wax for 5 minutes collect saliva measure volume wide variation among individuals mean 1.6 ml/min < 3.5 ml After 5 min: ml > 5 ml Martin J Tyas (21( 21)
22 BUFFERING CAPACITY ability to neutralise acid depends on level of bicarbonate use saliva collected for flow rate use test strip as directed assess against colour standard GC IVOCLAR Low Moderate High Martin J Tyas (22( 22)
23 MR CHAIWAT SATHORN 15-FEB-2009 Martin J Tyas (23( 23)
24 GC (JAPAN) TRAFFIC LIGHT SYSTEM saliva five criteria diet # of CHO exposures/day # of acid exposures/day fluoride exposure past and current plaque three criteria modifying factors five criteria Martin J Tyas (24( 24)
25 DIET: FREQUENCY OF CARBOHYDRATE INTAKE high CHO intake immediate 2-4 point ph (depends on bacteria, plaque thickness, salivary buffering) ph recovery; 20 min hours Martin J Tyas (25( 25)
26 DIET: FREQUENCY OF EXPOSURE TO ACIDS non-bacterial acid sources intrinsic acid (e.g., gastric reflux, bulimia) extrinsic acid (e.g., black cola drinks, sports drinks) caries erosion (corrosion) Martin J Tyas (26( 26)
27 ASSESSMENT OF DIET # CHO EXPOSURES BETWEEN MEALS > 2 > 1 Nil # ACID EXPOSURES BETWEEN MEALS > 3 > 2 1 Martin J Tyas (27( 27)
28 GC (JAPAN) TRAFFIC LIGHT SYSTEM saliva five criteria diet # of CHO exposures/day # of acid exposures/day fluoride exposure past and current plaque three criteria modifying factors five criteria Martin J Tyas (28( 28)
29 CLINICAL EFFECTS OF FLUORIDE remineralisation of incipient enamel caries ( white spot lesion) slow down/partly remineralise carious dentine in cavitated lesion remineralise root caries lesion hypermineralisation most effective for smooth-surface caries Martin J Tyas (29( 29)
30 EXPOSURE TO FLUORIDE EXPOSURE TO FLUORIDE Nil Water OR toothpaste Water AND toothpaste Martin J Tyas (30( 30)
31 GC (JAPAN) TRAFFIC LIGHT SYSTEM saliva five criteria diet # of CHO exposures/day # of acid exposures/day fluoride exposure past and current plaque three criteria modifying factors five criteria Martin J Tyas (31( 31)
32 ASSESSMENT OF BIOFILM (PLAQUE) Plaque Check (GC Corporation) thickness/maturity 2-colour disclosing gel pink = thin, new plaque blue = thick, mature plaque sucrose challenge and resultant ph Martin J Tyas (32( 32)
33 DR HIEN NGO GC Corporation Martin J Tyas (33( 33)
34 Ivoclar Vivadent Martin J Tyas (34( 34)
35 CRT Buffer, CRT Bacteria (Ivoclar Vivadent) Martin J Tyas (35( 35)
36 MODIFYING FACTORS (5) 1. dental history active caries lesions restorations (past or current risk?) 2. medical history numerous medications xerostomia, e.g., antidepressants; hypotensives; anticholinergics; antipsychotics; diuretics; anti-parkinson 3. lifestyle caffeine, alcohol (diuretics) smoking (effect on saliva) Martin J Tyas (36( 36)
37 MODIFYING FACTORS (5) 4. socio-economic status (SES) low SES may indicate low educational level, thus low level of understanding financial issues cost of treatment cost of accessing treatment 5. compliance; depends on patient attitude practicality/appropriateness of treatment plan Martin J Tyas (37( 37)
38 ASSESSMENT OF MODIFYING FACTORS any drugs (OTC/Rx/recreational) which reduce salivary flow? any diseases which result in dry mouth? fixed/removable appliances? recent active caries? poor compliance? YES to any ONE above NO to all above Martin J Tyas (38( 38)
39 DAVID AGED 24 lives in unfluoridated town labourer on building site not well educated works outdoors in hot climate potential dehydration drinks low ph black cola drinks ( Coca Cola ) frequent refined CHO intake poor oral hygiene poor attitude (parents F/F) Martin J Tyas (39( 39)
40 DAVID AGED 24 diet (high acid; high CHO) - fluoride exposure (nil) - plaque (thick) - dental history (poor attender) - SES (low) - attitude and compliance (poor) - challenges risk factors: red green Martin J Tyas (40( 40)
41 DAVID AGED 24 Saliva Plaque Diet Fluoride Modifying factors Martin J Tyas (41( 41)
42 Dr Douglas Bratthall CARIOGRAM SCORE CARD FREQUENCY OF INTAKE OF FERMENTABLE CARBOHYDRATE Martin J Tyas (42( 42)
43 2 1 Martin J Tyas (43( 43)
44 AGED CARE FACILITY Dr Jane Chalmers Dr Jane Chalmers Dr Jane Chalmers Martin J Tyas (44( 44)
45 Dr MA Stacey, University of Melbourne SJOGREN S S SYNDROME Dr MA Stacey, University of Melbourne Martin J Tyas (45( 45)
46 RADIATION CARIES Dr MA Stacey, University of Melbourne Martin J Tyas (46( 46)
47 ELEMENTS OF MINIMUM INTERVENTION the dentist as a physician (requires a knowledge of the factors associated with the development of caries) individualised assessment of caries risk appropriate preventive strategies remineralisation/arrest of non-cavitated lesions the dentist as a surgeon (requires a knowledge of the caries lesion) minimum surgical intervention of cavitated lesions appropriate maintenance of existing restorations Martin J Tyas (47( 47)
48 ELEMENTS OF MINIMUM INTERVENTION the dentist as a physician (requires a knowledge of the factors associated with the development of caries) individualised assessment of caries risk appropriate preventive strategies remineralisation/arrest of non-cavitated lesions the dentist as a surgeon (requires a knowledge of the caries lesion) minimum surgical intervention of cavitated lesions appropriate maintenance of existing restorations Martin J Tyas (48( 48)
49 DEMIN-REMIN CYCLE Critical ph of HA Critical ph of FA ph H + reacts with PO -- 4 in saliva and plaque FA and HA reform DEMINERALISATION HA dissolves; FA forms if F - present FA reforms REMINERALISATION FA and HA dissolve If H+ neutralised, and Ca++ and PO -- 4 present ph Martin J Tyas (49( 49)
50 FACTORS PROMOTING REMIN ph > 5.5 phosphate ions calcium ions fluoride ions Martin J Tyas (50( 50)
51 Clinical use of calcium phosphates for remineralization not successful insoluble calcium phosphates low solubility (particularly with F) not easily applied nor effectively localized at tooth surface require acid for solubility to produce remineralizing ions soluble calcium phosphates can only be used at low concentrations do not effectively localize at tooth surface Martin J Tyas (51( 51)
52 CALCIUM PHOSPHOPEPTIDE-AMORPHOUS CALCIUM PHOSPHATE casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP) 25+ years research by Reynolds et al. (Melbourne Dental School, University of Melbourne) based on milk protein Recaldent (Cadbury Schweppes) Martin J Tyas (52( 52)
53 CLINICAL APPLICATIONS OF CPP-ACP CPP-ACP products Recaldent chewing gum Tooth Mousse / MI Paste (GC, Japan) addition to glass-ionomer cement (Mazzaoui, Tyas et al.) compressive strength bond strength to dentine current work: addition to other GICs (Burrow et al.) Martin J Tyas (53( 53)
54 Martin J Tyas (54( 54)
