PRES is a clinicoradiologic entity with acute onset of seizures,
|
|
|
- Dwain Thornton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CLINICAL REPORT A. Pirker L. Kramer B. Voller B. Loader E. Auff D. Prayer Type of Edema in Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Depends on Serum Albumin Levels: An MR Imaging Study in 28 Patients SUMMARY: PRES is a clinicoradiologic entity, combining seizures, blindness, and coma with MR imaging findings of predominantly vasogenic and occasional cytotoxic edema. In this clinical report, we determined the type of edema by using DWI and FLAIR sequences on MR imaging as well as ADC maps in 28 patients with PRES. The neuradiologic findings were correlated with levels of serum albumin, which is a main contributor to colloid osmotic pressure and vascular integrity. The presence of vasogenic edema was significantly associated with decreased serum albumin levels, which may be a particular risk factor for the development of PRES. ABBREVIATIONS: ADC apparent diffusion coefficient; ANOVA analysis of variance; CI confidence interval; COP colloid osmotic pressure; DWI diffusion-weighted imaging; FLAIR fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; IL Interleukin; KS Kolmogorov-Smirnov; MWU Mann Whitney U; NO nitric oxide; PRES posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome; ROS reactive oxygen species PRES is a clinicoradiologic entity with acute onset of seizures, blindness, alterations of consciousness, and headache. MR imaging is of great importance in the diagnosis of this clinically inhomogeneous syndrome, which typically shows bilateral signal-intensity alterations in cortical and subcortical regions of the posterior circulation, indicating vasogenic edema. 1 A low proportion of patients show cytotoxic edema or lesions outside the posterior circulation. 2 An association between the etiology of PRES and MR imaging findings has been negated in a recent investigation. 3 Additionally, it remains unclear why patients develop either vasogenic or cytotoxic edema in PRES. Cytotoxic and vasogenic edema in PRES can be differentiated by using DWI and FLAIR sequences. 4 It has been postulated that PRES is caused by endothelial damage and dysfunctional cerebral autoregulation due to excessive hypertension, leading to hyperperfusion and subsequent vasogenic edema in susceptible vessels. 5,6 Other risk factors are pre-eclampsia, sepsis, cytotoxic and immunosuppressant drugs, and nephrotic syndrome. 7 These conditions all involve high oxidative stress and a systemic proinflammatory process, 8 hinting at additional mechanisms involved in PRES pathogenesis, such as vasoactive substances, vasospasm, and microinfarctions. 9 As seen in nephrotic syndrome, most diseases associated with PRES exhibit significantly reduced serum albumin levels. 10 Serum albumin accounts for 75% of plasma protein and, Received June 2, 2010; accepted after revision August 16. From the Departments of Neurology (A.P., B.V., E.A.), Otorhinolaryngology (B.L.), and Neuroradiology (D.P.), Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria; and Department of Medicine (L.K.), Krankenhaus Hietzing, Vienna, Austria. Paper previously presented at: Symposium Neuroradiologicum and The World Congress of Neuroradiology, October 4 9, 2010; Bologna, Italy. Please address correspondence to Agnes Pirker, MD, Department of Neurology, Allgemeines Krankenhaus der Stadt Wien, Währinger Gürtel 18 20, A-1090 Vienna, Austria; agnes.pirker@meduniwien.ac.at DOI /ajnr.A2332 therefore, is a main contributor to COP, reducing perfusion pressure, which results in retention of fluid in the vessel. 11 Vasogenic edema can be aggravated by a marked decrease in COP. 12 Albumin protects vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress and damage, 13 acting as an important antioxidant that preserves vascular integrity. This clinical report describes 28 patients with PRES and focuses on the type of edema in correlation with serum albumin. We show that vasogenic edema in PRES occurs significantly more often in patients with reduced serum albumin. Case Series Patients and Methods Twenty-eight patients (7 men, 21 women; mean age, years) with typical clinical symptoms of PRES and characteristic MR imaging findings were included in this study. Primary clinical data were retrieved via chart review, and the exact date of primary symptom presentation was determined. MR imaging was performed at a single institution on 1.5T and 3T MR imaging scanners between 1999 and Due to the extended period of study, protocols differed slightly with time, but FLAIR, DWI, and coronal T2-weighted sequences were available for all patients. While ADC maps were available in 17 patients, 11 had no ADC maps calculated. In those patients, the type of edema was determined by using DWI and FLAIR sequences. 4 All MR imaging scans were reviewed by a single investigator (D.P.) blinded to clinical data. Vasogenic edema was diagnosed in cases of signal-intensity hyperintensity on FLAIR combined with signal-intensity hypointensity on DWI sequences and high signal intensity on ADC maps. Cytotoxic edema was diagnosed by the combination of DWI hyperintensity with hypo- or isointensity on FLAIR, T2- weighted sequences, and ADC maps. 4,14 The location of lesions was classified as typical (uni- or bilateral occipital lesions, with or without involvement of frontal, temporal, or parietal lobes), atypical (supratentorial lesions without involvement of 1 or both occipital lobes), or BRAIN CLINICAL REPORT AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32: Mar
2 extended (deep gray matter involvement and/or infratentorial involvement). For statistical analysis, the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences software, Version for Windows (SPSS, Chicago, Illinois) was used. Results are expressed as mean SD. Normal distribution of data was tested with the KS test. Intergroup comparison was performed by using the MWU test for variables not normally distributed, the Student t test for normally distributed variables, and the 2 test for dichotomous variables. Stepwise multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to identify factors related to PRES occurrence and to exclude possible confounders. Univariate ANOVA was performed to correct for multiple testing. Results A total of 28 patients with PRES were included in this analysis (7 men, 21 women; mean age, years). Risk factors for PRES, such as pregnancy and eclampsia, were present in 8/21 female patients (36%). Eleven patients were on cytotoxic medication at the onset (including cyclosporine, cyclophosphamide, vinchristine, and the combination of gemcitabine with oxaliplatin) either because of organ transplantation in 5 patients, malignancies in 5 patients, or autoimmune disorder (systemic lupus erythematosus) in 1 patient. Serum levels were within therapeutic range in all patients at onset. One patient was in the intensive care unit due to sepsis. Blood pressure was