Clinical Study Decreased Gastric Motility in Type II Diabetic Patients
|
|
|
- Karen Shelton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BioMed Research International, Article ID 89487, 6 pages Clinical Study Decreased Gastric Motility in Type II Diabetic Patients Yi-Chun Chiu, Ming-Chun Kuo, 2 Christopher K. Rayner, 3 Jung-Fu Chen, 2 Keng-Liang Wu, Yeh-Pin Chou, Wei-Chen Tai, and Ming-Luen Hu Division of Hepatogastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chang Gung University, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung, Taiwan 2 Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chang Gung University, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung, Taiwan 3 University of Adelaide, Discipline of Medicine, Royal Adelaide Hospital, Adelaide, SA 55, Australia Correspondence should be addressed to Keng-Liang Wu; kengliang wu@yahoo.com.tw Received 4 May 24; Accepted 8 June 24; Published 23 July 24 Academic Editor: Deng-Chyang Wu Copyright 24 Yi-Chun Chiu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Background. To differentiate gastric motility and sensation between type II diabetic patients and controls and explore different expressions of gastric motility peptides. Methods. Eleven type II diabetic patients and health volunteers of similar age and body mass index were invited. All underwent transabdominal ultrasound for gastric motility and visual analogue scales. Blood samples were taken for glucose and plasma peptides (ghrelin, motilin, and glucacon-like peptides-) by ELISA method. Results. Gastric emptying was significantly slower in diabetic patients than controls (T5: 46.3 ( ) min versus 2.8 ( ) min, P.5) and less antral contractions in type II diabetic patients were observed (P =.2). Fundus dimensions did not differ. There were a trend for less changes in gastrointestinal sensations in type II diabetic patients especially abdomen fullness, hunger, and abdominal discomfort. Although the serum peptides between the two groups were similar a trend for less serum GLP-in type II diabetic patients was observed (P =.98). Conclusion. Type II diabetic patients have delayed gastric emptying and less antral contractions than controls. The observation that there were lower serum GLP- in type II diabetic patients could offer a clue to suggest that delayed gastric emptying in diabetic patients is not mainly influenced by GLP-.. Introduction Gastrointestinal tract disorders are common in diabetic patients [, 2]. More than 75% of patients visiting diabetes mellitus clinics reported significant gastrointestinal symptoms [] such as dysphasia, early satiety, reflux, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and diarrhea. The symptoms may be severe enough to substantially affect quality of life, induce poor sugar control, and progress with duration of diabetes mellitus. The pathogenesis of the gastrointestinal abnormalities is multifactorial complex in nature which may involve autonomic neuropathy, motor dysfunction, glycemic control, psychological factors, and so forth and is not well understood [3]. In diabetic patients with gastrointestinal symptoms, 68% were found to have delayed gastric emptying [4] that influences the quality of life and sugar control in these patients. Owing to the fact that the pathogenesis is still poorly understood, it is rational that the effective medical treatment for these patients with diabetic dyspepsia is yet unavailable. Gastric motility is regulated by gastrointestinal motility hormones such as cholecystokinin, gastric inhibitor peptide, motilin, and ghrelin. Previous publications reported that motilin [5, 6] andghrelin[7, 8] stimulated gastric motility and glucagon-like peptide- (GLP- ) inhibited gastric motility [9, ]. We hypothesized that diabetic patients had lower motilin and ghrelin or higher GLP- and hence inhibited gastric motility and induced gastrointestinal symptoms. Therefore, we conducted this study to compare gastric motility and sensation between type II diabetic patients and normal controls and explore the roles of different gastric motility peptides in this motility effect. 2. Methods Eleven patients (2 female) with long-standing (>5 years) type II diabetes mellitus () and healthy controls (2 female)
2 2 BioMed Research International Table : The basic characteristics between type II and normal control. Type II () controls () P Age (years) 58 ± 2 5 ± 5 NS Gender (female/male) 2/ 2/ NS BMI (kg/m 2 ) 23.7 ± ± 2.2 NS Duration of (years). ± 5.6. Fasting glucose 26. ± ± HbAC 9.5 ± ±.. Significant statistic difference. of similar age (58 ± 2 years; 5 ± 5 years) andbody mass index (25. ± 2.2 kg/m 2 ; 23.7 ± 2.5) were invited to participatein current study from August 29 to July 2. The basic demographic data were listed in Table. All patients gave written, informed consent, and the protocol was approved by both the institutional Review Board and the Research Ethics Committee of Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan (IRB B). Patients were excluded if they had a historyof ketosis or dysautonomic or gastrointestinal symptoms determined by interview or from the review of medical records. All patients with type II diabetes mellitus in current study were prescribed with oral hypoglycemic agents instead of insulin therapy. Subjects were also excluded if they had previous gastrointestinal disease or abdominal surgery with the exception of uncomplicated appendectomy, herniorrhaphy, or gynecologicsurgery. All patients must discontinue medications including anticholinergics, calcium channel blockers, 3-adrenergicantagonists, or hormones 48 hours before the study except oral hypoglycemic agents. They underwent physical examination, laboratory blood tests (including white-cell and red-cell counts, measurement of blood sugar during fasting, and liver-function tests), abdominal ultrasonography, and upper gastrointestinal endoscopy to rule out any structural cause for the symptoms. Each subject was studied on afternoons. Following a fast of 8 h for solids and liquids, the patients consumed 5 ml of chicken and corn soup (United Kanboo, Taipei, Taiwan), containing 8.6 kcal (2.6 g protein, 2.6 g fat, 2.2 g carbohydrate). The soup was boiled and subsequently cooled to 37 Candwas consumed over 5 min (t = 5 min). All patients underwent transabdominal ultrasound to record antral area, fundic area, and diameterandantral contractions in regular time by using an Aloka SSD-2 CL Ultrasound Machine (Aloka, Tokyo, Japan) with a 3.5-MHz annular array probe. The frequency of antral contractions was defined as the number of contractions during a 25-minute interval, recorded per five minutes, and the antral contractions were defined as one time while the maximal contraction-induced reduction of the antral area (difference between relaxed and contracted area) as a fraction of the relaxed area (ΔA/A) > 5% as our previous study []. All subjects were invited to denote their symptoms min before test meal ingestion and min after test meal ingestion. A questionnaire with visual analogue scales () for the symptoms of pain, nausea, abdominal discomfort, bloating, and abdominal fullness was administered every ten minutes till 9 min. Grading was made on a mm unmarked line between no symptom at one end and excruciating symptoms at the other. Blood samples were taken at T=, 3, 6, and 9 minutes for measurement of blood glucose and plasma peptide levels. Blood glucose concentrations were immediately determined using a portable blood glucose meter (MediSense Companion 2 meter; MediSense Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). The accuracy of this method has been confirmed using the hexokinase technique. Venous blood samples were collected into ice-chilled EDTA-treated tubes containing 4 KIU aprotinin/ml blood. Plasma was separated and samples stored at 7 C for subsequent analysis of GLP-, ghrelin and motilin concentrations. Plasma ghrelin, motilin, and GLP- concentrations were measured by ELISA (Ghrelin was measured by a commercial ELISA kit (Phoenix Pharmaceuticals Inc., Burlingame, CA); intra- and interassay coefficients of variation (CV) were less than 5% and less than 9%, respectively; motilin and GLP- were also measured by a commercial ELISA kit. 3. Statistical Analysis The curves for antral area, fundic area, diameter, antral contractions, and gastrointestinal sensation scores were compared by using repeated measures ANOVA. Linear regression analysis was used to examine relationships between gastrointestinal sensations and gastric motility (antral area, fundic area, diameter, and frequency of antral contraction). Results were shown as means ± standard deviation. P values <.5 were considered significant. Mean values and standard deviations (SD) of each variable were calculated if not specifically noted otherwise. Statistical analysis was performed with Student s t-test for paired comparison. The tests are twotailed, and P <.5 is considered significant. 4. Results All subjects tolerated the study well. 4.. Antral Area and Gastric Emptying. Antral area was larger in type II diabetic patients than normal controls especially after test meal (antal area 5.6 ± 2.3 cm 2 versus 2.6 ± 2.4 cm 2 ). Gastric emptying was more significant in normal controls than diabetic patients (T5: 2.8 ( ) min versus 46.3 ( ) min, P =.3). There was a statistical significance trend for smaller antral area in the normal controls between the two groups, P =.4 (Figure (a)).