55 Clinical study of enamel de- and re- mineralization by chewing gum 2720 subjects ( 12.5 y old) Normal use of fluoride toothpaste, fluoridated water Sugar-free gum containing CPP-ACP; control gum randomly assigned, double blinded Gum chewed 3 x daily for 2 years Standardized digital radiographs at baseline and 24 months Caries progression/regression analyzed using a transition matrix Morgan et al. (2006) J Dent Res Martin J Tyas (55( 55)
56 Clinical study of enamel de- and re- mineralization by chewing gum Recaldent in sugar-free gum significantly slowed progression promoted regression (remineralization) of dental caries relative to a control sugar-free gum in school children in an optimally fluoridated city and using fluoride-containing toothpaste Morgan et al. (2006) J Dent Res Martin J Tyas (56( 56)
57 MI PASTE Martin J Tyas (57( 57)
58 BEFORE TREATMENT AFTER RECALDENT Martin J Tyas (58( 58)
59 Prof L J Walsh, U of Q Prof L J Walsh, U of Q Martin J Tyas (59( 59)
60 CONCLUSION Recaldent TM (CPP-ACP) technology remineralizes enamel subsurface lesions in situ slows the progression of coronal caries promotes regression of caries CPP-ACP plus F (Tooth Mousse Plus) is a superior form of fluoride should be clinicians first choice for the prevention of caries and erosion for the treatment of dentinal hypersensitivity for the repair of white spot lesions Martin J Tyas (60( 60)
61 RESIN INFILTRATION infiltration of non-cavitated lesions by low viscosity polymerisable resin Icon ; DMG Co, Hamburg several published laboratory studies clinical studies in progress Martin J Tyas (61( 61)
62 Martin J Tyas (62( 62)
63 Courtesy of DMG GmbH Martin J Tyas (63( 63)
64 ELEMENTS OF MINIMUM INTERVENTION the dentist as a physician (requires a knowledge of the factors associated with the development of caries) individualised assessment of caries risk appropriate preventive strategies remineralisation/arrest of non-cavitated lesions the dentist as a surgeon (requires a knowledge of the caries lesion) minimum surgical intervention of cavitated lesions appropriate maintenance of existing restorations Martin J Tyas (64( 64)
65 GV BLACK Greene Vardiman BLACK ( ) 1915) extensive research on amalgam (Dental Cosmos, 1896) A Work on Operative Dentistry in Two Volumes (1908) Martin J Tyas (65( 65)
66 BLACK S S TEACHINGS highly formalised cavity designs; precise size and geometry weak, non-adhesive materials extension for prevention Martin J Tyas (66( 66)
67 A Work on Operative Dentistry in Two Volumes (5 th Ed, 1922) Martin J Tyas (67( 67)
68 SURGICAL MODEL ( s) caries can be cured by excision of all decayed tooth structure, and replacement with a filling material now known to be incorrect Martin J Tyas (68( 68)
69 STRUCTURALLY WEAKENED TOOTH + NON-ADHESIVE RESTORATIVE MATERIAL HIGH INCIDENCE OF SUBSEQUENT TOOTH FRACTURE Martin J Tyas (69( 69)
70 Martin J Tyas (70( 70)
71 WHAT S S CHANGED? enhanced understanding of the carious process an infectious disease demineralisation/remineralisation cycle recognition of the rôle of fluoride inhibiting demineralisation enhancing remineralisation development of adhesive materials glass-ionomer cement resin-based materials Martin J Tyas (71( 71)
72 MINIMUM INTERVENTION IN OPERATIVE DENTISTRY (1990s ONWARDS) remineralisation of non-cavitated lesions arrest of active lesions restoration (surgical treatment) only if required for plaque control or aesthetics removal of caries only ( infected dentine ) restoration with adhesive materials repair of defective restorations Martin J Tyas (72( 72)
73 INDICATIONS FOR RESTORATION ( SURGICAL APPROACH ) cavitation rendering plaque control unachievable aesthetics unsatisfactory function compromised Martin J Tyas (73( 73)
74 ADHESIVE PREPARATIONS conservative cavity macromechanical retention not required reduction in microleakage reduced incidence of secondary caries reduced marginal staining reduced pulp damage restoration of tooth strength Martin J Tyas (74( 74)
75 DENTINE CARIES (Fusayama( Fusayama; Massler) infected (outer carious) dentine (A) moist, soft, pale yellow heavy bacterial load collagen degraded non-remineralisable affected (inner carious) dentine (B) dry, hard, brown/black few or no bacteria collagen cross-links intact remineralisable A B Martin J Tyas (75( 75)
76 TREATMENT OF CARIOUS DENTIN EXCAVATION TECHNIQUES Manual excavation Rotary excavation Controlled selective rotary excavation torque control handpiece polymer burs Sono-abrasion Air abrasion Chemo-mechanical mechanical excavation Enzymatic digestion Laser photo-ablation Accepted procedure Gold standard but should be modified Experimental Unconvincing Experimental Experimental Limited applications Experimental Experimental Noack et al., Oral Health & Prev Dent 2004;2 (Supp 1): Martin J Tyas (76( 76)
77 TREATMENT OF CARIOUS DENTIN DISINFECTION TECHNIQUES Ozone Photodynamic therapy Primary root caries More research for other applications Promising Antibacterial therapy Adjunctive to other methods Fluoride-releasing releasing materials Dentin adhesives SEALING TECHNIQUES Antibacterial materials Limited acceptance Promising Promising Noack et al., Oral Health & Prev Dent 2004;2 (Supp 1): Martin J Tyas (77( 77)
78 Martin J Tyas (78( 78)
79 EXCAVATE WITH FIRM PRESSURE UNTIL HARD, DRY, DARK COLOUR Martin J Tyas (79( 79)
80 PRINCIPLES OF MINIMUM INTERVENTION RESTORATIONS remove only degraded enamel and infected dentine leave affected dentine support undermined enamel by the adhesive restorative material the cavity shape is dictated by the caries and is unique Black s formal cavity designs are obsolete Martin J Tyas (80( 80)
81 MANAGEMENT OF CARIOUS DENTINE John Tomes (1859) it is better that a layer of discoloured dentine should be allowed to remain for the protection of the pulp rather than run the risk of sacrificing the tooth Martin J Tyas (81( 81)
82 When removing caries make the the enamel-dentine junction hard Excavate demineralized dentine over the the pulpal surface to to the the level of of firm firm dentine provided there is is no no likelihood of of pulpal exposure Deep lesions, in in symptomless vital vital teeth, should be be gently excavated. Soft Soft demineralized dentine may may remain where its its removal might expose the the pulp Where it it is is not not possible to to remove soft, infected dentine (perhaps the the patient is is anxious or or not not cooperative), seal sealin in the the infected dentine. A permanent restoration is is placed. Do Do not not re-enter enter In In a symptomless, vital vital tooth,, this this should have a high success rate. Kidd EAM, Essentials of Dental Caries, 3 rd Ed Martin J Tyas (82( 82)
83 Martin J Tyas (83( 83)
84 ADHESIVE MATERIALS resin composite highly effective to enamel questionable to dentine excellent mechanical properties glass-ionomer highly effective to enamel highly effective to dentine brittle Martin J Tyas (84( 84)
85 GLASS-IONOMER CEMENTS significant properties in minimum intervention dentistry achieves reliable adhesion may prevent secondary caries may remineralise affected dentine Martin J Tyas (85( 85)