reported to be elevated at onset in 11/15 patients, with hypertension being the only risk factor for PRES in 3 of them. Symptoms were delirium in 9/28 patients, qualitative changes of consciousness in 12/28 patients, and epileptic seizures in 19/28 patients. Furthermore, 10 patients reported deterioration of visual acuity, while headache was reported in 6 patients. No association between etiology, clinical presentation, or distribution of lesions on MR imaging could be identified. According to the described MR imaging criteria, 22 patients had vasogenic and 6 patients had cytotoxic edema (Fig 1). MR imaging was performed on the day of onset in 21/28 patients, on day 1 after symptom onset in 3/28, on day 2 in 1, on day 3 in 1, and on day 5 in 2 patients. The type of edema was not associated with the interval between the onset of symptoms and MR imaging (MWU, P.89). Serum albumin was normally distributed (P 0.941, KS test). Decreased serum albumin concentration ( 35 mg/ml) was noted in 21/28 patients (71%; mean, 31 7 mg/dl) in general. Serum albumin decrease was more common in patients with vasogenic edema (19/22, 86%) compared with edema with cytotoxic components (1/6, 17%), ( 2, P.001). In cases of pure vasogenic edema, serum albumin concentration was significantly lower ( mg/dl) than in cases with cytotoxic components ( mg/dl; Student t test, P.004; 95% CI, ) (Fig 2). None of the other serum parameters tested were significantly associated with the type of edema (Table). Regarding etiologic factors, the presence of malignancies only showed a weak association with cytotoxic edema ( 2, P.05) (Table). Clinically, only headaches were significantly associated with the presence of cytotoxic edema ( 2, P.023). After logistic regression (parameters: albumin, presence of tumor, age, and sex), only the influence of reduced serum albumin concentration on the type of edema remained statistically significant (P.019; adjusted odds ratio, 0.87; 95% CI, ). Albumin also remained the only parameter significantly associated with the type of edema after correction for multiple testing by using ANOVA (P.004). No association was found between albumin levels and other laboratory parameters or etiology. Three patients had pure vasogenic edema despite normal serum albumin levels at onset. In 2 of these 3 patients, the MR imaging had been performed 3 and 5 days after onset, respectively, when the type of edema may possibly already have changed. The third patient had undergone pulmonary transplantation 1 year before onset of PRES. Chronic graft rejection had been diagnosed before the onset of PRES, and the patient died several months after primary PRES presentation as a result of the graft rejection. The vasogenic edema in this patient might have been related to excessive inflammatory activity with consequent vascular damage (see Discussion ). Typical PRES with uni- or bilateral occipital involvement was present in all patients, and no patient had atypical PRES without occipital involvement. Nine patients had extended PRES with additional involvement of deep gray matter, infratentorial involvement, or both. Patients with extended PRES had lower serum albumin concentrations ( ) than patients with typical PRES ( ) without reaching statistical significance (Student t test, P.23; 95% CI, ). A follow-up MR imaging was performed in 22/28 patients, between day 1 and day 307. Complete edema remission was achieved in 10 patients (45%); partial remission, in the remainder. Visual disturbances recovered in 10/13 patients. The level of consciousness recovered in 14/16 patients, while 2/21 patients were still in delirium at follow-up. Additionally, 10/14 patients were free of seizures at follow-up. Complete edema remission on MR imaging was associated with complete remission of seizures ( 2, P.018). There was no statistical association between complete edema remission on MR imaging and etiology, type of edema, serum albumin level, or clinical presentation at onset. Discussion In a clinical report of 28 consecutive patients with PRES, we focused on the type of edema and serum albumin levels. We found that patients with vasogenic edema had significantly decreased serum albumin levels compared with edema with cytotoxic components, indicating that low serum albumin levels may be involved in the development of vasogenic edema in PRES. Vasogenic edema in PRES has been attributed so far to the hypothesis that increased perfusion pressure overwhelms cerebral autoregulation with consecutive hyperperfusion and fluid extravasation. However, PRES has been increasingly observed in patients on immunosuppressive therapy or chemotherapy and in patients with infection, sepsis, and shock without elevation of systemic blood pressure, 15 suggesting additional pathophysiologic mechanisms. 2 As mentioned below, many conditions prone to PRES are characterized by decreased serum albumin levels and a proinflammatory systemic process, as has been recently reviewed by Bartynski 8 : Proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, interferon-, and tumor necrosis factor- are elevated during sepsis and pre- 528 Pirker AJNR 32 Mar
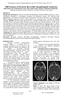
3 Fig 1. A, A 22-year-old woman with an albumin level of 24.7 mg/dl, on immunosuppressive medication (steroids and cyclosporine) and having systemic lupus erythematosus. Signal intensity is hyperintense bilaterally occipitally on FLAIR (left), isointense on DWI (middle), and hyperintense on ADC, indicating vasogenic edema. B, A 40-year-old woman with an albumin level of 21 mg/dl and blood pressure at the onset of 180/95 mm Hg and nephritis. Signal intensity is hyperintense bilaterally occipitally on FLAIR (left), isointense on DWI (middle), and hyperintense on ADC (right), indicating vasogenic edema. C, A 68-year-old woman with albumin levels of 38.3 mg/dl and chronic alcohol abuse. Her blood pressure at onset was 180/90 mm Hg. Signal intensity is isointense on FLAIR (left), hyperintense on DWI (middle), and hypointense on ADC (right), indicating cytotoxic edema. D, A 29-year-old woman with albumin levels of 37.8 mg/dl and eclampsia. Signal intensity is slightly hyperintense on FLAIR (left), hyperintense on DWI (middle), and isointense on ADC (right), indicating cytotoxic edema but also vasogenic components. E, A 19-year-old woman with an albumin level of 28.9 mg/dl, a hypertensive episode of 170/90 mm Hg, and renal failure. Signal intensity is hyperintense on FLAIR (left); there are no signal-intensity abnormalities on T1 (middle) and no gadolinium enhancement (left). F, A 78-year-old man with albumin levels of 22.6 mg/dl with immunosuppression (cyclosporine), renal transplantation, and blood pressure of 160/ 70 mm Hg. Signal intensity is hyperintense on FLAIR (left), isointense on DWI (middle left), hyperintense on ADC (middle right), and isointense on T1, indicating vasogenic edema. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32: Mar
