Lab Urinalysis PFN: 18DLAL04. Lab Urinalysis. Lab Urinalysis. Hours: 2.0
|
|
|
- Spencer Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab Urinalysis PFN: 18DLAL04 Hours: 2.0 Slide 1 Lab Urinalysis OBJECTIVE: Action: Perform a complete Urinalysis on 5 separate specimens Condition: Given the necessary equipment Standard: Within 75% accuracy Slide 2 Lab Urinalysis References used to develop this Lesson: Laboratory subjects book TM Clinical Lab Procedures, Urinalysis Slide 3 1
2 Topics Describe proper urine collection procedures Describe methods of urine preservation Describe normal/abnormal urine output Given the proper equipment describe and perform a macroscopic and microscopic procedure Slide 4 Reason Urinalysis can be an important diagnostic tool providing evidence of the disease process since 25% of the bodies blood flows through the Kidneys each minute Slide 5 Types of Urine Specimen Collection Random most commonly received specimen Purpose Routine screening Inadequate for microbiological exam Container Clean dry container with tight fitting lid Method Void directly into container or bedpan Slide 6 2
3 Types of Urine Specimen Collection First morning void specimen of choice for qualitative analysis Purpose Routine screening Concentrated Container Clean dry container with tight fitting lid Method Collect first specimen immediately upon rising Slide 7 Types of Urine Specimen Collection Midstream clean catch Purpose Most commonly used for bacteriological exam Alternative to catheterized specimens Container Sterile container Method Clean area around urethra and discard initial stream Slide 8 Types of Urine Specimen Collection Catheterized Purpose Bacterial culture Routine urinalysis Collection Container Same as midstream clean catch Method Collected under sterile conditions from catheter Slide 9 3
4 Types of Urine Specimen Collection Slide 10 Types of Urine Specimen Collection Suprapubic aspiration Purpose Bacterial culture Cytological exam Container Same as clean catch Method External introduction of a needle into the bladder Slide 11 Types of Urine Specimen Collection Slide 12 4
5 Types of Urine Specimen Collection Two hour postprandial Purpose Monitoring insulin therapy (diabetes mellitus) Used to compare fasting specimen results Container Clean and dry with tight fitting lid Method Void, Consume meal, collect specimen 2 hours later Slide 13 Types of Urine Specimen Collection Twenty four hour urine Purpose To measure exact amount of urine chemicals Specimen of choice for quantitative chemical testing Container Clean, dark, dry container designed to hold large volume Method Void first morning, collect all other voids to include day 2 first morning void Slide 14 Types of Urine Specimen Collection Slide 15 5
6 Urine Preservative Purpose to prevent changes in urine composition Increased Ph Decreased glucose Decreased ketones Decreased bilirubin Decreased urobilinogen Increased nitrite Increased bacteria Increased turbidity Disintegration cellular elements Color changes Slide 16 Functions of Preservatives Prevent oxygen contact with specimen Maintains acid ph Retard microbial growth Fix organized sediment Slide 17 Types of Urine Preservatives Refrigeration Tolulene Formaline Boric Acid /HCL Slide 18 6
7 Refrigeration Short term preservation of chemical and cellular elements Advantages and disadvantages Easiest and most common No interference Acceptable for urine culture Slide 19 Freezing Used for bilirubin and urobilinogen Advantages and disadvantages Preserves bilirubin and urobilinogen Turbidity occurs upon freezing Slide 20 Formalin Used for sediment preservation Preserves formed elements Disadvantage May cause clumping of sediment Slide 21 7
8 Boric Acid Used for proteins, uric acid and hormones Advantage Acceptable for urine culture Slide 22 Hydrochloric Acid (HCL) Used for calcium, d aminolevulinic acid, and oxalate testing Disadvantages Destroys formed elements Precipitates solutes Slide 23 Boric acid/hcl Test dependent Precautions May interfere with some tests When in doubt look it up When shipping Preserve the specimen as directed by the receiving Laboratory CAUTION: Chemicals may cause burns Slide 24 8
9 Sub Summary Do chemical preservatives interfere with urine dip stix tests? Yes What is the most common urine preservative? Refrigeration Slide 25 Volume Normal excretory output of the kidneys Normal void (600 to 2,000) ml/24 hours Normal average void per 24 hours (1200 to 1500) ml/24hrs Slide 26 Volume Factors affecting normal urine production Temperature Cold (increased) Heat (decreased) Diet Liquid (increased) Less (decreased) Exercise Sweat (decreased) Slide 27 9
10 Abnormal Urine Volume Polyuria Oliguria Anuria Slide 28 Polyuria Increased urine production greater than 2,000 ml/24 hrs Clinical conditions Diabetes insipidus Diabetes mellitus Nervousness and anxiety Increased fluid intake Diuretic medications Diuretic drinks Chronic renal disease Slide 29 Oliguria Decreased urine production less than 500 ml/24 hr Clinical conditions Decrease fluid intake Increase ingestion of salt Excessive perspiration Dehydration Partial renal shutdown Slide 30 10
11 Anuria Cessation of urine flow 100 ml/24 hr Clinical conditions Total renal shutdown Massive fluid loss Heavy metal poisoning Blockage of renal tubules Slide 31 Sub Summary What is increased urine out put? Polyurea What is normal urine output? Normal void 600 to 2,000 ml/24 hours Slide 32 Color Normal color due to varying amounts of pigment called urochrome Straw Yellow Amber normal unless caused by the presence of bilirubin Colorless normal if caused by recent fluid consumption Slide 33 11
12 Abnormal Urine Color Red Fresh blood Orange Medications Brown Hemoglobin Black Malaria Blue green Pseudomonas infections; medications Colorless Due to the absence of urochrome Amber Bilirubin Slide 34 Appearance Clear No turbidity Hazy Slightly turbid Cloudy Excessive turbidity Slide 35 Sub Summary What will cause a normal urine to become cloudy? If it sits for more then an hour the ph changes and amorphous sediment builds up What are normal urine colors? Yellow, straw, amber Slide 36 12
13 Specific Gravity Measure of total solids in urine Density of urine sample compared to the density of distilled water Purpose Measures concentrating and diluting abilities of kidneys Best routine test for total kidney function Slide 37 Clinical significance Specific Gravity Hyposthenuric Low specific gravity <1.010 Glomerulonephritis Pyelonephritis Diabetes insipidus Large intake of fluids Slide 38 Specific Gravity Hypersthenuric High specific gravity >1.010 Hepatic disease Congestive heart failure Excessive loss of water (dehydration) First morning specimen Slide 39 13
14 Specific Gravity Isosthenuric Specific gravity of consistently Severe renal damage Indicates loss of both the concentrating and diluting abilities of the kidneys Slide 40 Specific Gravity Determination Refractometer QC Use one or two drops Hold refractometer Read far left scale Reference range Wipe clean Test sample DI water Slide 41 Specific Gravity Determination Slide 42 14
