Original Research. Evaluation of sealing ability among restorative materials Velagapudi NJ et al
|
|
|
- Amberlynn Berry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evaluation of sealing ability among restorative materials Velagapudi NJ et al Journal of International Oral Health 2016; 8(2): Received: 15 th September 2015 Accepted: 20 th December 2015 Conflict of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research Comparative Evaluation of Marginal Integrity and Microleakage in Nanoionomer and Low Shrinkage Posterior Composite Restorative Materials: An In Vitro Study Naga Jyothi Velagapudi 1, E Rajendra Reddy 2, Rajesh Aduri 3, M Ghanashyam Prasad 4, Suzan Sahana 5, Ashmita Vaila 6 Contributors: 1 Senior Lecturer, Department of Pedodontics, St. Joseph Dental College, Eluru, Andhra Pradesh, India; 2 Professor and Head, Department of Pedodontics, Kamineni Institute of Dental and Medical Sciences, Nalgonda, Telangana, India; 3 Reader, Department of Pedodontics, Saraswathi Dhanwantari Dental College, Parbhani, Maharashtra, India; 4 Professor and Head, Department of Pedodontics, St. Joseph Dental College, Eluru, Andhra Pradesh, India; 5 Reader, Department of Pedodontics, St. Joseph Dental College, Eluru, Andhra Pradesh, India; 6 Private Practitioner, Hyderabad, Telangana, India. Correspondence: Dr. Velagapudi NJ. Department of Pedodontics, St. Joseph Dental College and Hospital, Eluru , Andhra Pradesh, India. Phone: jyovelagapudi@gmail.com How to cite the article: Velagapudi NJ, Reddy ER, Aduri R, Prasad MG, Sahana S, Vaila A. Comparitive evaluation of marginal integrity and microleakage in nanoionomer and low shrinkage posterior composite restorative materials: An in vitro study. J Int Oral Health 2016;8(2): Abstract: Background: Restorative dentistry had shown considerable progress, leading to the development of improved tooth-colored restorative materials. The main concern regarding these refers to the durability and integrity of marginal sealing. The aim of this study was to evaluate and correlate microleakage and marginal integrity of silorane based low shrinkage posterior composite with nano-filled resin modified glass ionomer cement (RMGIC). Materials and Methods: In this in vitro study, Class V cavity preparations were made and the specimens were divided into two equal groups. Specimens in Group I were restored with silorane based (Filtek P90) TM and Group II with nano filled RMGIC (Ketac N 100). TM Specimens were subjected to thermocycling and later sectioned using hard tissue microtome. Microleakage was evaluated under a stereomicroscope and later scanning electron microscope is used to assess the marginal adaptation. The obtained values were tabulated and subjected to statistical analysis. Results: Silorane based composite demonstrated least microleakage with a mean score of 0.25 and the interface gap of 2.46 compared with nanoionomer with mean microleakage score of 0.44 and interface gap of 14.73, respectively. Conclusion: Silorane based low shrinkage posterior composite (Filtek P90) exhibited adequate resistance to microleakage and better interface gap than nano-filled RMGICs. Considering the limitations of the in-vitro studies, it can be clinically correlated that Filtek P90 has better marginal properties than Ketac N 100. Key Words: Composite, glass ionomer, interface gap, marginal integrity, nanoionomer Introduction Over the past years, restorative dentistry had shown considerable progress, leading to the development of improved composites and glass ionomer cements (GICs). The ultimate success of a material is indicated by its longevity in the oral cavity. Currently, the main concern regarding the performance of these tooth colored adhesive restorative materials refer to their durability and the integrity of marginal sealing. 1 To overcome several negative characteristics plagued by GIC, development in the field has led to the introduction of nanoionomer which combines the benefit of resin modified GIC (RMGIC) with nanofiller technology. Unlike other GICs, nanoionomer is a two paste system that provides faster, easier, less messy, and more reproducible dispensing and mixing. 2 The other adhesive restorative material available was the composite which was one of the viable options for dental restorations. Early composite resins were relatively weak, with low compressive strength, tensile strength, and flexural strength, and they exhibited a high degree of polymerization shrinkage and shrinkage stress. They were also poorly bonded to the clinical site with primitive adhesive techniques, resulting in marginal leakage, and sensitivity. 3 Disadvantages associated with using composites are usually a direct or indirect result of polymerization shrinkage. 4 Several methods were advocated to reduce polymerization shrinkage, which is an area of continuous research. The earliest attempts regarding this were made by Bowen. Spiro-orthocarbonates which were developed later were based on the ring opening mechanism and produced an expansion of about 3.5%, which could offset shrinkage. However, they exhibited incomplete ring opening and minimal copolymerization, which resulted in a minimal reduction of shrinkage. 5 The new innovative low-shrinking Filtek LS TM restorative was based on the new ring-opening silorane chemistry. New innovations composite is the silorane based resin which claims less negligible volumetric shrinkage, improved marginal integrity at both the enamel and dentin interfaces, improved biocompatibility than the previous generation methacrylates, and decreased mutagenic potential when compared to oxiranes. 6 The present in vitro study was aimed at testing the improved properties such as marginal integrity and microleakage of nano-filled glass ionomer (Ketac N 100) TM and silorane based composite (Filtek P90) TM. 261
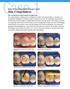
2 Evaluation of sealing ability among restorative materials Velagapudi NJ et al Journal of International Oral Health 2016; 8(2): Materials and Methods Sample collection A total of 90 non-carious premolars, extracted atraumatically for orthodontic purpose were collected. These teeth were stored in distilled water until they were subjected to the inclusion and exclusion criteria which were as follows: Inclusion criteria Non-carious premolars indicated for extraction for orthodontic purpose. Exclusion criteria Teeth with craze lines and cracks Cervical abrasions Affected by abfraction Endodontically treated teeth Dental caries. Figure 1: Group I samples after application of nail varnish. The craze lines if present on the collected teeth were detected by tactile examination and transillumination. Specimen preparation/preparation of samples Total of 40 teeth out of collected sample which satisfied the criteria of the study were surface debrided with ultrasonic scaling unit and preserved in deionized water. Standardized Class V cavity of size 4 mm 3 mm 2 mm mesio-distal width, occluso gingival length, depth, respectively were made on the facial surface of each tooth, 1 mm above the cementoenamel junction. William s graduated periodontal probe and a steel scale were used to gauge the dimensions Figure 2: Group II samples after application of nail varnish Grouping of specimens All the prepared teeth were randomly divided into two groups. The groupings are as follows. Group 1: Teeth were restored with low shrinkage posterior composite (Filtek P 90). Group 2: Teeth were restored with nanoionomer (Ketac N 100). All the restorations were performed by a single operator. For Group I and Group II, the materials were mixed and restored according to the manufacturer instructions and stored in deionized water. The teeth were then subjected to thermocycling for 250 cycles between 5 ± 2 C and 55 ± 5 C with an immersion time of 30 s and transfer time of 10 s. The apices of the teeth were sealed with acrylic resin, and the teeth were coated with a double layer of nail varnish except for 1 mm around the restoration (Figures 1 and 2). After drying, all the teeth were immersed in the prepared 2% methylene blue dye solution for 24 h. After removal from the dye solution, teeth were allowed to dry. Sectioning and testing For each tooth, later sectioning is done in buccolingual direction through the center of restoration using hard tissue microtome (Leica SP 1600) (Figure 3). Figure 3: Sectioning of sample using hard tissue microtome. The specimens were studied under a stereomicroscope (Magnus Olympus Corp, India) with a magnification of 40 by appreciating the degree of penetration of the dye solution on the occlusal and gingival walls of the sectioned samples (Figures 4-6) and scoring is given which allows the quantitative analysis. Later, the samples were evaluated under scanning electron microscope (SEM) (S-3700N, Hitachi) for qualitative evaluation of marginal properties between the restorative material and tooth biostructure. 262
