CORRELATION BETWEEN STIGMA AND QUALITY OF LIFE IN LEPROSY PATIENTS IN MEHRAB KHAN REGION OF MASHHAD
|
|
|
- Oswald Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pharmacophore ISSN Journal home page: CORRELATION BETWEEN STIGMA AND QUALITY OF LIFE IN LEPROSY PATIENTS IN MEHRAB KHAN REGION OF MASHHAD Hamideh Ebrahimi 1,Wim Van Brakel 2, Zahra safavi bayat 3*, Nadere Naderi ravesh 3, Nezhat Sakeri 4,Masomeh Ebrahimi 5, Gholamreza Ghaedamini Harouni 6,,Vahid rahmani 7, Ehsan Karvani 8 1. MSc student of nursing, Student Research Committee, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran 2. Head Technical Department, Netherlands leprosy relief, Amsterdam, Netherlands 3. Assistant Professor, Nursing Department, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Shahid Beheshty University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran 4. Assistant Professor of Biostatistics, School of Paramedical, Shahid Beheshty University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran 5. Clinical Research Development Unit of Poursina Hospital, Guilan University of Medical Sciences, Rasht, Guilan, Iran 6. PhD in Health and Social Welfare, Social Welfare Management Research Center, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Science, Tehran, Iran 7. Student of Surgical Technician, Iran University of medical science, Tehran, Iran 8. MSc in Curriculum Planning, Urmia University of Medical Science, Urmia, Iran ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT Received: 03 th Jun 2017 Accepted: 29 th Nov 2017 Available online: 14 th Dec 2017 Keywords: Leprosy, Quality of Life, Questionnaire,. Leprosy is one of the oldest chronic diseases and similar to other infectious diseases, it causes longterm physical and social effects on the lives of patients and their families. This study was aimed to evaluate the correlation between stigma and quality of life in leprosy patients in mehrab khan region of mashhad in 2017.This was a cross-sectional study conducted with 103 patients with leprosy in Mashhad in the Mehrab Khan region in March The sampling method was convenience sampling. The data was analyzed using SPSS version 19, descriptive statistics (frequency, percentage, mean and standard deviation) and inferential tests (ANOVA, Pearson correlation and independent t-test) were used.the results showed that the mean age of patients was 65.2±8.1 years and the mean age of developing leprosy was 15.3±7.03. There was an inverse correlation between the score of overall stigma, internal stigma and all dimensions of quality of life that was statistically significant, except for the social dimension (r = ; p = 0.067). There was an inverse correlation between the psychological dimension of quality of life and experienced stigma. The highest score of the overall quality of life was related to the divorced patients with mean score of 79.7, which was statistically significant (p = 0.016) from those who were not divorced.according to results, there was a negative correlation between quality of life and all aspect of stigma using SARI tool. Copyright All Rights Reserved - Pharmacophore To Cite This Article: Hamideh Ebrahimi, Wim Van Brakel, Zahra safavi bayat, Nadere Naderi ravesh, Nezhat Sakeri, Masomeh Ebrahimi, Gholamreza Ghaedamini Harouni, Vahid rahmani, (2017), Correlation Between and Quality of Life in Leprosy Patients In Mehrab Khan Region Of Mashhad, Pharmacophore, 8(6S), e Introduction The chronic nature of many infectious diseases causes long-term physical and social effects in the lives of patients and their families [1]. Leprosy is one of the oldest and most devastating chronic diseases [2] and its history goes back to the writings on Egyptian papyrus in 1550 BC and manuscripts in Hindi to 600 years before Christ [3]. In Iran, we have heard much about leprosy how Sultan Mohammad sought refuge in a location where leprosy patients resided and remained until the end of his life at the same place, because he was aware that the attackers were afraid of that place [4]. Corresponding Author: Zahra Safavi bayat, Assistant Professor, Nursing Department, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Shahid Beheshty University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. zahrasb16@yahoo.com
2 The bacillus Mycobacterium leprae, the causative agent of leprosy, was discovered in 1873 by a Norwegian physician called Gerhard Hansen [5]. The proliferation of Mycobacterium leprae in peripheral nerves in the Schwann cells gradually causes loss of sensation, deformity in limbs and muscle atrophy [6]. Standard treatment for leprosy was announced by WHO in 1982, consisting of multiple drug therapy (MDT), a combination of rifampicin, dapsone and clofazimine, which, if a patient receives early treatment would prevent the spread of disabilities, and prevent drug resistance [7]. In the absence of effective treatment, permanent damage may happen in the skin, nerves, limbs [8] and eyes [9]. In 2013, 215,656 new cases of leprosy were reported by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the three countries with the highest prevalence were India, Brazil and Indonesia [10]. Despite the significant advances in treatment and control of leprosy, the disease is still prevalent in many developing countries [11]. Brief information about leprosy status in Iran Leprosy in the north and northwest of Iran is prevalent compared to other part of Iran. Actually its prevalence starts from Kermanshah city and passes from West Azerbaijan, Gilan, Mazandaran cities and finally ends in Mashhad city. The cause of prevalence in these area is unknown. Although rare report of leprosy was obsereved from south of Iran but totally there are two center in order to treat leprosy people in Iran, Mehrab Khan of Mashhad in the east of Iran and Baba Baghi of Tabriz in the west of Iran. Approximately 700 patients with leprosy are living in Mashhad because of the shrine of Imam Reza who is eight Imam of Shia religion, leprosy people believe that the existence of Imam Reza helps them to treat faster. Not only Iranian move on Mashhad to treat their leprosy but also from different cities of Afghanistan. The ruler of Mashhad had decided to build special region for treatment of these patient in the next of the Shrine of Imam Reza and called as Mehrab Khan Region in In the report of leprosy program by the Ministry of Health of the Islamic Republic, it was presented that there were patients with leprosy in Iran by the end of 2015 Iran which 9011 patients of them have been improved in terms of infection transmission, 2371 patients were dead, 413 patients were missed and 18 patients were under treatment of multidrug therapy (MDT). There were 120 Afghan among 413 missed patients. But there is not exact statistics still because of fear, the continued existence of social stigma associated with leprosy in public, traffic and entry of Afghans, failure to provide timely statistics from the Department of Health and the lack of consistent pursuit of leprosy patients in treatment [12]. The concept of leprosy evokes horrible images of the disease from the ancient past due to the effects of this disease, when untreated, on the face and limbs. Despite the effective treatment, the fear among people did not reduce. The existence of difficulties in finding work, education, marriage and deprivation of social amenities and facilities in the community and a lower livelihood status have an effect on their quality of life [13]. In the book of the Old Testament of the Bible and in many cultures and countries such as Nepal, India and Nigeria, leprosy is seen as a sign of God's punishment for committing a great sin, because of the changes in appearance and limbs of these patients [14]. This causes the social sensitivity and isolation of patients from the community, which has a negative impact on the quality of life [15]. Also in Thailand, those suffering from leprosy were treated negatively by neighbours and even health providers, causing some of these patients suffering from leprosy to refuse the treatment due to stigma. In other words, these patients feel that they are not accepted by the community due to the signs of the disease. They then feel shame and frustration and try to live on the outside of the community, deprived from citizenship and individual rights [16]. Leprosy is an ugly word in people's minds. In some cultures, the word leprosy is uses as a curse word in conversation [17]. The person who receives the stigma of leprosy is facing a variety of mental health problems, such as emotional stress, anxiety, depression and even suicide risk, as well as isolation and a variety of family problems [18]. People may abandon the stigmatized person and his/her family and children and leprosy can even cause divorce [19]. Given that all of the problems listed affect the quality of life of patients with leprosy and even that of the family, the aim of this study was to determine the relationship between the stigma and quality of life of patients with leprosy in Mehrab Khan of Mashhad. Methods This was a cross-sectional study that conducted on 103 persons affected by leprosy in Mashhad in the Mehrab Khan region in March The sampling method was convenience sampling. Inclusion criteria: 1. Degree of disability of patients is 1 or 2 as defined WHO 2. Having no other acute or chronic disease 3. Having no disease which is related to stigma such as HIV/AIDS, TB and hepatitis 4. Having no addiction to opium or drug 5 Being between years old Data collection instrument: Data collection instruments in this research were the World Health Organization Quality of Life Questionnaire (WHOQOL- BREF) and Assessment and Reduction of Impact (SARI) scale (Dadun et al, in press) and a questionnaire on gender, age, number of children, marital status, education level, employment status and development age. WHO Quality of Life-BREF (WHOQOL-BREF)
3 The WHOQOL-BREF instrument comprises 26 items, which measure the following broad domains: physical health, psychological health, social relationships, and environment. The WHOQOL-BREF is a shorter version of the original instrument that is recommended for use in large research studies or clinical trials. This questionnaire was translated and its reliability and validity was confirmed by Nedjat et al. [20]. Indeed, this questionnaire is used in many parts of the world. The values of the reliability coefficient using Intra Class Correlation (ICC) was 0.77 in the area of physical health (physical), 0.77 in the psychological area, 0.75 in the social area and 0.84 in the environment area. Considering that this instrument is in the public domain and has good reliability and validity, it can be used in different target groups. Assessment and Reduction of Impact (SARI) In this study, SARI was used to measure perceived stigma of leprosy patients [21]. This instrument is based on Berger HIV Scale that was created for persons living with HIV/AIDS. The SARI project aimed to assess the effectiveness of three stigma reduction interventions for people affected by leprosy in Cirebon District, Indonesia. The scale consists of 22 items and is scored using a Likert scale (always, often, rarely and do not know). The SARI stigma scale has 4 sub-scales. The internal consistency measured with Cronbach's alpha was 0.82 for experienced stigma, 0.79 for perceived stigma, 0.79 for internal stigma and 0.79 for expected stigma [22] and again achieved a Kappa score of 0.75 for test-retest reliability of the SARI scale which indicates good reliability of this instrument. Therefore, it is a comprehensive, reliable and valid instrument to assess different aspects of stigma in people affected by leprosy [23]. Translation, and testing of validity and reliability of SARI was done in Iran after obtaining permission of the authors responsible for producing the SARI scale (Dr van Brakel). We then determined its face and content validity and reliability. In this study, Cronbach's alpha coefficient was calculated in two stages for the SARI scale. In the first stage, after determination of its face and content validity and reliability, internal consistency was determined using pilot sample of 30 patients with leprosy located in Mehrab Khan region of Mashhad city. In the second stage, Cronbach's alpha for each operator for the whole scale was calculated in a sample of 106 patients. Cronbach's alpha of SARI was 0.87 in the first stage and 0.88 in the second stage. Statistical analysis The data was analyzed using SPSS version 19 and descriptive statistics (frequency, percentage, mean and standard deviation) and inferential tests (ANOVA, Pearson correlation and independent t-test) were used. Results The study conducted on 103 patients with leprosy in Mehrab Khan of Mashhad city that the mean age of patients was 65.2±8.1 years and the mean age of developing leprosy was 15.3±7.03 (Table 1). In terms of gender, 74 patients were male (71.8%) and 29 patients were female (28.2 %). 79 patients (76.7%) were illiterate, 44 patients (42.7%) retired, 65 (63.1%) are married (Table 2). According to Table 3, there was a statistically significant inverse correlation between overall SARI stigma score and each dimension of quality of life, except the social dimension, which was only borderline significant (p = 0.067). Thus the score of quality of life decreased with an increasing score of stigma. There was also an inverse correlation between the score of internalised stigma and all dimension of quality of life, except for the physical dimension (p = 0.195), which was not statistically significant. There was an inverse correlation between psychological dimension of quality of life and the experienced stigma score. According to Table 4, the highest score of overall stigma was found among affected persons who were divorced with mean score of 57, the highest score of experienced stigma was related to singles with mean score of 21.9 and the highest score of internalised stigma was related to married patients with mean score of The highest score of disclosure concerns and expected stigma was related to divorced patients with mean score of and 11, respectively. There was no significant relationship between marital status and overall score of stigma. In terms of occupation status, the highest overall score of stigma was related to retired patients with mean score of which was statistically significantly different from the other groups (p = 0.003). The highest score of all stigma dimensions was related to unemployed persons, who had a mean score of disclosure concerns of which was statistically significant from the other employment groups (p = 0.05). The mean score of expected stigma was 11.73, which was also significantly different (p = 0.045). Table 5 shows that the highest score of overall quality of life was found among divorced persons with mean score of The difference was statistically significant (p = 0.016). The highest score of all dimensions of quality of life except for the social dimension was found among divorced persons. The mean score of their physical dimension was 22 which was significantly higher than in the other groups (p = 0.036). The mean score of their psychological and environments dimension was 17 and 22.33, respectively. The mean score of social dimension of quality of life in single patients was 8.33 statistically significant (p = 0.002). In terms of occupation status, the highest score of overall quality of life was found among retired patients with mean score of which was significantly higher than among the other occupations (p = 0.04). The highest score for the social and environment dimension of quality of life of was related to housekeepers with mean score of 8.36 and 20.45, respectively. These differences were significant (p=0.02 and p=0.016).