3 BioMed Research International 3 Area (cm 2 ) Antral area P =.4 Number per 5 min Antral contractions Period (min) P =.2 (a) (b) 5 Fundus area P = Fundus diameter P =.33 (cm 2 ) (cm) (c) (d) Figure : (a) There was a statistical significance trend for smaller antral area in the normal controls between the two groups; P =.4. (b) There was a significant trend for less antral contractions in type II diabetic patients during 9 minutes after the test meal (P =.2). (c) Fundus dimensions did not differ between normal controls and type II diabetic patients (fundic area: P =.454; fundic diameter: P =.33) Antral Contractions. There was a significant trend for less antral contractions in type II diabetic patients during 9 minutes after the test meal (P =.2)(Figure (b)) Fundic Area and Diameter. Fundus dimensions did not differ between normal controls and type II diabetic patients (fundic area: P =.454;fundicdiameter:P =.33) (Figures (c) and (d)) Gastrointestinal Sensations. Soup ingestion was associated with increased abdominal fullness and bloating and decreased hunger and appetite scores only in control group but not in type II diabetic patients. Figure 2 demonstrated a trend for less significant changes in gastrointestinal sensations in type II diabetic patients especially abdomen fullness, hunger, and appetite in current study Gastric Motility Peptides. There were no differences in serum peptide (motilin, ghrelin, and GLP-) between the two groups but a trend for less serum GLP- in patients with type II diabetes mellitus was observed (P =.98)(Figure 3). 5. Discussion Faraj and colleagues reported as high as 68% of the diabetic patients with gastrointestinal symptoms were associated with delayed gastric emptying [4]. In current study, we observed that type II diabetic patients were found to have larger gastric antral area on sonography. Type II diabetic patients had delayed gastric emptying and less gastric contraction and experienced less postprandial sensation than normal volunteers probably owing to gastric atony and gastric paralysis (gastroparesis) in diabetic patients. As we had shown that less gastric contraction in diabetic patients were correlated with less gastric emptying, there were reports indicating that diabetic patients had postprandial antral hypomotility, decreased temporal organization of antral pressure waves, and increased small intestinal motor activity. All these gastric disorders occurred in long-term diabetic patients and were associated with peripheral neuropathy. Prolonged poor sugar control induced sympathetic nerve dysfunction. Samsom and colleagues observed a lower fasting fundal tone and a decrease in volume change of the gastric fundus after a nutrient drink in patients with
4 4 BioMed Research International Fullness 3 Nausea P =.4 P = Discomfort P =.7 4 Motility P = Hunger P = Appetite P = Figure 2: A trend for less significant changes in gastrointestinal sensation in type II diabetic patients especially abdomen fullness, hunger, and appetite in current study (abdomen fullness (P =.4), hunger (P =.39), appetite (P =.2), nausea (P =.94), discomfort (P =.7), and motility (P =.485)). autonomic neuropathy due to type I diabetes mellitus but the fundus dimensions between type II diabetic patients with normal controls were not different in current study. They used barostat to measure fundic volume and tone but we used ultrasound to detect fundic dimensions. Kumar and colleagues then emphasized more significant impairment in gastricfundicvolumeandtheaccommodationresponseto atestmealindiabeticpatients[2] butwestilldidnot observethedifferenceinourstudy.theplausibleexplanation could be the low nutrient test meal we used in current study. Low volume test meal would not remain in the fundus long enough to be detected by abdominal ultrasound. Perhaps such drawback could be overcome if higher nutrient test meals were used. Other than this, computer tomography might be a better imaging study to overcome the difference. Type II diabetic patients experienced less gastrointestinal sensation after a test meal than normal controls in spite of significant delaying gastric emptying and decreasing gastric contraction. Loo and colleagues found out that approximately 5% of these patients with gastric motor disorders might be asymptomatic [3]. It is still unclear about the actual roles of different motility expression in diabetic patients. Motilin had been reported to regulate the interdigestive migrating contractions (IMC), thefastedmotorpatterninthegastrointestinaltract[4], and ghrelinstimulatedgimotility.ghrelininducedpremature phase III contractions of IMC in the human stomach [7]and intravenous ghrelin injection could accelerate gastric emptying and improve meal-related symptoms. All these reports suggested that ghrelin could be a potential prokinetic agent. More studies are mandatory to clarify the physiological role of plasma ghrelin and motilin in these digestive physiological events and stimulation of gastric emptying. However, we observed no different motilin and ghrelin between diabetic
5 BioMed Research International 5 Concentration (ng/ml) Concentration (ng/m) Concentration (ng/ml) Motilin Gastrin GLP P =.893 P =.95 P =.98 Figure 3: There were no differences in serum peptides (motilin, ghrelin, and GLP-) between two groups but a trend for less serum GLP-inpatientswithtypeIIdiabetesmellituswasobserved(P=.98). patients and normal controls, only a trend of less serum GLP- expressionintypeiidiabeticpatientsincurrentstudy.this could not well explain the pathology of delayed gastric emptying in our diabetic patients. This was consistent with the findings of Pala and colleagues who reported that GLP- levels were significantly lower in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes mellitus compared to those with normalglucose tolerance [5]. Shirra and Delgado-Aros and colleagues observed that GLP- significantly inhibited gastric emptying and vagal function [6, 7]. Rosenstock and colleagues even used GLP- agonists to treat diabetic patients [8, 9]. There was limitation in our study, small patient number that could cause why there was no difference in motility peptides in current study. In conclusion, Type