3 Evaluation of sealing ability among restorative materials Velagapudi NJ et al Journal of International Oral Health 2016; 8(2): Microleakage estimation All the scoring was carried out by a single person, and scoring criteria are done as described by Khera and Chan 7 /Khera and Chan: 0 = No leakage. 1 = Less than and up to one-half of the depth of the cavity preparation penetrated by the dye. 2 = More than one-half of the depth of the cavity preparation penetrated by the dye but not up to the junction of the axial and occlusal or gingival wall. 3 = Dye penetration up to the junction of the axial and occlusal or gingival wall but not including the axial wall. 4 = Dye penetration including the axial wall. Marginal integrity estimation After the scoring procedure under a stereomicroscope, the same sectioned samples were observed under SEM at 200 magnification to evaluate the interface gap. Scoring criteria under SEM is given as: (Figures 7 and 8) Margin not visible, no gap Gap visible - measurement of the gap. Figure 4: Diagrammatic representation of dye penetration on cavity walls and scoring. Results Microleakage scores are given in Table 1. Figure 5: Specimen under stereomicroscope showing dye penetration. Figure 7: Specimen under scanning electron microscope with no interface gap. Figure 6: Specimen under stereomicroscope showing no penetration of dye. Figure 8: Specimen under scanning electron microscope with interface gap. 263
4 Evaluation of sealing ability among restorative materials Velagapudi NJ et al Journal of International Oral Health 2016; 8(2): The wall with maximum scores was considered for this study, as there is no significant difference in score values between occlusal and gingival walls. In Group I, microleakage score did not exceed score 1, both occlusally and gingivally. In Group II, microleakage score ranged between 0-4 occlusally and 0-3 gingivally. Comparing the mean microleakage values between the Group I and Group II using Mann Whitney U-test disclosed statistically significant difference (P < 0.05) revealing that Group I showed lesser microleakage comparing Group II (Graph 1). Interface gap scores are given in Table 2. Table 1: Microleakage scores of two materials used. Specimen Group I Group II No. Occlusal Gingival Occlusal Gingival Comparing the mean interface gap between the two groups using t-test, disclosed statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). Group II disclosed high interface gap compared to Group I (Graph 2). Correlating the two parameters - Microleakage and marginal integrity for both the groups using spearman s rank correlation revealed 93% of correlation in Group I which is significant statistically and 95% of correlation in Group II which was statistically significant. Discussion Till date, the alternative restorative materials available to amalgam are composite and GICs. The present in vitro study was carried out to determine the marginal properties of silorane based low shrinkage composite and nano-filled RMGIC. Nano-filled RMGI combines the benefits of a resinmodified light-cure glass ionomer and bonded nanofiller technology, 8 which is available commercially as paste-paste system dispensed in a syringe system with the constant amount of material expelled each time the syringe is pressed. This provides an advantage of correct proportioning of two pastes. 2 Table 2: Interface gap scores of two materials used. Specimen no. Group I Group II Graph 1: Intergroup comparision of mean microleakage. Graph 2: Intergroup comparision of marginal integrity. 264
5 Evaluation of sealing ability among restorative materials Velagapudi NJ et al Journal of International Oral Health 2016; 8(2): Silorane based system was developed which does not contain methacrylates and exhibits complete ring opening monomers. It is filled with a combination of fine quartz particles and radiopaque yttrium fluoride. The quartz surface is modified with a silorane layer to provide the proper interface of the filler to the resin for long-term, excellent mechanical properties. 9 The monomer is obtained from the reaction of oxirane and silorane molecules. The volumetric shrinkage of silorane based composite was determined to be 0.99 vol% using Archimedes method. 10 In this study Class V cavities were prepared with margins partly in enamel and partly in dentin which presents a challenging scenario for the restorative material, as the large bonding area (high C-factor) allows greater stress development at the adhesive interface. 11 It had both enamel and dentinal margins which do not offer any inherent macro-mechanical retention and was relatively easy to restore with minimized interoperator variability. 12 However, as the number of cycles vary in different studies, in our study, the restored teeth were subjected to 250 cycles to replicate the intraoral environment. 7 Dye penetration testing is one of the methods to assess microleakage. The sample can be subjected to a dye marker such as methylene blue, basic fuchsin silver nitrate, and rarely India ink; as there is no gold standard due to lack of evidence supporting any correlation between clinical testing and in vitro dye penetration testing. 13 Since there is no gold standard for this method, in this study, we used 2% methylene blue for 24 h as previously used by Fahad et al. (2011). 14 Comparison of leakage at the occlusal and gingival margins revealed no statistically significant difference in this study. Puckett et al. found that the degree of microleakage of the conventional GIC was less than that of the resin-modified cement. 15 However, Brackett et al., on the contrary, found that the RMGIC sealed with the cavity adequately. 16 Previous studies proved that nanoionomer is best due its lower microleakage values compared with the conventional glass ionomer, and RMGIC. 7,17 The higher leakage produced by conventional GIC and RMGIC may be due to the fact that primer was not used with these type of glass ionomers while nano-filled RMGIC gets the benefits of using primer 1 which modifies the smear layer and adequately wets the tooth surface to facilitate the adhesion of the material to the hard tissue. The silorane-based composite/adhesive system showed the best marginal stability compared with different methacrylate based restoratives. The comparative significant leakage decrease in the microleakage for Filtek low shrink composite can be attributed to the ring opening system and replacement of the methylacrylates. 9 Palin et al., 6 Yamazaki et al., 18 Al-Boni and Raja, 19 and Bagis et al. 20 has proved that silorane based composite shows better marginal adaptation comparing previous generations of the composite. Comparison of these two restorative materials in our study demonstrated that none of the two restorative cements were free from microleakage. However, the silorane based low shrinkage resin composite showed significantly less microleakage, than the nanoionomer cement, and emphasized the efficacy of silorane based restorative material to be used in routine dental practice. However, as there were no other studies comparing these two improved restorative materials in the major parameter of marginal adaptation, further research have to be conducted in this aspect which is the main cause for the failure of both the restorative materials. Conclusion The results showed in this study demonstrate that: SEM and the stereomicroscope investigations allowed the qualitative and quantitative evaluation of the marginal properties. None of the two restorative materials were free from microleakage and interface gap. Silorane based low shrinkage posterior composite (P90) demonstrated lesser microleakage, interface gap, and proved to be better restorative material than nano-filled RMGI restorative material (Ketac N 100). This study suggests the better efficacy of silorane based low shrinkage composite in terms of cavity sealing. References 1. Gupta SK, Gupta J, Saraswathi V, Ballal V, Acharya SR. Comparative evaluation of micro leakage in Class V cavities using various glass ionomer cements: An in vitro study. J Interdiscip Dent 2012;2: Available from: [ (Last Accessed on 2015 Aug 10]. 3. Eliades GC, Caputo AA, Vougiouklakis GJ. Composition, wetting properties and bond strength with dentin of 6 new dentin adhesives. Dent Mater 1985;1(5): Burke FJ, Shortall AC. Succesful restoration of load-bearing cavities in posterior teeth with direct-replacement resinbased composite. Dent Update 2001;28:388-94,96, Malhotra N, Kundabala M, Shashirashmi A. Strategies to overcome polymerization shrinkage Materials and techniques. A review. Dent Update 2010;37:115-8, 120-2, Palin WM, Fleming GJ, Nathwani H, Burke FJ, Randall RC. In vitro cuspal deflection and microleakage of maxillary premolars restored with novel low-shrink dental composites. Dent Mater 2005;21(4): Upadhyay S, Rao A. Nanoionomer: Evaluation of microleakage. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent 2011;29: Graham L. Advances in Tooth-Colored Restoratives. December Available at: [Last accessed on October 2013]. 265
