Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset
|
|
|
- Reginald Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 For reference only Do Not Use For more information contact: Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset March 2006 National Clinical Dataset Development Programme (NCDDP) Support Team Information Services Area 54E Gyle Square 1 South Gyle Crescent Edinburgh EH12 9EB Tel: to: NCDDPsupportteam@isd.csa.scot.nhs.uk Website:
2 Contents 1. Patient Administration and Demographics...4 Patient Administration and Demographics Table Ethnic, Cultural and Diversity Details...5 Ethnic, Cultural and Diversity Details Table General Medical Practitioner Details...5 General Medical Practitioner Details Table Associated Professional Details...6 Associated Professional Details Table Class of Retinopathy Grader Diagnosis Details...7 Diagnosis Details Table Care Episode Administration Details...8 Care Episode Administration Details Table Review Date Appointment Type {Diabetes Retinopathy} Patient Status (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Date Temporarily Suspended Until (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Reason for Suspension (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Location Preferred (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Attendance Time Preferred (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Eye Clinic Attendance (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Quality Assurance Details...12 Quality Assurance Details Table Retinopathy Grading Referral Error (Quality Assurance) Date of Retinal Grading (Quality Assurance) Assessment and Management...13 Assessment and Management Table Image Capture Details...13 Image Capture Details Table Pupil Dilation Status Mydriatic Drug Batch Number Mydriatic Drug Expiry Date Retinal Screening Camera Number Retinal Image Status Image Interpretation Details...16 Image Interpretation Details Table Fundus Assessment Retinal Grading Date Diabetic Retinopathy Image Quality Diabetic Retinopathy Image Grading Status Microaneurysms Flame Haemorrhages Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 2
3 10.7 Cotton Wool Spots Blot Haemorrhages Venous Beading Intra-retinal Microvascular Abnormalities Vessels Elsewhere Vessels at Disc Vitreous Haemorrhages Retinal Detachment Exudates Blot Haemorrhages within 1 Disc Diameter Macular Oedema Cataract Details...24 Cataract Details Table Cataract Causing Disability Cataract Surgery Recommendation Cataract Surgery Decision Cataract Surgery Status Visual Acuity Details...26 Visual Acuity Details Table Visual Acuity Obtained Outcomes Details...27 Outcomes Details Table Retinopathy Grading Outcome Retinopathy Grading Outcome - Overwrite Non-diabetic Retinal Lesions Grader Referral Non-diabetic Retinal Lesions Final Grader Referral Ophthalmic Exam Details...29 Ophthalmic Exam Details Table Date Referred to Ophthalmologist Ophthalmology Outcome for Retinopathy Screening Programme Ophthalmic Exam Recommendation Ophthalmic Exam Recommendation Accepted Date...31 Date Table Appendix 1 - Membership of the Diabetes Retinopathy Dataset Clinical Working Group...32 Appendix 2 - Consultation Distribution List...33 Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 3
4 1. Patient Administration and Demographics Patient Administration and Demographics Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Structured Name 1 - Person Title - Person Family Name - Person Given Name - Person Preferred Forename - Previous Person Family Name An ordered sequence of person name elements such as title, forename(s) and family name. 35 characters (each) Person Full Name 1 (Unstructured) Person Current Gender Person Birth Date CHI Number Health Record Identifier Address (BS7666) 2 UK Postal Address 2 Postcode 2 UK Telephone Number This alternative to recording structured name involves the whole name being recorded as a single character string with no separately identified elements. A statement by the individual about the gender they currently identify themselves to be (i.e. self-assigned). The date on which a person was born or is officially deemed to have been born, as recorded on the Birth Certificate. The Community Health Index (CHI) is a population register, which is used in Scotland for health care purposes. The CHI number uniquely identifies a person on the index. A Patient Health Record Identifier is a code (set of characters) used to uniquely identify a patient within a health register or a HEALTH RECORDS SYSTEM, e.g. PAS. A collection of data describing the addressing of locations. Alternatively, address can be recorded in up to 5 lines of unstructured text (minimum 2 lines). The code allocated by the Post Office to identify a group of postal delivery points. A minimum standard is provided for holding a UK STD code. An extended set of component parts is provided for systems to hold more information. 70 characters 1 character 10 characters (CCYY- MM-DD) 10 characters 14 characters See Government Data Standards Website 5x35 characters 8 characters 35 characters Note: All of the above data items have already been approved and are available in the Health & Social Care Data Dictionary. 1 It is recommended that Structured Name should be used in all new IT systems. Person Full Name (Unstructured) should only be used in legacy systems, which should migrate to use of Structured Name in due course. 2 It is recommended that Address (BS7666), which is a structured address, should be used in all new IT systems. Unstructured UK Postal Address plus Postcode should only be used in legacy systems, which should migrate to use of Address (BS7666) in due course. Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 4
5 2. Ethnic, Cultural and Diversity Details Ethnic, Cultural and Diversity Details Table Data Item Description Format & Field Length Ethnic Group (Self-Assigned) A statement made by the service user 3 characters about their current ethnic group. Religion A statement made by the service user 6 (2+4) characters about their current religious affiliation / faith community. Preferred Language This data item is defined as the 6 characters person s language of preference and may differ from first language (as defined as the language spoken at home) and is required for effective communication with the person. Interpretation Assistance Indicator Indication of requirement for assistance to communicate in English. Note: All of the above data items have already been approved and are available in the Health & Social Care Data Dictionary. 3. General Medical Practitioner Details General Medical Practitioner Details Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Registered GP Practice Code Each GP practice in Scotland is 6 characters identified by a unique GP practice code. General Practice Registration Status of Patient The registration status of the patient with the general practice from which they are receiving care. 3 characters Note: All of the above data items have already been approved and are available in the Health & Social Care Data Dictionary. Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 5
6 4. Associated Professional Details Associated Professional Details Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Associated Professional Associated Professionals are Detailed in this table those individuals who are involved with the client/ patient in a professional capacity e.g. consultant, social worker, occupational therapist, etc. Structured Name - Title - Surname/ Family Name - First Forename An ordered sequence of person name elements such as title, forename(s) and family name. 35 characters Person Full Name (Unstructured) Associated Professional Identifier This alternative to recording structured name involves the whole name being recorded as a single character string with no separately identified elements. The unique identifier issued to all health and social care professionals by their professional regulatory body. 70 characters 8 characters Class of Retinopathy Grader For Consultation The above data items have already been approved and are available in the Health & Social Care Data Dictionary. 4.1 Class of Retinopathy Grader Definition: The level of grader grading the images, as defined by the national occupational standards for retinopathy screening. Explanatory Notes 00 Not Applicable 01 Level 1 Grader A level 1 grader, as defined by the national occupational standards for retinopathy screening, will grade images for image quality and the presence or absence of diabetic retinopathy. Images with any retinopathy (whatever level) will be passed on to the level 2 grader. The level 1 grader should have undergone a recognised and accredited training programme. Level 1 grading could, in some circumstances, be performed by camera operators who have received sufficient training. In due course it is hoped the level 1 grading role will be performed by automated grading systems. Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 6
7 02 Level 2 Grader A level 2 grader, as defined by the national occupational standards for retinopathy screening, will be presented with a list of images that have been referred by a level 1 grader. Level 2 graders will be required to undergo a more intensive training programme which has been recognised and accredited. Level 2 grading could, in some circumstances, be performed by camera operators who have received sufficient training The purpose of level 2 grading is to identify sight threatening retinopathy and other retinal problems that may be amenable to treatment. Such images will be passed on to the level 3 grader for final assessment. 03 Level 3 Grader A level 3 grader, as defined by the national occupational standards for retinopathy screening, will be presented with a list of images that have been referred by a level 2 grader. Level 3 graders (who usually but not necessarily will be ophthalmologists) confirm or refute the need for referral to ophthalmology. Related data items: See Associated Professional Details Table 5. Diagnosis Details Diagnosis Details Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Date of Diagnosis For Future Development 10 characters (CCYY- MM-DD) Diabetes Mellitus Type For Consultation see Diabetes Core Further information on this data item can be found in the Diabetes Core Data Standards. Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 7