4 According to table 6, there is no significant correlation between total score and all dimensions with the age of the patients. According to table 7, there was an inverse correlation between the physical dimension (p = 0.016) and psychological dimension (p = 0.016) that is statistically significant, however, as the age of the patients increases, the quality of life decreases in patients with leprosy. There was no significant correlation between quality of life score and its dimensions and the age of the patients. Table 1. Demographic characteristics (quantitative) of patients in the medical center of Khan Mashhad Variable Age Infected Age Mean Standard Deviation Frequency Lower Limit 33 4 Upper Limit Table 2. Demographic characteristics (qualitative) of patients in the medical center of Khan Mashhad Variable Frequency Percent Gender Male Female Illiterate Education Elementary III Middle 1 1 Rent House House Personal House Occupation Marital Status Organizational Unemployed Self-Employed Retired Housekeeper Single Married Widow Divorced Dimensions Overall Internalized Disclosure Expected Experienced Table 3: Pearson correlation coefficient between scores of quality of life and stigma Quality Of Life (Environment Area) R = , P=0.000 R =-0.316, P=0.000 R =-0.238, P=0.001 R = , P=0.000 R =-0.009, P=0.903 Correlation Coefficient And Value Of Dimensions Of Quality Of Life (Social Area) R =-0.181,P=0.067 R = , P=0.040 R = , P=0.075 R = , P=0.001 R= , P=0.903 Quality Of Life (Psychological Area) R = , P=0.001 R =-0.176, P=0.015 R= , P=0.028 R = , P=0.000 R = , P=0.032 Quality Of Life (Physical Area) R =-0.126,P=0.07 R= ,P=0.195 R=-0.067,P=0.362 R = ,P=0.002 R = ,P=0.292 Quality Of Life (Overall) R =-0.356, P=0.000 R= , P=0.002 R= , P=0.012 R =-0342, P=0.000 R =-0.163, P=0.019 Marital Status Table 4. The relationship between demographic characteristics and stigma dimensions Dimensions Expected Internal Revealed Experienced Overall Variables Mean Mean Mean Mean Mean Value Value Value Value Value Single Married Widow Divorced Unemployed Occupation Self-Employed
5 Retired Housekeeper Table 5. The relationship between demographic variables and mean score of quality of life Quality of Life Dimensions Variables Environment Social Psychological Physical Overall Value Mean Value Mean Value Mean Value Mean Value Mean Single Married Marital Widow Status Divorced Occupat ion Unemployed Self-Employed Retired Housekeeper Table 6. Correlation coefficient of stigma and its dimensions with age of patients Variable Correlation Coefficient And Value Of Dimensions Of Age Infected Age Revealed R=0.076, P=0.305 R=-.055, P=0.440 Expected R=0.003, P=0.964 R=0.081, P=0.258 Internal R=0.059, P=0.417 R=0.110, P=0.137 Experienced R=-0.049, P=0.495 R=0.047, P=0.500 Overall R=-0.054, P=0.442 R=0.035, P=0.633 Table 7. Correlation coefficient of quality of life and its dimensions with the age of patients Variable Correlation Coefficient And Value Of Dimensions Of Quality Of Life Age Infected Age Environment R=0.020, P=0.781 R=0.067, P=0.350 Social R=0.047, P=0.525 R=0.024, P=0.742 Psychological R=0.018, P=0.048 R=-0.011, P=0.878 Physical R=0.143, P=0.048 R=0.015, P=0.836 Total R=0.012, P=0.861 R=0.035, P=0.633 Discussion Leprosy is one of the oldest and most notorious diseases and similar to other infectious diseases, may cause long-term physical and psychosocial effects on the lives of patients and their families [24]. The existence of difficulties in finding work, education, marriage and exclusion from social amenities and facilities in the community and the lower livelihood status have an effect on their quality of life [25]. The current study conducted on 103 persons affected by leprosy in Mehrab Khan of Mashhad city, studied the relationship between different aspects of stigma they experienced and their quality of life. Here you should insert the below paragraph on the relationship between stigma and QoL. This is your main topic! The mean age of affected persons was 65.2±8.1 years and the mean age of developing leprosy was 15.3±7.03 (Table 1). (76.7%) were illiterate. We used the WHOQOL-BREF standard questionnaire to measure health-related quality of life. In the study of Reis et al. [26], the mean age of the developing leprosy was 47.7 years, 71.4% of them had elementary education and 28.6% of them had middle education, 66.3% of patients had a neuropathic pain. In their study, which also used the WHOQOL-BREF, the physical dimension of quality of life had the lowest values (10.8± 3.3) and the highest score was related to social dimension (6.41±3.7). The score of overall, environmental, and psychological of quality of the study were 12±4.1, 2.21±3.1 and 7.31±3.3, respectively. These results are best expressed as mean and 95% confidence interval; this is much more relevant than a standard deviation. Also you would need to give the normal reference values for each QoL domain, since readers do not know whether the figures given are high or low seems higher than 6.4, yet you say 10.8 is the lowest value. I assume you mean relative to the normal value for that domain? You could include a table with normal reference
6 values for Iran, if you have these. In our study scores of quality of life were higher than in the study of Reis et al. This may be due to the high proportion of persons with neuropathic pain in the latter study. In the study of Joseph et al. [27] WHOQOL-BREF was used to evaluate the quality of life in the two groups, cases (n=30) and controls (n=20). The scores in each dimension were higher for controls than cases. The mean score of quality of life in females was 94.1 and in males was In the physical and psychological aspects of quality of life, scores were better than for the other aspects, so that these results were consistent with our study. In another study of Reis et al. [28] evaluating QOL with the WHOQOL-BREF among leprosy patients, the scores of overall quality of life, and the physical, environment, psychological and social dimensions were 11.2 ±3.63, 11±3.56, 11.47±2.11, 13.29±2.79 and ±3.66, respectively. *how can the social dimension be 115? * Females reported better quality of life, which was consistent with our findings of higher scores among females. Some studies have reported different results, indicating that geographical conditions, employment, community support, severity of illness and other ideological beliefs may affect quality of life [27, 28-29]. Level of education is one of the factors that may have an effect on stigma and quality of life. In the present study, 76.7% of patients were illiterate. In the study of Reis et al [26], only 51.5% of patients had elementary education. So this doesn t show how education and QOL are related. Brouwers et al. [30] found a significant relationship between education and quality of life (p =0.02). They found that people with leprosy disease had lower quality of life and the most affected aspect was the physical dimension. According to the authors, the reason was physical and neurological pain. In the study of Brouwers et al, the level of quality of life was better than in our study which we think may be due to an employment level of over 90% in their study compared to only 25% or so in our study. Employment plays an important role in the promotion of quality of life. Tsutsumi et al. [31], in their study on leprosy patients in Bangladesh, found significant differences between the physical and psychological QOL dimensions. They attributed these differences to vision disorders. The QOL score of overall quality of life in males (78.61) was higher than among females (74.21). The score of quality of life in males experiencing leprosyrelated stigma was and in females was These values are very close to and consistent with the findings in our study. In the study of Kaehler et al. [26], people aged over 61 had the maximum level of perceived stigma (p = 0.021). These results were consistent with the results of Kushwah et al. in India [32], who found that age had a significant relationship with perceived stigma. These results were inconsistent with our study because we did not find a significant relationship between age and stigma. In the study of Calcraft et al. in Nepal [33], most patients declared that the main factor related to perceived stigma in their life was to lose a job. This is consistent with the results of our study, which showed a significant relationship between the occupation status and stigma dimensions (p = 0.045). In the study of Bello et al. [34] conducted in Ghana, the mean age of patients was 59.7±13.5. In this study, 90% of patients had no formal education. There was no significant relationship between age and dimensions of health (P> 0. 05). In this study, quality of life of males was better than that of females, as measured with the HRQOL (health related quality of life questionnaire). The highest and lowest scores were related to the social dimension and physical dimension. Martins et al. [35] reported the physical dimension as the one scoring lowest on the HRQOL. In the present study, the physical dimension had a good score compared to the other dimensions, except for the environment dimension. There was an inverse correlation between internalised stigma and the overall quality of life score. This was also true for each specific dimension of quality of life, except for the physical dimension (p = 0.195). This means that, as stigma increases, quality of life decreases. In the study of Jegede et al. [36] no relationship was found is this true between age and quality of life in leprosy patients, which is consistent with the findings the present study. In Nepal, Adhikari et al. [37] showed that the highest level of perceived stigma was in patients who were illiterate (p = 0.008),). In the study of Rao et al. [38] in India, perceived stigma was strongest among illiterate patients. Age also was a risk factor for perceived stigma, with stigma level being high in older people. In a study in Brazil, perceived stigma was reported by 27% of leprosy patients [39]. In our study, the highest score of all dimensions of stigma was among unemployed persons. Their mean score of disclosure concerns was 12.50, which was statistically significant (p = 0.05), the mean score of expected stigma was 11.73, which also was statistically significant (p = 0.045). In the study of Van Brakel et al. [40] in Indonesia, leprosy patients were evaluated in terms of the activity restrictions using a toolkit containing the Screening of Activity Limitation and Safety Awareness (SALSA) scale. The Explanatory Model Interview Catalogue (EMIC) scale was also used. In this study, 77% of patients had leprosy-related disabilities and 60% had limited mobility. Perceived stigma was reported by 36%. The crucial problems of patients revealed by the EMIC were related to shame and embarrassment. This may lead to self-stigma, which can cause anxiety, depression and communication problems with the family and friends [41-43]. There is no other published study yet that has evaluated the relationship between stigma dimensions (expected, internal, revealed and experienced) assessed with the SARI scale and quality of life in leprosy patients. The present study is therefore not directly comparable to the above-mentioned studies. The SARI Scale used in the present study was devised in the SARI Project in Indonesia and was validated in 2012 (Dadun et al, in press).
