JCDP. Original research ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
|
|
|
- Clarissa Goodman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JCDP Original research Evaluation of Clinical Periodontal /jp-journals Indices and Serum Interleukin-27 Evaluation of Clinical Periodontal Indices and Serum Interleukin-27 by One-stage Full-mouth Disinfection and Quadrant Scaling and Root Planing in Periodontitis 1 Amirreza Babaloo, 2 Mahdi Rahbar, 3 Zohre Babaloo, 4 Shima Ghasemi, 5 Amjad Amini ABSTRACT Introduction: One-stage oral disinfection technique has been developed to prevent cross-contamination between the treated and untreated areas between treatment sessions. Considering the role of inflammatory mediators in periodontitis, this study has been designed to compare the effects of one-stage oral disinfection with quadrant scaling and root planing (Q-SRP) on serum interleukin-27 (IL-27) levels in patients with moderateto-advanced periodontitis. Materials and methods: In this study, two groups were considered. One group was treated with one-stage full-mouth oral disinfection (FMD), while the other group was treated with Q-SRP. In each group, 20 patients with chronic periodontitis were randomly selected based on the inclusion criteria. To evaluate the periodontal status, the clinical parameters of bleeding on probing (BOP), clinical attachment level (CAL), and probing depth (PD) were measured before treatment as well as at 2- and 4-month intervals after treatment. At the same intervals, the immunological index of the study (serum IL-27) was measured by special laboratory kits. The data were analyzed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, version 16 1,5 Department of Periodontics, Dental School, Dental and Periodontal Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences Tabriz, Islamic Republic of Iran 2 Department of Operative and Esthetic Dentistry, Dental School Dental and Periodontal Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Islamic Republic of Iran 3 Department of Immunology, Faculty of Medicine, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Islamic Republic of Iran 4 Department of Prosthodontics, Dental School, Dental and Periodontal Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Islamic Republic of Iran Corresponding Author: Shima Ghasemi, Department of Prosthodontics, Dental School, Dental and Periodontal Research Center Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz Islamic Republic of Iran, Phone: , dr_ shimaghasemi@yahoo.com (SPSS 16) software. In this study, p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results: The results of this study indicate that there has been an elevation in the mean of serum IL-27 after treatment in both treatment groups. There is no significant difference between the levels of IL-27 in the FMD group during the study period (p = 0.20). All periodontal indices (BOP, CAL, and PD) show clinical improvement in each group (p < 0.001). However, no significant difference was observed in the improvement of periodontal indices of CAL and PD (p < 0.05). Conclusion: According to the findings of this study, it can be said that both FMD and Q-SRP improve the periodontal indices and increase the serum level of the inflammatory mediator IL-27 in patients with periodontitis. Clinical significance: Considering the benefits of the FMD method, such as patient and dentist comfort, systemic effects, and its cost-effectiveness, use of this method is suggested in patients suffering from periodontitis. Keywords: Chronic periodontitis, Interleukin-27, One-stage full-mouth disinfection, Quadrant scaling and root planning. How to cite this article: Babaloo A, Rahbar M, Babaloo Z, Ghasemi S, Amini A. Evaluation of Clinical Periodontal Indices and Serum Interleukin-27 by One-stage Full-mouth Disinfection and Quadrant Scaling and Root Planing in Periodontitis. J Contemp Dent Pract 2018;19(8): Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None INTRODUCTION Periodontal diseases are among the most common oral and dental diseases. 1 Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease in which an inflammatory process destroys the dental supporting structures and bone lysis, and creates periodontal envelopes. 2 Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Tannerella forsythia, and Porphyromonas gingivalis are known as primary microbial agents, but The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, August 2018;19(8):
2 Amirreza Babaloo et al several other microorganisms are associated with periodontal diseases. 3-6 Most of these bacterial species are not only the microbial flora of the subgingival plaque, but are also colonized on mucosal surfaces, the tongue, and tonsil; they are commonly found in saliva Since the individual s susceptibility to develop such diseases cannot be changed at the clinical level (except for anti-inflammatory drugs), periodontal treatment will focus on reducing or eliminating periodontal pathogens, eliminating the possibility of their recolonization (mainly through the removal of envelopes), and creation of an inappropriate environment (with less anaerobic conditions) for bacterial pathogens. It should be noted that modern therapies are based on nonspecific plaque hypothesis, which also eliminates the useful bacterial species Several studies have shown that the presence of periodontal pathogens (restoration or colonization after treatment) is associated with the adverse outcomes of periodontal treatment The usual nonsurgical method for treatment of periodontitis is Q-SRP through multiple sessions. After mechanical removal, the microbial volume of the subgingival plaque decreases to 0.1% before treatment. 8 However, after a week, the periodontal envelopes are occupied by the same amount of bacteria, but with less pathogenicity. 17,18 The proliferation of bacteria in the subgingival region, 19 junctional epithelium, and envelope epithelium, 20 or bacteria in the dentinal tubules, posterior surface of the tongue, and tonsils are considered as potential sources of this gingival colonization. 21 Observations show that plaque along with bacteria in the tongue, oral mucosa, tonsils, and saliva affect the colonization of bacteria in the gingival area after treatment. 21 Based on the above perspective, Quirynen et al 22 suggested a one-stage FMD method, which aims to eliminate or at least suppress all periodontal pathogens from the oropharyngeal area (periodontal envelope, saliva, oral mucosa, and tonsils) within 24 hours using SRP of the entire mouth. In this method, until the periodontal envelope is restored, recolonization of bacteria is delayed through cross-contamination. The above method is a relatively new method and there is a lot of discussion about the effectiveness, rationality, comfort of the patient and the dentist, systemic effects, as well as its cost-effectiveness. Therefore, numerous clinical and paraclinical studies have been conducted with dissimilar results that have made it difficult to judge the method in this field. Some studies did not find any difference between this method and the conventional method of Q-SRP, whereas others emphasized the benefits of the new method. 27,28 The clinical parameters, including BOP, CAL (clinical adhesion loss), and PD indicate the disease activity, degree of degradation, and progression of the disease. 29 Several studies, using these parameters, 998 compared FMD method with Q-SRP. One study clearly showed the benefits of FMD as (1) attachment gain; (2) decreased depth of the envelope; and (3) decreased microbiological tendency. 29,30 Apatzidou and Kinane 31 also reported the benefits of FMD (0.88 mm attachment) in deep envelopes. Most studies have addressed the clinical and microbiological parameters of this method; only one study reported the immunological effects of this method by suggesting a significant reduction in preinflammatory and inflammatory mediators. 31,32 Another new and effective method for the diagnosis and determination of periodontal disease activity is the measurement of serum biomarkers. Interleukin-27 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine that inhibits IL In this study, in addition to clinical parameters, the inflammatory process between the FMD method and Q-SRP was investigated by the measurement of serum IL-27. Furthermore, IL-27 changes were also examined before and after applying two different therapeutic strategies to investigate the periodontal therapeutic effects on the serum levels of inflammatory cytokines, the efficacy of the two above-mentioned treatments in increasing these cytokines, and the disease progression. MATERIALS AND METHODS Twenty patients were randomly assigned to two groups using toss of a coin, after meeting the inclusion and exclusion criteria (the first group was treated by FMD, and the second group was treated using standard method, namely Q-SRP). Blood samples were taken once before treatment, and then at 2- and 4-month intervals after treatment. They were sent to the laboratory for evaluation of biomarkers (IL-27) with specific kits. Inclusion Criteria Patients with moderate-to-advanced periodontitis. Patients aged 25 to 70 years with at least 12 teeth (without considering the third molars and teeth with orthodontic bridges, crowns, and implants) and diagnosis of advanced chronic periodontitis with 30% presence of teeth with loss of clinical attachment of 3 mm or more and the presence of radiographic signs of bone resorption. Exclusion Criteria Systemic diseases (such as diabetes mellitus, cancer, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, and bone metabolic diseases) Diseases that delay wound healing; history of radiotherapy or treatment with immune system suppressor, autoimmune diseases, allergy, and other infectious diseases