86 Ngo, in Mount 2002 Martin J Tyas (86( 86)
87 MINIMAL INTERVENTION APPROACHES occlusal surfaces fissure sealant preventive resin restoration posterior approximal surfaces tunnel and internal preparations slot preparations Martin J Tyas (87( 87)
88 PREVENTIVE RESIN RESTORATION Dr Hien Ngo Adelaide Martin J Tyas (88( 88)
89 FISSUROTOMY BURS Martin J Tyas (89( 89)
90 Martin J Tyas (90( 90)
91 GIC Martin J Tyas (91( 91)
92 Martin J Tyas (92( 92)
93 THE APPROXIMAL CAVITY Martin J Tyas (93( 93)
94 E1 OUTER HALF OF ENAMEL E2 INNER HALF OF ENAMEL APPLY TOPICAL FLUORIDE AND MONITOR D1 JUST INTO DENTINE D2 OUTER 1/3 OF DENTINE DO NOT RESTORE WITHOUT FURTHER CONSIDERATION D3 INNER 2/3 OF DENTINE RESTORE NOW Martin J Tyas (94( 94)
95 EVOLUTION OF THE APPROXIMAL CAVITY Soderholm, Tyas & Jokstad. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 1998;9: Martin J Tyas (95( 95)
96 TUNNEL AND INTERNAL PREPARATIONS Martin J Tyas (96( 96)
97 Jinks GM, J Dent Child 1963;30: Martin J Tyas (97( 97)
98 TUNNEL AND INTERNAL PREPARATIONS access through marginal fossa to approximal caries maintains marginal ridge tunnel preparation cavity exits into approximal space internal preparation demineralised approximal enamel retained Martin J Tyas (98( 98)
99 Martin J Tyas (99( 99)
100 Martin J Tyas (100( 100)
101 INTERNAL PREPARATION INTERNAL Martin J Tyas (101( 101)
102 INTERNAL PREPARATION 1.5 mm INTERNAL Martin J Tyas (102( 102)
103 CONDITION (PAA) INTERNAL PREPARATION WASH; DRY; PLACE S/C GIC INTERNAL Martin J Tyas (103( 103)
104 ETCH (PHOSPHORIC ACID); WASH; DRY INTERNAL PREPARATION APPLY BOND; BLOW THIN; CURE; PLACE COMPOSITE; (PLACE SEALANT); CURE; APPLY NEUTRAL FLUORIDE INTERNAL Martin J Tyas (104( 104)
105 TUNNEL PREPARATION AFFECTED DENTINE GIC COMPOSITE 3 mm Martin J Tyas (105( 105)
106 TUNNEL PREPARATION Martin J Tyas (106( 106)
107 CLINICAL REVIEW OF TUNNEL AND INTERNAL RESTORATIONS 15 clinical trials in permanent teeth reviewed 57 90% success up to 3 years main reasons for failure caries marginal ridge fracture placement of resin composite over GIC does not increase fracture resistance of marginal ridge failure in one study 3 y 10%; 5 y 65% Wiegand & Attin,, Dent Mater 2007;23: Martin J Tyas (107( 107)
108 CLINICAL REVIEW OF TUNNEL AND INTERNAL RESTORATIONS median survival times GIC tunnel 6 y resin composite approximal up to 9 y amalgam approximal up to 13 y annual failure rate GIC tunnel 7-10% GIC approximal 7-10% resin composite approximal 2.3% amalgam approximal 3.3% Wiegand & Attin,, Dent Mater 2007;23: Martin J Tyas (108( 108)
109 CLINICAL REVIEW OF TUNNEL AND INTERNAL RESTORATIONS factors affecting success tooth type, lesion size, tunnel or internal: equivocal data on influence on performance preservation of approximal enamel in internal preparation may support ridge, BUT complete caries removal more difficult to assess in internal preparation strong operator influence 9 50% failure among 12 dentists median survival mo among 5 dentists Wiegand & Attin,, Dent Mater 2007;23: Martin J Tyas (109( 109)
110 CLINICAL REVIEW OF TUNNEL AND INTERNAL RESTORATIONS influence of caries activity conflicting data on success v caries activity one trial: higher failure of GIC restorations (no resin composite over GIC) in high caries active patients Wiegand & Attin,, Dent Mater 2007;23: Martin J Tyas (110( 110)
111 OVERALL CONCLUSION clinical success may be related to mechanical strength of cavity characteristics of restorative material operator skill patient caries activity demanding procedure requiring practice rubber dam; lighting; magnification Wiegand & Attin,, Dent Mater 2007;23: Martin J Tyas (111( 111)
112 SLOT PREPARATION Lasfargues et al. Martin J Tyas (112( 112)
113 ELEMENTS OF MINIMUM INTERVENTION the dentist as a physician (requires a knowledge of the factors associated with the development of caries) individualised assessment of caries risk appropriate preventive strategies remineralisation/arrest of non-cavitated lesions the dentist as a surgeon (requires a knowledge of the caries lesion) minimum surgical intervention of cavitated lesions appropriate maintenance of existing restorations Martin J Tyas (113( 113)
114 MANAGEMENT OF DEFECTIVE RESTORATIONS Martin J Tyas (114( 114)
115 RESTORATION REPLACEMENT about 60% of a general practitioner s time is spent replacing restorations most frequent reason is secondary caries replacement results in larger cavity damage to adjacent teeth increased risk of more complex restorations new defects introduced Martin J Tyas (115( 115)
116 Martin J Tyas (116( 116)
117 DIAGNOSIS OF SECONDARY CARIES ditched margins correlate poorly with secondary caries (Pimenta et al., JPD 1995;74:219, Rudolphy et al., Caries Res 1995;29:371 only amalgam restorations with marginal defects > 0.4 mm wide should be replaced (Kidd et al., J Dent Res 1995;74:1206) Martin J Tyas (117( 117)
118 OPTIONS FOR MANAGEMENT recontour and/or polish fissure seal margins repair local defect replace restoration INCREASINGLY INVASIVE Martin J Tyas (118( 118)
119 Martin J Tyas (119( 119)
120 Martin J Tyas (120( 120)
121 Martin J Tyas (121( 121)
122 Martin J Tyas (122( 122)
123 Martin J Tyas (123( 123)
124 Martin J Tyas (124( 124)
125 Martin J Tyas (125( 125)
126 SOME INDICATIONS FOR RESTORATION REPLACEMENT extensive secondary caries cannot be removed in a repair procedure aesthetic need pulpal pathology fixed prosthodontic procedure Martin J Tyas (126( 126)
127 OPERATIVE DENTISTRY TWENTIETH CENTURY (GV BLACK) Extension for prevention TWENTY-FIRST CENTURY Prevention of extension Martin J Tyas (127( 127)
128 Graham Mount Hien Ngo Lawrie Walsh Sue Gaffney John McIntyre Eric Reynolds Martin J Tyas (128( 128)
129 Martin J Tyas (129( 129)
stabilisation and surface protection
 Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
Saliva. Introduction. Salivary Flow. Saliva and the Plaque Biofilm. The Minerals in Saliva
 Saliva Introduction Saliva is like a bloodstream to the mouth. As does blood, saliva helps build and maintain the health of the soft and hard tissues. Saliva removes waste products and provides disease-fighting
Saliva Introduction Saliva is like a bloodstream to the mouth. As does blood, saliva helps build and maintain the health of the soft and hard tissues. Saliva removes waste products and provides disease-fighting
The 21 st Century vision on. caries management, now brought into your. daily practice
 The 21 st Century vision on caries management, now brought into your daily practice Minimum Intervention A 21 st century vision on Patient Caries Management The concept of minimal intervention dentistry
The 21 st Century vision on caries management, now brought into your daily practice Minimum Intervention A 21 st century vision on Patient Caries Management The concept of minimal intervention dentistry
Root Surface Protection Simple. Effective. Important.