8 6. Care Episode Administration Details Care Episode Administration Details Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Location Code A location is any building or set of 5 characters buildings where events pertinent to NHS Scotland take place. Locations include hospitals, health centres, GP surgeries, clinics, NHS board offices, nursing homes, schools and patient/ client s home. Clinic Code A code assigned locally to identify a 9 characters clinic session or group of clinic sessions. Date of Contact The date on which a contact took place between a patient/ client and an 10 characters (CCYY- MM-DD) individual care professional for the purpose of care. A contact can take place when the Health Care Professional (HCP) is on care premises or visiting the patient and may be in person, by telephone, e- mail, letter, text message or telemedicine. Contact Status A record of whether or not the patient/ client attended for their appointment or was present for a planned home visit. Eye Examination Method For Consultation see Diabetes Core Review Date For Consultation 10 characters (CCYY- MM-DD) Appointment Type For Consultation {Diabetes Retinopathy} Patient Status (Diabetic For Consultation Retinopathy Screening) Date Temporarily Suspended Until (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Reason for Suspension (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Location Preferred (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Attendance Time Preferred (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Eye Clinic Attendance (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Transport Access For Consultation For Consultation For Consultation For Consultation For Consultation The means of transport used by the patient in order to access care services. This includes aspects of the mode of transport and dependency upon another person. 10 characters (CCYY- MM-DD) 198 characters The above data items have already been approved and are available in the Health & Social Care Data Dictionary. Further information on this data item can be found in the Diabetes Core Data Standards. Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 8
9 6.1 Review Date Definition: The date of the next scheduled contact between the patient and the care professional, team or service. This is a date planned for the future and may not necessarily happen. (CCYY-MM-DD) Field length: 10 N/A 6.2 Appointment Type {Diabetes Retinopathy} Definition: Records the type of Diabetic Retinopathy Screening programme (DRSP) appointment made for the patient st Screening Appointment 02 6 Month Recall Month Recall 04 Recall for Slit-lamp Biomicroscopy 6 Month 05 Recall for Slit-lamp Biomicroscopy 12 Month 06 Ophthalmology 6.3 Patient Status (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Definition: Records the activity for the patient that is associated with delivering a result and outcome from the Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme (DRSP). 01 Ready for Screening 02 Invited 03 Booked 04 DNA 05 Examination Started 06 Awaiting Result Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 9
10 07 Temporarily Suspended 08 Permanently Suspended 6.4 Date Temporarily Suspended Until (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Definition: Records the date until when temporary suspension from the Diabetic retinopathy Screening Programme is valid. (CCYY-MM-DD) Field length: 10 N/A Related data item: Reason for Suspension (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) 6.5 Reason for Suspension (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Definition: Records the reason for suspending the patient from the Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme. 01 Registered Blind 02 Deceased 03 Under Age 04 Unfit 05 Consent Not Given 06 Eye Clinic Patient 07 Lives Abroad 08 Lives Elsewhere 09 Unable to Cooperate 10 Not Diabetic 11 DNA X3 98 Other Related data item: Date Temporarily Suspended Until (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Recording guidance: Where 98 Other is recorded, systems may be configured to include a text box to allow specification of the Reason for Suspension. Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 10
11 6.6 Location Preferred (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Definition: Records the patient s preferred attendance location for a Diabetic Retinopathy Screening appointment. Field length: 198 N/A 6.7 Attendance Time Preferred (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Definition: Records the patient s preferred attendance time for a Diabetic Retinopathy Screening appointment. 01 Weekday 02 Evening 03 Saturday Morning 04 No Preference 6.8 Eye Clinic Attendance (Diabetic Retinopathy Screening) Definition: Records whether or not the patient is attending a diabetic retinopathy eye clinic. 01 No 02 Yes Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 11
12 7. Quality Assurance Details Quality Assurance Details Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Retinopathy Grading Referral For Consultation Error (Quality Assurance) Date of Retinal Grading (Quality Assurance) For Consultation 10 characters (CCYY- MM-DD) 7.1 Retinopathy Grading Referral Error (Quality Assurance) Definition: Records the type of error identified in the Retinopathy grading process as part of quality assurance. Explanatory Notes 00 No Error Noted in the Quality Assurance re-grader agrees with original grading. Referral Process 01 Level 1 Grader Failed to Notice Signs of No Quality Assurance re-grader identifies 'no retinopathy' [R0] which was not identified by level 1 grader. Retinopathy 02 Level 1 Grader Failed to Quality Assurance re-grader identifies retinopathy, which Notice Signs of Retinopathy 03 Level 1 Grader Failed to Refer for Slit Lamp Examination 04 Level 2 Grader Failed to Notice Signs of No Retinopathy 05 Level 2 Grader Failed to Notice Signs of Observable Retinopathy/ Maculopathy 06 Level 2 Grader Failed to Notice Signs of Referable Retinopathy 07 Level 2 Grader Failed to Refer for Slit Lamp Examination 08 Level 3 Grader Failed to Notice Signs of No Retinopathy was not identified by level 1 grader. Quality Assurance re-grader identifies poor image quality/technical failure, which should have been referred for slit-lamp examination by level 1 grader. Quality Assurance re-grader identifies 'no retinopathy' [R0] which was not identified by level 2 grader. Quality Assurance re-grader identifies mild retinopathy [R1], observable retinopathy [R2] or observable maculopathy [M1], which was not identified by level 2 grader. Quality Assurance re-grader identifies referable maculopathy [M2], referable retinopathy [R3], proliferative retinopathy [R4] or other referable condition, which was not identified by level 2 grader. Quality Assurance re-grader identifies poor image quality/technical failure, which should have been referred for slit-lamp examination by level 2 grader. Quality Assurance re-grader identifies 'no retinopathy' [R0] which was not identified by level 3 grader. Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 12
13 09 Level 3 Grader Failed to Notice Signs of Observable Retinopathy/ Maculopathy 10 Level 3 Grader Failed to Notice Signs of Referable Retinopathy 11 Level 3 Grader Failed to Identify Other Condition Requiring Action Quality Assurance re-grader identifies mild retinopathy [R1], observable retinopathy [R2] or observable maculopathy [M1], which was not identified by level 3 grader. Quality Assurance re-grader identifies referable maculopathy [M2], referable retinopathy [R3], proliferative retinopathy [R4] or other referable condition, which was not identified by level 3 grader. Quality Assurance re-grader identifies coincidental findings/non-diabetic retinopathy condition requiring action that level 3 grader failed to identify. 7.2 Date of Retinal Grading (Quality Assurance) Definition: Indicates the date when retinal grading is repeated as part of the quality assurance process of the screening programme. (CCYY-MM-DD) Field length: 10 N/A 8. Assessment and Management Assessment and Management Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Diabetes Care Type For Consultation see Diabetes Core Diabetes Management The type(s) of management of a patient's diabetes. The above data item has already been approved and is available in the Health & Social Care Data Dictionary. Further information on this data item can be found in the Diabetes Core Data Standards. 9. Image Capture Details Image Capture Details Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Pupil Dilation Status For Consultation Mydriatic Drug Batch For Consultation 4 characters Number Mydriatic Drug Expiry Date For Consultation 7 characters (CCYY- MM) Retinal Screening Camera Number For Consultation 4 characters Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 13
14 Retinal Image Status For Consultation 3 characters 9.1 Pupil Dilation Status Definition: Records whether or not a mydriatic drug was used during the Diabetic Retinopathy Screening and if so, which drug was used. Subcode Sub-value Explanatory notes 00 Pupils Undilated No Mydriatic drug used. 01 Pupils Dilated A 1% Tropicamide Note that this is the drug of choice for DRSP (0.5% Tropicamide is not recommended). B 1% Cyclopentolate Some people may be allergic to tropicamide and may be given cyclopentolate as an alternative. C 0.05% Proxymetacaine Related data items: Mydriatic Drug Batch Number Mydriatic Drug Expiry Date 9.2 Mydriatic Drug Batch Number Definition: The batch number of the Mydriatic drug used, as printed on the drug packaging. Field length: 4 N/A Related data items: Pupil Dilation Status Mydriatic Drug Expiry Date 9.3 Mydriatic Drug Expiry Date Definition: The expiry date of the Mydriatic drug used, as printed on the drug packaging. (CCYY-MM) Field length: 7 Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 14
15 N/A Related data items: Pupil Dilation Status Mydriatic Drug Batch Number 9.4 Retinal Screening Camera Number Definition: The reference number of the camera used in the retinal screening programme. Field length: 4 N/A Further Information: NHS board identifier 1 character plus 3 digits starting at Retinal Image Status Definition: Records whether or not a retinal image of the eye was captured and if not, the reason why not. Field length: 3 Subcode Sub-value Explanatory notes 00 No A Patient Factor Patient was not able to comply with photographic process. B Operator Error Photographer failed to follow correct procedure for obtaining digital image. C Equipment Failure Digital imaging equipment failed to perform. D Blind or Enucleated 01 Yes Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 15