II diabetic patients have delayed gastric emptying and less antral contractions than normal controls and may be associated to less postprandial sensation. The observation that less serum GLP- in type II diabetic patients could offer a clue to understand that delayed gastric emptying in diabetic patients is not mainly regulated by GLP-. Conflict of Interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper. Acknowledgment Financial support: this study was funded by research grants, CMRP 844, from Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chang Gung University, Taiwan. References [] C. Folwaczny, R.Riepl, M.Tschöp, and R. Landgraf, Gastrointestinal involvement in patients with diabetes mellitus: Part I (first of two parts) epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical findings, Zeitschrift fur Gastroenterologie, vol. 37, no. 9, pp , 999. [2] G.N.VerneandC.A.Sninsky, Diabetesandthegastrointestinal tract, Gastroenterology Clinics of North America,vol.27,no. 4, pp , 998. [3] M. Horowitz and M. Samsom, Gastrointestinal Function in Diabetes Mellitus,JohnWiley&Sons,Chichester,UK,24. [4]J.Faraj,O.Melander,G.Sundkvistetal., Oesophagealdysmotility, delayed gastric emptying and gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetic Medicine, vol. 24,no.,pp ,27. [5] T. Tomomasa, T. Kuroume, H. Arai, K. Wakabayashi, and Z. Itoh, Erythromycin induces migrating motor complex in human gastrointestinal tract, Digestive Diseases and Sciences, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 57 6, 986. [6] J.Tack,J.Janssens,G.Vantrappenetal., Effectoferythromycin on gastric motility in controls and in diabetic gastroparesis, Gastroenterology,vol.3,no.,pp.72 79,992. [7] J. Tack, I. Depoortere, R. Bisschops et al., Influence of ghrelin on interdigestive gastrointestinal motility in humans, Gut, vol. 55,no.3,pp ,26. [8] T. Kitazawa, B. de Smet, K. Verbeke, I. Depoortere, and T. L. Peeters, Gastric motor effects of peptide and non-peptide ghrelin agonists in mice in vivo and in vitro, Gut,vol.54,no.8, pp , 25. [9]J.Schirra,P.Leicht,P.Hildebrandetal., Mechanismsofthe antidiabetic action of subcutaneous glucagon-like peptide-(7-36)amide in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, Journal of Endocrinology,vol.56,no.,pp.77 86,998. [] T. Miki, K. Minami, H. Shinozaki et al., Distinct effects of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagonlike peptide- on insulin secretion and gut motility, Diabetes, vol. 54, no. 4, pp , 25. [] K. L. Wu, C. K. Rayner, S. K. Chuah et al., Effects of ginger on gastric emptying and motility in healthy humans, European Gastroenterology and Hepatology, vol.2,no.5,pp , 28. [2]A.Kumar,A.Attaluri,S.Hashmi,K.S.Schulze,andS.S.C. Rao, Visceral hypersensitivity and impaired accommodation in refractory diabetic gastroparesis, Neurogastroenterology and Motility,vol.2,no.6,pp ,28. [3] F.D.Loo,D.W.Palmer,K.H.Soergel,J.H.Kalbfleisch,andC. M. Wood, Gastric emptying in patients with diabetes mellitus, Gastroenterology,vol.86,no.3,pp ,984.
6 6 BioMed Research International [4] Z. Itoh, Motilin and clinical application, Peptides, vol.8,no. 4, pp , 997. [5] L. Pala, S. Ciani, I. Dicembrini et al., Relationship between GLP- levels and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 activity in different glucose tolerance conditions, Diabetic Medicine, vol. 27, no. 6, pp ,2. [6] J. Schirra, P. Kuwert, U. Wank et al., Differential effects of subcutaneous GLP- on gastric emptying, antroduodenal motility, and pancreatic function in men, Proceedings of the Association of American Physicians,vol.9,no.,pp.84 97,997. [7] S. Delgado-Aros, D. Kim, D. D. Burton et al., Effect of GLP- on gastric volume, emptying, maximum volume ingested, and postprandial symptoms in humans, The American Physiology Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, vol.282,no. 3, pp. G424 G43, 22. [8]J.Rosenstock,J.Reusch,M.Bush,F.Yang,andM.Stewart, Potential of albiglutide, a long-acting GLP- receptor agonist, in type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial exploring weekly, biweekly, and monthly dosing, Diabetes Care, vol. 32, no., pp , 29. [9] R. Ratner, M. Nauck, C. Kapitza, V. Asnaghi, M. Boldrin, and R. Balena, Safety and tolerability of high doses of taspoglutide, a once-weekly human GLP- analogue, in diabetic patients treated with metformin: a randomized double-blind placebocontrolled study, Diabetic Medicine,vol.27,no.5,pp , 2.
7 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Diabetes Research International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Obesity Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
Effect of ginger on gastric motility and symptoms of functional dyspepsia
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/17-9327office wjg@wjgnet.com doi:1.3748/wjg.v17.i1.15 World J Gastroenterol 211 January 7; 17(1): 15-11 ISSN 17-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-284 (online) 211 Baishideng.
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/17-9327office wjg@wjgnet.com doi:1.3748/wjg.v17.i1.15 World J Gastroenterol 211 January 7; 17(1): 15-11 ISSN 17-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-284 (online) 211 Baishideng.
Practical Strategies for the Clinical Use of Incretin Mimetics CME/CE. CME/CE Released: 09/15/2009; Valid for credit through 09/15/2010
 Practical Strategies for the Clinical Use of Incretin Mimetics CME/CE Robert R. Henry, MD Authors and Disclosures CME/CE Released: 09/15/2009; Valid for credit through 09/15/2010 Introduction Type 2 diabetes
Practical Strategies for the Clinical Use of Incretin Mimetics CME/CE Robert R. Henry, MD Authors and Disclosures CME/CE Released: 09/15/2009; Valid for credit through 09/15/2010 Introduction Type 2 diabetes
Dr. Patsy Smyth, FNP-BC
 Dr. Patsy Smyth, FNP-BC Gastroparesis literally translated means stomach paralysis. Gastroparesis is a syndrome characterized by delayed gastric emptying in absence of mechanical obstruction of the stomach.
Dr. Patsy Smyth, FNP-BC Gastroparesis literally translated means stomach paralysis. Gastroparesis is a syndrome characterized by delayed gastric emptying in absence of mechanical obstruction of the stomach.