6 Evaluation of sealing ability among restorative materials Velagapudi NJ et al Journal of International Oral Health 2016; 8(2): Available from: [Last accessed on 2015 July 14]. 10. Weinmann W, Thalacker C, Guggenberger R. Siloranes in dental composites. Dent Mater 2005;21(1): Smith DC. Polyacrylic acid-based cements: Adhesion to enamel and dentin. Oper Dent 1992;Suppl 5: Ritter AV, Swift EJ Jr, Heymann HO, Sturdevant JR, Wilder AD Jr. An eight-year clinical evaluation of filled and unfilled one-bottle dental adhesives. J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140(1): Heintze SD. Systematic reviews: I. The correlation between laboratory tests on marginal quality and bond strength. II. The correlation between marginal quality and clinical outcome. J Adhes Dent 2007;9 Suppl 1: Umer F, Naz F, Khan FR. An in vitro evaluation of microleakage in class V preparations restored with Hybrid versus Silorane composites. J Conserv Dent 2011;14: Puckett AD, Fitchie JG, Bennett B, Hembree JH. Microleakage and thermal properties of hybrid ionomer restoratives. Quintessence Int 1995;26: Brackett WW, Gunnin TD, Johnson WW, Conkin JE. Microleakage of light-cured glass-ionomer restorative materials. Quintessence Int 1995;26(8): Goresta K,Glavina D, Skrinjaric I. Microleakage of newly developed nano-ionomer and glass ionomer cement restoration. Available from: com/iadr/ced09/webprogram/paper html. [Last accessed on 2014 July 16]. 18. Yamazaki PC, Bedran-Russo AK, Pereira PN, Wsift EJ Jr. Microleakage evaluation of a new low-shrinkage composite restorative material. Oper Dent 2006;31: Al-Boni R, Raja OM. Microleakage evaluation of silorane based composite versus methacrylate based composite. J Conserv Dent 2010;13(3): Bagis YH, Baltacioglu IH, Kahyaogullari S. Comparing microleakage and the layering methods of silorane-based resin composite in wide Class II MOD cavities. Oper Dent 2009;34(5):
Nanoionomer: Evaluation of microleakage
 Original Article Nanoionomer: Evaluation of microleakage Abstract Background: Glass ionomer cements are widely used in pediatric practice due to their advantage of fluoride release and chemical bond to
Original Article Nanoionomer: Evaluation of microleakage Abstract Background: Glass ionomer cements are widely used in pediatric practice due to their advantage of fluoride release and chemical bond to
EQUIA. Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System
 EQUIA EQUIA Fil EQUIA Coat + Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System From the World Leader in Glass Ionomer Technology - A Complete Glass Ionomer Based Bulk Fill Rapid Restorative System Class
EQUIA EQUIA Fil EQUIA Coat + Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System From the World Leader in Glass Ionomer Technology - A Complete Glass Ionomer Based Bulk Fill Rapid Restorative System Class
shrink less than 1 %
 Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System The first composite to shrink less than 1 % Filtek Silorane The first posterior composite to shrink less than 1% 1 Any time you restore a patient
Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System The first composite to shrink less than 1 % Filtek Silorane The first posterior composite to shrink less than 1% 1 Any time you restore a patient
shrink less than 1 %
 Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System The first composite to shrink less than 1 % Filtek Silorane The first posterior composite to shrink less than 1% 1 Any time you restore a patient
Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System The first composite to shrink less than 1 % Filtek Silorane The first posterior composite to shrink less than 1% 1 Any time you restore a patient
< 1% shrinkage! * new record: Low Shrink Posterior Restorative. volumetric. The fi rst direct posterior composite to achieve less than 1 % shrinkage.
 Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative The new record: volumetric < 1% shrinkage! * * < 1 % volumetric shrinkage tested by bonded disc method. The fi rst direct posterior composite to achieve
Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative The new record: volumetric < 1% shrinkage! * * < 1 % volumetric shrinkage tested by bonded disc method. The fi rst direct posterior composite to achieve
Original Article. in depth, 4 mm in mesiodistal width and 3 mm occlusogingival
 Original Article A Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage in Class V Composite Restorations using a Fifth Generation Adhesive and a Glass Ionomer Bonding Agent - An In Vitro Dye Leakage Study Dipali Shah
Original Article A Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage in Class V Composite Restorations using a Fifth Generation Adhesive and a Glass Ionomer Bonding Agent - An In Vitro Dye Leakage Study Dipali Shah
Comparative evaluation of micro leakage of four recent resin-based core materials - an in vitro study
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparative evaluation of micro leakage of four recent resin-based core materials - an in vitro study B Rajkumar*, Mohammad Iqbal**, Juhi Hussain***, Amandeep Thind#, Gaurav Jain#, Chitrang
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparative evaluation of micro leakage of four recent resin-based core materials - an in vitro study B Rajkumar*, Mohammad Iqbal**, Juhi Hussain***, Amandeep Thind#, Gaurav Jain#, Chitrang
Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance of Dental Amalgam, Z350 Composite Resin and Cention-N Restoration In Class II Cavity
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 4 Ver.1 April. (2018), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 4 Ver.1 April. (2018), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance
Comparative Evaluation of Two Different Pit & Fissure Sealants and a Restorative Material to check their Microleakage An In Vitro Study
 Comparative Evaluation of Two Different Pit & Fissure Sealants and a Restorative Material to check their Microleakage An In Vitro Study Keyur Joshi 1, Bhavna Dave 2, Niyanta Joshi 3, BS Rajashekhara 4,
Comparative Evaluation of Two Different Pit & Fissure Sealants and a Restorative Material to check their Microleakage An In Vitro Study Keyur Joshi 1, Bhavna Dave 2, Niyanta Joshi 3, BS Rajashekhara 4,
Filtek LS. Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System. Techniques and Results. Clinical Cases
 Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Techniques and Results Clinical Cases What a composite that shrinks less than 1% 1 can mean to your practice. When restoring a tooth, a dentist takes great
Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Techniques and Results Clinical Cases What a composite that shrinks less than 1% 1 can mean to your practice. When restoring a tooth, a dentist takes great
Microleakage of class II packable resin composite lined with flowable composite and resin modified glass ionomer cement: An in vitro study
 Microleakage of class II packable resin composite lined with flowable composite and resin modified glass ionomer cement: An in vitro study Dr. Haitham J. AL-Azzawi, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Dr. Nagham A. AL-Hyali,
Microleakage of class II packable resin composite lined with flowable composite and resin modified glass ionomer cement: An in vitro study Dr. Haitham J. AL-Azzawi, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Dr. Nagham A. AL-Hyali,
Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin
 Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin Bright Chang D2 Dental Student UAB School of Dentistry Final report (revision) July 26, 2017 Mentors: Nathaniel Lawson,
Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin Bright Chang D2 Dental Student UAB School of Dentistry Final report (revision) July 26, 2017 Mentors: Nathaniel Lawson,
Evaluation of Microleakage in Class V Cavities Filled with Methacrylate-based versus Silorane-based Composites
 Journal of Dental Biomaterials. 2015;2(2) Evaluation of Microleakage in Class V Cavities Filled with Methacrylate-based versus Silorane-based Composites Sharafeddin F a, Koohpeima F b, Palizian B c a.