16 10. Image Interpretation Details Image Interpretation Details Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Fundus Assessment For Consultation Retinal Grading Date For Consultation 10 characters (CCYY- MM-DD) Diabetic Retinopathy Image For Consultation Quality Diabetic Retinopathy Image For Consultation Grading Status Microaneurysms For Consultation Flame Haemorrhages For Consultation Cotton Wool Spots For Consultation Blot Haemorrhages For Consultation 3 characters Venous Beading For Consultation Intra-retinal Microvascular For Consultation Abnormalities Vessels Elsewhere For Consultation 3 characters Vessels at Disc For Consultation 3 characters Vitreous Haemorrhages For Consultation Retinal Detachment For Consultation Exudates For Consultation Blot Haemorrhages within 1 For Consultation Disc Diameter Macular Oedema For Consultation Non-diabetic Retinal For Consultation see Diabetes Lesions Core Laser Photocoagulation Scars (Grading Exam) For Consultation see Diabetes Core Further information on these data items can be found in the Diabetes Core Data Standards Fundus Assessment Definition: Records the result of the fundus assessment. 01 Fundus Gradable 02 Fundus Not Gradable 03 Unscreenable 04 Blind/ Enucleated Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 16
17 10.2 Retinal Grading Date Definition: Records the date on which the retinal grading was performed. (CCYY-MM-DD) Field length: 10 N/A 10.3 Diabetic Retinopathy Image Quality Definition: Records the quality of image. Explanatory notes 01 Image Quality Grade 1 Nerve fibre layer visible this is the best quality image. 02 Image Quality Grade 2 Nerve fibre layer not visible. 03 Image Quality Grade 3 Small vessels blurred. 04 Image Quality Grade 4 Major arcade vessels just blurred. 05 Image Quality Grade 5 Significant blurring of major arcade vessels in >1/3 of image in the absence of visible reference retinopathy. Patient is deemed a technical failure (patient factor) and has to be screened using slit-lamp biomicroscopy at a separate technical failure screening session. 06 Image Quality Grade 6 Enucleated eye. Patient is not classed as a technical failure despite only one eye's images being available for grading. Further information: The image quality grading is consistent with Facey et al (2002) Organisation of services for diabetic retinopathy screening Health Technology Assessment Report 1. Glasgow: Health Technology Board for Scotland. Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 17
18 10.4 Diabetic Retinopathy Image Grading Status Definition: The status of the grading process relating to digital images following Diabetic Retinopathy Screening. Explanatory notes 00 Not Yet Graded The digital image has not been graded. 01 Level 1 Graded, Referred for Level 2 Grading The digital image has been graded by a level 1 grader and referred for level 2 assessment. 02 Level 2 Graded, Referred for Level 3 Grading The digital image has been graded by a level 2 grader and referred for level 3 assessment. 03 Final Graded The digital image has been graded to final level. This may be reached by any level of grader as appropriate to the clinical findings. 04 Ungradable The digital image is not of gradable quality and the patient has been referred for slit lamp examination Microaneurysms Definition: Records whether or not there are microaneurysms in the eye. 00 No 01 Yes Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 18
19 10.6 Flame Haemorrhages Definition: Records whether or not there are flame haemorrhages in the eye. 00 No 01 Yes 10.7 Cotton Wool Spots Definition: Records whether or not there are cotton wool spots in the eye. 00 No 01 Yes 10.8 Blot Haemorrhages Definition: Records whether or not there are blot haemorrhages in the eye and if so, the quantity in each hemi-field. Field length: 3 Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 19
20 Subcode Sub-value Explanatory notes 00 No 01 Yes A < 4 in One Hemi-field Only In one hemi-field the fundal area covered by retinal haemorrhages < AH standard photograph 2a. B < 4 in Both Hemi-fields In both hemi-fields the fundal area covered by retinal haemorrhages < AH standard photograph 2a. C 4 in One Hemi-field Only In one hemi-field the fundal area covered by retinal haemorrhages AH standard photograph 2a. D 4 in Both Hemi-fields In both hemi-fields the fundal area covered by retinal haemorrhages AH standard photograph 2a Venous Beading Definition: Records whether or not there is venous beading in the eye. Explanatory notes 00 No 01 Yes Venous beading AH standard photograph 6a Intra-retinal Microvascular Abnormalities Definition: Records whether or not there are intra-retinal microvascular abnormalities (IRMA) in the eye. Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 20
21 Explanatory notes 00 No 01 Yes IRMA AH standard photograph 8a Vessels Elsewhere Definition: Records whether or not there are vessels elsewhere in the eye, other than at the disc and whether they are active or inactive. Field length: 3 Subcode 00 No 01 Yes A B Sub-value Active Inactive Vessels at Disc Definition: Records whether or not there are vessels at the disc in the eye and whether they are active or inactive. Field length: 3 Subcode 00 No 01 Yes A B Sub-value Active Inactive Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 21
22 10.13 Vitreous Haemorrhages Definition: Records whether or not there are vitreous haemorrhages in the eye. 00 No 01 Yes Retinal Detachment Definition: Records whether or not there is any retinal detachment in the eye. 00 No 01 Yes Exudates Definition: Records the occurrence of exudates in the eye. 01 > 1 but 2 Disc Diameters 02 Within a Radius of 1 Disc Diameter Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 22
23 10.16 Blot Haemorrhages within 1 Disc Diameter Definition: Records whether or not there are blot haemorrhages present within 1 disc diameter in the eye. 00 No 01 Yes Macular Oedema Definition: Records the occurrence of macular oedema in the eye. 01 > 1 but </= 2 Disc Diameters 02 Within a Radius of </= 1 Disc Diameter Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 23
24 11. Cataract Details Cataract Details Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Cataract Status For Consultation see Diabetes Core Cataract Causing Disability For Consultation Cataract Surgery For Consultation Recommendation Cataract Surgery Decision For Consultation Cataract Surgery Status For Consultation Further information on this data item can be found in the Diabetes Core Data Standards Cataract Causing Disability Definition: Records whether or not the cataract present causes visual function limitation. Explanatory notes 01 No Patient may have a cataract in left eye, but does not report consequent visual functional limitation. 02 Yes Patient has cataract in left eye and reports consequent visual functional limitation Cataract Surgery Recommendation Definition: Records whether or not cataract surgery is recommended for either or both eyes. Explanatory notes 01 Referral for Cataract Surgery Recommended Cataract surgery clinically indicated and recommended. 02 Referral for Cataract Surgery not Indicated Cataract not clinically indicated. Related data item: Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 24
25 Cataract Surgery Decision 11.3 Cataract Surgery Decision Definition: Records the decision of the patient regarding referral for cataract surgery. Explanatory notes 01 Agrees to Referral for Cataract Surgery Patient offered referral for cataract surgery and agrees. 02 Referral for Cataract Surgery Declined Patient offered referral for cataract surgery but declined. Related data item: Cataract Surgery Recommendation 11.4 Cataract Surgery Status Definition: Records whether or not the patient is listed for cataract surgery. 00 Patient not listed for surgery 01 Patient listed for surgery Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 25
26 12. Visual Acuity Details Visual Acuity Details Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Visual Acuity Obtained For Consultation Visual Acuity (Logmar) - For Consultation see Diabetes Corrected Core Visual Acuity (Snellen) - Corrected For Consultation see Diabetes Core Further information on these data items can be found in the Diabetes Core Data Standards Visual Acuity Obtained Definition: Records how the patient can obtain visual acuity. 01 Unaided 02 Spectacles 03 Contact Lens 04 Pin Hole 05 Acuity Unobtainable Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 26
27 13. Outcomes Details Outcomes Details Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Retinal Status {Diabetes} For Consultation see Diabetes Core Diabetic Maculopathy For Consultation see Diabetes Status Core Retinopathy Grading For Consultation Outcome Retinopathy Grading For Consultation Outcome Overwrite Non-diabetic Retinal Lesions For Consultation Grader Referral Non-diabetic Retinal Lesions Final Grader Referral For Consultation 3 characters Further information on these data items can be found in the Diabetes Core Data Standards Retinopathy Grading Outcome Definition: Records the overall grading outcome or recommendations as a result of the diabetic retinopathy screening. 01 Rescreen 12 Months 02 Rescreen 6 Months 03 Refer Ophthalmology 04 Technical Failure Related data item: Retinopathy Grading Outcome - Overwrite Further Information: Where each eye has a different grading outcome, the overall outcome recorded is that for the worse eye Retinopathy Grading Outcome - Overwrite Definition: The overwritten outcome or recommendations by the level 3 grader. Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 27
28 Subcode Sub-value 01 Fundus Photography A 6 Months Rescreen B 12 Months 02 Slit Lamp Rescreen A 6 Months B 12 Months 03 Refer for Ophthalmology for Diabetic Retinopathy 04 Fast Track Referral Related data item: Retinopathy Grading Outcome 13.3 Non-diabetic Retinal Lesions Grader Referral Definition: Records whether or not a level 1 or level 2 Grader refers to the next level of Grader for non-diabetic Retinopathy feature issues. 00 No 01 Yes 13.4 Non-diabetic Retinal Lesions Final Grader Referral Definition: Records whether or not the level 3 Grader refers the patient for non-diabetic retinopathy issues. Field length: 3 Subcode 00 No 01 Yes A B Sub-value Refer to Ophthalmology Refer to Elsewhere Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 28
29 14. Ophthalmic Exam Details Ophthalmic Exam Details Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Date Referred to Ophthalmologist For Consultation 10 characters (CCYY- MM-DD) Ophthalmology Outcome for For Consultation Retinopathy Screening Programme Ophthalmic Exam For Consultation Recommendation Ophthalmic Exam Recommendation Accepted For Consultation 14.1 Date Referred to Ophthalmologist Definition: Records the date on which a referral is made for the patient to attend an ophthalmologist. (CCYY-MM-DD) Field length: 10 N/A 14.2 Ophthalmology Outcome for Retinopathy Screening Programme Definition: The outcome following an examination by an ophthalmologist. Subcode Sub-value 01 Fundus Photography A 6 Months Rescreen B 12 Months 02 Slit Lamp Rescreen A 6 Months B 12 Months 03 Continued Ophthalmology Review Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 29
