BP230- and BP180-Specific Auto-Antibodies in Bullous Pemphigoid
|
|
|
- Valentine Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BP230- and BP180-Specific Auto-Antibodies in Bullous Pemphigoid Sybille Thoma-Uszynski, Wolfgang Uter,w Susanne Schwietzke, Silke C. Hofmann, Thomas Hunziker,z Philippe Bernard,y Regina Treudler,z Christos C. Zouboulis,z Gerold Schuler, Luca Borradori,# and Michael Hertl Departments of Dermatology and wmedical Statistics, Biometry and Epidemiology, Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nürnberg, Germany; zdepartment of Dermatology, University Hospital, Bern, Switzerland; ydepartment of Dermatology, University of Reims, France; zdepartment of Dermatology, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Charité University Medicine Berlin, Germany; #Department of Dermatology, University Hospital, Geneva, Switzerland Bullous pemphigoid is a subepidermal blistering disease associated with auto-antibodies (auto-ab) to BP180 and BP230. We developed ELISAs utilizing baculovirus-encoded recombinant proteins of BP230 and BP180 and studied their diagnostic and prognostic values by assessing the profile of the auto-ab response in 127 patients with BP. 39 patients had focal involvement, whereas 88 had generalized disease; 51 individuals served as controls. The results indicate: (1) BP180 IgG reactivity was associated with an overall sensitivity of and specificity of 0.940; (2) 105 of 127 BP patients also displayed BP230 auto-reactivity, the global diagnostic performance of which, however, was moderate compared to BP180-auto-reactivity (sensitivity vs 0.953, specificity vs 0.940); (3) 101 patients (79.5%) had concordant BP180 and BP230 reactivity; (4) the association between the presence of BP230 autoreactivity and focal involvement was stronger than in generalized disease (odds ratio (OR) 17.7 vs 10.2), independently from BP180 auto-ab profile; (5) correlation of total IgG with IgG 1 and IgG 4 was variable for both BP180 and BP230. Collectively, the global diagnostic properties of the BP180-ELISA outperform those of the BP230-ELISA. Presence of BP230 auto-reactivity, however, supports the diagnosis of BP and might be indicative for the extent of the disease. Key words: adhesion molecules/auto-immunity/bp180/bp230 auto-antibodies/bullous pemphigoid/hemidesmosome J Invest Dermatol 122: , 2004 Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is an auto-immune blistering disorder of the skin that usually affects the elderly. The disease is associated with tissue-bound and circulating auto-antibodies (auto-ab) directed against components of the epidermal basement membrane zone (Jordon et al, 1967). Clinically, BP is characterized by generalized tense subepidermal blisters arising on apparently normal or erythematous skin and occasionally involvement of mucous membranes (Lever, 1953). Previous studies have demonstrated that BP auto-ab predominantly recognize BP180 (BPAG2 or type XVII collagen) and/or BP230 (BPAG1) (Labib et al, 1986; Stanley et al, 1988; Giudice et al, 1992), two structural components of hemidesmosomes, junctional complexes promoting the adhesion of basal keratinocytes Abbreviations: auto-ab, autoantibodies; BP, bullous pemphigoid; BP180ex, baculoprotein containing the ECD of BP180 (residue ); BP230-N, baculoprotein containing the NH 2 -terminus of BP230 (residue ); BP230-C1, baculoprotein containing the COOH-terminus (residue ) of BP230; BP230-C2, baculoprotein containing the COOH-terminus (residue ) of BP230; ECD, extracellular domain; GST, glutathione-s-transferase; IIF, indirect immunofluorescence; OD, optical density; OR, odds ratio; ROC, receiver operating characteristics; RT, room temperature to the underlying basement membrane zone (reviewed in Borradori et al (1999)). The cytoplasmic protein BP230, that was originally identified as a target antigen of BP (Stanley et al, 1988) is a cytoplasmic component of hemidesmosomes that belongs to the plakin family of cytolinkers (reviewed in Guo et al (1995), Borradori et al (1999), Ruhrberg et al (1997)). This protein is implicated in the linkage of the keratin intermediate filament network to the basal cell side (Guo et al, 1995; Ruhrberg et al, 1997; Borradori et al, 1999; Koster et al, 2003). The transmembrane protein BP180 has a large extracellular domain (ECD) which consists of 15 interrupted collagenous subdomains (Giudice et al, 1992; Hopkinson et al, 1992). It serves as a cell-surface receptor, contributing to the maintenance of dermo-epidermal cohesion by binding most likely to the extracellular matrix component laminin 5 (Giudice et al, 1992; Hopkinson et al, 1992; Borradori et al, 1999; Nievers et al, 2000; Nishiyama et al, 2000). Furthermore, BP180 is probably involved in epidermal differentiation by shedding and facilitating detachment of keratinocytes from the basal cell layer (Giudice et al, 1992; Hopkinson et al, 1992; Borradori et al, 1999; Nievers et al, 2000; Nishiyama et al, 2000). Mutations of the BP180 gene (COL17A1) may cause a clinical variant of non-herlitz Copyright r 2004 by The Society for Investigative Dermatology, Inc. 1413
2 1414 THOMA-USZYNSKI ET AL THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY junctional epidermolysis bullosa, a heritable disorder characterized by skin fragility and blistering (McGrath et al, 1995; Pulkkinen et al, 1998). The commonly accepted idea that auto-ab to BP180 are critical in subepidermal blister formation in BP patients has been supported by a passive murine transfer model, in which rabbit antibodies raised against the murine homologue of the human immunodominant region of BP180, the NC16A domain, were able to reproduce all key features of BP (Liu et al, 1993). Furthermore, serum levels of IgG autoab directed against the ECD of BP180 were directly related to the severity of BP (Haase et al, 1998; Schmidt et al, 2000) or distinct clinical phenotypes of BP (Hofmann et al, 2002). Auto-ab from patients with BP and gestational pemphigoid, a clinical variant occurring during pregnancy, have been found to be predominantly directed against distinct antigenic regions of the ECD of BP180: Specifically, the NC16A subdomain, a region adjacent to the membrane spanning domain of BP180, contains major epitopes recognized by most sera from patients with BP and gestational pemphigoid (Giudice et al, 1993; Matsumura et al, 1996). Preadsorption of patients IgG with recombinant NC16A protein leads to almost complete abolishment of BP180-specific serum reactivity (Zillikens et al, 1997b; Hata et al, 2000; Lin et al, 2000). The COOH-terminal region of the ECD of BP180 has been shown to be recognized by approximately one-third of BP sera (Murakami et al, 1998; Nakatani et al, 1998; Hofmann et al, 2002) as well as by sera from a subset of patients with cicatricial pemphigoid (CP), a related auto-immune bullous disorder characterized by a scarring phenotype of the mucous membranes (Balding et al, 1996; Bedane et al, 1997; Murakami et al, 1998; Nie et al, 1999). In contrast, the cytoplasmic BP230 as target for auto-ab has been the focus of only few studies (Ishiko et al, 1993; Savage et al, 1999; Seishima et al, 1999a, b; Skaria et al, 2000). Preliminary studies by Husz et al suggest that anti- BP230 antibodies directly contribute to tissue damage (Husz et al, 2002). The purpose of this study was to investigate the diagnostic properties of auto-ab against BP180 and BP230 in BP serum samples utilizing newly established ELISA assays with baculovirus-encoded recombinant proteins and the relationship between auto-ab profiles and distinct clinical variants of BP. Results Production of baculovirus-encoded BP180- and BP230 recombinant proteins Using baculovirus expression, relatively large BP180- and BP230 recombinant proteins were successfully produced and purified. After purification, BP180- and BP230-like recombinant proteins displayed the expected size and were specifically immunoreactive using appropriate monoclonal antibodies directed at the tags (data not shown) and specific antisera (see Figs 1 and 2). IgG reactivity of BP sera against the ECD of BP180, BP180ex, is highly diagnostic for BP in all clinical variants Sera from BP patients and controls were tested against recombinant BP180ex which was immobilized onto ELISA microtiter plates. The BP180ex recombinant protein used for ELISA preparation presumably possessed a conformation which allowed specific detection of BP180- specific auto-ab and thus perhaps similar to the native ECD of BP180 (Fig 3). This notion is supported by the fact that BP180ex reactive sera were also reactive to BP180ex-virusinfected insect cells, but not the appropriate controls, e.g., wild-type-virus/vector-infected insect cells did not react with BP180-reactive serum and irrelevant control serum did not react with BP180ex-infected insect cells (Fig 2C). Based on the maximization of the Youden index, the cut-off point for the ELISA with BP180ex protein was set at OD units which corresponds to a Youden index of (Table I). The diagnostic accuracy of this assay was high regarding both sensitivity and specificity (Tables I and II). The distribution of IgG levels (OD s) in the two clinical variants and the controls, respectively, is shown in Fig 3. The difference between generalized versus focal involvement was significant, indicating that higher levels of BP180- specific IgG are correlated to the severity of the clinical variant. IgG reactivity of BP sera against BP230 Further characterization of the BP sera was performed utilizing BP230 recombinant proteins. Similar to BP180ex, recombinant BP230 proteins were recognized both, as native proteins expressed by baculovirus-infected insect cells and after purification under denaturing conditions in immobilized form (Fig 2B, C). Again, the cutpoints for the ELISA with BP230- C1, BP230-C2, and BP230-N proteins were determined by maximization of the Youden indices and corresponding ROC curves were generated (Fig 4, Table I). Among clinical variants, BP230 reactivity is strongly associated with focal BP The results of the polytomous logistic regression analysis confirmed the highly significant association between the diagnosis of BP (both clinical variants) and positive BP180 reactivity. Independently from this, IgG reactivity to BP230 was significantly associated with the outcome, in particular with focal BP (Table III, Fig 5). In the multifactorial analysis (polytomous logistic regression) adjusted for BP 180 reactivity and age, IgG reactivity to BP230 was significantly associated with the outcome focal BP (OR 17.7, 95% CI: ) and, to a lesser extent, with the outcome generalized BP (OR 10.2, 95% CI: ). Diagnostic properties of BP180 and BP230 IgG reactivity A comparison between positive seroreactivity towards BP180 and BP230, as defined above, is shown in Table II. Discordance is fairly symmetric (p ¼ 0.64, exact McNemar test). Concordance between the two diagnostic classifications as quantified with Cohen s kappa coefficient is moderate: k ¼ 0.45 (95% CI: ). Diagnostic properties of BP230 seropositivity ; regarding both sensitivity and specificity were less favorable than BP180 IgG reactivity (Table II). Table III describes the joint distribution of BP180 and BP230 reactivity within the clinical variants.
