Immunofluorescence in Oral Pathology Part III: Pathology and Immunofluorescent Patterns in Intraepithelial Immunobullous Disorders
|
|
|
- Olivia Rose
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
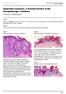
2 /jp-journals Roopa S Rao et al REVIEW ARTICLE Immunofluorescence in Oral Pathology Part III: Pathology and Immunofluorescent Patterns in Intraepithelial Immunobullous Disorders Roopa S Rao, BR Premalatha, Vijaya Mysorekar, Saurabh Juneja ABSTRACT Dermatologic disorders frequently parallel with oral involvement which dental practitioners should be familiar with. In continuation with part II, the immunofluorescence patterns in the intraepidermal pemphigus group and its variants: Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) and paraneoplastic pemphigus (PNP) are dealt in this section. Also, a brief note is added on other mucocutaneous disorders showing similar immunofluorescence patterns. The above listed immunobullous disorders are reviewed in detail with a summary of pathogenesis and characteristic histopathological findings. This review is to facilitate the clinicopathologist in the early diagnosis and subsequent treatment of these debilitating conditions. Keywords: Intraepidermal immunobullous diseases, Immunofluorescence patterns, Oral mucosa. How to cite this article: Rao RS, Premalatha BR, Mysorekar V, Juneja S. Immunofluorescence in Oral Pathology-Part III: Pathology and Immunofluorescent Patterns in Intraepithelial Immunobullous Disorders. World J Dent 2012;3(2): Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None declared INTRODUCTION Immunobullous diseases constitute an important group of dermatological disorders caused by autoantibodies directed against antigens in the intercellular substance or dermoepidermal/epithelial junction resulting in the formation of cutaneous and mucosal blisters. 1 Immunobullous diseases with oral mucosal involvement can be divided into intraepithelial/intraepidermal and subepithelial/subepidermal. The intraepithelial diseases include the pemphigus group and its variants: Pemphigus vulgaris (PV), pemphigus foliaceus (PF), etc. The subepithelial immunobullous group of lesions was discussed in detail in part II of this series. The intraepidermal immunobullous disorders and other mucocutaneous disorders sharing similar immunofluorescence patterns namely lichen planus (LP), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) and erythema multiforme (EM) are dealt in this section. PEMPHIGUS GROUP OF LESIONS It includes a group of chronic mucocutaneous, autoimmune blistering diseases that develop in cycles characterized by intraepithelial blisters histologically, and immunologically, 202 circulating IgG directed against the cell surface of keratinocytes. Pemphigus can be classified into 6 types: pemphigus vulgaris (PV), pemphigus vegetans, pemphigus erythematosus, pemphigus foliaceus (PF), paraneoplastic pemphigus (PNP), and immunoglobulin IgA pemphigus. 2,3 Pemphigus vulgaris is the main variant followed by PNP that usually affects the mouth and precedes skin lesions in most cases. 3 PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS Pemphigus vulgaris is an autoimmune mucocutaneous disorder mediated by circulating autoantibodies directed against keratinocyte cell surfaces. Oral lesions are seen in 90% of patients, usually at an early stage and can precede cutaneous lesions in weeks, months or more than 1 year. Histopathology The histopathological features of PV reflect the action of the circulating antibody on the cell surface of the prickle cells and consequent destruction of the desmosomes termed as acantholysis. This results in the formation of clefts and then blisters or bullae in a predominantly suprabasal location 4-8 (Fig. 1). The acantholytic cells called Tzanck cells are found in the vesicular space (Fig. 2). Sometimes the entire superficial layers of the epithelium are stripped away, leaving only the basal cells forming a row of tomb stones as the basal cells are firmly attached to the basement membrane by hemidesmosomes 5,6,8 (Fig. 3). Fig. 1: Pemphigus vulgaris: H and E stained section at 4 showing a suprabasal blister JAYPEE
3 WJD Immunofluorescence in Oral Pathology-Part III: Pathology and Immunofluorescent Patterns Fig. 2: Pemphigus vulgaris: H and E stained section at 40 showing acantholytic cells in the suprabasal blister Fig. 4: Pemphigus vulgaris: Direct immunofluorescence showing the suprabasal cleavage. Lace-like deposition of IgG is seen in the squamous intercellular spaces in the lower epidermis (Courtesy: Dr HC Mahadeva and Dr Arundati) Fig. 3: Pemphigus vulgaris: H and E stained section at 10x showing dermal papillae (villi) lined by a single layer of preserved basal keratinocytes presenting a row of tomestones appearance A feature that is often helpful diagnostically is the villous projections that may develop at the base of the bulla. When the surface epithelium ultimately separates, the mucosa will appear to have a surface of papillary projections lined by basal cells with some acantholytic cells. Once the bulla ruptures, the underlying connective tissue becomes highly inflammed. The eosinophilic infiltrate often seen in skin occurs infrequently in oral mucosa. 9 Pathogenesis The etiology and pathogenesis of PV are not completely clear. Compelling evidence has accumulated that IgG serum autoantibodies are directed against a cadherin-type cell adhesion molecule in stratified squamous epithelia, called desmoglein 3 and In PV IgG antibodies are directed particularly to desmoglein 3, and since oral epithelium Fig. 5: Pemphigus vulgaris: Direct immunofluorescence showing the suprabasal cleavage. Lace-like deposition of C3 is seen in the squamous intercellular spaces in the lower epidermis (Courtesy: Dr HC Mahadeva and Dr Arundati) expresses largely desmoglein 3, oral lesions appear at an early stage. The presence of antibodies against desmoglein 1 (found in over 50% of cases) may result in cutaneous involvement. Damage to the intercellular area between keratinocytes leads to apoptosis resulting in separation of the keratinocytes, acantholysis (cleavage) and then blistering. 10 This occurs mostly at the level just superficial to basal cells. 5 Antibody binding may activate complement with release of inflammatory mediators and recruitment of activated T cells. 11 Immunofluorescent Patterns and its Significance Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) testing is a very reliable and sensitive diagnostic test for pemphigus vulgaris. IgG or IgM and C3 expression are present in the squamous intercellular/cell surface areas in up to 95% of cases, including early cases and those with very few lesions. World Journal of Dentistry, April-June 2012;3(2):
4 Roopa S Rao et al Intercellular expression of IgG or IgM and C3 are present in up to 100% of cases with active disease. 12 IgG deposits are greater than IgM, IgA and C3. Fluorescence of greatest intensity is seen in the parabasal region. Chicken wire/ fishnet pattern of deposition is noted around spinous cells of the epithelium in intercellular spaces. 1,5,11 Complement component C3 may be seen in a pattern similar to that of IgG, but with lower frequency and intensity. However, the diagnosis of pemphigus should not be made when only C3 is deposited 1 (Figs 4 and 5). Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) may be used to assess disease activity during therapy-induced remission. Negative DIF findings may be a good prognostic indicator when the patient is in remission. 13 Indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) studies during active disease reveal an IgG antibody to the intercellular cement substance of stratified cornified epithelium in almost 90% of cases. 14 The calcium enhancement technique will enhance detection of these antibodies whose titer reflects disease activity. 15,16 A two-fold or greater increase in the titer suggests impending relapse. 17 The absolute titer may be a poorer predictor of clinical status than the trend over some time although very high or absent levels usually correlate with active or inactive disease respectively. 18 Antibodies are predominantly IgG4 subclass. 19 PARANEOPLASTIC PEMPHIGUS Paraneoplastic pemphigus (PNP) is a specific paraneoplastic disorder most commonly associated with lymphomas. 20 Oral mucosal involvement is the earliest feature of PNP. Histopathology: Histology shows suprabasal acantholytic separation, satellite keratinocyte necrosis, basal cell vacuolation, spongiosis and a lymphoid infiltrate at the epithelial-connective tissue interface. 