EFFECT OF IMPLANT DESIGN ON INITIAL STABILITY
|
|
|
- Leo Harvey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CLINICAL EFFECT OF IMPLANT DESIGN ON INITIAL STABILITY OF TAPERED IMPLANTS Linus Chong, DDS, MS; Ahmed Khocht, DDS, MSD; Jon B. Suzuki, DDS, PhD; John Gaughan, PhD Implant design is one of the parameters for achieving successful primary stability. This study aims to examine the effect of a self-tapping blades implant design on initial stability in tapered implants. Polyurethane blocks of different densities were used to simulate different bone densities. The two different implant designs included one with self-tapping blades and one without self-tapping blades. Implants were placed at 3 different depths: apical third, middle third, and fully inserted at 3 different densities of polyurethane blocks. A resonance frequency (RF) analyzer was then used to measure stability of the implants. Repeated-measures analysis of variance was used to examine the effect of implant design, insertion depth, and block density on RF. Analysis of covariance was used to examine the strength of association between RF and the aforementioned factors. In both medium-density (P ¼.017) and high-density (P ¼.002) blocks, fully inserted non-self-tapping implants showed higher initial stability than self-tapping implants. No differences were noted between the 2 implant designs that were not fully inserted. The highest strength of association was with insertion depth (standardized beta [std b] ¼ 0.60, P ¼.0001), followed by block density (std b ¼ 0.15, P ¼.0002). Implant design showed a weak association (std b ¼ 0.07, P ¼.09). In conclusion, fully inserted implants without selftapping blades have higher initial stability than implants with self-tapping blades. However, the association strength between implant design and initial stability is less relevant than other factors, such as insertion depth and block density. Thus, if bone quality and quantity are optimal, they may compensate for design inadequacy. Key Words: dental implants, implant design, vibration, polyurethane INTRODUCTION Many studies have agreed that primary stability of a dental implant is important for the success and longevity of osseointegrated implants. Primary stability is known to be a prerequisite and a useful predictor for achieving osseointegration. 1 Adequate stability of an implant is important to allow undisturbed healing Linus Chong, DDS, MS, is in private practice in Los Angeles, Calif. Ahmed Khocht, DDS, MSD, and Jon B. Suzuki, DDS, PhD, are with the Temple University School of Dentistry, Philadelphia, Pa. Address correspondence to Dr Khocht at the Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology, Temple University, Maurice H. Kornberg School of Dentistry, 3223 North Broad Street, Philadelphia, PA ( akhocht@temple.edu) John Gaughan, PhD, is at Temple University Biostatistics Center, Philadelphia, Pa. and bone formation to occur, thereby permitting optimal stress distribution from masticatory and occlusal functional loads. There are 3 main parameters for achieving primary stability: implant design, surgical technique (drill size/implant size, whether a pretapped or a self-tapped drill is used), and bone quality of the recipient site. 1 The interplay of these three parameters determines the initial stability of the implant. This study focuses mainly on implant design. Original endosseous implants were parallel in design. However, the original design was not suitable for all applications. Other designs were introduced, including tapered implants. Tapered implants have been used to improve esthetics and facilitate implant placement between adjacent natural teeth. 2 It was initially designed especially to serve for immediate implant placement after tooth extraction. The theory behind the use of tapered implants is to provide for a 130 Vol. XXXV / No. Three / 2009
2 Linus Chong et al degree of compression of the cortical bone in a poor bone implant site. 3 Tapered implants distribute forces into the surrounding bone, thereby creating a more uniform compaction of bone in adjacent osteotomy walls compared with parallel-walled implants. Thus, when inserted, it creates a lateral compression of the bone. 4 The advantages can be seen especially with anatomic constraints, including ridges with concavities or narrow ridges. Cylindrical wide-bodied implants tend to run the risk of labial perforation due to buccal concavities, while the decrease in diameter toward the apical region of the tapered implant accommodates for the labial concavity. 5 Most implant companies offer tapered implants. Nobel Biocare introduced an externally hexed, tapered titanium implant with diminishing threads in March Currently, all of the major implant companies carry tapered implants: Replace Select (Nobel Biocare, Yorba Linda, Calif), Osteotite NT (Biomet 3I, Palm Beach Gardens, Fla), and Tapered Effect (Straumann, Basel, Switzerland). Other design modifications include self-tapping implants. Self-tapping implants have been specifically designed for use in bones with poor quality (ie, Type 3 and 4 bone). Its design emphasis is placed on enhancing the primary stability of the implant. It is thought that when the self-tapping design is inserted, the denser cortical bone is compressed, thereby increasing the primary stability of the implant. The self-tapping implant also has an increased cutting characteristic. This design would help eliminate pretapping procedures in immediate implant placement resulting in improved initial implant stability. 7 Self-tapping implants are usually designed with vertical cutting blades in the apical third of the implant. The cutting blades reduce the thread surface area and thus may minimize implant-bone contact in the apical third. It is not clear if the cutting blades influence the initial stability of the implant. This knowledge is important as it would allow for better understanding of how implant design affects implant stability and would translate clinically into a more successful outcome. The present study aims to examine the effect of self-tapping blades on initial stability in tapered implants. The hypothesis is that because self-tapping implants have fewer threads, they will have less primary stability than implants that are not self-tapping and have continuous threads throughout the implant. METHODS AND MATERIALS For the purpose of this study, polyurethane blocks (Pacific Research Laboratories, Vashon, Wash) were used to simulate differing bone density. Two different implant designs were used: one with self-tapping blades (Biohorizons, Birmingham, Ala) and one without self-tapping blades (Nobel Biocare) as seen in Figure 1. A resonance frequency (RF) analyzer, Osstell Mentor (Ostell, Göteberg, Sweden), was used to measure implant stability. Polyurethane blocks Polyurethane blocks were used at different densities to simulate bone in an in vitro setting. Rigid polyurethane blocks of 13 cm 3 18 cm 3 4 cm were used. 8 The American Society for Testing Materials has shown that polyurethane blocks have mechanical properties simulating human bone. 9 Polyurethane is considered to be the standard material used for performing mechanical tests on orthopedic implants. 10 The blocks came from the same batch and were accurately weighed. Using the Misch classification of bone density, 11 D1 bone (high-density bone) was simulated using 50 pounds per cubic foot (pcf) polyurethane blocks, D2 bone (medium-density bone) was simulated using 40 pcf polyurethane blocks, and D3 bone (low-density bone) was simulated using 10 pcf polyurethane blocks. 12 Implants Twenty implants were used in the study: 10 tapered self-tapping and 10 tapered non-self-tapping. The diameter of the self-tapping implants was 4.6 mm and the diameter of the non-self-tapping implants was 4.3 mm. The length was 12 mm for self-tapping implants and 13 mm for non-self-tapping implants. The same 20 implants were used for each of the polyurethane blocks used in the study. Resonance frequency measurements Implant stability was measured using an Osstell Mentor. 13 The measuring technique used does not require any contact with the implant and is noninvasive. A SmartPeg is attached to the implant or abutment and is dependent on the implant manufacturer and implant diameter. The Osstell Mentor is then placed at 2 different directions, as recommended by the manufacturer. 13 An RF measurement of the peg is then taken and displayed as an implant stability quotient (ISQ) value, which is dependent on the stability of the implant. The clinical range of ISQ has been found to be normally at 50 to 80 for implant stability. Four readings were taken for each implant, and the ISQ values were then averaged. Journal of Oral Implantology 131