3 122 : 6 JUNE 2004 AUTO-ANTIBODY PROFILES AND BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID 1415 Figure 1 Bullous pemphigoid (BP)230 recombinant proteins utilized in this ELISA study. (A) BP230 is an intracellular hemidesmosomal component which consists of a central rod flanked by globular end domains. (B) The recombinant BP230 fusion proteins are 6xHis- and glutathione-s-transferase (GST) tagged at their NH 2 terminus. Two COOH-terminal constructs (BP230-C1, containing residues and BP230-C2, residues ) and one NH 2 -terminal construct (BP230-N, residues ) were expressed. The purified BP230 recombinant proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and Coomassie stained. (C) SF21 insect cells infected with recombinant BP230 baculovirus for 3 d were recognized by a representative BP serum. Figure 2 Bullous pemphigoid (BP)180 recombinant protein utilized in this ELISA study. (A) BP180 is a type II transmembrane protein containing an intracellular, a transmembrane, and an extracellular domain with 15 interrupted collagenous regions. (B) The recombinant fusion protein BP180ex is 6xHis- and glutathione-s-transferase (GST)-tagged at its NH 2 end (residues ). The purified BP180ex protein was transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and Coomassie stained. (C) SF21 insect cells infected with BP180ex baculovirus for 3 d were recognized by a representative BP serum. BP230 domains and clinical variants BP230 reactive BP sera recognize epitopes within the COOH- and NH 2 - terminal regions (BP230-C1, BP230-C2, and BP230-N) without significant differences between the two clinical variants (after adjustment for multiple testing) (Fig 5). Relationship of IgG subtypes within clinical variants against BP230 and BP180 In addition to total BP230 and BP180 IgG, the major auto-ab subtypes (IgG 1 and IgG 4 ) were analyzed. Thus, it appeared that in active BP, IgG 4 was the predominant IgG subtype reactive with the COOH-
4 1416 THOMA-USZYNSKI ET AL THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Figure 3 IgG reactivity against the extracellular domain of bullous pemphigoid (BP)180ex is highly indicative for BP. BP patient and control serum samples were tested by ELISA using recombinant BP180ex. Sera of patients with BP (n ¼ 127) and of 51 controls were incubated with 0.5 mg of immobilized BP180ex protein. IgG binding was detected with an alkaline-phosphatase-labeled anti-human IgG ab. Samples were run in duplicate and mean outer diameter reading at 405 nm of a serum sample with BP230 recombinants. Data are displayed as box plots: The box shows first and third quartiles, the median (as line), and the arithmetic mean (as dot), the whiskers represent values below the first quartile and above the third quartile within the 1.5-fold inter-quartile range, respectively, and outliers beyond the whiskers are shown as squares. The dotted lines indicate the cut-off values as evaluated by maximization of Youden index. The inset visualizes the corresponding receiver operating characteristic curve. There was a highly significant difference between clinical variants and controls as well as between generalized and focal BP. terminus, but not the NH 2 -terminus of BP230 (Fig 6A C). Regarding the IgG subtype reactivity against BP180 (BP180ex), IgG 1 and IgG 4 were nearly equally distributed (Fig 6D). Correlation between COOH- and NH 2 -terminal constructs of BP IgG reactivity to the overlapping COOHterminal BP230 constructs, BP230-C1 and BP230-C2, revealed a high correlation (0.94, po unadjusted, BP230-C1 vs BP230-C2). When IgG reactivity against NH 2 - terminal versus COOH-terminal BP230-like recombinant proteins was plotted, correlation was only moderate (r ¼ 0.43, po0.0001, unadjusted). This indicates that relevant epitopes are distributed over both globular domains of BP230; however, relevant BP230 epitopes of the COOHterminus are harbored in BP230-C2 (residues ). Discussion The aim of this study was to analyze the relationship between IgG auto-ab directed against the intracellular BP230 and the transmembranous BP180 proteins, the major auto-antigens of BP, as diagnostic markers in BP. For this purpose, we developed novel ELISA assays utilizing four recombinant eukaryotic proteins encompassing immunodominant regions of BP230 (BP230-C1, BP230-C2, BP230-N) and BP180 (BP180ex), respectively. The results demonstrate a highly diagnostic BP180 ELISA utilizing the entire ECD of BP180 which detected BP180 as a specific auto-ab in the majority of the patients sera. Throughout both clinical variants (focal vs generalized BP), BP180 reactivity was highly associated with the diagnosis of BP. In contrast, BP230-specific IgG was also detected in the majority of the BP sera, although less frequently than BP180-specific IgG and was associated with a less severe clinical variant of BP. At present, it is unclear whether BP230 auto-ab reactivity is part of the disease initiation and directly contributes to blister formation or whether these auto-ab represent an epiphenomenon. A serological approach towards elucidation of the potential functional role of BP230 auto-ab was the thorough analysis of auto-ab profiles in BP patients. Although in terms of diagnostic power, BP230-specific IgG was outperformed by anti-bp180 IgG, the majority of our patients also showed BP230 reactivity, particularly those with focal BP. Thus, valuable diagnostic information was obtained by the present novel BP230 ELISA in addition to the already established BP180 ELISA. ELISA systems detecting auto-ab specific for defined regions of the ECD of BP180 utilized mainly prokaryotic BP180-like recombinant proteins (Giudice et al, 1994; Zillikens et al, 1997a; Nakatani et al, 1998). Zillikens et al detected IgG reactivity against the NC16A domain of BP180 in 94% of 50 BP sera (Zillikens et al, 1997a). Another ELISA utilizing bacterial recombinant proteins demonstrated the presence of IgG auto-ab against the NC16A subdomain and the COOH-extremity of BP180 in 96% and 38% of the BP sera, respectively (Nakatani et al, 1998). A recent study from our laboratory with eukaryotic BP180-like recombinant proteins demonstrated that auto-ab against the NH 2 - terminus of the BP180 ectodomain were associated with a more extensive phenotype of BP while auto-ab against the COOH-terminus of BP180 were not (Hofmann et al, 2002). Consistent with previous passive transfer studies with rabbit sera reactive with the murine homologue of the
5 122 : 6 JUNE 2004 AUTO-ANTIBODY PROFILES AND BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID 1417 Table I. Cutpoints (outer diameter (OD) values with maximum corresponding Youden Index (YI) a with sensitivity and specificity, including exact 95% confidence intervals (CIs)) Cutpoint Yi a Sensitivity Specificity BP230-C1 Total IgG ( ) ( ) IgG ( ) ( ) IgG ( ) ( ) BP230-C2 Total IgG ( ) ( ) IgG ( ) ( ) IgG ( ) ( ) BP230-N Total IgG ( ) ( ) IgG ( ) ( ) IgG ( ) ( ) BP180ex Total IgG ( ) ( ) IgG ( ) ( ) IgG ( ) ( ) a BP, bullous pemphigoid; Youden index (sensitivity þ specificity 1). Table II. Concordance between IgG reactivity against bullous pemphigoid (BP)180 and BP230, and global diagnostic properties of BP230 IgG reactivity BP230 a Pos. Neg. Total BP180 b Pos Neg Pos. Neg. BP Yes No a Pos. : either BP230-C1-, BP230-C2- or BP230-N-reactive IgG above cutpoint. b Using BP180 as an alternative gold standard, i.e. case definition criterion: Sensitivity of BP230: (95% CI: ); Specificity of BP230: (95% CI: ). NC16A domain (Liu et al, 1993), our findings further support the notion that auto-ab against the ECD of BP180 are pathogenic. Recent studies from our group and others with prokaryotic and eukaryotic BP180 recombinant proteins also suggested a possible relationship between disease activity and auto-ab levels against the BP180 ectodomain (Haase et al, 1998; Dopp et al, 2000; Schmidt et al, 2000; Hofmann et al, 2002). In line with the latter, here we also found a significant difference of BP180 auto-ab levels between generalized and focal involvement (Hofmann et al, 2002). A recent serological study showed that auto-ab against BP230 were mainly directed against the B -the linker, and C subdomains of the COOH-terminus of BP230 (Skaria et al, 2000). This analysis, which is an extensive serological study utilizing an ELISA system with baculovirus-derived eukaryotic BP230 recombinant proteins, confirms these findings showing that both, NH 2 - and COOH-terminus of BP230 are major immunodominant regions targeted by IgG auto-ab in BP. Several observations support the hypothesis that BP230-specific auto-ab are relevant for the pathogenesis of BP and not just an epiphenomenon: (1) Immunization of rabbits with BP230-derived peptides appeared to increase the local inflammatory response following epidermal damage (Hall et al, 1993); (2) BP230-specific auto-ab were readily detectable in the majority of patients even even after a relatively short disease duration (1.5 mo); (3) preliminary results by Husz et al, indicate that BP230 is relevant for pathogenesis of BP: Immunization of rabbits with human BP230 fragments yielded high-titer BP230-specific polyclonal rabbit serum which, after subcutaneous injection into neonatal mice induced an inflammatory response and skin fragility. Immunohistological analysis revealed IgG deposition along the basement membrane zone, few animals even