3 JCDP Pregnancy or lactation History of systemic antibiotic use in the last 2 months History of continuous use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) History of SRP in the previous year Patients in the control group underwent SRP treatments at 2-week intervals for each quadrant after the blood samples were taken. In the test group, after sampling, the whole mouth was cleaned by an ultrasonic scaling apparatus in two sessions with a time interval of less than 24 hours to reduce the count of pathogenic organisms. Subgingival rinsing of all envelopes was carried out with 0.2% chlorhexidine using an insulin syringe to remove all the remaining bacteria. An antiseptic agent (0.2% chlorhexidine) was used to brush the tongue s posterior surface to decrease the bacterial load in the area and an antiseptic mouthwash (0.2% chlorhexidine) was used to reduce bacteria in the saliva and on the tonsils. The variables studied included serum IL-27 levels, as well as the clinical parameters, such as BOP, CAL, and PD, which were measured before starting treatment and then again at 2- and 4-month intervals after treatment. The plaque index was measured by the O Leary method with the aim of maintaining this index at a value below 10% (by educating on the plaque control methods) in the 2nd, 4th, 8th, 12th, and 16th week intervals after treatment. The plaque and gingival indexes were considered as control variables and patients with inappropriate cooperation (high plaque index in periodic examinations) were excluded from the study process. Measurement of the Clinical Parameters Bleeding on probing: Each tooth was probed at four levels of mesial, distal, buccal, and lingual; the probe was slowly drawn and removed with gentle force from the depth of the envelope. We waited for 30 to 60 seconds before examining the bleeding in each area. 34 Clinical pocket depth (probe depth): Keeping the probe parallel to the longitudinal axis of the tooth, it enters the depth of the envelope with a force of approx. 25 g, moving around the tooth by the walking method. The PD is recorded in the periodic chart in the four areas of mesiobuccal, midbuccal, distobuccal, and midlingual/midpalatal. Clinical attachment level: The result of the difference between the gingival margin and the envelope floor from the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) distance to the gum margin. It should be noted that the initial examination, patient selection, clinical interventions, patient sampling, and follow-up examinations were conducted at the Periodontics Department and Research Center of Gingival and Oral Evaluation of Clinical Periodontal Indices and Serum Interleukin-27 Diseases, Tabriz Dental School and para-clinical studies in immunology labs at the Faculty of Medicine of Tabriz in the Applied Pharmaceutical Research Center. Finally, the data obtained from the study were analyzed by descriptive statistics [mean ± standard deviation (SD)] and parametric statistical methods including the mean of dependent groups by paired samples t-test and analyzed by SPSS 16 software. The normal distribution of data was assessed by Kolmogorov Smirnov test and analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was used to compare any probable difference between the tested groups. In this study, p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS In the FMD group, 45% were male and 55% were female. In the Q-SRP group, 60% were male and 40% were female. Chi-square test did not show any significant difference in the gender frequency between the two groups. The mean age in the FMD group was 43 years and in Q-SRP group was 47.7 years and there was no significant difference in the mean age of the patients (p = 0.26). The distribution of data was evaluated at three different times (before treatment, then at 2- and 4-month intervals after treatment) by Kolmogorov Smirnov test. The results showed that all the data in the study had a normal distribution (p > 0.05). According to Table 1 and Graph 1, in the FMD group, the mean serum IL-27 was 50.5 before treatment, which increased to 59.3 after 2 months of treatment and reached 59.6 after the 4-month interval of treatment. The ANOVA (within group) indicated no significant difference in serum IL-27 levels at the studied intervals (before treatment, 2- and 4-month intervals after treatment). In the Q-SRP group, the mean serum IL-27 before treatment was 46.6, which increased to 55.7 in 2 months after treatment and reached 57.4 in 4 months after treatment. The ANOVA (within group) of Q-SRP group showed a significant difference in serum IL-27 levels among intervals (before treatment, 2, and 4 months after treatment) (p < 0.05). The Scheffe post hoc test was used to evaluate and compare the intervals pairwise in the Q-SRP group. The procedure showed that serum IL-27 levels differed significantly before treatment and 2 months later with a mean difference of 9.1 (p < 0.05). The mean serum IL-27 had a significant difference of 10.8% before the treatment and 4 months after treatment (p < 0.05) as well. There was no significant difference (1.7%) in the serum IL-17 levels between the 2- and 4-month intervals after treatment. According to Table 2 and Graph 2, in the FMD group, the mean PD before treatment was 4.1; 2 months after treatment, it was 2.7, and 4 months after treatment, it was 2.6, which showed a significant difference in PD among The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, August 2018;19(8):
4 Amirreza Babaloo et al Table 1: Descriptive and analytical statistics (ANOVA test) for comparing serum IL-27 before and after FMD and Q-SRP Index Time Mean ± SD Min Max p-value IL-27 Baseline 50.5 ± < 0.05 (FMD) 2 months 59.3 ± months 59.6 ± IL-27 Baseline 46.6 ± < 0.05 (Q-SRP) 2 months 55.7 ± months 57.4 ± Table 2: Descriptive and analytical statistics (ANOVA test) for comparing PD before and after FMD and Q-SRP Index Time Mean ± SD Min Max p-value PD (FMD) Baseline 4.18 ± < months 2.76 ± months 2.60 ± PD Baseline 4.18 ± < 0.05 (Q-SRP) 2 months 2.74 ± months 2.57 ± Graph 1: Comparison of serum IL-27 between FMD and Q-SRP before and after treatment Graph 2: Comparison of PD between FMD and Q-SRP before and after treatment the studied intervals, according to ANOVA test (within group) (p < 0.01). The Scheffe post hoc test showed that PD had a significant difference before the treatment and 2 months after the treatment (p < 0.05) with mean difference of 1.42 mm. Also, the mean PD had a significant difference before the treatment and 4 months after treatment with a mean difference of 1.5 mm (p < 0.05). However, there was no significant difference in PD levels between the 2- and 4-month intervals after treatment with only a 0.15 mm difference in mean values. In the Q-SRP group, the mean PD before treatment was 4.18; 2 months after treatment, it was 2.7, and 4 months after treatment, it was 2.57, which according to ANOVA (within group) is a significant difference in PD among the tested intervals (p < 0.01). Based on the Scheffe post hoc test, PD had a significant difference before treatment and 2 months later with a mean difference of 1.43 mm (p < 0.05). Also, the mean PD had a significant difference before treatment and 4 months after treatment with mean difference of 1.61 mm (p < 0.05). The PD levels did not differ significantly between 2 and 4 months after treatment with 0.17 mm difference (p > 0.05). According to Table 3 and Graph 3, in the FMD group, the mean CAL before treatment was 4.2 mm; 2 months after treatment, it was 3.4 mm, and 4 months after treatment, it was 2.78 mm. According to the ANOVA test (within group), there was a significant difference in mean CAL at the tested intervals (p < 0.01). In the Q-SRP group, the mean CAL before treatment was 4.2 mm; 2 months after treatment, it was 3.02 mm, and 4 months after treatment, it was 2.57, which according to the ANOVA test (within group) is a significant difference in CAL among the studied intervals (p < 0.01). According to Table 4 and Graph 4, in the FMD group, the mean BOP before treatment was 73.8%; 2 months after treatment, it was 17.9%, and 4 months after treatment, it was 2.7%. According to ANOVA test (within group), there was a significant difference in BOP among the studied intervals (p < 0.01). In the Q-SRP group, the mean BOP before treatment was 72.75%; 2 months after treatment, it was 15.7%, and 4 months after treatment, it was 6.6%, which according to ANOVA test (within group) is a significant difference in BOP among the studied intervals (p < 0.01). The Scheffe post hoc test in both groups, while examining CAL and BOP indices, shows that (Tables 3, 4 and Graphs 3, 4): CAL and BOP before treatment and 2 months later had a significant difference in each group (p < 0.05). The mean CAL and BOP before treatment and 4 months after treatment were significantly different in each group (p < 0.05). 1000