 GC Fuji VII / Fuji VII EP Root Surface Protection Simple. Effective. Important. Brush up your painting skills and help your patients Q&A Prof. Laurie Walsh University of Queensland lifestyle factors (frequency
GC Fuji VII / Fuji VII EP Root Surface Protection Simple. Effective. Important. Brush up your painting skills and help your patients Q&A Prof. Laurie Walsh University of Queensland lifestyle factors (frequency
Fuji VII Fuji VII EP. For all-round protection
 Fuji VII Fuji VII EP For all-round protection Fuji VII and Fuji VII EP are purpose designed for: Protection of erupting molars Increasing rates of enamel hypomineralisation and childhood caries have amplified
Fuji VII Fuji VII EP For all-round protection Fuji VII and Fuji VII EP are purpose designed for: Protection of erupting molars Increasing rates of enamel hypomineralisation and childhood caries have amplified
FRANK OSEI-BONSU UGDS/KBTH
 FRANK OSEI-BONSU UGDS/KBTH Definition Introduction G. V. Black s concept of Restoration New classification of Caries Principles & Concept of MID Conclusion An approach to the management of dental caries
FRANK OSEI-BONSU UGDS/KBTH Definition Introduction G. V. Black s concept of Restoration New classification of Caries Principles & Concept of MID Conclusion An approach to the management of dental caries
Management of ECC and Minimally Invasive Dentistry
 Management of ECC and Minimally Invasive Dentistry Ranbir Singh DMD MPH NYU-Lutheran Phoenix Pgy1 Pediatric Dental Resident Phoenix ECC Management Management of dental caries includes identification of
Management of ECC and Minimally Invasive Dentistry Ranbir Singh DMD MPH NYU-Lutheran Phoenix Pgy1 Pediatric Dental Resident Phoenix ECC Management Management of dental caries includes identification of
Minimal Intervention in Pediatric Dentistry
 10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1059 Sachin Gunda, Narendra Varma REVIEW ARTICLE Sachin Gunda, Narendra Varma ABSTRACT Dental caries is an infectious disease, identifying the risk factors and controlling them
10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1059 Sachin Gunda, Narendra Varma REVIEW ARTICLE Sachin Gunda, Narendra Varma ABSTRACT Dental caries is an infectious disease, identifying the risk factors and controlling them
Innovative Dental Therapies for the Aging Population
 Innovative Dental Therapies for the Aging Population By Daniel H Ward DDS 1080 Polaris Pkwy Ste 130 Columbus OH 43240 614-430-8990 dward@columbus.rr.com US Population is Aging 1970-28 million>60 14% of
Innovative Dental Therapies for the Aging Population By Daniel H Ward DDS 1080 Polaris Pkwy Ste 130 Columbus OH 43240 614-430-8990 dward@columbus.rr.com US Population is Aging 1970-28 million>60 14% of
CARIES STABILIZATION AND TEMPORARY RESTORATION
 CARIES STABILIZATION AND TEMPORARY RESTORATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Justify the importance of caries stabilisation procedure in operative care. List and discuss the methods to stabilise caries ( include preventive
CARIES STABILIZATION AND TEMPORARY RESTORATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Justify the importance of caries stabilisation procedure in operative care. List and discuss the methods to stabilise caries ( include preventive
Linking Research to Clinical Practice
 Prevention of Root Caries Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS Linking Research to Clinical Practice The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information to clinical dental
Prevention of Root Caries Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS Linking Research to Clinical Practice The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information to clinical dental
Electronic Dental Records
 Electronic Dental Records Dr. Douglas K Benn, Professor of Maxillofacial Radiology & Director of Oral Diagnostic Systems, University of Florida and Health Conundrums LLC 8/2/2008 Dr Benn, University of
Electronic Dental Records Dr. Douglas K Benn, Professor of Maxillofacial Radiology & Director of Oral Diagnostic Systems, University of Florida and Health Conundrums LLC 8/2/2008 Dr Benn, University of
CAries Management By Risk Assessment"(CAMBRA) - a must in preventive dentistry
 CAries Management By Risk Assessment"(CAMBRA) - a must in preventive dentistry Nanda Kishor KM* *MDS, Reader, Department of Conservative and Endodontics Pacific Dental College, Udaipur, Rajasthan, India
CAries Management By Risk Assessment"(CAMBRA) - a must in preventive dentistry Nanda Kishor KM* *MDS, Reader, Department of Conservative and Endodontics Pacific Dental College, Udaipur, Rajasthan, India
Examination and Treatment Protocols for Dental Caries and Inflammatory Periodontal Disease
 Examination and Treatment Protocols for Dental Caries and Inflammatory Periodontal Disease Dental Caries The current understanding of the caries process supports the shift in caries management from a restorative-only
Examination and Treatment Protocols for Dental Caries and Inflammatory Periodontal Disease Dental Caries The current understanding of the caries process supports the shift in caries management from a restorative-only
Chapter 14 Outline. Chapter 14: Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders. Dental Caries. Dental Caries. Prevention. Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders
 Chapter 14 Outline Chapter 14: Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders Dental caries Prevention Gingivitis Prevention Tooth hypersensitivity Pathophysiology Treatment 2 Hygiene-Related
Chapter 14 Outline Chapter 14: Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders Dental caries Prevention Gingivitis Prevention Tooth hypersensitivity Pathophysiology Treatment 2 Hygiene-Related
EQUIA. Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System
 EQUIA EQUIA Fil EQUIA Coat + Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System From the World Leader in Glass Ionomer Technology - A Complete Glass Ionomer Based Bulk Fill Rapid Restorative System Class
EQUIA EQUIA Fil EQUIA Coat + Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System From the World Leader in Glass Ionomer Technology - A Complete Glass Ionomer Based Bulk Fill Rapid Restorative System Class
GC Tooth Mousse Plus for Orthodontics. Helps keep you smiling. Made from milk
 GC Tooth Mousse Plus for Orthodontics Helps keep you smiling Made from milk Prevention Daily application of GC Tooth Mousse Plus with RECALDENT (CPP-ACP) throughout the full course of orthodontic treatment
GC Tooth Mousse Plus for Orthodontics Helps keep you smiling Made from milk Prevention Daily application of GC Tooth Mousse Plus with RECALDENT (CPP-ACP) throughout the full course of orthodontic treatment
General dentists in private practice place numerous
 PROACTIVE INTERVENTION DENTISTRY Incorporating Glass Ionomers into Everyday Dental Practice Todd Snyder, DDS, FAACD, FIADFE Introduction General dentists in private practice place numerous direct tooth
PROACTIVE INTERVENTION DENTISTRY Incorporating Glass Ionomers into Everyday Dental Practice Todd Snyder, DDS, FAACD, FIADFE Introduction General dentists in private practice place numerous direct tooth
Restorative treatment The history of dental caries management consisted of many restorations placed as well as many teeth removed and prosthetic
 Restorative treatment The history of dental caries management consisted of many restorations placed as well as many teeth removed and prosthetic replacements provided. Paradigm shift towards a medical
Restorative treatment The history of dental caries management consisted of many restorations placed as well as many teeth removed and prosthetic replacements provided. Paradigm shift towards a medical
Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials
 Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials A case study by Ann-Christin Meier, Dr. med. dent., Stapelfeld, Germany When large
Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials A case study by Ann-Christin Meier, Dr. med. dent., Stapelfeld, Germany When large
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material
 Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
Seniors Oral Care
 For information about oral health care, please contact the Ontario Dental Association at 416-922-3900 or visit www.youroralhealth.ca The Ontario Dental Association gratefully acknowledges UBC ELDERS Education,
For information about oral health care, please contact the Ontario Dental Association at 416-922-3900 or visit www.youroralhealth.ca The Ontario Dental Association gratefully acknowledges UBC ELDERS Education,
GC Tooth Mousse Plus. Made from milk. Perfect for teeth.