9,21,22 Pathogenesis Patients with PNP develop IgG autoantibodies against multiple antigens. Mainly members of the plakin family, as well as desmogleins, are targeted by IgG autoantibodies in PNP. Antidesmoglein antibodies play a role in inducing the loss of cellular adhesion of keratinocytes and blister formation. The intracellular location of plakin proteins makes them unlikely initial targets. The damage to cell membranes induced by antidesmoglein IgG provides access into the cell for antiplakin autoantibodies; the latter then bind to their target antigens, inhibit their functions, and perhaps precipitate some unique features of PNP, such as dyskeratosis. 23 In addition to the humoral autoimmunity, autoreactive cellular responses mediated by CD8+ cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, natural killer cells, and monocytes/ 204 macrophages appear to be important in the pathogenesis of paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome. 23 Immunofluorescent Patterns and its Significance DIF studies may show weakly positive deposition of immunoreactants IgG and C3 almost invariably in the intercellular substance in perilesional skin and mucosa C3, IgG and IgM may also be deposited along the basement membrane zone. 20,22 However, false-negative DIF is more commonly noticed in PNP than in other forms of pemphigus. 1,5,9,11 Indirect immunofluorescence testing using rat bladder transitional epithelium is highly specific for this disease. 5,9,24,25 Circulating IgG anti-intercellular substance antibodies are almost always present in high titer. 20 In pemphigus, titers of circulating intercellular antibodies can be correlated with disease activity; a twofold rise in titer may indicate an impending relapse. Of the four classes of IgG, IgG1 is the best indicator of disease. 26 Other dermatological conditions sharing similar immunofluorescence patterns like lichen planus (LP) systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) and erythema multiforme (EM) are discussed briefly in this section. LICHEN PLANUS Immunofluorescent Patterns and its Significance Direct IF: The shaggy deposits react with anti-fibrinogen to exhibit intensely positive fluorescnece in the basement membrane zone. 27 Occasionally there are granular deposits of IgM or linear deposits of C3. 28 The colloid apoptotic cells can also be demonstrated. They typically stain for IgM, but staining with IgG, IgA, C3 and fibrin may also be seen. 9 Indirect IF: Negative and can be used to demonstrate lichen planus specific antigen (LPSA), which is expressed in the stratum granulosum and stratum spinosum. LPSA is specific for lichen planus and is found in 80% of patients with and without oral lesions. 26 BULLOUS SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Immunofluorescent Patterns and its Significance Direct IF: IgG and C3 are deposited at the epidermal basement membrane zone. The pattern is linear, but sometimes may be shaggy or granular band-like. A linear rather than granular pattern along the BMZ is associated with the presence of higher titer of circulating auto- JAYPEE
5 WJD Immunofluorescence in Oral Pathology-Part III: Pathology and Immunofluorescent Patterns antibodies. 29,30 IgM and IgA are present in approximately 50 to 60% of cases respectively. In general, granular patterns (60%) represent deposition of circulating immune complexes in situ or in situ binding of antigen and antibody in compartmentalized zones. Similar deposition of IgG, IgM or complement in the normal skin is known as positive lupus band test. 5 Bullous SLE is associated with a higher incidence of IgA deposition (76%) than other forms of SLE (17%) and this may also correlate with renal involvement. 31 C3 is usually deposited in lesional skin. 30 DISCOID LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Immunofluorescent Patterns Direct IF: It is similar to SLE; most cases will demonstrate a granular pattern of IgG, IgM, IgA, C3 and fibrinogen in the basement membrane zone of involved mucosa or skin. 9 But, Ig can never be demonstrated in the uninvolved skin and mucosa in DLE. 11 ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME Immunofluorescent Patterns Direct IF: By DIF, the superficial vessels of the connective tissue are seen to contain IgM and C3 in their walls. At the dermal-epidermal junction, granular deposits of IgM, fibrinogen and C3 may be seen. Circulating immune complexes have also been found. 9 Indirect immunofluorescence is negative for circulating antibodies. CONCLUSION The gist of the entire article regarding antibodies, target antigen, structural target and immunofluorescence pzatterns of pemphigus and its variants and other mucocutaneous disorders sharing similar immunofluorescent patterns has been summarized in Table 1. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We personally thank Dr S Kumar, President, Gokula Education Foundation and Dr Saraswathi Rao, Dean and Table 1: Immunofluorescence findings in intraepithelial immunobullous disorders 26,32 Epidermal bullous diseases Antibodies Target antigen Structural target Immunofluorescence patterns IgG IgM IgA C3 Fibrin Pemphigus group +ve ve ve +ve ve Mucosal PV Desmoglein 3 Desmosomes Ig-Chicken wire/fishnet (130 Kda) pattern Mucocutaneous PV Desmoglein 3 and 1 C3-Chicken wire/ fishnet pattern Paraneoplastic Desmoglein 3 and 1 IgG membrane Pemphigus: PNP Periplakin, fluorescence of Desmoplakin Tzanck cells and envoplakin Other dermal conditions with oral involvement SLE (Ig from +ve +ve ve +ve ve Coarse granularity at uninvolved skin) BMZ DLE (Ig from effected skill) +ve +ve +ve +ve +ve Coarse granularity at BMZ Lichen planus ve ±ve ve ±ve +ve Fibrinogen: Shaggy/ fibrillar pattern C3: Fine granular deposition (not diagnostic) Rarely IgM, IgA, IgG, C3 +ve colloid bodies located in the epithelium and superficial connective tissue Erythema multiforme ve ve ve +ve ve Nondiagnostic IIF: ve IgM: Perivascular deep in connective tissue World Journal of Dentistry, April-June 2012;3(2):
6 Roopa S Rao et al Principal of MS Ramaiah Medical College, Bengaluru for having permitted us to use the facilities available at MSRMC. Photo courtesy: We are greatful to Dr KC Mahadeva, Professor and Head, Department of Pathology, MS Ramaiah Medical College and Dr Arundati, Tutor, Department of Pathology, MSRMC, Bangalore, for having helped us in procuring the photographs. REFERENCES 1. Zahida Rani, Ijaz Hussain. Immunofluorescence in immunobullous diseases. Journal of Pakistan Association of Dermatologists 2003;13: Hashimoto T. Recent advances in the study of the pathophysiology of pemphigus. Arch Dermatol Res 2003;295(Suppl 1): S Robinson JC, Lozada-Nur F, Frieden I. Oral pemphigus vulgaris: A review of the literature and a report on the management of 12 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1997;84: The vesiculobullous reaction pattern. In: Weedon D (Ed): Systemic Pathology. The Skin. (3rd ed). Edinburgh: Churchill- Livingstone 1992;9: Oral and maxillofacial pathology. Neville Damm Allen Bonquot (2nd ed). WB Saunders Company Lever WF. Pemphigus and pemphigoid. Springfield, IL: Charles C Thomas, Tappeiner J, Pfleger L. Pemphigus vulgaris: Dermatitis herpetiformis. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol 1962;214: Rajendran R, Sivapathasundaram B. Shafer s textbook of oral pathology (5th ed). Elsevier, Oral and maxillofacial pathology. Robert E Marx and Diane Stern, Quintessence Publishing Co, inc 2003; Amagai M, Karpati S, Prussick R, et al. Autoantibodies against the amino- terminal cadherin-like binding domain of pemphigus vulgaris antigen are pathogenic. J CLI Invest 1992;90: Cullings cellular pathology technique. CFA Cullings (4th ed), Butterworths Korman NJ, Pemphigus. J Am Acad Dermatol 1988;18: Ratnam KV, Pang BK. Pemphigus in remission: Value of negative direct immunofluorescence in management. J Am Acad Dermatol 1994;30: Fellner MJ, Fukuyama K, Moshell A, Klaus MV. Intercellular antibodies in blood and epidermis. Br J Dermatol 1973;89: Matis WL, Anhalt GJ, Diaz LA, et al. Calcium enhances the sensitivity of immunofluorescence for pemphigus antibodies. J Invest Dermatol 1987;89: Creswell SN, Black MM, Bhogal B, Skeete MVH. Correlation of circulating intercellular antibody titers in pemphigus with disease activity. Clin Exp Dermatol 1981;6: Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP, Jablonska S. Clinical significance of immunofluorescence test of sera and skin in bullous diseases: A cooperative study in immunopathology of the skin (3rd ed). New York: Jhon Wiley & Sons Inc, Krasny SA, Beutner EH, Chrzelski TP. Specificity and