7 Conclusion According to results, there was a negative correlation between quality of life and all aspect of stigma using SARI tool. The results of the present study showed that the reliability and validity of SARI is enough to use in related research in Iran, but it is requested to make an appropriate tool with the native scenario of Iran which has spiritual and religious dimensions. References 1. Yamaguchi N, Poudel KC, Jimba M. Health-related quality of life, depression, and self-esteem in adolescents with leprosy-affected parents: results of a cross-sectional study in Nepal. BMC public health Jan 10;13(1): Peters RM, Zweekhorst MB, Bunders JF, van Brakel WH. A cluster-randomized controlled intervention study to assess the effect of a contact intervention in reducing leprosy-related stigma in Indonesia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis Oct 20;9(10):e Luka EE. Understanding the stigma of leprosy. South Sudan Medical Journal. 2010;3(3): Azizi MH, Bahadori M. A history of leprosy in Iran during the 19th and 20th centuries. Archives of Iranian medicine Nov 1;14(6): Suchonwanit P, Triamchaisri S, Wittayakornrerk S, Rattanakaemakorn P. Leprosy reaction in Thai population: a 20- year retrospective study. Dermatology research and practice Oct 5; Virmond M, Grzybowski A, Virmond L. Leprosy: A glossary. Clinics in dermatology Feb 28;33(1): Hegde SP, Shenoy MM, Pinto M, Amin VB. Leprosy: Chronicles of a disabling disease. Archives of Medicine and Health Sciences Jul 1;3(2): Breen DP, Deeb J, Vaidya S, Lockwood DN, Radunovic A. Leprosy: a'common'and curable cause of peripheral neuropathy with skin lesions. The journal of the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Mar;45(1): McLaren DS, Shaw MJ, Dalley KR. Eye Disease in Leprosy Patients. A Study in Central Tanganyika. International Journal of Leprosy. 1961;29(28). 10. Power M. World Health Organization Quality of Life Disabilities Module. InEncyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research 2014 (pp ). Springer Netherlands. 11. White C, Franco-Paredes C. Leprosy in the 21st century. Clinical microbiology reviews Jan 1;28(1): Sanabadi Aziz N. Astan Quds Razavi and Mehrab Khan Region relying on documents of leprosy people. Iran (IR): Islamic Research Foundation of Astane Quds Razavi; 2016.Vol 1 P Van Brakel WH, Miranda Galarza B. Infectious diseases: a case study of leprosy-related stigma. The stigma of disease and disability: understanding causes and overcoming injustices. American Psychological Association. 2013: Grzybowski A, Nita M. Leprosy in the Bible. Clinics in dermatology Feb 29;34(1): Rafferty J. Curing the stigma of leprosy. Leprosy review Jun 1;76(2): Sermrittirong S, Brakel WV, Kraipui N, Traithip S, Bunders-Aelen JF. Comparing the perception of community members towards leprosy and tuberculosis stigmatisation. Lepr Rev Mar 1;86: Frist T. Don't treat me like I have leprosy. ILEP; Adhikari B, Kaehler N, Raut S, Marahatta SB, Gyanwali K, Chapman RS. Risk factors of stigma related to leprosy- A systematic review. Journal of Manmohan Memorial Health Sciences. 2013;1(2): Van Brakel WH. Measuring leprosy stigma-a preliminary review of the leprosy literature1. International Journal of Leprosy and Other Mycobacterial Diseases Sep 1;71(3): Nejat SA, Montazeri A, Holakouie Naieni K, Mohammad KA, Majdzadeh SR. The World Health Organization quality of Life (WHOQOL-BREF) questionnaire: Translation and validation study of the Iranian version. Journal of School of Public Health and Institute of Public Health Research Jul 15;4(4): Peters R. A reflection on positionality and knowledge processes in transdisciplinary research. Knowledge Management for Development Journal. 2013;9(2). 22. Lusli MI, Peters RM, Zweekhorst MB, Van Brakel WH, Seda FS, Bunders JF. Lay and peer counsellors to reduce leprosy-related stigma lessons learnt in Cirebon, Indonesia. Lepr Rev Mar 1;86: Whoqol Group. Development of the World Health Organization WHOQOL-BREF quality of life assessment. Psychological medicine May;28(3): F. H. Pucci, C. R. Teofilo, S. G. A. Arag ao, and L. G. F. T avora, Pain in hansen s disease patients, Revista DOR, vol. 12, no. 1, pp , Kaehler N, Adhikar B, Raut S, Marahatta SB, Chapman RS. Perceived towards Leprosy among Community Members Living Close to Nonsomboon Leprosy Colony in Thailand. PloS one Jun 5; 10(6):e Reis FJ, Gomes MK, Rodrigues J, Gosling AP, Fontana AP, Cunha AJ. Pain and its consequences in quality of life: a study with WHOQOL-BREF in leprosy patients with neuropathic pain. ISRN Tropical Medicine Apr 30; Joseph GA, Sunder Rao PS. Impact of leprosy on the quality of life. BULLETIN-WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION Jun 1; 77:515-7.