4 Fig 2. Boxplots show serum albumin levels (milligrams per deciliter) in cytotoxic (left) and vasogenic (right) edema. eclampsia. The proinflammatory cytokine milieu and, in some conditions, additional T-cell activation lead to endothelial cell activation and eventually to T-cell trafficking, 16 endothelial cell swelling, and production of vasoactive substances resulting in disturbed microcirculation with either increased vascular permeability or vasoconstriction. 8 Albumin plays an integral part in this systemic process. In addition to inflammation, clinical conditions particularly prone to PRES are often associated with high oxidative stress and decreased serum albumin levels. 17,18 Serum albumin has a mean life span of days. 19 In healthy individuals, 30% 40% of serum albumin is maintained within the vascular compartment; it leaks from plasma at a rate of 5% per hour and is returned at an equivalent rate. 20 Albumin can be reduced as a consequence of an elevated metabolic albumin turnover, accelerated aging of the molecules through oxidative stress, or increased leakage due to immunemediated vasculopathy. 20,21 In line with these characteristics, 71% of our patients had decreased serum albumin levels. Serum albumin normally accounts for 75% of protein in blood plasma and, therefore, also for 75% of COP. COP affects osmotic pressure because the negative charges attract sodium, thus holding water and exerting an antagonistic effect on perfusion pressure. 12,18 In conditions with endothelial damage due to inflammatory processes, reduction of COP may facilitate fluid extravasation and development of vasogenic edema. Albumin is one of the most important plasma antioxidants, scavenging and detoxifying ROS. 22 Excessive production of ROS, as seen in conditions predisposing to PRES, can lead to damage of several molecules, including albumin, and endothelial dysfunction, and may contribute to disease progression. 21 Low albumin levels or damage to albumin molecules themselves in the context of abundant oxidative stress (eg, in proinflammatory conditions) may blunt the antioxidative properties of albumin and promote endothelial damage. 10 Laboratory and clinical parameters KS Test a Vasogenic Edema c Cytotoxic Edema c P d Age (yr).54 b 40.9 (16.76) (24).38 Female 16 (72) 6 (100).149 Sodium.904 b (3.4) (5.5).54 Potassium.945 b 4.2 (0.32) 3.6 (0.32).153 Chloride e.608 b (3.92) 98.2 (7.33).07 Calcium.890 b 2.16 (0.31) 2.2 (0.23).9 Creatinine ( ) 0.91 ( ).76 Albumin f.941 b (6.71) (4.2).004 Aspartate transaminase (24 79) 32 (21 45).22 Alanine aminotransferase (10 145) 23 (18 41).98 -Glutamyltransferase (18 178) 130 (79 200).37 Red blood cells.718 b 3.61 (0.78) 4.11 (0.60).26 Hemoglobin.937 b 11 (2.56) 12 (2.15).14 Hematocrit.985 b (7.72) (5.74).25 White blood cells.809 b (5.69) 7.62 (5.11).18 Threonine.957 b (110.45) (155.77).7 Hypertension 8 (73) 3 (75).73 Pregnancy 7 (44) 1 (16).35 Immunosuppression 9 (41) 2 (33).56 Tumor e 2 (9) 3 (50).05 Transplantation 4 (18) 1 (16).72 Coma, delirium 17 (90) 4 (80).52 Seizure 15 (83) 4 (80).65 Disturbance of vision 7 (64) 3 (60).65 Headache e 2 (17) 4 (80).03 a P value of KS test. Normally distributed variables. c Mean ( SD) for normally distributed variables, median (25% 75% quartile) for variables not normally distributed, or n (%) for nominal variables. d P values of the Student t test for normally distributed variables, the MWU test for variables not normally distributed, and the 2 test for paired variables. Significance is indicated as P.05 and P.01. e P f P Pirker AJNR 32 Mar
5 Moreover, albumin may directly influence vascular integrity by binding to the extracellular matrix and subendothelium and by reducing the permeability of these layers to large molecules. 13,18 In accordance, vasogenic edema in PRES was significantly more frequent in patients with decreased serum albumin levels, whereas cytotoxic components occurred more frequently in patients with normal serum albumin levels. A possible correlation between low albumin levels and PRES is supported by Ishikura et al, 23 who reported 7 pediatric patients who developed PRES during nephrotic syndrome and low levels of serum albumin. In these patients, PRES rapidly abated after substitution of albumin, despite further treatment with cytotoxic substances. Similarly, ifosfamide-induced cerebral vasogenic edema, a condition resembling PRES, seems to occur exclusively in patients with low serum albumin levels. 24 In contrast, cytotoxic edema in PRES may contribute to cerebral vasospasm, with endothelial activation or injury leading to reduced cerebral blood flow with consequent hypoxia, as described in several PRES studies using MR imaging or conventional angiography. 9,25 Due to the retrospective character of our case series, we acknowledge certain limitations of our results. MR imaging protocols differed between patients, and ADC maps were not available for 9 of our patients. In those patients, the type of edema was determined by using only DWI and FLAIR sequences. Clinical data were obtained from medical reports. Therefore, it is conceded that certain minimal symptoms at presentation may have been missed due to a lack of documentation. Caution is needed in interpreting blood pressure in the context of albumin in our patient sample, because blood pressure was documented at the onset of symptoms in only 15 patients. Unfortunately, our retrospective sample size (N 28) does not provide sufficient information to draw statistically sound conclusions on whether PRES present outside the posterior circulation is associated with decreased serum albumin levels and, second, whether the extent of vasogenic edema might be associated with reduction of serum albumin levels. Patients developing a decrease in serum albumin levels seem to be at particular risk for the development of vasogenic edema and eventually PRES. Because PRES is not necessarily benign and reversible in all patients, more focused and accurate treatment strategies are needed. Infusion of human serum albumin at an early and reversible phase to increase oncotic pressure and restore antioxidative potential could theoretically prevent widespread oxidative and/or ischemic damage to vulnerable vascular structures in PRES and should be subjected to prospective studies. References 1. Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignan B, et al. A reversible posterior encephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med 1996;334: Fugate JE, Claassen DO, Cloft HJ, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: associated clinical and radiological findings. Mayo Clin Proc 2010;85: Mueller-Mang C, Mang T, Pirker A, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: do predisposing risk factors make a difference in MRI appearance? Neuroradiol 2009;51: Doelken M, Lanz S, Rennert J, et al. Differentiation of cytotoxic and vasogenic edema in a patient with reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome using diffusion-weighted MRI. Diagn Interv Radiol 2007;13: Ijima T, Kubota Y, Kuroiwa T, et al. Blood-brain barrier opening following transient reflex sympathetic hypertension. Acta Neurochir Suppl 1994;60: Sheth R, Rigs J, Bodensteiner J, et al. Parietal occipital edema in hypertensive encephalopathy: a pathologic mechanism. Eur Neurol 1996;36: Gocmen R, Ozgen B, Oguz K. Widening the spectrum of PRES: a series from a tertiary care center. Eur J Radiol 2007;62: Bartynski WS. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Part 2. Controversies surrounding pathophysiology of vasogenic edema. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008;29: Epub 2008 Apr Weidauer S, Gaa J, Sitzer M, et al. Posterior encephalopathy with vasospasm: MRI and angiography. Neuroradiology 2003;45: Lewis D, Tooke J, Meaman M, et al. Peripheral microvascular parameters in the nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 1998;54: Quinlan G, Martin GS, Evans TW. Albumin: biochemical properties and therapeutic potential. Hepatology 2005;41: Vande Walle J, Dockerwolcke R. Pathogenesis of edema formation in the nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 2001;16: Vogel SM, Minshall RD, Pilipovic M, et al. Albumin uptake and transcytosis in endothelial cells in vivo induced by albumin-binding protein. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2001;281:L Chou M, Lai P, Yen L, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging in 12 cases. Kaoshiung J Med Sci 2004;20: Bartynski WS, Boardman J, Zeiger Z, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in infection, sepsis, and shock. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006;27: Horbinski C, Bartynski WS, Carson-Walter E, et al. Reversible encephalopathy after cardiac transplantation: histologic evidence of endothelial activation, T-cell specific trafficking, and vascular endothelial growth factor expression. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009;30: Epub 2008 Oct Kaysen G. Biochemistry and biomarkers of inflamed patients: why look, what to assess. Clin Am Soc Nephrol 2009;4(suppl 1):S Margarson M, Soni N. Serum albumin: touchstone or totem. Anaesthesia 1998;53: Peters T. All About Albumin: Biochemistry, Genetics and Medical Applications. San Diego: Academic Press; Nicholson J, Wolmarans M, Park G. The role of albumin in critical illness. Br J Anaesthes 2000;85: Bito R, Hino S, Baba A, et al. Degradation of oxidative stress induced denatured serum albumin in rat liver endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2005;289 91:C Epub 2005 May Fernandez J, Navasa M, Garcia-Pagan JC, et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on systemic and hepatic hemodynamics and vasoactive neurohormonal systems in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. J Hepatol 2004;41: Ishikura K, Ikeda M, Hamasaki Y, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in children: its high prevalence and more extensive imaging findings. Am J Kidney Dis 2006;48: Sweiss K, Beri R, Shord SS. Encephalopathy after high dose ifosfamide: a retrospective cohort study and review of the literature. Drug Saf 2008;31: Bartynski WS, Boardman J. Catheter angiography, MR angiography, and MR perfusion in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008;29: AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32: Mar
In 1996, Hinchey et al
 Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in patients with hematologic tumor confers worse outcome Hui Li, Ying Liu, Jing Chen, Xia Tan, Xiu-Yun Ye, Ming-Sheng Ma, Jian-Ping Huang, Li-Ping Zou Beijing,
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in patients with hematologic tumor confers worse outcome Hui Li, Ying Liu, Jing Chen, Xia Tan, Xiu-Yun Ye, Ming-Sheng Ma, Jian-Ping Huang, Li-Ping Zou Beijing,
On-line Table 1: Dementia diagnoses and related ICD codes for the diagnostic groups a
 On-line Table 1: diagnoses and related ICD codes for the diagnostic groups a Diagnosis (N = 1504) ICD Code Patients Scanned with 3T; SWI (%) Subjective cognitive impairment (n 385) Z03.2A, Z03.3, and R41.8A
On-line Table 1: diagnoses and related ICD codes for the diagnostic groups a Diagnosis (N = 1504) ICD Code Patients Scanned with 3T; SWI (%) Subjective cognitive impairment (n 385) Z03.2A, Z03.3, and R41.8A
Atypical Unilateral Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Mimicking a Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction
 Case Report Neuroimaging and Head & Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.5.1104 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(5):1104-1108 Atypical Unilateral Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy
Case Report Neuroimaging and Head & Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.5.1104 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(5):1104-1108 Atypical Unilateral Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy
Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy
 Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy Jeong-Am Ryu 1, Oh Young Bang 2, Daesang Lee 1, Jinkyeong Park 1, Jeong Hoon Yang 1, Gee Young Suh 1, Joongbum Cho 1, Chi Ryang Chung 1, Chi-Min
Ischemic Stroke in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy Jeong-Am Ryu 1, Oh Young Bang 2, Daesang Lee 1, Jinkyeong Park 1, Jeong Hoon Yang 1, Gee Young Suh 1, Joongbum Cho 1, Chi Ryang Chung 1, Chi-Min
Hypertensive disorders are the most common medical complications
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Neuroimaging Features and Predictors of Outcome in Eclamptic Encephalopathy: A Prospective Observational Study V. Junewar, R. Verma, P.L. Sankhwar, R.K. Garg, M.K. Singh, H.S. Malhotra,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Neuroimaging Features and Predictors of Outcome in Eclamptic Encephalopathy: A Prospective Observational Study V. Junewar, R. Verma, P.L. Sankhwar, R.K. Garg, M.K. Singh, H.S. Malhotra,
A 7 MONTH PREGNANT FEMALE PRESENTED WITH POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME WITHOUT ECLAMPSIA AND HYPERTENSION: A CASE REPORT
 A 7 MONTH PREGNANT FEMALE PRESENTED WITH POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME WITHOUT ECLAMPSIA AND HYPERTENSION: A CASE REPORT Dr. S.R Meena 1, Dr. Manoj Saluja 2, Dr. Surendra Khosya 3 and Dr.
A 7 MONTH PREGNANT FEMALE PRESENTED WITH POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME WITHOUT ECLAMPSIA AND HYPERTENSION: A CASE REPORT Dr. S.R Meena 1, Dr. Manoj Saluja 2, Dr. Surendra Khosya 3 and Dr.
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES
 Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
Imaging PRES syndrome: typical, atypical and follow up findings.
 Imaging PRES syndrome: typical, atypical and follow up findings. Poster No.: C-2361 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Borrego Jimenez, A. Villalba Gutiérrez, M. Á. López Pino, P.
Imaging PRES syndrome: typical, atypical and follow up findings. Poster No.: C-2361 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Borrego Jimenez, A. Villalba Gutiérrez, M. Á. López Pino, P.