Journal of Dental Biomaterials. 2015;2(2) Evaluation of Microleakage in Class V Cavities Filled with Methacrylate-based versus Silorane-based Composites Sharafeddin F a, Koohpeima F b, Palizian B c a.
Results:Mean microleakage score of group G1, G2 and G3 was 2.86 ± 1.43, 1.86 ± 1.65 and 2.46 ± 1.50 respectively.
 Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry original article Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage in Class 2 Cavities Restored with A Nanohybrid Composite Using Three Different Increment Techniques-
Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry original article Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage in Class 2 Cavities Restored with A Nanohybrid Composite Using Three Different Increment Techniques-
DH220 Dental Materials
 DH220 Dental Materials Lecture #5 Prof. Lamanna RDH, MS Restorative Dentistry: Glass Ionomer Bird & Robinson p.740-741 I. Use Liner Base Luting agent Restorative material: Class III, V, & eroded/abraded
DH220 Dental Materials Lecture #5 Prof. Lamanna RDH, MS Restorative Dentistry: Glass Ionomer Bird & Robinson p.740-741 I. Use Liner Base Luting agent Restorative material: Class III, V, & eroded/abraded
Evaluation of Microleakage in Composite-Composite and Amalgam-Composite Interfaces in Tooth with Preventive Resin Restoration (Ex-viva)
 Original Article Evaluation of Microleakage in Composite-Composite and Amalgam-Composite Interfaces in Tooth with Preventive Resin Restoration (Ex-viva) H. Afshar 1, A. Jafari 2, M. R. Khami 2,3, S. Razeghi
Original Article Evaluation of Microleakage in Composite-Composite and Amalgam-Composite Interfaces in Tooth with Preventive Resin Restoration (Ex-viva) H. Afshar 1, A. Jafari 2, M. R. Khami 2,3, S. Razeghi
Fuji II LC. A Perfect Choice
 A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
Adper Easy Bond. Self-Etch Adhesive. Technical Product Profile
 Adper Easy Bond Self-Etch Adhesive Technical Product Profile Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction... 4 Product Description... 4 Composition...5-8 Background... 5 Mechanism of Adhesion to Enamel
Adper Easy Bond Self-Etch Adhesive Technical Product Profile Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction... 4 Product Description... 4 Composition...5-8 Background... 5 Mechanism of Adhesion to Enamel
Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up
 Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
Is there any clinical evidence?
 Current treatment objectives Anticariogenic capacity of restorative materials in paediatric dentistry: in vitro evidence vs. clinical efficiency Prof. Lisa Papagianoulis Restoration with minimal intervention
Current treatment objectives Anticariogenic capacity of restorative materials in paediatric dentistry: in vitro evidence vs. clinical efficiency Prof. Lisa Papagianoulis Restoration with minimal intervention
how to technique How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. Disadvantages. 1 Issue Full coverage crown. >>
 Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
Glass Ionomers. Ingredients. acid. Glass Ionomers
 Glass Ionomers Ingredients The glass should contain strontium too! (This is important) Polyacrylic acid acid Calcium fluoroalumino silicate glass base Glass Ionomers Bioavailable once called bioac/ve Inhibits
Glass Ionomers Ingredients The glass should contain strontium too! (This is important) Polyacrylic acid acid Calcium fluoroalumino silicate glass base Glass Ionomers Bioavailable once called bioac/ve Inhibits
Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland School of Dentistry
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
Clinical use of Filtek Silorane. Low Shrink Posterior Restorative
 Clinical use of Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative In collaboration with Dr. Gabriel Krastl Department of Periodontology, Endodontics and Cariology at the University of Basel Dental Hospital
Clinical use of Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative In collaboration with Dr. Gabriel Krastl Department of Periodontology, Endodontics and Cariology at the University of Basel Dental Hospital
Evaluation of Microleakage of Various Restorative Materials: An in Vitro Study
 Kamla-Raj 2011 J Life Sci, 3(1): 29-33 (2011) Evaluation of Microleakage of Various Restorative Materials: An in Vitro Study Kanika Verma Gupta 1, Pradhuman Verma 2 and Ashwarya Trivedi 3 1 Department
Kamla-Raj 2011 J Life Sci, 3(1): 29-33 (2011) Evaluation of Microleakage of Various Restorative Materials: An in Vitro Study Kanika Verma Gupta 1, Pradhuman Verma 2 and Ashwarya Trivedi 3 1 Department
4 is the new 2: Bulk fill composites continue to evolve
 1 3M SM Health Care Academy 4 is the new 2: Bulk fill composites continue to evolve by Joseph Allbeury An interview with Dr John Burgess. If there is a dental equivalent to a Myth buster on the dental
1 3M SM Health Care Academy 4 is the new 2: Bulk fill composites continue to evolve by Joseph Allbeury An interview with Dr John Burgess. If there is a dental equivalent to a Myth buster on the dental
RESTORATIVE MATERIALS
 Position Statement / Media Release RESTORATIVE MATERIALS Dental restorative materials are specially fabricated materials designed for use as dental restorations (fillings). Dental restorations are used
Position Statement / Media Release RESTORATIVE MATERIALS Dental restorative materials are specially fabricated materials designed for use as dental restorations (fillings). Dental restorations are used
riva helping you help your patients
 riva helping you help your patients what is a glass ionomer? how will a dentist benefit from using glass ionomers? how will a patient benefit from their glass ionomer? Glass ionomer is the generic name
riva helping you help your patients what is a glass ionomer? how will a dentist benefit from using glass ionomers? how will a patient benefit from their glass ionomer? Glass ionomer is the generic name
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry. Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer)
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
General dentists in private practice place numerous
 PROACTIVE INTERVENTION DENTISTRY Incorporating Glass Ionomers into Everyday Dental Practice Todd Snyder, DDS, FAACD, FIADFE Introduction General dentists in private practice place numerous direct tooth
PROACTIVE INTERVENTION DENTISTRY Incorporating Glass Ionomers into Everyday Dental Practice Todd Snyder, DDS, FAACD, FIADFE Introduction General dentists in private practice place numerous direct tooth
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (3), 457:461 September, 2008
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (3), 457:461 September, 2008 An In Vitro Assessment of The Marginal Leakage of Compomer, Amalgam and Bonded Amalgam Restoration Salah Eldin Mostafa Elbehery; 1 Naguib Mahmoud
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (3), 457:461 September, 2008 An In Vitro Assessment of The Marginal Leakage of Compomer, Amalgam and Bonded Amalgam Restoration Salah Eldin Mostafa Elbehery; 1 Naguib Mahmoud
Bonding to dentine: How it works. The future of restorative dentistry
 Bonding to dentine: How it works The future of restorative dentistry There are 82 adhesive systems on the market today! Are dentists confused about bonding? Michael Buonocore Buonocore MG. A simple method
Bonding to dentine: How it works The future of restorative dentistry There are 82 adhesive systems on the market today! Are dentists confused about bonding? Michael Buonocore Buonocore MG. A simple method
Comparison of shear bond strength of aesthetic restorative materials
 Comparison of shear bond strength of aesthetic restorative materials Suryakumari B. P. Nujella, Manisha T. Choudary 1, Satyanarayana P. Reddy 2, Kiran kumar M. 3, Gopal T. 4 Abstract Aim: The present study