8 28. Reis FJ, Cunha AJ, Gosling AP, Fontana AP, Gomes MK. Quality of life and its domains in leprosy patients after neurolysis: a study using WHOQOL-BREF. Lepr Rev Jun 1; 84(2): A. G. Mellagi and Y. N. Monteiro, The religious imaginary of Hansen s disease patients: a comparative study of former inmates of the asylums of S ao Paulo and current Hansen s disease patients, Historia, Ciencias, Saude- Manguinhos, vol. 16, no. 2, pp , Brouwers C, Van Brakel W, Cornielje H et al. Quality of life, perceived stigma, activity and participation of people with leprosy-related disabilities in south-east Nepal. Disability, CBR and Inclusive Development, 2011; 22: Tsutsumi A, Izutsu T, Islam AM et al. The quality of life, mental health, and perceived stigma of leprosy patients in Bangladesh. Soc Sci Med, 2007; 64: Kushwah SS, Govila AK, Upadhyay S, Kushwah J (1981) A study of social stigma among leprosy patients attending leprosy clinic in Gwalior. Lepr India. 53(2): PMID: Calcraft JH (2006) The efffects of the stigma of leprosy on the income generation of leprosy affected people in the terai area of south east nepal. Asia pacific Diability Rehab Journal 17(2): Bello AI, Dengzee SA, Iyor FT. Health related quality of life amongst people affected by leprosy in south ghana: A needs assessment. Lepr Rev Mar 1; 84(1): Martins BDL, Torres FN, Oliveira ML. Impact on the quality of life of patients with Hansen s disease: Correlation between Dermatology Life Quality Index and disease status. A Bras Dermatol, 2008; 83: Jegede AS. The Yoruba culturalconstruction of health and illness. Nordic J Afr Stud, 2002; 11: Adhikari B, Kaehler N, Chapman RS, Raut S, Roche P. Factors affecting perceived stigma in leprosy affected persons in western Nepal. PLoS Negl Trop Dis Jun 5; 8(6):e Rao VP, Rao IR, Palande DD. Socio-economic rehabilitation programmes of LEPRA India: Methodology, results and application of needs-based socio-economic evaluation. Lepr Rev, 2000; 71: Lustosa AA, Nogueira LT, Pedrosa JI, Teles JB, Campelo V. The impact of leprosy on health-related quality of life. Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical Oct; 44(5): Van Brakel WH, Sihombing B, Djarir H, Beise K, Kusumawardhani L, Yulihane R, Kurniasari I, Kasim M, Kesumaningsih KI, Wilder-Smith A. Disability in people affected by leprosy: the role of impairment, activity, social participation, stigma and discrimination. Global health action Jul 19; Fung KM, Tsang HW, Corrigan PW, Lam CS, Cheung WM. Measuring self-stigma of mental illness in China and its implications for recovery. Int J Soc Psychiatry 2007; 53: Fung KM, Tsang HW, Corrigan PW. Self-stigma of people with schizophrenia as predictor of their adherence to psychosocial treatment. Psychiatr Rehabil J 2008; 32: Corrigan PW, Larson JE, Rusch N. Self-stigma and the why try effect: impact on life goals and evidence-based practices. World Psychiatry 2009; 8:
Psychometric evaluation of the SARI stigma assessment scale and an understanding of stigma amongst people affected by leprosy in Iran
 Lepr Rev (2017) 88, 554 562 Psychometric evaluation of the SARI stigma assessment scale and an understanding of stigma amongst people affected by leprosy in Iran HAMIDEH EBRAHIMI*, ZAHRA SAFAVI BAYAT*,
Lepr Rev (2017) 88, 554 562 Psychometric evaluation of the SARI stigma assessment scale and an understanding of stigma amongst people affected by leprosy in Iran HAMIDEH EBRAHIMI*, ZAHRA SAFAVI BAYAT*,
Downloaded from unmf.umsu.ac.ir at 20: on Friday March 22nd 2019
 *2 1 1392/03/19 1392/01/20 :... :. (P
*2 1 1392/03/19 1392/01/20 :... :. (P
Measurement of Change in the Knowledge and Attitude about Leprosy in Physiotherapy Students Undergoing Intensive One Week Training in Leprosy
 Indian J Lepr 2014, 86 : 99-104 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article Measurement of Change in the Knowledge and Attitude about Leprosy in Physiotherapy Students Undergoing
Indian J Lepr 2014, 86 : 99-104 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article Measurement of Change in the Knowledge and Attitude about Leprosy in Physiotherapy Students Undergoing
The differences in leprosy-related stigma between 30 sub-districts in Cirebon District, Indonesia
 Lepr Rev (2018) 89, 65 76 The differences in leprosy-related stigma between 30 sub-districts in Cirebon District, Indonesia JESSICA MICHGELSEN*, RUTH M.H. PETERS*, WIM H. VAN BRAKEL**, *** & IRWANTO****
Lepr Rev (2018) 89, 65 76 The differences in leprosy-related stigma between 30 sub-districts in Cirebon District, Indonesia JESSICA MICHGELSEN*, RUTH M.H. PETERS*, WIM H. VAN BRAKEL**, *** & IRWANTO****
Effect of impairment and disability on health related quality of life of elderly
 Original Research Article Effect of impairment and disability on health related quality of life of elderly Charulata V Pandit * Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, Narayan Medical College
Original Research Article Effect of impairment and disability on health related quality of life of elderly Charulata V Pandit * Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, Narayan Medical College
WILLIAM THOMAS NICHOLAS HUNT*, VASILIS NIKOLAOU***, NGÔ DUY ÐĂNG KHOA** &
 Lepr Rev (2018) 89, 46 55 A case-control study comparing the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) ratings of patients undergoing leprosy treatment, people cured of leprosy, and controls in Vietnam WILLIAM
Lepr Rev (2018) 89, 46 55 A case-control study comparing the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) ratings of patients undergoing leprosy treatment, people cured of leprosy, and controls in Vietnam WILLIAM
Stigma in Patients Using Mental Health Services
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861Volume 17, Issue 12 Ver 2 (December 2018), PP 16-23 wwwiosrjournalsorg Stigma in Patients Using Mental Health
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861Volume 17, Issue 12 Ver 2 (December 2018), PP 16-23 wwwiosrjournalsorg Stigma in Patients Using Mental Health
Dr. Olugbenga-Bello A.I Department of Community Medicine, LAUTECH Teaching Hospital, Ogbomoso
 Dr. Olugbenga-Bello A.I Department of Community Medicine, LAUTECH Teaching Hospital, Ogbomoso Nigeria is located in West Africa, with an estimated 3.7 percent of the population living with HIV (VERT, 2012)
Dr. Olugbenga-Bello A.I Department of Community Medicine, LAUTECH Teaching Hospital, Ogbomoso Nigeria is located in West Africa, with an estimated 3.7 percent of the population living with HIV (VERT, 2012)
overal QOL whereas level of education and disease related variables i.e. CD4 counts and
 Original Article 9 Assessment of Quality of Life of People Living with HIV and AIDS Receiving Anti-Retroviral Therapy in Kathmandu Valley Acharya DK Department of Adult Health Nursing, M aharajgunj Nursing
Original Article 9 Assessment of Quality of Life of People Living with HIV and AIDS Receiving Anti-Retroviral Therapy in Kathmandu Valley Acharya DK Department of Adult Health Nursing, M aharajgunj Nursing
Quality of life of people with non communicable diseases
 Original Article NUJHS Vol. 5, No.3, September 015, ISSN 49-7110 Quality of life of people with non communicable diseases 1 3 Anju Rose, Shashidhara Y.N. & Manjula 1 3 MSc Nursing Student, Associate Professor
Original Article NUJHS Vol. 5, No.3, September 015, ISSN 49-7110 Quality of life of people with non communicable diseases 1 3 Anju Rose, Shashidhara Y.N. & Manjula 1 3 MSc Nursing Student, Associate Professor
Reliability and Validity Assessment of Multi-Dimensional Sexual Self- Concept Questionnaire in Iran
 Iranian Journal of Military Medicine Vol. 14, No. 4, Winter 2013; 249-24 Reliability and Validity Assessment of Multi-Dimensional Sexual Self- Concept Questionnaire in Iran Ramezani MA. 1,2 PhD, Ghaemmaghami
Iranian Journal of Military Medicine Vol. 14, No. 4, Winter 2013; 249-24 Reliability and Validity Assessment of Multi-Dimensional Sexual Self- Concept Questionnaire in Iran Ramezani MA. 1,2 PhD, Ghaemmaghami
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Narratives Around Concealment and Agency for Stigmareduction: A Study of Women Affected by Leprosy in Cirebon District, Indonesia
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Narratives Around Concealment and Agency for Stigmareduction: A Study of Women Affected by Leprosy in Cirebon District, Indonesia Ruth M H Peters 1*, Miranda E Hofker 1, Wim H van Brakel
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Narratives Around Concealment and Agency for Stigmareduction: A Study of Women Affected by Leprosy in Cirebon District, Indonesia Ruth M H Peters 1*, Miranda E Hofker 1, Wim H van Brakel
CORRELATES OF DELAYED INITIATION OF TREATMENT AFTER CONFIRMED DIAGNOSIS UNDER RNTCP: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY IN AHMEDABAD MUNICIPAL CORPORATION, INDIA
 Original Article CORRELATES OF DELAYED INITIATION OF TREATMENT AFTER CONFIRMED DIAGNOSIS UNDER RNTCP: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY IN AHMEDABAD MUNICIPAL CORPORATION, INDIA Financial Support: None declared
Original Article CORRELATES OF DELAYED INITIATION OF TREATMENT AFTER CONFIRMED DIAGNOSIS UNDER RNTCP: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY IN AHMEDABAD MUNICIPAL CORPORATION, INDIA Financial Support: None declared
Research Article Leprosy Reaction in Thai Population: A 20-Year Retrospective Study
 Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 215, Article ID 253154, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/253154 Research Article Leprosy Reaction in Thai Population: A 2-Year Retrospective Study Poonkiat
Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 215, Article ID 253154, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/253154 Research Article Leprosy Reaction in Thai Population: A 2-Year Retrospective Study Poonkiat
ijer.skums.ac.ir Health related quality of life in the female-headed households Received: 20/Apr/2015 Accepted: 6/Jul/2015
 Original article International Journal of Epidemiologic Research, 2015; 2(4):178-183. ijer.skums.ac.ir Health related quality of life in the female-headed households Yousef Veisani 1,2, Ali Delpisheh 1,2*,
Original article International Journal of Epidemiologic Research, 2015; 2(4):178-183. ijer.skums.ac.ir Health related quality of life in the female-headed households Yousef Veisani 1,2, Ali Delpisheh 1,2*,
Investigating the correlation between personal characteristics and health status of Community- Living Elders and Intensity of Fear of Falling
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2013 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 4 (5): 1146-1150 Science Explorer Publications Investigating the correlation between
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2013 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 4 (5): 1146-1150 Science Explorer Publications Investigating the correlation between
Positive Living among women infected with HIV.