15 Specific Gravity Determination Slide 43 ph Determines the acidity/alkalinity of urine Urine becomes alkaline upon standing Useful in identification of crystals Used to rule out acidosis/alkalosis Slide 44 ph Clinical significance Acidic Diabetic acidosis Gout Dehydratioin Severe diarrhea High protein diet Certain medicatioin Slide 45 15
16 ph Clinical significance Alkaline Vomiting Renal tubular acidosis Certain medications Urinary tract infection After meals Slide 46 Protein Purpose best routine test to detect renal disease Clinical significance proteinuria (increase protein) Strenuous physical exercise Emotional stress Pregnancy Infections Slide 47 Protein Epithelial cells in urine Severe renal disease Multiple myeloma Leukemia Glomerulonephrites Hematuria Hemoglobinuria WBC in urine Slide 48 16
17 Protein Confirmation Sulfosalicylic acid (SSA) Confirmation of urinary proteins SSA will precipitate protein Rules out false positives Procedure Equal amounts Turbidity Reactions semi quantitated Slide 49 Protein Confirmation Slide 50 Glucose Most common sugar found in urine Presence of detectable amounts known as Glycosuria Occurs when glucose levels exceeds reabsorption capacity Clinical significance Diabetes mellitus Renal tubular dysfunction Pregnancy with possible latent gestational diabetes Slide 51 17
18 Glucose Confirmation Clinitest confirmation for glucose Non specific test Clinitest procedures Add 5 drops of urine and 10 drops of water Add 1 clinitest tablet NOTE: do not touch test tube Shake tube Compare color of liquid Watch for pass through Slide 52 Ketone Bodies Ketonuria Intermediate products of fat metabolism Presence do to altered carbohydrate metabolism Clinical significance Diabetes mellitus Anorexia nervosa Starvation or fad diets Slide 53 Ketone Bodies Confirmation Acetest Confirmation for ketone Procedure Place one drop on tablet Compare color with reaction chart Positive is any purple color Slide 54 18
19 Ketone Bodies Confirmation Slide 55 Blood and Hemoglobin Hematuria presence of intact RBC s in the urine Bleeding in the urinary tract Glomerular damage Trauma Hemoglobinuria presence of free hemoglobin in the urine Slide 56 Blood and Hemoglobin Due to intravascular hemolysis Hemolytic anemia Hemolytic transfusion reactions Malaria Due to lysis of RBC s in urinary tract Traumatic passage of RBC s thru kidney to bladder Exposure of RBC s to dilute urine in the bladder Slide 57 19
20 Bilirubin Bilirubinuria Degrades upon standing while exposed to light Clinical significance Diagnostic sign of liver disease Possible billary obstruction In crease in diseases that causes conjugated bilirubin to be increase in bloodstream Slide 58 Bilirubin Confirmation Ictotest Confirmation test for bilirubin in urine Procedure Place 10 drops of urine on test mat Place one ictotest tablet on mat Place one drop of water on tablet Wait 5 seconds Add one drop of water After 60 seconds observe area around mat Positive reaction (blue or purple color) Slide 59 Bilirubin Confirmation Slide 60 20
21 Urobilinogen Increase in condition with increase bilirubin Hemolytic anemia Malaria Increased in conditions that prevents reabsorption Hepatitis cirrhosis Slide 61 Nitrites Suggests 10⁵ (100,000) or more bacteria per ml of urine Indicative of a infection by nitrate reducing bacteria Slide 62 Leukocyte Esterase White blood cells release esterases in urine Pyuria white blood cells in urine Indication of bacteriuria Indirectly indicates UTI Slide 63 21
22 Leukocyte Esterase Determination False negatives High levels of glucose and proteins High urine specific gravity Slide 64 Slide 65 Sub Summary Which chemical test is indicative of a bacteria infection? Nitrite What is the purpose of specific gravity test? To measure the kidneys ability to concentrate urine Slide 66 22
23 Microscopic Examination Preparation of specimen Pour specimen Spin Pour off supernatant Resuspend button Place one drop on slide Add cover slip Slide 67 Microscopic Examination Stains used in analysis Sterheimer Malbin Protein Peroxidase Differentiates WBC s from renal epithelial cells 3% acetic acid Differentiates RBC s from yeast Sudan III Fat globules will stain orange Iodine Starch globules will stain blue to black Slide 68 Microscopic Examination Examine entire cover slipped area under 10X using subdued light Low power Scan for casts, mucus and even distribution Scan fields under high power 40X High and Dry power objective Identify and enumerate sedimentary elements Slide 69 23
24 Sub Summary How do you differentiate WBC s from renal epithelial cells? Peroxidase How do you differentiate RBC s from yeast? 3% acetic acid Slide 70 White Blood Cell More than 5 WBC/HPF is abnormal Indentifying characteristics Round to oval shape. Segmented or lobulated nucleus (if visible) Granular cytoplasm Report all WBC s as number per high power field (#/HPF) Slide 71 Slide 72 24
25 Slide 73 Red Blood Cell More than 3 RBC/HPF is abnormal Increased in Internal bleeding UTI Traumatic catherterization Some type of trauma Strenuous exercise Menstruation Slide 74 Red Blood Cell Indentifying characteristics Pale, refractive biconcave discs Variation in size In concentrated urine, small and crenated In dilute urine, large and swollen Report all RBC s number per high power field (#/HPF) Slide 75 25
26 Red Blood Cell Slide 76 Red Blood Cell Slide 77 Epithelial Cell Originate from the genitourinary system Three types Squamous Transitional Renal Report all epithelial cells number per high power field (#/HPF) Slide 78 26
27 Epithelial Cell Squamous From distal of urethra Large, flat irregularly shaped Small central nucleus Abundant cytoplasm Slide 79 Slide 80 Slide 81 27
28 Epithelial Cell Transitional From renal pelvis and bladder Round or pear shaped May have tail like projections Large, centrally located nucleus May have two nuclei May be seen in renal disease Slide 82 Slide 83 Slide 84 28
29 Epithelial Cell Renal From renal tubules and nephron Slightly larger than WBC Nucleus usually off center May be flay, cubodial or columnar Suggestive of tubular damage Slide 85 Slide 86 Slide 87 29
30 Sub Summary What would cause RBC s in urine? Bleeding, UTI, or menstrual cycles for women What type of disease would you find transitional cells in? Renal Slide 88 Casts Formation Usually in distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct May also be formed in the ascending loop of henle Slide 89 Casts Cast formation Aggregation of Tamm Horsfall protein Attachment of fibrils Interweaving of fibrils Further protein fibril interweaving Possible attachment Detachment of protein fibrils Excretion of cast Slide 90 30
31 Casts General identifying characteristics Parallel sides Round to blunt ends Slide 91 Types of Casts Hyaline cast White blood cell cast Red blood cell cast Hemoglobin cast Epithelial cell cast Granular cast Waxy cast Fatty cast Slide 92 Types of Casts Hyaline casts consist of Refractive index Normal following strenuous exercise, dehydration, heat exposure and emotional stress Increased in acute glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, chronic renal disease, and congestive heart failure Possible basis for all other casts Slide 93 31