Comparison of shear bond strength of aesthetic restorative materials Suryakumari B. P. Nujella, Manisha T. Choudary 1, Satyanarayana P. Reddy 2, Kiran kumar M. 3, Gopal T. 4 Abstract Aim: The present study
Ketac Universal Aplicap
 Ketac Universal Aplicap Technical Data Sheet 2 Introduction Ketac Universal Aplicap is the latest development in a long history of proven glass ionomer technology from 3M. It s designed to save steps for
Ketac Universal Aplicap Technical Data Sheet 2 Introduction Ketac Universal Aplicap is the latest development in a long history of proven glass ionomer technology from 3M. It s designed to save steps for
EQUIA Forte Glass Hybrid Restorative System. For long term posterior restorations
 EQUIA Forte Glass Hybrid Restorative System For long term posterior restorations The original EQUIA system EQUIA is a self-adhesive posterior restorative system that combines the chemical-bonding, bulk-fill
EQUIA Forte Glass Hybrid Restorative System For long term posterior restorations The original EQUIA system EQUIA is a self-adhesive posterior restorative system that combines the chemical-bonding, bulk-fill
lec: Dental material dr. Aseel Mohammed Filling material
 Filling material Filling material: the material that is used to replace a missing part of the tooth which may result from dental caries, trauma or abrasion. It can be divided in to: 1. Direct filling materials:
Filling material Filling material: the material that is used to replace a missing part of the tooth which may result from dental caries, trauma or abrasion. It can be divided in to: 1. Direct filling materials:
Pelagia Research Library. Comparison of microleakage in bonded amalgam restrorations using different adhesive materials: An invitro study
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2011, 1 (2):92-96 ISSN: 2248 9215 Comparison of microleakage in bonded amalgam restrorations using different
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2011, 1 (2):92-96 ISSN: 2248 9215 Comparison of microleakage in bonded amalgam restrorations using different
Effect of Composite Insertion Technique on Cuspal Deflection Using an In Vitro Simulation Model
 Ó Operative Dentistry, 2012, 37-2, 000-000 Effect of Composite Insertion Technique on Cuspal Deflection Using an In Vitro Simulation Model W El-Badrawy S Jafarpour HS Jazi D McComb Clinical Relevance All
Ó Operative Dentistry, 2012, 37-2, 000-000 Effect of Composite Insertion Technique on Cuspal Deflection Using an In Vitro Simulation Model W El-Badrawy S Jafarpour HS Jazi D McComb Clinical Relevance All
A real leader takes you further.
 A real leader takes you further. The unmatched SDR bulk fill technology In 2009, SureFil SDR flow material with SDR technology was the first product that allowed 4mm bulk placement in flowable consistency.
A real leader takes you further. The unmatched SDR bulk fill technology In 2009, SureFil SDR flow material with SDR technology was the first product that allowed 4mm bulk placement in flowable consistency.
Alternatives to Amalgam
 Alternatives to Amalgam Introduction: Minemata convention on Mercury The Minamata Convention on Mercury is a global treaty, signed by the UK and over one hundred countries from all over the world in October
Alternatives to Amalgam Introduction: Minemata convention on Mercury The Minamata Convention on Mercury is a global treaty, signed by the UK and over one hundred countries from all over the world in October
Original Article INTRODUCTION. Abstract
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/211 Comparative Evaluation of Marginal Microleakage of Conventional Fissure Sealants and Self-adhering Flowable Composites
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/211 Comparative Evaluation of Marginal Microleakage of Conventional Fissure Sealants and Self-adhering Flowable Composites
Effect of Composite Insertion Technique on Cuspal Deflection Using an In Vitro Simulation Model
 Ó Operative Dentistry, 2012, 37-3, 299-305 Effect of Composite Insertion Technique on Cuspal Deflection Using an In Vitro Simulation Model S Jafarpour W El-Badrawy HS Jazi D McComb Clinical Relevance All
Ó Operative Dentistry, 2012, 37-3, 299-305 Effect of Composite Insertion Technique on Cuspal Deflection Using an In Vitro Simulation Model S Jafarpour W El-Badrawy HS Jazi D McComb Clinical Relevance All
International J. of Healthcare & Biomedical Research, Volume: 2, Issue: 1, October 2013, Pages 43-47
 Original article: Effect of cavity disinfection with chlorhexidine on microleakage of composite restorations using total etch and self etch single bottle adhesive systems: an in-vitro study 1Dr. Neha Agrawal
Original article: Effect of cavity disinfection with chlorhexidine on microleakage of composite restorations using total etch and self etch single bottle adhesive systems: an in-vitro study 1Dr. Neha Agrawal
Near-UV light detection
 C L I N I C A L Near-UV light detection Javier Tapia Guadix 1 Near-UV light induced fluorescence has already proven to be very useful as an alternative to classic caries-detector dyes. However its potential
C L I N I C A L Near-UV light detection Javier Tapia Guadix 1 Near-UV light induced fluorescence has already proven to be very useful as an alternative to classic caries-detector dyes. However its potential
Senior Lecturer, Dept. of Conservative &Endodontics, Geetanjali Dental & Research Institute / Geetanjali University, Udaipur, India 2
 Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 06 COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF MICROLEAKAGE IN CLASS II RESTORATION USING FLOWABLE RESIN COMPOSITE AND RESIN MODIFIED
Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 06 COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF MICROLEAKAGE IN CLASS II RESTORATION USING FLOWABLE RESIN COMPOSITE AND RESIN MODIFIED
THE FIRST ALL CERAMIC-BASED FLOWABLE DIRECT RESTORATIVE
 THE FIRST ALL CERAMIC-BASED FLOWABLE DIRECT RESTORATIVE Admira Fusion Flow FLOWABLE NANO-ORMOCER DIRECT RESTORATIVE Admira Fusion / Admira Fusion Flow THE WORLD S FIRST ALL CERAMIC-BASED FLOWABLE DIRECT
THE FIRST ALL CERAMIC-BASED FLOWABLE DIRECT RESTORATIVE Admira Fusion Flow FLOWABLE NANO-ORMOCER DIRECT RESTORATIVE Admira Fusion / Admira Fusion Flow THE WORLD S FIRST ALL CERAMIC-BASED FLOWABLE DIRECT
Evaluation of Microleakage Between Silorane Based And Supra Nanofill Composite In Class II Cavities: An In-Vitro Study
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 4 (2015) pp. 321-327 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Evaluation of Microleakage Between Based And Supra Nanofill Composite In Class II Cavities: An In-Vitro
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 4 (2015) pp. 321-327 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Evaluation of Microleakage Between Based And Supra Nanofill Composite In Class II Cavities: An In-Vitro
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material
 Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
New Nano-Hybrid Technology for your everyday Use
 New Nano-Hybrid Technology for your everyday Use NEW New NANO-HYBRID TECHNOLOGY For Your every Day USE You need a composite that allows you to easily achieve high quality restorations? Polofil NHT, the
New Nano-Hybrid Technology for your everyday Use NEW New NANO-HYBRID TECHNOLOGY For Your every Day USE You need a composite that allows you to easily achieve high quality restorations? Polofil NHT, the
COMPARING METAL AND TRANSPARENT MATRICES IN PREVENTING GINGIVAL OVERHANG WITH DIFFERENT RESIN MATERIAL IN CLASS II RESTORATIONS AN SEM S TUDY
 Original article Pravara Med Rev 2010; 2(2) COMPARING METAL AND TRANSPARENT MATRICES IN PREVENTING GINGIVAL OVERHANG WITH DIFFERENT RESIN MATERIAL IN CLASS II RESTORATIONS AN SEM S TUDY Shetty Dinesh*,
Original article Pravara Med Rev 2010; 2(2) COMPARING METAL AND TRANSPARENT MATRICES IN PREVENTING GINGIVAL OVERHANG WITH DIFFERENT RESIN MATERIAL IN CLASS II RESTORATIONS AN SEM S TUDY Shetty Dinesh*,
A real leader takes you further.