3 EFFECT OF IMPLANT DESIGN ON INITIAL STABILITY OF TAPERED IMPLANTS FIGURE 1. Implant designs used in the study, self-tapping (left) and non-self-tapping (right). Study protocol Based on their density, the blocks were divided into 3 groups: low-density (9 blocks), medium-density (9 blocks), and high-density (9 blocks). Each density group was subdivided into 3 depth subgroups, 1/3 insertion depth (3 blocks), 2/3 insertion depth (3 blocks), and full-insertion depth (3 blocks). Thus, 27 blocks were used. The surface of each of the 27 blocks was divided into 20 equal divisions. The experiment was started with a low-density block at 1/3 insertion depth. Twenty implant insertion sites were prepared in each division on the block surface: 10 to receive self-tapping implants and 10 to receive non-selftapping implants. Site preparation was performed as per manufacturer s recommendation for each of the 2 respective implant designs. The non-self-tapping site preparation involved 3 drills and the self-tapping site preparation involved 5 drills. The sites were prepared to receive the implant at 1/3 of their total length. Rubber stoppers were used on the cutting burs to help maintain the correct measurements. Twenty implants, 10 self-tapping and 10 non-self-tapping, were inserted in their respective sites at 1/3 of their total length. The RF was measured using the Osstell mentor device (Figure 2). Two readings in ISQ were recorded for each inserted implant. The 20 implants were then removed. Using the same 20 implants that were used previously, the same procedures were repeated again on 2 additional blocks at 1/3 insertion depth. The same procedures were repeated again on 3 new lowdensity blocks at 2/3 insertion depth, and repeated again on 3 new low-density blocks at full-insertion FIGURE 2. Use of Osstell machine to obtain resonance frequency reading. depth. The same protocol was repeated for the medium-density blocks and the high-density blocks. Thirty duplicate RF readings were recorded for each implant design for each density block group and each insertion depth subgroup. The total of duplicate RF readings for each implant design was 270. Statistical analysis The data were analyzed using version 9.1 SAS software (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). The RF double readings recorded were averaged. The averaged RF data failed the test for normality so the data were transformed into normalized ranks in order to use analysis of variance (ANOVA) methods. Repeated-measures AN- OVA using compound symmetry for the covariance structure was used. The dependent variable was resonance frequency. Main effects and interactions of manufacturer, depth, block density, and implant run were tested. Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was used to examine the strength of association between implant design and the independent variables of initial stability, block density, insertion depth, and implant run (number of times the implant was used, expressed as continuous variables). RESULTS Readings recorded from low-density blocks were unreliable and their data were excluded from the analysis. Only data obtained from medium-density and high-density blocks could be used. Table 1 compares the initial implant stability of self-tapping versus non-self-tapping implant design 132 Vol. XXXV / No. Three / 2009
4 Linus Chong et al TABLE 1 Initial stability of self-tapping vs non-self-tapping implants by block density and insertion depth Block Density N Insertion Depth Self-tapping Mean (SD) Non-self-tapping Mean (SD) P Value Medium (D2) 30 1/ (9.20) (11.18) NS* 30 2/ (4.56) (4.35) NS 30 3/ (4.67) (5.06).017 High (D1) 30 1/ (2.80) (4.32) NS 30 2/ (4.18) (4.18) NS 30 3/ (6.27) (5.51).002 All 180 All (10.63) (11.89).001 *NS indicates not significant at P..05. TABLE 2 Analysis of covariance evaluating the effect of implant design on initial stability combined with bone quality, insertion depth, and number of implant usage* Dependent Variable Independent Variables Standard b P Value Initial stability Block density Insertion depth Implant design Run (n times the implant was used) 0.01 NSÀ *Number of observations ¼ 180. ÀNS indicates not significant at P..05. by block density and insertion depth. In mediumdensity blocks, fully inserted non-self-tapping implants showed higher initial stability than self-tapping implants (P ¼.017). No differences were noted between the 2 implant designs that were not fully inserted. High-density block RF readings were similar to medium-density block RF readings. Again, fully inserted non-self-tapping implants showed higher initial stability than self-tapping implants (P ¼.002). No differences were noted between the 2 implant designs that were not fully inserted. Overall comparisons between the 2 implant designs in all bone types and insertion depths showed that non-self-tapping implants have higher initial stability than self-tapping implants (P ¼.001). Thus, data from this analysis indicate that in general non-self-tapping implants have greater initial stability than self-tapping implants. Table 2 summarizes ANCOVA analysis examining the association of implant design, block density, insertion depth, and number of runs (analyzed as continuous variables) on initial stability. Implant design, block density, and insertion depth all showed an independent relevant effect on initial stability. The highest strength of association was with insertion depth (standard beta [std b] ¼ 0.60, P ¼.0001), followed by block density (std b ¼ 0.15, P ¼.0002). Association with implant design was weak (std b ¼ 0.07, P ¼.09). The number of runs (number of times the implant was used) showed no association with implant stability. Thus, implant design seems to have a less relevant effect on initial implant stability than insertion depth and block density. DISCUSSION This study attempted to investigate the effect of selftapping design on initial stability of tapered implants in polyurethane bone blocks. The findings indicate that tapered implants without self-tapping blades have higher initial stability than implants with selftapping blades. It is of interest to note that no difference in initial stability was found between self-tapping and non-selftapping implant designs in both medium-density and high-density blocks at the 1/3 and 2/3 insertion depths. This indicates that the overall higher initial stability of the non-self-tapping implant at full insertion depth is not solely associated with the design of the apical third of the implant but is most likely associated with the design of the entire implant surface. The non-self-tapping implant has a higher number of threads than the self-tapping implant, thus increasing the surface area in contact with adjacent block/bone walls. In the self-tapping implant design, the self-tapping blades present in the apical third of the implant replace implant threads and minimize the contact surface area of the implant. Interestingly, the lateral compression of material/bone associated with self-tapping thread design did not enhance the primary stability of the self-tapping design used in this study. Other factors that were not investigated in this study include differences in the osteotomy preparation protocols and surface texture of the 2 different implants. The different implant designs require different osteotomy preparation protocols. The nonself-tapping osteotomy preparation protocol used a fewer sequential cutting burs. Also, the 2 implants used had different surface textures: the non-selftapping implant had a roughened surface and the self-tapping had a smooth surface. Thus, the higher initial stability of the non-self-tapping implant may be due to a combination of factors, including more threads on the implant surface, a roughened surface, absence of self-tapping blades, and a conservative osteotomy drilling sequence. The American Society for Testing Materials has validated polyurethane blocks as having mechanical Journal of Oral Implantology 133