sensitivity of indirect and direct immunofluorescent findings in the diagnosis of pemphigus in immunopathology of the skin (3rd ed). New York: Jhon Wiley & Sons Inc, 1987; Wilson CL, Wojnarowska F, Dean D, Pasricha JS. IgG subclasses in pemphigus in Indian and UK populations. Clin Exp Dermatol 1993;18: Anhalt GJ, Kim S, Stanley JR, et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus: An autoimmune mucocutaneous disease associated with neoplasia. N Eng J Med 1990;323: Horn TD, Analt GJ. Histologic features of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Arch Dermatol 1992;128: Mehregan DR, Oursler JR, Leiferman KM, et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus: A subset of patients with pemphigus and neoplasias. J Cut Pathol 1993;20: Nguyen VT, Ndoye A, Bassler KD, et al. Classification, clinical manifestations, and immunological mechanisms of the epithelial variant of paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome: Reappraisal of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Arch Dermatol 2001; 137: Liu AY, Valenzuela R, Helm TN, et al. Indirect immunofluorescence on rat bladder transitinal epithelium: A test with high specificity for paraneoplastic pemphigus. J Am Acad Dermatol 1993;28: Camisa C, Helm TN, Valenzuela R, Korman NJ. Paraneoplastic pemphigus: Three new cases. J Invest Dermatol 1992;98:590 (abstract). 26. Mohan KH, Pai S, Rao R, Sripathi H, Prabhu S. Techniques of immunofluorescence and their significance. Indian J of Dermatol, Venereol and Leprol 2008; 74(4): Mc Whirter JD, Hashimoto K, Fayne S, et al. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis related to lithium carbonate. Arch Dermatol 1987; 123: Van der Meer JB, Remme JJ, Nelkins MJJ, et al. IgA antibasement membrane antibodies in a boy with pemphigoid. Arch Dermatol 1977;113: Burrows NP, Bhogal BS, Black MM, et al. Bullous eruption of systemic lupus erthematosus: A clinicopathological study of four cases. Br J Dermatol 1993;128: Gammon WR, Briggaman RA. Bullous SLE: A phenotypically distinctive but immunologically heterogeneous bullous disorder. J Invest Dermatol 1993;100: Gammon WR, Wilson BD, Briggaman RA. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. In: Immunopathology of the skin (3rd ed). New York: Jhon Wiley & Sons Inc 1987; Chan PT. Cilinical features and diagnosis of common autoimmune bullous diseases. Hong Kong Medical Bulletin 2008 Oct;13:10. ABOUT THE AUTHORS Roopa S Rao (Corresponding Author) Professor, Department of Oral Pathology, MS Ramaiah Dental College and Hospital, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India, drroopasrao1971@ gmail.com BR Premalatha Senior Lecturer, Department of Oral Pathology, MS Ramaiah Dental College and Hospital, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India Vijaya Mysorekar Professor, Department of Pathology, MS Ramaiah Medical College and Hospital, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India Saurabh Juneja Postgraduate Student, Department of Oral Pathology, MS Ramaiah Dental College and Hospital, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India JAYPEE
Department of Dermatology, Nippon Medical School, 1-1-5, Sendagi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo , Japan 2
 Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2010, Article ID 931340, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/931340 Case Report Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Presenting as Mild Cutaneous Features of Pemphigus Foliaceus and Lichenoid
Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2010, Article ID 931340, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/931340 Case Report Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Presenting as Mild Cutaneous Features of Pemphigus Foliaceus and Lichenoid
A cross-sectional study of clinical, histopathological and direct immmunofluorescence diagnosis in autoimmune bullous diseases
 Original Article A cross-sectional study of clinical, histopathological and direct immmunofluorescence diagnosis in autoimmune bullous diseases Anchal Jindal, MD 1 Rushikesh Shah, MBBS 2 Neela Patel, MD
Original Article A cross-sectional study of clinical, histopathological and direct immmunofluorescence diagnosis in autoimmune bullous diseases Anchal Jindal, MD 1 Rushikesh Shah, MBBS 2 Neela Patel, MD
Clinicopathological correlation of blistering diseases of skin
 Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 2008; 34: 48-53 Copyright 2008 by Bangladesh Medical Research Council Clinicopathological correlation of blistering diseases of skin A.K.M. Nurul Kabir 1, Mohammed Kamal 1
Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 2008; 34: 48-53 Copyright 2008 by Bangladesh Medical Research Council Clinicopathological correlation of blistering diseases of skin A.K.M. Nurul Kabir 1, Mohammed Kamal 1
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations
 Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
Original Contribution
 Direct Immunofluorescence Test of Skin Biopsy Samples Results of 204 Cases Kabir AN, 1 Das RK, 2 Kamal M 3 Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) test of skin and renal biopsy specimens is being done on regular
Direct Immunofluorescence Test of Skin Biopsy Samples Results of 204 Cases Kabir AN, 1 Das RK, 2 Kamal M 3 Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) test of skin and renal biopsy specimens is being done on regular
Immunofluorescence in Oral Dermatological Disorders- No Shiny Matter
 Journal of Academy of Dental Education Journal of Academy of Dental Education, 24-28, DOI: 10.18311/jade/2015-2016/15951 ISSN (Print): 2348-1595 ISSN (Online) : 2348-2621 Immunofluorescence in Oral Dermatological
Journal of Academy of Dental Education Journal of Academy of Dental Education, 24-28, DOI: 10.18311/jade/2015-2016/15951 ISSN (Print): 2348-1595 ISSN (Online) : 2348-2621 Immunofluorescence in Oral Dermatological
Pemphigus in younger age group in Bangladeshi population
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE in younger age group in Bangladeshi population Abdul Wahab 1, MD, Lubna Khondker 1, MD, Jamal Uddin 1, MD, Ishrat Bhuiyan 2, MD Shirajul Islam Khan 3, MD, Zafrul Islam 1, MD, Rahmat Ali
ORIGINAL ARTICLE in younger age group in Bangladeshi population Abdul Wahab 1, MD, Lubna Khondker 1, MD, Jamal Uddin 1, MD, Ishrat Bhuiyan 2, MD Shirajul Islam Khan 3, MD, Zafrul Islam 1, MD, Rahmat Ali
University of Groningen. Acantholysis in pemphigus van der Wier, Gerda
 University of Groningen Acantholysis in pemphigus van der Wier, Gerda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the
University of Groningen Acantholysis in pemphigus van der Wier, Gerda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the
Immunobullous Diseases: Review and Update. May P. Chan, MD Associate Professor of Pathology and Dermatology University of Michigan
 Immunobullous Diseases: Review and Update May P. Chan, MD Associate Professor of Pathology and Dermatology University of Michigan Diagnosis of Immunobullous Diseases Clinical H&E DIF DIAGNOSIS IIF ELISA
Immunobullous Diseases: Review and Update May P. Chan, MD Associate Professor of Pathology and Dermatology University of Michigan Diagnosis of Immunobullous Diseases Clinical H&E DIF DIAGNOSIS IIF ELISA
DERMATOLOGY VOLUME 40 NUMBER 5 PART 1 MAY 1999
 CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION The new pemphigus variants Journal of the American Academy of DERMATOLOGY VOLUME 40 NUMBER 5 PART 1 MAY 1999 Neha D. Robinson, MD, a Takashi Hashimoto, MD, b Masayuki Amagai,
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION The new pemphigus variants Journal of the American Academy of DERMATOLOGY VOLUME 40 NUMBER 5 PART 1 MAY 1999 Neha D. Robinson, MD, a Takashi Hashimoto, MD, b Masayuki Amagai,
Indian Journal of Dermatopathology and Diagnostic Dermatology
 Volume 1 Issue 1 Jan-Jun 2014 Online full text at www.ijdpdd.com Indian Journal of Dermatopathology and Diagnostic Dermatology DSI IADVL Karnataka Branch Official Publication of Dermatopathology Society
Volume 1 Issue 1 Jan-Jun 2014 Online full text at www.ijdpdd.com Indian Journal of Dermatopathology and Diagnostic Dermatology DSI IADVL Karnataka Branch Official Publication of Dermatopathology Society
Role of direct immunofluorescence on Tzanck smear and plucked hair in the diagnosis of pemphigus vulgaris
 Original Article Role of direct immunofluorescence on Tzanck smear and plucked hair in the diagnosis of pemphigus vulgaris Kehkshan Tahir, Saelah Batool, Muhammad Shahid, Shahbaz Aman Department of Dermatology,