 A real leader takes you further. 2017 Dentsply Sirona. All rights reserved. The unmatched SDR bulk fill technology In 2009, SureFil SDR flow with SDR technology was the first product that allowed 4mm bulk
A real leader takes you further. 2017 Dentsply Sirona. All rights reserved. The unmatched SDR bulk fill technology In 2009, SureFil SDR flow with SDR technology was the first product that allowed 4mm bulk
All Ceramic Inlays - Coming of Age
 CASE REPORT All Ceramic Inlays - Coming of Age Ahmad Naeem 1 & Bashir Taseer 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: In the past decade and a half there has been an explosion in the introduction of restorative
CASE REPORT All Ceramic Inlays - Coming of Age Ahmad Naeem 1 & Bashir Taseer 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: In the past decade and a half there has been an explosion in the introduction of restorative
Operative dentistry. Lec: 10. Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE):
 Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
THE EFFECTS OF MECHANICAL STRESSES ON THE COMPARATIVE MICROLEAKAGE OF TWO DIFFERENT RESTORATIVE MATERIALS
 Original Article THE EFFECTS OF MECHANICAL STRESSES ON THE COMPARATIVE MICROLEAKAGE OF TWO DIFFERENT RESTORATIVE MATERIALS Naghma Parveen 1, Bilal Ahmed 2, Aamir Mehmood Butt 3, Amjad Bari 4 1 Associate
Original Article THE EFFECTS OF MECHANICAL STRESSES ON THE COMPARATIVE MICROLEAKAGE OF TWO DIFFERENT RESTORATIVE MATERIALS Naghma Parveen 1, Bilal Ahmed 2, Aamir Mehmood Butt 3, Amjad Bari 4 1 Associate
Glass-ionomer cements: Current Status and Future Trends. John Nicholson University of Greenwich
 Glass-ionomer cements: Current Status and Future Trends John Nicholson University of Greenwich Glass-ionomer cements: Current Status and Future Trends Composition Setting Physical properties Chemical behaviour
Glass-ionomer cements: Current Status and Future Trends John Nicholson University of Greenwich Glass-ionomer cements: Current Status and Future Trends Composition Setting Physical properties Chemical behaviour
Adaptation of Different Compomers to Primary Teeth Cavities
 10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1007 ORIGINAL RESEARCH JOFR Adaptation of Different Compomers to Primary Teeth Cavities Adaptation of Different Compomers to Primary Teeth Cavities Sumanth M Shetty, Rashmi G
10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1007 ORIGINAL RESEARCH JOFR Adaptation of Different Compomers to Primary Teeth Cavities Adaptation of Different Compomers to Primary Teeth Cavities Sumanth M Shetty, Rashmi G
***Handout*** Adhesive Dentistry Harald O. Heymann, DDS MEd Dentin Bonding Rewetting/Desensitization
 ***Handout*** Adhesive Dentistry Harald O. Heymann, DDS MEd Dentin Bonding * Regardless of the type dentinal adhesive used, the primary mechanism for dentin adhesion is still establishment of the hybrid
***Handout*** Adhesive Dentistry Harald O. Heymann, DDS MEd Dentin Bonding * Regardless of the type dentinal adhesive used, the primary mechanism for dentin adhesion is still establishment of the hybrid
G-COAT PLUS G-COAT PLUS GET THE BEST OF BOTH WORLDS WITH THE STROKE OF A BRUSH
 G-COAT PLUS BEAUTY BRAWN GET THE BEST OF BOTH WORLDS WITH THE STROKE OF A BRUSH 1 Introducing a Revolutionary new Coating G-COAT PLUS gives your restorations the Best of Both Worlds: A beautiful new finish
G-COAT PLUS BEAUTY BRAWN GET THE BEST OF BOTH WORLDS WITH THE STROKE OF A BRUSH 1 Introducing a Revolutionary new Coating G-COAT PLUS gives your restorations the Best of Both Worlds: A beautiful new finish
Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1035 CLINICAL ARTICLE Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1035 CLINICAL ARTICLE Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate
World Journal of Pharmaceutical and Life Sciences WJPLS
 wjpls, 2018, Vol. 4, Issue 10, 101-105 Research Article ISSN 2454-2229 Stuti et al. WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 5.088 COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF MICROLEAKAGE OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF PIT AND FISSURE
wjpls, 2018, Vol. 4, Issue 10, 101-105 Research Article ISSN 2454-2229 Stuti et al. WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 5.088 COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF MICROLEAKAGE OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF PIT AND FISSURE
Ketac Nano Light-Curing Glass Ionomer Restorative. An esthetic glass ionomer. Fewer steps. Faster treatment.
 Ketac Nano Light-Curing Glass Ionomer Restorative An esthetic glass ionomer. Fewer steps. Faster treatment. The innovative Quick Mix Capsule saves time, steps, and improves overall mixing results. No measuring
Ketac Nano Light-Curing Glass Ionomer Restorative An esthetic glass ionomer. Fewer steps. Faster treatment. The innovative Quick Mix Capsule saves time, steps, and improves overall mixing results. No measuring
Adper Scotchbond SE. Self-Etch Adhesive. Self-etch technology that s visibly better
 Adper Scotchbond SE Self-Etch Adhesive Self-etch technology that s visibly better Radiopacity: be confident in your future diagnosis. One confidence-inspiring feature of Adper Scotchbond SE Self-Etch Adhesive
Adper Scotchbond SE Self-Etch Adhesive Self-etch technology that s visibly better Radiopacity: be confident in your future diagnosis. One confidence-inspiring feature of Adper Scotchbond SE Self-Etch Adhesive
XBW BW A1 A2 A3 A3.5 A4 B1 B2 B3 C3 CV CVD. Outside Translucent Shades DT CT GT NT WT CVT. GRADIA DIRECT Flo & LoFlo - 7 Shades (radiopaque) Standard
 GRADIA DIRECT Anterior - No Barium or FAS fillers for ultimate aesthetics and handling (radiolucent) Standard XBW BW A1 A2 A3 A3.5 A4 B1 B2 B3 C3 CV CVD 002275 002050 001988 001989 001990 001991 002042
GRADIA DIRECT Anterior - No Barium or FAS fillers for ultimate aesthetics and handling (radiolucent) Standard XBW BW A1 A2 A3 A3.5 A4 B1 B2 B3 C3 CV CVD 002275 002050 001988 001989 001990 001991 002042
Filling materials are used to replace missing parts of the tooth.
 Filling materials are used to replace missing parts of the tooth. 1- Dental caries. 2- Trauma. 3- Abrasion. Parts of teeth which require replacement by restorative materials vary in size of cavity, shape,
Filling materials are used to replace missing parts of the tooth. 1- Dental caries. 2- Trauma. 3- Abrasion. Parts of teeth which require replacement by restorative materials vary in size of cavity, shape,
Effect of Three Light Curing Protocols and Load Cycling on Microleakage of Class V Composite Restorations
 Journal of Dental School 2014; 32 (2): 71-79 Original Article Effect of Three Light Curing Protocols and Load Cycling on Microleakage of Class V Composite Restorations * 1 Abdolrahim Davari 2 Alireza Daneshkazemi
Journal of Dental School 2014; 32 (2): 71-79 Original Article Effect of Three Light Curing Protocols and Load Cycling on Microleakage of Class V Composite Restorations * 1 Abdolrahim Davari 2 Alireza Daneshkazemi
Adhese Universal. The universal adhesive. Direct Indirect Total-Etch Selective-Etch Self-Etch Wet & Dry. All in. one click
 Adhese Universal The universal adhesive Direct Indirect Total-Etch Selective-Etch Self-Etch Wet & Dry All in one click 1 Universal Adhesion with advanced delivery Adhese Universal is a singlecomponent,
Adhese Universal The universal adhesive Direct Indirect Total-Etch Selective-Etch Self-Etch Wet & Dry All in one click 1 Universal Adhesion with advanced delivery Adhese Universal is a singlecomponent,
stabilisation and surface protection
 Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
Product Information. Charisma Diamond Discover the next dimension of natural beauty. Giving a hand to oral health.