32 Slide 94 Slide 95 Slide 96 32
33 Types of Casts White blood cell cast Refractile and granulated Unless disintegration has begun Indicate infection or inflammation Slide 97 Slide 98 Types of Casts Red blood cell cast Refractive, yellow to brown May contain RBC s Primarily associated with glomerulonephrites Other conditions Slide 99 33
34 Slide 100 Slide 101 Types of Casts Hemoglobin cast Homogenous Reddish brown color Associated with same conditions as RBC cast Slide
35 Slide 103 Slide 104 Types of Casts Epithelial cell cast Formed by excessive shedding of epithelial cells Indicative of Glomerulonephritis Pyelonephrites Slide
36 Slide 106 Slide 107 Types of Casts Granular cast Contains homogenous granular material Represent stages of degeneration May occasionally be seen in normal urine May indicate glomerulonephritis or pyelonephritis Slide
37 Slide 109 Slide 110 Types of Casts Waxy cast Result of granular cast degeneration Refractile Brittle appearance Irregularly shaped Indicative of extreme stasis of urine flow Slide
38 Slide 112 Slide 113 Slide
39 Types of Casts Fatty cast Formed by attachment of lipids Highly refractile Contains yellow brown fat droplets Seen in disorders causing lipiduria Slide 115 Slide 116 Slide
40 Report all casts as number per high power field #/LPF Slide 118 Mucous Irregularly shaped Low refractive index Increased amounts Not considered clinically significant Report as occasional, few, or many (OFM) Slide 119 Slide
41 Slide 121 Miscellanious Structures Schistosoma hematobium Common in the Nile valley, Middle East and Mediterranean regions Infection with this parasite occurs from contaminated water The adult worms live in bladder Ovum has terminal spine Rarely seen in united states Report as present Slide 122 Slide
42 Miscellanious Structures Trichomonas Vaginalis Results of contamination In fresh specimen Highly motile Multiple flagella Left out specimens Loss of motility Degeneration Report as Trichomonas spp. present Slide 124 Slide 125 Slide
43 Miscellanious Structures Examples of parasites that can be found in urine as a result of fecal contamination Enterobious vermicularis Ascaris lumbricoides Giardia lamblia Slide 127 Slide 128 Slide
44 Slide 130 Miscellanious Structures Report all parasites as present Slide 131 Miscellanious Structures Bacteria Not normally present in urine May indicate UTI or contamination Presence of WBC s and positive nitrite Report Bacteria as present Slide
45 Slide 133 Slide 134 Slide
46 Miscellanious Structures Yeast Candida albicans most common Smooth, colorless, usually ovoid cells Often confused with RBC s Addition of 3% acetic acid will lyse RBC s May show budding or hyphae Found in UTI s Report as present Slide 136 Slide 137 Slide
47 Slide 139 Miscellanious Structures Spermatozoa Oval bodies with, thin tails Usually found After sexual intercourse Nocturnal emissions Found in female patient due to contact Slide 140 Miscellanious Structures Verbally report spermatozoa as present Slide
48 Slide 142 Artifact Many contaminants can be found in urine Cotton threads Hair Starch granules, powder granules Plant matter Vegetable fibers Glass fragments Must be recognize but not reported Slide 143 Slide
49 Slide 145 Slide 146 Slide
50 Amorphous urates ph <7.0 Normal crystals Acidic urine Yellow brown small granules If present in large amounts, may give urine sediment pink color Slide 148 Slide 149 Slide
51 Uric acid Yellow reddish brown Normal crystal Acidic urine May take on a variety of shapes Rhombic plates Rosettes Wedges Needles Slide 151 Slide 152 Slide
52 Calcium oxalate Normal crystal Acidic urine Colorless squares with a prismatic X inside Dumbbell and oval forms also occur May also be seen in neutral urine Slide 154 Slide 155 Slide
53 Sodium urate Colorless Normal crystal Acidic urine Appears as elongated plates in a Chinese fan arrangement Slide 157 Slide 158 Normal crystal Alkaline urine Amorphous phosphate ph >7.0 Appear as small irregularly shaped granules When present in large amounts, cause a white turbidity in specimen Slide
54 Slide 160 Slide 161 Triple phosphate Three to six sided Normal crystal Alkaline urine Often referred to as coffin lids Slide
55 Slide 163 Slide 164 Ammonium biurate Yellow brown color Normal crystal Alkaline urine Frequently described as thorny apples Slide
56 Slide 166 Slide 167 Calcium carbonate Colorless Normal crystal Alkaline urine Wedge shaped prisms, seen in singles or rosettes Slide
57 Slide 169 Calcium phosphate Colorless thin prisms Normal crystal Alkaline urine May be found in neutral ph Soluble in dilute acetic acid Slide 170 Slide
58 Slide 172 Leucine Abnormal crystal Neutral or Acidic urine Yellow brown spheres with concentric circles with radial striations Seen in liver disease Present in conjunction tyrosine crytsals Slide 173 Slide
59 Tyrosine Abnormal crystal Neutral or Acidic urine Resembles fine silky needles Seen in liver disease Present with leucine Slide 175 Slide 176 Slide
60 Cystine Abnormal crystal Neutral or Acidic urine Appears as colorless hexagonal plates Appear due to inherited inability to reabsorb cysitne Indicates potential for renal calculi formation Slide 178 Slide 179 Slide
61 Cholesterol Abnormal crystal Neutral or Acidic urine Appears as a rectangular plate with notched corners May have a stair step affect Indicative of renal damage Slide 181 Slide 182 Slide
62 Abnormal crystal Neutral or Acidic urine Sulfonamids (sulfa crystals) Presence due to sulfa drug therapy Many different forms Must know patient drug history to rule out Slide 184 Slide 185 Slide
63 Slide 187 Crystals Report all crystals as occasional, few or many (OFM) Slide 188 Sub Summary Leucine is found in what disease? Acute liver disease due to hepatitis What causes cholesterol? Renal damage Slide
64 Summary What is increased urine output? Polyuria How long can you refrigerate a urine specimen? 8 hours How could you get a normal cloudy Urine? If it sits for more then an hour the ph changes and amorphous sediment builds up Slide 190 Summary Which chemical test is indicative of a bacterial infection? Nitrite How do you differentiate WBC s from renal epithelial cells? Peroxidase What would cause RBC s in urine? Bleeding, UTI, or menstrual cycles for women Slide 191 Summary What does 3% acetic acid do? It lyses RBC c to differentiate from yeast How do you report Sperm? Verbally to the Dr Slide
65 Questions? Slide 193 Break Slide
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS
 PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS)
 GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS) Physiology Lab-8 December, 2018 Lect. Asst. Zakariya A. Mahdi MSc Pharmacology Background Urine (from Latin Urina,) is a typically sterile liquid by-product of
GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS) Physiology Lab-8 December, 2018 Lect. Asst. Zakariya A. Mahdi MSc Pharmacology Background Urine (from Latin Urina,) is a typically sterile liquid by-product of
It s not just water! What is Urinalysis?