5 JCDP Evaluation of Clinical Periodontal Indices and Serum Interleukin-27 Table 3: Descriptive and analytical statistics (ANOVA test) for comparing CAL before and after FMD and Q-SRP Index Time Mean ± SD Min Max p-value CAL (FMD) Baseline 4.20 ± < months 3.04 ± months 2.78 ± CAL Baseline 4.20 ± < 0.05 (Q-SRP) 2 months 3.02 ± months 2.75 ± Table 4: Descriptive and analytical statistics (ANOVA test) for comparing BOP before and after FMD and Q-SRP Index Time Mean ± SD Min Max p-value BOP Baseline ± < 0.05 (FMD) 2 months ± months ± BOP Baseline ± < 0.05 (Q-SRP) 2 months ± months 6.60 ± Graph 3: Comparison of CAL between FMD and Q-SRP before and after treatment Graph 4: Comparison of BOP between FMD and Q-SRP before and after treatment This test showed no significant difference in CAL and BOP between the 2- and 4-month intervals after treatment in each group (p > 0.05). According to Table 5 and in accordance with t-test, PD and CAL levels before treatment, and after the 2- and 4-month intervals of treatment did not show significant difference between FMD and Q-SRP groups (p > 0.05). According to the same table, serum levels of IL-27 before treatment and BOP in the 2- and 4-month intervals after treatment showed a significant difference between FMD and Q-SRP groups (p < 0.05). DISCUSSION Both FMD and Q-SRP are effective methods for the treatment of periodontal diseases, and many studies confirm this claim. 28,34-38 The purpose of FMD is to remove or at least suppress all periodontal pathogens rapidly from the oropharyngeal area. 39,40 In this method, bacterial colonization is postponed until better restoration of the periodontal envelope. The above method is a relatively new method and there is a lot of discussion about the effectiveness, rationale, comfort level of patient and dentist, systemic effects, as well as its cost-effectiveness. 39,40 Therefore, many clinical and paraclinical studies have been conducted with varying results, making it difficult to pronounce a clear judgment. 39,40 A new and effective method for diagnosis of periodontal disease and determination of its activity is by the measurement of serum biomarkers. In this regard, at this center, serum levels of interleukins 17 and β1 were evaluated during the course of scaling treatments and the results indicate a reduction in serum levels of these two proinflammatory interleukins. 34 Further, to complete these activities and continue the previous research, we investigated the level of IL-27 changes as an anti-inflammatory interleukin during treatment. Interleukin-27 is a relatively new cytokine that belongs to the IL-12 family. Interleukin-27 is a cytokine derived from antigen-presenting cells, which, in recent years, is a major cytokine in acquired immune responses, and plays its role through the regulation of T-cell-dependent immune responses. The receptor of this cytokine is found in natural killer T cells, B, T, and mast cell, macrophage, dendritic cell, and endothelial cells. 40,41 According to some studies, IL-27 has a proinflammatory role in some diseases, such as autoimmune diseases, while some studies have defined an anti-inflammatory role for this IL. The existing theory suggests that IL-27 prevents the production of IL-1, IL-6, and IL-17 preinflammatory cytokines, and induces production of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL ,41 The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, August 2018;19(8):
6 Amirreza Babaloo et al Table 5: Comparison of IL-27, PD, CAL, and BOP in two types of disinfection before and after treatment Index Time Treatment type Mean ± SD p-value Baseline FMD 5050 ± Q-SRP ± IL-27 2 months FMD ± Q-SRP ± months FMD ± Q-SRP ± Baseline FMD 4.18 ± Q-SRP 4.18 ± 0.66 PD 2 months FMD 2.76 ± Q-SRP 2.74 ± months FMD 2.60 ± Q-SRP 2.57 ± 0.56 Baseline FMD 4.20 ± Q-SRP 4.20 ± 0.67 CAL 2 months FMD 3.04 ± 0.59 Q-SRP 3.02 ± months FMD 2.78 ± 0.54 Q-SRP 2.75 ± Baseline FMD ± Q-SRP ± PI 2 months FMD ± Q-SRP ± months FMD 5.45 ± 3.25 Q-SRP 5.55 ± Baseline FMD ± Q-SRP ± BOP 2 months FMD ± 9.32 Q-SRP ± months FMD ± Q-SRP 6.6 ± Most studies on IL-27 have evaluated the clinical and microbiological aspects of this cytokine. However, in this study, in addition to clinical parameters, the immunological effects have been investigated too, suggesting that an increase in IL-27 acts as an anti-inflammatory interleukin. In the study of Apatzidou et al, 23 the effects of FMD and quadrant method were evaluated on antibody titers. The results of this study showed that both treatments reduced the antibody titer during the study period (6 months). In this study, the effect of FMD and Q-SRP on serum levels of IL-27 was compared in patients with moderateto-advanced periodontitis. The results showed that the mean serum IL-27 increased in the 4th month in both methods without a significant difference in mean serum levels of IL-27 between the 2- and 4-month intervals after treatment in any of the groups. In the FMD group, there was no significant difference between the mean serum IL-27 levels of the study intervals. In the Q-SRP group, there was a significant difference between the 2- or 4 month intervals after treatment and before the treatment values. Following the cause of this phenomena, it can be stated that according to previous studies, due to the stimulatory effect of the first session of scaling on production of an immune response (vaccine-like effect), the level of IL-27 increased during these two follow-up periods. On examining the periodontal indices (BOP, CAL, and PD), clinical improvements were observed in both groups, but there was no significant difference in improvement of CAL and PD periodontal indices between the two groups. In a systematic study, published in 2008, a very small difference was observed in the clinical parameters, evaluated between the two methods in the treatment of chronic adult periodontitis. 38 Predin et al 42 stated in a similar study that both methods led to significant improvement in clinical indices without significant difference between the two groups. Apatzidou and Kinane 43 and Koshy et al 44 also obtained similar results in separate studies. De Genaro Modanese et al 45 also examined the immunological and clinical indices of FMD in generalized periodontitis patients and concluded that it significantly reduced the plaque index, pocket depth, and bleeding. The effect of FMD has been studied in several prospective studies All of these studies are conducted in accordance with the main standard. In the control group, recolonization of the treated envelopes occurred long before the debridement time of all quadrants (during 6 weeks), and there was inappropriate oral hygiene in the untreated quadrants. In addition, only patients with severe periodontitis with significant amounts of plaque subgingival and upper gingival plaque were selected. In contrast, in the test group, debridement of all periodontal envelopes in two consecutive days, along with the use of chlorhexidine, was performed for all the microbial nests, to significantly reduce the amount of bacteria in the oropharynx All the studies reported better clinical outcomes in the experimental group, including a significant reduction in BOP, CAL, and PD These clinical results were confirmed by the improvement of clinical indicators in these studies. The disinfection technique in FMD dramatically reduces the incidence of periodontal abnormal pathogens, especially in the subgingival area and to a lesser extent in the internal oral nests. Several possible explanations were considered for the reported success of FMD. All of the above studies stated that when the possibility of transfer and transduction of intraoral periodontal pathogens decreases, the nonsurgical periodontal treatment will improve. The mechanism of intraoral transfer of these pathogens is still not well defined. However, it seems that the saliva, in which all bacterial species are able to survive, plays an important role in this regard. Changing the direct position of the periodontal pathogens through the flow of 1002
7 JCDP Evaluation of Clinical Periodontal Indices and Serum Interleukin-27 saliva into periodontal envelopes appears to be unlikely due to the outflow of the subgingival fluid. The indirect impact of any change in the upper gingival plaque that may gradually expand to the subgingival area is a more rational explanation for this phenomenon. In fact, several studies have suggested that at least a portion of the gingival microbiota depends on the presence of upper gingival plaque However, it should be noted that bacteria can also be displaced by contaminated health supplies and infected dentistry devices that enter the envelope. 54 Many studies have reported that toothbrushes used daily could be a reservoir for complex periodontal microbiota. 55 CONCLUSION According to the findings of this study, both FMD and Q-SRP procedures have been successful in improving clinical periodontal indices. Both methods increased serum levels of the inflammatory mediator IL-27 during the study period along with the improvement of periodontal clinical indicators. REFERENCES 1. Ryan ME. Nonsurgical approaches for the treatment of periodontal diseases. Dent Clin North Am 2005 Jul;49(3): Hannigan E, O Connell DP, Hannigan A, Buckley LA. Soluble cell adhesion molecules in gingival crevicular fluid in periodontal health and disease. J Periodontol 2004 Apr;75(4): American Academy of Periodontology. Proceedings of the 1996 World Workshop in Periodontics. Consensus report. Periodontal diseases: pathogenesis and microbial factors. Ann Periodontol 1996 Nov;1(1): Slots J, Rams TE. New views on periodontal microbiota in special patient categories. J Clin Periodontol 1991 Jul;18(6): Socransky SS, Haffajee AD. The bacterial etiology of destructive periodontal disease: current concepts. J Periodontol 1992 Apr;63(4 Suppl): Wolff L, Dahlén G, Aeppli D. Bacteria as risk markers for periodontitis. J Periodontol 1994 May;65(5 Suppl): Beikler T, Abdeen G, Schnitzer S, Sälzer S, Ehmke B, Heinecke A, Flemmig TF. Microbiological shifts in intra- and extraoral habitats following mechanical periodontal therapy. J Clin Periodontol 2004 Sep;31(9): Danser MM, Timmerman MF, van Winkelhoff AJ, van der Velden U. The effect of periodontal treatment on periodontal bacteria on the oral mucous membranes. J Periodontol 1996 May;67(5): Danser MM, van Winkelhoff AJ, de Graaff J, Loos BG, van der Velden U. Short-term effect of full-mouth extraction on periodontal pathogens colonizing the oral mucous membranes. J Clin Periodontol 1994 Aug;21(7): Petit MD, van Steenbergen TJ, Timmerman MF, de Graaff J, van der Velden U. Prevalence of periodontitis and suspected periodontal pathogens in families of adult periodontitis patients. J Clin Periodontol 1994 Feb;21(2): von Troll-Linden B, Saarela M, Mättö J, Alaluusua S, Jousimies- Somer H, Asikainen S. Source of suspected periodontal pathogens reemerging after periodontal treatment. J Clin Periodontol l 996 Jun;23(6): Cugini MA, Haffajee AD, Smith C, Kent RL, Socransky SS. The effect of scaling and root planing on the clinical and microbiological parameters of periodontal diseases: 12-month results. J Clin Periodontol 2000 Jan;27(1): Haffajee AD, Cugini MA, Dibart S, Smith C, Kent RL, Socransky SS. The effect of SRP on the clinical and microbiological parameters