Case Report Off-Label Use of Liraglutide in the Management of a Pediatric Patient with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2013, Article ID 703925, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/703925 Case Report Off-Label Use of Liraglutide in the Management of a Pediatric Patient with Type 2 Diabetes
Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2013, Article ID 703925, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/703925 Case Report Off-Label Use of Liraglutide in the Management of a Pediatric Patient with Type 2 Diabetes
Introduction. The oxytocin/ / vasopressin receptor antagonist, atosiban, delays the gastric emptying of a semisolid meal compared to saline in human
 The oxytocin/ / vasopressin receptor antagonist, atosiban, delays the gastric emptying of a semisolid meal compared to saline in human Bodil Ohlsson, et. al., Sweden BMC Gastroenterology, 2006 Presented
The oxytocin/ / vasopressin receptor antagonist, atosiban, delays the gastric emptying of a semisolid meal compared to saline in human Bodil Ohlsson, et. al., Sweden BMC Gastroenterology, 2006 Presented
Research Article Opioid Use Is Not Associated with Incomplete Wireless Capsule Endoscopy for Inpatient or Outpatient Procedures
 Diagnostic and erapeutic Endoscopy, Article ID 651259, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/651259 Research Article Opioid Use Is Not Associated with Incomplete Wireless Capsule Endoscopy for Inpatient
Diagnostic and erapeutic Endoscopy, Article ID 651259, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/651259 Research Article Opioid Use Is Not Associated with Incomplete Wireless Capsule Endoscopy for Inpatient
Gastroparesis: Diagnosis and Management
 Gastroparesis: Diagnosis and Management Rodica Pop-Busui MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine, Metabolism, Endocrinology and Diabetes, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Disclosures Astra Zeneca Research
Gastroparesis: Diagnosis and Management Rodica Pop-Busui MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine, Metabolism, Endocrinology and Diabetes, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI Disclosures Astra Zeneca Research
Why would fatty foods aggravate the patient s RUQ pain? What effect does cholecystokinin (CCK) have on gastric emptying?
 CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
Effect of macronutrients and mixed meals on incretin hormone secretion and islet cell function
 Effect of macronutrients and mixed meals on incretin hormone secretion and islet cell function Background. Following meal ingestion, several hormones are released from the gastrointestinal tract. Some
Effect of macronutrients and mixed meals on incretin hormone secretion and islet cell function Background. Following meal ingestion, several hormones are released from the gastrointestinal tract. Some
Motility Conference Ghrelin
 Motility Conference Ghrelin Emori Bizer, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology November 21, 2007 Ghrelin: Basics Hormone produced by the A-like A endocrine cells in the oxyntic mucosa (stomach body
Motility Conference Ghrelin Emori Bizer, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology November 21, 2007 Ghrelin: Basics Hormone produced by the A-like A endocrine cells in the oxyntic mucosa (stomach body
Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-1-(7-36)amide (GLP-1) on Gastric Motor Function in Health and Diabetes: Potential Mechanism of Action
 Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-1-(7-36)amide (GLP-1) on Gastric Motor Function in Health and Diabetes: Potential Mechanism of Action Doctoral thesis submitted to the Autonomous University of Barcelona
Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-1-(7-36)amide (GLP-1) on Gastric Motor Function in Health and Diabetes: Potential Mechanism of Action Doctoral thesis submitted to the Autonomous University of Barcelona
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University
 CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
Does the Injection of Botulinum Toxin Improve Symptoms in Patients With Gastroparesis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 Does the Injection of Botulinum Toxin
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 Does the Injection of Botulinum Toxin
Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy
 Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
Chapter 1. General introduction and outline
 Chapter 1 General introduction and outline General introduction The function of the stomach comprises storage of ingested food, production of gastric secretion and mixing food with gastric secretion,
Chapter 1 General introduction and outline General introduction The function of the stomach comprises storage of ingested food, production of gastric secretion and mixing food with gastric secretion,
Functional Dyspepsia
 Functional Dyspepsia American College of Gastroenterology Boston Massachusetts, June 2015 Brian E. Lacy, PhD, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Chief, Section of Gastroenterology
Functional Dyspepsia American College of Gastroenterology Boston Massachusetts, June 2015 Brian E. Lacy, PhD, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Chief, Section of Gastroenterology
Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles
 Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 732694, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/732694 Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles Hon-Ping Ma, 1,2
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 732694, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/732694 Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles Hon-Ping Ma, 1,2
GASTROPARESIS. C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis
 GASTROPARESIS C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Symptom Definitions Nausea: a subjective feeling of wanting to vomit Vomiting: forceful expulsion of gastroduodenal
GASTROPARESIS C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Symptom Definitions Nausea: a subjective feeling of wanting to vomit Vomiting: forceful expulsion of gastroduodenal
Management of Gastroparesis
 Management of Gastroparesis Bible Class Jan Hendrik Niess As published in Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan;108(1):18-37 What is the definition of gastroparesis? What are cardinal symptoms of gastroparesis?
Management of Gastroparesis Bible Class Jan Hendrik Niess As published in Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan;108(1):18-37 What is the definition of gastroparesis? What are cardinal symptoms of gastroparesis?
Research Article The Need for Improved Management of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in Primary Care
 Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 1974863, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1974863 Research Article The Need for Improved Management of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in Primary
Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 1974863, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1974863 Research Article The Need for Improved Management of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in Primary
DIABETIC GASTROPARESIS OBESE VERSUS NON OBESE PATIENTS
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 4 (53) No. 2-2011 DIABETIC GASTROPARESIS OBESE VERSUS NON OBESE PATIENTS L. POANTA 1 D. L. DUMITRAŞCU 1 Abstract: Symptoms
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 4 (53) No. 2-2011 DIABETIC GASTROPARESIS OBESE VERSUS NON OBESE PATIENTS L. POANTA 1 D. L. DUMITRAŞCU 1 Abstract: Symptoms
Gut involvement in PoTS an overview
 Gut involvement in PoTS an overview Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology Case Hx * 28 year old lady presents with a long hx of constipation
Gut involvement in PoTS an overview Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology Case Hx * 28 year old lady presents with a long hx of constipation
Sitagliptin: first DPP-4 inhibitor to treat type 2 diabetes Steve Chaplin MSc, MRPharmS and Andrew Krentz MD, FRCP
 Sitagliptin: first DPP-4 inhibitor to treat type 2 diabetes Steve Chaplin MSc, MRPharmS and Andrew Krentz MD, FRCP KEY POINTS sitagliptin (Januvia) is a DPP-4 inhibitor that blocks the breakdown of the
Sitagliptin: first DPP-4 inhibitor to treat type 2 diabetes Steve Chaplin MSc, MRPharmS and Andrew Krentz MD, FRCP KEY POINTS sitagliptin (Januvia) is a DPP-4 inhibitor that blocks the breakdown of the
Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum Abdominal Aortic Aneurysmal Diameter
 International Vascular Medicine, Article ID 574762, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/574762 Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum
International Vascular Medicine, Article ID 574762, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/574762 Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum
Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis
 Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210972, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210972 Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis Hiroaki
Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210972, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210972 Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis Hiroaki
Is a field of radiology that uses unsealed radiation for diagnostic or therapeutic reasons Is a method of physiologic imaging, very different than
 Jeremy Flowers DNP Is a field of radiology that uses unsealed radiation for diagnostic or therapeutic reasons Is a method of physiologic imaging, very different than x-ray or CT that is anatomic imaging
Jeremy Flowers DNP Is a field of radiology that uses unsealed radiation for diagnostic or therapeutic reasons Is a method of physiologic imaging, very different than x-ray or CT that is anatomic imaging
Initially more rapid small intestinal glucose delivery increases plasma. insulin, GIP and GLP-1, but does not improve overall glycemia in
 Articles in PresS. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab (May 10, 2005). doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00099.2005 E-00099-2005.R1 Final accepted version 1 Initially more rapid small intestinal glucose delivery increases
Articles in PresS. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab (May 10, 2005). doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00099.2005 E-00099-2005.R1 Final accepted version 1 Initially more rapid small intestinal glucose delivery increases
Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 560712, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/560712 Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach Shigeo
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 560712, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/560712 Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach Shigeo
Research Article Prevalence and Trends of Adult Obesity in the US,
 ISRN Obesity, Article ID 185132, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/14/185132 Research Article Prevalence and Trends of Adult Obesity in the US, 1999 12 Ruopeng An CollegeofAppliedHealthSciences,UniversityofIllinoisatUrbana-Champaign,GeorgeHuffHallRoom13,16South4thStreet,
ISRN Obesity, Article ID 185132, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/14/185132 Research Article Prevalence and Trends of Adult Obesity in the US, 1999 12 Ruopeng An CollegeofAppliedHealthSciences,UniversityofIllinoisatUrbana-Champaign,GeorgeHuffHallRoom13,16South4thStreet,
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities
 The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
Gastroparesis. - Recent advances in the pathophysiology and treatment -
 ICDM 2015 Gastroparesis - Recent advances in the pathophysiology and treatment - Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, St. Paul s hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
ICDM 2015 Gastroparesis - Recent advances in the pathophysiology and treatment - Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, St. Paul s hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Research Article C-Peptide Levels Predict the Effectiveness of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Therapy
 Diabetes Research Volume 2016, Article ID 4509603, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4509603 Research Article C-Peptide Levels Predict the Effectiveness of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Therapy
Diabetes Research Volume 2016, Article ID 4509603, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4509603 Research Article C-Peptide Levels Predict the Effectiveness of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Therapy
SLENDESTA POTATO EXTRACT PROMOTES SATIETY IN HEALTHY HUMAN SUBJECTS: IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY STUDY Sheila Dana, Michael Louie, Ph.D. and Jiang Hu, Ph.D.
 SLENDESTA POTATO EXTRACT PROMOTES SATIETY IN HEALTHY HUMAN SUBJECTS: IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY STUDY Sheila Dana, Michael Louie, Ph.D. and Jiang Hu, Ph.D. INTRODUCTION KEY CONCLUSIONS Excessive calorie intake
SLENDESTA POTATO EXTRACT PROMOTES SATIETY IN HEALTHY HUMAN SUBJECTS: IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY STUDY Sheila Dana, Michael Louie, Ph.D. and Jiang Hu, Ph.D. INTRODUCTION KEY CONCLUSIONS Excessive calorie intake
Gut complications in autonomic dysfunction Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP
 Gut complications in autonomic dysfunction Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology GI involvement in autonomic dysfunction Conditions Diabetes
Gut complications in autonomic dysfunction Qasim Aziz, PhD, FRCP Centre for Neuroscience and Trauma Wingate Institute of Neurogastroenterology GI involvement in autonomic dysfunction Conditions Diabetes
GLUCAGON LIKE PEPTIDE (GLP) 1 AGONISTS FOR THE TREATMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES, WEIGHT CONTROL AND CARDIOVASCULAR PROTECTION.
 GLUCAGON LIKE PEPTIDE (GLP) 1 AGONISTS FOR THE TREATMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES, WEIGHT CONTROL AND CARDIOVASCULAR PROTECTION. Patricia Garnica MS, ANP-BC, CDE, CDTC Inpatient Diabetes Nurse Practitioner North
GLUCAGON LIKE PEPTIDE (GLP) 1 AGONISTS FOR THE TREATMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES, WEIGHT CONTROL AND CARDIOVASCULAR PROTECTION. Patricia Garnica MS, ANP-BC, CDE, CDTC Inpatient Diabetes Nurse Practitioner North
EXENATIDE (BYETTA ) PROTOCOL, 5mcg and 10mcg SC injection pre-filled pens
 EXENATIDE (BYETTA ) PROTOCOL, 5mcg and 10mcg SC injection pre-filled pens This document should be read in conjunction with the current Summary of Product Characteristics http://www.medicines.org.uk 1.
EXENATIDE (BYETTA ) PROTOCOL, 5mcg and 10mcg SC injection pre-filled pens This document should be read in conjunction with the current Summary of Product Characteristics http://www.medicines.org.uk 1.
Case Report Overlap of Acute Cholecystitis with Gallstones and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Gallbladder in an Elderly Patient
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2015, Article ID 767196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/767196 Case Report Overlap of Acute Cholecystitis with Gallstones and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Gallbladder
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2015, Article ID 767196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/767196 Case Report Overlap of Acute Cholecystitis with Gallstones and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Gallbladder
Type 2 DM in Adolescents: Use of GLP-1 RA. Objectives. Scope of Problem: Obesity. Background. Pathophysiology of T2DM
 Type 2 DM in Adolescents: Use of GLP-1 RA Objectives Identify patients in the pediatric population with T2DM that would potentially benefit from the use of GLP-1 RA Discuss changes in glycemic outcomes
Type 2 DM in Adolescents: Use of GLP-1 RA Objectives Identify patients in the pediatric population with T2DM that would potentially benefit from the use of GLP-1 RA Discuss changes in glycemic outcomes
GLP-1 agonists. Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK
 GLP-1 agonists Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What do GLP-1 agonists do? Physiology of postprandial glucose regulation Meal ❶ ❷ Insulin Rising plasma
GLP-1 agonists Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What do GLP-1 agonists do? Physiology of postprandial glucose regulation Meal ❶ ❷ Insulin Rising plasma
A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders
 A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord André Smout Jan Tack A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical
A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord André Smout Jan Tack A Guide to Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders Albert J. Bredenoord Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical
Gastric Emptying Time after Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 4, Issue 7-2018 Gastric Emptying Time
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 4, Issue 7-2018 Gastric Emptying Time
Correspondence should be addressed to Vitharon Boon-yasidhi;
 Psychiatry Journal, Article ID 136158, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/136158 Research Article Adverse Effects of Risperidone in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders in a Naturalistic Clinical
Psychiatry Journal, Article ID 136158, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/136158 Research Article Adverse Effects of Risperidone in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders in a Naturalistic Clinical
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
Correspondence should be addressed to Alicia McMaster;
 Cancer Research Volume 2013, Article ID 308236, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/308236 Research Article Taxpas: Epidemiological and Survival Data in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with a Docetaxel-Based