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 12, December 2016 320 Positive Living among women infected with HIV. * Prof.N.Meenakumari B.Sc(N)M.Sc(N) ** Dr.C.Susila RN.RM,
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 12, December 2016 320 Positive Living among women infected with HIV. * Prof.N.Meenakumari B.Sc(N)M.Sc(N) ** Dr.C.Susila RN.RM,
Knowledge And Attitude on Self Monitoring of Blood Glucose (Smbg) Among Diabetic Patients Belongs to Waghodia Taluka
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 5 Ver. II (Sep. - Oct. 2016), PP 06-11 www.iosrjournals.org Knowledge And Attitude on Self Monitoring
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 5 Ver. II (Sep. - Oct. 2016), PP 06-11 www.iosrjournals.org Knowledge And Attitude on Self Monitoring
Downloaded from:
 Van Brakel, WH; Nicholls, PG; Lockwood, DN; Rao, PS; Smith, WC (2007) A scale to assess the severity of leprosy reactions. Leprosy review, 78 (2). pp. 161-4. ISSN 0305-7518 Downloaded from: http://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/7152/
Van Brakel, WH; Nicholls, PG; Lockwood, DN; Rao, PS; Smith, WC (2007) A scale to assess the severity of leprosy reactions. Leprosy review, 78 (2). pp. 161-4. ISSN 0305-7518 Downloaded from: http://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/7152/
A new method to promote the quality of life based on spiritual wellbeing in health care workers: A predictive model
 A new method to promote the quality of life based on spiritual wellbeing in health care workers: A predictive model SArash Ackabery Iranian Research Center on Healthy Aging, Sabzevar University of Medical
A new method to promote the quality of life based on spiritual wellbeing in health care workers: A predictive model SArash Ackabery Iranian Research Center on Healthy Aging, Sabzevar University of Medical
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 05 Page May 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.22 Clinical profile of Leprosy Patients who
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.22 Clinical profile of Leprosy Patients who
The effects of self-care training on quality of life in patients with multiple sclerosis
 Original Article The effects of self-care training on quality of life in patients with multiple sclerosis Mohammad Sahebalzamani 1, Maryam Zamiri 2, Farnoosh Rashvand 3 ABSTRACT Background: Multiple sclerosis
Original Article The effects of self-care training on quality of life in patients with multiple sclerosis Mohammad Sahebalzamani 1, Maryam Zamiri 2, Farnoosh Rashvand 3 ABSTRACT Background: Multiple sclerosis
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
 CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY Research design is the structure of any scientific work. It gives direction and systematizes the research. It ensures that the evidence obtained enables us to answer the
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY Research design is the structure of any scientific work. It gives direction and systematizes the research. It ensures that the evidence obtained enables us to answer the
Downloaded from irje.tums.ac.ir at 0:43 IRST on Sunday January 6th 2019
 .66-74 :4 9 1392 5 4 3 2 1 1 MPH 2 MPH 4 5 zaeri.sima@yahoo.com : 021-22439936: :. :.. 60 287 92/3/4 : 91/3/18 :. :.. 100 0.. SPSS 16.0 58/41 ( ) :. 82/42 59/53 13/53. : 687 2006 2050 923 153 968 60.(5).(7
.66-74 :4 9 1392 5 4 3 2 1 1 MPH 2 MPH 4 5 zaeri.sima@yahoo.com : 021-22439936: :. :.. 60 287 92/3/4 : 91/3/18 :. :.. 100 0.. SPSS 16.0 58/41 ( ) :. 82/42 59/53 13/53. : 687 2006 2050 923 153 968 60.(5).(7
Investigation of Relationship between "Self-Esteem and Assertiveness" and "Employees' Performance" in National Iranian Bank Branches in Tonekabon city
 J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci., ()8-87, 0 0, TextRoad Publication ISSN: 090-7 Journal of Applied Environmental and Biological Sciences www.textroad.com Investigation of Relationship between "Self-Esteem
J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci., ()8-87, 0 0, TextRoad Publication ISSN: 090-7 Journal of Applied Environmental and Biological Sciences www.textroad.com Investigation of Relationship between "Self-Esteem
The People Living With HIV Stigma Index: South Africa 2014
 The People Living With HIV Stigma Index: South Africa 2014 A Cloete 1, Leickness Simbayi 1, K Zuma 1, S Jooste 1, S Blose 1, S Zimela 1,N Mathabathe 2, D Pelisa 3, & The South Africa PLHIV HIV Stigma Index
The People Living With HIV Stigma Index: South Africa 2014 A Cloete 1, Leickness Simbayi 1, K Zuma 1, S Jooste 1, S Blose 1, S Zimela 1,N Mathabathe 2, D Pelisa 3, & The South Africa PLHIV HIV Stigma Index
Quality of Life in Children with Β-Thalassemia Major at Center for Special Diseases
 Original Article Quality of Life in Children with Β-Thalassemia Major at Center for Special Diseases Downloaded from ijpho.ssu.ac.ir at 3:46 IRST on Wednesday January 2nd 2019 Kaheni S MSc 1, Yaghobian
Original Article Quality of Life in Children with Β-Thalassemia Major at Center for Special Diseases Downloaded from ijpho.ssu.ac.ir at 3:46 IRST on Wednesday January 2nd 2019 Kaheni S MSc 1, Yaghobian
Assessment of sexual function by DSFI among the Iranian married individuals
 Basic Research Journal of Medicine and Clinical Sciences ISSN 2315-6864 Vol. 4(2) pp. 68-74 February 2015 Available online http//www.basicresearchjournals.org Copyright 2015 Basic Research Journal Full
Basic Research Journal of Medicine and Clinical Sciences ISSN 2315-6864 Vol. 4(2) pp. 68-74 February 2015 Available online http//www.basicresearchjournals.org Copyright 2015 Basic Research Journal Full
Health Related Quality of Life, Anxiety and Depression among Tuberculosis Patients in Kathmandu, Nepal Devkota J* 1,3, Devkota N 2, Lohani SP 1
 Research Article JMCJMS Health Related Quality of Life, Anxiety and Depression among Tuberculosis Patients in Kathmandu, Nepal Devkota J* 1,3, Devkota N 2, Lohani SP 1 Department of Public Health, Nobel
Research Article JMCJMS Health Related Quality of Life, Anxiety and Depression among Tuberculosis Patients in Kathmandu, Nepal Devkota J* 1,3, Devkota N 2, Lohani SP 1 Department of Public Health, Nobel
Quality of life factors affecting quality of life in people living with HIV/AIDS in an urban area
 International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Jadhav PS et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Aug;4(8):3031-3036 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Jadhav PS et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Aug;4(8):3031-3036 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
PREDICTORS OF QUALITY OF LIFE IN HIV INFECTED WOMEN, MEDAN, INDONESIA
 Original Research Article S31 PREDICTORS OF QUALITY OF LIFE IN HIV INFECTED WOMEN, MEDAN, INDONESIA Siska Evi Martina 1,*, Sunanta Thongpat 2, Pornruedee Nitirat 3 1 Sint Carolus School of Health Sciences,
Original Research Article S31 PREDICTORS OF QUALITY OF LIFE IN HIV INFECTED WOMEN, MEDAN, INDONESIA Siska Evi Martina 1,*, Sunanta Thongpat 2, Pornruedee Nitirat 3 1 Sint Carolus School of Health Sciences,
Out of the silos: identifying cross-cutting features of health-related stigma to advance measurement and intervention
 Brakel et al. BMC Medicine (2019) 17:13 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-018-1245-x Collection on: Stigma Research and Global Health OPINION Open Access Out of the silos: identifying cross-cutting features
Brakel et al. BMC Medicine (2019) 17:13 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-018-1245-x Collection on: Stigma Research and Global Health OPINION Open Access Out of the silos: identifying cross-cutting features
Help-seeking behaviour and its impact on patients attending a psychiatry clinic at National Hospital of Sri Lanka
 Help-seeking behaviour and its impact on patients attending a psychiatry clinic at National Hospital of Sri Lanka DM Gomez, C Gunarathna, S Gunarathna, K Gnanapragasam, R Hanwella Abstract Background Mental
Help-seeking behaviour and its impact on patients attending a psychiatry clinic at National Hospital of Sri Lanka DM Gomez, C Gunarathna, S Gunarathna, K Gnanapragasam, R Hanwella Abstract Background Mental
Test-Retest Reliability of the Screening Activity Limitation and Safety Awareness (SALSA) Scale in North-West Nigeria
 Lepr Rev (2009) 80, 197 204 Test-Retest Reliability of the Screening Activity Limitation and Safety Awareness (SALSA) Scale in North-West Nigeria JANNINE EBENSO & JOHAN P. VELEMA The Leprosy Mission International,
Lepr Rev (2009) 80, 197 204 Test-Retest Reliability of the Screening Activity Limitation and Safety Awareness (SALSA) Scale in North-West Nigeria JANNINE EBENSO & JOHAN P. VELEMA The Leprosy Mission International,
QUALITY OF LIFE OF MOTHERS HAVING CHILDREN WITH AUTISTIC SPECTRUM DISORDERS AND LEARNING DISABILITIES
 QUALITY OF LIFE OF MOTHERS HAVING CHILDREN WITH AUTISTIC SPECTRUM DISORDERS AND LEARNING DISABILITIES MOHD. FAIJULLAH KHAN 1, M. KHYOTHUNGLO HUMTSOE 2 1 Department of Teacher Training and Non Formal Education,
QUALITY OF LIFE OF MOTHERS HAVING CHILDREN WITH AUTISTIC SPECTRUM DISORDERS AND LEARNING DISABILITIES MOHD. FAIJULLAH KHAN 1, M. KHYOTHUNGLO HUMTSOE 2 1 Department of Teacher Training and Non Formal Education,
Application of World Health Organization Quality of Life Instrument, Short Form (WHOQOL-BREF) in measuring quality of life in patients with cataract
 Application of World Health Organization Quality of Life Instrument, Short Form (WHOQOL-BREF) in measuring quality of life in patients with cataract Ali Gholami 1, 2, Mahmood Tavakoli Araghi 3, Fatemeh
Application of World Health Organization Quality of Life Instrument, Short Form (WHOQOL-BREF) in measuring quality of life in patients with cataract Ali Gholami 1, 2, Mahmood Tavakoli Araghi 3, Fatemeh