Syuichi Tetsuka 1* and Hiroaki Nonaka 2
 Tetsuka and Nonaka BMC Medical Imaging (2017) 17:35 DOI 10.1186/s12880-017-0208-6 CASE REPORT Importance of correctly interpreting magnetic resonance imaging to diagnose posterior reversible encephalopathy
Tetsuka and Nonaka BMC Medical Imaging (2017) 17:35 DOI 10.1186/s12880-017-0208-6 CASE REPORT Importance of correctly interpreting magnetic resonance imaging to diagnose posterior reversible encephalopathy
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
OBSERVATION. Postpartum Angiopathy With Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy
 Postpartum Angiopathy With Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Aneesh B. Singhal, MD OBSERVATION Background: Postpartum angiopathy (PPA) is a cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome of uncertain cause
Postpartum Angiopathy With Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Aneesh B. Singhal, MD OBSERVATION Background: Postpartum angiopathy (PPA) is a cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome of uncertain cause
Case Report Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus/Systemic Sclerosis Overlap Syndrome
 Case Reports in Rheumatology, Article ID 862570, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/862570 Case Report Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus/Systemic
Case Reports in Rheumatology, Article ID 862570, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/862570 Case Report Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus/Systemic
Situaciones estresantes en el lupus
 Situaciones estresantes en el lupus Munther A Khamashta MD FRCP PhD Director: Lupus Research Unit Barcelona, Noviembre 2008 What is Lupus? Lupus is a neurological disease and sometimes affects other organs
Situaciones estresantes en el lupus Munther A Khamashta MD FRCP PhD Director: Lupus Research Unit Barcelona, Noviembre 2008 What is Lupus? Lupus is a neurological disease and sometimes affects other organs
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 196 Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome: Case Report and Review of the Literature Ching-Sen Shih, Yu-Te Lin, Sui-Hing Yan, and Yuk-Keung Lo bstract- 23-year-old man with minimal-changed nephrotic
196 Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome: Case Report and Review of the Literature Ching-Sen Shih, Yu-Te Lin, Sui-Hing Yan, and Yuk-Keung Lo bstract- 23-year-old man with minimal-changed nephrotic
What would be the response of the sympathetic system to this patient s decrease in arterial pressure?
 CASE 51 A 62-year-old man undergoes surgery to correct a herniated disc in his spine. The patient is thought to have an uncomplicated surgery until he complains of extreme abdominal distention and pain
CASE 51 A 62-year-old man undergoes surgery to correct a herniated disc in his spine. The patient is thought to have an uncomplicated surgery until he complains of extreme abdominal distention and pain
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain John R. Hesselink, M.D. T1-Weighted Images Normal White Matter Contents Axons with envelope of myelin Neuroglia
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain John R. Hesselink, M.D. T1-Weighted Images Normal White Matter Contents Axons with envelope of myelin Neuroglia
Preeclampsia is a disease characterized by hypertension, peripheral
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2005; 11:189-194 Turkish Society of Radiology 2005 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cranial MR imaging with clinical correlation in preeclampsia and eclampsia Özgür Demirtaş, Fazıl Gelal,
Diagn Interv Radiol 2005; 11:189-194 Turkish Society of Radiology 2005 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cranial MR imaging with clinical correlation in preeclampsia and eclampsia Özgür Demirtaş, Fazıl Gelal,
Case Report Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome Developing After Restart of Sunitinib Therapy for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 6852951, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6852951 Case Report Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome Developing After Restart of Sunitinib
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 6852951, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6852951 Case Report Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome Developing After Restart of Sunitinib
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and MRI: About 6 pediatric cases
 Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and MRI: About 6 pediatric cases Poster No.: C-0395 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Hruba, C. ROZEL, C. Treguier, B. CARSIN-NICOL,
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and MRI: About 6 pediatric cases Poster No.: C-0395 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Hruba, C. ROZEL, C. Treguier, B. CARSIN-NICOL,
Blood Vessels. Chapter 20
 Blood Vessels Chapter 20 Summary of the Characteristics of Arteries and Veins Characteristic Artery Vein Wall thickness thick thin Shape in cross section round flattened Thickest tunic media externa Collagen
Blood Vessels Chapter 20 Summary of the Characteristics of Arteries and Veins Characteristic Artery Vein Wall thickness thick thin Shape in cross section round flattened Thickest tunic media externa Collagen
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Hypertensive encephalopathy and cerebral infarction
 Edvardsson SpringerPlus 2014, 3:741 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Hypertensive encephalopathy and cerebral infarction Bengt Edvardsson Abstract Introduction: Hypertensive encephalopathy
Edvardsson SpringerPlus 2014, 3:741 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Hypertensive encephalopathy and cerebral infarction Bengt Edvardsson Abstract Introduction: Hypertensive encephalopathy
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Central Variant Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome: A Masquerader with Brainstem and Basal Ganglia
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Central Variant Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome: A Masquerader with Brainstem and Basal Ganglia
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Rapid Regression of White Matter Changes in Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy
 www.ksmrm.org JKSMRM 18(4) : 357-361, 2014 pissn 1226-9751 / eissn 2288-3800 Case Report Rapid Regression of White Matter Changes in Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy Sang-wook Son, Kye-ho Lee, Dong-soo Yoo
www.ksmrm.org JKSMRM 18(4) : 357-361, 2014 pissn 1226-9751 / eissn 2288-3800 Case Report Rapid Regression of White Matter Changes in Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy Sang-wook Son, Kye-ho Lee, Dong-soo Yoo
A Case of Unilateral Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Occurring after Carotid Artery Stenting
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 403 408 Online April 17, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0125 Osamu Kikuchi and Kenichi Ishizaki A Case of Unilateral Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 403 408 Online April 17, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0125 Osamu Kikuchi and Kenichi Ishizaki A Case of Unilateral Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome
Maria B. ALBUJA-CRUZ, MD ALBUMIN: OVERRATED. Surgical Grand Rounds
 Maria B. ALBUJA-CRUZ, MD ALBUMIN: OVERRATED Surgical Grand Rounds ALBUMIN Most abundant plasma protein 1/3 intravascular 50% of interstitial SKIN Synthesized in hepatocytes Transcapillary escape rate COP
Maria B. ALBUJA-CRUZ, MD ALBUMIN: OVERRATED Surgical Grand Rounds ALBUMIN Most abundant plasma protein 1/3 intravascular 50% of interstitial SKIN Synthesized in hepatocytes Transcapillary escape rate COP
Atypical brain stem variant of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES)
 Atypical brain stem variant of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) Poster No.: C-2289 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. Kim, S. J. Jeon, S.-S. Choi, C. J. Song, I. K.
Atypical brain stem variant of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) Poster No.: C-2289 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. Kim, S. J. Jeon, S.-S. Choi, C. J. Song, I. K.
Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
Imaging ischemic strokes: Correlating radiological findings with the pathophysiological evolution of an infarct
 Imaging ischemic strokes: Correlating radiological findings with the pathophysiological evolution of an infarct Jay Chyung,, PhD, HMS III Patient A: history 91 y.o. woman Acute onset R sided weakness and
Imaging ischemic strokes: Correlating radiological findings with the pathophysiological evolution of an infarct Jay Chyung,, PhD, HMS III Patient A: history 91 y.o. woman Acute onset R sided weakness and
Reversible Posterior Encephalopathy Syndrome as the Presentation of Late Postpartum Eclampsia: A Case Report
 Case Reports 158 Reversible Posterior Encephalopathy Syndrome as the Presentation of Late Postpartum Eclampsia: A Case Report Yih-Hwa Chiou and Ping-Hong Chen Abstract- We presented a case of previous
Case Reports 158 Reversible Posterior Encephalopathy Syndrome as the Presentation of Late Postpartum Eclampsia: A Case Report Yih-Hwa Chiou and Ping-Hong Chen Abstract- We presented a case of previous
Recurrent posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus
 www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Recurrent posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus Melissa Ng, Sadia Saber, Richard Stratton ABSTRACT Posterior
www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Recurrent posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus Melissa Ng, Sadia Saber, Richard Stratton ABSTRACT Posterior
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI)
 Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
Imaging Acute Stroke and Cerebral Ischemia
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging Acute Stroke and Cerebral Ischemia John R. Hesselink, M.D. Causes of Stroke Arterial stenosis Thrombosis Embolism Dissection Hypotension
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging Acute Stroke and Cerebral Ischemia John R. Hesselink, M.D. Causes of Stroke Arterial stenosis Thrombosis Embolism Dissection Hypotension
Hypertensives Emergency and Urgency
 Hypertensives Emergency and Urgency Budi Yuli Setianto Cardiology Divisision Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine UGM Sardjito Hospital Yogyakarta Background USA: Hypertension is 30% of
Hypertensives Emergency and Urgency Budi Yuli Setianto Cardiology Divisision Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine UGM Sardjito Hospital Yogyakarta Background USA: Hypertension is 30% of
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain
 DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
Marchiafava-Bignami Disease
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Marchiafava-Bignami Disease Fahd Al-Khamis, MBBS, UODFN* Fozaih Al-Shamrani, MBBS, UODFN** Ibrahim Al- Ghanimi, MBBS, UODFN*** Sarah Abdulhafiz,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Marchiafava-Bignami Disease Fahd Al-Khamis, MBBS, UODFN* Fozaih Al-Shamrani, MBBS, UODFN** Ibrahim Al- Ghanimi, MBBS, UODFN*** Sarah Abdulhafiz,
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors
 Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Individual Study Table Referring to Part of the Dossier. Use only) Name of Finished Product:
 SYNOPSIS Fresenius Title of the study: A double-blind, randomized study comparing the safety and torelance of SMOFlipid 20% and Intralipid 20% in long-term treatment with parenteral nutrition Coordinating
SYNOPSIS Fresenius Title of the study: A double-blind, randomized study comparing the safety and torelance of SMOFlipid 20% and Intralipid 20% in long-term treatment with parenteral nutrition Coordinating
Supratentorial multiple little meningiomas with transitory stroke symptoms like. MRI case presentation
 114 Romanian Neurosurgery (2010) XVII 1: 114-121 Supratentorial multiple little meningiomas with transitory stroke symptoms like. MRI case presentation E. Moldovanu 1,2, Adriana Moldovanu 1,2, Carmen Gherman
114 Romanian Neurosurgery (2010) XVII 1: 114-121 Supratentorial multiple little meningiomas with transitory stroke symptoms like. MRI case presentation E. Moldovanu 1,2, Adriana Moldovanu 1,2, Carmen Gherman
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Star Fruit Intoxication in a Patient with Moderate Renal Insufficiency Presents as a Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome
 287 Star Fruit Intoxication in a Patient with Moderate Renal Insufficiency Presents as a Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Shang-Hang Chen 1, Meng-HangTsai 1, Yu-Lung Tseng 1, Chun-Chung Lui
287 Star Fruit Intoxication in a Patient with Moderate Renal Insufficiency Presents as a Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Shang-Hang Chen 1, Meng-HangTsai 1, Yu-Lung Tseng 1, Chun-Chung Lui
Brain under pressure Impact of vasopressors
 Brain under pressure Impact of vasopressors Brain dysfunction in sepsis Incidence: - Varying nomenclature: sepsis-associated encephalopathy, delirium, brain dysfunction - Consistently recognized as frequent:
Brain under pressure Impact of vasopressors Brain dysfunction in sepsis Incidence: - Varying nomenclature: sepsis-associated encephalopathy, delirium, brain dysfunction - Consistently recognized as frequent:
Acute Intermittent Porphyria Presenting with Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome, Accompanied by Prolonged Vasoconstriction
 CASE REPORT Acute Intermittent Porphyria Presenting with Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome, Accompanied by Prolonged Vasoconstriction Tadayuki Takata 1, Kodai Kume 2, Yohei Kokudo 3, Kazuyo
CASE REPORT Acute Intermittent Porphyria Presenting with Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome, Accompanied by Prolonged Vasoconstriction Tadayuki Takata 1, Kodai Kume 2, Yohei Kokudo 3, Kazuyo
Human Herpes Virus-6 Limbic Encephalitis
 Case Studies [1] March 19, 2013 Case history: A 32-year-old Caucasian female with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) was treated with induction chemotherapy and attained complete remission. She
Case Studies [1] March 19, 2013 Case history: A 32-year-old Caucasian female with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) was treated with induction chemotherapy and attained complete remission. She
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 03 Page March 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i3.55 Imaging of Postpartum Encephalopathy:
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i3.55 Imaging of Postpartum Encephalopathy:
Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon
 Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Epidemiology & Definition Pathophysiology Clinical Studies Management Summary Hobart W. Harris,
Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Epidemiology & Definition Pathophysiology Clinical Studies Management Summary Hobart W. Harris,
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2
 Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
Neuroradiology of AIDS
 Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Case Report Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Newly Diagnosed HIV Infection and End Stage Renal Disease
 Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 473618, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/473618 Case Report Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Newly Diagnosed
Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 473618, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/473618 Case Report Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Newly Diagnosed
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.S. Bartynski J.F. Boardman Distinct Imaging Patterns and Lesion Distribution in Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Although the term posterior reversible
ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.S. Bartynski J.F. Boardman Distinct Imaging Patterns and Lesion Distribution in Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Although the term posterior reversible
What is the Role of Albumin in Sepsis? An Evidenced Based Affair. Justin Belsky MD PGY3 2/6/14
 What is the Role of Albumin in Sepsis? An Evidenced Based Affair Justin Belsky MD PGY3 2/6/14 Microcirculation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xao1gsyur7q Capillary Leak in Sepsis Asking the RIGHT Question
What is the Role of Albumin in Sepsis? An Evidenced Based Affair Justin Belsky MD PGY3 2/6/14 Microcirculation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xao1gsyur7q Capillary Leak in Sepsis Asking the RIGHT Question
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI
 Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
Clinical Significance of ARF. Hospital Acquired Renal Insufficiency. Case - Acute Renal Failure. Hospital Acquired Renal Insufficiency
 Case - Acute Renal Failure 73 yo diabetic F w hx of mild HBP but normal renal function develops infection of R foot. Over 1 week fever, chills, inflammation swelling of her R foot and leg. She takes Motrin
Case - Acute Renal Failure 73 yo diabetic F w hx of mild HBP but normal renal function develops infection of R foot. Over 1 week fever, chills, inflammation swelling of her R foot and leg. She takes Motrin
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
THE KIDNEY IN HYPOTENSIVE STATES. Benita S. Padilla, M.D.