 It s not just water! An introduction to Urinalysis What is Urinalysis? Urinalysis or the analysis of urine is one of the oldest laboratory procedures in the practice of medicine. It is a good test for
It s not just water! An introduction to Urinalysis What is Urinalysis? Urinalysis or the analysis of urine is one of the oldest laboratory procedures in the practice of medicine. It is a good test for
Urine analysis. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 Urine analysis By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Functions of Renal system Excretory functions Metabolic waste Drug clearance Toxin clearance Urea, Creatinin Regulatory functions Water balance Blood / urine
Urine analysis By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Functions of Renal system Excretory functions Metabolic waste Drug clearance Toxin clearance Urea, Creatinin Regulatory functions Water balance Blood / urine
SCBM343- Urinalysis. Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul. Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University
 SCBM343- Urinalysis Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 OBJECTIVES 1.
SCBM343- Urinalysis Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 OBJECTIVES 1.
Assisting in the Analysis of Urine. Copyright 2011, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assisting in the Analysis of Urine Urinalysis Why is Urine is analyzed? To detect extrinsic conditions those in which the kidney is functioning normally, but abnormal end-products of metabolism are excreted
Assisting in the Analysis of Urine Urinalysis Why is Urine is analyzed? To detect extrinsic conditions those in which the kidney is functioning normally, but abnormal end-products of metabolism are excreted
LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis
 LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis Notes 1. This lab combines the objectives and activities of the macroscopic and microscopic lab activities. Students are expected to review those labs for reference.
LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis Notes 1. This lab combines the objectives and activities of the macroscopic and microscopic lab activities. Students are expected to review those labs for reference.
BCH472 [Practical] 1
![BCH472 [Practical] 1 BCH472 [Practical] 1](/thumbs/89/98494556.jpg) BCH472 [Practical] 1 Physical Examination Chemical Examination 2 ph Color Specific Gravity Volume Odor Appearance Acidic: -Diabetic Ketoacidosis. -Starvation. -UTIs (E. coli). Alkaline: -UTIs (ureasplitting
BCH472 [Practical] 1 Physical Examination Chemical Examination 2 ph Color Specific Gravity Volume Odor Appearance Acidic: -Diabetic Ketoacidosis. -Starvation. -UTIs (E. coli). Alkaline: -UTIs (ureasplitting
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis
 LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Objectives Upon completion of this laboratory exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Perform microscopic examinations on a minimum of five urine specimens, obtaining
LABORATORY 3: Microscopic Urinalysis Objectives Upon completion of this laboratory exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Perform microscopic examinations on a minimum of five urine specimens, obtaining
Microscopic Examination of Urine
 Download http://www.vetlab.com/kova.htm Definition of urine sediment: all solid materials suspended in the urine - a semiquantative evaluation of the urine sediment Significance of formed elements in the
Download http://www.vetlab.com/kova.htm Definition of urine sediment: all solid materials suspended in the urine - a semiquantative evaluation of the urine sediment Significance of formed elements in the
Microscopic Sediment Miscellaneous
 Miscellaneous urine sediment structures Mucous - threadlike, transparent. Low light is needed in order to be able to see mucous threads. Usually a vaginal contaminant. Do not confuse with casts. Mucous
Miscellaneous urine sediment structures Mucous - threadlike, transparent. Low light is needed in order to be able to see mucous threads. Usually a vaginal contaminant. Do not confuse with casts. Mucous
URINANLYSIS. Pre-Lab Guide
 URINANLYSIS Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions on
URINANLYSIS Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions on
Light yellow to dark golden yellow Clear ph range Specific gravity Sediments
 #11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
#11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today
 III. THE ROUTINE URINALYSIS A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today 1. Cave man noted change in urine properties associated with disease 2. Babylonians and Egyptians noted
III. THE ROUTINE URINALYSIS A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today 1. Cave man noted change in urine properties associated with disease 2. Babylonians and Egyptians noted
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg CAUTION. Abnormal Crystals of Metabolic Origin. Unit 2; Session 5. Abnormal crystals
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 5 Crystals Found in the Urine Microscopic Examination - Part D, Abnormal Crystals CAUTION Abnormal crystals should not be reported haphazardly are rarely
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 5 Crystals Found in the Urine Microscopic Examination - Part D, Abnormal Crystals CAUTION Abnormal crystals should not be reported haphazardly are rarely
Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents. Amal Alamri
 Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents Amal Alamri Lecture Over view Abnormal constituent of urine Urine analysis Experiments Physical Chemical Micro/Macro 1-Detection of some abnormal
Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents Amal Alamri Lecture Over view Abnormal constituent of urine Urine analysis Experiments Physical Chemical Micro/Macro 1-Detection of some abnormal
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE
 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
By Sandipkumar Kanazariya. Tuesday, December 11,
 By Sandipkumar Kanazariya Tuesday, December 11, 2018 1 Under pathological conditions urine excreted by patient shows the presence of abnormal constituents along with normal constituents. Abnormal constituents
By Sandipkumar Kanazariya Tuesday, December 11, 2018 1 Under pathological conditions urine excreted by patient shows the presence of abnormal constituents along with normal constituents. Abnormal constituents
The Urinary System. Lab Exercise 38. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Urinary System Objectives - Be able to identify the structures of the urinary system and give their function - Be able to recognize the gross anatomy of the kidney - Identify the components
Lab Exercise The Urinary System Objectives - Be able to identify the structures of the urinary system and give their function - Be able to recognize the gross anatomy of the kidney - Identify the components