Cancer Research Volume 2013, Article ID 308236, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/308236 Research Article Taxpas: Epidemiological and Survival Data in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with a Docetaxel-Based
Overview of Gastroenterology
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
Motilin. Edited by. Zen Itoh. Gastrointestinal Laboratories College of Medical Technology Gunma University Maebashi, Japan
 Motilin Edited by Zen Itoh Gastrointestinal Laboratories College of Medical Technology Gunma University Maebashi, Japan Academic Press, Inc. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Publishers San Diego New York Berkeley
Motilin Edited by Zen Itoh Gastrointestinal Laboratories College of Medical Technology Gunma University Maebashi, Japan Academic Press, Inc. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Publishers San Diego New York Berkeley
Clinical Policy: Gastric Electrical Stimulation Reference Number: CP.MP.40
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.40 Effective Date: 09/09 Last Review Date: 10/16 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.40 Effective Date: 09/09 Last Review Date: 10/16 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
Diabesity. Metabolic dysfunction that ranges from mild blood glucose imbalance to full fledged Type 2 DM Signs
 Diabesity Metabolic dysfunction that ranges from mild blood glucose imbalance to full fledged Type 2 DM Signs Abdominal obesity Low HDL, high LDL, and high triglycerides HTN High blood glucose (F>100l,
Diabesity Metabolic dysfunction that ranges from mild blood glucose imbalance to full fledged Type 2 DM Signs Abdominal obesity Low HDL, high LDL, and high triglycerides HTN High blood glucose (F>100l,
Outline. Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology Management With an emphasis on recent developments
 Chronic Dyspepsia Eamonn M M Quigley MD FRCP FACP MACG FRCPI Lynda K and David M Underwood Center for Digestive Disorders Houston Methodist Hospital Houston, Texas Outline Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology
Chronic Dyspepsia Eamonn M M Quigley MD FRCP FACP MACG FRCPI Lynda K and David M Underwood Center for Digestive Disorders Houston Methodist Hospital Houston, Texas Outline Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology
I. ALL CLAIMS: HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS
 HCP Prescribing Information Date/Version January 2015 Version 2 Page: 1 of 5 I. ALL CLAIMS: HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS Indications and Usage Saxenda (liraglutide [rdna origin] injection) is indicated as
HCP Prescribing Information Date/Version January 2015 Version 2 Page: 1 of 5 I. ALL CLAIMS: HEALTH CARE PROFESSIONALS Indications and Usage Saxenda (liraglutide [rdna origin] injection) is indicated as
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors. Debbie Hicks
 GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors Debbie Hicks Prescribing and Adverse Event reporting information is available at this meeting from the AstraZeneca representative The views expressed by the
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors Debbie Hicks Prescribing and Adverse Event reporting information is available at this meeting from the AstraZeneca representative The views expressed by the
Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital
 Targeting the Incretins System: Can it Improve Our Ability to Treat Type 2 Diabetes? Darshi Sunderam, MD Darshi Sunderam, MD Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital Age-adjusted Percentage
Targeting the Incretins System: Can it Improve Our Ability to Treat Type 2 Diabetes? Darshi Sunderam, MD Darshi Sunderam, MD Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital Age-adjusted Percentage
Case Report Tortuous Common Carotid Artery: A Report of Four Cases Observed in Cadaveric Dissections
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 2028402, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2028402 Case Report Tortuous Common Carotid Artery: A Report of Four Cases Observed in Cadaveric Dissections
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 2028402, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2028402 Case Report Tortuous Common Carotid Artery: A Report of Four Cases Observed in Cadaveric Dissections
Treating Type 2 Diabetes with Bariatric Surgery. Goal of Treating T2DM. Remission of T2DM with Bariatric
 Treating Type 2 Diabetes with Bariatric Surgery Number (in Millions) of Persons with Diagnosed Diabetes, United States, 198 25 The number of Americans with diabetes increased from 5.6 to 15.8 million Guilherme
Treating Type 2 Diabetes with Bariatric Surgery Number (in Millions) of Persons with Diagnosed Diabetes, United States, 198 25 The number of Americans with diabetes increased from 5.6 to 15.8 million Guilherme
Medical Policy. MP Ingestible ph and Pressure Capsule
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.81 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.20 Esophageal ph Monitoring 6.01.33 Wireless Capsule Endoscopy as a
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.81 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.20 Esophageal ph Monitoring 6.01.33 Wireless Capsule Endoscopy as a
Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr. C. Dinesh M. Naidu Professor of Pharmacology, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Pathogenesis
Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr. C. Dinesh M. Naidu Professor of Pharmacology, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Pathogenesis
Chapter 12. Ingestive Behavior
 Chapter 12 Ingestive Behavior Drinking a. fluid compartments b. osmometric thirst c. volumetric thirst Eating a. energy sources b. starting a meal c. stopping a meal d. eating disordersd Drinking a. fluid
Chapter 12 Ingestive Behavior Drinking a. fluid compartments b. osmometric thirst c. volumetric thirst Eating a. energy sources b. starting a meal c. stopping a meal d. eating disordersd Drinking a. fluid
Daofang Zhu, Xianming Dou, Liang Tang, Dongdong Tang, Guiyi Liao, Weihua Fang, and Xiansheng Zhang
 Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2017, Article ID 3473796, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3473796 Clinical Study Prevalence of Prostatitis-Like Symptoms and Outcomes of NIH-CPSI in Outpatients
Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2017, Article ID 3473796, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3473796 Clinical Study Prevalence of Prostatitis-Like Symptoms and Outcomes of NIH-CPSI in Outpatients
Research Article Serum Ratio of Leptin to Adiponectin in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 ISRN Biomarkers, Article ID 952636, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/952636 Research Article Serum Ratio of Leptin to Adiponectin in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
ISRN Biomarkers, Article ID 952636, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/952636 Research Article Serum Ratio of Leptin to Adiponectin in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Conference Paper Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Biological Markers and Personalized Medicine
 Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 719, pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/13/719 Conference Paper Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Biological Markers and Personalized
Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 719, pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/13/719 Conference Paper Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Biological Markers and Personalized
Ertugliflozin (Steglatro ) 5 mg daily. May increase to 15 mg daily. Take in the morning +/- food. < 60: Do not initiate; discontinue therapy
 Sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) s Inhibit SGLT in proximal renal tubules, reducing reabsorption of filtered glucose from tubular lumen Lowers renal threshold for glucose à increase urinary excretion
Sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) s Inhibit SGLT in proximal renal tubules, reducing reabsorption of filtered glucose from tubular lumen Lowers renal threshold for glucose à increase urinary excretion
Research Article Hb A1c Separation by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Hemoglobinopathies
 Scientifica Volume 2016, Article ID 2698362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2698362 Research Article Hb A1c Separation by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Hemoglobinopathies Vani Chandrashekar
Scientifica Volume 2016, Article ID 2698362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/2698362 Research Article Hb A1c Separation by High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Hemoglobinopathies Vani Chandrashekar
Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders.
 Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders. SmartPill benefits your practice: Convenient performed right in your office Test standardization Provides direct
Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders. SmartPill benefits your practice: Convenient performed right in your office Test standardization Provides direct
Asma Karameh. -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة -
 -2 Asma Karameh -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة - 1 P a g e Gastrointestinal motilities Chewing: once you introduce the first bolus to the mouth you started what we call chewing reflex appears by muscle
-2 Asma Karameh -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة - 1 P a g e Gastrointestinal motilities Chewing: once you introduce the first bolus to the mouth you started what we call chewing reflex appears by muscle
Research Article Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms and Coronary Artery Disease in a Small Country with High Cardiovascular Burden
 ISRN Cardiology, Article ID 825461, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/825461 Research Article Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms and Coronary Artery Disease in a Small Country with High Cardiovascular Burden
ISRN Cardiology, Article ID 825461, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/825461 Research Article Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms and Coronary Artery Disease in a Small Country with High Cardiovascular Burden
Clinical Study Metastasectomy of Pulmonary Metastases from Osteosarcoma: Prognostic Factors and Indication for Repeat Metastasectomy
 Respiratory Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 570314, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/570314 Clinical Study Metastasectomy of Pulmonary Metastases from Osteosarcoma: Prognostic Factors and Indication
Respiratory Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 570314, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/570314 Clinical Study Metastasectomy of Pulmonary Metastases from Osteosarcoma: Prognostic Factors and Indication
Case Report Two Cases of Small Cell Cancer of the Maxillary Sinus Treated with Cisplatin plus Irinotecan and Radiotherapy
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 893638, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/893638 Case Report Two Cases of Small Cell Cancer of the Maxillary Sinus Treated with Cisplatin plus
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 893638, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/893638 Case Report Two Cases of Small Cell Cancer of the Maxillary Sinus Treated with Cisplatin plus
Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy
 Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Volume 2016, Article ID 5184196, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5184196 Case Report Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis in Isolated Tuberculous Cervical Lymphadenopathy Sanjay Khaladkar, Avadhesh
Research Article Subcutaneous Single Injection Digital Block with Epinephrine
 Anesthesiology Research and Practice Volume 2012, Article ID 487650, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/487650 Research Article Subcutaneous Single Injection Digital Block with Epinephrine Motoki Sonohata, 1 Satomi
Anesthesiology Research and Practice Volume 2012, Article ID 487650, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/487650 Research Article Subcutaneous Single Injection Digital Block with Epinephrine Motoki Sonohata, 1 Satomi
Discussion & Conclusion
 Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
(*) (*) Ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination. Uptake of nutrients by body cells (intestine)
 Human Digestive System Food is pushed along the digestive tract by peristalsis the rhythmic waves of contraction of smooth muscles in the wall of the canal Accessory glands. Main stages of food processing
Human Digestive System Food is pushed along the digestive tract by peristalsis the rhythmic waves of contraction of smooth muscles in the wall of the canal Accessory glands. Main stages of food processing
New Treatments for Type 2 diabetes. Nandini Seevaratnam April 2016 Rushcliffe Patient Forum
 New Treatments for Type 2 diabetes Nandini Seevaratnam April 2016 Rushcliffe Patient Forum Overview Growing population of Type 2 diabetes Basic science on what goes wrong Current treatments Why there is
New Treatments for Type 2 diabetes Nandini Seevaratnam April 2016 Rushcliffe Patient Forum Overview Growing population of Type 2 diabetes Basic science on what goes wrong Current treatments Why there is
Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 4979182, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4979182 Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2016, Article ID 4979182, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4979182 Case Report Asymptomatic Pulmonary Vein Stenosis: Hemodynamic Adaptation and Successful Ablation
Research Article Reduction of Pain and Edema of the Legs by Walking Wearing Elastic Stockings
 International Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 648074, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/648074 Research Article Reduction of Pain and Edema of the Legs by Walking Wearing Elastic Stockings
International Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 648074, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/648074 Research Article Reduction of Pain and Edema of the Legs by Walking Wearing Elastic Stockings
Case Report Optic Disk Pit with Sudden Central Visual Field Scotoma
 Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 1423481, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1423481 Case Report Optic Disk Pit with Sudden Central Visual Field Scotoma Nikol Panou
Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 1423481, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1423481 Case Report Optic Disk Pit with Sudden Central Visual Field Scotoma Nikol Panou
April-May, Diabetes - the Medical Perspective. Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions
 April-May, 2017 Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Gastroparesis Diabetic neuropathy is a potential complication of
April-May, 2017 Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Diabetes and Food Recipes to Try Menu Suggestions Diabetes - the Medical Perspective Gastroparesis Diabetic neuropathy is a potential complication of
Diabetic Gastroparesis. Evan M. Klass, MD, FACP February 16, 2017
 Diabetic Gastroparesis Evan M. Klass, MD, FACP February 16, 2017 Scope of the problem The disorder can affect any part of the GI tract Although 10-20% of the general population suffer from functional GI
Diabetic Gastroparesis Evan M. Klass, MD, FACP February 16, 2017 Scope of the problem The disorder can affect any part of the GI tract Although 10-20% of the general population suffer from functional GI
Gut hormones KHATTAB
 Gut hormones PROF:ABD ALHAFIZ HASSAN KHATTAB Gut as an endocrine gland The talk will cover the following : Historical background. Why this subject is chosen. Gastro-intestinal hormones and their function.
Gut hormones PROF:ABD ALHAFIZ HASSAN KHATTAB Gut as an endocrine gland The talk will cover the following : Historical background. Why this subject is chosen. Gastro-intestinal hormones and their function.
Number of studies. Endoscopic finding. Number of subjects. Pooled prevalence 95% CI
 Clinical Approach to the Patient t with Dyspepsia William D. Chey, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Prevalence of Endoscopic Findings in Individuals with Dyspepsia Systematic Review
Clinical Approach to the Patient t with Dyspepsia William D. Chey, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Prevalence of Endoscopic Findings in Individuals with Dyspepsia Systematic Review
VICTOSA and Renal impairment DR.R.S.SAJAD
 VICTOSA and Renal impairment DR.R.S.SAJAD February 2019 Main effect of GLP-1 is : Stimulating glucose dependent insulin release from the pancreatic islets. Slow gastric emptying Inhibit inappropriate
VICTOSA and Renal impairment DR.R.S.SAJAD February 2019 Main effect of GLP-1 is : Stimulating glucose dependent insulin release from the pancreatic islets. Slow gastric emptying Inhibit inappropriate
Clinical Policy: Gastric Electrical Stimulation
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.40 Last Review Date: 08/18 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Description
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.40 Last Review Date: 08/18 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Description
Adlyxin. (lixisenatide) New Product Slideshow
 Adlyxin (lixisenatide) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Adlyxin Generic name: Lixisenatide Pharmacological class: Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist Strength and Formulation:
Adlyxin (lixisenatide) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Adlyxin Generic name: Lixisenatide Pharmacological class: Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist Strength and Formulation:
Mechanisms and Clinical Efficacy of Lixisenatide for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Adv Ther (2013) 30(2):81 101. DOI 10.1007/s12325-013-0009-4 REVIEW Mechanisms and Clinical Efficacy of Lixisenatide for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Michael Horowitz Christopher K. Rayner Karen L.