of periodontal diseases. J Clin Periodontol 1997 May;24(5): Renvert S, Dahlén G, Wikström M. Treatment of periodontal disease based on microbiological diagnosis. Relation between microbiological and clinical parameters during 5 years. J Periodontol 1996 Jun;67(6): Renvert S, Dahlén G, Wikström M. The clinical and microbiological effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy in smokers and non-smokers. J Clin Periodontol 1998 Feb;25(2): Socransky SS, Haffajee AD, Cugini MA, Smith C, Kent RL. Microbial complexes in subgingival plaque. J Clin Periodontol 1998 Feb;25(2): Harper DS, Robinson PJ. Correlation of histometric, microbial, and clinical indicators of periodontal disease status before and after root planing. J Clin Periodontol 1987 Apr;14(4): Wade WG, Moran J, Morgan JR, Newcombe R, Addy M. The effects of antimicrobial acrylic strips on the subgingival microflora in chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 1992 Feb;19(2): Petersilka GJ, Ehmke B, Flemmig TF. Antimicrobial effects of mechanical debridement. Periodontol Jul;28: Lamont RJ, Yilmaz O. In or out: the invasiveness of oral bacteria. Periodontol Sep;30: Adriaens PA, De Boever JA, Loesche WJ. Bacterial invasion in root cementum and radicular dentin of periodontally diseased teeth in humans. A reservoir of periodontopathic bacteria. J Periodontol 1988 Apr;59(4): Quirynen M, Bollen CM, Vandekerckhove BN, Dekeyser C, Papaioannou W, Eyssen H. Full- vs. partial-mouth disinfection in the treatment of periodontal infections: short-term clinical and microbiological observations. J Dent Res 1995 Aug;74(8): Apatzidou DA, Riggio MP, Kinane DF. Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing. 11. Microbiological findings. J Clin Periodontol 2004 Feb;31(2): Jervoe-Storm PM, Koltzscher M, Falk W, Dörfler A, Jepsen S. Comparison of culture and real-time PCR for detection and quantification of five putative periodontopathogenic bacteria in subgingival plaque samples. J Clin Periodontol 2005 Jul;32(7): Wennstrom JL, Tomasi C, Bertelle A, Dellasega E. Full-mouth ultrasonic debridement versus quadrant scaling and root planing as an initial approach in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 2005 Aug;32(8): Zanatta GM, Bittencourt S, Nociti FH, Sallum EA, Sallum AW, Casati MZ. Periodontal debridement with povidone-iodine in periodontal treatment: short-term clinical and biochemical observations. J Periodontol 2006 Mar;77(3): Mongardini C, van Steenberghe D, Dekeyser C, Quirynen M. One stage full- versus partial-mouth disinfection in the treatment of chronic adult or generalized early-onset The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, August 2018;19(8):
8 Amirreza Babaloo et al penodontitis. I. Long-term clinical observations. J Periodontol 1999 Jun;70(6): Quirynen M, De Soete M, Boschmans G, Pauwels M, Coucke W, Teughels W, van Steenberghe D. Benefit of one-stage fullmouth disinfection is explained by disinfection and root planing within 24 hours: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Periodontol 2006 Sep;33(9): Quirynen M, De Soete M, Dierickx K, van Steenberghe D. The intraoral translocation of periodontopathogens jeopardises the outcome of periodontal therapy. A review of the literature. J Clin Periodontol 2001 Jun;28(6): Hussain Bokhari SA, Khan AA, Tatakis DN, Azhar M, Hanif M, Izhar M. Non-surgical periodontal therapy lowers serum inflammatory markers: a pilot study. J Periodontol 2009 Oct;80(10): Apatzidou DA, Kinane DF. Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing. J Clin Periodontol 2004 Mar;31(3): Teughels W, Dekeyser C, Van Essche M, Quirynen M. Onestage, full-mouth disinfection: fiction or reality?. Periodontol Apr;50: Carl JW, Bai XF. IL27: its roles in the induction and inhibition of inflammation. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2008;1(2): Shirmohammadi A, Babaloo Z, Eskandari A, Purabbas R, Babaloo A. The effects of one-stage full-mouth disinfection and Quadrant-Wise scaling and root planing on serum levels of IL-17 and IL-1β and clinical parameters (A randomized controlled trial study). J Dent (Tehran) 2013 May;10(3): Zijnge V, Meijer HF, Lie MA, Tromp JA, Degener JE, Harmsen HJ, Abbas F. The recolonization hypothesis in a full mouth or multiple-session treatment protocol: a blinded, randomized clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol 2010 Jun;37(6): Swierkot K, Nonnenmacher CI, Mutters R, Flores-de-Jacoby L, Mengel R. Onestage full-mouth disinfection versus quadrant and full-mouth root planing. J Clin Periodontol 2009 Mar;36(3): Del Peloso Ribeiro E, Bittencourt S, Sallum EA, Nociti FH, Gonc alves RB, Casati MZ. Periodontal debridement as a therapeutic approach for severe chronic periodontitis: a clinical, microbiological and immunological study. J Clin Periodontol 2008 Sep;35(9): Eberhard J, Jervøe-Storm PM, Needleman I, Worthington H, Jepsen S. Full mouth treatment concepts for chronic periodontitis: a systematic review. J Clin Periodontol 2008 Jul;35(7): Fang H, Han M, Li QL, Cao CY, Xia R, Zhang ZH. Comparison of full mouth disinfection and quadrant wise scaling in the treatment of adult chronic periodontitis: a systematic review and meta analysis. J Periodontal Res 2016 Aug;51(4): Mitani A, Niedbala W, Fujimura T, Mogi M, Miyamae S, Higuchi N, Abe A, Hishikawa T, Mizutani M, Ishihara Y, et al. Increased expression of interleukin (IL)-35 and IL-17, but not IL-27, in gingival tissues with chronic periodontitis. J Periodontol 2015 Feb;86(2): Meka RR, Venkatesha SH, Dudics S, Acharya B, Moudgil KD. IL-27-induced modulation of autoimmunity and its therapeutic potential. Autoimmun Rev 2015 Dec;14(12): Predin T, Djuric M, Nikolic N, Mirnic J, Gusic I, Petrovic D, Milasin J. Clinical and microbiological effects of quadrant versus full-mouth root planing a randomized study. J Dent Sci 2014 Dec;9(4): Apatzidou D, Kinane D. Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing. I. Clinical finding. J Clin Periodontol 2004 Feb;31(2): Koshy G, Kawashima Y, Kiji M, Nitta H, Umeda M, Nagasawa T, Ishikawa I. Effects of single-visit full-mouth ultrasonic debridement versus quadrant-wise ultrasonic debridement. J Clin Periodontol 2005 Jul;32(7): De Genaro Modanese D, Tiosso-Tamburi R, Furletti de Goes VF, de Cássia Bergamaschi C, Martinez EF, Napimoga MH, Peruzzo DC. Clinical and immunoinflammatory evaluation of one-stage full-mouth ultrasonic debridement as a therapeutic approach for smokers with generalized aggressive periodontitis: a short-term follow-up study. J Periodontol 2016 Sep;87(9): De Soete M, Mongardini C, Peuwels M, Haffajee A, Socransky S, van Steenberghe D, Quirynen M. One-stage full-mouth disinfection. Long-term microbiological results analyzed by checkerboard DNA-DNA hybridization. J Periodontol 2001 Mar;72(3): Bollen CM, Vandekerckhove BN, Papaioannou W, Van Eldere J, Quirynen M. Full- versus partial-mouth disinfection in the treatment of periodontal infections. A pilot study: longterm microbiological observations. J Clin Periodontol 1996 Oct;23(10): Quirynen M, Mongardini C, de Soete M, Pauwels M, Coucke W, van Eldere J, van Steenberghe D. The role of chlorhexidine in the one-stage full-mouth disinfection treatment of patients with advanced adult periodontitis. Long-term clinical and microbiological observations. J Clin Periodontol 2000 Aug;27(8): Hellstrom MK, Ramberg P, Krok L, Lindhe J. The effect of supragingival plaque control on the subgingival microflora periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 1996 Oct;23(10): Dahlen G, Lindhe J, Sato K, Hanamura H, Okamoto H. The effect of supragingival plaque control on the subgingival microbiota in subjects with periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol 1992 Nov;19(10): Listgarten MA. The structure of dental plaque. Periodontol Jun;5: McNabb H, Mombelli A, Lang NP. supragingival cleaning 3 times a week. The microbiological effects in moderately deep pockets. J Clin Periodontol 1992 May;19(5): Westfelt E, Rylander H, Dahlen G, Lindhe J. The effect of supragingival plaque control on the progression of advanced periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol 1998 Jul;25(7): Waerhaug J. Effect of toothbrushing on subgingival plaque formation. J Periodontol 1981 Jan;52(1): Quirynen M, de Soete M, Pauwels M, Goossens K, Teughels W, van Eldere J, van Steenberghe D. Bacterial survival rate on tooth- and interdental brushes in relation to the use of toothpaste. J Clin Periodontol 2001 Dec;28(12):
One-stage, full-mouth disinfection: fiction or reality?
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 50, 2009, 39 51 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Ó 2009 John Wiley & Sons A/S PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 disinfection: fiction or reality? WIM TEUGHELS,CHRISTEL DEKEYSER,MARK
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 50, 2009, 39 51 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Ó 2009 John Wiley & Sons A/S PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 disinfection: fiction or reality? WIM TEUGHELS,CHRISTEL DEKEYSER,MARK
Essentials of Periodontal Management in General Practice
 Essentials of Periodontal Management in General Practice Phil Ower MSc BDS MGDSRCS Specialist in Periodontics Briars Dental Centre, Newbury and www.periocourses.co.uk Introduction Effective management
Essentials of Periodontal Management in General Practice Phil Ower MSc BDS MGDSRCS Specialist in Periodontics Briars Dental Centre, Newbury and www.periocourses.co.uk Introduction Effective management
Khosropanah H., et al J Dent Shiraz Univ Med Scien June; 13(2): 44-48
 Original Article The Clinical Effectiveness of Subgingival Irrigation with Povidone-Iodine and Hydrogen Peroxide in Treatment of Moderate to Severe Chronic Periodontitis Khosropanah H. a, Koohpeima F.
Original Article The Clinical Effectiveness of Subgingival Irrigation with Povidone-Iodine and Hydrogen Peroxide in Treatment of Moderate to Severe Chronic Periodontitis Khosropanah H. a, Koohpeima F.