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Urine Casts. Microscopic Sediment Casts. Unit 2; Session 6
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 6 Urine Casts Urine Casts Overview of Urinary Cast Formation Hyaline Casts Cellular Casts Granular Casts Waxy Casts Pseudo Casts Microscopic Sediment Casts
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 6 Urine Casts Urine Casts Overview of Urinary Cast Formation Hyaline Casts Cellular Casts Granular Casts Waxy Casts Pseudo Casts Microscopic Sediment Casts
EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE
 EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Skills: 30 points Objectives: 1. State the specimen of choice for chemical analysis of urine. 2. List two macroscopic observations of urine and
EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Skills: 30 points Objectives: 1. State the specimen of choice for chemical analysis of urine. 2. List two macroscopic observations of urine and
URINE DIPSTICK AND SULPHOSALICYLIC ACID TEST. Špela Borštnar UREX 2015, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 URINE DIPSTICK AND SULPHOSALICYLIC ACID TEST Špela Borštnar UREX 2015, Ljubljana, Slovenia KIDNEY DISEASE? severity of kidney disease = estimating GFR cause of kidney disease = urinalysis URINE EXAMINATION
URINE DIPSTICK AND SULPHOSALICYLIC ACID TEST Špela Borštnar UREX 2015, Ljubljana, Slovenia KIDNEY DISEASE? severity of kidney disease = estimating GFR cause of kidney disease = urinalysis URINE EXAMINATION
Physical Characteristics of
 Physical Characteristics of Urine Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The urinary system s ability to filter the blood resides in about 2 to 3 million tufts of specialized capillaries the glomeruli distributed more or
Physical Characteristics of Urine Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The urinary system s ability to filter the blood resides in about 2 to 3 million tufts of specialized capillaries the glomeruli distributed more or
Urinalysis Review and Case Studies
 Urinalysis Review and Case Studies A Complete Urinalysis John H. Landis, MS, MLS(ASCP) Adjunct Professor, University of Cincinnati Adjunct Professor, Oakland University Professor Emeritus, Ferris State
Urinalysis Review and Case Studies A Complete Urinalysis John H. Landis, MS, MLS(ASCP) Adjunct Professor, University of Cincinnati Adjunct Professor, Oakland University Professor Emeritus, Ferris State
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
Clinical Laboratory Science: Urinalysis
 Clinical Laboratory Science: Urinalysis Urine is produced by the kidney to maintain constant plasma osmotic concentration; to regulate ph, electrolyte and fluid balances and to excrete some 50 grams of
Clinical Laboratory Science: Urinalysis Urine is produced by the kidney to maintain constant plasma osmotic concentration; to regulate ph, electrolyte and fluid balances and to excrete some 50 grams of
The Minimum Diagnostic Database: Urinalysis
 The Minimum Diagnostic Database: Urinalysis Jeff Niziolek, DVM Professional Services Veterinarian IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. 208 Bay Meadows Drive Holland, MI 49424 The minimum database includes three types
The Minimum Diagnostic Database: Urinalysis Jeff Niziolek, DVM Professional Services Veterinarian IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. 208 Bay Meadows Drive Holland, MI 49424 The minimum database includes three types
Topic Objectives. Physical Examination LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE. Appearance. Odor Specific Gravity Volume
 LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Topic Objectives 1. Identify the colors which commonly associated with abnormal urine. 2. State two possible causes for urine turbidity in a sample that
LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Topic Objectives 1. Identify the colors which commonly associated with abnormal urine. 2. State two possible causes for urine turbidity in a sample that
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 1. Urinanalysis
 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 1 Urinanalysis PLEASE NOTE: The actual urinanalysis goes rather quickly. You may want to skip directly to the Lab Exercise, collect data, and read the Introduction
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Urinanalysis 1 Urinanalysis PLEASE NOTE: The actual urinanalysis goes rather quickly. You may want to skip directly to the Lab Exercise, collect data, and read the Introduction
Pathological components of urine
 Pathological components of urine Physical examination of urine colour of urine very bright, colourless yellow-brown orange cause polyuria with enormous drink, diabetes mellitus, kidney failure water deficiency,
Pathological components of urine Physical examination of urine colour of urine very bright, colourless yellow-brown orange cause polyuria with enormous drink, diabetes mellitus, kidney failure water deficiency,
Urine bench. Urine test for: SARAH Sugar
 Urine bench Urine test for: Sugar It's normal to occasionally have a small amount of sugar in your urine during pregnancy, but if you have elevated levels at a couple of prenatal visits in a row or a very
Urine bench Urine test for: Sugar It's normal to occasionally have a small amount of sugar in your urine during pregnancy, but if you have elevated levels at a couple of prenatal visits in a row or a very
URINALYSIS/URINE CHEMISTRIES
 Deborah Burgess, M.D. Nephrology Department 16 Oct 90 URINALYSIS/URINE CHEMISTRIES The kidney regulates the internal environment of the body by controlling electrolyte and water balance; and establishes
Deborah Burgess, M.D. Nephrology Department 16 Oct 90 URINALYSIS/URINE CHEMISTRIES The kidney regulates the internal environment of the body by controlling electrolyte and water balance; and establishes
Urinalysis Made Easy: The Complete Urinalysis with Images from a Fully Automated Analyzer
 Urinalysis Made Easy: The Complete Urinalysis with Images from a Fully Automated Analyzer A. Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DABVP, DACVP Lighthouse Veterinary Consultants, LLC Gainesville, FL Ideal conditions
Urinalysis Made Easy: The Complete Urinalysis with Images from a Fully Automated Analyzer A. Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DABVP, DACVP Lighthouse Veterinary Consultants, LLC Gainesville, FL Ideal conditions
URINARY CRYSTALS. by Geoffrey K. Dube and Robert S. Brown
 URINARY CRYSTALS by Geoffrey K. Dube and Robert S. Brown A 26 year-old man presents with a fever and weakness. His WBC is 133,000, with 83% blasts. Creatinine is 2.0 mg/dl and serum uric acid is 15.4 mg/dl.
URINARY CRYSTALS by Geoffrey K. Dube and Robert S. Brown A 26 year-old man presents with a fever and weakness. His WBC is 133,000, with 83% blasts. Creatinine is 2.0 mg/dl and serum uric acid is 15.4 mg/dl.