30 14.3 Ophthalmic Exam Recommendation Definition: Type of treatment recommended following ophthalmic exam. 01 Pan Retinal Photocoagulation (PRP) 02 Macular Grid 03 Macula Focal 04 VitreoRetinal (VR) Surgery 98 Other Related data item: Ophthalmic Exam Recommendation Accepted Recording guidance: Where 98 Other is recorded, systems may be configured to include a text box to allow specification of the Ophthalmic Exam Recommendation Ophthalmic Exam Recommendation Accepted Definition: Records whether or not the type of treatment recommended following an ophthalmic exam is accepted. 00 No 01 Yes Related data item: Ophthalmic Exam Recommendation Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 30
31 15. Date Date Table Data Item Definition Format & Field Length Date The day, month, year and century, or truncated combination of these elements, of an event. 10 characters (CCYY- MM-DD, CCYY-MM or CCYY) Note: The above data item has already been approved and is available in the Health & Social Care Data Dictionary. Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 31
32 Appendix 1 - Membership of the Diabetes Retinopathy Dataset Clinical Working Group Nicola O Keefe(chair) Angela Ellingford David Cromie Fiona Heggie Ginny Shapter Lorraine Cowie Michael Craig Ross Paterson Ruby Sloan Sam Philip Richmond Davies Dieter Arnold Gillian Cameron Hans-Dieter Schuell Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 32
33 Appendix 2 - Consultation Distribution List Diabetes Managed Clinical Networks (Scotland) NCDDP Stakeholders Centre for Change & Innovation (CCI) Clinical ehealth Leads Health & Social Care Information Centre, Datasets Development Programme (England) Improving Mental Health Information Programme Information Services Division, NSS Information Standards Group NHS Quality Improvement Scotland Royal College of General Practitioners (Scotland) Royal College of Nursing (Scotland) Royal College of Physicians Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons Glasgow Royal College of Physicians, London Royal College of Surgeons Scottish Care Information (SCI) Scottish Clinical Information Management Practice (SCIMP) Scottish Executive Data Standards Branch Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network Scottish Executive Health Department NCDDP Diabetes Clinical Working Groups Diabetes Core Diabetes Secondary Care Extension Diabetes Paediatric Extension Diabetes Specialist Nursing Extension Diabetes Dietetics Extension Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Diabetes Foot Care Extension Diabetes Retinopathy Extension Dataset 33
Central Mersey Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme. Referring patients for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
 Central Mersey Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme Referring patients for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Information for GPs in Halton & St Helens, Knowsley and Warrington PCT Version: June 2008 Review
Central Mersey Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme Referring patients for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Information for GPs in Halton & St Helens, Knowsley and Warrington PCT Version: June 2008 Review
Sponsored by. Shared care and referral pathways. Part 2: diabetes screening leading from the front
 CET CONTINUING Sponsored by 1 CET POINT Shared care and referral pathways Part 2: diabetes screening leading from the front Chris Steele, BSc (Hons), FCOptom, DCLP, DipOC, DipTp(IP), FBCLA The alarming
CET CONTINUING Sponsored by 1 CET POINT Shared care and referral pathways Part 2: diabetes screening leading from the front Chris Steele, BSc (Hons), FCOptom, DCLP, DipOC, DipTp(IP), FBCLA The alarming
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong. Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong
 Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong Co-Investigators Prof. David Wong Prof. Sarah McGhee Dr. Wico
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong Co-Investigators Prof. David Wong Prof. Sarah McGhee Dr. Wico
POSITION STATEMENT. Diabetic eye screening April Key points
 POSITION STATEMENT Title Date Diabetic eye screening April 2013 Key points Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of sight loss in the working age population (1) All people with any type of diabetes
POSITION STATEMENT Title Date Diabetic eye screening April 2013 Key points Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of sight loss in the working age population (1) All people with any type of diabetes
SCOTTISH DIABETIC RETINOPATHY SCREENING PROGRAMME. Follow up Protocol
 Follow up Protocol Version Authorised by Date of Issue 1.0 Reviewers: working groups: Clinicians Group Board Coordinators Group Service Managers Group Executive 2 nd April 2007 1.1 Changes: Section 2.
Follow up Protocol Version Authorised by Date of Issue 1.0 Reviewers: working groups: Clinicians Group Board Coordinators Group Service Managers Group Executive 2 nd April 2007 1.1 Changes: Section 2.
National Diabetes Retinal Screening Grading System and Referral Guidelines
 National Diabetes Retinal Screening Grading System and Referral Guidelines 2006 Citation: Ministry of Health. 2006. National Diabetes Retinal Screening Grading System and Referral Guidelines 2006. Wellington:
National Diabetes Retinal Screening Grading System and Referral Guidelines 2006 Citation: Ministry of Health. 2006. National Diabetes Retinal Screening Grading System and Referral Guidelines 2006. Wellington:
RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy #
 RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy # Patient Presents a. Screen for Diabetic Retinopathy every 2 years b. Begin screening at diagnosis of Diabetes * Clinical Modifi ers Yearly
RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy # Patient Presents a. Screen for Diabetic Retinopathy every 2 years b. Begin screening at diagnosis of Diabetes * Clinical Modifi ers Yearly
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City
 Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
Longitudinal study of a cohort of people with diabetes screened by the Exeter Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme
 (2002) 16, 140 145 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1470-269X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Longitudinal study of a cohort of people with diabetes screened by the Exeter Diabetic
(2002) 16, 140 145 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1470-269X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Longitudinal study of a cohort of people with diabetes screened by the Exeter Diabetic
Annual Report. Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Service (Croydon Diabetic Eye Screening Programme)
 Annual Report Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Service (Croydon Diabetic Eye Screening Programme) 1 st June 2010 30 th November 2011 1 Content Page i Chairs Message 3 1.0 Mission Statement, Aims and Objectives
Annual Report Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Service (Croydon Diabetic Eye Screening Programme) 1 st June 2010 30 th November 2011 1 Content Page i Chairs Message 3 1.0 Mission Statement, Aims and Objectives
Preparing for laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy and maculopathy
 Preparing for laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy and maculopathy Information for patients Preparing for laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy and maculopathy. This leaflet sets out to answer the
Preparing for laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy and maculopathy Information for patients Preparing for laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy and maculopathy. This leaflet sets out to answer the
FREQUENCY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL USING DIGITAL RETINAL IMAGING TECHNOLOGY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE FREQUENCY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL USING DIGITAL RETINAL IMAGING TECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION As more and more people are being affected with diabetes and with poor
ORIGINAL ARTICLE FREQUENCY OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL USING DIGITAL RETINAL IMAGING TECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION As more and more people are being affected with diabetes and with poor
FRANZCO, MD, MBBS. Royal Darwin Hospital
 Diabetes and Eye By Dr. Nishantha Wijesinghe FRANZCO, MD, MBBS Consultant Ophthalmologist Royal Darwin Hospital 98% of Diabetics do not need to suffer from severe visual loss Yet Diabetic eye disease is
Diabetes and Eye By Dr. Nishantha Wijesinghe FRANZCO, MD, MBBS Consultant Ophthalmologist Royal Darwin Hospital 98% of Diabetics do not need to suffer from severe visual loss Yet Diabetic eye disease is
Diabetic Retinopathy. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012
 Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
 THE UK GUIDE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY Everything you need to know about diabetic retinopathy Jaheed Khan BSc (Hons) MBBS MD FRCOphth Fellow of the Royal College of Ophthalmologists Association for Research
THE UK GUIDE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY Everything you need to know about diabetic retinopathy Jaheed Khan BSc (Hons) MBBS MD FRCOphth Fellow of the Royal College of Ophthalmologists Association for Research
The College of Optometrists - Learning outcomes for the Professional Certificate in Medical Retina
 Learning outcomes for the Professional Certificate in Medical Retina, incorporating diabetic retinopathy screening and age related macular degeneration The professional certificate is a prerequisite to
Learning outcomes for the Professional Certificate in Medical Retina, incorporating diabetic retinopathy screening and age related macular degeneration The professional certificate is a prerequisite to
D iabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in
 920 EXTENDED REPORT Effect of mydriasis and different field strategies on digital image screening of diabetic eye disease H Murgatroyd, A Ellingford, A Cox, M Binnie, J D Ellis, C J MacEwen, G P Leese...