Predisposing Factors of Post-natal Depression
 Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 4 [9] August 2015: 07-14 2015 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 4 [9] August 2015: 07-14 2015 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
Prevalence of mental morbidities among the slum dwellers of Kolkata, West Bengal
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 79-0853, p-issn: 79-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. III (Jan. 16), PP 44-48 www.iosrjournals.org Prevalence of mental morbidities among the
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 79-0853, p-issn: 79-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. III (Jan. 16), PP 44-48 www.iosrjournals.org Prevalence of mental morbidities among the
Clinical Study Pain and Its Consequences in Quality of Life: A Study with WHOQOL-Bref in Leprosy Patients with Neuropathic Pain
 ISRN Tropical Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 987683, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/987683 Clinical Study Pain and Its Consequences in Quality of Life: A Study with WHOQOL-Bref in Leprosy Patients
ISRN Tropical Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 987683, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/987683 Clinical Study Pain and Its Consequences in Quality of Life: A Study with WHOQOL-Bref in Leprosy Patients
Advances in Environmental Biology
 AENSI Journals Advances in Environmental Biology ISSN-1995-0756 EISSN-1998-1066 Journal home page: http://www.aensiweb.com/aeb/ A survey of the relationship between EQ and resilience among married students
AENSI Journals Advances in Environmental Biology ISSN-1995-0756 EISSN-1998-1066 Journal home page: http://www.aensiweb.com/aeb/ A survey of the relationship between EQ and resilience among married students
The Impact of Premenstrual Disorders on Healthrelated Quality of Life (HRQOL)
 The Impact of Premenstrual Disorders on Healthrelated Quality of Life (HRQOL) Fahime Maleki 1, Abbas Pourshahbaz 2 *, Abbasali Asadi 4, Afsane Yoosefi 4 1. Clinical Psychology Department, University of
The Impact of Premenstrual Disorders on Healthrelated Quality of Life (HRQOL) Fahime Maleki 1, Abbas Pourshahbaz 2 *, Abbasali Asadi 4, Afsane Yoosefi 4 1. Clinical Psychology Department, University of
20 TH APRIL 2012 AT SILVER SPRING HOTEL NAIROBI
 Post Leprosy Elimination and Reemergence of Leprosy in HIV/AIDS Era: Where have we reached, what needs to be done to reach the desired goal; a Kenya without Leprosy 20 TH APRIL 2012 AT SILVER SPRING HOTEL
Post Leprosy Elimination and Reemergence of Leprosy in HIV/AIDS Era: Where have we reached, what needs to be done to reach the desired goal; a Kenya without Leprosy 20 TH APRIL 2012 AT SILVER SPRING HOTEL
Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis Scale (QOL-RA Scale)
 Advances in Medical Sciences Vol. 54(1) 2009 pp 27-31 DOI: 10.2478/v10039-009-0012-9 Medical University of Bialystok, Poland Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis
Advances in Medical Sciences Vol. 54(1) 2009 pp 27-31 DOI: 10.2478/v10039-009-0012-9 Medical University of Bialystok, Poland Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis
Results. Variables N = 100 (%) Variables N = 100 (%)
 ht t p: / / doi. or g/ 10. 4038/ s l j ps yc. v8i 2. 8157 Stigma experienced by persons diagnosed to have a mental illness turn to see the doctor in the clinic. Participants were invited to complete the
ht t p: / / doi. or g/ 10. 4038/ s l j ps yc. v8i 2. 8157 Stigma experienced by persons diagnosed to have a mental illness turn to see the doctor in the clinic. Participants were invited to complete the
Karl Peltzer Nancy Phaswana-Mafuya
 Health-related quality of life in a sample of HIV-infected South Africans International Conference on Health Promotion and Quality of Health Services in Bangkok, 20 Nov 08 Karl Peltzer Nancy Phaswana-Mafuya
Health-related quality of life in a sample of HIV-infected South Africans International Conference on Health Promotion and Quality of Health Services in Bangkok, 20 Nov 08 Karl Peltzer Nancy Phaswana-Mafuya
ELDER ABUSE IN SAVOJBOLAGH - IRAN
 Pharmacophore, 8(6S) 2017, Pages: 01-09 Pharmacophore ISSN-2229-5402 Journal home page: http://www.pharmacophorejournal.com ELDER ABUSE IN SAVOJBOLAGH - IRAN Shahrbanoo Ghahari 1,2, Maryam Yekefallah 3*
Pharmacophore, 8(6S) 2017, Pages: 01-09 Pharmacophore ISSN-2229-5402 Journal home page: http://www.pharmacophorejournal.com ELDER ABUSE IN SAVOJBOLAGH - IRAN Shahrbanoo Ghahari 1,2, Maryam Yekefallah 3*
By Sahreen Bhanji MScN, BScN (Aga Khan University School of Nursing and Midwifery) Senior Lecturer (Liaquat National College of Nursing) 12/21/2015 1
 By Sahreen Bhanji MScN, BScN (Aga Khan University School of Nursing and Midwifery) Senior Lecturer (Liaquat National College of Nursing) 12/21/2015 1 Disclosure This study was carried out as part of the
By Sahreen Bhanji MScN, BScN (Aga Khan University School of Nursing and Midwifery) Senior Lecturer (Liaquat National College of Nursing) 12/21/2015 1 Disclosure This study was carried out as part of the
Katayoon Razjouyan, M.D.
 Katayoon Razjouyan, M.D. Personal Information General Female Email: k_razjouyan@sbmu.ac.ir Work Address: Shahid Madani street Imam Hossein Hospital Child Psychiatry Department Occupation Child and Adolescent
Katayoon Razjouyan, M.D. Personal Information General Female Email: k_razjouyan@sbmu.ac.ir Work Address: Shahid Madani street Imam Hossein Hospital Child Psychiatry Department Occupation Child and Adolescent
Introduction. Abodulaziz Aflakseir 1*, Azam Farmani 2
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Exploring Illness Causal Beliefs and its Relationship with Medication Adherence and Demographic Characteristics among a Sample of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Isfahan-Iran Abodulaziz
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Exploring Illness Causal Beliefs and its Relationship with Medication Adherence and Demographic Characteristics among a Sample of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Isfahan-Iran Abodulaziz
Tzu-Ting Wang, MSN, RN 1 Su-Chen Lo, MSN, RN 2 Chiu-Yi Lin, BSN, RN 3 Chiu-Yueh Yang, PhD, RN 3
 Tzu-Ting Wang, MSN, RN 1 Su-Chen Lo, MSN, RN 2 Chiu-Yi Lin, BSN, RN 3 Chiu-Yueh Yang, PhD, RN 3 (1)Department of Nursing, Cardinal Tien College of Healthcare & Management, New Taipei, Taiwan (2)Bali Psychiatric
Tzu-Ting Wang, MSN, RN 1 Su-Chen Lo, MSN, RN 2 Chiu-Yi Lin, BSN, RN 3 Chiu-Yueh Yang, PhD, RN 3 (1)Department of Nursing, Cardinal Tien College of Healthcare & Management, New Taipei, Taiwan (2)Bali Psychiatric
DETERMINANTS OF QUALITY OF LIFE AMONG PEOPLE LIVING WITH HIV/AIDS: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY IN CENTRAL KARNATAKA, INDIA
 DETERMINANTS OF QUALITY OF LIFE AMONG PEOPLE LIVING WITH HIV/AIDS: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY IN CENTRAL KARNATAKA, INDIA Aswin Kumar 1, HO Girish 2, Ayesha S Nawaz 1, PS Balu 3, B Vijay Kumar 4 1 Department
DETERMINANTS OF QUALITY OF LIFE AMONG PEOPLE LIVING WITH HIV/AIDS: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY IN CENTRAL KARNATAKA, INDIA Aswin Kumar 1, HO Girish 2, Ayesha S Nawaz 1, PS Balu 3, B Vijay Kumar 4 1 Department
King s Research Portal
 King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1080/13548506.2011.555945 Document Version Early version, also known as pre-print Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA):
King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1080/13548506.2011.555945 Document Version Early version, also known as pre-print Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA):
Factors associated with treatment lag in mental health care
 Buckshey award Factors associated with treatment lag in mental health care Rohit Garg, Ajeet Sidana, Bir Singh Chavan Abstract Background: Despite the substantial distress and impairment caused by mental
Buckshey award Factors associated with treatment lag in mental health care Rohit Garg, Ajeet Sidana, Bir Singh Chavan Abstract Background: Despite the substantial distress and impairment caused by mental
Original Research Article
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, Vol-, No, Jul-Sept Effectiveness of Structured Teaching Programme on Knowledge regarding Risk factors and Prevention of Suicidal Behaviour among Adolescents
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, Vol-, No, Jul-Sept Effectiveness of Structured Teaching Programme on Knowledge regarding Risk factors and Prevention of Suicidal Behaviour among Adolescents
Relapse in MB leprosy patients treated with 24 months of MDT in South West China: a short report
 Lepr Rev (2006) 77, 219 224 Relapse in MB leprosy patients treated with 24 months of MDT in South West China: a short report JIANPING SHEN*, MUSANG LIU*, JIANHUA ZHANG**, WENYI SU*** & GUOXING DING þ *Department
Lepr Rev (2006) 77, 219 224 Relapse in MB leprosy patients treated with 24 months of MDT in South West China: a short report JIANPING SHEN*, MUSANG LIU*, JIANHUA ZHANG**, WENYI SU*** & GUOXING DING þ *Department
Fit to play but goalless: Labour market outcomes in a cohort of public sector ART patients in Free State province, South Africa
 Fit to play but goalless: Labour market outcomes in a cohort of public sector ART patients in Free State province, South Africa Frikkie Booysen Department of Economics / Centre for Health Systems Research
Fit to play but goalless: Labour market outcomes in a cohort of public sector ART patients in Free State province, South Africa Frikkie Booysen Department of Economics / Centre for Health Systems Research
Katayoon Razjouyan, M.D.