Original Article Role of direct immunofluorescence on Tzanck smear and plucked hair in the diagnosis of pemphigus vulgaris Kehkshan Tahir, Saelah Batool, Muhammad Shahid, Shahbaz Aman Department of Dermatology,
B. Autoimmune blistering diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details formation immediately above the basal layer. The dermal papillae, which are covered by basal cells in the single layer that is left in
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details formation immediately above the basal layer. The dermal papillae, which are covered by basal cells in the single layer that is left in
Autoimmune bullous dermatoses
 Autoimmune bullous dermatoses Overview of serological diagnostics in autoimmune blister-forming diseases of the skin Pemphigoid diseases Pemphigus diseases Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita Dermatitis herpetiformis
Autoimmune bullous dermatoses Overview of serological diagnostics in autoimmune blister-forming diseases of the skin Pemphigoid diseases Pemphigus diseases Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita Dermatitis herpetiformis
Acquired and Inherited Bullous Diseases
 Acquired and Inherited Bullous Diseases Erin Wei MD Brigham and Women s Hospital, Department of Dermatology Instructor, Harvard Medical School Director, Bullous Disease Clinic No disclosures Conflict of
Acquired and Inherited Bullous Diseases Erin Wei MD Brigham and Women s Hospital, Department of Dermatology Instructor, Harvard Medical School Director, Bullous Disease Clinic No disclosures Conflict of
Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease:
 Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease: Hematological GIT Behcet s HIV 5. Associated with dermatological diseases:
Classification: 1. Infective: 2. Traumatic: 3. Idiopathic: Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis (RAS) 4. Associated with systemic disease: Hematological GIT Behcet s HIV 5. Associated with dermatological diseases:
Current concepts of autoimmune bullous diseases Advances in pathogenesis. Luca Borradori
 Current concepts of autoimmune bullous diseases Advances in pathogenesis Luca Borradori Dept. of Dermatology Inselspital, University Hospital of Berne Switzerland Luca.Borradori@insel.ch Autoimmune bullous
Current concepts of autoimmune bullous diseases Advances in pathogenesis Luca Borradori Dept. of Dermatology Inselspital, University Hospital of Berne Switzerland Luca.Borradori@insel.ch Autoimmune bullous
To Correlate Clinical Diagnosis with Histopathology and DIF Pattern of Autoimmune Based Vesiculobullous Disorders In A Tertiary Teaching Hospital
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 7 Ver. 2 (July. 2018), PP 01-06 www.iosrjournals.org To Correlate Clinical Diagnosis with Histopathology
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 7 Ver. 2 (July. 2018), PP 01-06 www.iosrjournals.org To Correlate Clinical Diagnosis with Histopathology
Definitive and Differential Diagnosis of Desquamative Gingivitis Through Direct Immunofluorescence Studies
 Volume 83 Number 10 Definitive and Differential Diagnosis of Desquamative Gingivitis Through Direct Immunofluorescence Studies Lakshmanan Suresh* and Mirdza E. Neiders* Background: Desquamative gingivitis
Volume 83 Number 10 Definitive and Differential Diagnosis of Desquamative Gingivitis Through Direct Immunofluorescence Studies Lakshmanan Suresh* and Mirdza E. Neiders* Background: Desquamative gingivitis
A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus
 #2228 A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus Priyanka Vedak MD 1, Danielle Levine MD 1,3, Lyn Duncan MD 2,3, Hensin Tsao 1,3, Daniela Kroshinsky MD MPH 1,3 1. Department of Dermatology,
#2228 A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus Priyanka Vedak MD 1, Danielle Levine MD 1,3, Lyn Duncan MD 2,3, Hensin Tsao 1,3, Daniela Kroshinsky MD MPH 1,3 1. Department of Dermatology,
atorvastatin 10mg, amlodipine 5mg and dilitazem 60mg. He had unexplained iron deficiency anaemia (hemoglobin-8.4gm/dl, ferritin- 4.73ng/ml, total iron
 Pemphigus herpetiformis : A rare clinical variant of pemphigus Shrestha P 1, Tajhya RB 2, Pokharel A 3 1,2 Consultant Dermatologist, Department of Dermatology, Vayodha Hospital Pvt. Ltd, Balkhu, Kathmandu,
Pemphigus herpetiformis : A rare clinical variant of pemphigus Shrestha P 1, Tajhya RB 2, Pokharel A 3 1,2 Consultant Dermatologist, Department of Dermatology, Vayodha Hospital Pvt. Ltd, Balkhu, Kathmandu,
Interesting Case Series. Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis
 Interesting Case Series Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis Sean Chen, BA, a Peter Mattei, MD, a Max Fischer, MD, MPH, a Joshua D. Gay, PA-C, b Stephen M. Milner, MBBS, BDS, FRCS (Ed), FACS, b and Leigh Ann
Interesting Case Series Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis Sean Chen, BA, a Peter Mattei, MD, a Max Fischer, MD, MPH, a Joshua D. Gay, PA-C, b Stephen M. Milner, MBBS, BDS, FRCS (Ed), FACS, b and Leigh Ann
Background information of DIF
 Napa Dermatopathology Meeting 2018: Immunobullous Disease Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng whitney.high@ucdenver.edu Professor of Dermatology & Pathology Vice-Chairman, Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology
Napa Dermatopathology Meeting 2018: Immunobullous Disease Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng whitney.high@ucdenver.edu Professor of Dermatology & Pathology Vice-Chairman, Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology
Blistering mucocutaneous disease of oral cavity Pemphigus vulgaris 8 year study in Nalgonda population
 Original Research Article Blistering mucocutaneous disease of oral cavity Pemphigus vulgaris 8 year study in Nalgonda population P Pavan 1*, T Madhusudan Rao 2, Pavan G Kulkarni 3, SRK Nandan 4, Shyam
Original Research Article Blistering mucocutaneous disease of oral cavity Pemphigus vulgaris 8 year study in Nalgonda population P Pavan 1*, T Madhusudan Rao 2, Pavan G Kulkarni 3, SRK Nandan 4, Shyam
Diagnostic Immunopathology in 21 ST Century Dermatology Part I: Basics and Epidermal Deposits
 Review Diagnostic Immunopathology in 21 ST Century Dermatology Part I: Basics and Epidermal Deposits Maria Jasmin J. Jamora Immunofluorescence techniques and other immunopathologic diagnostic techniques
Review Diagnostic Immunopathology in 21 ST Century Dermatology Part I: Basics and Epidermal Deposits Maria Jasmin J. Jamora Immunofluorescence techniques and other immunopathologic diagnostic techniques
Comparative study of indirect immunofluorescence, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and the Tzanck smear test for the diagnosis of pemphigus
 (2016) 45: 786 790 2016 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/jop doi: 10.1111/jop.12439 Comparative study of indirect immunofluorescence, enzyme-linked
(2016) 45: 786 790 2016 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/jop doi: 10.1111/jop.12439 Comparative study of indirect immunofluorescence, enzyme-linked
CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE
 CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE Generalized vesiculo-bullous and pustular eruption in an adult man Hassab El-Naby H, MD, El-Khalawany M, MD Department of Dermatology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt CLINICAL
CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE Generalized vesiculo-bullous and pustular eruption in an adult man Hassab El-Naby H, MD, El-Khalawany M, MD Department of Dermatology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt CLINICAL
Comparative microanatomy of the normal skin with that of immunobullous condition
 Original article: Comparative microanatomy of the normal skin with that of immunobullous condition 1Dr BananiKundu, 2 DrAnirban Sadhu, 3 DrRudradev Meyur, 4 Dr SauravKundu, 5 Dr Alpana De, 6Dr SatabdiSarkar
Original article: Comparative microanatomy of the normal skin with that of immunobullous condition 1Dr BananiKundu, 2 DrAnirban Sadhu, 3 DrRudradev Meyur, 4 Dr SauravKundu, 5 Dr Alpana De, 6Dr SatabdiSarkar
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology Dermatologic Diseases Chapter 16 ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA o Two or more ectodermally derived anatomic structures fail to develop o
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology Dermatologic Diseases Chapter 16 ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA o Two or more ectodermally derived anatomic structures fail to develop o
Sarolta Kárpáti. Technology Transfer in Diagnostic Pathology, 5th Central European Regional Meeting May 1, 2010, Siófok