Routine urine examination
 Routine urine examination 尿常规检查 Huawei Liang, PhD E-mail: hwliang99@163.com Objectives To examine urine for the presence of normal and abnormal constituents by routine urine analysis Principles Urine formation
Routine urine examination 尿常规检查 Huawei Liang, PhD E-mail: hwliang99@163.com Objectives To examine urine for the presence of normal and abnormal constituents by routine urine analysis Principles Urine formation
More than 100 different tests can be done on urine. A regular urinalysis often includes the following tests:
 Urine Test Table of Contents Test Overview Why It Is Done How To Prepare How It Is Done How It Feels Risks Results What Affects the Test What To Think About References Credits Test Overview A urine test
Urine Test Table of Contents Test Overview Why It Is Done How To Prepare How It Is Done How It Feels Risks Results What Affects the Test What To Think About References Credits Test Overview A urine test
Taking a dip into urinalysis
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Taking a dip into urinalysis Author : Christine Jameison Categories : RVNs Date : July 1, 2009 Christine Jameison RVN, probes
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Taking a dip into urinalysis Author : Christine Jameison Categories : RVNs Date : July 1, 2009 Christine Jameison RVN, probes
References Required document for Laboratory Accreditation by the College of American Pathologists.
 Subject Urinalysis Clinitek Advantus Regional Index Number Lab-1589 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional Clinic / Affiliate Hospital Laboratories Category Departmental Contact Elizabeth A Kamprud Last
Subject Urinalysis Clinitek Advantus Regional Index Number Lab-1589 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional Clinic / Affiliate Hospital Laboratories Category Departmental Contact Elizabeth A Kamprud Last
Urinalysis (Testing Urine Samples)
 Name: Date: Period: Urinalysis (Testing Urine Samples) Case Studies: Patient 1: Patient 2: Patient 3: Patient 4: Mr. Bob has normal looking urine. He has regular yearly checkups and has no visible symptoms.
Name: Date: Period: Urinalysis (Testing Urine Samples) Case Studies: Patient 1: Patient 2: Patient 3: Patient 4: Mr. Bob has normal looking urine. He has regular yearly checkups and has no visible symptoms.
Microscopic Sediment Epithelial Cells
 Epithelial Cells Cells sloughed from the kidney, urethra, bladder and genital track. Unless increased in number or abnormal forms, they are normal part of sediment. Three major types classified according
Epithelial Cells Cells sloughed from the kidney, urethra, bladder and genital track. Unless increased in number or abnormal forms, they are normal part of sediment. Three major types classified according
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs
 Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs Case History CMP-17 This urine sample is from a 48-year-old male with a 30-year history of diabetes mellitus and new onset renal failure. Laboratory data include:
Urine Sediment Photomicrographs/Photographs Case History CMP-17 This urine sample is from a 48-year-old male with a 30-year history of diabetes mellitus and new onset renal failure. Laboratory data include:
Application Note. Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1
 Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Author: Carl Zeiss
Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Author: Carl Zeiss
MLS Continuing Education Conference November PACE Session # Urinary Casts: The Importance of Laboratory Identification
 MLS Continuing Education Conference November 2014 PACE Session # 304 113-14 Urinary Casts: The Importance of Laboratory Identification 1 Urinalysis The Beginning The field of laboratory medicine started
MLS Continuing Education Conference November 2014 PACE Session # 304 113-14 Urinary Casts: The Importance of Laboratory Identification 1 Urinalysis The Beginning The field of laboratory medicine started
Squamous epithelial cells in urine 0-5
 Toggle navigation Squamous epithelial cells in urine 0-5 13-10-2017 Finding epithelial cells in urine is a diagnostic result found during urinalysis and may raise some red flags for physicians to several
Toggle navigation Squamous epithelial cells in urine 0-5 13-10-2017 Finding epithelial cells in urine is a diagnostic result found during urinalysis and may raise some red flags for physicians to several
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a.
 I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
Ward s. Stimulating Urinalysis Lab Activity Student Study Guide. Background
 Ward s Stimulating Urinalysis Lab Activity Student Study Guide Background Recognition of the presence of disease is based to some extend on the existence of objective signs or recognizable abnormalities
Ward s Stimulating Urinalysis Lab Activity Student Study Guide Background Recognition of the presence of disease is based to some extend on the existence of objective signs or recognizable abnormalities
RELEASES TOXIC FUMES!
 Name(s): Block: Date: Urinary System Lab Activity: Urinalysis Background: Urinalysis, the physical, chemical, and microscopic analysis or examination of urine can provide information about a person s carbohydrate
Name(s): Block: Date: Urinary System Lab Activity: Urinalysis Background: Urinalysis, the physical, chemical, and microscopic analysis or examination of urine can provide information about a person s carbohydrate
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Michelle Moy, MAd Ed, MT(ASCP)SC Program Director Clinical Laboratory Science Program Loyola University Chicago, Illinois
 Reviewers Lorraine Doucette, MS, MLS(ASCP)CM Associate Professor and Medical Laboratory Technician Program Coordinator Anne Arundel Community College Arnold, Maryland Pamela B. Lonergan, MS, MT(ASCP)SC
Reviewers Lorraine Doucette, MS, MLS(ASCP)CM Associate Professor and Medical Laboratory Technician Program Coordinator Anne Arundel Community College Arnold, Maryland Pamela B. Lonergan, MS, MT(ASCP)SC
Controls (positive and negative) for quality assessment-located in central laboratory Note: See central lab UA procedure for QC. Read strips visually.
 ACTION DATE INITIAL Adopted Reviewed 2/8/16 KLW Reviewed 12/12/16 KLW Reviewed Reviewed Revised 5/11/10 MAS Supersedes 2/6/08 name change from Bayer to Siemens TITLE: URINALYSIS TESTING USING Siemens MULTISTIX
ACTION DATE INITIAL Adopted Reviewed 2/8/16 KLW Reviewed 12/12/16 KLW Reviewed Reviewed Revised 5/11/10 MAS Supersedes 2/6/08 name change from Bayer to Siemens TITLE: URINALYSIS TESTING USING Siemens MULTISTIX
Sample collection. night break 6-8 h first morning sample dry, sterile container clean genital area mid-stream 2 hrs: collection - test
 Urinalysis Sample collection night break 6-8 h first morning sample dry, sterile container clean genital area mid-stream 2 hrs: collection - test if it s immpossible store in the fridge (+4C) (up to 24
Urinalysis Sample collection night break 6-8 h first morning sample dry, sterile container clean genital area mid-stream 2 hrs: collection - test if it s immpossible store in the fridge (+4C) (up to 24