Full-mouth treatment concepts for chronic periodontitis: a systematic review
 J Clin Periodontol 2008; 35: 591 604 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01239.x Full-mouth treatment concepts for chronic periodontitis: a systematic review Eberhard J, Jervøe-Storm P-M, Needleman I, Worthington
J Clin Periodontol 2008; 35: 591 604 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01239.x Full-mouth treatment concepts for chronic periodontitis: a systematic review Eberhard J, Jervøe-Storm P-M, Needleman I, Worthington
THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS
 THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS Adriana Monea, Lecturer, DMD, PhD Department of Odontology and Periodontology Faculty of Dental Medicine, UMF Tîrgu-Mureş, Romania
THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS Adriana Monea, Lecturer, DMD, PhD Department of Odontology and Periodontology Faculty of Dental Medicine, UMF Tîrgu-Mureş, Romania
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of
 Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing I. Clinical findings
 J Clin Periodontol 24; 31: 132 14 Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 24 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing I. Clinical findings D. A. Apatzidou
J Clin Periodontol 24; 31: 132 14 Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 24 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing I. Clinical findings D. A. Apatzidou
Oral hygiene reinforcement in the simplified periodontal treatment of 1 hour
 J Clin Periodontol 2014; 41: 149 156 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12200 Oral hygiene reinforcement in the simplified periodontal treatment of 1 hour Danae A. Apatzidou, Penelope Zygogianni, Dimitra Sakellari and
J Clin Periodontol 2014; 41: 149 156 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12200 Oral hygiene reinforcement in the simplified periodontal treatment of 1 hour Danae A. Apatzidou, Penelope Zygogianni, Dimitra Sakellari and
Home care. Home care. Core Values for Treating Patients in Practice. Professional care. BSP Roadshows 2008/9
 3. Periodontal Treatment BSP Roadshows 2008/9 Core Values for Treating Patients in Practice 3. Periodontal Treatment Phil Ower www.periocourses.co.uk Why is it so important? Oral hygiene methods what s
3. Periodontal Treatment BSP Roadshows 2008/9 Core Values for Treating Patients in Practice 3. Periodontal Treatment Phil Ower www.periocourses.co.uk Why is it so important? Oral hygiene methods what s
Periodontitis is characterized by
 Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry original article Povidone Iodine vs Tetracycline Fibers- To Analyse the Therapeutic Effect Suchetha A 1, Garg A 2, Lakshmi P 3,Sapna N 4, Mundinamane DB 5,
Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry original article Povidone Iodine vs Tetracycline Fibers- To Analyse the Therapeutic Effect Suchetha A 1, Garg A 2, Lakshmi P 3,Sapna N 4, Mundinamane DB 5,
Journal of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
 Comparison of Systemic Ciprofloxacin in Elimination of A.a from Active Sites with Combination of Metronidzole and Amoxicillin in Patients with Aggressive Periodontitis: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled
Comparison of Systemic Ciprofloxacin in Elimination of A.a from Active Sites with Combination of Metronidzole and Amoxicillin in Patients with Aggressive Periodontitis: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled
Research Article Full Mouth Disinfection Versus Scaling and Root Planing per Quadrant in Aggressive Periodontitis: A Systematic Review
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Full Mouth Disinfection Versus Scaling and Root Planing per Quadrant in Aggressive Periodontitis: A Systematic Review Maísa Casarin 1 *, Danilo Antonio
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Full Mouth Disinfection Versus Scaling and Root Planing per Quadrant in Aggressive Periodontitis: A Systematic Review Maísa Casarin 1 *, Danilo Antonio
Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 1, Issue 4 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 36-41 Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool 1 Ashu Bhardwaj,
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 1, Issue 4 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 36-41 Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool 1 Ashu Bhardwaj,
What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers
 http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2017/v72no8a8 < 387 What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers SADJ September 2017, Vol 72 no 8 p387- p391 Compiled and
http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2017/v72no8a8 < 387 What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers SADJ September 2017, Vol 72 no 8 p387- p391 Compiled and
- BANA Hydrolysis as a Comparative Tool in the Evaluation of Amoxicillin and Azithromycin in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article - BANA Hydrolysis as a Comparative Tool in the Evaluation of Amoxicillin and Azithromycin in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis Rosaiah
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article - BANA Hydrolysis as a Comparative Tool in the Evaluation of Amoxicillin and Azithromycin in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis Rosaiah
COMPARISON OF HAND AND ULTRASONIC INSTRUMENTATION ON PERIODONTAL PARAMETERS IN GHANAIAN PATIENTS WITH MODERATE CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS
 March 216 Vol. 5, No. 1 PostgraduateMedical Journal of Ghana COMPARISON OF AND INSTRUMENTATION ON PERIODONTAL PARAMETERS IN GHANAIAN PATIENTS WITH MODERATE CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS Abstract Vasco E, Kwamin
March 216 Vol. 5, No. 1 PostgraduateMedical Journal of Ghana COMPARISON OF AND INSTRUMENTATION ON PERIODONTAL PARAMETERS IN GHANAIAN PATIENTS WITH MODERATE CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS Abstract Vasco E, Kwamin
Clinical efficacy of phase I therapy combined with a triclosan/copolymer dentifrice on generalized chronic periodontitis
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2010) 5, 216e220 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com Original Article Clinical efficacy of phase I therapy combined with a triclosan/copolymer
Journal of Dental Sciences (2010) 5, 216e220 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com Original Article Clinical efficacy of phase I therapy combined with a triclosan/copolymer
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
FACULTY OF HEALTH SCIENCES INSTITUTE OF CLINICAL DENTISTRY
 Professor Gottfried Schmalz Editor-in-Chief Clinical Oral Investigations Universität Regensburg Fakultät für Medizin Poliklinik für Zahnerhatungskunde und Parodontologie Frans-Josef-Strauss-Allee 11 93053
Professor Gottfried Schmalz Editor-in-Chief Clinical Oral Investigations Universität Regensburg Fakultät für Medizin Poliklinik für Zahnerhatungskunde und Parodontologie Frans-Josef-Strauss-Allee 11 93053
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
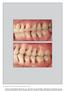 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
Microbial and Genetic Testing in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease
 Microbial and Genetic Testing in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Mr P.Renton-Harper Specialist in Periodontics prh@perio.co.uk www.perio.co.uk Periodontal Disease A bacterial infection in a susceptible
Microbial and Genetic Testing in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Mr P.Renton-Harper Specialist in Periodontics prh@perio.co.uk www.perio.co.uk Periodontal Disease A bacterial infection in a susceptible
The use of povidone iodine and hydrogen peroxide mixture as an adjunct to non-surgical treatment of slight to moderate chronic periodontitis
 The Saudi Dental Journal (2009) 21, 127 133 King Saud University The Saudi Dental Journal www.ksu.edu.sa www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE The use of povidone iodine and hydrogen peroxide mixture
The Saudi Dental Journal (2009) 21, 127 133 King Saud University The Saudi Dental Journal www.ksu.edu.sa www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE The use of povidone iodine and hydrogen peroxide mixture
NEW 12-MONTH CLINICAL STUDY RESULTS
 NEW 12-MONTH CLINICAL STUDY RESULTS March 30, 2015 Dear Oxyfresh Professional: We are thrilled to share with you the exciting results of a NEW 12-month, double blind clinical study published in the International
NEW 12-MONTH CLINICAL STUDY RESULTS March 30, 2015 Dear Oxyfresh Professional: We are thrilled to share with you the exciting results of a NEW 12-month, double blind clinical study published in the International
Rate of cultivable subgingival periodontopathogenic bacteria in chronic periodontitis
 157 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 46, No. 3, 157-161, 2004 Original Rate of cultivable subgingival periodontopathogenic bacteria in chronic periodontitis Mohammad Hossein Salari and Zainab Kadkhoda Department
157 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 46, No. 3, 157-161, 2004 Original Rate of cultivable subgingival periodontopathogenic bacteria in chronic periodontitis Mohammad Hossein Salari and Zainab Kadkhoda Department
Initial Therapy. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS. Oral sulcular epithelium. Oral. epithelium. Junctional. epithelium. Connective tissue.
 Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
Please visit the C.E. Pavilion to validate your course attendance Or If There s a Line Go cdapresents.com
 UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1234-1240, 2002 Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars Raymond P. White, Jr, DDS, PhD,* Phoebus N. Madianos,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1234-1240, 2002 Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars Raymond P. White, Jr, DDS, PhD,* Phoebus N. Madianos,
Comparison of Effectiveness of Two Designs of Interdental Toothbrushes in removing Dental Plaque
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparison of Effectiveness of Two Designs of Interdental Toothbrushes 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1147 in removing Dental Plaque Comparison of Effectiveness of Two Designs of Interdental
RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparison of Effectiveness of Two Designs of Interdental Toothbrushes 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1147 in removing Dental Plaque Comparison of Effectiveness of Two Designs of Interdental
Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters
 Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters REVIEWED PAPER Most patients visiting dental surgeries suffer from various types of periodontopathies. Since
Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters REVIEWED PAPER Most patients visiting dental surgeries suffer from various types of periodontopathies. Since
Volume 2 Issue
 Volume 2 Issue 2 2017 Page 333 to 340 Research Article Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 The Anti-Inflammatory Actions of an Intra-Oral Adhesive Patch Containing Botanical Extracts Exert Inhibitory
Volume 2 Issue 2 2017 Page 333 to 340 Research Article Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 The Anti-Inflammatory Actions of an Intra-Oral Adhesive Patch Containing Botanical Extracts Exert Inhibitory
Longitudinal Supportive Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Furcation Involvement: A 12-year Follow-up Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2013) 54(4): 243 250 Case Report Longitudinal Supportive Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Furcation Involvement: A 12-year Follow-up Report Akiyo Komiya-Ito,
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2013) 54(4): 243 250 Case Report Longitudinal Supportive Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Furcation Involvement: A 12-year Follow-up Report Akiyo Komiya-Ito,
Materials and Methods: Literature review and Authors opinion.