5 EFFECT OF IMPLANT DESIGN ON INITIAL STABILITY OF TAPERED IMPLANTS properties simulating human cancellous bone. 9 Polyurethane has been used as a standard material for performing mechanical tests for orthopedic implants. This study uses polyurethane blocks at different densities to simulate the different bone densities in humans according to the Misch classification of D1, D2, and D3 bone. 12 In this study, D3 polyurethane blocks could not be included because the blocks did not have the same dampening effect as the maxilla and mandible. Stability at 1/3 depth could not be measured because of significant vibration of the D3 block once resonance frequency was emitted. Placing the blocks on sticky pads and holding them in place did not decrease the amount of vibration; therefore, results could not be determined. However, the different densities were consistent with what was expected in that an increase in stability of the implants was found as the density of the bone blocks increased. In the past, different tests have been done to test stability of implants, including percussion, finger pressure, radiographs, Periotest (Medizintechnik Guldne, Modautal, Germany) RF analysis, and insertion torque. According to Andreaza da Cunha et al, 14 RF analysis and insertion torque methods appear to be most efficient and have fewer contraindications. One way of quantitatively evaluating implant stability and osseointegration is through RF analysis. Meredith et al 15 introduced a noninvasive method for quantitatively measuring implant stability through RF measurements related to the effective length of an implant above the level of the bone. This method requires placement of an electronic transducer onto the implant head or prosthetic abutment with a retaining screw. A low-voltage current, undetectable by the patient, is then passed through the transducer. Original measurements were made in Hertz. These measurements are then calibrated for each transducer and converted into ISQ units by a computer. A decrease in the RF value is related to a decrease in stiffness, which can indicate a potential for failure. Thus, RF analysis can be used to show differences between successful implants and clinical failures in order to predict conditions that predispose an implant to fail. 16 The RF analysis value is also a measurement of stiffness of the implant/transducer/bone complex and is influenced by the length of the implant above the bone crest. 16 It has been used for to determine changes in implant stability in bone healing or failure of implants to integrate. One way of measuring RF is through the use of an Ostell RF analyzer. The values are calculated from peak amplitude, called the ISQ value, which is measured on a scale from 1 to 100. A high ISQ value indicates high stability, and a low ISQ value shows low stability. 13 Several studies have used the Osstell Mentor in obtaining RF analysis measurements of implant stability. In addition, RF analysis has been noted as an objective method in determining implant stability. 17 It can also be applied as a predictor of implant success. In this study, a standardized measuring protocol was developed to ensure obtaining consistent results. Balshi et al 18 recommended that a parallel orientation of the transducer should be used for all clinical RF analysis measurements. The ISQ level is often influenced by the orientation of the transducer to the axis of the alveolar ridge, where it has been found that perpendicular measurements have ISQs equal to or higher than their parallel measurements. 18 In the current study, 2 readings of both orientations were taken and then averaged. A comparison of different implant designs has been examined in the past. O Sullivan et al 19 compared the primary stability characteristics of five different implant designs, specifically the standard Branemark, Mark II self-tapping implant and Mark IV self-tapping tapered implant (Nobel Biocare AB, Goteburg, Sweden), Osseotite (Biomet 3I), and Tioblast implant (AstraTech AB, Molndahl, Sweden). The study demonstrated higher RF analysis and insertion torque values for tapered implants than for nontapered implants, suggesting increased stability in tapered implants. 19 In looking at the Branemark system and the Mark II, III, and IV implants, Glauser et al 20 also found higher RF analysis values for tapered implants (Mark IV) than for nontapered implants (Branemark, Mark II and III). The current in vitro study extends the findings of these 2 reports by examining the effect of the self-tapping design on the initial stability of the tapered implant. In conclusion, the current study demonstrates that the design of the entire implant surface, not just the apical third, is important for initial implant stability. The non-self-tapping design tested in this study had greater initial stability when fully inserted. However, the findings also indicate that insertion depth and bone density have stronger association with initial stability than implant design. Thus, when an adequate amount of high-quality bone surrounds the implant, it may compensate for design inadequacy. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This study was sponsored in part by a 2007 American Academy of Implant Dentistry Grant and a 2007/ Vol. XXXV / No. Three / 2009
6 Linus Chong et al Temple University School of Dentistry Research Incentive Grant. REFERENCES 1. Meredith N. Assessment of implant stability as a prognostic determinant. Int J Prosthodont. 1998;11: Shapoff C. Clinical advantages of tapered root form dental implants. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2002;23: O Sullivan D, Sennerby L, Meredith N. Influence of implant taper on the primary and secondary stability of osseointegrated titanium implants. Clin Oral Implant Res. 2004;15: Glauser R, Sennerby L, Meredith N, et al. Resonance frequency analysis of implants subjected to immediate or early functional occlusal loading. Successful vs. failing implants. Clin Oral Implant Res. 2004;15: Garber DA, Salama H, Salama M. Two stage versus one stage is there really a controversy? J Periodontol. 2001;72: Callan DP, Hahn J, Hebel K, et al. Retrospective multicenter study of an anodized, tapered, diminishing thread implant: success rate at exposure. Implant Dent. 2000;9: Olsson M, Friberg B, Nilson H, Kultje C. MkII a modified selftapping Branemark implant: 3-year results of a controlled prospective pilot study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1995;10: Sawbones Worldwide. Products and services. Pacific Research Laboratories Ltd., Vashon, Wash. Accessed March 11, American Society for Testing Materials. Standard specification for rigid polyurethane foam for use as a standard material for testing orthopaedic devices and instruments. Report: F Accessed June 11, Sunit P, Mahon A, Green S, McMurtry I, Port A. A biomechanical study comparing a raft of 3.5 mm cortical screws with 6.5 mm cancellous screws in depressed tibial plateau fractures. Knee. 2006;13: Misch CE. Contemporary Implant Dentistry. 2nd ed. St Louis, Mo: Mosby Co; 1999: Orchid-Orthopedics. Markets/dental. Orchid-Orthopedics.com. Accessed June 11, Osstell Mentor. Osstell. Göteberg, Sweden. asstell.com. Accessed March 12, Andreaza da Cunha H, Francischone CE, Filho H, Gomes de Oliveira R. A comparison between cutting torque and resonance frequency in the assessment of primary stability and final torque capacity of standard and TiUnite single-tooth implants under immediate loading. Int J Oral Maxillofacial Implants. 2004;19: Meredith N, Alleyne D, Cawley P. Quantitative determination of the stability of the implant tissue interface using resonance frequency analysis. Clin Oral Impl Res. 1996:7: Meredith N, Book K, Friberg B, Jemt T, Sennerby L. Resonance frequency measurements of implants stability in vivo. A cross-sectional and longitudinal study of resonance frequency measurements on implants in the edentulous and partially dentate maxilla. Clin Oral Impl Res. 1997:8: Becker W, Sennerby L, Bedrossian E, Becker B, Lucchini JP. Implant stability measurements for implants placed at the time of extraction: a cohort, prospective clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2005;76: Balshi SF, Allen FD, Wolfinger GJ, Balshi TJ. A resonance frequency analysis assessment of maxillary and mandibular immediately loaded implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2005; 20: O Sullivan D, Sennerby L, Meredith N. Measurements comparing the initial stability of five designs of dental implants: a human cadaver study. Clin Implant Dent Rel Res. 2000;2: Glauser R, Portmann M, Ruhstaller P, Gottlow J, Scharer P. Initial implant stability using different implant designs and surgical techniques. A comparative clinical study using insertion torque and resonance frequency analysis. Appl Osseointegration Res. 2001; 2:6 8. Journal of Oral Implantology 135
Hiron Andreaza da Cunha, MS 1 /Carlos Eduardo Francischone, DMD 2 /Hugo Nary Filho, DDS 3 / Rubelisa Cândido Gomes de Oliveira, BDS 4
 A Comparison Between Cutting Torque and Resonance Frequency in the Assessment of Primary Stability and Final Torque Capacity of and TiUnite Single-Tooth Implants Under Immediate Loading Hiron Andreaza
A Comparison Between Cutting Torque and Resonance Frequency in the Assessment of Primary Stability and Final Torque Capacity of and TiUnite Single-Tooth Implants Under Immediate Loading Hiron Andreaza
DEVELOPMENT OF PREDICTABLE STABILITY TEST FOR ASSESSMENT OF OPTIMUM LOADING TIME IN DENTAL IMPLANT
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI:10.4047/jkap.2008.46.6.628 DEVELOPMENT OF PREDICTABLE STABILITY TEST FOR ASSESSMENT OF OPTIMUM LOADING TIME IN DENTAL IMPLANT Seong-Kyun Kim 1, DDS, PhD, Seong-Joo Heo 2, DDS, PhD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI:10.4047/jkap.2008.46.6.628 DEVELOPMENT OF PREDICTABLE STABILITY TEST FOR ASSESSMENT OF OPTIMUM LOADING TIME IN DENTAL IMPLANT Seong-Kyun Kim 1, DDS, PhD, Seong-Joo Heo 2, DDS, PhD,
NobelActive Inventor s perspective on this new direction for implants
 NobelActive Inventor s perspective on this new direction for implants Nobel Biocare launches a unique new implant with revolutionary features due to the advanced design of its implant body NobelActive.