6 1418 THOMA-USZYNSKI ET AL THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Figure 4 Cutpoint determination by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for bullous pemphigoid (BP)230-reactive total IgG. Detection of serum IgG against the NH 2 -terminus (BP230-N) and COOH-terminus (BP230-C1 and BP230-C2) of BP230 is shown as ROC curves. Sera of patients with BP (n ¼ 127) and 51 controls were incubated with 0.5 mg of immobilized BP230-N, BP230-C-1, BP230-C-2 proteins. IgG binding was detected with an alkaline phosphatase (AP)-labeled anti-human IgG ab. Samples were run in duplicate and mean OD reading at 405 nm of a serum sample with BP230-like recombinant proteins. The solid lines indicate the cut-off values as evaluated by maximization of Youden index. Table III. Comparison of IgG reactivity against BP180 and/or BP230 and clinical variant of BP Clinical variant of BP Auto-ab reactivity Generalized Focal Controls BP 180 only BP 230 only Both Neither Auto-ab, auto-antibodies; BP, bullous pemphigoid. developed subcutaneous blisters (Husz et al, 2002). In addition to participating to the inflammatory reaction, autoab to BP230 may interfere with the function of BP230 and its molecular interactions with the other components of the hemidesmosomal adhesion complex. Further evidence that functional BP230 is essential for skin stability comes from BP230-null mutant mice which exhibit an increased; however, intraepidermal skin fragility due to the lack of the inner hemidesmosomal plate (Guo et al, 1995). Since the various IgG subclasses have distinct functional properties and their secretion is differentially regulated, we have also assessed the relative isotype distribution among the major IgG subclasses specific for both BP180 and BP230, most studies reported a preferential detection of IgG 1 and IgG 4 auto-ab against BP180, while BP180-specific IgG 2 and IgG 3 auto-ab were detected in few BP serum samples only (Bernard et al, 1990; Dopp et al, 2000; Laffitte et al, 2001). In this study, BP180-reactive IgG 1 and IgG 4 auto-ab were almost equally distributed in the studied patient cohort. A recent study from our laboratory, however, indicated that IgG 1 auto-ab against the immunodominant NH 2 -terminal ECD of BP180 were predominant in acute onset BP, while IgG 4 auto-ab predominated in remittent BP (Hofmann et al, 2002). Noteworthy, a dual IgG 1 and IgG 4 response against the NH 2 -terminus of the ECD of BP180 was associated with a more severe skin involvement in BP (Hofmann et al, 2002). Two additional previous studies reported a predominance of BP180-specific IgG 1 (Bernard et al, 1990; Laffitte et al, 2001), while another study detected more BP180-specific IgG 4 than IgG 1 (Dopp et al, 2000). In this study, IgG reactivity against BP230 was mediated both by IgG 1 and IgG 4 auto-ab. There was no significant difference of the IgG 1 and IgG 4 titers with regard to their specificity for distinct BP230 regions, i.e., NH 2 -terminus (BP230-N) or COOH-terminus (BP230-C1/C2). Noteworthy, IgG 4 but not IgG 1 auto-ab against the C-terminus of BP230 were particularly elevated in the sera of BP patients with focal BP. In a previous study, auto-ab binding to the immunodominant COOH-terminal region of BP230 predominantly belonged to the IgG 4 and IgG 1 subclasses (Skaria et al, 2000) while a serological study by Bernard et al showed also a predominant IgG 4 restriction of anti-bp230 auto-ab (Bernard et al, 1990). The concept that, in addition to IgG 4, complement-fixing IgG 1 plays a key role in the initiation of BP is supported by the clinical finding that, in addition to IgG, perilesional C3 is in most cases detectable at the basement membrane in BP patients (Jordon et al, 1967). In summary, the present novel ELISA assays utilizing eukaryotic recombinant proteins of the NH 2 - and COOH-terminal regions of BP230 and the entire BP180 ectodomain are highly useful for rapid and sensitive analysis of the auto-ab profile, which reflects disease activity of BP. In this investigation, auto-ab against the BP180 ectodomain were highly diagnostic for BP and their titers were correlated with the severity of BP. Auto-ab against BP230 were also found in the majority of the BP serum samples, and thus are of confirmatory diagnostic value. Noteworthy, the presence of anti-bp230 IgG auto-ab was particularly associated with a less severe clinical manifestation of BP and may thus be of potential prognostic value. Materials and Methods Patients and control sera Serum samples were obtained from patients with clinically active BP (n ¼ 127), and control donors
7 122 : 6 JUNE 2004 AUTO-ANTIBODY PROFILES AND BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID 1419 Figure 5 Bullous pemphigoid (BP)230 IgG levels in clinical variants. Total IgG responses against the BP230 recombinant proteins were compared between serum samples from patients with generalized versus focal BP. Box plot presentation depicting median, arithmetic mean, and range from first to third quartile as in Fig 3. BP230- specific IgG reactivity against all three BP230 recombinants in both generalized and focal BP. Overall, higher, significantly different IgG levels were observed in localized BP. Thus, BP230 IgG-reactivity was significantly associated with the outcome focal BP. which included healthy volunteers and patients with unrelated conditions (n ¼ 51). Patients and volunteers gave written consent to participate in this study which was adherent to the Declaration of Helsinki Guidelines and which has been approved by the institutional review board. Serum samples were stored at 201C prior to analysis. Diagnosis of BP was based on the following criteria: (i) typical clinical presentation with tense cutaneous blisters, (ii) histopathological evidence of subepidermal blister formation, (iii) linear IgG and/or C3 deposits at the dermo-epidermal junction of perilesional skin by direct immunofluorescence. Severity of BP was classified according to the extent and number of blisters as either focal disease (only few bullae at limited areas of the body involving maximum 20% of total body surface) or generalized disease with total body surface involvement greater than 20% and wide spread innumerable bullae. Patient characteristics This analysis includes 127 patients with BP (39 with focal involvement and 88 with generalized disease) and 51 age- and sex-matched controls with unrelated skin conditions such as herpes zoster, erysipelas or atopic dermatitis or allergic conditions. Among the patients, there were 51.1% females, with no significant difference between the two clinical groups (p ¼ 0.85, Fisher s exact test). Median age was 80 y (range: y), with no significant differences between the clinical variants (p ¼ 0.45, Wilcoxon Mann Whitney test) (Table IV). Furthermore, the duration of disease (overall median: 1.5 mo) did not differ significantly between generalized and focal cases (p ¼ 0.99, Wilcoxon Mann Whitney test) (Table IV). Oral mucosa involvement was observed in three patients with focal and ten patients with generalized disease, none of which displayed a scaring phenotype or ocular involvement. The majority of patients was untreated when the serum samples were obtained. The few patients under therapy were receiving various regimens of immunosuppressive drugs and/or local treatment. They did not preferentially belong to either one of the defined clinical categories. Expression and purification of BP180 and BP230 recombinant proteins The recombinant BP proteins were produced as glutathione-s-transferase (GST) and 6xHis tag tagged fusion proteins in a baculovirus expression system as described below (Fig 1). cdna expression constructs for human BP180 and BP230 were generated as previously reported (Borradori et al, 1997; Skaria et al, 2000). In brief, cdnas for BP180 or BP230 were used as a template to amplify by Pfu DNA polymerase with forward and reverse primers containing either an EcoR I or a Not I site the desired target sequence (Stratagene, La Jolla, California). The amplified cdna fragments were subsequently subcloned into the pacghlt-a baculovirus transfer vector (Pharmingen, San Diego, California) by ligation of double-digested PCR fragments into the correspondingly cut vectors. Correctness of both constructs was verified by sequencing. pacghlt-a vectors were cotransfected with Baculo-DNA (SixPack, Clontech, Palo Alto, California) into Sf21 insect cells and recombinant baculoviruses were amplified using a previously described protocol (Amagai et al, 1994). The recombinant proteins and the GST/6xHis control protein (generated by cotransfection of an empty pacghlt-a vector) were expressed in Sf21 cells as previously described (Haase et al, 1998). BP230- and BP180 recombinant proteins were purified as follows: 3 d after infection, baculovirus-infected insect cells were suspended in 1 ml of 6 M guanidine-hydrochloride, incubated for 24 h at 201C and then centrifuged (2000 g, 15 min). Solubilized proteins were purified by affinity-chromatography over Nickel NTA agarose (Quiagen, Hilden, Germany) using the batch method according to the manufacturer s protocol. The BP230 and BP180 recombinant proteins and the GST/6xHis control protein were purified under denaturing conditions by adding 6 M guanidinehydrochloride to the lysis buffer and 8 M urea to washing and elution buffers. Finally, purified proteins were gradually dialyzed against PBS supplemented with 8 3 M urea at 41C for 48 h (BP180ex, GST/6xHis). Affinity-purified proteins were stored in aliquots at 801C. Protein concentrations were determined by a commercial kit (DC Protein Assay, Bio-Rad, Munich, Germany) according to a modified protocol by Lowry. BP180ex, BP230-N, and BP230-C1/C2 were fractionated by 10% SDS-Page and visualized by Coomassie staining and western blot with a monoclonal mouse anti-gst antibody (1:2000, clone GST3-4C, Zymed, San Francisco, California) to verify molecular weight and immunoreactivity (Figs 1B and 2B). ELISA analysis utilizing BP230 and BP180 recombinant proteins Optimal conditions for the ELISA were established by