 Blistering diseases Sarolta Kárpáti SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, BUDAPEST Technology Transfer in Diagnostic Pathology, 5th Central European Regional Meeting May 1, 2010, Siófok Blistering diseases Autoimmune
Blistering diseases Sarolta Kárpáti SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, BUDAPEST Technology Transfer in Diagnostic Pathology, 5th Central European Regional Meeting May 1, 2010, Siófok Blistering diseases Autoimmune
Oral Manifestation in Patients diagnosed with Dermatological Diseases
 JCDP ORIGINAL RESEARCH Oral Manifestation in Patients diagnosed 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2191 with Dermatological Diseases Oral Manifestation in Patients diagnosed with Dermatological Diseases 1 Sanjay
JCDP ORIGINAL RESEARCH Oral Manifestation in Patients diagnosed 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2191 with Dermatological Diseases Oral Manifestation in Patients diagnosed with Dermatological Diseases 1 Sanjay
When your patient complains of
 WILLIAM LAWSON, MD, DDS Mount Sinai School of Medicine ABSTRACT: Certain clues can help you identify the cause of bullous oral lesions. Diffuse oral and labial bullous erosions, sometimes accompanied by
WILLIAM LAWSON, MD, DDS Mount Sinai School of Medicine ABSTRACT: Certain clues can help you identify the cause of bullous oral lesions. Diffuse oral and labial bullous erosions, sometimes accompanied by
Recent Advances in the Molecular Pathology of Bullous Skin Disorders
 1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 2, June 2005 Recent Advances in the Molecular Pathology of Bullous Skin Disorders John A McGrath* Maintenance of an intact epidermis depends on secure adhesion
1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 2, June 2005 Recent Advances in the Molecular Pathology of Bullous Skin Disorders John A McGrath* Maintenance of an intact epidermis depends on secure adhesion
Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis
 Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis A. España C. Sitaru* M. Pretel L. Aguado J. Jimenez# Department of Dermatology, University
Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis A. España C. Sitaru* M. Pretel L. Aguado J. Jimenez# Department of Dermatology, University
Bullous Pemphigoid with Lymphocytic Colitis: A Case Report and Short Literature Review
 Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) (2016) 6:437 441 DOI 10.1007/s13555-016-0135-4 CASE REPORT Bullous Pemphigoid with Lymphocytic Colitis: A Case Report and Short Literature Review Alexandra Sperl. Johann W. Bauer.
Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) (2016) 6:437 441 DOI 10.1007/s13555-016-0135-4 CASE REPORT Bullous Pemphigoid with Lymphocytic Colitis: A Case Report and Short Literature Review Alexandra Sperl. Johann W. Bauer.
Importance of serological tests in diagnosis of autoimmune blistering diseases
 doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12703 Journal of Dermatology 2015; 42: 3 10 REVIEW ARTICLE Importance of serological tests in diagnosis of autoimmune blistering diseases Ken ISHII Department of Dermatology, Toho
doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12703 Journal of Dermatology 2015; 42: 3 10 REVIEW ARTICLE Importance of serological tests in diagnosis of autoimmune blistering diseases Ken ISHII Department of Dermatology, Toho
Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections
 Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections SL MERA, EW YOUNG, AND JWB BRADFIELD J Clin Pathol 1980; 33: 365-369 From the University Department ofpathology, University
Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections SL MERA, EW YOUNG, AND JWB BRADFIELD J Clin Pathol 1980; 33: 365-369 From the University Department ofpathology, University
A Study of 75 Cases of Pemphigus in Saurashtra Region of India
 Original Article A Study of 75 Cases of in Saurashtra Region of India Deval Vora, MD 1 Vijay Popat, MD 2 Viral Bhanvadia, MD 2 Dimple A. Mehta, MD 2 Bharat Bhetariya, MD 2 Meet Kumar, MD 2 1. Department
Original Article A Study of 75 Cases of in Saurashtra Region of India Deval Vora, MD 1 Vijay Popat, MD 2 Viral Bhanvadia, MD 2 Dimple A. Mehta, MD 2 Bharat Bhetariya, MD 2 Meet Kumar, MD 2 1. Department
Original Article. Direct Immunofluorescence in Clinically Diagnosed Oral Lichen Planus
 JOMP Journal of Oral Medicine and Pain Original Article pissn 2288-9272 eissn 2383-8493 J Oral Med Pain 2016;41(1):16-20 http://dx.doi.org/10.14476/jomp.2016.41.1.16 Direct Immunofluorescence in Clinically
JOMP Journal of Oral Medicine and Pain Original Article pissn 2288-9272 eissn 2383-8493 J Oral Med Pain 2016;41(1):16-20 http://dx.doi.org/10.14476/jomp.2016.41.1.16 Direct Immunofluorescence in Clinically
Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2
 Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
Autoimmune bullous disorders 1)
 Clin Chem Lab Med 2006;44(2):144 149 2006 by Walter de Gruyter Berlin New York. DOI 10.1515/CCLM.2006.027 2006/39 Review Autoimmune bullous disorders 1) Rüdiger Eming* and Michael Hertl for the members
Clin Chem Lab Med 2006;44(2):144 149 2006 by Walter de Gruyter Berlin New York. DOI 10.1515/CCLM.2006.027 2006/39 Review Autoimmune bullous disorders 1) Rüdiger Eming* and Michael Hertl for the members
Original Article ABSTRACT
 Original Article doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2015.01345 Utility of Direct Immunofluorescence Studies in Subclassification of Autoimmune Sub-Epidermal Bullous Diseases: A 2-Year Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital
Original Article doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2015.01345 Utility of Direct Immunofluorescence Studies in Subclassification of Autoimmune Sub-Epidermal Bullous Diseases: A 2-Year Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital
The incidence of internal malignancies in autoimmune bullous diseases
 Tokai J Exp Clin Med., Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. 42-47, 2007 The incidence of internal malignancies in autoimmune bullous diseases Kenichi IWASHITA, Takashi MATSUYAMA, Emiko AKASAKA, Kimihiko MIZUTANI, Kozo
Tokai J Exp Clin Med., Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. 42-47, 2007 The incidence of internal malignancies in autoimmune bullous diseases Kenichi IWASHITA, Takashi MATSUYAMA, Emiko AKASAKA, Kimihiko MIZUTANI, Kozo
Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita
 Introduction Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita Pages with reference to book, From 192 To 194 Nasser Rashid Dar ( Departments of Dermatology, Combined Military Hospital, Peshawar. ) Ahsan Hameed, Ashfaq Ahmad
Introduction Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita Pages with reference to book, From 192 To 194 Nasser Rashid Dar ( Departments of Dermatology, Combined Military Hospital, Peshawar. ) Ahsan Hameed, Ashfaq Ahmad
Pemphigus foliaceus: a clinical study of 32 cases in Hong Kong 32
 H.K. Dermatol. Venereol. Bull. (2004) 12, 126-132 Original Article Pemphigus foliaceus: a clinical study of 32 cases in Hong Kong 32 This is a cross-sectional, retrospective study of 32 Hong Kong Chinese
H.K. Dermatol. Venereol. Bull. (2004) 12, 126-132 Original Article Pemphigus foliaceus: a clinical study of 32 cases in Hong Kong 32 This is a cross-sectional, retrospective study of 32 Hong Kong Chinese
Citation for published version (APA): Poot, A. M. (2016). Pemphigus: Insights in diagnosis and pathogenesis [Groningen]: University of Groningen
![Citation for published version (APA): Poot, A. M. (2016). Pemphigus: Insights in diagnosis and pathogenesis [Groningen]: University of Groningen Citation for published version (APA): Poot, A. M. (2016). Pemphigus: Insights in diagnosis and pathogenesis [Groningen]: University of Groningen](/thumbs/90/103903199.jpg) University of Groningen Pemphigus Poot, Angelique Muriel IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version
University of Groningen Pemphigus Poot, Angelique Muriel IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version
Indirect cutaneous immunofluorescence1
 J. clin. Path., 1973, 26, 268-272 Indirect cutaneous immunofluorescence1 II Clinical significance THOMAS K. BURNHAM From the Department ofdermatology, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Michigan, USA SYNOPSIS
J. clin. Path., 1973, 26, 268-272 Indirect cutaneous immunofluorescence1 II Clinical significance THOMAS K. BURNHAM From the Department ofdermatology, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Michigan, USA SYNOPSIS
Grover s disease: A case report.