NobelActive Inventor s perspective on this new direction for implants Nobel Biocare launches a unique new implant with revolutionary features due to the advanced design of its implant body NobelActive.
Preliminary Data of a Prospective Clinical Study on the Osseotite NT Implant: 18-month Follow-up
 Preliminary Data of a Prospective Clinical Study on the Osseotite NT Implant: 18-month Follow-up Mithridade Davarpanah, MD, DDS 1 / Mihaela Caraman, DDS 2 /Serge Szmukler-Moncler, DDS, PhD 3 / Boris Jakubowicz-Kohen,
Preliminary Data of a Prospective Clinical Study on the Osseotite NT Implant: 18-month Follow-up Mithridade Davarpanah, MD, DDS 1 / Mihaela Caraman, DDS 2 /Serge Szmukler-Moncler, DDS, PhD 3 / Boris Jakubowicz-Kohen,
Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration: An Editorial White Paper*
 Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration: An Editorial White Paper* Alan Meltzer, DMD, MScD; Harold Baumgarten, DMD; Tiziano Testori, MD, DDS; Paolo Trisi, DDS, PhD Published by Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration:
Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration: An Editorial White Paper* Alan Meltzer, DMD, MScD; Harold Baumgarten, DMD; Tiziano Testori, MD, DDS; Paolo Trisi, DDS, PhD Published by Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration:
A comparative study on the initial stability of different implants placed above the bone level using resonance frequency analysis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2011.3.4.190 A comparative study on the initial stability of different implants placed above the bone level using resonance frequency analysis In-Ho Kang,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2011.3.4.190 A comparative study on the initial stability of different implants placed above the bone level using resonance frequency analysis In-Ho Kang,
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Assessment of Implant Stability of Two-piece Zirconium Dioxide Implants using the Resonance Frequency Analysis: A Pilot Study
 IJEDS Assessment of Implant Stability of Two-piece Zirconium Dioxide Implants using 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1103 the Resonance Frequency Analysis RESEARCH ARTICLE Assessment of Implant Stability of Two-piece
IJEDS Assessment of Implant Stability of Two-piece Zirconium Dioxide Implants using 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1103 the Resonance Frequency Analysis RESEARCH ARTICLE Assessment of Implant Stability of Two-piece
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Natural Tapered Implant Primary Implant Stability Starts With The BIOMET 3i Tapered Implant System
 Natural Tapered Implant Primary Implant Stability Starts With The BIOMET 3i Tapered Implant System BIOMET 3i s Tapered Implant provides for primary stability through its macrogeometric design. This Tapered
Natural Tapered Implant Primary Implant Stability Starts With The BIOMET 3i Tapered Implant System BIOMET 3i s Tapered Implant provides for primary stability through its macrogeometric design. This Tapered
10 Years of XiVE Implantology Unlimited
 10 Years of XiVE Implantology Unlimited Implantology Unlimited is obligate for XiVE and every limit gives always a push to surrender new challenges: Primary stability in low bone quality? No problem with
10 Years of XiVE Implantology Unlimited Implantology Unlimited is obligate for XiVE and every limit gives always a push to surrender new challenges: Primary stability in low bone quality? No problem with
Dental Research Journal
 Dental Research Journal Original Article The effect of shape, length and diameter of implants on primary stability based on resonance frequency analysis Hamidreza Barikani, Shadab Rashtak, Soolmaz Akbari,
Dental Research Journal Original Article The effect of shape, length and diameter of implants on primary stability based on resonance frequency analysis Hamidreza Barikani, Shadab Rashtak, Soolmaz Akbari,
Bicortically Stabilized Implant Load Transfer
 Bicortically Stabilized Implant Load Transfer Chang Mo Jeong, DDS, PhD 1 /Angelo A. Caputo, PhD 2 /Robert S. Wylie, DDS 3 / Seung C. Son, DDS, MS 3 /Young Chan Jeon, DDS, PhD 4 Purpose: Questions exist
Bicortically Stabilized Implant Load Transfer Chang Mo Jeong, DDS, PhD 1 /Angelo A. Caputo, PhD 2 /Robert S. Wylie, DDS 3 / Seung C. Son, DDS, MS 3 /Young Chan Jeon, DDS, PhD 4 Purpose: Questions exist
P rimary or mechanical implant
 IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 0, NUMBER 0 2013 1 Effect of Location on Primary Stability and Healing of Dental Implants Alberto Monje, DDS,* Fernando Suarez, DDS,* Carlos Andrés Garaicoa, DDS, Florencio Monje,
IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 0, NUMBER 0 2013 1 Effect of Location on Primary Stability and Healing of Dental Implants Alberto Monje, DDS,* Fernando Suarez, DDS,* Carlos Andrés Garaicoa, DDS, Florencio Monje,
Resonance Frequency Measurement of Implant Stability In Vivo on Implants with a Sandblasted and Acid-Etched Surface
 Resonance Frequency Measurement of Implant Stability In Vivo on Implants with a Sandblasted and Acid-Etched Surface Reva M. Barewal, DDS, MS 1 /Thomas W. Oates, DMD, PhD 2 /Neil Meredith, BDS, MSc, PhD
Resonance Frequency Measurement of Implant Stability In Vivo on Implants with a Sandblasted and Acid-Etched Surface Reva M. Barewal, DDS, MS 1 /Thomas W. Oates, DMD, PhD 2 /Neil Meredith, BDS, MSc, PhD
planning Primary stability and initial bone-to-implant contact: The effects on immediate placement and restoration of dental implants
 planning Primary stability and initial bone-to-implant contact: The effects on immediate placement and restoration of dental implants Alan M. Meltzer, DMD, MScD With the growing popularity of immediate