8 1420 THOMA-USZYNSKI ET AL THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Figure 6 (A D) IgG subclass analysis (IgG 1 and IgG 4 ) of bullous pemphigoid (BP)230 and BP180 reactive auto-antibodies (auto-ab). IgG 1 and IgG 4 auto-ab against BP230 (A C) and BP180 (D) were compared between the sera from patients with generalized versus focal BP. Box plot presentation depicting median, arithmetic mean, and range from first to third quartiles as in Fig 3. There was neither a significant correlation for IgG 1 or IgG 4 reactivity against BP230 (BP230-N; BP230-C1/C2) nor to BP180 (BP180ex) with the outcome generalized versus focal BP. various chessboard titrations. The affinity-purified recombinant proteins of BP230 and BP180 were immobilized on 96-well polystyrene plates (Maxisorb Immunoplate, Nunc, Wiesbaden, Germany) by coating each well with 0.5 mg of BP230-N, BP230-C1, BP230-C2, and BP180ex, or a molar equivalent amount of the control protein GST/6xHis in 100 ml of 0.1 M bicarbonate buffer, ph 9.8, at 41C for 5 h. ELISA plates were then washed 5 with TTBS (TBS ph 7.5 with 0.05% Tween 20; Merck, Nürnberg, Germany) and blocked for 2 h with 100 ml of 5% skimmed milk powder (MP) in TTBS at room temperature (RT). BP and control sera were diluted in blocking-buffer 50-fold and added to the wells in duplicate. After an incubation period of 12 h at 41C and consecutive washes, reactions with alkaline phosphatase (AP)-labeled goat anti-human IgG (g) (1:6000, Kirkegaard and Perry, Gaithersburg, Maryland), monoclonal biotinylated mouse anti-human IgG 1 (1:800, clone HP6069) or monoclonal biotinylated mouse anti-human IgG 4 (1:500, clone HP6025) (both Zymed, San Francisco, California), were performed in the wells 1 2 h. After incubation of biotinylated antibodies for 1 h, wells were washed as above and incubated with streptavidin-ap (ZyMAX, Zymed) diluted at 1:2000 in TBS for 1 h at RT. After another series of washes, 100 ml of p-nitrophenylphosphate (Kirkegaard and Perry) or the peroxidase substrate 2,2 0 - azino-bis[3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid] (Sigma, Deisenhofen, Germany) were added to the wells and optical density (OD) was measured at 405 nm when a defined patient serum (positive reference control) reached an OD of 1.0 as determined by a Wallac 1420 microplate reader (Wallac, Freiburg, Germany). All extinction data were standardized based on the positive and negative internal standards, which were set to 1 and 0 OD U, respectively. The background reactivity of IgG to the control protein GST/6xHis was subtracted from the mean OD values obtained with BP180-N and BP180-C proteins. For detection of IgG 1 and IgG 4 reactivity to BP180 and BP230, the GST/6xHis control protein was not routinely used, because a relevant total IgG reactivity against GST/6xHis had not been detected in any of the serum samples by ELISA. To evaluate plate-to-plate variability, each plate included identical internal controls (two positive serum samples, one control serum).
9 122 : 6 JUNE 2004 AUTO-ANTIBODY PROFILES AND BULLOUS PEMPHIGOID 1421 Table IV. Clinical and immunopathological characteristics of the studied BP patients Patient description Generalized Focal Total N Age (y, median) Disease duration (mo, median and range) IIF (SSS) a 1.5 ( ) 1.25 ( ) 1.5 ( ) Epidermal Dermal þ epidermal 1 1 Negative a IIF, indirect immunofluorescence; SSS, saline split skin. 2 of 127 false-negative against case definition; sensitivity: (95% CI: ). Statistical analysis In view of the skewed distribution of OD values, which was scarcely amenable to log-transformation, OD values were analyzed with non-parametric statistical methods, e.g., Spearman rank correlation coefficient and Wilcoxon Mann Whitney or Kruskal Wallis test for overall equality of mean scores. p-values were adjusted for multiple testing with the Bonferroni method, values less than 0.05 were considered significant. The distribution of data is shown as box plot : The box shows first and third quartiles, the median (as line) and the arithmetic mean (as dot), the whiskers represent values below the first quartile and above the third quartile within the 1.5-fold inter-quartile range, respectively, and outliers beyond the whiskers are shown as squares. For data analysis, the statistical software package SAS, version 8.2, was used (SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC)curveswerecompiledbyadditionallyutilizingafreewareSAS macro package (Witte, 2002) to evaluate the diagnostic properties of BP230 and BP180 IgG antibodies with respect to correctly classifying cases of BP. As there are no natural cutpoints for these antibody levels, and as there are no previous studies which had provided evidence concerning an appropriate diagnostic threshold, an optimum cutpoint was determined data adaptively by choosing the OD values with the largest Youden-Index (YI ¼ sensitivity þ specificity 1). For those analyses requiring dichotomization of ELISA results as positive and negative, BP180 seroreactivity was considered positive, if the OD value for total against BP180ex was above the cutpoint (0.207 U) and negative otherwise. BP230 seroreactivity was regarded as positive, if OD values for either total IgG against BP230-C1, BP230-C2, or BP230-N were above the cutpoint (Table I). To assess the independent association between positive BP230 seroreactivity (i.e., any single subclass above cutpoint) and the diagnosis BP, adjusting for BP180 reactivity as well-established factor, and age as potential confounder, a polytomous logistic regression analysis, with the two clinical variants of the disease versus control as outcomes, was performed. The degree of association between BP230 seroreactivity on one hand, and localized and generalized involvement, respectively, on the other hand, was quantified with the odds ratio (OR), accompanied by the corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI). Unique non-proprietary reagents described will be made freely available to qualified scientists. We are grateful to Dr Giovanna Zambruno, Dr Peter von den Driesch, and Dr Nicolas Hunzelmann for providing sera of BP patients. This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (He1602/6-1 to M.H.), European Community (QLG1-CT to L.B. and M.H.), the Interdisciplinary Center for Clinical Research (IZKF; C9 to M.H.), the ELAN Fonds ( to S.T.U.) at the University of Erlangen, Germany and the Swiss National Foundation of Scientific Research ( to L.B.). The authors are also indebted to Dr J.R. Stanley (University of Pennsylvania, Phildelphia) and Dr J. Uitto, (Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia), who generously provided cdnas for human BP230. DOI: /j X x Manuscript received August 27, 2003; revised January 12, 2004; accepted for publication January 26, 2004 Address correspondence to: Sybille Thoma-Uszynski, Department of Dermatology, Friedrich-Alexander-University of Erlangen-Nürnberg, Hartmannstrae 14, D Erlangen, Germany. sybille. thoma-uszynski@derma.imed.uni-erlangen.de References Amagai M, Hashimoto T, Shimizu N, et al: Absorption of pathogenic autoantibodies by the extracellular domain of pemphigus vulgaris antigen (Dsg3) produced by baculovirus. J Clin Invest 94:59 67, 1994 Balding SD, Prost C, Diaz LA, et al: Cicatricial pemphigoid autoantibodies react with multiple sites on the BP180 extracellular domain. J Invest Dermatol 106: , 1996 Bedane C, McMillan JR, Balding SD, et al: Bullous pemphigoid and cicatricial pemphigoid autoantibodies react with ultrastructurally separable epitopes on the BP180 ectodomain: Evidence that BP180 spans the lamina lucida. J Invest Dermatol 108: , 1997 Bernard P, Aucouturier P, Denis F, et al: Immunoblot analysis of IgG subclasses of circulating antibodies in bullous pemphigoid. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 54: , 1990 Borradori L, Koch PJ, Niessen CM, et al: The localization of bullous pemphigoid antigen 180 (BP180) in hemidesmosomes is mediated by its cytoplasmic domain and seems to be regulated by the beta4 integrin subunit. J Cell Biol 136: , 1997 Borradori L, Sonnenberg A: Structure and function of hemidesmosomes: More than simple adhesion complexes. J Invest Dermatol 112: , 1999 Dopp R, Schmidt E, Chimanovitch I, et al: IgG4 and IgE are the major immunoglobulins targeting the NC16A domain of BP180 in Bullous pemphigoid: Serum levels of these immunoglobulins reflect disease activity. J Am Acad Dermatol 42: , 2000 Giudice GJ, Emery DJ, Diaz LA: Cloning and primary structural analysis of the bullous pemphigoid autoantigen BP180. J Invest Dermatol 99: , 1992 Giudice GJ, Emery DJ, Zelickson BD, et al: Bullous pemphigoid and herpes gestationis autoantibodies recognize a common non-collagenous site on the BP180 ectodomain. J Immunol 151: , 1993 Giudice GJ, Wilske KC, Anhalt GJ, et al: Development of an ELISA to detect anti- BP180 autoantibodies in bullous pemphigoid and herpes gestationis. J Invest Dermatol 102: , 1994 Guo L, Degenstein L, Dowling J, et al: Gene targeting of BPAG1: Abnormalities in mechanical strength and cell migration in stratified epithelia and neurologic degeneration. Cell 81: , 1995 Haase C, Budinger L, Borradori L, et al: Detection of IgG autoantibodies in the sera of patients with bullous and gestational pemphigoid: ELISA studies utilizing a baculovirus- encoded form of bullous pemphigoid antigen 2. J Invest Dermatol 110: , 1998 Hall RP III, Murray JC, McCord MM, et al: Rabbits immunized with a peptide encoded for by the 230-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen cdna develop an enhanced inflammatory response to UVB irradiation: A potential animal model for bullous pemphigoid. J Invest Dermatol 101:9 14, 1993 Hata Y, Fujii Y, Tsunoda K, et al: Production of the entire extracellular domain of BP180 (type XVII collagen) by baculovirus expression. J Dermatol Sci 23: , 2000 Hofmann S, Thoma-Uszynski S, Hunziker T, et al: Severity and phenotype of bullous pemphigoid relate to autoantibody profile against the NH2- and COOH-terminal regions of the BP180 ectodomain. J Invest Dermatol 119: , 2002 Hopkinson SB, Riddelle KS, Jones JC: Cytoplasmic domain of the 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen, a hemidesmosomal component: Molecular and cell biologic characterization. J Invest Dermatol 99: , 1992 Husz S, Kiss M, Janossy T, et al: Experimental mouse model of bullous pemphigoid using antibodies generated against an antigenic epitope of