 320 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2011 ABSTRACT: Grover s disease: A case report. Supicha Chavanich MD, Praneet Sajjachareonpong MD. CHAVANICH C, SAJJACHAREONPONG P. GROVER S DISEASE: A
320 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2011 ABSTRACT: Grover s disease: A case report. Supicha Chavanich MD, Praneet Sajjachareonpong MD. CHAVANICH C, SAJJACHAREONPONG P. GROVER S DISEASE: A
Prognostic factors in pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus M. Saha, 1 B. Bhogal, 1 M.M. Black, 1 D. Cooper, 2 R.W. Vaughan 3 and R.W.
 CLINICAL AND LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS BJD British Journal of Dermatology Prognostic factors in pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus M. Saha, 1 B. Bhogal, 1 M.M. Black, 1 D. Cooper, 2 R.W. Vaughan
CLINICAL AND LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS BJD British Journal of Dermatology Prognostic factors in pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus M. Saha, 1 B. Bhogal, 1 M.M. Black, 1 D. Cooper, 2 R.W. Vaughan
Oral Pemphigus Vulgaris: Case Report
 Oral Pemphigus Vulgaris Rai A. et al 367 CASE REPORT Oral Pemphigus Vulgaris: Case Report Rai Arpita 1, Arora Monica 2, Naikmasur Venkatesh 3, Sattur Atul 3, Malhotra Varun 2 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Pemphigus
Oral Pemphigus Vulgaris Rai A. et al 367 CASE REPORT Oral Pemphigus Vulgaris: Case Report Rai Arpita 1, Arora Monica 2, Naikmasur Venkatesh 3, Sattur Atul 3, Malhotra Varun 2 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Pemphigus
Paul K. Shitabata, M.D. Dermatopathology Institute
 Paul K. Shitabata, M.D. Dermatopathology Institute Technical Considerations Storage of slides at room temperature
Paul K. Shitabata, M.D. Dermatopathology Institute Technical Considerations Storage of slides at room temperature
Autoimmune Blistering Disease
 life. science. discovery. life. science. discovery. Autoimmune Blistering Disease - Diagnostic Methodology for Pemphigus and Pemphigoid - Pemphigus Epidermal cell-cell junction EBA Epidermal side Epidermal
life. science. discovery. life. science. discovery. Autoimmune Blistering Disease - Diagnostic Methodology for Pemphigus and Pemphigoid - Pemphigus Epidermal cell-cell junction EBA Epidermal side Epidermal
Mucous membrane pemphigoid in a patient with hypertension treated with atenolol: a case report
 Kanjanabuch et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:373 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Mucous membrane pemphigoid in a patient with hypertension treated with atenolol: a
Kanjanabuch et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:373 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Mucous membrane pemphigoid in a patient with hypertension treated with atenolol: a
Psoriasiform pemphigus foliaceus: a report of two cases
 J Cutan Pathol 2012: 39: 549 553 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2012.01866.x John Wiley & Sons. Printed in Singapore Copyright 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S Journal of Cutaneous Pathology Psoriasiform pemphigus
J Cutan Pathol 2012: 39: 549 553 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2012.01866.x John Wiley & Sons. Printed in Singapore Copyright 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S Journal of Cutaneous Pathology Psoriasiform pemphigus
Study of early diagnosis of various vesiculobullous lesions of the skin using histopathology
 Original article: Study of early of various vesiculobullous lesions of the skin using histopathology Dr Sachin Parhe* Department of Pathology, DVVPF s Medical College & Hospital, Ahmednagar -414111. Corresponding
Original article: Study of early of various vesiculobullous lesions of the skin using histopathology Dr Sachin Parhe* Department of Pathology, DVVPF s Medical College & Hospital, Ahmednagar -414111. Corresponding
Introduction to Pemphigoid: Spectrum of Disease & Treatment
 Introduction to Pemphigoid: Spectrum of Disease & Treatment A Razzaque Ahmed, MD Center for Blistering Diseases Boston, MA A.Razzaque.Ahmed@tufts.edu centerforblisteringdiseases.com SPECTRUM OF PEMPHIGOID
Introduction to Pemphigoid: Spectrum of Disease & Treatment A Razzaque Ahmed, MD Center for Blistering Diseases Boston, MA A.Razzaque.Ahmed@tufts.edu centerforblisteringdiseases.com SPECTRUM OF PEMPHIGOID
MUCOCUTANEOUS LESIONS Normal structures in epithelium cell adhesion to each other and to underlying connective tissue:
 ORAL DERMATOSES AND MUCOSAL/GINGIVAL LESIONS MUCOCUTANEOUS LESIONS Normal structures in epithelium cell adhesion to each other and to underlying connective tissue: Diagram taken from: Oral and Maxillofacial
ORAL DERMATOSES AND MUCOSAL/GINGIVAL LESIONS MUCOCUTANEOUS LESIONS Normal structures in epithelium cell adhesion to each other and to underlying connective tissue: Diagram taken from: Oral and Maxillofacial
A Clinical Study of Oral Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
 The Journal of International Medical Research 2003; 31: 340 344 A Clinical Study of Oral Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid A ALKAN 1, Ö GÜNHAN 3, A ALKAN 2 AND F OTAN 2 1 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial
The Journal of International Medical Research 2003; 31: 340 344 A Clinical Study of Oral Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid A ALKAN 1, Ö GÜNHAN 3, A ALKAN 2 AND F OTAN 2 1 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial
السكري للداء مرافقة فقاعات diabeticorum= Bullosis
 1 / 6 Bullosis diabeticorum Bullous disease of diabetes (bullosis diabeticorum) is a distinct, spontaneous, noninflammatory, blistering condition of acral skin unique to patients with diabetes mellitus.
1 / 6 Bullosis diabeticorum Bullous disease of diabetes (bullosis diabeticorum) is a distinct, spontaneous, noninflammatory, blistering condition of acral skin unique to patients with diabetes mellitus.