planning Primary stability and initial bone-to-implant contact: The effects on immediate placement and restoration of dental implants Alan M. Meltzer, DMD, MScD With the growing popularity of immediate
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
It is of interest to develop and evaluate
 RESEARCH Validation of Resonance Frequency Analysis by Comparing Implant Stability Quotient Values With Histomorphometric Data Ashish Thomas Kunnekel, MDS 1 * K. Chandrasekharan Nair, MDS 2 E. Munirathnam
RESEARCH Validation of Resonance Frequency Analysis by Comparing Implant Stability Quotient Values With Histomorphometric Data Ashish Thomas Kunnekel, MDS 1 * K. Chandrasekharan Nair, MDS 2 E. Munirathnam
A STUDY ON THE CORRELATION BETWEEN IMPLANT STABILITY VALUES AND INITIAL INSERTION TORQUE
 J Korean Acad Prosthodont : Volume 44, Number 3, 2006 A STUDY ON THE CORRELATION BETWEEN IMPLANT STABILITY VALUES AND INITIAL INSERTION TORQUE Jong-Hyuk Lee 1,2, D.D.S., M.S.D., Jae-Ho Yang 1, D.D.S.,
J Korean Acad Prosthodont : Volume 44, Number 3, 2006 A STUDY ON THE CORRELATION BETWEEN IMPLANT STABILITY VALUES AND INITIAL INSERTION TORQUE Jong-Hyuk Lee 1,2, D.D.S., M.S.D., Jae-Ho Yang 1, D.D.S.,
Young-Jin Park, DDS,* and Sung-Am Cho, DDS, MS, PhD
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology
 Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD As a general dentist who has placed nearly 7,000 dental implants, I
Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD As a general dentist who has placed nearly 7,000 dental implants, I
Local alveolar bone quality and quantity,
 RESEARCH Use of Osteotomes for Implant Bed Preparation Effect on Material Properties of Bone and Primary Implant Stability Tim Krafft, PD Dr Dr Friedrich Graef, Dr Werner Winter, Dr-Ing Manfred Wichmann,
RESEARCH Use of Osteotomes for Implant Bed Preparation Effect on Material Properties of Bone and Primary Implant Stability Tim Krafft, PD Dr Dr Friedrich Graef, Dr Werner Winter, Dr-Ing Manfred Wichmann,
The Implant Stability Quotient Whitebook. The relationship between reliable diagnostics and safe, successful dental implant procedures 1 st edition
 The Implant Stability Quotient Whitebook The relationship between reliable diagnostics and safe, successful dental implant procedures 1 st edition Executive summary 4 Foreword by Professor Lars Sennerby,
The Implant Stability Quotient Whitebook The relationship between reliable diagnostics and safe, successful dental implant procedures 1 st edition Executive summary 4 Foreword by Professor Lars Sennerby,
Bone Density Assessments of Dental Implant Sites: 3. Bone Quality Evaluation During Osteotomy and Implant Placement
 Bone Density Assessments of Dental Implant Sites: 3. Bone Quality Evaluation During Osteotomy and Implant Placement Scott Lee, DDS, MS 1 /Bernard Gantes, DDS, MS 2 /Matt Riggs, PhD 3 /Max Crigger, DDS,
Bone Density Assessments of Dental Implant Sites: 3. Bone Quality Evaluation During Osteotomy and Implant Placement Scott Lee, DDS, MS 1 /Bernard Gantes, DDS, MS 2 /Matt Riggs, PhD 3 /Max Crigger, DDS,
STABILITY OF IMPLANTS AND NATURAL TEETH MONTHS OF FUNCTION AS DETERMINED BY THE PERIOTEST OVER 60 CLINICAL
 CLINICAL STABILITY OF IMPLANTS AND NATURAL TEETH AS DETERMINED BY THE PERIOTEST OVER 60 MONTHS OF FUNCTION Sheldon Winkler, DDS Harold F. Morris, DDS, MS J. Robert Spray, DDS KEY WORDS Implant Natural
CLINICAL STABILITY OF IMPLANTS AND NATURAL TEETH AS DETERMINED BY THE PERIOTEST OVER 60 MONTHS OF FUNCTION Sheldon Winkler, DDS Harold F. Morris, DDS, MS J. Robert Spray, DDS KEY WORDS Implant Natural
Areview of recent studies concerning molar. Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report
 Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report George E. Romanos, Dr med dent 1 /Georg H. Nentwig, Prof Dr med dent 2 Many clinical studies have
Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report George E. Romanos, Dr med dent 1 /Georg H. Nentwig, Prof Dr med dent 2 Many clinical studies have
Immediate function or immediate
 Immediate function with dental implants Immediate function or immediate loading is defined as the placement of a dental implant fixture, abutment and functional (provisional) restoration all at stage one
Immediate function with dental implants Immediate function or immediate loading is defined as the placement of a dental implant fixture, abutment and functional (provisional) restoration all at stage one
In 1981, Dr. Albrektsson, a member of
 Osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability in the maxilla: part II case report with 2-year follow-up Drs. Ann Marie Hofbauer and Salah Huwais offer another case study
Osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability in the maxilla: part II case report with 2-year follow-up Drs. Ann Marie Hofbauer and Salah Huwais offer another case study
The success rate for osseointegration of
 RESEARCH CLINICAL EVALUATION OF THE NOBELACTIVE IMPLANT SYSTEM: ACASE SERIES OF 107 CONSECUTIVELY PLACED IMPLANTS AND A REVIEW OF THE IMPLANT FEATURES Tassos Irinakis, DDS, MSc; Colin Wiebe, DDS, MSc The
RESEARCH CLINICAL EVALUATION OF THE NOBELACTIVE IMPLANT SYSTEM: ACASE SERIES OF 107 CONSECUTIVELY PLACED IMPLANTS AND A REVIEW OF THE IMPLANT FEATURES Tassos Irinakis, DDS, MSc; Colin Wiebe, DDS, MSc The
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
NobelActive Product overview
 NobelActive Product overview High primary stability even in demanding situations NobelActive s expanding tapered implant body condenses bone gradually while the apex with drilling blades enables a smaller
NobelActive Product overview High primary stability even in demanding situations NobelActive s expanding tapered implant body condenses bone gradually while the apex with drilling blades enables a smaller
Osstell ISQ. The objective way to measure implant stability.