10 1422 THOMA-USZYNSKI ET AL THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY hemidesmosomal plaque protein BP230. J Invest Dermatol 119:724, 2002 (abstract) Ishiko A, Shimizu H, Kikuchi A, et al: Human autoantibodies against the 230-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG1) bind only to the intracellular domain of the hemidesmosome, whereas those against the 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG2) bind along the plasma membrane of the hemidesmosome in normal human and swine skin. J Clin Invest 91: , 1993 Jordon RE, Beutner EH, Witebsky E, et al: Basement zone antibodies in bullous pemphigoid. JAMA 200: , 1967 Koster J, Geerts D, Favre B, et al: Analysis of the interactions between BP180, BP230, plectin and the integrin alpha6beta4 important for hemidesmosome assembly. J Cell Sci 116: , 2003 Labib RS, Anhalt GJ, Patel HP, et al: Molecular heterogeneity of the bullous pemphigoid antigens as detected by immunoblotting. J Immunol 136: , 1986 Laffitte E, Skaria M, Jaunin F, et al: Autoantibodies to the extracellular and intracellular domain of bullous pemphigoid 180, the putative key autoantigen in bullous pemphigoid, belong predominantly to the IgG1 and IgG4 subclasses. Br J Dermatol 144: , 2001 Lever WF: Pemphigus. Medicine 32:1 123, 1953 Lin MS, Fu CL, Giudice GJ, et al: Epitopes targeted by bullous pemphigoid T lymphocytes and autoantibodies map to the same sites on the bullous pemphigoid 180 ectodomain. J Invest Dermatol 115: , 2000 Liu Z, Diaz LA, Troy JL, et al: A passive transfer model of the organ-specific autoimmune disease, bullous pemphigoid, using antibodies generated against the hemidesmosomal antigen, BP180. J Clin Invest 92: , 1993 Matsumura K, Amagai M, Nishikawa T, et al: The majority of bullous pemphigoid and herpes gestationis serum samples react with the NC16a domain of the 180-kDa bullous pemphigoid antigen. Arch Dermatol Res 288: , 1996 McGrath JA, Gatalica B, Christiano AM, et al: Mutations in the 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG2), a hemidesmosomal transmembrane collagen (COL17A1), in generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa. Nat Genet 11:83 86, 1995 Murakami H, Nishioka S, Setterfield J, et al: Analysis of antigens targeted by circulating IgG and IgA autoantibodies in 50 patients with cicatricial pemphigoid. J Dermatol Sci 17:39 44, 1998 Nakatani C, Muramatsu T, Shirai T: Immunoreactivity of bullous pemphigoid (BP) autoantibodies against the NC16A and C-terminal domains of the 180 kda BP antigen (BP180): Immunoblot analysis and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using BP180 recombinant proteins. Br J Dermatol 139: , 1998 Nie Z, Hashimoto T: IgA antibodies of cicatricial pemphigoid sera specifically react with C-terminus of BP180. J Invest Dermatol 112: , 1999 Nievers MG, Kuikman I, Geerts D, et al: Formation of hemidesmosome-like structures in the absence of ligand binding by the (alpha)6(beta)4 integrin requires binding of HD1/plectin to the cytoplasmic domain of the (beta)4 integrin subunit. J Cell Sci 113 (Pt 6): , 2000 Nishiyama T, Amano S, Tsunenaga M, et al: The importance of laminin 5 in the dermal-epidermal basement membrane. J Dermatol Sci 24 (Suppl. 1): S51 S59, 2000 Pulkkinen L, Uitto J: Hemidesmosomal variants of epidermolysis bullosa. Mutations in the alpha6beta4 integrin and the 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen/type XVII collagen genes. Exp Dermatol 7:46 64, 1998 Ruhrberg C, Watt FM: The plakin family: Versatile organizers of cytoskeletal architecture. Curr Opin Genet Dev 7: , 1997 Savage PA, Boniface JJ, Davis MM: A kinetic basis for T cell receptor repertoire selection during an immune response. Immunity 10: , 1999 Schmidt E, Obe K, Brocker EB, et al: Serum levels of autoantibodies to BP180 correlate with disease activity in patients with bullous pemphigoid. Arch Dermatol 136: , 2000 Seishima M, Izumi T, Kanoh H, et al: Demonstration of antibody to 230 kda bullous pemphigoid antigen in lichen planus-like keratosis. Eur J Dermatol 9: , 1999a Seishima M, Izumi T, Kitajima Y: Antibody to bullous pemphigoid antigen 1 binds to the antigen at perilesional but not uninvolved skin, in localized bullous pemphigoid. Eur J Dermatol 9:39 42, 1999b Skaria M, Jaunin F, Hunziker T, et al: IgG autoantibodies from bullous pemphigoid patients recognize multiple antigenic reactive sites located predominantly within the B and C subdomains of the COOH-terminus of BP230. J Invest Dermatol 114: , 2000 Stanley JR, Tanaka T, Mueller S, et al: Isolation of complementary DNA for bullous pemphigoid antigen by use of patients autoantibodies. J Clin Invest 82: , 1988 Witte S: Macro for generation of ROC-curves. Proceedings of the Sixth Conference of SAS Application in Research and Development, Dortmund, 2002 Zillikens D, Mascaro JM, Rose PA, et al: A highly sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of circulating anti-bp180 autoantibodies in patients with bullous pemphigoid. J Invest Dermatol 109: , 1997a Zillikens D, Rose PA, Balding SD, et al: Tight clustering of extracellular BP180 epitopes recognized by bullous pemphigoid autoantibodies. J Invest Dermatol 109: , 1997b
Autoreactive T and B Cells from Bullous. Clustered in Distinct Regions of BP180 and BP230. This information is current as of November 1, 2018.
 This information is current as of November 1, 2018. References Subscription Permissions Email Alerts Autoreactive T and B Cells from Bullous Pemphigoid (BP) Patients Recognize Epitopes Clustered in Distinct
This information is current as of November 1, 2018. References Subscription Permissions Email Alerts Autoreactive T and B Cells from Bullous Pemphigoid (BP) Patients Recognize Epitopes Clustered in Distinct
Current concepts of autoimmune bullous diseases Advances in pathogenesis. Luca Borradori
 Current concepts of autoimmune bullous diseases Advances in pathogenesis Luca Borradori Dept. of Dermatology Inselspital, University Hospital of Berne Switzerland Luca.Borradori@insel.ch Autoimmune bullous
Current concepts of autoimmune bullous diseases Advances in pathogenesis Luca Borradori Dept. of Dermatology Inselspital, University Hospital of Berne Switzerland Luca.Borradori@insel.ch Autoimmune bullous
Ann Dermatol Vol. 24, No 1,
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 24, No 1, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2012.24.1.45 ORIGINAL ARTICAL Usefulness of Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay Using Recombinant BP180 and BP230 for Serodiagnosis and Monitoring
Ann Dermatol Vol. 24, No 1, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2012.24.1.45 ORIGINAL ARTICAL Usefulness of Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay Using Recombinant BP180 and BP230 for Serodiagnosis and Monitoring
Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis
 Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis A. España C. Sitaru* M. Pretel L. Aguado J. Jimenez# Department of Dermatology, University
Erythema gyratumrepens-like eruption in a patient with epidermolysisbullosaacquisita associated with ulcerative colitis A. España C. Sitaru* M. Pretel L. Aguado J. Jimenez# Department of Dermatology, University
Autoimmune bullous dermatoses
 Autoimmune bullous dermatoses Overview of serological diagnostics in autoimmune blister-forming diseases of the skin Pemphigoid diseases Pemphigus diseases Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita Dermatitis herpetiformis
Autoimmune bullous dermatoses Overview of serological diagnostics in autoimmune blister-forming diseases of the skin Pemphigoid diseases Pemphigus diseases Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita Dermatitis herpetiformis
Bullous Pemphigoid with Lymphocytic Colitis: A Case Report and Short Literature Review
 Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) (2016) 6:437 441 DOI 10.1007/s13555-016-0135-4 CASE REPORT Bullous Pemphigoid with Lymphocytic Colitis: A Case Report and Short Literature Review Alexandra Sperl. Johann W. Bauer.
Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) (2016) 6:437 441 DOI 10.1007/s13555-016-0135-4 CASE REPORT Bullous Pemphigoid with Lymphocytic Colitis: A Case Report and Short Literature Review Alexandra Sperl. Johann W. Bauer.