 GC Tooth GC Tooth Made from milk. Perfect for teeth. 1 We all brush our teeth everyday. But people who really want to care for their teeth are discovering the many benefits that come from moussing their
GC Tooth GC Tooth Made from milk. Perfect for teeth. 1 We all brush our teeth everyday. But people who really want to care for their teeth are discovering the many benefits that come from moussing their
EFFICACY OF AMORPHOUS CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, G.C. TOOTH MOUSSE AND GLUMA DESENSITIZER IN TREATING DENTIN HYPERSENSITIVITY : A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL
 Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 01,Issue 02 EFFICACY OF AMORPHOUS CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, G.C. TOOTH MOUSSE AND GLUMA DESENSITIZER IN TREATING DENTIN HYPERSENSITIVITY
Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 01,Issue 02 EFFICACY OF AMORPHOUS CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, G.C. TOOTH MOUSSE AND GLUMA DESENSITIZER IN TREATING DENTIN HYPERSENSITIVITY
Healing and Sealing Dental Caries: The Paradigm Has Shifted
 Healing and Sealing Dental Caries: The Paradigm Has Shifted Edmond R. Hewlett, D.D.S. This Afternoon s Topics Caries Management by Risk Assessment (CAMBRA) Remineralization with CPP/ACP Restoring carious
Healing and Sealing Dental Caries: The Paradigm Has Shifted Edmond R. Hewlett, D.D.S. This Afternoon s Topics Caries Management by Risk Assessment (CAMBRA) Remineralization with CPP/ACP Restoring carious
Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases. As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
 Melissa Rudzinski Preventive Dentistry Shaunda Clark November 2013 Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
Melissa Rudzinski Preventive Dentistry Shaunda Clark November 2013 Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
SmartCrown. The Cavity Fighting SmartCrown. Patient Education Booklet. SmartCrown.com Toll Free Local
 The Cavity Fighting SmartCrown SmartCrown Ca2+ SmartCrown.com Patient Education Booklet www.smartcrown.com support@smartcrown.com 800.255.2839 Toll Free 801.281.4012 Local 801.281.4022 Fax F- PO43- Origin
The Cavity Fighting SmartCrown SmartCrown Ca2+ SmartCrown.com Patient Education Booklet www.smartcrown.com support@smartcrown.com 800.255.2839 Toll Free 801.281.4012 Local 801.281.4022 Fax F- PO43- Origin
Caries Clinical Guidelines. Low Caries Risk
 Caries Clinical Guidelines Clinical guidelines Low Caries Risk at LOW RISK for future dental caries. Your patient does not show any disease indicators or factors that predict dental caries in the immediate
Caries Clinical Guidelines Clinical guidelines Low Caries Risk at LOW RISK for future dental caries. Your patient does not show any disease indicators or factors that predict dental caries in the immediate
A new cavity classifica
 Scientific articles Australian Dental Journal 1998;43:(3):153-9 A new cavity classifica t i o n Graham J. Mount, BDS(Syd), DDSc(Adel), FRACDS* W. Rory Hume, BDS, PhD, DDSc, FRACDS Abstract With the development
Scientific articles Australian Dental Journal 1998;43:(3):153-9 A new cavity classifica t i o n Graham J. Mount, BDS(Syd), DDSc(Adel), FRACDS* W. Rory Hume, BDS, PhD, DDSc, FRACDS Abstract With the development
DEPOSITS. Dentalelle Tutoring 1
 DEPOSITS Dentalelle Tutoring WWW.DENTALELLE.COM 1 PH SCALE WWW.DENTALELLE.COM 2 DENTAL CARIES Dental caries is a dynamic process that involves a susceptible tooth, cariogenic bacteria in dental plaque
DEPOSITS Dentalelle Tutoring WWW.DENTALELLE.COM 1 PH SCALE WWW.DENTALELLE.COM 2 DENTAL CARIES Dental caries is a dynamic process that involves a susceptible tooth, cariogenic bacteria in dental plaque
RESTORATIVE MATERIALS
 Position Statement / Media Release RESTORATIVE MATERIALS Dental restorative materials are specially fabricated materials designed for use as dental restorations (fillings). Dental restorations are used
Position Statement / Media Release RESTORATIVE MATERIALS Dental restorative materials are specially fabricated materials designed for use as dental restorations (fillings). Dental restorations are used
The Future of Dentistry Now in Your Hands Changes everything you know about traditional Composites, Glass Ionomers and RMGIs
 The Future of Dentistry Now in Your Hands Changes everything you know about traditional Composites, Glass Ionomers and RMGIs PULPDENT BioACTIVE Products for ProACTIVE Dentistry Advances in dental materials
The Future of Dentistry Now in Your Hands Changes everything you know about traditional Composites, Glass Ionomers and RMGIs PULPDENT BioACTIVE Products for ProACTIVE Dentistry Advances in dental materials
Margherita Fontana, DDS, PhD
 Chu et al., 2014 Margherita Fontana, DDS, PhD University of Michigan School of Dentistry Department of Cariology, Restorative Sciences and Endodontics mfontan@umich.edu Objectives Attendees will be able
Chu et al., 2014 Margherita Fontana, DDS, PhD University of Michigan School of Dentistry Department of Cariology, Restorative Sciences and Endodontics mfontan@umich.edu Objectives Attendees will be able
BASCD Trainers Pack for Caries Prevalence Studies. Updated: June 2014 for UK Training & Calibration exercise for the Deciduous Dentition
 BASCD Trainers Pack for Caries Prevalence Studies Updated: June 2014 for UK Training & Calibration exercise for the Deciduous Dentition Prepared by Helen Paisley, Cynthia Pine and Girvan Burnside Administrative
BASCD Trainers Pack for Caries Prevalence Studies Updated: June 2014 for UK Training & Calibration exercise for the Deciduous Dentition Prepared by Helen Paisley, Cynthia Pine and Girvan Burnside Administrative
Food, Nutrition & Dental Health Summary
 By Liz Pearson, RD www.lizpearson.com Food, Nutrition & Dental Health Summary Canadian Health Measures Survey (2007 to 2009) 57% of 6 11 year olds have or have had a cavity 59% of 12 19 year olds have
By Liz Pearson, RD www.lizpearson.com Food, Nutrition & Dental Health Summary Canadian Health Measures Survey (2007 to 2009) 57% of 6 11 year olds have or have had a cavity 59% of 12 19 year olds have
riva helping you help your patients
 riva helping you help your patients what is a glass ionomer? how will a dentist benefit from using glass ionomers? how will a patient benefit from their glass ionomer? Glass ionomer is the generic name
riva helping you help your patients what is a glass ionomer? how will a dentist benefit from using glass ionomers? how will a patient benefit from their glass ionomer? Glass ionomer is the generic name
OUR EXPERIENCE WITH GRADIA DIRECT IN THE RESTORATION OF ANTERIOR TEETH
 ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 OUR EXPERIENCE WITH GRADIA DIRECT IN THE RESTORATION OF ANTERIOR TEETH Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska,
ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 OUR EXPERIENCE WITH GRADIA DIRECT IN THE RESTORATION OF ANTERIOR TEETH Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska,
The 4Cs in Solving the Caries Puzzle
 The 4Cs in Solving the Caries Puzzle CAMBRA Caries Detection & Assesment System (ICDAS) Case-based protocol Calcium/Phosphate & Fluoride Objectives: Engaging in this program, the participant will be able
The 4Cs in Solving the Caries Puzzle CAMBRA Caries Detection & Assesment System (ICDAS) Case-based protocol Calcium/Phosphate & Fluoride Objectives: Engaging in this program, the participant will be able
EVALUATION OF COLOR CHANGE IN WHITE SPOT LESIONS OF ENAMEL FLUOROSIS USING A RESIN INFILTRATE
 EVALUATION OF COLOR CHANGE IN WHITE SPOT LESIONS OF ENAMEL FLUOROSIS USING A RESIN INFILTRATE Monisha Singhal PG STUDENT DEPARTMENT OF PEDODONTICS & PREVENTIVE DENTISTRY CHANDRA DENTAL COLLEGE & HOSPITAL
EVALUATION OF COLOR CHANGE IN WHITE SPOT LESIONS OF ENAMEL FLUOROSIS USING A RESIN INFILTRATE Monisha Singhal PG STUDENT DEPARTMENT OF PEDODONTICS & PREVENTIVE DENTISTRY CHANDRA DENTAL COLLEGE & HOSPITAL
Molar Hypomin. A silent epidemic damaging. 1 in 6 children s teeth