 Osstell ISQ. The objective way to measure implant stability. www.osstell.com Three reasons why you need Osstell ISQ. Dr Tiziano Testori, Private Practice, Como, Italy: I use the Osstell meter as a quality-assurance
Osstell ISQ. The objective way to measure implant stability. www.osstell.com Three reasons why you need Osstell ISQ. Dr Tiziano Testori, Private Practice, Como, Italy: I use the Osstell meter as a quality-assurance
An evaluation of TimPlant using Osstell: A device for non-invasive assessment of dental implants stability
 An evaluation of TimPlant using Osstell: A device for non-invasive assessment of dental implants stability Sebastian Soicu 1, Emanuel Bratu 2, Dorin Bratu 3, Ioan Borsanu 4 1 D.M.D. Department of Prosthodontics,
An evaluation of TimPlant using Osstell: A device for non-invasive assessment of dental implants stability Sebastian Soicu 1, Emanuel Bratu 2, Dorin Bratu 3, Ioan Borsanu 4 1 D.M.D. Department of Prosthodontics,
NanoTite Tapered Implants: An Implant Designed For Performance. Review And Clinical Results
 NanoTite Tapered Implants: An Implant Designed For Performance Review And Clinical Results NanoTite Tapered Implants: Review and Clinical Results INTRODUCTION For more than ten years and with documentation
NanoTite Tapered Implants: An Implant Designed For Performance Review And Clinical Results NanoTite Tapered Implants: Review and Clinical Results INTRODUCTION For more than ten years and with documentation
Endosseous dental implants initially showed very
 Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Objectives: The purpose of this investigation was to evaluate the effects of different
 www.scielo.br/jaos Comparison of implant stability after different implant surface treatments in dog bone Sun-Jong Kim 1, Myung-Rae Kim 2, Jae-Suk RIM 3, Sung-Min CHUNG 4, Sang-Wan Shin 5 1- DDS, MSD,
www.scielo.br/jaos Comparison of implant stability after different implant surface treatments in dog bone Sun-Jong Kim 1, Myung-Rae Kim 2, Jae-Suk RIM 3, Sung-Min CHUNG 4, Sang-Wan Shin 5 1- DDS, MSD,
The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study
 26 News No.26 January 2011 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study Make it Simple 2 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone
26 News No.26 January 2011 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study Make it Simple 2 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone
Replacement of missing teeth with
 A simple surgical technique to maximise prosthetic results Timothy Kosinski presents a technique to help minimise surgical risk, as well as helping the dentist to understand anatomy and proper implant
A simple surgical technique to maximise prosthetic results Timothy Kosinski presents a technique to help minimise surgical risk, as well as helping the dentist to understand anatomy and proper implant
The development of modern Oral
 RESEARCH In Vitro Evaluation of the Removal Force of Abutments in Frictional Dental Implants João César Zielak, DDS, MSc, PhD* Murilo Rorbacker, DDS Rodrigo Gomes, DDS Celso Yamashita, DDS, MSc, PhD Carla
RESEARCH In Vitro Evaluation of the Removal Force of Abutments in Frictional Dental Implants João César Zielak, DDS, MSc, PhD* Murilo Rorbacker, DDS Rodrigo Gomes, DDS Celso Yamashita, DDS, MSc, PhD Carla
Resonance Frequency Analysis Measurements of Implants at Placement Surgery
 Resonance Frequency Analysis Measurements of Implants at Placement Surgery Pär-Olov Östman, DDS a /Mats Hellman, DDS a /Inger Wendelhag, PhD b /Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD c Purpose: The knowledge of what
Resonance Frequency Analysis Measurements of Implants at Placement Surgery Pär-Olov Östman, DDS a /Mats Hellman, DDS a /Inger Wendelhag, PhD b /Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD c Purpose: The knowledge of what
immediate implantation and loading with Paltop Osteotomes for bone expansion Case Study
 immediate implantation and loading with Paltop Osteotomes for bone expansion Case Study Osteotomes for bone expansion 2 This 55-year-old female patient presents with a failing maxillary cuspid. 3 A fistula
immediate implantation and loading with Paltop Osteotomes for bone expansion Case Study Osteotomes for bone expansion 2 This 55-year-old female patient presents with a failing maxillary cuspid. 3 A fistula
Components Of Implant Protective Occlusion A Review
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 7 Number 2 Components Of Implant Protective Occlusion A Review E Prashanti, K Sumanth, J Reddy Citation E Prashanti, K Sumanth, J Reddy. Components
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 7 Number 2 Components Of Implant Protective Occlusion A Review E Prashanti, K Sumanth, J Reddy Citation E Prashanti, K Sumanth, J Reddy. Components
Predictability of the resonance frequency analysis in the survival of dental implants placed in the anterior non-atrophied edentulous mandible
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.16982 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.16982 Predictability of the resonance frequency analysis in the survival of dental
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.16982 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.16982 Predictability of the resonance frequency analysis in the survival of dental
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System
 Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Clinical Perspectives
 Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Evaluation of implant stability and crestal bone loss around the implant prior to prosthetic loading: A six month study
 Original Article Evaluation of implant stability and crestal bone loss around the implant prior to prosthetic loading: A six month study P. Singh, H. G. Garge*, V. S. Parmar, M. Viswambaran*, M. M. Goswami*
Original Article Evaluation of implant stability and crestal bone loss around the implant prior to prosthetic loading: A six month study P. Singh, H. G. Garge*, V. S. Parmar, M. Viswambaran*, M. M. Goswami*
Computer-aided design/computer-assisted manufacturing
 Use of a Digitally Planned and Fabricated Mandibular Complete Denture for Easy Conversion to an Immediately Loaded Provisional Fixed Complete Denture. Part 1. Planning and Surgical Phase Jaime L. Lozada,
Use of a Digitally Planned and Fabricated Mandibular Complete Denture for Easy Conversion to an Immediately Loaded Provisional Fixed Complete Denture. Part 1. Planning and Surgical Phase Jaime L. Lozada,
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Immediate Implant Considerations for Interradicular Bone in Maxillary Molars: Case Reports. Abstract
 Immediate Implant Considerations for Interradicular Bone in Maxillary Molars: Case Reports Wilcko et al Miguel A Iglesia-Puig, DDS 1 Fernando Jimenez Solana MD, DDS 1 Dan Holtzclaw, DDS, MS 2 Nicholas
Immediate Implant Considerations for Interradicular Bone in Maxillary Molars: Case Reports Wilcko et al Miguel A Iglesia-Puig, DDS 1 Fernando Jimenez Solana MD, DDS 1 Dan Holtzclaw, DDS, MS 2 Nicholas
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up
 Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
Using immediate implant placement to address aesthetic and biomechanical challenges: A clinical presentation
 Clinical Using immediate implant placement to address aesthetic and biomechanical challenges: A clinical presentation Pär-Olov Östman 1 Immediate implant loading has become an attractive option for meeting
Clinical Using immediate implant placement to address aesthetic and biomechanical challenges: A clinical presentation Pär-Olov Östman 1 Immediate implant loading has become an attractive option for meeting
Computer-guided minimally invasive