Recent Advances in the Molecular Pathology of Bullous Skin Disorders
 1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 2, June 2005 Recent Advances in the Molecular Pathology of Bullous Skin Disorders John A McGrath* Maintenance of an intact epidermis depends on secure adhesion
1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 2, June 2005 Recent Advances in the Molecular Pathology of Bullous Skin Disorders John A McGrath* Maintenance of an intact epidermis depends on secure adhesion
Index. derm.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
Introduction to Pemphigoid: Spectrum of Disease & Treatment
 Introduction to Pemphigoid: Spectrum of Disease & Treatment A Razzaque Ahmed, MD Center for Blistering Diseases Boston, MA A.Razzaque.Ahmed@tufts.edu centerforblisteringdiseases.com SPECTRUM OF PEMPHIGOID
Introduction to Pemphigoid: Spectrum of Disease & Treatment A Razzaque Ahmed, MD Center for Blistering Diseases Boston, MA A.Razzaque.Ahmed@tufts.edu centerforblisteringdiseases.com SPECTRUM OF PEMPHIGOID
Department of Dermatology, Nippon Medical School, 1-1-5, Sendagi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo , Japan 2
 Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2010, Article ID 931340, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/931340 Case Report Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Presenting as Mild Cutaneous Features of Pemphigus Foliaceus and Lichenoid
Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2010, Article ID 931340, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/931340 Case Report Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Presenting as Mild Cutaneous Features of Pemphigus Foliaceus and Lichenoid
Acquired and Inherited Bullous Diseases
 Acquired and Inherited Bullous Diseases Erin Wei MD Brigham and Women s Hospital, Department of Dermatology Instructor, Harvard Medical School Director, Bullous Disease Clinic No disclosures Conflict of
Acquired and Inherited Bullous Diseases Erin Wei MD Brigham and Women s Hospital, Department of Dermatology Instructor, Harvard Medical School Director, Bullous Disease Clinic No disclosures Conflict of
Sarolta Kárpáti. Technology Transfer in Diagnostic Pathology, 5th Central European Regional Meeting May 1, 2010, Siófok
 Blistering diseases Sarolta Kárpáti SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, BUDAPEST Technology Transfer in Diagnostic Pathology, 5th Central European Regional Meeting May 1, 2010, Siófok Blistering diseases Autoimmune
Blistering diseases Sarolta Kárpáti SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, BUDAPEST Technology Transfer in Diagnostic Pathology, 5th Central European Regional Meeting May 1, 2010, Siófok Blistering diseases Autoimmune
Bullous colon lesions in a patient with bullous pemphigoid
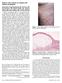 Bullous colon lesions in a patient with bullous pemphigoid Evelyn Maria Sachsenberg-Studer, MD, Ulf Runne, MD, Till Wehrmann, MD, Manfred Wolter, MD, Susanne Kriener, MD, Knut Engels, MD, Thomas Elshorst-
Bullous colon lesions in a patient with bullous pemphigoid Evelyn Maria Sachsenberg-Studer, MD, Ulf Runne, MD, Till Wehrmann, MD, Manfred Wolter, MD, Susanne Kriener, MD, Knut Engels, MD, Thomas Elshorst-
Background information of DIF
 Napa Dermatopathology Meeting 2018: Immunobullous Disease Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng whitney.high@ucdenver.edu Professor of Dermatology & Pathology Vice-Chairman, Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology
Napa Dermatopathology Meeting 2018: Immunobullous Disease Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng whitney.high@ucdenver.edu Professor of Dermatology & Pathology Vice-Chairman, Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology
Pemphigoid gestationis: new insights into the pathogenesis lead to novel diagnostic tools
 BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology September 2002, Vol. 109, pp. 970 976 Pemphigoid gestationis: new insights into the pathogenesis lead to novel diagnostic tools Introduction
BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology September 2002, Vol. 109, pp. 970 976 Pemphigoid gestationis: new insights into the pathogenesis lead to novel diagnostic tools Introduction
Diagnostic performance of the MESACUP anti-skin profile TEST
 Investigative report Eur J Dermatol 216; 26(1): 56-63 Orsolya N. HORVÁTH 1,2 Rita VARGA 1 Makoto KANEDA 3 Enno SCHMIDT 4 Thomas RUZICKA 1 Miklós SÁRDY 1 1 Department of Dermatology, Allergology, Ludwig
Investigative report Eur J Dermatol 216; 26(1): 56-63 Orsolya N. HORVÁTH 1,2 Rita VARGA 1 Makoto KANEDA 3 Enno SCHMIDT 4 Thomas RUZICKA 1 Miklós SÁRDY 1 1 Department of Dermatology, Allergology, Ludwig
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
MESACUP BP180 ELISA Kit
 Semi-quantitative test kit for anti-bp180 antibodies ELISA Kit for measuring anti BP180 antibodies MESACUP BP180 ELISA Kit CONTENTS INTENDED USE... 1 SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION... 1 PRINCIPLE... 1 BRIEF ASSAY
Semi-quantitative test kit for anti-bp180 antibodies ELISA Kit for measuring anti BP180 antibodies MESACUP BP180 ELISA Kit CONTENTS INTENDED USE... 1 SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION... 1 PRINCIPLE... 1 BRIEF ASSAY
Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations
 Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
Autoimmune Diseases with Oral Manifestations Martin S. Greenberg DDS, FDS RCSEd Professor Emeritus Department of Oral Medicine University of Pennsylvania Disclosure Statement I have no actual or potential
Importance of serological tests in diagnosis of autoimmune blistering diseases
 doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12703 Journal of Dermatology 2015; 42: 3 10 REVIEW ARTICLE Importance of serological tests in diagnosis of autoimmune blistering diseases Ken ISHII Department of Dermatology, Toho
doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12703 Journal of Dermatology 2015; 42: 3 10 REVIEW ARTICLE Importance of serological tests in diagnosis of autoimmune blistering diseases Ken ISHII Department of Dermatology, Toho
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Nair S, Branagan AR, Liu J, Boddupalli CS, Mistry PK, Dhodapkar
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Nair S, Branagan AR, Liu J, Boddupalli CS, Mistry PK, Dhodapkar
Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita
 Introduction Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita Pages with reference to book, From 192 To 194 Nasser Rashid Dar ( Departments of Dermatology, Combined Military Hospital, Peshawar. ) Ahsan Hameed, Ashfaq Ahmad
Introduction Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita Pages with reference to book, From 192 To 194 Nasser Rashid Dar ( Departments of Dermatology, Combined Military Hospital, Peshawar. ) Ahsan Hameed, Ashfaq Ahmad
A critical role for neutrophil elastase in experimental bullous pemphigoid
 A critical role for neutrophil elastase in experimental bullous pemphigoid Zhi Liu, 1 Steven D. Shapiro, 2,3 Xiaoye Zhou, 1 Sally S. Twining, 4 Robert M. Senior, 2 George J. Giudice, 1,4 Janet A. Fairley,
A critical role for neutrophil elastase in experimental bullous pemphigoid Zhi Liu, 1 Steven D. Shapiro, 2,3 Xiaoye Zhou, 1 Sally S. Twining, 4 Robert M. Senior, 2 George J. Giudice, 1,4 Janet A. Fairley,
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit
 Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
Immunobullous Diseases: Review and Update. May P. Chan, MD Associate Professor of Pathology and Dermatology University of Michigan
 Immunobullous Diseases: Review and Update May P. Chan, MD Associate Professor of Pathology and Dermatology University of Michigan Diagnosis of Immunobullous Diseases Clinical H&E DIF DIAGNOSIS IIF ELISA
Immunobullous Diseases: Review and Update May P. Chan, MD Associate Professor of Pathology and Dermatology University of Michigan Diagnosis of Immunobullous Diseases Clinical H&E DIF DIAGNOSIS IIF ELISA
A cross-sectional study of clinical, histopathological and direct immmunofluorescence diagnosis in autoimmune bullous diseases
 Original Article A cross-sectional study of clinical, histopathological and direct immmunofluorescence diagnosis in autoimmune bullous diseases Anchal Jindal, MD 1 Rushikesh Shah, MBBS 2 Neela Patel, MD
Original Article A cross-sectional study of clinical, histopathological and direct immmunofluorescence diagnosis in autoimmune bullous diseases Anchal Jindal, MD 1 Rushikesh Shah, MBBS 2 Neela Patel, MD
RSR RSR RSR RSR RSR. ElisaRSR AQP4 Ab RSR. Aquaporin-4 Autoantibody Assay Kit
 To aid diagnosis of Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO) and NMO spectrum disorder (NMOSD) To confirm diagnosis before initial treatment of patients with demyelinating inflammatory disease NMO, NMOSD and AQP4 Elisa
To aid diagnosis of Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO) and NMO spectrum disorder (NMOSD) To confirm diagnosis before initial treatment of patients with demyelinating inflammatory disease NMO, NMOSD and AQP4 Elisa
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content van Beek N, Lüttmann N, Huebner F, et al. Correlation of serum levels of IgE autoantibodies against BP180 with bullous pemphigoid disease activity. JAMA Dermatol. Published
Supplementary Online Content van Beek N, Lüttmann N, Huebner F, et al. Correlation of serum levels of IgE autoantibodies against BP180 with bullous pemphigoid disease activity. JAMA Dermatol. Published
TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet
 Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Autoimmune bullous disorders 1)
 Clin Chem Lab Med 2006;44(2):144 149 2006 by Walter de Gruyter Berlin New York. DOI 10.1515/CCLM.2006.027 2006/39 Review Autoimmune bullous disorders 1) Rüdiger Eming* and Michael Hertl for the members
Clin Chem Lab Med 2006;44(2):144 149 2006 by Walter de Gruyter Berlin New York. DOI 10.1515/CCLM.2006.027 2006/39 Review Autoimmune bullous disorders 1) Rüdiger Eming* and Michael Hertl for the members
Nori Rabbit IL-2 ELISA Kit DataSheet
 Nori Rabbit IL-2 ELISA Kit DataSheet IL-2 is an interleukin, a type of cytokine immune system signaling molecule. IL-2 is a T cell stimulatory cytokine best known for inducing T cell proliferation, the
Nori Rabbit IL-2 ELISA Kit DataSheet IL-2 is an interleukin, a type of cytokine immune system signaling molecule. IL-2 is a T cell stimulatory cytokine best known for inducing T cell proliferation, the
Analysis of the interactions between BP180, BP230, plectin and the integrin α6β4 important for hemidesmosome assembly