D. Explain the rationale for performing a proper clean catch collection to a patient.
 Chapter 42 Urinalysis 815 UNIT 9 LABORATORY PROCEDURES CHAPTER 42 URINALYSIS Overview Urinalysis is an important tool in patient diagnosis and in following the course of a disease. It is vital that medical
Chapter 42 Urinalysis 815 UNIT 9 LABORATORY PROCEDURES CHAPTER 42 URINALYSIS Overview Urinalysis is an important tool in patient diagnosis and in following the course of a disease. It is vital that medical
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Session Outline. Routine Urinalysis a historical perspective. Unit 2; Session 8
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 8 Session Outline Historical perspective Importance of testing Basic urine composition Types of collection Timing of collection Urine preservatives Urinalysis
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 8 Session Outline Historical perspective Importance of testing Basic urine composition Types of collection Timing of collection Urine preservatives Urinalysis
Urine. Dr.Mohamed Saad Daoud
 Urine 1 Reference Books: Urinanalysis and body fluids (Susan King Strasinger- Marjorie Schaub De Lorenzo) Fifth edition Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry (Tietz) Sixth edition 2 Urine: Sterile fluid (in
Urine 1 Reference Books: Urinanalysis and body fluids (Susan King Strasinger- Marjorie Schaub De Lorenzo) Fifth edition Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry (Tietz) Sixth edition 2 Urine: Sterile fluid (in
RENAL FUNCTION TESTS - Lecture
 #Clinical Chemistry RENAL FUNCTION TESTS - Lecture Dr. Kakul Husain # The Kidney Kidneys are bean-shaped organs, each about the size of fist, located near the middle of the back, just below the ribs cage.
#Clinical Chemistry RENAL FUNCTION TESTS - Lecture Dr. Kakul Husain # The Kidney Kidneys are bean-shaped organs, each about the size of fist, located near the middle of the back, just below the ribs cage.
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
To briefly review the anatomy and physiology of the urinary system To review the basics of urinalysis and urine sediment in
 Stefan G Kiessling, MD, FAAP To briefly review the anatomy and physiology of the urinary system To review the basics of urinalysis and urine sediment in children pertinent to a primary care provider s
Stefan G Kiessling, MD, FAAP To briefly review the anatomy and physiology of the urinary system To review the basics of urinalysis and urine sediment in children pertinent to a primary care provider s
How to interpret your urine sample results
 How to interpret your urine sample results Chronic UTI Info Factsheet Series Once you have submitted your urine sample for analysis, it will be sent off to the local laboratory or hospital laboratory if
How to interpret your urine sample results Chronic UTI Info Factsheet Series Once you have submitted your urine sample for analysis, it will be sent off to the local laboratory or hospital laboratory if
How to interpret your urine sample results
 How to interpret your urine sample results Chronic UTI Info Factsheet Series Once you have submitted your urine sample for analysis, it will be sent off to the local laboratory or hospital laboratory if
How to interpret your urine sample results Chronic UTI Info Factsheet Series Once you have submitted your urine sample for analysis, it will be sent off to the local laboratory or hospital laboratory if
Assessment of urine of a bovine patient
 Commonwealth of Australia Copyright regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been copied and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Adelaide pursuant of Part VB of the Copyright Act
Commonwealth of Australia Copyright regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been copied and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Adelaide pursuant of Part VB of the Copyright Act
Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
 Barger both02.tex V3-07/08/2015 7:05 P.M. Page 1 Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Getting Started with Clinical Pathology 1. Which component of the microscope should be adjusted when evaluating
Barger both02.tex V3-07/08/2015 7:05 P.M. Page 1 Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Getting Started with Clinical Pathology 1. Which component of the microscope should be adjusted when evaluating
Science of Veterinary Medicine. Urinary System Unit Handouts
 Science of Veterinary Medicine Urinary System Unit Handouts Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Regulate aspects of homeostasis Organs of the Urinary system The
Science of Veterinary Medicine Urinary System Unit Handouts Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Regulate aspects of homeostasis Organs of the Urinary system The
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
Urinary System. Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system
 Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Routine Clinic Lab Studies
 Routine Lab Studies Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a Tacrolimus level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not too much anti-rejection
Routine Lab Studies Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a Tacrolimus level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not too much anti-rejection
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis
 Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylor-Jones & Ms C Tierney. Urinalysis Aims and Objectives Aim: For the student to be able to safely conduct a urinalysis on
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylor-Jones & Ms C Tierney. Urinalysis Aims and Objectives Aim: For the student to be able to safely conduct a urinalysis on
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion
 Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Some normal urine constituents excreted (in g/24 hours): PROCEDURES
 Urinalysis Monograph Urine is produced by the kidney to maintain constant plasma osmotic concentration; to regulate ph, electrolyte and fluid balances and to excrete some 50 grams of waste solids (mostly
Urinalysis Monograph Urine is produced by the kidney to maintain constant plasma osmotic concentration; to regulate ph, electrolyte and fluid balances and to excrete some 50 grams of waste solids (mostly
Please circulate to your laboratory staff. ALL staff can now earn free CME/CE credit with the Clinical Microscopy Survey (CM-B)!
 Please circulate to your laboratory staff. ALL staff can now earn free CME/CE credit with the Clinical Microscopy Survey (CM-B)! Complete the specified reading in the 2006 CM-B Participant Summary and
Please circulate to your laboratory staff. ALL staff can now earn free CME/CE credit with the Clinical Microscopy Survey (CM-B)! Complete the specified reading in the 2006 CM-B Participant Summary and
Ch17-18 Urinary System
 Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students. Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile in urinary bladder.. It contains fluids,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile in urinary bladder.. It contains fluids,
LABORATORY 6: The Complete Urinalysis with Automation
 LABORATORY 6: The Complete Urinalysis with Automation PreLab Preparation: 1. Review YouTube videos on Clinitek Status Principle & Operation http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j-8loszd-u8&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s1tpqqh9m88&feature=endscreen&nr=1
LABORATORY 6: The Complete Urinalysis with Automation PreLab Preparation: 1. Review YouTube videos on Clinitek Status Principle & Operation http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j-8loszd-u8&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s1tpqqh9m88&feature=endscreen&nr=1
Urine Sediment Photographs
 Urine Sediment Photographs Case History CMP-04 This urine sample is from a 35-year-old female as part of a routine exam. Laboratory data include: Specific Gravity = 1.015; ph = 7.0; ketones, glucose, protein,
Urine Sediment Photographs Case History CMP-04 This urine sample is from a 35-year-old female as part of a routine exam. Laboratory data include: Specific Gravity = 1.015; ph = 7.0; ketones, glucose, protein,
Lecture 7. The Urinary System
 Lecture 7 The Urinary System Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning The Urinary System The urinary system removes wastes from the body The urinary system also maintains homeostasis or a constant internal
Lecture 7 The Urinary System Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning The Urinary System The urinary system removes wastes from the body The urinary system also maintains homeostasis or a constant internal
Digestive Anatomy Lab System Overview
 Digestive Anatomy Lab System Overview In-Lab Exercises Read Me This is a very diverse lab. We will be looking at the gross anatomy of the urinary tract, the microscopic anatomy on both models and slides,
Digestive Anatomy Lab System Overview In-Lab Exercises Read Me This is a very diverse lab. We will be looking at the gross anatomy of the urinary tract, the microscopic anatomy on both models and slides,
Excretory System. Biology 2201
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System. Excretory System
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
100,000 cfu ml gram negative rods Address Submit
 100,000 cfu ml gram negative rods Email Address Submit A microscopic exam is performed if blood, protein, or leukocyte esterase results are abnormal or if a microscopic exam is specifically requested.