Adv Ther (2013) 30(2):81 101. DOI 10.1007/s12325-013-0009-4 REVIEW Mechanisms and Clinical Efficacy of Lixisenatide for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Michael Horowitz Christopher K. Rayner Karen L.
Objectives. Define satiety and satiation Summarize the satiety cascade Describe potential dietary interventions aimed at improving satiety
 Foods that Fill Monica Esquivel PhD RDN Assistant Professor, Dietetics Program Director Department of Human Nutrition, Food and Animal Sciences November 8, 2017 Objectives Define satiety and satiation
Foods that Fill Monica Esquivel PhD RDN Assistant Professor, Dietetics Program Director Department of Human Nutrition, Food and Animal Sciences November 8, 2017 Objectives Define satiety and satiation
R. J. L. F. Loffeld, 1 P. E. P. Dekkers, 2 and M. Flens Introduction
 ISRN Gastroenterology Volume 213, Article ID 87138, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/87138 Research Article The Incidence of Colorectal Cancer Is Decreasing in the Older Age Cohorts in the Zaanstreek
ISRN Gastroenterology Volume 213, Article ID 87138, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/87138 Research Article The Incidence of Colorectal Cancer Is Decreasing in the Older Age Cohorts in the Zaanstreek
Case Report Pseudothrombocytopenia due to Platelet Clumping: A Case Report and Brief Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2016, Article ID 3036476, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3036476 Case Report Pseudothrombocytopenia due to Platelet Clumping: A Case Report and Brief Review of
Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2016, Article ID 3036476, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3036476 Case Report Pseudothrombocytopenia due to Platelet Clumping: A Case Report and Brief Review of
GASTRIC EMPTYING STUDY (SOLID)
 GASTRIC EMPTYING STUDY (SOLID) Aim To evaluate patients with symptoms of altered of gastric emptying and/or motility, and quantitatively measure the rate of gastric emptying. This study provides a physiologic,
GASTRIC EMPTYING STUDY (SOLID) Aim To evaluate patients with symptoms of altered of gastric emptying and/or motility, and quantitatively measure the rate of gastric emptying. This study provides a physiologic,
Efficacy/pharmacodynamics: 85 Safety: 89
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor/Company: Sanofi Drug substance:
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor/Company: Sanofi Drug substance:
Effects of intraduodenal lipid and protein on gut motility and hormone release, glycemia, appetite, and energy intake in lean men 1 3
 Effects of intraduodenal lipid and protein on gut motility and hormone release, glycemia, appetite, and energy intake in lean men 1 3 Amy T Ryan, Natalie D Luscombe-Marsh, Alexander A Saies, Tanya J Little,
Effects of intraduodenal lipid and protein on gut motility and hormone release, glycemia, appetite, and energy intake in lean men 1 3 Amy T Ryan, Natalie D Luscombe-Marsh, Alexander A Saies, Tanya J Little,
Disclosure. Learning Objectives. Case. Diabetes Update: Incretin Agents in Diabetes-When to Use Them? I have no disclosures to declare
 Disclosure Diabetes Update: Incretin Agents in Diabetes-When to Use Them? I have no disclosures to declare Spring Therapeutics Update 2011 CSHP BC Branch Anar Dossa BScPharm Pharm D CDE April 20, 2011
Disclosure Diabetes Update: Incretin Agents in Diabetes-When to Use Them? I have no disclosures to declare Spring Therapeutics Update 2011 CSHP BC Branch Anar Dossa BScPharm Pharm D CDE April 20, 2011
GASTROPARESIS 101: BEGINNERS GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING GASTROPARESIS By: Dr. Josh Ferguson 2017
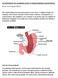 GASTROPARESIS 101: BEGINNERS GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING GASTROPARESIS By: Dr. Josh Ferguson 2017 This tough looking word, pronounced gas-tro-par-ees-is, is simple enough in its meaning. Gastro means stomach.
GASTROPARESIS 101: BEGINNERS GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING GASTROPARESIS By: Dr. Josh Ferguson 2017 This tough looking word, pronounced gas-tro-par-ees-is, is simple enough in its meaning. Gastro means stomach.
Data from an epidemiologic analysis of
 CLINICAL TRIAL RESULTS OF GLP-1 RELATED AGENTS: THE EARLY EVIDENCE Lawrence Blonde, MD, FACP, FACE ABSTRACT Although it is well known that lowering A 1c (also known as glycated hemoglobin) is associated
CLINICAL TRIAL RESULTS OF GLP-1 RELATED AGENTS: THE EARLY EVIDENCE Lawrence Blonde, MD, FACP, FACE ABSTRACT Although it is well known that lowering A 1c (also known as glycated hemoglobin) is associated
Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting and Stone Visualization in Urolithiasis
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 646087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/646087 Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 646087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/646087 Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting
Case Report PET/CT Imaging in Oncology: Exceptions That Prove the Rule
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 865032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/865032 Case Report PET/CT Imaging in Oncology: Exceptions That Prove the Rule M. Casali, 1 A.
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 865032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/865032 Case Report PET/CT Imaging in Oncology: Exceptions That Prove the Rule M. Casali, 1 A.
Case Report Hyperechogenicity of the Substantia Nigra in Parkinson s Disease: Insights from Two Brothers with Markedly Different Disease Durations
 Hindawi Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 3673159, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3673159 Case Report Hyperechogenicity of the Substantia Nigra in Parkinson s Disease:
Hindawi Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 3673159, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3673159 Case Report Hyperechogenicity of the Substantia Nigra in Parkinson s Disease:
GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) Agonists (Byetta, Bydureon, Tanzeum, Trulicity, Victoza ) Step Therapy and Quantity Limit Criteria Program Summary
 OBJECTIVE The intent of the GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) s (Byetta/exenatide, Bydureon/ exenatide extended-release, Tanzeum/albiglutide, Trulicity/dulaglutide, and Victoza/liraglutide) Step Therapy
OBJECTIVE The intent of the GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) s (Byetta/exenatide, Bydureon/ exenatide extended-release, Tanzeum/albiglutide, Trulicity/dulaglutide, and Victoza/liraglutide) Step Therapy
New and Emerging Therapies for Type 2 DM
 Dale Clayton MHSc, MD, FRCPC Dalhousie University/Capital Health April 28, 2011 New and Emerging Therapies for Type 2 DM The science of today, is the technology of tomorrow. Edward Teller American Physicist
Dale Clayton MHSc, MD, FRCPC Dalhousie University/Capital Health April 28, 2011 New and Emerging Therapies for Type 2 DM The science of today, is the technology of tomorrow. Edward Teller American Physicist