 A silent epidemic damaging * 1 in 6 children s teeth Q&A Prof. David John Manton BDSc MDSc PhD FRACDS FICD FADI Elsdon Storey Chair of Child Dental Health Melbourne Dental School, University of Melbourne
A silent epidemic damaging * 1 in 6 children s teeth Q&A Prof. David John Manton BDSc MDSc PhD FRACDS FICD FADI Elsdon Storey Chair of Child Dental Health Melbourne Dental School, University of Melbourne
Practice Impact Questionnaire
 Practice Impact Questionnaire Your practitioner identifier is: XXXXXXXX It is very important that ONLY YOU complete this questionnaire because your responses will be compared to responses that you provided
Practice Impact Questionnaire Your practitioner identifier is: XXXXXXXX It is very important that ONLY YOU complete this questionnaire because your responses will be compared to responses that you provided
Importance of Oral Health
 8th October 2015 Importance of Oral Health Oral health means more than just an attractive smile Condition of the mouth mirrors the condition of the body as a whole An unhealthy mouth, especially gum disease,
8th October 2015 Importance of Oral Health Oral health means more than just an attractive smile Condition of the mouth mirrors the condition of the body as a whole An unhealthy mouth, especially gum disease,
Pediatric endodontics. Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR
 Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
GC Tooth Mousse Portfolio
 GC Tooth Mousse Portfolio Since its introduction in late 2002, GC Tooth Mousse has quickly become a firm favourite with dental professionals as a topical coating for teeth with a myriad of uses. More and
GC Tooth Mousse Portfolio Since its introduction in late 2002, GC Tooth Mousse has quickly become a firm favourite with dental professionals as a topical coating for teeth with a myriad of uses. More and
Linking Research to Clinical Practice
 Linking Research to Clinical Practice Non Fluoride Caries Preventive Agents Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information to clinical
Linking Research to Clinical Practice Non Fluoride Caries Preventive Agents Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information to clinical
Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control
 Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
Remaining dentin thickness Shallow cavity depth Preparation 0.5 mm into dentin (ideal depth) Moderate cavity depth Remaining dentin over pulp of at le
 Deep carious lesions management Remaining dentin thickness Shallow cavity depth Preparation 0.5 mm into dentin (ideal depth) Moderate cavity depth Remaining dentin over pulp of at least 1-2 mm Deep cavity
Deep carious lesions management Remaining dentin thickness Shallow cavity depth Preparation 0.5 mm into dentin (ideal depth) Moderate cavity depth Remaining dentin over pulp of at least 1-2 mm Deep cavity
2 during treatment... how to technique. How to handle white spot lesions associated with orthodontic treatment. Issue
 Issue 17 2013 How to handle white spot lesions associated with orthodontic treatment. 1 background... It is well recognised that the placement of fixed orthodontic appliances increases a patient s risk
Issue 17 2013 How to handle white spot lesions associated with orthodontic treatment. 1 background... It is well recognised that the placement of fixed orthodontic appliances increases a patient s risk
TOOTH DISCOLORATION. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage dental health. All decisions about the management of tooth discoloration must be made in conjunction with your dentist
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage dental health. All decisions about the management of tooth discoloration must be made in conjunction with your dentist
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV.
 Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
Fuji II LC. A Perfect Choice
 A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
Contemporary Policy Implications to Control and Prevent Dental Caries. Policies are formed to achieve outcomes? Are outcomes being achieved?
 Contemporary Policy Implications to Control and Prevent Dental Caries Policies are formed to achieve outcomes? Are outcomes being achieved? 2 3 4 Temple University School of Dentistry s Mission is the
Contemporary Policy Implications to Control and Prevent Dental Caries Policies are formed to achieve outcomes? Are outcomes being achieved? 2 3 4 Temple University School of Dentistry s Mission is the
Title:Is there a place for Tooth Mousse(R) in the prevention and treatment of early dental caries? A systematic review.
 Author's response to reviews Title:Is there a place for Tooth Mousse(R) in the prevention and treatment of early dental caries? A systematic review. Authors: Sarah L Raphael (sarah.raphael@sydney.edu.au)
Author's response to reviews Title:Is there a place for Tooth Mousse(R) in the prevention and treatment of early dental caries? A systematic review. Authors: Sarah L Raphael (sarah.raphael@sydney.edu.au)
DENTAL CLINICS OF NORTH AMERICA. Emmiam. Incipient and Hidden Caries. GUEST EDITOR Daniel W. Boston, DMD. October 2005 Volume49 Number4
 DENTAL CLINICS OF NORTH AMERICA Incipient and Hidden Caries GUEST EDITOR Daniel W. Boston, DMD October 2005 Volume49 Number4 Emmiam An Imprint of Elsevier, Inc. PHILADELPHIA LONDON TORONTO MONTREAL SYDNEY
DENTAL CLINICS OF NORTH AMERICA Incipient and Hidden Caries GUEST EDITOR Daniel W. Boston, DMD October 2005 Volume49 Number4 Emmiam An Imprint of Elsevier, Inc. PHILADELPHIA LONDON TORONTO MONTREAL SYDNEY
The Dental Board of California - Dental Materials Fact Sheet Adopted by the Board on October 17, 2001
 The Dental Board of California - Dental Materials Fact Sheet Adopted by the Board on October 17, 2001 As required by Chapter 801, Statutes of 1992, the Dental Board of California has prepared this fact
The Dental Board of California - Dental Materials Fact Sheet Adopted by the Board on October 17, 2001 As required by Chapter 801, Statutes of 1992, the Dental Board of California has prepared this fact
Colourf low. light cured dental flowable composite
 Colourf low light cured dental flowable composite DENTAL LIFE SCIENCES (mfg) Ltd. Unit A3, Wigan Enterprise Court, Wigan Enterprise Park, WN2 2LE United Kingdom www.dentallifesciences.com Colourf low flowable
Colourf low light cured dental flowable composite DENTAL LIFE SCIENCES (mfg) Ltd. Unit A3, Wigan Enterprise Court, Wigan Enterprise Park, WN2 2LE United Kingdom www.dentallifesciences.com Colourf low flowable
FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS
 FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS Glass Ionomers Solve Clinicians Quandaries Amalgam fillings have been around for almost two centuries,
FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS Glass Ionomers Solve Clinicians Quandaries Amalgam fillings have been around for almost two centuries,
Caries Risk Assessment and Prevention
 Caries Risk Assessment and Prevention Introduction of the disease, prevalence and global impact Dental caries is the most common dental disease that requires restorative treatment. In 2010, the Global
Caries Risk Assessment and Prevention Introduction of the disease, prevalence and global impact Dental caries is the most common dental disease that requires restorative treatment. In 2010, the Global
Essentials of. Dental Assisting. Edition 6. Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird
 Essentials of Dental Assisting Edition 6 Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird CHAPTER21 Restorative Procedures http://evolve.elsevier.com/robinson/essentials/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES KEY TERMS 1. Pronounce, define,
Essentials of Dental Assisting Edition 6 Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird CHAPTER21 Restorative Procedures http://evolve.elsevier.com/robinson/essentials/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES KEY TERMS 1. Pronounce, define,