 THE KIDNEY IN HYPOTENSIVE STATES Benita S. Padilla, M.D. Objectives To discuss what happens when the kidney encounters low perfusion To discuss new developments and clinical application points in two scenarios
THE KIDNEY IN HYPOTENSIVE STATES Benita S. Padilla, M.D. Objectives To discuss what happens when the kidney encounters low perfusion To discuss new developments and clinical application points in two scenarios
Continuous Peritransplant Assessment of Consciousness using Bispectral Index Monitoring for Patients with Fulminant Hepatic Failure
 Continuous Peritransplant Assessment of Consciousness using Bispectral Index Monitoring for Patients with Fulminant Hepatic Failure Purpose: Deterioration of consciousness is the most critical problem
Continuous Peritransplant Assessment of Consciousness using Bispectral Index Monitoring for Patients with Fulminant Hepatic Failure Purpose: Deterioration of consciousness is the most critical problem
Diabetes. Albumin. Analyte Information
 Diabetes Albumin Analyte Information -1-2014-05-02 Albumin Introduction Albumin consists of a single polypeptide chain of 585 amino acids with molecular weight of 66.5 kda. The chain is characterized by
Diabetes Albumin Analyte Information -1-2014-05-02 Albumin Introduction Albumin consists of a single polypeptide chain of 585 amino acids with molecular weight of 66.5 kda. The chain is characterized by
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Carrera J-P, Forrester N, Wang E, et al. Eastern equine encephalitis
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Carrera J-P, Forrester N, Wang E, et al. Eastern equine encephalitis
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1229-1235 Abdul-Qader Isam Abdul-Hameed, Salwa Taha Ahmed Isma'il, Shaimaa Abdelsattar Mohammad Radiology Department, Faculty of Medicine,
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1229-1235 Abdul-Qader Isam Abdul-Hameed, Salwa Taha Ahmed Isma'il, Shaimaa Abdelsattar Mohammad Radiology Department, Faculty of Medicine,
41 year old female with headache. Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD
 41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
The tale of global hypoxic ischaemic injury
 The tale of global hypoxic ischaemic injury Poster No.: C-0400 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. M. Zammit, R. Grech ; Paola/MT, Dublin 9/IE Keywords: CNS, CT, MR, Education, Computer
The tale of global hypoxic ischaemic injury Poster No.: C-0400 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. M. Zammit, R. Grech ; Paola/MT, Dublin 9/IE Keywords: CNS, CT, MR, Education, Computer
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement
 The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Chin J Radiol 2004; 29: 343-348 343 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage TZU-LUNG HO 1 HUEY-JEN LEE 2 Department of Medical Imaging
Chin J Radiol 2004; 29: 343-348 343 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage TZU-LUNG HO 1 HUEY-JEN LEE 2 Department of Medical Imaging
Functional aspects of anatomical imaging techniques
 Functional aspects of anatomical imaging techniques Nilendu Purandare Associate Professor & Consultant Radiologist Tata Memorial Centre Functional/metabolic/molecular imaging (radioisotope scanning) PET
Functional aspects of anatomical imaging techniques Nilendu Purandare Associate Professor & Consultant Radiologist Tata Memorial Centre Functional/metabolic/molecular imaging (radioisotope scanning) PET
OBJECTVES OF LEARNING
 OBJECTVES OF LEARNING ACUTE RENAL FAILURE AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY DR.TAI CHENG SHENG RECOGNITION OF DEFINITION OF ARF RECOGNITION OF CAUSE OF ARF RECOGNITION OF PATHOGENESIS OF ARF RECOGNITION OF
OBJECTVES OF LEARNING ACUTE RENAL FAILURE AND RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY DR.TAI CHENG SHENG RECOGNITION OF DEFINITION OF ARF RECOGNITION OF CAUSE OF ARF RECOGNITION OF PATHOGENESIS OF ARF RECOGNITION OF
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings
 Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Cerebral small vessel disease
 Cerebral small vessel disease What is it? What are the clinical syndromes? How do we diagnose it? What is the pathophysiology? New insights from genetics? Possible therapies? Small Vessel disease Changes
Cerebral small vessel disease What is it? What are the clinical syndromes? How do we diagnose it? What is the pathophysiology? New insights from genetics? Possible therapies? Small Vessel disease Changes
1 Maiser. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Induced Acute Toxic Leukoencephalopathy. Samuel Maiser, MD. Department of Neurology, University of Minnesota
 1 Maiser 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Induced Acute Toxic Leukoencephalopathy Samuel Maiser, MD Department of Neurology, University of Minnesota Case This is a 57-year-old right-handed male with a history of
1 Maiser 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Induced Acute Toxic Leukoencephalopathy Samuel Maiser, MD Department of Neurology, University of Minnesota Case This is a 57-year-old right-handed male with a history of
Vascular Dementia. Laura Pedelty, PhD MD The University of Illinois at Chicago and Jesse Brown VA Medical Center
 Vascular Dementia Laura Pedelty, PhD MD The University of Illinois at Chicago and Jesse Brown VA Medical Center none Disclosures Objectives To review the definition of Vascular Cognitive Impairment (VCI);
Vascular Dementia Laura Pedelty, PhD MD The University of Illinois at Chicago and Jesse Brown VA Medical Center none Disclosures Objectives To review the definition of Vascular Cognitive Impairment (VCI);
Diabetes Case Study: Co-morbidity of Nonadherence
 Diabetes Case Study: Co-morbidity of Nonadherence Maureen Dever, MSN, CRNP, PPCNP.BC, CDE PENS 5/18 Comorbidity of Diabetes Case Study Objective: the learner will discuss an underreported comorbidity of
Diabetes Case Study: Co-morbidity of Nonadherence Maureen Dever, MSN, CRNP, PPCNP.BC, CDE PENS 5/18 Comorbidity of Diabetes Case Study Objective: the learner will discuss an underreported comorbidity of
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Severe Uremia without Hypertension
 CASE REPORT Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Severe Uremia without Hypertension Yoichi Iwafuchi 1, Kouichirou Okamoto 2, Yuko Oyama 1 and Ichiei Narita 3 Abstract A 28-year-old
CASE REPORT Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient with Severe Uremia without Hypertension Yoichi Iwafuchi 1, Kouichirou Okamoto 2, Yuko Oyama 1 and Ichiei Narita 3 Abstract A 28-year-old
Unilateral Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome after Coiling of an Aneurysm
 CSE REPORT J Clin Neurol 2014;10:59-63 Print ISSN 1738-6586 / On-line ISSN 2005-5013 http://dx.doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2014.10.1.59 Open ccess Unilateral Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome after
CSE REPORT J Clin Neurol 2014;10:59-63 Print ISSN 1738-6586 / On-line ISSN 2005-5013 http://dx.doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2014.10.1.59 Open ccess Unilateral Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome after
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
APACHE II: A Severity of Disease Classification System Standard Operating Procedure for Accurate Calculations
 BACKGROUND APACHE II: A Severity of Disease Classification System Standard Operating Procedure for Accurate Calculations The APACHE prognostic scoring system was developed in 1981 at the George Washington
BACKGROUND APACHE II: A Severity of Disease Classification System Standard Operating Procedure for Accurate Calculations The APACHE prognostic scoring system was developed in 1981 at the George Washington
Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis complicated by reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome
 Case report Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis complicated by reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome Daimei Sasayama, Yasuhiro Shimojima, Takahisa Gono, Kazuma Kaneko, Masayuki Matsuda, Shu-ichi
Case report Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis complicated by reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome Daimei Sasayama, Yasuhiro Shimojima, Takahisa Gono, Kazuma Kaneko, Masayuki Matsuda, Shu-ichi
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum
 Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
PART ONE. Peritoneal Kinetics and Anatomy
 PART ONE Peritoneal Kinetics and Anatomy Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 22, 2006 Paul A. Fein, Irfan Fazil, Muhammad A. Rafiq, Teresa Schloth, Betty Matza, Jyotiprakas Chattopadhyay, Morrell M.