920 EXTENDED REPORT Effect of mydriasis and different field strategies on digital image screening of diabetic eye disease H Murgatroyd, A Ellingford, A Cox, M Binnie, J D Ellis, C J MacEwen, G P Leese...
Diabetic Eye Screening
 Diabetic Eye Screening Lorraine Lockwood Engagement Manager Health Intelligence Classification: Internal / Public 26/10/16 Who we are (EDESP) formed on 1 st April 2016 Who should be screened? All patients
Diabetic Eye Screening Lorraine Lockwood Engagement Manager Health Intelligence Classification: Internal / Public 26/10/16 Who we are (EDESP) formed on 1 st April 2016 Who should be screened? All patients
Diabetic Eye Disease Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs
 + Diabetic Eye Disease Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs Quiz created by CLEARVIEW Training Jane Macnaughton MCOptom & Peter Chapman MCOptom FBDO + CET Accreditation C 19106 2 CET Points
+ Diabetic Eye Disease Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs Quiz created by CLEARVIEW Training Jane Macnaughton MCOptom & Peter Chapman MCOptom FBDO + CET Accreditation C 19106 2 CET Points
Manual. Manual Welsh Eye Care Initiative. A Welsh Eye Care Initiative. Protocol. The Assessment and Management of Age-related Macular Degeneration
 A Protocol 1.0 Definitions The following terms are important in this text: Wet Macular Degeneration Condition caused by the growth of abnormal blood vessels under the retina. Symptoms appear suddenly and
A Protocol 1.0 Definitions The following terms are important in this text: Wet Macular Degeneration Condition caused by the growth of abnormal blood vessels under the retina. Symptoms appear suddenly and
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
 DIABETIC RETINOPATHY C. L. B. Canny, MD FRCSC Diabetic retinopathy is the most serious eye manifestation of diabetes and is responsible for most of the blindness caused by diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY C. L. B. Canny, MD FRCSC Diabetic retinopathy is the most serious eye manifestation of diabetes and is responsible for most of the blindness caused by diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy
A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies
 Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Ophthalmology Retinal Imaging Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: OPXRET_D.XPT December 2008 NHANES 2005 2006 Data Documentation Exam Component:
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Ophthalmology Retinal Imaging Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: OPXRET_D.XPT December 2008 NHANES 2005 2006 Data Documentation Exam Component:
Amber Priority. Image Library
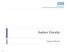 Amber Priority Image Library Amber flag Diabetic Maculopathy (M1) Pre-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (R2) Old, treated and now inactive DR (R1/M0/P1or R0/M0/P1) Where only partial or incomplete images
Amber Priority Image Library Amber flag Diabetic Maculopathy (M1) Pre-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (R2) Old, treated and now inactive DR (R1/M0/P1or R0/M0/P1) Where only partial or incomplete images
Statement of Originality This Clinical Audit Project is my own original work and has not been submitted elsewhere in fulfilment of this or any other
 Paper 6 The Role of OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) within the Diabetic Retinal Screening Service in identifying referable Diabetic Macular Oedema and looking at correlation for Ethnicity, Postcode,
Paper 6 The Role of OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) within the Diabetic Retinal Screening Service in identifying referable Diabetic Macular Oedema and looking at correlation for Ethnicity, Postcode,
SCREENING PROTOCOL. September 2018
 SCREENING PROTOCOL September 2018 Please note that adherence to this protocol forms part of the contractual arrangement between providers and the programme. Failure to comply with the protocol constitutes
SCREENING PROTOCOL September 2018 Please note that adherence to this protocol forms part of the contractual arrangement between providers and the programme. Failure to comply with the protocol constitutes
From Programme Development Grant to Programme Grant
 From Programme Development Grant to Programme Grant Example of the ISDR programme Professor Simon Harding & Ms Katharine Abba Department of Eye and Vision Science University of Liverpool Development Phase
From Programme Development Grant to Programme Grant Example of the ISDR programme Professor Simon Harding & Ms Katharine Abba Department of Eye and Vision Science University of Liverpool Development Phase
The Human Eye. Cornea Iris. Pupil. Lens. Retina
 The Retina Thin layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (the film of the camera). Light rays are focused on the retina then transmitted to the brain. The macula is the very small area in
The Retina Thin layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (the film of the camera). Light rays are focused on the retina then transmitted to the brain. The macula is the very small area in
Diabetes and Eye Health more than meets the eye Vision Initiative - in association with PSA
 Diabetes and Eye Health more than meets the eye Vision Initiative - in association with PSA Vision 2020 Australia Vision Initiative RANZCO & OAA (Vic) Proud members of Vision 2020 Australia Outline Vision
Diabetes and Eye Health more than meets the eye Vision Initiative - in association with PSA Vision 2020 Australia Vision Initiative RANZCO & OAA (Vic) Proud members of Vision 2020 Australia Outline Vision
amendments to the NHS (General Ophthalmic Services) (Scotland) Regulations 2006 ( the 2006 Regulations ); and
 NHS: PCA(O)(2014)1 Health and Social Care Integration Directorate Primary Care Division Dear Colleague GENERAL OPHTHALMIC SERVICES 1. THE NHS (GENERAL OPHTHALMIC SERVICES) (SCOTLAND) AMENDMENT REGULATIONS
NHS: PCA(O)(2014)1 Health and Social Care Integration Directorate Primary Care Division Dear Colleague GENERAL OPHTHALMIC SERVICES 1. THE NHS (GENERAL OPHTHALMIC SERVICES) (SCOTLAND) AMENDMENT REGULATIONS
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY
 PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
NHS Diabetic Eye Screening Programme
 NHS Diabetic Eye Screening Programme Slit lamp examination Public Health England leads the NHS Screening Programmes Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet is for people who need to be examined for diabetic
NHS Diabetic Eye Screening Programme Slit lamp examination Public Health England leads the NHS Screening Programmes Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet is for people who need to be examined for diabetic
SCOTTISH DIABETIC RETINOPATHY SCREENING SERVICE
 SCOTTISH DIABETIC RETINOPATHY SCREENING SERVICE TRAINING & ACCREDITATION STANDARDS FOR SLIT LAMP EXAMINERS WORKING WITHIN THE SCOTTISH DIABETIC RETINOPATHY SCREENING PROGRAMME Version 1.0 Reviewed by:
SCOTTISH DIABETIC RETINOPATHY SCREENING SERVICE TRAINING & ACCREDITATION STANDARDS FOR SLIT LAMP EXAMINERS WORKING WITHIN THE SCOTTISH DIABETIC RETINOPATHY SCREENING PROGRAMME Version 1.0 Reviewed by:
DR Screening In Singapore: Achievements & Future Challenges
 DR Screening In Singapore: Achievements & Future Challenges Ecosse Lamoureux Director, Population Research Platform Singapore Eye Research Institute (SERI) Background About 600,000 of Singaporeans aged
DR Screening In Singapore: Achievements & Future Challenges Ecosse Lamoureux Director, Population Research Platform Singapore Eye Research Institute (SERI) Background About 600,000 of Singaporeans aged
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME)
 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Overview This presentation covers the following topics: Definitions Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy Evidence for public health approaches Screening for diabetic retinopathy Health
Diabetic Retinopathy Overview This presentation covers the following topics: Definitions Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy Evidence for public health approaches Screening for diabetic retinopathy Health
abcdefghijklmnopqrstu
 NHS: PCA(O)(2010)1 Primary and Community Care Directorate Primary Care Division abcdefghijklmnopqrstu Dear Colleague GENERAL OPHTHALMIC SERVICES 1. THE NHS (GENERAL OPHTHALMIC SERVICES) (SCOTLAND) AMENDMENT
NHS: PCA(O)(2010)1 Primary and Community Care Directorate Primary Care Division abcdefghijklmnopqrstu Dear Colleague GENERAL OPHTHALMIC SERVICES 1. THE NHS (GENERAL OPHTHALMIC SERVICES) (SCOTLAND) AMENDMENT
INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
Outline. Preventing & Treating Diabetes Related Blindness. Eye Care Center Doctors. Justin Kanoff, MD. Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado
 Outline Preventing & Treating Diabetes Related Blindness Justin Kanoff, MD Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado 303 974 4302 Introduction to Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado How the eye works Eye problems
Outline Preventing & Treating Diabetes Related Blindness Justin Kanoff, MD Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado 303 974 4302 Introduction to Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado How the eye works Eye problems
Automated grading for diabetic retinopathy: a large-scale audit using arbitration by clinical experts