100,000 cfu ml gram negative rods Email Address Submit A microscopic exam is performed if blood, protein, or leukocyte esterase results are abnormal or if a microscopic exam is specifically requested.
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
Identification and qualitative Analysis. of Renal Calculi
 Identification and qualitative Analysis of Renal Calculi 1 -Renal Calculi: Kidney stones, renal calculi or renal lithiasis (stone formation) are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. The
Identification and qualitative Analysis of Renal Calculi 1 -Renal Calculi: Kidney stones, renal calculi or renal lithiasis (stone formation) are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. The
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis. Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017
 320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
Hematuria. Ramzi El-Baroudy (ESPNT)
 Hematuria Ramzi El-Baroudy (ESPNT) Hematuria is the presence of RBCs in urine. If the amount of blood in urine is big enough, the urine will, then, look red. Something which is, undoubtedly, terrifying.
Hematuria Ramzi El-Baroudy (ESPNT) Hematuria is the presence of RBCs in urine. If the amount of blood in urine is big enough, the urine will, then, look red. Something which is, undoubtedly, terrifying.
A. SAP is the D-Lab's name for a specific set of serum biochemical tests.
 Understanding CBC, SAP, UA/Laura J. Steadman, DVM I. CBC - Complete Blood Count A. Three major types of cells are counted 1. Red Blood Cells 2. White Blood Cells 3. Platelets B. Cells are counted at the
Understanding CBC, SAP, UA/Laura J. Steadman, DVM I. CBC - Complete Blood Count A. Three major types of cells are counted 1. Red Blood Cells 2. White Blood Cells 3. Platelets B. Cells are counted at the
WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Unit Outline. Chemical Exam of Urine. Unit 3. Reagent strip manufactures
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 3 Chemical Examination of Urine Part 1 Overview of Procedure & ph Unit Outline Introduction to reagent strip testing ph Glucose & Carbohydrates Ketones Protein Bilirubin
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 3 Chemical Examination of Urine Part 1 Overview of Procedure & ph Unit Outline Introduction to reagent strip testing ph Glucose & Carbohydrates Ketones Protein Bilirubin
Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I
 Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I 1 Assessment of renal function Clinical manifestations Laboratory tests Urinalysis Urine culture and sensitivity Renal/bladder ultrasound Testicular
Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I 1 Assessment of renal function Clinical manifestations Laboratory tests Urinalysis Urine culture and sensitivity Renal/bladder ultrasound Testicular
Biomarkers of renal diseases. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Introduction Renal system performs several functions Excretory Waste products like urea, creatinine, drug, toxins clearance Regulatory Water, electrolyte and acid base balance
By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Introduction Renal system performs several functions Excretory Waste products like urea, creatinine, drug, toxins clearance Regulatory Water, electrolyte and acid base balance
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System
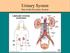 Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
Instructions for Performing In-Office Lab Tests
 Instructions for Performing In-Office Lab Tests SALIVARY PH- STATIC MEASUREMENT Testing must be done at least 30 minutes from any food or beverage. 1. Simply place a ph testing strip in the patient s mouth
Instructions for Performing In-Office Lab Tests SALIVARY PH- STATIC MEASUREMENT Testing must be done at least 30 minutes from any food or beverage. 1. Simply place a ph testing strip in the patient s mouth
31 August 2016 Urinalysis - a review
 31 August 2016 Urinalysis - a review Bradley Galgut, BVSc (Hons), DACVP Specialist Veterinary Clinical Pathologist Urinalysis A Review Bradley Galgut, BVSc (Hons), DACVP Specialist Veterinary Clinical
31 August 2016 Urinalysis - a review Bradley Galgut, BVSc (Hons), DACVP Specialist Veterinary Clinical Pathologist Urinalysis A Review Bradley Galgut, BVSc (Hons), DACVP Specialist Veterinary Clinical
Urinalysis Review 3/23/18. Types of Urine Specimens. Changes in Unpreserved Urine. Changes in Unpreserved Urine. Urine Collection Techniques
 Types of Urine Specimens Urinalysis Review Lauren Brandenburg, MS, MLS (ASCP) CM Random- collected at any time without patient preparation Most convenient Hydration dependent First Morning Void- patient
Types of Urine Specimens Urinalysis Review Lauren Brandenburg, MS, MLS (ASCP) CM Random- collected at any time without patient preparation Most convenient Hydration dependent First Morning Void- patient
Urinalysis (Macroscopic( Chemical Tests) ) Background. Ishihara Color Blindness Tests 12/22/2012. Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari DCLS, PhD
 Urinalysis (Macroscopic( Chemical Tests) ) Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari DCLS, PhD Background Routine chemical examination of urine has changed dramatically since the early days of urine testing, owing to the
Urinalysis (Macroscopic( Chemical Tests) ) Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari DCLS, PhD Background Routine chemical examination of urine has changed dramatically since the early days of urine testing, owing to the
Urinary. Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac stores urine. Figure Slide 15.21a
 Urinary Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac stores urine Figure 15.6 Slide 15.21a Urinary Bladder Wall Walls are and folded in an empty bladder Bladder can significantly without increasing internal pressure
Urinary Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac stores urine Figure 15.6 Slide 15.21a Urinary Bladder Wall Walls are and folded in an empty bladder Bladder can significantly without increasing internal pressure
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS URINALYSIS SUBCOURSE MD0852 EDITION 200
 U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 URINALYSIS SUBCOURSE MD0852 EDITION 200 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence course instruction.
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 URINALYSIS SUBCOURSE MD0852 EDITION 200 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence course instruction.
Urinalysis (UA) provides information about the urinary
 Today s TeChniCian PEER REVIEWED URINALYSIS IN COMPANION ANIMALS Part 1: Collection, Sample Handling, & Initial Evaluation Theresa E Rizzi, DVM, Diplomate ACVP (Clinical Pathology) Oklahoma State University
Today s TeChniCian PEER REVIEWED URINALYSIS IN COMPANION ANIMALS Part 1: Collection, Sample Handling, & Initial Evaluation Theresa E Rizzi, DVM, Diplomate ACVP (Clinical Pathology) Oklahoma State University