 Katayoon Razjouyan, M.D. Personal Information General Female Email: k_razjouyan@sbmu.ac.ir Work Address: Shahid Madani street Imam Hossein Hospital Child Psychiatry Department Occupation Child and Adolescent
Katayoon Razjouyan, M.D. Personal Information General Female Email: k_razjouyan@sbmu.ac.ir Work Address: Shahid Madani street Imam Hossein Hospital Child Psychiatry Department Occupation Child and Adolescent
Family motivation card: An innovative tool for increasing case detection in a resource poor setting
 Lepr Rev (2015) 86, 170 175 Family motivation card: An innovative tool for increasing case detection in a resource poor setting TANMAY PADHI* & SWETALINA PRADHAN* *Veer Surendra Sai Medical College, Burla,
Lepr Rev (2015) 86, 170 175 Family motivation card: An innovative tool for increasing case detection in a resource poor setting TANMAY PADHI* & SWETALINA PRADHAN* *Veer Surendra Sai Medical College, Burla,
Available online at ISSN No:
 Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 12:302-306 The Effect of Stress Coping Skills Training on Family Functioning
Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 12:302-306 The Effect of Stress Coping Skills Training on Family Functioning
SOCIAL SUPPORT FOR MEDICATION ADHERENCE AMONG THAI PEOPLE WITH POST-ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION: FACTOR ANALYSIS
 Original Research Article 1 SOCIAL SUPPORT FOR MEDICATION ADHERENCE AMONG THAI PEOPLE WITH POST-ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION: FACTOR ANALYSIS Rapin Polsook *, Yupin Aungsuroch, Sureeporn Thanasilp Faculty
Original Research Article 1 SOCIAL SUPPORT FOR MEDICATION ADHERENCE AMONG THAI PEOPLE WITH POST-ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION: FACTOR ANALYSIS Rapin Polsook *, Yupin Aungsuroch, Sureeporn Thanasilp Faculty
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005
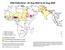 Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
The Effectiveness of Hypnotherapy to Increase Self-esteem of Patients Treated with Methadone
 International Journal of Basic Sciences & Applied Research. Vol., 4 (11), 682-687, 2015 Available online at http://www.isicenter.org ISSN 2147-3749 2015 The Effectiveness of Hypnotherapy to Increase Self-esteem
International Journal of Basic Sciences & Applied Research. Vol., 4 (11), 682-687, 2015 Available online at http://www.isicenter.org ISSN 2147-3749 2015 The Effectiveness of Hypnotherapy to Increase Self-esteem
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LIFE SATISFACTION AND ATTACHMENT STYLES WITH PSYCHOLOGICAL WELL-BEING OF CHILDREN ON COVERED BY BEHZISTEY IN TEHRAN
 THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LIFE SATISFACTION AND ATTACHMENT STYLES WITH PSYCHOLOGICAL WELL-BEING OF CHILDREN ON COVERED BY BEHZISTEY IN TEHRAN *Masomeh Azimi Qadeyklaey and Farideh Dokaneheei Fard Department
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LIFE SATISFACTION AND ATTACHMENT STYLES WITH PSYCHOLOGICAL WELL-BEING OF CHILDREN ON COVERED BY BEHZISTEY IN TEHRAN *Masomeh Azimi Qadeyklaey and Farideh Dokaneheei Fard Department
Relationship between Demographic Factors, Stage of Disease and Adherence among HIV/AIDS Patients Receiving Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy
 Relationship between Demographic Factors, Stage of Disease and Adherence among HIV/AIDS Patients Receiving Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy Chongthawonsatid S, Ruansawang P, Prasithsirikul W, et al
Relationship between Demographic Factors, Stage of Disease and Adherence among HIV/AIDS Patients Receiving Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy Chongthawonsatid S, Ruansawang P, Prasithsirikul W, et al
GENERAL PROFILE AND SURVIVAL PROBABILITIES OF HIV PATIENTS REGISTERED AT ANTI RETROVIRAL THERAPY CENTRE, NEW CIVIL HOSPITAL, SURAT, GUJARAT
 Original article GENERAL PROFILE AND SURVIVAL PROBABILITIES OF HIV PATIENTS REGISTERED AT ANTI RETROVIRAL THERAPY CENTRE, NEW CIVIL HOSPITAL, SURAT, GUJARAT Sridhar P Ryavanki 1, J K Kosambiya 2, Alap
Original article GENERAL PROFILE AND SURVIVAL PROBABILITIES OF HIV PATIENTS REGISTERED AT ANTI RETROVIRAL THERAPY CENTRE, NEW CIVIL HOSPITAL, SURAT, GUJARAT Sridhar P Ryavanki 1, J K Kosambiya 2, Alap
Quality of life among the geriatric population in a rural area of Dakshina Kannada, Karnataka, India
 GLOBAL JOURNAL OF MEDICINE AND PUBLIC HEALTH Quality of life among the geriatric population in a rural area of Dakshina Kannada, Karnataka, India Shahul Hameed 1*, Krutarth R Brahmbhatt 2, Dipak C Patil
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF MEDICINE AND PUBLIC HEALTH Quality of life among the geriatric population in a rural area of Dakshina Kannada, Karnataka, India Shahul Hameed 1*, Krutarth R Brahmbhatt 2, Dipak C Patil
(Received 25 Jun 2016; accepted 14 Oct 2016) Keywords: Quality of life (QOL), Human development index (HDI), General population, Meta-analysis
 Review Article Quality of Life among General Populations of Different Countries in the Past 10 Years, with a Focus on Human Development Index: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Fatemeh KOOHI 1, *Saharnaz
Review Article Quality of Life among General Populations of Different Countries in the Past 10 Years, with a Focus on Human Development Index: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Fatemeh KOOHI 1, *Saharnaz
Recent Interventions to Reduce Stigma & Discrimination in Nigeria
 Recent Interventions to Reduce Stigma & Discrimination in Nigeria By ENR 04/05/2015 # Background Nigeria has developed initiatives to reduce stigma and discrimination at national or local settings Community
Recent Interventions to Reduce Stigma & Discrimination in Nigeria By ENR 04/05/2015 # Background Nigeria has developed initiatives to reduce stigma and discrimination at national or local settings Community
BRIEF REPORTS KNOWLEDGE AND ATTITUDE OF NIGERIAN PHYSIOTHERAPY STUDENTS ABOUT LEPROSY
 BRIEF REPORTS Asia Pacific Disability Rehabilitation Journal KNOWLEDGE AND ATTITUDE OF NIGERIAN PHYSIOTHERAPY STUDENTS ABOUT LEPROSY Fidelis T. Iyor* ABSTRACT Knowledge and attitude about leprosy was evaluated
BRIEF REPORTS Asia Pacific Disability Rehabilitation Journal KNOWLEDGE AND ATTITUDE OF NIGERIAN PHYSIOTHERAPY STUDENTS ABOUT LEPROSY Fidelis T. Iyor* ABSTRACT Knowledge and attitude about leprosy was evaluated
Study on Level of Depression among Elderly Residing in an Old Age. Home in Hyderabad, Telangana
 The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 1, No.6, DIP: C00393V3I12015 http://www.ijip.in October December, 2015 Study on Level of Depression
The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 1, No.6, DIP: C00393V3I12015 http://www.ijip.in October December, 2015 Study on Level of Depression
Occurrence and management of leprosy reaction in China in 2005
 Lepr Rev (2009) 80, 164 169 Occurrence and management of leprosy reaction in China in 2005 JIANPING SHEN, MUSANG LIU, MIN ZHOU & LI WENGZHONG Department of Leprosy Field Control, Institute of Dermatology,
Lepr Rev (2009) 80, 164 169 Occurrence and management of leprosy reaction in China in 2005 JIANPING SHEN, MUSANG LIU, MIN ZHOU & LI WENGZHONG Department of Leprosy Field Control, Institute of Dermatology,
Last Updated: February 17, 2016 Articles up-to-date as of: July 2015
 Reviewer ID: Mohit Singh, Nicole Elfring, Brodie Sakakibara, John Zhu, Jeremy Mak Type of Outcome Measure: SF-36 Total articles: 14 Author ID Study Design Setting Population (sample size, age) and Group
Reviewer ID: Mohit Singh, Nicole Elfring, Brodie Sakakibara, John Zhu, Jeremy Mak Type of Outcome Measure: SF-36 Total articles: 14 Author ID Study Design Setting Population (sample size, age) and Group
Perceptions & Predictors of Inequality among Afghan & Pakistani Women
 Perceptions & Predictors of Inequality among Afghan & Pakistani Women Stephen R. Shamblen Melissa H. Abadi Stacey Frank Kirsten Thompson Pacific Institute for Research and Evaluation www.pire.org Paper
Perceptions & Predictors of Inequality among Afghan & Pakistani Women Stephen R. Shamblen Melissa H. Abadi Stacey Frank Kirsten Thompson Pacific Institute for Research and Evaluation www.pire.org Paper
Assessment of Quality of Life among HIV Positive People Attending Tertiary Hospital of Delhi, India
 J. Commun. Dis. 41 (2) 2009 : 101-108 Assessment of Quality of Life among HIV Positive People Attending Tertiary Hospital of Delhi, India Marashi T*, Garg S*, Gupta VK*, Singh MM*, Sinha Pragya*, Dewan
J. Commun. Dis. 41 (2) 2009 : 101-108 Assessment of Quality of Life among HIV Positive People Attending Tertiary Hospital of Delhi, India Marashi T*, Garg S*, Gupta VK*, Singh MM*, Sinha Pragya*, Dewan
Evaluating the Greek Version of Religious Commitment Inventory-10 on a Sample of Pomak Households
 (Volume 12, Issue 2/2016), pp. 5-11 Evaluating the Greek Version of Religious Commitment Inventory-10 on a Sample of Pomak Households Nikolaos Satsios 1+ 1 University of Nicosia, Cyprus Abstract. The aim
(Volume 12, Issue 2/2016), pp. 5-11 Evaluating the Greek Version of Religious Commitment Inventory-10 on a Sample of Pomak Households Nikolaos Satsios 1+ 1 University of Nicosia, Cyprus Abstract. The aim
SOCIO-DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS AFFECTING THE TREATMENT OUTCOME IN PATIENTS OF TUBERCULOSIS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 0976 3325 eissn 2229 6816 Open Access Article www.njcmindia.org SOCIO-DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS AFFECTING THE TREATMENT OUTCOME IN PATIENTS OF TUBERCULOSIS Pooja Sadana 1, Tejbir Singh
ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 0976 3325 eissn 2229 6816 Open Access Article www.njcmindia.org SOCIO-DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS AFFECTING THE TREATMENT OUTCOME IN PATIENTS OF TUBERCULOSIS Pooja Sadana 1, Tejbir Singh
The Study of Relationship between the Awareness Level of Management Tasks with Self-efficacy in Sport Managers of Isfahan City
 The Study of Relationship between the Awareness Level of Management Tasks with Self-efficacy in Sport Managers of Isfahan City Mohammadjavad GHAZAEI 1, Mohammad KHAKI 2, Somayyeh NADERI, Saeed SHAMS 4
The Study of Relationship between the Awareness Level of Management Tasks with Self-efficacy in Sport Managers of Isfahan City Mohammadjavad GHAZAEI 1, Mohammad KHAKI 2, Somayyeh NADERI, Saeed SHAMS 4
SELECTED EPIDEMIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY AT TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN MAHARASHTRA
 Original Article SELECTED EPIDEMIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY AT TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN MAHARASHTRA Madhura D Ashturkar 1, Jaggnath V Dixit 2 Financial Support: None declared
Original Article SELECTED EPIDEMIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY AT TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN MAHARASHTRA Madhura D Ashturkar 1, Jaggnath V Dixit 2 Financial Support: None declared
HBsAg PREVALENCE AND KNOWLEDGE ON HEPATITIS B AMONG STIENG TRIBE ADULTS IN BINH PHUOC PROVINCE, VIETNAM
 Original Article 123 HBsAg PREVALENCE AND KNOWLEDGE ON HEPATITIS B AMONG STIENG TRIBE ADULTS IN BINH PHUOC PROVINCE, VIETNAM Ai Thien Nhan Lam, Khemika Yamarat *, Robert Sedgwick Chapman College of Public
Original Article 123 HBsAg PREVALENCE AND KNOWLEDGE ON HEPATITIS B AMONG STIENG TRIBE ADULTS IN BINH PHUOC PROVINCE, VIETNAM Ai Thien Nhan Lam, Khemika Yamarat *, Robert Sedgwick Chapman College of Public
Internet Journal of Medical Update
 Internet Journal of Medical Update 2012 January;7(1):47-51 Internet Journal of Medical Update Journal home page: http://www.akspublication.com/ijmu Original Work CIFKAS A Measurer of Functional Disability
Internet Journal of Medical Update 2012 January;7(1):47-51 Internet Journal of Medical Update Journal home page: http://www.akspublication.com/ijmu Original Work CIFKAS A Measurer of Functional Disability
Effect of Instructional Module on Drug Adherence in Terms of Attitude among Patients with Schizophrenia
 Original Article NUJHS Vol. 6, No.1, March 2016, ISSN 2249-7110 Effect of Instructional Module on Drug Adherence in Terms of Attitude among Patients with Schizophrenia 1 S. Mary Metilda, S. Santhi² & G.