 Automated grading for diabetic retinopathy: a large-scale audit using arbitration by clinical experts Alan D Fleming, Keith A Goatman, Sam Philip, Gordon J Prescott, Peter F Sharp, John A Olson To cite
Automated grading for diabetic retinopathy: a large-scale audit using arbitration by clinical experts Alan D Fleming, Keith A Goatman, Sam Philip, Gordon J Prescott, Peter F Sharp, John A Olson To cite
 measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
7.1 Grading Diabetic Retinopathy
 Chapter 7 DIABETIC RETINOPATHYGRADING -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- A consistent approach to the
Chapter 7 DIABETIC RETINOPATHYGRADING -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- A consistent approach to the
Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy. Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP
 Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP Content OCT imaging Retinal layers OCT features in Diabetes Some NON DR features
Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP Content OCT imaging Retinal layers OCT features in Diabetes Some NON DR features
Diabetes & Your Eyes
 Diabetes & Your Eyes Diabetes is a disease that occurs when the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin or the body is unable to process it properly. Insulin is the hormone that regulates the level of
Diabetes & Your Eyes Diabetes is a disease that occurs when the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin or the body is unable to process it properly. Insulin is the hormone that regulates the level of
eye conditions related to diabetes
 Understanding eye conditions related to diabetes RCOphth RNIB s Understanding series The Understanding series is designed to help you, your friends and family understand a little bit more about your eye
Understanding eye conditions related to diabetes RCOphth RNIB s Understanding series The Understanding series is designed to help you, your friends and family understand a little bit more about your eye
Cataract Surgery Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives
 NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Cataract Surgery Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives 1. INTRODUCTION AND SCOPE NHS DORSET CLINICAL COMMISSIONING GROUP
NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Cataract Surgery Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives 1. INTRODUCTION AND SCOPE NHS DORSET CLINICAL COMMISSIONING GROUP
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme
 Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme Information for patients As you have diabetes, your GP has arranged for you to attend the Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Service. This service is free and is provided
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme Information for patients As you have diabetes, your GP has arranged for you to attend the Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Service. This service is free and is provided
Medical Retina 2011 Nicholas Lee
 Medical Retina 2011 Nicholas Lee 1 Diabetic Retinopathy Epidemiology 1000 registered blind each year 2% diabetics registered as blind (8% of all Blind Registrations) 42% with Mild Background DR will progress
Medical Retina 2011 Nicholas Lee 1 Diabetic Retinopathy Epidemiology 1000 registered blind each year 2% diabetics registered as blind (8% of all Blind Registrations) 42% with Mild Background DR will progress
Diabetic Management beyond traditional risk factors and LDL-C control: Can we improve macro and microvascular risks?
 Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
Guidance for Optometrists in relation to Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Schemes. June 2004
 Guidance for Optometrists in relation to Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Schemes June 2004 Over the next few years formal screening schemes designed to detect diabetic retinopathy will be introduced across
Guidance for Optometrists in relation to Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Schemes June 2004 Over the next few years formal screening schemes designed to detect diabetic retinopathy will be introduced across
EyePACS Grading System (Part 3): Detecting Proliferative (Neovascular) Diabetic Retinopathy. George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD
 EyePACS Grading System (Part 3): Detecting Proliferative (Neovascular) Diabetic Retinopathy George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina Retinal Arcades Macula Optic
EyePACS Grading System (Part 3): Detecting Proliferative (Neovascular) Diabetic Retinopathy George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina Retinal Arcades Macula Optic
Management of diabetic eye disease: an overview
 Peter Blows Photographic screening for diabetic eye disease can identify patients who will benefit from laser treatment. BOTSWANA MANAGEMENT Management of diabetic eye disease: an overview Laser for DR
Peter Blows Photographic screening for diabetic eye disease can identify patients who will benefit from laser treatment. BOTSWANA MANAGEMENT Management of diabetic eye disease: an overview Laser for DR
Clinical biomicroscopy versus fluorescein angiography: Effectiveness and sensitivity in detecting diabetic retinopathy
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 1, 2007 / pp. 84-88 Clinical biomicroscopy versus fluorescein angiography: Effectiveness and sensitivity in detecting diabetic retinopathy S.S. KHALAF, M.D.
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 1, 2007 / pp. 84-88 Clinical biomicroscopy versus fluorescein angiography: Effectiveness and sensitivity in detecting diabetic retinopathy S.S. KHALAF, M.D.
Diabetic Eye Disease
 Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Medical Retinal Services Information for Patients Diabetic Eye Disease This leaflet sets out to answer some of your questions about diabetic eye disease. You may wish to discuss
Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Medical Retinal Services Information for Patients Diabetic Eye Disease This leaflet sets out to answer some of your questions about diabetic eye disease. You may wish to discuss
Abstract. Introduction. Original paper. Comparison of screening for diabetic retinopathy by non-specialists and specialists
 Comparison of screening for diabetic retinopathy by non-specialists and specialists Effectiveness of screening for diabetic retinopathy by nonspecialist doctors: the importance of physician-ophthalmologist
Comparison of screening for diabetic retinopathy by non-specialists and specialists Effectiveness of screening for diabetic retinopathy by nonspecialist doctors: the importance of physician-ophthalmologist
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Introduction People with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina that is caused by diabetes.
Diabetic Retinopathy Introduction People with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina that is caused by diabetes.
Level 3 Qualifications in Diabetic Retinopathy Screening (7360)
 Level 3 Qualifications in Diabetic Retinopathy Screening (7360) Assignment guide 500/6895/7, 500/6892/1, 500/6891/X, www.cityandguilds.com September 2009 500/6897/0, 500/6896/9 Version 1.0 About City &
Level 3 Qualifications in Diabetic Retinopathy Screening (7360) Assignment guide 500/6895/7, 500/6892/1, 500/6891/X, www.cityandguilds.com September 2009 500/6897/0, 500/6896/9 Version 1.0 About City &
Treatment of Diabetic Macular Oedema by Intravitreal Injection with Ranibizumab (Lucentis)
 Information for Patients Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Medical Retina Services Treatment of Diabetic Macular Oedema by Intravitreal Injection with Ranibizumab (Lucentis) Eye problems are common in people
Information for Patients Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Medical Retina Services Treatment of Diabetic Macular Oedema by Intravitreal Injection with Ranibizumab (Lucentis) Eye problems are common in people
Diabetic Retinopathy WHAT IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? WHAT CAUSES DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? WHAT ARE THE STAGES OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY?
 Diabetic Retinopathy WHAT IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? Diabetic retinopathy affects 8 million Americans with diabetes. A leading cause of blindness in American adults, it is caused by damage to the small blood
Diabetic Retinopathy WHAT IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? Diabetic retinopathy affects 8 million Americans with diabetes. A leading cause of blindness in American adults, it is caused by damage to the small blood
Epilepsy Data Standards
 For reference only Do Not Use For more information contact: cdsis@nhs.net Epilepsy Data Standards September 2006 National Clinical Dataset Development Programme (NCDDP) Support Team Information Services
For reference only Do Not Use For more information contact: cdsis@nhs.net Epilepsy Data Standards September 2006 National Clinical Dataset Development Programme (NCDDP) Support Team Information Services
Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO Cedar Springs Eye Clinic
 Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO Cedar Springs Eye Clinic 25.6 million adults 11.3% of the adult population 10.9 million adults 65 years and older 26.9% of this age population 79 million people are Pre-diabetic!!
Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO Cedar Springs Eye Clinic 25.6 million adults 11.3% of the adult population 10.9 million adults 65 years and older 26.9% of this age population 79 million people are Pre-diabetic!!
Dear Colleague GENERAL OPHTHALMIC SERVICES OPTOMETRY INDEPENDENT PRESCRIBING. Summary
 NHS: PCA(O)(2013)4 Health and Social Care Integration Directorate Primary Care Division Dear Colleague GENERAL OPHTHALMIC SERVICES OPTOMETRY INDEPENDENT PRESCRIBING Summary 1. This letter advises NHS Boards
NHS: PCA(O)(2013)4 Health and Social Care Integration Directorate Primary Care Division Dear Colleague GENERAL OPHTHALMIC SERVICES OPTOMETRY INDEPENDENT PRESCRIBING Summary 1. This letter advises NHS Boards
Diabetic retinopathy is a SPOTLIGHT ON RETINAL SCREENING MEDICINE DIGEST
 SPOTLIGHT ON PHOTO: NCL DESP AT NMUH NHS TRUST Diabetic retinopathy is no longer the leading cause of blindness among people of working age thanks, at least in part, to retinal screening. But there are
SPOTLIGHT ON PHOTO: NCL DESP AT NMUH NHS TRUST Diabetic retinopathy is no longer the leading cause of blindness among people of working age thanks, at least in part, to retinal screening. But there are
Grading Diabetic Retinopathy R2 - dots, blots and multiple headaches!
 Grading Diabetic Retinopathy R2 - dots, blots and multiple headaches! Simon Harding FRCOphth FRCS MD Professor of Clinical Ophthalmology University of Liverpool BARS 2010 Manchester English National Grading
Grading Diabetic Retinopathy R2 - dots, blots and multiple headaches! Simon Harding FRCOphth FRCS MD Professor of Clinical Ophthalmology University of Liverpool BARS 2010 Manchester English National Grading
Use of eye care services by people with diabetes: the Melbourne Visual Impairment Project
 410 Department of Ophthalmology, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia C A McCarty C W Lloyd-Smith P M Livingston Y L Stanislavsky H R Taylor Victorian WorkCover Authority, Melbourne, Australia
410 Department of Ophthalmology, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia C A McCarty C W Lloyd-Smith P M Livingston Y L Stanislavsky H R Taylor Victorian WorkCover Authority, Melbourne, Australia
The Common Clinical Competency Framework for Non-medical Ophthalmic Healthcare Professionals in Secondary Care
 The Common Clinical Competency Framework for Non-medical Ophthalmic Healthcare Professionals in Secondary Care Medical Retina November 2016 Association of Health Professions in Ophthalmology General basic
The Common Clinical Competency Framework for Non-medical Ophthalmic Healthcare Professionals in Secondary Care Medical Retina November 2016 Association of Health Professions in Ophthalmology General basic
Population base eye screening in Scotland. Challenges of equity and coverage. Graham Leese University of Dundee
 Population base eye screening in Scotland. Challenges of equity and coverage Graham Leese University of Dundee Edinburgh July 16 th 2018 NUMBER OF PATIENTS RECEIVING LASER IN TAYSIDE 300 250 200 Number
Population base eye screening in Scotland. Challenges of equity and coverage Graham Leese University of Dundee Edinburgh July 16 th 2018 NUMBER OF PATIENTS RECEIVING LASER IN TAYSIDE 300 250 200 Number
Annual Report. Public Health Screening Programmes TO 31 MARCH Extract: Chapter 8 : Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
 Public Health Screening Programmes Annual Report TO 31 MARCH 2007 Extract: Chapter 8 : Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Version 1.0 Published: 18 December 2007 1 Contents INTRODUCTION...3 SUMMARY...5 CHAPTER
Public Health Screening Programmes Annual Report TO 31 MARCH 2007 Extract: Chapter 8 : Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Version 1.0 Published: 18 December 2007 1 Contents INTRODUCTION...3 SUMMARY...5 CHAPTER
Retinal Telescreening for Diabetic Retinopathy
 Retinal Telescreening for Diabetic Retinopathy Policy Number: 9.03.13 Last Review: 7/2014 Origination: 7/2008 Next Review: 7/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide
Retinal Telescreening for Diabetic Retinopathy Policy Number: 9.03.13 Last Review: 7/2014 Origination: 7/2008 Next Review: 7/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide
OUR EYES & HOW WE SEE
 OUR EYES & HOW WE SEE UNDERSTAND MORE ABOUT OUR EYES & HOW WE SEE Our Eyes & How We See The eye is our visual gateway to the world. Within it, an array of delicate components labour away to give us the
OUR EYES & HOW WE SEE UNDERSTAND MORE ABOUT OUR EYES & HOW WE SEE Our Eyes & How We See The eye is our visual gateway to the world. Within it, an array of delicate components labour away to give us the
Eye screening for patients taking hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil )
 Eye screening for patients taking hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil ) This leaflet contains important information for people taking hydroxychloroquine. This leaflet is available on audio CD. No one need face
Eye screening for patients taking hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil ) This leaflet contains important information for people taking hydroxychloroquine. This leaflet is available on audio CD. No one need face
One-Field of View vs. Two-Fields of View; Is a Macula Centered Photograph Adequate for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening? -
 International Journal of Ophthalmology & Vision Research Research Article One-Field of View vs. Two-Fields of View; Is a Macula Centered Photograph Adequate for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening? - Mirriam
International Journal of Ophthalmology & Vision Research Research Article One-Field of View vs. Two-Fields of View; Is a Macula Centered Photograph Adequate for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening? - Mirriam
Eye screening for patients taking hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil )
 Eye screening for patients taking hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil ) Support throughout central vision loss This leaflet contains important information about eye health checks for people taking hydroxychloroquine.
Eye screening for patients taking hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil ) Support throughout central vision loss This leaflet contains important information about eye health checks for people taking hydroxychloroquine.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy
 Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy What Is Diabetic Retinopathy? Diabetes damages blood vessels in the rear of the eye. This condition is called diabetic retinopathy. It can lead to vision loss or blindness.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy What Is Diabetic Retinopathy? Diabetes damages blood vessels in the rear of the eye. This condition is called diabetic retinopathy. It can lead to vision loss or blindness.
X-Plain Diabetic Retinopathy Reference Summary
 X-Plain Diabetic Retinopathy Reference Summary Introduction Patients with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina
X-Plain Diabetic Retinopathy Reference Summary Introduction Patients with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina
The Future of Optometric Services in Primary Care in Wales
 IMPROVING HEALTH IN WALES The Future of Optometric Services in Primary Care in Wales a consultation document ISBN 0 7504 2968 2 Designed by CartoGraphic Services G/254/02-03 September 2002 INA - 15-02
IMPROVING HEALTH IN WALES The Future of Optometric Services in Primary Care in Wales a consultation document ISBN 0 7504 2968 2 Designed by CartoGraphic Services G/254/02-03 September 2002 INA - 15-02
Subclinical Diabetic Macular Edema Study
 Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Subclinical Diabetic Macular Edema Study Version 2.0 March 21, 2006 Subclinical DME Protocol v2 0 3-21-06.doc Table of Contents Chapter 1. Background Information
Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Subclinical Diabetic Macular Edema Study Version 2.0 March 21, 2006 Subclinical DME Protocol v2 0 3-21-06.doc Table of Contents Chapter 1. Background Information
In all cases, a doctor will explain the procedure to you and answer any questions you may have.
 Vitrectomy surgery Information for patients This leaflet answers common questions about having vitrectomy surgery. If you would like further information, or have any particular worries, please do not hesitate
Vitrectomy surgery Information for patients This leaflet answers common questions about having vitrectomy surgery. If you would like further information, or have any particular worries, please do not hesitate
e Scottish Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme
 e Scottish Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme the Version 1.1 Reviewers: DRS Collaborative working groups: Clinicians Group Board Coordinators Group DRS Executivee Authorised by Dr C Styles Lead
e Scottish Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme the Version 1.1 Reviewers: DRS Collaborative working groups: Clinicians Group Board Coordinators Group DRS Executivee Authorised by Dr C Styles Lead
SWINDON PCT CATARACT DIRECT REFERRAL SCHEME SERVICE LEVEL AGREEMENT
 SWINDON PCT CATARACT DIRECT REFERRAL SCHEME SERVICE LEVEL AGREEMENT PROTOCOL This document sets out the details of the administrative protocol for the direct referral by Optometrists/OMPs of cataract patients.