 Haffajee AD, Bogren A, Hasturk H et al. Subgingival microbiota of chronic periodontitis subjects from different geographic locations. J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31:996-1002. Purpose: To compare the subgingival
Haffajee AD, Bogren A, Hasturk H et al. Subgingival microbiota of chronic periodontitis subjects from different geographic locations. J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31:996-1002. Purpose: To compare the subgingival
Periodontist-Dental Hygienist Collaboration in Periodontal Care for Chronic Periodontitis: An 11-year Case Report
 ull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 177 186 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0039 Periodontist-Dental Hygienist Collaboration in Periodontal Care for Chronic Periodontitis: An 11-year Case Report
ull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 177 186 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0039 Periodontist-Dental Hygienist Collaboration in Periodontal Care for Chronic Periodontitis: An 11-year Case Report
Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
Scaling and root planing and chlorhexidine mouthrinses in the treatment of chronic periodontitis: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial
 J Clin Periodontol 26; 33: 819 828 doi: 1.1111/j.16-51X.26.994.x Scaling and root planing and chlorhexidine mouthrinses in the treatment of chronic periodontitis: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical
J Clin Periodontol 26; 33: 819 828 doi: 1.1111/j.16-51X.26.994.x Scaling and root planing and chlorhexidine mouthrinses in the treatment of chronic periodontitis: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical
Systemic antibiotics Vs Local antibiotics in the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases BY: ABRAHEEM JAMAL ABRAHEEM & AYOUB NAGIBB BURWEISS
 Systemic antibiotics Vs Local antibiotics in the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases BY: ABRAHEEM JAMAL ABRAHEEM & AYOUB NAGIBB BURWEISS Guidelines for use of antibiotics in periodontal therapy 1. The clinical
Systemic antibiotics Vs Local antibiotics in the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases BY: ABRAHEEM JAMAL ABRAHEEM & AYOUB NAGIBB BURWEISS Guidelines for use of antibiotics in periodontal therapy 1. The clinical
-70% Visible plaque index(vpi) -60% Bleeding on probing (BOP) -10% Probing depth (PD)
 Deep studies carried out by the Second University of Naples show the effectiveness of SoWash System and its accessories. After only 14 days use of SoWash System: -70% Visible plaque index(vpi) -60% Bleeding
Deep studies carried out by the Second University of Naples show the effectiveness of SoWash System and its accessories. After only 14 days use of SoWash System: -70% Visible plaque index(vpi) -60% Bleeding
Periodontal disease is characterized by progressive periodontal pathogens. It is known that coronary heart disease is
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com PREVALENCE OF PERIODONTAL DISEASES IN PATIENTS WITH CORONARY HEART DISEASE Niha Naveed* BDS student, Saveetha
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com PREVALENCE OF PERIODONTAL DISEASES IN PATIENTS WITH CORONARY HEART DISEASE Niha Naveed* BDS student, Saveetha
JSS Medical and Dental College and Hospital, JSS University, Mysore, India *Author for Correspondence
 CLINICAL, MICROBIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR STUDY OF PORPHYROMONAS GINGIVALIS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS *Mayuri Vajawat 1, Vijay Kumar 2, K.G. Rajeshwari 3 and P.C. Deepika 4 1&4 Department of
CLINICAL, MICROBIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR STUDY OF PORPHYROMONAS GINGIVALIS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS *Mayuri Vajawat 1, Vijay Kumar 2, K.G. Rajeshwari 3 and P.C. Deepika 4 1&4 Department of
Dental Water Jet. By: Jennifer Buffington, Lindsay Hunt, Ruth Gardner
 Dental Water Jet By: Jennifer Buffington, Lindsay Hunt, Ruth Gardner What is a Dental Water Jet? A home, dental self-care device that uses a stream of pulsating water to irrigate the subgingival sulcus
Dental Water Jet By: Jennifer Buffington, Lindsay Hunt, Ruth Gardner What is a Dental Water Jet? A home, dental self-care device that uses a stream of pulsating water to irrigate the subgingival sulcus
Root Dentine Sensitivity
 Indian Medical Gazette JULY 2012 269 Original Study Root Dentine Sensitivity Jyoti Ajay Khade, Associate Professor, Dept. of Dentistry, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS) Adilabad, A.P.
Indian Medical Gazette JULY 2012 269 Original Study Root Dentine Sensitivity Jyoti Ajay Khade, Associate Professor, Dept. of Dentistry, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS) Adilabad, A.P.
Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Framework and Proposal of a New Classification and Case Definition. By: Kimberly Hawrylyshyn
 Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Framework and Proposal of a New Classification and Case Definition By: Kimberly Hawrylyshyn Background Periodontitis is a microbe induced inflammatory disease that
Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Framework and Proposal of a New Classification and Case Definition By: Kimberly Hawrylyshyn Background Periodontitis is a microbe induced inflammatory disease that
Is Biologic Width of Anterior and Posterior Teeth Similar?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Biologic Width of Anterior and Posterior Teeth Similar? Amir Alireza Rasouli Ghahroudi 1, Afshin Khorsand 1, Siamak Yaghobee 1,2, and Farideh Haghighati 1 1 Department of Periodontology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Biologic Width of Anterior and Posterior Teeth Similar? Amir Alireza Rasouli Ghahroudi 1, Afshin Khorsand 1, Siamak Yaghobee 1,2, and Farideh Haghighati 1 1 Department of Periodontology,
Subgingival Root Brushing in Deep Human Periodontal Pockets
 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2013 15/2:55-63 Subgingival Root Brushing in Deep Human Periodontal Pockets 1 1,2 Lawrence R. Page and Thomas E. Rams 1 Department of Periodontology
Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2013 15/2:55-63 Subgingival Root Brushing in Deep Human Periodontal Pockets 1 1,2 Lawrence R. Page and Thomas E. Rams 1 Department of Periodontology
Subject: Periodontal Maintenance Guideline #: Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/05/2018
 Dental Policy Subject: Periodontal Maintenance Guideline #: 04-901 Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/05/2018 Description This document addresses periodontal maintenance. Note:
Dental Policy Subject: Periodontal Maintenance Guideline #: 04-901 Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/05/2018 Description This document addresses periodontal maintenance. Note:
ELIMINATE POCKETS. Periodontal pocket is the consequence of periodontal infection But also a major risk factor for the further progression of disease
 ELIMINATE POCKETS Periodontal pocket is the consequence of periodontal infection But also a major risk factor for the further progression of disease CONSEQUENTLY Periodontal pockets should be eliminated
ELIMINATE POCKETS Periodontal pocket is the consequence of periodontal infection But also a major risk factor for the further progression of disease CONSEQUENTLY Periodontal pockets should be eliminated
Bacterial colonization of the peri-implant sulcus in dentate patients: a prospective observational study
 Clin Oral Invest (2017) 21:717 724 DOI 10.1007/s00784-016-1941-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bacterial colonization of the peri-implant sulcus in dentate patients: a prospective observational study M. A. Stokman
Clin Oral Invest (2017) 21:717 724 DOI 10.1007/s00784-016-1941-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bacterial colonization of the peri-implant sulcus in dentate patients: a prospective observational study M. A. Stokman
ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder
 ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
Department of Oral Surgery, Heinrich Heine University, D Düsseldorf, Germany.
 Lasers Surg Med. 2007 Jun;39(5):428-40 Immunohistochemical characterization of periodontal wound healing following nonsurgical treatment with fluorescence controlled Er:YAG laser radiation in dogs. Schwarz
Lasers Surg Med. 2007 Jun;39(5):428-40 Immunohistochemical characterization of periodontal wound healing following nonsurgical treatment with fluorescence controlled Er:YAG laser radiation in dogs. Schwarz
Show biofilm the red card
 Show biofilm the red card BIOFILM-ERASER 1 A NEW APPLICATION Effective treatment for periodontal and peri-implant inflammation Periodontitis and peri-implantitis are bacterial inflammations with similar
Show biofilm the red card BIOFILM-ERASER 1 A NEW APPLICATION Effective treatment for periodontal and peri-implant inflammation Periodontitis and peri-implantitis are bacterial inflammations with similar
Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement
 Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to report a case of conditioned gingival enlargement managed by nonsurgical periodontal therapy.
Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to report a case of conditioned gingival enlargement managed by nonsurgical periodontal therapy.