Original Article NUJHS Vol. 6, No.1, March 2016, ISSN 2249-7110 Effect of Instructional Module on Drug Adherence in Terms of Attitude among Patients with Schizophrenia 1 S. Mary Metilda, S. Santhi² & G.
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Mozhgan Patoo 1 *, Abbas Ali Allahyari 1 Ali Reza Moradi 2, Mehrdad Payandeh 3. Abstract. Introduction
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.9.3799 RESEARCH ARTICLE Persian Version of Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy- Breast (FACT-B) Scale: Confirmatory Factor Analysis and Psychometric Properties
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.9.3799 RESEARCH ARTICLE Persian Version of Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy- Breast (FACT-B) Scale: Confirmatory Factor Analysis and Psychometric Properties
DEPRESSION AMONG RURAL ELDERLY POPULATION
 DEPRESSION AMONG RURAL ELDERLY POPULATION Mr. Sharad V. Dighe Lecturer, PIMS (DU), CON, Loni Mr. Eknath M. Gawade Lecturer, PIMS (DU), CON, Loni Abstract Statement: A study to assess the depression among
DEPRESSION AMONG RURAL ELDERLY POPULATION Mr. Sharad V. Dighe Lecturer, PIMS (DU), CON, Loni Mr. Eknath M. Gawade Lecturer, PIMS (DU), CON, Loni Abstract Statement: A study to assess the depression among
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Effectiveness of Structured Teaching Programme on Knowledge and Attitude Regarding Early Detection
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Effectiveness of Structured Teaching Programme on Knowledge and Attitude Regarding Early Detection
A RANDOMISED CONTROLLED TRIAL OF CONQUER FEAR DELIVERED IN A GROUP FORMAT
 A RANDOMISED CONTROLLED TRIAL OF CONQUER FEAR DELIVERED IN A GROUP FORMAT Nina Moeller Tauber, MSc. in psychology and Ph.D. fellow 1, Professor Robert Bobby Zachariae 1, Associate Professor Mia Skytte
A RANDOMISED CONTROLLED TRIAL OF CONQUER FEAR DELIVERED IN A GROUP FORMAT Nina Moeller Tauber, MSc. in psychology and Ph.D. fellow 1, Professor Robert Bobby Zachariae 1, Associate Professor Mia Skytte
Prevalence and Associated Factors of Depression among Elderly Population Living in Geriatric Homes in Kathmandu Valley
 39 Prevalence and Associated Factors of Depression among Elderly Population Living in Geriatric Homes in Kathmandu Valley Choulagai P S, Sharma C K, Choulagai B P Tribhuvan University, Institute of Medicine,
39 Prevalence and Associated Factors of Depression among Elderly Population Living in Geriatric Homes in Kathmandu Valley Choulagai P S, Sharma C K, Choulagai B P Tribhuvan University, Institute of Medicine,
Coping Repertoire in Caregivers of Schizophrenic Patients: An Indian Study
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn: 2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 9, Issue 5 Ver. IV (Sep -Oct. 2014), PP 37-41 Coping Repertoire in Caregivers of Schizophrenic Patients:
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn: 2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 9, Issue 5 Ver. IV (Sep -Oct. 2014), PP 37-41 Coping Repertoire in Caregivers of Schizophrenic Patients:
Validity and reliability of physical education teachers' beliefs and intentions toward teaching students with disabilities (TBITSD) questionnaire
 Advances in Environmental Biology, 7(11) Oct 201, Pages: 469-47 AENSI Journals Advances in Environmental Biology Journal home page: http://www.aensiweb.com/aeb.html Validity and reliability of physical
Advances in Environmental Biology, 7(11) Oct 201, Pages: 469-47 AENSI Journals Advances in Environmental Biology Journal home page: http://www.aensiweb.com/aeb.html Validity and reliability of physical
Health related quality of life and antiretroviral treatment in patients over a period of 20 months in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
 Health related quality of life and antiretroviral treatment in patients over a period of 20 months in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa Karl Peltzer, HIV/AIDS/SIT & TB (HAST Research programmes Background African
Health related quality of life and antiretroviral treatment in patients over a period of 20 months in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa Karl Peltzer, HIV/AIDS/SIT & TB (HAST Research programmes Background African
Methodology Introduction of the study Statement of Problem Objective Hypothesis Method
 3.1. Introduction of the study 3.2. Statement of Problem 3.3. Objective 3.4. Hypothesis 3.5. Method 3.5.1. Procedure Sample A.5.2. Variable A.5.3. Research Design A.5.4. Operational Definition Of The Terms
3.1. Introduction of the study 3.2. Statement of Problem 3.3. Objective 3.4. Hypothesis 3.5. Method 3.5.1. Procedure Sample A.5.2. Variable A.5.3. Research Design A.5.4. Operational Definition Of The Terms
Published by: PIONEER RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT GROUP ( 108
 Stress Coping Strategies By It Professionals In South India V. Sreecharan 1, S. Gautami 2, V. Satish Kumar 3 1,2,3 Department of Management Studies, RIIMS, Tirupati, Chittoor(Dist.), Andhra Pradesh ABSTRACT
Stress Coping Strategies By It Professionals In South India V. Sreecharan 1, S. Gautami 2, V. Satish Kumar 3 1,2,3 Department of Management Studies, RIIMS, Tirupati, Chittoor(Dist.), Andhra Pradesh ABSTRACT
Open Access Article pissn eissn
 Original article AN ASSESSMENT OF THE IMPACT OF ONE DAY TRAINING PROGRAMME ON KNOWLEDGE AND ATTITUDE OF UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS ON LEPROSY AT G. R MEDICAL COLLEGE, GWALIOR, MADHYA PRADESH Ranjana Tiwari
Original article AN ASSESSMENT OF THE IMPACT OF ONE DAY TRAINING PROGRAMME ON KNOWLEDGE AND ATTITUDE OF UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS ON LEPROSY AT G. R MEDICAL COLLEGE, GWALIOR, MADHYA PRADESH Ranjana Tiwari
Current management of Leprosy
 Current management of Leprosy Diana NJ Lockwood Department of Infectious and Tropical Diseases London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine Diana.lockwood@lshtm.ac.uk EDCTP Paris Oct 2013 Improving health
Current management of Leprosy Diana NJ Lockwood Department of Infectious and Tropical Diseases London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine Diana.lockwood@lshtm.ac.uk EDCTP Paris Oct 2013 Improving health
HIV in the UK: Changes and Challenges; Actions and Answers The People Living With HIV Stigma Survey UK 2015 London STIGMA SURVEY UK 2015
 HIV in the UK: Changes and Challenges; Actions and Answers The People Living With HIV Stigma Survey UK 2015 London STIGMA SURVEY UK 2015 LONDON The landscape for people living with HIV in the United Kingdom
HIV in the UK: Changes and Challenges; Actions and Answers The People Living With HIV Stigma Survey UK 2015 London STIGMA SURVEY UK 2015 LONDON The landscape for people living with HIV in the United Kingdom
Global, National, Regional
 Epidemiology of TB: Global, National, Regional September 13, 211 Edward Zuroweste, MD Chief Medical Officer Migrant Clinicians Network Assistant Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Epidemiology
Epidemiology of TB: Global, National, Regional September 13, 211 Edward Zuroweste, MD Chief Medical Officer Migrant Clinicians Network Assistant Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Epidemiology
Stigma Towards Tuberculosis patients in Kassala, Sudan
 Stigma Towards Tuberculosis patients in Kassala, Sudan Khalid F A 1, Frah E AM 2, Osman A 3, Abdlhameed T 3 1.Tuberculosis research center, University of Kassala, Kassala, Sudan 2.Institute of tropical
Stigma Towards Tuberculosis patients in Kassala, Sudan Khalid F A 1, Frah E AM 2, Osman A 3, Abdlhameed T 3 1.Tuberculosis research center, University of Kassala, Kassala, Sudan 2.Institute of tropical
Leprosy. Mycobacteriumleprae
 Leprosy Mycobacteriumleprae Quick Reference Environment: human, mice, nine-banded armadillo Microorganism: Gram + rod Spore former: NO Motile: NO Susceptibility: anyone Communicability: infectious Exposure:
Leprosy Mycobacteriumleprae Quick Reference Environment: human, mice, nine-banded armadillo Microorganism: Gram + rod Spore former: NO Motile: NO Susceptibility: anyone Communicability: infectious Exposure:
Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and General Health
 AENSI Journals Advances in Environmental Biology ISSN-1995-0756 EISSN-1998-1066 Journal home page: http://www.aensiweb.com/aeb.html Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and General Health Alireza
AENSI Journals Advances in Environmental Biology ISSN-1995-0756 EISSN-1998-1066 Journal home page: http://www.aensiweb.com/aeb.html Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and General Health Alireza
Quality Of Life and Self-Esteem among People Living With HIV/AIDS
 The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 4, Issue 2, No. 93, DIP: 18.01.127/20170402 ISBN: 978-1-365-78193-3 http://www.ijip.in January-March, 2017 Quality
The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 4, Issue 2, No. 93, DIP: 18.01.127/20170402 ISBN: 978-1-365-78193-3 http://www.ijip.in January-March, 2017 Quality