PART ONE Peritoneal Kinetics and Anatomy Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 22, 2006 Paul A. Fein, Irfan Fazil, Muhammad A. Rafiq, Teresa Schloth, Betty Matza, Jyotiprakas Chattopadhyay, Morrell M.
Diabetes Case Study: Co-morbidity of Nonadherence Maureen Dever, MSN, CRNP, PPCNP.BC, CDE PENS 5/18
 Diabetes Case Study: Co-morbidity of Nonadherence Maureen Dever, MSN, CRNP, PPCNP.BC, CDE PENS 5/18 Comorbidity of Diabetes Case Study Objective: the learner will discuss an underreported comorbidity of
Diabetes Case Study: Co-morbidity of Nonadherence Maureen Dever, MSN, CRNP, PPCNP.BC, CDE PENS 5/18 Comorbidity of Diabetes Case Study Objective: the learner will discuss an underreported comorbidity of
VOLUME RESPONSIVENESS IS DIFFERENT FROM NEED FOR FLUIDS BLOOD PRESSURE TARGETS IN SEPSIS
 Department of Intensive Care Medicine VOLUME RESPONSIVENESS IS DIFFERENT FROM NEED FOR FLUIDS BLOOD PRESSURE TARGETS IN SEPSIS SEPTIC SHOCK : THE CLINICAL SCENARIO HYPOTENSION DESPITE ADEQUATE VOLUME RESUSCITATION
Department of Intensive Care Medicine VOLUME RESPONSIVENESS IS DIFFERENT FROM NEED FOR FLUIDS BLOOD PRESSURE TARGETS IN SEPSIS SEPTIC SHOCK : THE CLINICAL SCENARIO HYPOTENSION DESPITE ADEQUATE VOLUME RESUSCITATION
Fluid Treatments in Sepsis: Meta-Analyses
 Fluid Treatments in Sepsis: Recent Trials and Meta-Analyses Lauralyn McIntyre MD, FRCP(C), MSc Scientist, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute Assistant Professor, University of Ottawa Department of Epidemiology
Fluid Treatments in Sepsis: Recent Trials and Meta-Analyses Lauralyn McIntyre MD, FRCP(C), MSc Scientist, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute Assistant Professor, University of Ottawa Department of Epidemiology
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies
 Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the
 Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the potential relation between whole-tumor apparent diffusion
Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the potential relation between whole-tumor apparent diffusion
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016)
 International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS
 IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
Heart Rate and Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy in Heart Transplant Recipients
 ESC Congress 2011 Paris 27-31 August Heart Rate and Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy in Heart Transplant Recipients M.T. La Rovere, F. Olmetti, G.D. Pinna, R. Maestri, D. Lilleri, A. D Armini, M. Viganò,
ESC Congress 2011 Paris 27-31 August Heart Rate and Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy in Heart Transplant Recipients M.T. La Rovere, F. Olmetti, G.D. Pinna, R. Maestri, D. Lilleri, A. D Armini, M. Viganò,
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in Kidney Disease
 NEPHROLOGY ROUNDS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 Q1 Q2 Q23 Q3 Q4 Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy
NEPHROLOGY ROUNDS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 Q1 Q2 Q23 Q3 Q4 Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to
 Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome Case Report POPOVA RD, KALCHEV EB, VALCHEV GN, KALOYANOVA DV, TENEVA TG, BALEV BD
 Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome Case Report POPOVA RD, KALCHEV EB, VALCHEV GN, KALOYANOVA DV, TENEVA TG, BALEV BD Once upon a time on a Saturday shift u An emergency head CT scan was ordered from the ICU
Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome Case Report POPOVA RD, KALCHEV EB, VALCHEV GN, KALOYANOVA DV, TENEVA TG, BALEV BD Once upon a time on a Saturday shift u An emergency head CT scan was ordered from the ICU
HST 071. IN SUMMARY PREGNANCY INDUCED HYPERTENSION Classification of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY Classification of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy HST
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY Classification of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy HST
Burn shock ( 燒燙傷休克 ) 馬偕紀念醫院整形重建外科 姚文騰醫師 2015/10/22
 Burn shock ( 燒燙傷休克 ) 馬偕紀念醫院整形重建外科 姚文騰醫師 2015/10/22 重建階梯 Sheet STSG FTSG Mesh Meek Stamp Meek Introduction Cutaneous thermal injury involving more than one-third of the total body surface area (TBSA)
Burn shock ( 燒燙傷休克 ) 馬偕紀念醫院整形重建外科 姚文騰醫師 2015/10/22 重建階梯 Sheet STSG FTSG Mesh Meek Stamp Meek Introduction Cutaneous thermal injury involving more than one-third of the total body surface area (TBSA)
Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
CASE REPORT. Muhammad Nauman Zahir *, Nehal Masood and Munira Shabbir-Moosajee
 Zahir et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:409 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Cisplatin-induced posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and successful re-treatment
Zahir et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:409 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Cisplatin-induced posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and successful re-treatment