 Research Article 387 Analysis of the interactions between BP180,, plectin and the integrin α6β4 important for hemidesmosome assembly Jan Koster 1, Dirk Geerts 1, *, Bertrand Favre 2, Luca Borradori 2 and
Research Article 387 Analysis of the interactions between BP180,, plectin and the integrin α6β4 important for hemidesmosome assembly Jan Koster 1, Dirk Geerts 1, *, Bertrand Favre 2, Luca Borradori 2 and
A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus
 #2228 A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus Priyanka Vedak MD 1, Danielle Levine MD 1,3, Lyn Duncan MD 2,3, Hensin Tsao 1,3, Daniela Kroshinsky MD MPH 1,3 1. Department of Dermatology,
#2228 A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus Priyanka Vedak MD 1, Danielle Levine MD 1,3, Lyn Duncan MD 2,3, Hensin Tsao 1,3, Daniela Kroshinsky MD MPH 1,3 1. Department of Dermatology,
Mouse Cathepsin B ELISA Kit
 GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Phone: 858.458.0866 Fax: 858.458.0833 Email: techline@genwaybio.com http://www.genwaybio.com Mouse Cathepsin B ELISA Kit Catalog No. GWB-ZZD154
GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Phone: 858.458.0866 Fax: 858.458.0833 Email: techline@genwaybio.com http://www.genwaybio.com Mouse Cathepsin B ELISA Kit Catalog No. GWB-ZZD154
GSI Canine IL-5 ELISA Kit-2 Plates DataSheet
 Interleukin5 (IL5) is a secreted glycoprotein that belongs to the α-helical group of cytokines (1, 2, 3). Unlike other family members, it is present as a covalently linked antiparallel dimer (4, 5). IL-5
Interleukin5 (IL5) is a secreted glycoprotein that belongs to the α-helical group of cytokines (1, 2, 3). Unlike other family members, it is present as a covalently linked antiparallel dimer (4, 5). IL-5
BULLOUS SYSTEMIC lupus erythematosus
 OBSERVATION Bullous Systemic Lupus Erythematosus With Autoantibodies Recognizing Multiple Skin Basement Membrane Components, Bullous Pemphigoid Antigen 1, Laminin-5, Laminin-6, and Type VII Collagen Lawrence
OBSERVATION Bullous Systemic Lupus Erythematosus With Autoantibodies Recognizing Multiple Skin Basement Membrane Components, Bullous Pemphigoid Antigen 1, Laminin-5, Laminin-6, and Type VII Collagen Lawrence
Clinical spectrum and therapeutic approach in pemphigus vulgaris
 Clinical spectrum and therapeutic approach in pemphigus vulgaris Michael Hertl Department of Dermatology and Allergology Philipps University, Marburg, Germany F125: Bullous Diseases: Diagnostic and Management
Clinical spectrum and therapeutic approach in pemphigus vulgaris Michael Hertl Department of Dermatology and Allergology Philipps University, Marburg, Germany F125: Bullous Diseases: Diagnostic and Management
Review Article Clinical Relevance of Autoantibodies in Patients with Autoimmune Bullous Dermatosis
 Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2012, Article ID 369546, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/369546 Review Article Clinical Relevance of Autoantibodies in Patients with Autoimmune Bullous Dermatosis
Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2012, Article ID 369546, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/369546 Review Article Clinical Relevance of Autoantibodies in Patients with Autoimmune Bullous Dermatosis
CONTENTS. STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1
 CONTENTS STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1 ELISA protocol for mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Group 2 ALLERGENS RESULTS (SUMMARY) TABLE
CONTENTS STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1 ELISA protocol for mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Group 2 ALLERGENS RESULTS (SUMMARY) TABLE
In 1953 Lever described the disease entity known as bullous
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bullous Pemphigoid: Using Animal Models to Study the Immunopathology Zhi Liu Departments of Dermatology, Microbiology, and Immunology, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bullous Pemphigoid: Using Animal Models to Study the Immunopathology Zhi Liu Departments of Dermatology, Microbiology, and Immunology, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North
Human Cathepsin D ELISA Kit
 GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Phone: 858.458.0866 Fax: 858.458.0833 Email: techline@genwaybio.com http://www.genwaybio.com Human Cathepsin D ELISA Kit Catalog No. GWB-J4JVV9
GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Phone: 858.458.0866 Fax: 858.458.0833 Email: techline@genwaybio.com http://www.genwaybio.com Human Cathepsin D ELISA Kit Catalog No. GWB-J4JVV9
GLP-2 (Rat) ELISA. For the quantitative determination of glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) in rat serum and plasma
 GLP-2 (Rat) ELISA For the quantitative determination of glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) in rat serum and plasma For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2RT-E01
GLP-2 (Rat) ELISA For the quantitative determination of glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) in rat serum and plasma For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2RT-E01
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set
 Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
Mouse Serum Anti-HDM IgE Antibody Assay Kit
 Mouse Serum Anti-HDM IgE Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3037 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease that affects 300 million people
Mouse Serum Anti-HDM IgE Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3037 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease that affects 300 million people
2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit
 2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as
2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as
University of Groningen. Acantholysis in pemphigus van der Wier, Gerda
 University of Groningen Acantholysis in pemphigus van der Wier, Gerda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the
University of Groningen Acantholysis in pemphigus van der Wier, Gerda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the
LDL (Human) ELISA Kit
 LDL (Human) ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA3864 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use This immunoassay kit allows for the specific measurement of human low density lipoprotein, LDL concentrations in cell culture supernates,
LDL (Human) ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA3864 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use This immunoassay kit allows for the specific measurement of human low density lipoprotein, LDL concentrations in cell culture supernates,
Autoimmune Blistering Disease
 life. science. discovery. life. science. discovery. Autoimmune Blistering Disease - Diagnostic Methodology for Pemphigus and Pemphigoid - Pemphigus Epidermal cell-cell junction EBA Epidermal side Epidermal
life. science. discovery. life. science. discovery. Autoimmune Blistering Disease - Diagnostic Methodology for Pemphigus and Pemphigoid - Pemphigus Epidermal cell-cell junction EBA Epidermal side Epidermal
Bordetella pertussis igg-pt elisa Kit
 Bordetella pertussis IgG-PT ELISA Kit Application Bordetella pertussis IgG-PT ELISA Kit is a quantitative test for the detection of IgG antibodies against pertussis toxin in human serum samples. Background
Bordetella pertussis IgG-PT ELISA Kit Application Bordetella pertussis IgG-PT ELISA Kit is a quantitative test for the detection of IgG antibodies against pertussis toxin in human serum samples. Background
Title. CitationBritish Journal of Dermatology, 155(5): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type. File Information
 Title Childhood epidermolysis bullosa acquisita with autoa collagen : case report and review of the literature Author(s)Mayuzumi, M.; Akiyama, M.; Nishie, W.; Ukae, S.; Abe CitationBritish Journal of Dermatology,
Title Childhood epidermolysis bullosa acquisita with autoa collagen : case report and review of the literature Author(s)Mayuzumi, M.; Akiyama, M.; Nishie, W.; Ukae, S.; Abe CitationBritish Journal of Dermatology,
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit
 PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
Prothrombin (Human) ELISA Kit
 Prothrombin (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0496 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General
Prothrombin (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0496 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General
Human Obestatin ELISA
 K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
B. Autoimmune blistering diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details formation immediately above the basal layer. The dermal papillae, which are covered by basal cells in the single layer that is left in
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details formation immediately above the basal layer. The dermal papillae, which are covered by basal cells in the single layer that is left in
Human HBcAb IgM ELISA kit
 Human HBcAb IgM ELISA kit Catalog number: NR-R10163 (96 wells) The kit is designed to qualitatively detect HBcAb IgM in human serum or plasma. FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC PURPOSES
Human HBcAb IgM ELISA kit Catalog number: NR-R10163 (96 wells) The kit is designed to qualitatively detect HBcAb IgM in human serum or plasma. FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC PURPOSES
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
HbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit
 HbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA3509 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use GHbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit is a sandwich enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative measurement of human GHbA1c. General Description vhemoglobin,
HbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA3509 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use GHbA1c (Human) ELISA Kit is a sandwich enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative measurement of human GHbA1c. General Description vhemoglobin,
and Isolation of Antibody in Linear Immunoglobulin A Bullous Dermatosis
 Identification of the Cutaneous Basement Membrane Zone Antigen and Isolation of Antibody in Linear Immunoglobulin A Bullous Dermatosis John J. Zone, Ted B. Taylor, Donald P. Kadunce, and Laurence J. Meyer
Identification of the Cutaneous Basement Membrane Zone Antigen and Isolation of Antibody in Linear Immunoglobulin A Bullous Dermatosis John J. Zone, Ted B. Taylor, Donald P. Kadunce, and Laurence J. Meyer
Human LDL ELISA Kit. Innovative Research, Inc.