 Product Information Charisma Diamond Discover the next dimension of natural beauty. Giving a hand to oral health. The new Charisma Diamond Welcome to the next dimension of natural beauty. We commit our
Product Information Charisma Diamond Discover the next dimension of natural beauty. Giving a hand to oral health. The new Charisma Diamond Welcome to the next dimension of natural beauty. We commit our
Press Release. Press Contact. The concept for Class II restoration Delicate preparation, rapid procedure and reliable results
 Press Release The concept for Class II restoration Delicate preparation, rapid procedure and reliable results by Dr. Arzu Tuna and Dr. Umut Baysal, Attendorn, Germany Composite restorations have always
Press Release The concept for Class II restoration Delicate preparation, rapid procedure and reliable results by Dr. Arzu Tuna and Dr. Umut Baysal, Attendorn, Germany Composite restorations have always
Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA in the Apical Sealing Ability of Lased And Unlased Root Canal Walls - A Pilot Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XIV (June 2016), PP 100-104 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XIV (June 2016), PP 100-104 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA
Finite element analysis of thermal stress distribution in different restorative materials used in class V cavities
 Original Article Finite element analysis of thermal stress distribution in different restorative materials used in class V cavities MS Guler, C Guler 1, F Cakici 2, EB Cakici 2, S Sen 3 Department of Maritime
Original Article Finite element analysis of thermal stress distribution in different restorative materials used in class V cavities MS Guler, C Guler 1, F Cakici 2, EB Cakici 2, S Sen 3 Department of Maritime
Shear Bond Strength of Acidic Primer, Light-Cure Glass Ionomer, Light-Cure and Self Cure Composite Adhesive Systems - An In Vitro Study
 Shear Bond Strength of Acidic Primer, Light-Cure Glass Ionomer, Light-Cure and Self Cure Composite Adhesive Systems - An In Vitro Study Krishnakanth Reddy D 1, Kishore M S V 2, Safeena Safeena 3 1 Professor,
Shear Bond Strength of Acidic Primer, Light-Cure Glass Ionomer, Light-Cure and Self Cure Composite Adhesive Systems - An In Vitro Study Krishnakanth Reddy D 1, Kishore M S V 2, Safeena Safeena 3 1 Professor,
Layering Methods of. YH Bagis IH Baltacioglu S Kahyaogullari
 Operative Dentistry, 2009, 34-5, 578-585 Comparing Microleakage and the Layering Methods of Silorane-based Resin Composite in Wide Class II MOD Cavities YH Bagis IH Baltacioglu S Kahyaogullari Clinical
Operative Dentistry, 2009, 34-5, 578-585 Comparing Microleakage and the Layering Methods of Silorane-based Resin Composite in Wide Class II MOD Cavities YH Bagis IH Baltacioglu S Kahyaogullari Clinical
Root Surface Protection Simple. Effective. Important.
 GC Fuji VII / Fuji VII EP Root Surface Protection Simple. Effective. Important. Brush up your painting skills and help your patients Q&A Prof. Laurie Walsh University of Queensland lifestyle factors (frequency
GC Fuji VII / Fuji VII EP Root Surface Protection Simple. Effective. Important. Brush up your painting skills and help your patients Q&A Prof. Laurie Walsh University of Queensland lifestyle factors (frequency
Downloaded from journal.qums.ac.ir at 11: on Thursday June 7th 2018
 23 JQUMS, Vol.13, No.3, Autumn 2009 Effect of flowable composite on Microleakage of packable resin composites in class II cavities AR Daneshkazemi* AR Davari** J Modaresi*** F Dastjerdi**** M Darezereshki*****
23 JQUMS, Vol.13, No.3, Autumn 2009 Effect of flowable composite on Microleakage of packable resin composites in class II cavities AR Daneshkazemi* AR Davari** J Modaresi*** F Dastjerdi**** M Darezereshki*****
ENDODONTOLOGY. An in-vitro evaluation of apical sealing of three epoxy resin based commercial preparations INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS ABSTRACT
 An in-vitro evaluation of apical sealing of three epoxy resin based commercial preparations Vishal A. Mahajan * Kamra A. I. ** ABSTRACT The aim of the present in vitro study was to evaluate and compare
An in-vitro evaluation of apical sealing of three epoxy resin based commercial preparations Vishal A. Mahajan * Kamra A. I. ** ABSTRACT The aim of the present in vitro study was to evaluate and compare
and get a Pentamix TM Lite free *
 Offers valid until 31st October 2014 Spend, Spend, Spend! Spend 450 on any 3M ESPE products and get a Pentamix TM Lite free * Order must include 1 Imprint TM 4 refill Download the free Layar app get.layar.com
Offers valid until 31st October 2014 Spend, Spend, Spend! Spend 450 on any 3M ESPE products and get a Pentamix TM Lite free * Order must include 1 Imprint TM 4 refill Download the free Layar app get.layar.com
Filtek. Any place. Any class. Supreme XTE. It s the one that can do it all. Universal Restorative. Class III. Class IV. Class II. Class I.