Plaque Removal Ability in Left- and Right-handed Patients in Different Parts of the Oral Cavity
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article Plaque Removal Ability in Left- and Right-handed Patients in Different Parts of the Oral Cavity Mahdi Kadkhodazadeh 1,2 * Amin Khodadustan
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article Plaque Removal Ability in Left- and Right-handed Patients in Different Parts of the Oral Cavity Mahdi Kadkhodazadeh 1,2 * Amin Khodadustan
Concordance of Porphyromonas gingivalis Colonization in Families
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1997, p. 455 461 Vol. 35, No. 2 0095-1137/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Concordance of Porphyromonas gingivalis Colonization in Families
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1997, p. 455 461 Vol. 35, No. 2 0095-1137/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Concordance of Porphyromonas gingivalis Colonization in Families
Original Research. which are considered important in causation of gingivitis and periodontitis. 1,2
 Tetracycline hydrochloride and spiramycin sub gingival irrigation in chronic Received: 20 th January 2015 Accepted: 15 th April 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research
Tetracycline hydrochloride and spiramycin sub gingival irrigation in chronic Received: 20 th January 2015 Accepted: 15 th April 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research
TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment. Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD
 TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE 2 The available evidence consistently shows that therapies intended to arrest and control periodontitis depend primarily
TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE 2 The available evidence consistently shows that therapies intended to arrest and control periodontitis depend primarily
Effect of Systemically Administered Azithromycin in Early Onset Aggressive Periodontitis
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Effect of Systemically Administered Azithromycin in Early Onset Aggressive Periodontitis Takeo Fujii, Pao-Li Wang, Yoichiro Hosokawa, Shinichi Shirai, Atsumu Tamura, Kazuhiro
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Effect of Systemically Administered Azithromycin in Early Onset Aggressive Periodontitis Takeo Fujii, Pao-Li Wang, Yoichiro Hosokawa, Shinichi Shirai, Atsumu Tamura, Kazuhiro
Microbiological outcomes from different periodontal maintenance interventions: a systematic review
 Systemaic Review Periodontics Microbiological outcomes from different periodontal maintenance interventions: a systematic review Patricia Daniela Melchiors ANGST (a) Amanda Finger STADLER (b) Rui Vicente
Systemaic Review Periodontics Microbiological outcomes from different periodontal maintenance interventions: a systematic review Patricia Daniela Melchiors ANGST (a) Amanda Finger STADLER (b) Rui Vicente
Research Effect of tetracycline HCL (periodontal plus AB) on Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans levels in chronic periodontitis
 ISSN 2058-7813 Research Effect of tetracycline HCL (periodontal plus AB) on Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans levels in chronic periodontitis Sneha Kataria 1, Kabbur Thippanna Chandrashekar 1*, Rohit
ISSN 2058-7813 Research Effect of tetracycline HCL (periodontal plus AB) on Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans levels in chronic periodontitis Sneha Kataria 1, Kabbur Thippanna Chandrashekar 1*, Rohit
The dentogingival junction to the
 Volume 79 Number 10 RedefiningtheBiologicWidthinSevere, Generalized, Chronic Periodontitis: Implications for Therapy M. John Novak,* Huda M. Albather, and John M. Close Background: Previous studies demonstrated
Volume 79 Number 10 RedefiningtheBiologicWidthinSevere, Generalized, Chronic Periodontitis: Implications for Therapy M. John Novak,* Huda M. Albather, and John M. Close Background: Previous studies demonstrated
Multidisciplinary treatment planning for patients with severe periodontal disease
 Clinical Multidisciplinary treatment planning for patients with severe periodontal disease Josselin Lethuillier, 1 Sébastien Felenc, 2 Philippe Bousquet 3 Abstract Periodontally compromised patients usually
Clinical Multidisciplinary treatment planning for patients with severe periodontal disease Josselin Lethuillier, 1 Sébastien Felenc, 2 Philippe Bousquet 3 Abstract Periodontally compromised patients usually
Efficacy Evaluation of a Chlorine Dioxide Containing Toothpaste (DioxiBrite ) on Plaque and Gingivitis. A Clinical Study
 Efficacy Evaluation of a Chlorine Dioxide Containing Toothpaste (DioxiBrite ) on Plaque and Gingivitis A Clinical Study Principle Investigator Laura Mueller-Joseph RDH, Ed.D. State University of New York
Efficacy Evaluation of a Chlorine Dioxide Containing Toothpaste (DioxiBrite ) on Plaque and Gingivitis A Clinical Study Principle Investigator Laura Mueller-Joseph RDH, Ed.D. State University of New York
Response of molars and non-molars to a strict supragingival control in periodontal patients
 Periodontics Response of molars and non-molars to a strict supragingival control in periodontal patients Patrícia Daniela elchiors Angst (a) Flávia Benetti Piccinin (a) Rui Vicente Oppermann (a) Rosemary
Periodontics Response of molars and non-molars to a strict supragingival control in periodontal patients Patrícia Daniela elchiors Angst (a) Flávia Benetti Piccinin (a) Rui Vicente Oppermann (a) Rosemary
EFFECT OF ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTIONS ON GINGIVAL INDEX AND PLAQUE SCORE AMONG PERIODONTAL PATIENTS VISITING THE UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI DENTAL HOSPITAL.
 EFFECT OF ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTIONS ON GINGIVAL INDEX AND PLAQUE SCORE AMONG PERIODONTAL PATIENTS VISITING THE UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI DENTAL HOSPITAL. INVESTIGATOR KAGURU GEORGE KARIUKI BDS III 2004/2005
EFFECT OF ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTIONS ON GINGIVAL INDEX AND PLAQUE SCORE AMONG PERIODONTAL PATIENTS VISITING THE UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI DENTAL HOSPITAL. INVESTIGATOR KAGURU GEORGE KARIUKI BDS III 2004/2005
Impact of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on oral malodor and microbial load of saliva
 대한치주과학회지 : Vol. 37, No. 1, 2007 Impact of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on oral malodor and microbial load of saliva Myung-Jin Kim, Sung-Jo Kim, Jeom-Il Choi, Ju-Youn Lee * Department of Periodontology,
대한치주과학회지 : Vol. 37, No. 1, 2007 Impact of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on oral malodor and microbial load of saliva Myung-Jin Kim, Sung-Jo Kim, Jeom-Il Choi, Ju-Youn Lee * Department of Periodontology,
Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder
 Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder 3M 2016. All Rights Reserved VIDEO 3M 2016. All Rights Reserved 2 Presentation Overview Air Polishing Procedure With Clinpro Glyciene Prophy Powder Use and Efficiency for
Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder 3M 2016. All Rights Reserved VIDEO 3M 2016. All Rights Reserved 2 Presentation Overview Air Polishing Procedure With Clinpro Glyciene Prophy Powder Use and Efficiency for
Periodontal Case Report
 Periodontal Case Report By Dan AlAhmed 431200041 Saleha AlZahrani 431200123 Raghad AlSaawy 431200297 Afnan AlAssiri 431200687 Mawadh Demyati 431200824 Hend Jaddoh 431201247 Alaa AlDoss 431201808 Rawan
Periodontal Case Report By Dan AlAhmed 431200041 Saleha AlZahrani 431200123 Raghad AlSaawy 431200297 Afnan AlAssiri 431200687 Mawadh Demyati 431200824 Hend Jaddoh 431201247 Alaa AlDoss 431201808 Rawan
IJEDS ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION /jp-journals
 Ameet Mani et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1145 Efficacy of Oral Probiotics as an Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in Nonsurgical Treatment Outcome of Generalized Chronic Periodontitis
Ameet Mani et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1145 Efficacy of Oral Probiotics as an Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in Nonsurgical Treatment Outcome of Generalized Chronic Periodontitis
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
A Prospective Experimental Comparative Study on the Clinical Effects of Calculus /jp-journals
 A Prospective Experimental Comparative Study on the Effects of Calculus 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1092 Dissolution based Oral Rinse ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Prospective Experimental Comparative Study on the
A Prospective Experimental Comparative Study on the Effects of Calculus 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1092 Dissolution based Oral Rinse ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Prospective Experimental Comparative Study on the
Sulphur By-Product: The Relationship between Volatile Sulphur Compounds and Dental Plaque-Induced Gingivitis
 Sulphur By-Product: The Relationship between Volatile Sulphur Compounds and Dental Plaque-Induced Gingivitis Abstract The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship between volatile sulphur
Sulphur By-Product: The Relationship between Volatile Sulphur Compounds and Dental Plaque-Induced Gingivitis Abstract The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship between volatile sulphur
The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org ( this information is current as of April 21, 2011 ):
 EFFICIENT ANTIMICROBIAL TREATMENT IN PERIODONTAL MAINTENANCE CARE JØRGEN SLOTS and MICHAEL G. JORGENSEN J Am Dent Assoc 2000;131;1293-1304 The following resources related to this article are available
EFFICIENT ANTIMICROBIAL TREATMENT IN PERIODONTAL MAINTENANCE CARE JØRGEN SLOTS and MICHAEL G. JORGENSEN J Am Dent Assoc 2000;131;1293-1304 The following resources related to this article are available
A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran
 Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient. Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club
 Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
Periodontal Treatment Guide
 Periodontal Treatment Guide Teamwork for treating periodontal disease The treatment of patients with periodontal disease should involve the application of standard procedures based on commonly accepted
Periodontal Treatment Guide Teamwork for treating periodontal disease The treatment of patients with periodontal disease should involve the application of standard procedures based on commonly accepted
Microbiota and Oral Disease Prof. Dennis Cvitkovitch
 1 Professor Dennis Cvitkovitch Faculty of Dentistry Dental Research Institute University of Toronto The human microbiome We are a composite species: eukaryotic, bacterial, archeal Every human harbors over
1 Professor Dennis Cvitkovitch Faculty of Dentistry Dental Research Institute University of Toronto The human microbiome We are a composite species: eukaryotic, bacterial, archeal Every human harbors over
JMSCR Volume 2 Issue 7 Page July
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 1.1147 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Clinical Evaluation of Locally Delivered 10% Doxycycline Hyclate Gel as An Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in the Treatment of Chronic
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 1.1147 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Clinical Evaluation of Locally Delivered 10% Doxycycline Hyclate Gel as An Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in the Treatment of Chronic