 Human LDL ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2582 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports cholesterol from the liver to tissues where it is incorporated into cell membranes.
Human LDL ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2582 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports cholesterol from the liver to tissues where it is incorporated into cell membranes.
EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA
 EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA Definition Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a term used to describe a group of rare mainly hereditary, chronic, non-inflammatory diseases of skin and mucous membranes. EB is characterized
EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA Definition Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a term used to describe a group of rare mainly hereditary, chronic, non-inflammatory diseases of skin and mucous membranes. EB is characterized
Clinicopathological correlation of blistering diseases of skin
 Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 2008; 34: 48-53 Copyright 2008 by Bangladesh Medical Research Council Clinicopathological correlation of blistering diseases of skin A.K.M. Nurul Kabir 1, Mohammed Kamal 1
Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 2008; 34: 48-53 Copyright 2008 by Bangladesh Medical Research Council Clinicopathological correlation of blistering diseases of skin A.K.M. Nurul Kabir 1, Mohammed Kamal 1
Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit
 Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit Catalog # 3019 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The total IgA levels in specimens are often determined in mouse disease models involving
Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit Catalog # 3019 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The total IgA levels in specimens are often determined in mouse disease models involving
Human Apolipoprotein A1 EIA Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Human Apolipoprotein A1 EIA Kit Catalog Number: 83901 96 assays 1 Table of Content Product Description 3 Assay Principle 3 Kit Components 3 Storage 4 Reagent
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Human Apolipoprotein A1 EIA Kit Catalog Number: 83901 96 assays 1 Table of Content Product Description 3 Assay Principle 3 Kit Components 3 Storage 4 Reagent
Human Thyroid-Peroxidase Antibody, TPO-Ab ELISA Kit
 Human Thyroid-Peroxidase Antibody, TPO-Ab ELISA Kit Catalog No: E0442h 96 Tests Operating instruction www.eiaab.com FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY; NOT FOR THERAPEUTIC OR DIAGNOSTIC APPLICATIONS! PLEASE READ THROUGH
Human Thyroid-Peroxidase Antibody, TPO-Ab ELISA Kit Catalog No: E0442h 96 Tests Operating instruction www.eiaab.com FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY; NOT FOR THERAPEUTIC OR DIAGNOSTIC APPLICATIONS! PLEASE READ THROUGH
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Supplementary Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of the primary Sjögren's syndrome patient cohort Number % Females/males 73/5 93.6/6.4 Age, median (range) years 65
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Supplementary Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of the primary Sjögren's syndrome patient cohort Number % Females/males 73/5 93.6/6.4 Age, median (range) years 65
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176
 human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual)
 HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Kit. purified polyclonal antibody raised against the full length recombinant p24 is used.
 HIV-1 p24 ELISA Kit 80-001 1 kit 96 assays This kit can measure the amount of HIV-1 Gag p24 antigen in cell culture medium handily by a sandwich ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) method. p24 antigen
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Kit 80-001 1 kit 96 assays This kit can measure the amount of HIV-1 Gag p24 antigen in cell culture medium handily by a sandwich ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) method. p24 antigen
Comment on Association of bullous pemphigoid with malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis
 Accepted Manuscript Comment on Association of bullous pemphigoid with malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis Maglie Roberto, MD, Antiga Emiliano, MD, PhD, Caproni Marzia, MD, PhD PII: S0190-9622(17)32812-8
Accepted Manuscript Comment on Association of bullous pemphigoid with malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis Maglie Roberto, MD, Antiga Emiliano, MD, PhD, Caproni Marzia, MD, PhD PII: S0190-9622(17)32812-8
OxisResearch A Division of OXIS Health Products, Inc.
 OxisResearch A Division of OXIS Health Products, Inc. BIOXYTECH pl GPx Enzyme Immunoassay Assay for Human Plasma Glutathione Peroxidase For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog
OxisResearch A Division of OXIS Health Products, Inc. BIOXYTECH pl GPx Enzyme Immunoassay Assay for Human Plasma Glutathione Peroxidase For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog
STAT3 (py705)/ Pan STAT3 (Human/Mouse/Rat) ELISA Kit
 STAT3 (py705)/ Pan STAT3 (Human/Mouse/Rat) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2176 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Principle of the Assay...
STAT3 (py705)/ Pan STAT3 (Human/Mouse/Rat) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2176 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Principle of the Assay...
STAT1 (ps727) (Human/Mouse) ELISA Kit
 STAT1 (ps727) (Human/Mouse) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2171 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com I. INTRODUCTION STAT1 (ps727) (Human/Mouse) ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent
STAT1 (ps727) (Human/Mouse) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2171 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com I. INTRODUCTION STAT1 (ps727) (Human/Mouse) ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent
NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254)
 Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
Mouse Anti-HDM IgG Antibody Assay Kit
 Mouse Anti-HDM IgG Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3030 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease that affects 300 million people of
Mouse Anti-HDM IgG Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3030 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease that affects 300 million people of
YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA
 YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA-SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Ⅰ. Introduction 2 Ⅱ. Characteristics 3 Ⅲ. Composition 4 Ⅳ. Method
YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA-SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Ⅰ. Introduction 2 Ⅱ. Characteristics 3 Ⅲ. Composition 4 Ⅳ. Method
AlphaScreen : A Straightforward and Powerful Alternative to ELISA. Martina Bielefeld-Sévigny Ph.D., R&D Director
 AlphaScreen : A Straightforward and Powerful Alternative to ELISA Martina Bielefeld-Sévigny Ph.D., R&D Director Overview AlphaScreen - an alternative to ELISA Why an alternative to ELISA? Assay principle
AlphaScreen : A Straightforward and Powerful Alternative to ELISA Martina Bielefeld-Sévigny Ph.D., R&D Director Overview AlphaScreen - an alternative to ELISA Why an alternative to ELISA? Assay principle
Jyotika Sharma, Feng Dong, Mustak Pirbhai, and Guangming Zhong*
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, July 2005, p. 4414 4419 Vol. 73, No. 7 0019-9567/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.73.7.4414 4419.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Inhibition
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, July 2005, p. 4414 4419 Vol. 73, No. 7 0019-9567/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.73.7.4414 4419.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Inhibition
Western Blot Analysis of Rat Pituitar Recognized by Human Antipituitary. y Antigens A. antibodies
 Endocrine Journal 1995, 42(1), 115-119 NOTE Western Blot Analysis of Rat Pituitar Recognized by Human Antipituitary y Antigens A ntibodies SHIGEKI YABE, MASAMI MURAKAMI*, KAYOKO MARUYAMA, HIDEKO MIWA,
Endocrine Journal 1995, 42(1), 115-119 NOTE Western Blot Analysis of Rat Pituitar Recognized by Human Antipituitary y Antigens A ntibodies SHIGEKI YABE, MASAMI MURAKAMI*, KAYOKO MARUYAMA, HIDEKO MIWA,
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. showed that all three replicates had similar growth trends (Figure 4.1) (p<0.05; p=0.0000)
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
See external label 2 C-8 C Σ=96 tests Cat # 3122Z MICROWELL ELISA THYROID STIMULATING HORMONE (TSH) ENZYME IMMUNOASSAY TEST KIT TSH.
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
HIV-1 p24 Antigen ELISA Catalog Number:
 INTENDED USE The RETRO-TEK HIV-1 p24 Antigen ELISA is supplied for research purposes only. It is not intended for use in the diagnosis or prognosis of disease, or for screening and may not be used as a
INTENDED USE The RETRO-TEK HIV-1 p24 Antigen ELISA is supplied for research purposes only. It is not intended for use in the diagnosis or prognosis of disease, or for screening and may not be used as a
For the quantitative measurement of ATP Synthase Specific activity in samples from Human, Rat and Cow
 ab109716 ATP Synthase Specific Activity Microplate Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the quantitative measurement of ATP Synthase Specific activity in samples from Human, Rat and Cow This product is for
ab109716 ATP Synthase Specific Activity Microplate Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the quantitative measurement of ATP Synthase Specific activity in samples from Human, Rat and Cow This product is for
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the solubility of amylin and huntingtin in living cells
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Contents Supporting Information Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Contents Supporting Information Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the
Mouse C-peptide EIA. Cat. No. YII-YK013-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY
 Mouse C-peptide EIA Cat. No. YII-YK013-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY TOYO 2CHOME, KOTO-KU, TOKYO, 135-0016, JAPAN http://www.cosmobio.co.jp e-mail : export@cosmobio.co.jp Phone : +81-3-5632-9617 FAX : +81-3-5632-9618
Mouse C-peptide EIA Cat. No. YII-YK013-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY TOYO 2CHOME, KOTO-KU, TOKYO, 135-0016, JAPAN http://www.cosmobio.co.jp e-mail : export@cosmobio.co.jp Phone : +81-3-5632-9617 FAX : +81-3-5632-9618
Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN
 YK051 Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418 0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
YK051 Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418 0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
EGFR (py1045)/ Pan EGFR (Human) ELISA Kit
 EGFR (py1045)/ Pan EGFR (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2156 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com I. INTRODUCTION EGFR (py1045)/pan EGFR (Human) ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent
EGFR (py1045)/ Pan EGFR (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2156 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com I. INTRODUCTION EGFR (py1045)/pan EGFR (Human) ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set
 Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human
 Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Mucous membrane pemphigoid in a patient with hypertension treated with atenolol: a case report
 Kanjanabuch et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:373 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Mucous membrane pemphigoid in a patient with hypertension treated with atenolol: a
Kanjanabuch et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:373 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Mucous membrane pemphigoid in a patient with hypertension treated with atenolol: a