ISSN: Volume 3 Issue Pemphigus Vegetans masquerading as Cutis Verticis Gyrata
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 4 2013 Pemphigus Vegetans masquerading as Cutis Verticis Gyrata *Aarthi b k Ramesh *Aravamudhan * Ratnavel Rajendrabose *Rajesh Huthur *Nanjunda Gowda, *Nishant Gupta Stanley
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 4 2013 Pemphigus Vegetans masquerading as Cutis Verticis Gyrata *Aarthi b k Ramesh *Aravamudhan * Ratnavel Rajendrabose *Rajesh Huthur *Nanjunda Gowda, *Nishant Gupta Stanley
INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I. Immunopathology Part I
 INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I Immunopathology Part I Nonspecific & T Cell Mediated Mucosal Inflammatory Lesions Nonspecific and Idiopathic Mucositis Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune T cell mediated Immunoglobulin
INFLAMMATORY DISEASES PART I Immunopathology Part I Nonspecific & T Cell Mediated Mucosal Inflammatory Lesions Nonspecific and Idiopathic Mucositis Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune T cell mediated Immunoglobulin
Effect of Substrate on Indirect Immunofluorescence Test for Canine Pemphigus Foliaceus
 Vet Pathol33:332336 (1996) Effect of Substrate on Indirect Immunofluorescence Test for Canine Pemphigus Foliaceus T. IWASAKI, M. SHIMIZU, H. OBATA, M. OGATA, M. NAGATA, T. YANAI, H. KITAGAWA, AND Y. SASAKI
Vet Pathol33:332336 (1996) Effect of Substrate on Indirect Immunofluorescence Test for Canine Pemphigus Foliaceus T. IWASAKI, M. SHIMIZU, H. OBATA, M. OGATA, M. NAGATA, T. YANAI, H. KITAGAWA, AND Y. SASAKI
University of Groningen. Pemphigus pathogenesis Sokol, Ena
 University of Groningen Pemphigus pathogenesis Sokol, Ena IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version
University of Groningen Pemphigus pathogenesis Sokol, Ena IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version
Paraneoplastic Pemphigus in A Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Case Report
 Case Report Paraneoplastic Pemphigus in A Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Case Report Arif Kuş 1, Abdulkerim Yıldız 2*, Betül Erdem 3, Murat Albayrak 2, Çiğdem Pala Öztürk 2, Müzeyyen Gönül
Case Report Paraneoplastic Pemphigus in A Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Case Report Arif Kuş 1, Abdulkerim Yıldız 2*, Betül Erdem 3, Murat Albayrak 2, Çiğdem Pala Öztürk 2, Müzeyyen Gönül
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE
 Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
THE USE OF HUMAN SKIN FOR THE DETECTION OF ANTI- EPITHELIAL AUTOANTIBODIES A DIAGNOSTIC AND PROGNOSTIC TEST*
 Tlia JOUStNAL OF INVF5T1WTiVF DEBM.,TLGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 53, No. 6 Printed 'in U.S.A. THE USE OF HUMAN SKIN FOR THE DETECTION OF ANTI- EPITHELIAL AUTOANTIBODIES A DIAGNOSTIC
Tlia JOUStNAL OF INVF5T1WTiVF DEBM.,TLGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 53, No. 6 Printed 'in U.S.A. THE USE OF HUMAN SKIN FOR THE DETECTION OF ANTI- EPITHELIAL AUTOANTIBODIES A DIAGNOSTIC
Index. derm.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
Immunohistochemical study of lichen planus
 Immunohistochemical study of lichen planus SAI SHOUSHA AND JOHN SVIRBELY1 rom the Department of Histopathology, Royal ree Hospital, London NW3 2QG J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 569-574 SUARY The distribution
Immunohistochemical study of lichen planus SAI SHOUSHA AND JOHN SVIRBELY1 rom the Department of Histopathology, Royal ree Hospital, London NW3 2QG J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 569-574 SUARY The distribution
A study on the effectiveness of Tzanck smear to diagnose the vesiculobullous lesions in comparison with histopathology
 Original Research Article A study on the effectiveness of Tzanck smear to diagnose the vesiculobullous lesions in comparison with histopathology B. Lakshminarayana 1, Rammohan 2*, G. Saisoumya 3, J. Tulasi
Original Research Article A study on the effectiveness of Tzanck smear to diagnose the vesiculobullous lesions in comparison with histopathology B. Lakshminarayana 1, Rammohan 2*, G. Saisoumya 3, J. Tulasi
Review Article Clinical Relevance of Autoantibodies in Patients with Autoimmune Bullous Dermatosis
 Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2012, Article ID 369546, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/369546 Review Article Clinical Relevance of Autoantibodies in Patients with Autoimmune Bullous Dermatosis
Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2012, Article ID 369546, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/369546 Review Article Clinical Relevance of Autoantibodies in Patients with Autoimmune Bullous Dermatosis
AUTOIMMUNE BLISTERING DISEASES; WINDOW TO SYSTEMIC DISEASE
 AUTOIMMUNE BLISTERING DISEASES; WINDOW TO SYSTEMIC DISEASE Ron Feldman, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Dermatology Emory University ron.j.feldman@emory.edu Disclosures I have no conflict of interest to
AUTOIMMUNE BLISTERING DISEASES; WINDOW TO SYSTEMIC DISEASE Ron Feldman, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Dermatology Emory University ron.j.feldman@emory.edu Disclosures I have no conflict of interest to
s Non-classical forms of pemphigus: pemphigus herpetiformis, IgA pemphigus, paraneoplastic pemphigus and IgG/IgA pemphigus *
 96 REVIEW s Non-classical forms of pemphigus: pemphigus herpetiformis, IgA pemphigus, paraneoplastic pemphigus and IgG/IgA pemphigus * Adriana Maria Porro 1 Livia de Vasconcelos Nasser Caetano 2 Laura
96 REVIEW s Non-classical forms of pemphigus: pemphigus herpetiformis, IgA pemphigus, paraneoplastic pemphigus and IgG/IgA pemphigus * Adriana Maria Porro 1 Livia de Vasconcelos Nasser Caetano 2 Laura
Title. CitationBritish Journal of Dermatology, 155(5): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type. File Information
 Title Childhood epidermolysis bullosa acquisita with autoa collagen : case report and review of the literature Author(s)Mayuzumi, M.; Akiyama, M.; Nishie, W.; Ukae, S.; Abe CitationBritish Journal of Dermatology,
Title Childhood epidermolysis bullosa acquisita with autoa collagen : case report and review of the literature Author(s)Mayuzumi, M.; Akiyama, M.; Nishie, W.; Ukae, S.; Abe CitationBritish Journal of Dermatology,
Quantification of Colloid Bodies in Oral Lichen Planus and Oral Lichenoid Reaction - A Histochemical Study
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:0.437/jced.3.e207 Quantification of Colloid Bodies in Oral Lichen Planus and Oral Lichenoid Reaction - A Histochemical Study
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:0.437/jced.3.e207 Quantification of Colloid Bodies in Oral Lichen Planus and Oral Lichenoid Reaction - A Histochemical Study
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide
 Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Skin biopsy. Sophia Otto SA Pathology
 Skin biopsy Sophia Otto SA Pathology RCPA (Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia) The RCPA is the leading organisation representing pathologists in Australasia. Its mission is to train and support
Skin biopsy Sophia Otto SA Pathology RCPA (Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia) The RCPA is the leading organisation representing pathologists in Australasia. Its mission is to train and support
Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
 Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS A CASE REPORT *Prathima
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. EROSIVE LICHEN PLANUS A CASE REPORT *Prathima
substance staining with IgG, C3 and IgA (trace) Linear deposition of IgG(+), IgA.M(trace) and C3(+++) at the DEJ
 Direct Immunofluorescence: Skin Diagnosis Findings Picture Pemphigus Vulgaris and it s Intracellular cement variants substance staining with IgG, C3 and IgA (trace) Bullous Pemphigoid and it s variants
Direct Immunofluorescence: Skin Diagnosis Findings Picture Pemphigus Vulgaris and it s Intracellular cement variants substance staining with IgG, C3 and IgA (trace) Bullous Pemphigoid and it s variants
The New England Journal of Medicine. Patient 1
 Brief Report THE MECHANISM OF RESPIRATORY FAILURE IN PARANEOPLASTIC PEMPHIGUS HOSSEIN C. NOUSARI, M.D., ROBIN DETERDING, M.D., HENRY WOJTCZACK, M.D., SIRPA AHO, PH.D., JOUNI UITTO, M.D., PH.D., TAKASHI
Brief Report THE MECHANISM OF RESPIRATORY FAILURE IN PARANEOPLASTIC PEMPHIGUS HOSSEIN C. NOUSARI, M.D., ROBIN DETERDING, M.D., HENRY WOJTCZACK, M.D., SIRPA AHO, PH.D., JOUNI UITTO, M.D., PH.D., TAKASHI