 Class III Class IV Class II Class I Class V Any place. Any class. It s the one that can do it all. Designed to be versatile. If you re still using one composite for strong posterior fillings, and another
Class III Class IV Class II Class I Class V Any place. Any class. It s the one that can do it all. Designed to be versatile. If you re still using one composite for strong posterior fillings, and another
EASY TO REMOVE HARD TO FORGET! PANAVIA SA Cement Plus Automix
 EASY TO REMOVE HARD TO FORGET! PANAVIA SA Cement Plus Automix the SMartESt WaY to EnJoY PanaVIa LonGEVItY Easy storage. Easy application. Easy removal of excess cement. The all-new PANAVIA SA Cement Plus
EASY TO REMOVE HARD TO FORGET! PANAVIA SA Cement Plus Automix the SMartESt WaY to EnJoY PanaVIa LonGEVItY Easy storage. Easy application. Easy removal of excess cement. The all-new PANAVIA SA Cement Plus
The Dental Board of California Dental Materials Fact Sheet Adopted by the Board on October 17, 2001
 The following document is the Dental Board of California s Dental Materials Fact Sheet. The Department of Consumer Affairs has no position with respect to the language of the Dental Materials Fact Sheet;
The following document is the Dental Board of California s Dental Materials Fact Sheet. The Department of Consumer Affairs has no position with respect to the language of the Dental Materials Fact Sheet;
Influence of an Intermediary Base on the Microleakage of Simulated Class II Composite Resin Restorations
 Ó Operative Dentistry, 2014, 39-3, 301-307 Influence of an Intermediary Base on the Microleakage of Simulated Class II Composite Resin Restorations MCC Giorgi NMAP Hernandes MM Sugii GMB Ambrosano GM Marchi
Ó Operative Dentistry, 2014, 39-3, 301-307 Influence of an Intermediary Base on the Microleakage of Simulated Class II Composite Resin Restorations MCC Giorgi NMAP Hernandes MM Sugii GMB Ambrosano GM Marchi
Tenure A&B and Tenure Quik With Fluoride Multipurpose Bonding Systems Research Reference Guide
 Tenure A&B Tenure A&B and Tenure Quik With Fluoride Multipurpose Bonding Systems Research Reference Guide Long-Term Clinical Studies Strassler, H.E. and Weiner, S., Long Term Clinical Evaluation of Etched
Tenure A&B Tenure A&B and Tenure Quik With Fluoride Multipurpose Bonding Systems Research Reference Guide Long-Term Clinical Studies Strassler, H.E. and Weiner, S., Long Term Clinical Evaluation of Etched
Practice Impact Questionnaire
 Practice Impact Questionnaire Your practitioner identifier is: XXXXXXXX It is very important that ONLY YOU complete this questionnaire because your responses will be compared to responses that you provided
Practice Impact Questionnaire Your practitioner identifier is: XXXXXXXX It is very important that ONLY YOU complete this questionnaire because your responses will be compared to responses that you provided
CERASMART. The new leader in hybrid ceramic blocks
 The new leader in hybrid ceramic blocks Introducing, a new force absorbing hybrid ceramic block 20 µm Contains high density of ultra fine homogeneously-dispersed fillers in a highly cross-linked resin
The new leader in hybrid ceramic blocks Introducing, a new force absorbing hybrid ceramic block 20 µm Contains high density of ultra fine homogeneously-dispersed fillers in a highly cross-linked resin
Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2006;51:(2):175-179 Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique GM Knight,* JM McIntyre,* Mulyani*
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2006;51:(2):175-179 Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique GM Knight,* JM McIntyre,* Mulyani*
Acknowledgments Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal
 Preface p. v Acknowledgments p. vii Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal Dental Material p. 5 Quality Assurance
Preface p. v Acknowledgments p. vii Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal Dental Material p. 5 Quality Assurance
The Effect of Heat on the Surface Properties of Conventional Glass Ionomer Cements: SEM Evaluation
 BALKAN JOURNAL OF STOMATOLOGY ISSN 1107-1141 TUPNBUPMPHJDBM!!TPDJFUZ The Effect of Heat on the Surface Properties of Conventional Glass Ionomer Cements: SEM Evaluation SUMMARY The objective of this study
BALKAN JOURNAL OF STOMATOLOGY ISSN 1107-1141 TUPNBUPMPHJDBM!!TPDJFUZ The Effect of Heat on the Surface Properties of Conventional Glass Ionomer Cements: SEM Evaluation SUMMARY The objective of this study
F i l t e k Z550. Nano Hybrid Universal Restorative. Technical Data Sheet
 F i l t e k Z550 Nano Hybrid Universal Restorative Technical Data Sheet Product Description Filtek Z550 Nano Hybrid Universal Restorative is a visible light-activated nanohybrid composite designed for
F i l t e k Z550 Nano Hybrid Universal Restorative Technical Data Sheet Product Description Filtek Z550 Nano Hybrid Universal Restorative is a visible light-activated nanohybrid composite designed for
Effect of Different Enamel Preparation Methods on Microleakage of Fissure Sealant: An In Vitro Study
 Journal of Dental School 2014; 32(4): 216-221 Original Article Effect of Different Enamel Preparation Methods on Microleakage of Fissure Sealant: An In Vitro Study *1 Atefeh Pakdel 2 Saman Partovi 3 Elnaz
Journal of Dental School 2014; 32(4): 216-221 Original Article Effect of Different Enamel Preparation Methods on Microleakage of Fissure Sealant: An In Vitro Study *1 Atefeh Pakdel 2 Saman Partovi 3 Elnaz
Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core
 Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core A post and core is a dental restoration used to sufficiently buildup tooth structure for future restoration with a crown when there is not enough tooth
Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core A post and core is a dental restoration used to sufficiently buildup tooth structure for future restoration with a crown when there is not enough tooth
Ketac Nano Light-Curing Glass Ionomer Restorative Quick Mix Capsule. An aesthetic glass ionomer. Fewer steps. Faster treatment.
 Light-Curing Glass Ionomer Restorative Quick Mix Capsule An aesthetic glass ionomer. Fewer steps. Faster treatment. The innovative Quick Mix Capsule saves time, steps, and improves overall mixing results.
Light-Curing Glass Ionomer Restorative Quick Mix Capsule An aesthetic glass ionomer. Fewer steps. Faster treatment. The innovative Quick Mix Capsule saves time, steps, and improves overall mixing results.
Glass ionomer cements in complex oral rehabilitations. A case report.
 Università degli Studi di Milano - Department of Technologies for the Health I.R.C.C.S Istituto Ortopedico Galeazzi Department of Odontology Director: Prof. Roberto Weinstein Glass ionomer cements in complex
Università degli Studi di Milano - Department of Technologies for the Health I.R.C.C.S Istituto Ortopedico Galeazzi Department of Odontology Director: Prof. Roberto Weinstein Glass ionomer cements in complex
Microleakage of Nanofilled Composite Resin Restorative Material
 Journal of Biomaterials and Nanobiotechnology, 2011, 2, 329-334 doi:10.4236/jbnb.2011.23040 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbnb) 329 Microleakage of Nanofilled Composite Resin
Journal of Biomaterials and Nanobiotechnology, 2011, 2, 329-334 doi:10.4236/jbnb.2011.23040 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbnb) 329 Microleakage of Nanofilled Composite Resin
Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations:
 1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH. Sandhya CA Shyam Lohakare, Pushpa Vinay Hazarey ABSTRACT
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparison of shear bond strength of no mix-composite resin, self cure resin reinforced glass ionomer cement and light cure resin reinforced glass ionomer cement: an in-vitro study Sandhya
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparison of shear bond strength of no mix-composite resin, self cure resin reinforced glass ionomer cement and light cure resin reinforced glass ionomer cement: an in-vitro study Sandhya
CARIES STABILIZATION AND TEMPORARY RESTORATION
 CARIES STABILIZATION AND TEMPORARY RESTORATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Justify the importance of caries stabilisation procedure in operative care. List and discuss the methods to stabilise caries ( include preventive
CARIES STABILIZATION AND TEMPORARY RESTORATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Justify the importance of caries stabilisation procedure in operative care. List and discuss the methods to stabilise caries ( include preventive
Glass Ionomers. Reputable, Durable, Long Lasting
 Glass Ionomers Reputable, Durable, Long Lasting Conventional Glass Ionomer Restoratives Glass Ionomeres Technology more up-to-date than ever before! Successfull well proven material Exhibit biocompatibility
Glass Ionomers Reputable, Durable, Long Lasting Conventional Glass Ionomer Restoratives Glass Ionomeres Technology more up-to-date than ever before! Successfull well proven material Exhibit biocompatibility
J Bagh College Dentistry Vol. 26(4), December 2014 Evaluation of marginal
 Evaluation of marginal gap at the composite/enamel interface in Class II composite resin restoration by SEM after thermal and mechanical load cycling (An in vitro comparative study) Mais Yaroub, B.D.S.,
Evaluation of marginal gap at the composite/enamel interface in Class II composite resin restoration by SEM after thermal and mechanical load cycling (An in vitro comparative study) Mais Yaroub, B.D.S.,
FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS
 FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS Glass Ionomers Solve Clinicians Quandaries Amalgam fillings have been around for almost two centuries,
FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS Glass Ionomers Solve Clinicians Quandaries Amalgam fillings have been around for almost two centuries,