What might be the barriers to providing high quality care using the surgical approach? Children find the surgical approach challenging
 An evidence based approach to managing children with a carious primary dentition Nicola Innes Clinical Senior Lecturer in Paediatric Dentistry University of Dundee, Scotland Nyborg, Denmark, September
An evidence based approach to managing children with a carious primary dentition Nicola Innes Clinical Senior Lecturer in Paediatric Dentistry University of Dundee, Scotland Nyborg, Denmark, September
The Dental Board of California Dental Materials Fact Sheet Adopted by the Board on October 17, 2001
 The following document is the Dental Board of California s Dental Materials Fact Sheet. The Department of Consumer Affairs has no position with respect to the language of the Dental Materials Fact Sheet;
The following document is the Dental Board of California s Dental Materials Fact Sheet. The Department of Consumer Affairs has no position with respect to the language of the Dental Materials Fact Sheet;
Fluor Protector Overview
 Fluor Protector Overview Superior protection against dental caries and erosion Fluoride Clinically proven Fluoride varnish Features and mechanism of action Application Intensive care gel Risks to teeth
Fluor Protector Overview Superior protection against dental caries and erosion Fluoride Clinically proven Fluoride varnish Features and mechanism of action Application Intensive care gel Risks to teeth
1 24% 25 49% 50 74% 75 99% Every time or 100% 2. Do you assess caries risk for individual patients in any way? Yes
 1. When you examine patients to determine if they have a primary caries lesion, on what percent of these patients do you use airdrying to help diagnose the lesion? Never or 0% (skip to question 3) 1 24%
1. When you examine patients to determine if they have a primary caries lesion, on what percent of these patients do you use airdrying to help diagnose the lesion? Never or 0% (skip to question 3) 1 24%
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children
 Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objective Discuss the role and importance of cements in paediatric dentistry Calcium hydroxide This is a colourless crystal or white powder prepared
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objective Discuss the role and importance of cements in paediatric dentistry Calcium hydroxide This is a colourless crystal or white powder prepared
A vision of caries. management in the 21st century
 A vision of caries management in the 21st century Minimum Intervention Dental caries is an infectious disease which requires a susceptible host and the presence of cariogenic plaque bacteria that are sustained
A vision of caries management in the 21st century Minimum Intervention Dental caries is an infectious disease which requires a susceptible host and the presence of cariogenic plaque bacteria that are sustained
GC Tooth Mousse Portfolio
 GC Tooth Mousse Portfolio 4TH EDITION THREE QUESTIONS YOU ARE PROBABLY ASKED ON A REGULAR BASIS ARE: Why do I need this treatment? How much will it cost? When finished, how long will it last? The first
GC Tooth Mousse Portfolio 4TH EDITION THREE QUESTIONS YOU ARE PROBABLY ASKED ON A REGULAR BASIS ARE: Why do I need this treatment? How much will it cost? When finished, how long will it last? The first
Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module C: Clinical applications
 Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module C: Clinical applications REST 528A Operative
Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module C: Clinical applications REST 528A Operative
Polymers in everyday things dentistry
 HOTOCOY olymers in everyday things dentistry (Background information) olymers are a part of everyday life and examples can be found almost anywhere. Many people think of polymers simply as plastics used
HOTOCOY olymers in everyday things dentistry (Background information) olymers are a part of everyday life and examples can be found almost anywhere. Many people think of polymers simply as plastics used
Tooth Mousse. Plus from GC. and MI Paste. Remineralising protective crèmes with triple the benefit: Strengthen. Protect. Replenish.
 Tooth Mousse and MI Paste Plus from GC. Remineralising protective crèmes with triple the benefit: Strengthen. Protect. Replenish. A healthy balance in the mouth, inhibit demineralisation of dentin and
Tooth Mousse and MI Paste Plus from GC. Remineralising protective crèmes with triple the benefit: Strengthen. Protect. Replenish. A healthy balance in the mouth, inhibit demineralisation of dentin and
Get in front of the 8 ball with the new Fuji VIII GP. The first auto-cure, resin reinforced glass ionomer restorative
 Get in front of the 8 ball with the new Fuji VIII GP The first auto-cure, resin reinforced glass ionomer restorative 8 reasons to choose Fuji VIII GP Auto-cure, resin reinforced glass ionomer restorative
Get in front of the 8 ball with the new Fuji VIII GP The first auto-cure, resin reinforced glass ionomer restorative 8 reasons to choose Fuji VIII GP Auto-cure, resin reinforced glass ionomer restorative
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR TREATING FISSURE CARIES. The problem of hidden caries. Current diagnostic methods
 A NOVEL APPROACH FOR TREATING FISSURE CARIES Daniel W. Boston, DMD. Associate Professor and Chairman Temple University School of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dentistry 3223 North Broad Street Philadelphia,
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR TREATING FISSURE CARIES Daniel W. Boston, DMD. Associate Professor and Chairman Temple University School of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dentistry 3223 North Broad Street Philadelphia,
DPI Luting Cement. DPI Restorative Cement
 DPI Luting Cement DPI Luting Cement is Type I glass ionomer white luting cement. DPI glass ionomers are remarkably biocompatible and can be safely used in deep cavities provided the pulp is not exposed,
DPI Luting Cement DPI Luting Cement is Type I glass ionomer white luting cement. DPI glass ionomers are remarkably biocompatible and can be safely used in deep cavities provided the pulp is not exposed,
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children
 Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objectives Discuss amalgam restorations Discuss resin restorations Describe the history and evolution of use of silicate cement Discuss the role
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objectives Discuss amalgam restorations Discuss resin restorations Describe the history and evolution of use of silicate cement Discuss the role
how to technique How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. Disadvantages. 1 Issue Full coverage crown. >>
 Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
The Cavity Fighting ProActive Crown
 The Cavity Fighting ProActive Crown Powered by Ketac Nano Patient Education Booklet www.proactivedentist.com support@proactivedentist.com 800.255.2839 Toll Free 801.281.4012 Local 801.281.4022 Fax Origin
The Cavity Fighting ProActive Crown Powered by Ketac Nano Patient Education Booklet www.proactivedentist.com support@proactivedentist.com 800.255.2839 Toll Free 801.281.4012 Local 801.281.4022 Fax Origin
Dental caries prevention. Preventive programs for children 5DM
 Dental caries prevention Preventive programs for children 5DM Definition of Terms Preventive dentistry: usage of all the means to achieve and maintain the optimal oral health prevention of dental caries,
Dental caries prevention Preventive programs for children 5DM Definition of Terms Preventive dentistry: usage of all the means to achieve and maintain the optimal oral health prevention of dental caries,
Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module A: Basic Concepts
 Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module A: Basic Concepts REST 528A Operative #3A
Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module A: Basic Concepts REST 528A Operative #3A
values is of great interest.