 CASE REPORT Guided Flapless Surgery With Immediate Loading for the High Narrow Ridge Without Grafting Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1,2 Sang J. Lee, DMD, MMSc 2 * Guillaume J. Campard, DMD, MMSc 3 Maria
CASE REPORT Guided Flapless Surgery With Immediate Loading for the High Narrow Ridge Without Grafting Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1,2 Sang J. Lee, DMD, MMSc 2 * Guillaume J. Campard, DMD, MMSc 3 Maria
NobelActive. The NobelActive technical story
 NobelActive The NobelActive technical story The NobelActive technical story NobelActive origins The life cycle of NobelActive began following years of research and development on a self-drilling and bone-condensing
NobelActive The NobelActive technical story The NobelActive technical story NobelActive origins The life cycle of NobelActive began following years of research and development on a self-drilling and bone-condensing
A Prospective Analysis of Immediate Provisionalization of Single Implants
 A Prospective Analysis of Immediate Provisionalization of Single Implants Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, FACP, Glenn J. Wolfinger, DDS, FACP, Daniel Wulc, & Stephen F. Balshi, MBE Institute for Facial Esthetics,
A Prospective Analysis of Immediate Provisionalization of Single Implants Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, FACP, Glenn J. Wolfinger, DDS, FACP, Daniel Wulc, & Stephen F. Balshi, MBE Institute for Facial Esthetics,
Retreatment: Fractured Implants Due To Biomechanical Overload
 Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD, FACP Retreatment: Fractured Implants Due To Biomechanical Overload Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, FACP he strength of osseointegration, T the biologic and biomechanical union of bone to
Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD, FACP Retreatment: Fractured Implants Due To Biomechanical Overload Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, FACP he strength of osseointegration, T the biologic and biomechanical union of bone to
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Identification of Stability Changes for Immediately Placed Dental Implants
 Identification of Stability Changes for Immediately Placed Dental Implants Jason D. West, DDS, MS 1 /Thomas W. Oates, DMD, PhD 2 Purpose: To evaluate the changes in stability of immediately placed implants
Identification of Stability Changes for Immediately Placed Dental Implants Jason D. West, DDS, MS 1 /Thomas W. Oates, DMD, PhD 2 Purpose: To evaluate the changes in stability of immediately placed implants
Since the introduction of osseointegrated dental implants
 CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
IQ IMPLANTS Smart Choice PRODUCT C ATA L O G
 IQ IMPLANTS Smart Choice PRODUCT C ATA L O G www.iqimplants.com info@iqimplants.com 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL Company Profile 3 IMPLANTS 5 PROSTHETICS 13 TOOLS 27 3 COMPANY PROFILE IQ Implants Ltd. reflects
IQ IMPLANTS Smart Choice PRODUCT C ATA L O G www.iqimplants.com info@iqimplants.com 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL Company Profile 3 IMPLANTS 5 PROSTHETICS 13 TOOLS 27 3 COMPANY PROFILE IQ Implants Ltd. reflects
During the last 30 years, endosseous oral
 Influence of Variations in Implant Diameters: A 3- to 5-Year Retrospective Clinical Report Carl-Johan Ivanoff, DDS*/Kerstin Gröndahl, DDS, PhD**/Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD***/ Christina Bergström, MSc****/Ulf
Influence of Variations in Implant Diameters: A 3- to 5-Year Retrospective Clinical Report Carl-Johan Ivanoff, DDS*/Kerstin Gröndahl, DDS, PhD**/Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD***/ Christina Bergström, MSc****/Ulf
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics.
 In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
The Brånemark osseointegration method, using titanium dental implants (fixtures)
 Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
The Importance of Implant Surface Characteristics in the Replacement of Failed Implants
 The Importance of Implant Surface Characteristics in the Replacement of Failed Implants Ghada Alsaadi, DDS, MSc 1 /Marc Quirynen, DDS, PhD 2 /Daniel van Steenberghe, MD, PhD, Dr hc 3 Purpose: The purpose
The Importance of Implant Surface Characteristics in the Replacement of Failed Implants Ghada Alsaadi, DDS, MSc 1 /Marc Quirynen, DDS, PhD 2 /Daniel van Steenberghe, MD, PhD, Dr hc 3 Purpose: The purpose
RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 01 RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 01 RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
Tapered Screw-Vent Implant System
 Tapered Screw-Vent Implant System The implant of choice brings flexibility to your practice. 1 clinical results and secondary stability Tapered Screw-Vent Implant Celebrates 11 Years of Quality Celebrating
Tapered Screw-Vent Implant System The implant of choice brings flexibility to your practice. 1 clinical results and secondary stability Tapered Screw-Vent Implant Celebrates 11 Years of Quality Celebrating
A retrospective clinical study of single short implants (less than 8 mm) in posterior edentulous areas
 https://jap.or.kr J Adv Prosthodont 2018;10:191-6 https://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2018.10.3.191 A retrospective clinical study of single short implants (less than 8 mm) in posterior edentulous areas Sang-Yun
https://jap.or.kr J Adv Prosthodont 2018;10:191-6 https://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2018.10.3.191 A retrospective clinical study of single short implants (less than 8 mm) in posterior edentulous areas Sang-Yun
Validating innovation.
 Validating innovation. NobelActive TM technical and clinical story 2 NobelActive technical and clinical story Developing NobelActive. NobelActive origins The life cycle of NobelActive began following years
Validating innovation. NobelActive TM technical and clinical story 2 NobelActive technical and clinical story Developing NobelActive. NobelActive origins The life cycle of NobelActive began following years
The Uniti implant system is designed to be simple to learn and use. A seamless surgical protocol renders the system user friendly.
 Surgical Manual The Uniti implant system is designed to be simple to learn and use. A seamless surgical protocol renders the system user friendly. For the experienced practitioner it will take no more
Surgical Manual The Uniti implant system is designed to be simple to learn and use. A seamless surgical protocol renders the system user friendly. For the experienced practitioner it will take no more
BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT. simultaneous implant placement and is an alternative Summer s osteotome both clinical use as well as the
 BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT AUTHORS: Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD*, João Carlos Paixão** ABSTRACT: Bone spreading technique (BST) is horizontal augmentation with minimal trauma for simultaneous
BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT AUTHORS: Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD*, João Carlos Paixão** ABSTRACT: Bone spreading technique (BST) is horizontal augmentation with minimal trauma for simultaneous
Accuracy of Electronic Implant Torque Controllers Following Time in Clinical Service
 Accuracy of Electronic Implant Torque Controllers Following Time in Clinical Service Ricardo Mitrani, DDS, MSD 1 /Jack I. Nicholls, PhD 2 /Keith M. Phillips, DMS, MSD 3 /Tsun Ma, DMD, MS, MDS 4 Tightening
Accuracy of Electronic Implant Torque Controllers Following Time in Clinical Service Ricardo Mitrani, DDS, MSD 1 /Jack I. Nicholls, PhD 2 /Keith M. Phillips, DMS, MSD 3 /Tsun Ma, DMD, MS, MDS 4 Tightening
More than pure esthetics. The natural and strong solution.