Inflammatory Dermatoses of the Vulva for the General/Gyn Pathologist with emphasis in the lichenoid pattern
 Inflammatory Dermatoses of the Vulva for the General/Gyn Pathologist with emphasis in the lichenoid pattern By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor
Inflammatory Dermatoses of the Vulva for the General/Gyn Pathologist with emphasis in the lichenoid pattern By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor
and Isolation of Antibody in Linear Immunoglobulin A Bullous Dermatosis
 Identification of the Cutaneous Basement Membrane Zone Antigen and Isolation of Antibody in Linear Immunoglobulin A Bullous Dermatosis John J. Zone, Ted B. Taylor, Donald P. Kadunce, and Laurence J. Meyer
Identification of the Cutaneous Basement Membrane Zone Antigen and Isolation of Antibody in Linear Immunoglobulin A Bullous Dermatosis John J. Zone, Ted B. Taylor, Donald P. Kadunce, and Laurence J. Meyer
Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita: A Retrospective Clinical Analysis of 30 Cases
 Acta Derm Venereol 2011 Epub ahead of print CLINICAL REPORT Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita: A Retrospective Clinical Analysis of 30 Cases Jong Hoon Kim 1, Yeon Hee Kim 2 and Soo-Chan Kim 1 1 Department
Acta Derm Venereol 2011 Epub ahead of print CLINICAL REPORT Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita: A Retrospective Clinical Analysis of 30 Cases Jong Hoon Kim 1, Yeon Hee Kim 2 and Soo-Chan Kim 1 1 Department
Discohesive malignant melanoma simulating a bullous dermatoses
 J Cutan Pathol 2009: 36: 274 279 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2007.01054.x Blackwell Munksgaard. Printed in Singapore Copyright # 2008 Blackwell Munksgaard Journal of Cutaneous Pathology Discohesive malignant
J Cutan Pathol 2009: 36: 274 279 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2007.01054.x Blackwell Munksgaard. Printed in Singapore Copyright # 2008 Blackwell Munksgaard Journal of Cutaneous Pathology Discohesive malignant
A RARE CASE OF LICHEN PLANUS PEMPHIGOIDES Ashok Jain 1, Anjali Dalal 2
 A RARE CASE OF LICHEN PLANUS PEMPHIGOIDES Ashok Jain 1, Anjali Dalal 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ashok Jain, Anjali Dalal. A Rare Case of Lichen Planus Pemphigoides. Journal of Evolution of Medical and
A RARE CASE OF LICHEN PLANUS PEMPHIGOIDES Ashok Jain 1, Anjali Dalal 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ashok Jain, Anjali Dalal. A Rare Case of Lichen Planus Pemphigoides. Journal of Evolution of Medical and
REF: Chap 1 (Pemphigus vulgaris/etiology and
 Chapter 1: Vesiculobullous Diseases Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Intercellular deposits of IgG are consistently found in oral epithelium in which of the following? a. Cicatricial pemphigoid b. Lichen planus
Chapter 1: Vesiculobullous Diseases Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Intercellular deposits of IgG are consistently found in oral epithelium in which of the following? a. Cicatricial pemphigoid b. Lichen planus
MORBILLIFORM ERUPTIONS CAUSED BY PENICILLIN A STUDY BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AND IMMUNOLOGIC TESTS*
 THE JoURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1970 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 55, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. MORBILLIFORM ERUPTIONS CAUSED BY PENICILLIN A STUDY BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AND IMMUNOLOGIC
THE JoURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1970 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 55, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. MORBILLIFORM ERUPTIONS CAUSED BY PENICILLIN A STUDY BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AND IMMUNOLOGIC
ANS: C REF: Chap 1 (Pemphigus vulgaris/etiology and pathogenesis), p 11
 Chapter 1: Vesiculobullous Diseases Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Intercellular deposits of IgG are consistently found in oral epithelium in which of the following? a. Cicatricial pemphigoid b. Lichen planus
Chapter 1: Vesiculobullous Diseases Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Intercellular deposits of IgG are consistently found in oral epithelium in which of the following? a. Cicatricial pemphigoid b. Lichen planus
Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC -
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies
 My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies P A U L H A U N, MD, MS, F A A D A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E R M A T O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O P A T H O L O G Y D E P A R T M E N T O F D E R M
My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies P A U L H A U N, MD, MS, F A A D A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E R M A T O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O P A T H O L O G Y D E P A R T M E N T O F D E R M
Dr Saleem Taibjee. Consultant Dermatologist & Dermatopathologist
 Dr Saleem Taibjee saleem.taibjee@dchft.nhs.uk Consultant Dermatologist & Dermatopathologist Case S14-10797 and S15-4023 F50. Previous blistering, now marked milia on dorsum of hands. 4mm punch biopsy The
Dr Saleem Taibjee saleem.taibjee@dchft.nhs.uk Consultant Dermatologist & Dermatopathologist Case S14-10797 and S15-4023 F50. Previous blistering, now marked milia on dorsum of hands. 4mm punch biopsy The
Diagnosis? 2/17/2018. Case year old female. F045 Dermpath Case Challenge
 Case 1 75 year old female F045 Dermpath Case Challenge Tammie Ferringer, MD Depts of Dermatology and Pathology Danville, PA tferringer@geisinger.edu 1 year history of undiagnosed joint pain and 6 month
Case 1 75 year old female F045 Dermpath Case Challenge Tammie Ferringer, MD Depts of Dermatology and Pathology Danville, PA tferringer@geisinger.edu 1 year history of undiagnosed joint pain and 6 month
Learning Objectives. Pathophysiology, clinical features, histology Evaluation and management
 Learning Objectives Pemphigus vulgaris Paraneoplastic pemphigus Bullous pemphigoid Pathophysiology, clinical features, histology Evaluation and management Pemphigus and Pemphigoid: Overview Distinct set
Learning Objectives Pemphigus vulgaris Paraneoplastic pemphigus Bullous pemphigoid Pathophysiology, clinical features, histology Evaluation and management Pemphigus and Pemphigoid: Overview Distinct set
In contrast to the flaccid blisters, erosions, and crusted. disease that occurs during the second or third trimester of
 Pemphigus and Pemphigoid as Paradigms of Organ-specific, Autoantibody-mediated Diseases John R. Stanley Dermatology Branch, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes ofhealth, Bethesda, Maryland 20892
Pemphigus and Pemphigoid as Paradigms of Organ-specific, Autoantibody-mediated Diseases John R. Stanley Dermatology Branch, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes ofhealth, Bethesda, Maryland 20892
Pharmacologyonline 1: 1-6 (2010) Case Report Ravishankar and Hiremath CIPROFLOXACIN INDUCED BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID: A CASE REPORT
 CIPROFLOXACIN INDUCED BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID: A CASE REPORT Ravishankar AC 1*, Hiremath SV 1 1 Dept of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics, JN Medical College, Belgaum, India. Summary Bullous pemphigoid
CIPROFLOXACIN INDUCED BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID: A CASE REPORT Ravishankar AC 1*, Hiremath SV 1 1 Dept of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics, JN Medical College, Belgaum, India. Summary Bullous pemphigoid
ISPUB.COM. Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations. D Sarma, S Repertinger
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY ORAL CAVITY. Oral Cavity Subsites 4/10/2013 LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL MUCOUS MEMBRANES PALATE TONGUE ORAL LYMPHOID TISSUES
 LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is the most common autoimmune. ActaDV ActaDV
 6 CLINICAL REPORT Diagnostic Value of Linear Fluorescence Along the Basement Membrane of Sweat Gland Ducts in Bullous Pemphigoid Işın SINEM BAĞCI,, Orsolya N. HORVÁTH, Enno SCHMIDT,, Thomas RUZICKA and
6 CLINICAL REPORT Diagnostic Value of Linear Fluorescence Along the Basement Membrane of Sweat Gland Ducts in Bullous Pemphigoid Işın SINEM BAĞCI,, Orsolya N. HORVÁTH, Enno SCHMIDT,, Thomas RUZICKA and
ISPUB.COM. A Case of Actinic Lichen Planus. K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
Some skin conditions
 Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