 User Report Dr. Ralph Schönemann, May 21, 2008 There are numerous self-etchbonding systems on the market that sometimes differ very much from one another with regards to their chemical composition. It
User Report Dr. Ralph Schönemann, May 21, 2008 There are numerous self-etchbonding systems on the market that sometimes differ very much from one another with regards to their chemical composition. It
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry. Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer)
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer. Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients
 Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
Index. , 66 Novamin, 66 TCP ACP. , 66 Bisphenol A (BPA), 114, 119 Byzantium diet, 87, 89
 A Acidulated phosphate fluoride (APF), 61 Adolescence aesthetic disturbance, 169 172 enamel carious lesions, orthodontic patients, 168 172 physical and sexual maturation, 168 Adulthood, 171 174 Advanced
A Acidulated phosphate fluoride (APF), 61 Adolescence aesthetic disturbance, 169 172 enamel carious lesions, orthodontic patients, 168 172 physical and sexual maturation, 168 Adulthood, 171 174 Advanced
MODULE 15: ORAL HEALTH ACROSS THE LIFESPAN
 MODULE 15: ORAL HEALTH ACROSS THE LIFESPAN Oral Health Across the Lifespan MODULE 15: ORAL HEALTH ACROSS THE LIFESPAN Part 4: Oral Health and Older Adults Mark Wolff DDS, PhD Healthy People 2020 Objectives
MODULE 15: ORAL HEALTH ACROSS THE LIFESPAN Oral Health Across the Lifespan MODULE 15: ORAL HEALTH ACROSS THE LIFESPAN Part 4: Oral Health and Older Adults Mark Wolff DDS, PhD Healthy People 2020 Objectives
Buccal defects - therapy
 Buccal defects - therapy Asbjørn Jokstad Institute of Clinical Dentistry University of Oslo, Norway 1 Management? 2 Therapy and Interventions Strategy 1 1. Establish status 2. Restore Caries & non-caries
Buccal defects - therapy Asbjørn Jokstad Institute of Clinical Dentistry University of Oslo, Norway 1 Management? 2 Therapy and Interventions Strategy 1 1. Establish status 2. Restore Caries & non-caries
Minimal intervention dentistry: cavity classification & preparation
 Scientific Minimal intervention dentistry: cavity classification & preparation Graham J Mount 1 Abstract The concept of minimal intervention operative dentistry is being accepted and taught in more places
Scientific Minimal intervention dentistry: cavity classification & preparation Graham J Mount 1 Abstract The concept of minimal intervention operative dentistry is being accepted and taught in more places
MINIMAL INVASIVE DENTISTRY- EVOLUTION OF CAVITY DESIGNING AND ITS RESTORATION
 wjpmr, 2017,3(5), 138-145 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.103 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.wjpmr.com Research Article ISSN 2455-3301 WJPMR MINIMAL INVASIVE DENTISTRY- EVOLUTION OF CAVITY
wjpmr, 2017,3(5), 138-145 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.103 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.wjpmr.com Research Article ISSN 2455-3301 WJPMR MINIMAL INVASIVE DENTISTRY- EVOLUTION OF CAVITY
The Benefits of Chewing Sugar Free Gum on Oral Health
 The Benefits of Chewing Sugar Free Gum on Oral Health Author Short, Leonie Published 2008 Conference Title Dental and Oral Health Therapist Association Inaugural Conference, The Sea Change Copyright Statement
The Benefits of Chewing Sugar Free Gum on Oral Health Author Short, Leonie Published 2008 Conference Title Dental and Oral Health Therapist Association Inaugural Conference, The Sea Change Copyright Statement
Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up
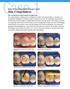 Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
Glass ionomer cements in complex oral rehabilitations. A case report.
 Università degli Studi di Milano - Department of Technologies for the Health I.R.C.C.S Istituto Ortopedico Galeazzi Department of Odontology Director: Prof. Roberto Weinstein Glass ionomer cements in complex
Università degli Studi di Milano - Department of Technologies for the Health I.R.C.C.S Istituto Ortopedico Galeazzi Department of Odontology Director: Prof. Roberto Weinstein Glass ionomer cements in complex
caries management research & clinical application
 caries management research & clinical application present dentistry It is a sad fact of life that every dentist is trained that if there is an area of decay in a tooth, the only way to treat this is to
caries management research & clinical application present dentistry It is a sad fact of life that every dentist is trained that if there is an area of decay in a tooth, the only way to treat this is to
Bonding to dentine: How it works. The future of restorative dentistry
 Bonding to dentine: How it works The future of restorative dentistry There are 82 adhesive systems on the market today! Are dentists confused about bonding? Michael Buonocore Buonocore MG. A simple method
Bonding to dentine: How it works The future of restorative dentistry There are 82 adhesive systems on the market today! Are dentists confused about bonding? Michael Buonocore Buonocore MG. A simple method
DENTAL TRAUMA IN DECIDUOUS TEETH
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of Dental Trauma in Deciduous Teeth must be made in conjunction with
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of Dental Trauma in Deciduous Teeth must be made in conjunction with
BioCoat Featuring SmartCap Technology
 R R Breakthrough! BioCoat Featuring SmartCap Technology The only bioactive pit and fissure sealant that provides relentless protection through daily release of fluoride, calcium and phosphate ions. Bioactive
R R Breakthrough! BioCoat Featuring SmartCap Technology The only bioactive pit and fissure sealant that provides relentless protection through daily release of fluoride, calcium and phosphate ions. Bioactive
Preclinical Dentistry. I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects. Lenka Roubalíková
 Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
Achieving Excellence In Lustre
 Achieving Excellence In Lustre FAM Dr. Suhas Lele is a 1980 graduate of University of Mumbai. He is founder of Vision Invisible Dental academy. Vision Invisible envisage to train practicing dental professionals
Achieving Excellence In Lustre FAM Dr. Suhas Lele is a 1980 graduate of University of Mumbai. He is founder of Vision Invisible Dental academy. Vision Invisible envisage to train practicing dental professionals
DiaDent Group International DIA.DENT DiaRoot BioAggregate. Root Canal Repair Material
 DiaDent Group International 1.877.DIA.DENT www.diadent.com DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material PRECISION. PURITY. RESULTS ABOUT DIAROOT... DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material is
DiaDent Group International 1.877.DIA.DENT www.diadent.com DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material PRECISION. PURITY. RESULTS ABOUT DIAROOT... DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material is
Fluor Protector S. The protective fluoride varnish. Superior protection against dental caries and erosion
 Fluor Protector S The protective fluoride varnish Superior protection against dental caries and erosion Fluor Protector S The strong fluoride varnish In order to stay healthy and look good, teeth need
Fluor Protector S The protective fluoride varnish Superior protection against dental caries and erosion Fluor Protector S The strong fluoride varnish In order to stay healthy and look good, teeth need
Management of Inadequate Margins and Gingival Recession Presenting as Tooth Sensitivity
 Management of Inadequate Margins and Gingival Recession Presenting as Tooth Sensitivity Nicolas Elian, DDS Private Practice Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey David Geon U Kim, DDS, MS Faculty and Research Coordinator
Management of Inadequate Margins and Gingival Recession Presenting as Tooth Sensitivity Nicolas Elian, DDS Private Practice Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey David Geon U Kim, DDS, MS Faculty and Research Coordinator
Clinical Technique/Case Report
 Operative Dentistry, 2008, 33-3, 345-349 Clinical Technique/Case Report Modified Matrix Band Design for Ultra-conservative Posterior Restorations S Deliperi Clinical Relevance The combination of minimally
Operative Dentistry, 2008, 33-3, 345-349 Clinical Technique/Case Report Modified Matrix Band Design for Ultra-conservative Posterior Restorations S Deliperi Clinical Relevance The combination of minimally
Minimally invasive dentistry approach in dental public health
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2011 Minimally invasive dentistry approach in dental public health Deise Cruz Oliveira University of Iowa Copyright 2011 Deise Oliveira
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2011 Minimally invasive dentistry approach in dental public health Deise Cruz Oliveira University of Iowa Copyright 2011 Deise Oliveira
Silver Diamine Fluoride
 Silver Diamine Fluoride Introduction Dental caries is a multifactorial disease that results from an imbalance between pathological and protective factors. Common non-operative treatments for incipient
Silver Diamine Fluoride Introduction Dental caries is a multifactorial disease that results from an imbalance between pathological and protective factors. Common non-operative treatments for incipient