 More than pure esthetics. The natural and strong solution. Expand your patient pool with an innovative solution. With the Straumann PURE Ceramic Implant, clinicians have an additional option to convince
More than pure esthetics. The natural and strong solution. Expand your patient pool with an innovative solution. With the Straumann PURE Ceramic Implant, clinicians have an additional option to convince
Enhanced Implant Stability with a Chemically Modified SLA Surface: A Randomized Pilot Study
 Enhanced Implant Stability with a Chemically Modified SLA Surface: A Randomized Pilot Study Thomas W. Oates, DMD, PhD 1 /Pilar Valderrama, DDS, MS 2 /Mark Bischof, Dr Med Dent 3 / Rabah Nedir, Dr Med Dent
Enhanced Implant Stability with a Chemically Modified SLA Surface: A Randomized Pilot Study Thomas W. Oates, DMD, PhD 1 /Pilar Valderrama, DDS, MS 2 /Mark Bischof, Dr Med Dent 3 / Rabah Nedir, Dr Med Dent
Implants are a part of IMPLANT TREATMENT IN AN URBAN GENERAL DENTISTRY RESIDENCY PROGRAM: A7-YEAR RETROSPECTIVE STUDY CLINICAL
 CLINICAL IMPLANT TREATMENT IN AN URBAN GENERAL DENTISTRY RESIDENCY PROGRAM: A7-YEAR RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Clifford B. Starr, DMD Mohamed A. Maksoud, DMD KEY WORDS Dental implants General dentistry Resident
CLINICAL IMPLANT TREATMENT IN AN URBAN GENERAL DENTISTRY RESIDENCY PROGRAM: A7-YEAR RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Clifford B. Starr, DMD Mohamed A. Maksoud, DMD KEY WORDS Dental implants General dentistry Resident
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
Simply straightforward NobelParallel Conical Connection
 Simply straightforward NobelParallel Conical Connection Stability and fl exibility in parallel The NobelParallel Conical Connection is straightforward in design and application. It offers extraordinary
Simply straightforward NobelParallel Conical Connection Stability and fl exibility in parallel The NobelParallel Conical Connection is straightforward in design and application. It offers extraordinary
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban
 Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Ridge Split Procedure
 Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Assessment of Implant Stability- A Critical Review
 Assessment of Implant Stability- A Critical Review Dr. Ginnia Bhayana 1, Dr. Ferah Rehman 2, Dr. Vinod Khanna 3, Dr. Sonia 4, Dr. Taruna Arora 5 1 Demonstrator (MDS), Department of Prosthodontics, PGIDS
Assessment of Implant Stability- A Critical Review Dr. Ginnia Bhayana 1, Dr. Ferah Rehman 2, Dr. Vinod Khanna 3, Dr. Sonia 4, Dr. Taruna Arora 5 1 Demonstrator (MDS), Department of Prosthodontics, PGIDS
THE ANKYLOS IMPLANT SYSTEM: CONCEPT
 SPECIAL REPORT EDITOR S NOTE: As of the printing date of this publication, the Ankylos SynCone and Cercon abutments were not yet approved for use in the United States. Ankylos implants are approved for
SPECIAL REPORT EDITOR S NOTE: As of the printing date of this publication, the Ankylos SynCone and Cercon abutments were not yet approved for use in the United States. Ankylos implants are approved for
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Specialty Dentistry. Dentistry has nine specialty fields recognized by the American Dental Association
 Specialty Dentistry Dentistry has nine specialty fields recognized by the American Dental Association Dental Public Health Endodontics Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
Specialty Dentistry Dentistry has nine specialty fields recognized by the American Dental Association Dental Public Health Endodontics Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
scientific compendium
 scientific compendium Zimmer Tapered Screw-Vent Implant Success Stories in Stability and Survival Rates Zimmer Tapered Screw-Vent Implant Scientific Compendium table of contents CLINICAL & PRE-CLINICAL
scientific compendium Zimmer Tapered Screw-Vent Implant Success Stories in Stability and Survival Rates Zimmer Tapered Screw-Vent Implant Scientific Compendium table of contents CLINICAL & PRE-CLINICAL
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 827 Thirty-Two Year Success of Dental Implants in Periodontally Compromised Dentition Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 Glenn J. Wolfinger,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 827 Thirty-Two Year Success of Dental Implants in Periodontally Compromised Dentition Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 Glenn J. Wolfinger,
BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
BONE SPREADER TECHNIQUE: APRELIMINARY 3-YEAR STUDY Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, MSc, PhD; Francisley Avila Souza, DDS, MSc
 RESEARCH BONE SPREADER TECHNIQUE: APRELIMINARY 3-YEAR STUDY Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, MSc, PhD; Francisley Avila Souza, DDS, MSc The purpose of this study was to observe the clinical outcome of bone
RESEARCH BONE SPREADER TECHNIQUE: APRELIMINARY 3-YEAR STUDY Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, MSc, PhD; Francisley Avila Souza, DDS, MSc The purpose of this study was to observe the clinical outcome of bone
All-on-4 treatment concept
 IMPLANT TEAM JAN to MAR 2018 ISSUE All-on-4 treatment concept Original Proven Life Changing Take the All-on-4 treatment concept to the next level with the new Multi-unit Abutment Plus for conical connection
IMPLANT TEAM JAN to MAR 2018 ISSUE All-on-4 treatment concept Original Proven Life Changing Take the All-on-4 treatment concept to the next level with the new Multi-unit Abutment Plus for conical connection
External Hexagon Hybrid Implants. External Hexagon Hybrid Implants. Versatility.
 External Hexagon Hybrid Implants Versatility. www.pibranemark.com HEX-S Solid Enhanced Macrogeometry Easy, Safe and Simplified installation (!). Special Conical Drills have the same geometry of Hybrid
External Hexagon Hybrid Implants Versatility. www.pibranemark.com HEX-S Solid Enhanced Macrogeometry Easy, Safe and Simplified installation (!). Special Conical Drills have the same geometry of Hybrid
Annals of Dental Research
 P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
The Self-tapping and ICE 3i Implants: A Prospective 3-Year Multicenter Evaluation
 The Self-tapping and ICE 3i Implants: A Prospective 3-Year Multicenter Evaluation Mithridade Davarpanah, MD, DDS 1 /Henry Martinez, DDS 2 /Jean-François Tecucianu, MD, DDS 3 / Gil Alcoforado, DDS 4 /Daniel
The Self-tapping and ICE 3i Implants: A Prospective 3-Year Multicenter Evaluation Mithridade Davarpanah, MD, DDS 1 /Henry Martinez, DDS 2 /Jean-François Tecucianu, MD, DDS 3 / Gil Alcoforado, DDS 4 /Daniel
Ilser Turkyilmaz Lars Sennerby Celal Tumer Muhittin Yenigul Mehmet Avci
 Ilser Turkyilmaz Lars Sennerby Celal Tumer Muhittin Yenigul Mehmet Avci Stability and marginal bone level measurements of unsplinted implants used for mandibular overdentures: a 1-year randomized prospective
Ilser Turkyilmaz Lars Sennerby Celal Tumer Muhittin Yenigul Mehmet Avci Stability and marginal bone level measurements of unsplinted implants used for mandibular overdentures: a 1-year randomized prospective
Immediate Loading of a Multi-Threaded Implant
 Immediate Loading of a Multi-Threaded Implant Dr. Jonathan Yahav, DDS (Northwestern University, Chicago, IL) Aye Myat, BS in Biological Sciences (University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago IL) Khasim Ali
Immediate Loading of a Multi-Threaded Implant Dr. Jonathan Yahav, DDS (Northwestern University, Chicago, IL) Aye Myat, BS in Biological Sciences (University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago IL) Khasim Ali
NobelReplace Conical Connection Product overview
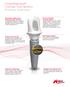 NobelReplace Conical Connection Product overview High primary stability, even in compromised bone situations1 The tapered implant body is designed for high primary stability and is ideal for Immediate
NobelReplace Conical Connection Product overview High primary stability, even in compromised bone situations1 The tapered implant body is designed for high primary stability and is ideal for Immediate
Inclusive Tooth Replacement System
 Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