Pathogens in Relation to Periodontal Status
 J Dent Res 74(11): 1789-1793, November, 1995 Salivary Levels of Suspected Periodontal Pathogens in Relation to Periodontal Status and Treatment B. von Troil-Lindenl*, H. Torkko2, S. Alaluusua3, H. Jousimies-Somer4,
J Dent Res 74(11): 1789-1793, November, 1995 Salivary Levels of Suspected Periodontal Pathogens in Relation to Periodontal Status and Treatment B. von Troil-Lindenl*, H. Torkko2, S. Alaluusua3, H. Jousimies-Somer4,
Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, :54 AM
 Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, 2015 9:54 AM 1. The definition of Trauma From Occlusion: Primary TFO, Secondary TFO, and Combined TFO 2. Clinical and Radiographic signs
Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, 2015 9:54 AM 1. The definition of Trauma From Occlusion: Primary TFO, Secondary TFO, and Combined TFO 2. Clinical and Radiographic signs
The effect of smoking on bleeding on probing after nonsurgical periodontal therapy: a quasi-experimental study
 Original Research Periodontics The effect of smoking on bleeding on probing after nonsurgical periodontal therapy: a quasi-experimental study Rodrigo ARDAIS Ticiane de Góes MÁRIO Jociana BOLIGON Karla
Original Research Periodontics The effect of smoking on bleeding on probing after nonsurgical periodontal therapy: a quasi-experimental study Rodrigo ARDAIS Ticiane de Góes MÁRIO Jociana BOLIGON Karla
Rare case of generalised aggressive periodontitis in the primary dentition
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2014 Rare case of generalised aggressive periodontitis in the primary dentition
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2014 Rare case of generalised aggressive periodontitis in the primary dentition
A STUDY OF PERIODONTAL DISEASE IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES SUMARRY
 A STUDY OF PERIODONTAL DISEASE IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES SUMARRY INTRODUCTION Marginal periodontium is the seat of acute and chronic diseases that pose a particular problem in general
A STUDY OF PERIODONTAL DISEASE IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES SUMARRY INTRODUCTION Marginal periodontium is the seat of acute and chronic diseases that pose a particular problem in general
Research Article. Chlorhexidine varnish: An attempt to vanish moderate periodontitis
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(1):339-345 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Chlorhexidine varnish: An attempt to vanish moderate
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(1):339-345 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Chlorhexidine varnish: An attempt to vanish moderate
Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical investigation
 American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Original Research Article Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical Ninad Moon 1, Prasant Pillai
American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Original Research Article Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical Ninad Moon 1, Prasant Pillai
Comparison of nonsurgical periodontal therapy with oral hygiene instruction alone for chronic periodontitis
 111 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 59, No. 1, 111-120, 2017 Original Comparison of nonsurgical periodontal therapy with oral hygiene instruction alone for chronic periodontitis Maaz Asad 1), Alwani W. Abdul
111 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 59, No. 1, 111-120, 2017 Original Comparison of nonsurgical periodontal therapy with oral hygiene instruction alone for chronic periodontitis Maaz Asad 1), Alwani W. Abdul
Antimicrobial Treatment for Advanced Periodontal Disease
 Antimicrobial Treatment for Advanced Periodontal Disease James S. Kohner, DDS DISCLOSURES December 15, 2011 Editor's Note: This author's case report is based on the work of Jorgen Slots, DDS, DMD, PhD,
Antimicrobial Treatment for Advanced Periodontal Disease James S. Kohner, DDS DISCLOSURES December 15, 2011 Editor's Note: This author's case report is based on the work of Jorgen Slots, DDS, DMD, PhD,
An intriguing case of gingival enlargement associated with generalised aggressive periodontitis
 CLINICAL REPORT 295 Ajay Mahajan, Jaya Dixit, Umesh Verma An intriguing case of gingival enlargement associated with generalised aggressive periodontitis KEY WORDS antimicrobial therapy, clinical findings,
CLINICAL REPORT 295 Ajay Mahajan, Jaya Dixit, Umesh Verma An intriguing case of gingival enlargement associated with generalised aggressive periodontitis KEY WORDS antimicrobial therapy, clinical findings,
Studies suggest that subgingival
 Volume 81 Number 5 Clinical and Microbiologic Follow-Up Evaluations After Non-Surgical Periodontal Treatment With Erbium:YAG Laser and Scaling and Root Planing Beatriz Maria Valério Lopes,* Leticia Helena
Volume 81 Number 5 Clinical and Microbiologic Follow-Up Evaluations After Non-Surgical Periodontal Treatment With Erbium:YAG Laser and Scaling and Root Planing Beatriz Maria Valério Lopes,* Leticia Helena
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1
 PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
Role of antibiotics in periodontal therapy
 BANGLADESH JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Volume-8 No. 4; October 2009 Review article Abstract Manas D 1, Srinivas SR 2, Jithendra KD 3 Loeshe in 1976 propounded the Specific Plaque Hypothesis and efforts
BANGLADESH JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Volume-8 No. 4; October 2009 Review article Abstract Manas D 1, Srinivas SR 2, Jithendra KD 3 Loeshe in 1976 propounded the Specific Plaque Hypothesis and efforts
Detection of predominant subgingival periopathogens around submerged and non submerged hydroxy apatite implants
 [Downloaded free from http://www.jdionline.org on Sunday, January 26, 2014, IP: 201.22.186.203] Click here to download free Android application for this journa ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detection of predominant
[Downloaded free from http://www.jdionline.org on Sunday, January 26, 2014, IP: 201.22.186.203] Click here to download free Android application for this journa ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detection of predominant
Specific Egg Yolk Antibody (Ovalgen PG) as a Novel Supportive Immunotherapy for Periodontitis
 7 th Vietnam International Dental Exhibition and congress (VIDEC) Aug 7-9, 2014 Specific Egg Yolk Antibody (Ovalgen PG) as a Novel Supportive Immunotherapy for Periodontitis Nguyen Van Sa, Ph.D Immunology
7 th Vietnam International Dental Exhibition and congress (VIDEC) Aug 7-9, 2014 Specific Egg Yolk Antibody (Ovalgen PG) as a Novel Supportive Immunotherapy for Periodontitis Nguyen Van Sa, Ph.D Immunology
Effectiveness of full- and partial-mouth disinfection on halitosis in periodontal patients
 1 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 57, No. 1, 1-6, 2015 Original Effectiveness of full- and partial-mouth disinfection on halitosis in periodontal patients Léo G. Soares 1), Lisiane Castagna 1), Sérgio C.
1 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 57, No. 1, 1-6, 2015 Original Effectiveness of full- and partial-mouth disinfection on halitosis in periodontal patients Léo G. Soares 1), Lisiane Castagna 1), Sérgio C.
Comparison of the Substantivity of Several Mouthwashesand their Effect on Microbial Plaque using Epifluorescence Microscope
 Original Article Comparison of the Substantivity of Several Mouthwashesand their Effect on Microbial Plaque using Epifluorescence Microscope M. Ghasemi 1, M. Rahbar 2, N. Valaei 3. 1 Associate Professor
Original Article Comparison of the Substantivity of Several Mouthwashesand their Effect on Microbial Plaque using Epifluorescence Microscope M. Ghasemi 1, M. Rahbar 2, N. Valaei 3. 1 Associate Professor
Tribal Distribution of Aggressive Periodontitis in Sudanese School Children (12-16 years) in Khartoum State
 American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences 2017, 7(9): 338-343 DOI: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20170709.03 Tribal Distribution of Aggressive Periodontitis in Sudanese School Children (12-16 years) in Khartoum
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences 2017, 7(9): 338-343 DOI: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20170709.03 Tribal Distribution of Aggressive Periodontitis in Sudanese School Children (12-16 years) in Khartoum
Diabetes and Periodontal Disease. Brianne Neelis & Katie Torres. Literature Review 1 11/4/08
 1 Diabetes and Periodontal Disease Brianne Neelis & Katie Torres Literature Review 1 11/4/08 2 Introduction Diabetes is a cardiovascular condition that effects an estimated 20 million people in the United
1 Diabetes and Periodontal Disease Brianne Neelis & Katie Torres Literature Review 1 11/4/08 2 Introduction Diabetes is a cardiovascular condition that effects an estimated 20 million people in the United
Product Information Clinpro Prophy Powder 4 Bottles à 100 g
 Ordering Information Item No. Product Information 671 Clinpro Prophy Powder 4 Bottles à 1 g Clinpro Prophy Powder 12613 Clinpro Prophy Paste 2 à 2 g Cherry Fine 12657 Clinpro Prophy Paste 2 à 2 g Mint
Ordering Information Item No. Product Information 671 Clinpro Prophy Powder 4 Bottles à 1 g Clinpro Prophy Powder 12613 Clinpro Prophy Paste 2 à 2 g Cherry Fine 12657 Clinpro Prophy Paste 2 à 2 g Mint
NEWSLETTER ABOUT LIGHT ACTIVATED DISINFECTION MARCH FotoSanNewsletter
 FotoSanNewsletter Biofilm modulation In this issue we will discuss Bacterial Replacement Therapy (BRT) - a new highly effective method to change a pathogen biofilm to non-pathogen. 1 Reduce the bacteria
FotoSanNewsletter Biofilm modulation In this issue we will discuss Bacterial Replacement Therapy (BRT) - a new highly effective method to change a pathogen biofilm to non-pathogen. 1 Reduce the bacteria
An Investigation of Antibiotic Resistance of Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas Gingivalis in Peri-implantitis Lesions
 Original Article An Investigation of Antibiotic Resistance of Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas Gingivalis in Peri-implantitis Lesions Z. Kadkhoda 1, S. Torabi 2, A. Aliramezani 3.
Original Article An Investigation of Antibiotic Resistance of Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas Gingivalis in Peri-implantitis Lesions Z. Kadkhoda 1, S. Torabi 2, A. Aliramezani 3.
Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402
 Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402 Subject Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Originating Department Clinical Professional Services Signature Authority Dental Director Type: New
Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402 Subject Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Originating Department Clinical Professional Services Signature Authority Dental Director Type: New
Detection of Herpes Simplex Virus in Chronic Generalized Periodontitis via Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Pilot Study
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article Detection of Herpes Simplex Virus in Chronic Generalized Periodontitis via Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Pilot Study Thomas George Veliyaveetil
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article Detection of Herpes Simplex Virus in Chronic Generalized Periodontitis via Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Pilot Study Thomas George Veliyaveetil