SWINDON PCT CATARACT DIRECT REFERRAL SCHEME SERVICE LEVEL AGREEMENT PROTOCOL This document sets out the details of the administrative protocol for the direct referral by Optometrists/OMPs of cataract patients.
Mobile Teleophthalmology. Primary care and Screening Model
 Mobile Teleophthalmology Primary care and Screening Model SNTOP MOBILE UNIT SNTOP MOBILE UNIT Mobile Teleophthalmology PRIMARY CARE MODEL ! Primary Care " It is a mobile unit with all latest equipments
Mobile Teleophthalmology Primary care and Screening Model SNTOP MOBILE UNIT SNTOP MOBILE UNIT Mobile Teleophthalmology PRIMARY CARE MODEL ! Primary Care " It is a mobile unit with all latest equipments
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes mellitus is one of the leading causes of irreversible blindness worldwide. In the United States, it is the most common cause of blindness in people younger than 65 years.
Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes mellitus is one of the leading causes of irreversible blindness worldwide. In the United States, it is the most common cause of blindness in people younger than 65 years.
Developed by Marion Wood and Children s Dental Needs Steering Group
 Title Document Type Issue no DNA Policy Policy Clinical Governance Support Team Use Issue date 30.05.13 Review date 30.05.15 Distribution Prepared by Dental Staff Marion Wood Developed by Marion Wood and
Title Document Type Issue no DNA Policy Policy Clinical Governance Support Team Use Issue date 30.05.13 Review date 30.05.15 Distribution Prepared by Dental Staff Marion Wood Developed by Marion Wood and
PLEASE COMPLETE ALL RELEVANT SECTIONS OF THIS FORM
 APPLICATION FOR INCLUSION IN THE DENTAL LIST OF THE HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE BOARD PLEASE COMPLETE ALL RELEVANT SECTIONS OF THIS FORM Return the completed form to the Health and Social Care Board local office
APPLICATION FOR INCLUSION IN THE DENTAL LIST OF THE HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE BOARD PLEASE COMPLETE ALL RELEVANT SECTIONS OF THIS FORM Return the completed form to the Health and Social Care Board local office
Level 3 Qualifications in Diabetic Retinopathy Screening (7360)
 Level 3 Qualifications in Diabetic Retinopathy Screening (7360) Qualification handbook for centres 500/6895/7, 500/6892/1, 500/6891/X, 500/6897/0, 500/6896/9 www.cityandguilds.com September 2009 Version
Level 3 Qualifications in Diabetic Retinopathy Screening (7360) Qualification handbook for centres 500/6895/7, 500/6892/1, 500/6891/X, 500/6897/0, 500/6896/9 www.cityandguilds.com September 2009 Version
Brampton Hurontario Street Brampton, ON L6Y 0P6
 Diabetic Retinopathy What is Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness world-wide. Diabetes damages blood vessels in many organs of the body including the eyes.
Diabetic Retinopathy What is Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness world-wide. Diabetes damages blood vessels in many organs of the body including the eyes.
Diabetic retinopathy damage to the blood vessels in the retina. Cataract clouding of the eye s lens. Cataracts develop at an earlier age in people
 Diabetic Retinopathy What is diabetic eye disease? Diabetic eye disease refers to a group of eye problems that people with diabetes may face as a complication of diabetes. All can cause severe vision loss
Diabetic Retinopathy What is diabetic eye disease? Diabetic eye disease refers to a group of eye problems that people with diabetes may face as a complication of diabetes. All can cause severe vision loss
Retinal Screening, Seeing Sense! Dinesh Nagi MBBS, PhD, FRCP Clinical Director Division of Medicine Mid- Yorkshire NHS Trust, Wakefield
 Retinal Screening, Seeing Sense! Dinesh Nagi MBBS, PhD, FRCP Clinical Director Division of Medicine Mid- Yorkshire NHS Trust, Wakefield York Race Course 11 th Nov 2014 Presentation Importance of regular
Retinal Screening, Seeing Sense! Dinesh Nagi MBBS, PhD, FRCP Clinical Director Division of Medicine Mid- Yorkshire NHS Trust, Wakefield York Race Course 11 th Nov 2014 Presentation Importance of regular
Treatment of wet macular degeneration by intravitreal injection with Ranibizumab (Lucentis) or Aflibercept (Eylea): Information and consent
 Patient information Treatment of wet macular degeneration by intravitreal injection with Ranibizumab (Lucentis) or Aflibercept (Eylea): Information and consent Introduction You have an eye condition called
Patient information Treatment of wet macular degeneration by intravitreal injection with Ranibizumab (Lucentis) or Aflibercept (Eylea): Information and consent Introduction You have an eye condition called
Five Things You re Missing with Your Fundus Camera
 ebook Five Things You re Missing with Your Fundus Camera By Donald J. Siegel, OD, Sun City West Eye Care Sponsored by: Before I began incorporating EIDON true-color imaging into my practice, my retinal
ebook Five Things You re Missing with Your Fundus Camera By Donald J. Siegel, OD, Sun City West Eye Care Sponsored by: Before I began incorporating EIDON true-color imaging into my practice, my retinal
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction
 Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Macular hole. Information for patients Ophthalmology (Vitreal Retina) Large Print
 Macular hole Information for patients Ophthalmology (Vitreal Retina) Large Print page 2 of 16 What is the macula? The back of the eye has a light-sensitive lining called the retina, similar to the film
Macular hole Information for patients Ophthalmology (Vitreal Retina) Large Print page 2 of 16 What is the macula? The back of the eye has a light-sensitive lining called the retina, similar to the film
OAKLEIGH EYE CENTRE. THE EYE Before looking at diabetic retinopathy it is important to understand what the healthy eye looks like and how it works.
 ABN: 80 836 359 971 Dr Mark Steiner 345 799X 135 Warrigal Road Dr Helen Steiner 292 419A OAKLEIGH VIC 3166 Tel: 03 9568 7706 Fax: 03 9568 4498 E-Mail: oakeye13@bigpond.com DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DIABETES
ABN: 80 836 359 971 Dr Mark Steiner 345 799X 135 Warrigal Road Dr Helen Steiner 292 419A OAKLEIGH VIC 3166 Tel: 03 9568 7706 Fax: 03 9568 4498 E-Mail: oakeye13@bigpond.com DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DIABETES
LOCSU Community Services. Glaucoma Repeat Readings & OHT Monitoring Community Service Pathway. Issued by Local Optical Committee Support Unit May 2009
 LOCSU Community Services Glaucoma Repeat Readings & OHT Monitoring Community Service Pathway Issued by Local Optical Committee Support Unit May 2009 [Revised November 2013] Contents Page Executive Summary...
LOCSU Community Services Glaucoma Repeat Readings & OHT Monitoring Community Service Pathway Issued by Local Optical Committee Support Unit May 2009 [Revised November 2013] Contents Page Executive Summary...
GENERAL INFORMATION DIABETIC EYE DISEASE
 GENERAL INFORMATION DIABETIC EYE DISEASE WHAT IS DIABETIC EYE DISEASE? Diabetic eye disease is a term used to describe the common eye complications seen in people with diabetes. It includes: Diabetic retinopathy
GENERAL INFORMATION DIABETIC EYE DISEASE WHAT IS DIABETIC EYE DISEASE? Diabetic eye disease is a term used to describe the common eye complications seen in people with diabetes. It includes: Diabetic retinopathy
Examining the Eyes. Mr. Nicholas Lee Lead Clinician Consultant Ophthalmologist at Hillingdon and The Western Eye Hospitals
 Examining the Eyes Mr. Nicholas Lee Lead Clinician Consultant Ophthalmologist at Hillingdon and The Western Eye Hospitals Ophthalmology - Eyes Ophthalmology Medical - Busiest outpatient department Glaucoma
Examining the Eyes Mr. Nicholas Lee Lead Clinician Consultant Ophthalmologist at Hillingdon and The Western Eye Hospitals Ophthalmology - Eyes Ophthalmology Medical - Busiest outpatient department Glaucoma
Perspectives on Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy. Dr. Dan Samaha, Optometrist, MSc Clinical Lecturer School of Optometry, Université de Montréal
 Perspectives on Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy 1 Dr. Dan Samaha, Optometrist, MSc Clinical Lecturer School of Optometry, Université de Montréal Current standards 2 According to the Canadian Diabetes
Perspectives on Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy 1 Dr. Dan Samaha, Optometrist, MSc Clinical Lecturer School of Optometry, Université de Montréal Current standards 2 According to the Canadian Diabetes
Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public
 Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public Ray M. Balyeat, MD The Eye Institute Tulsa, Oklahoma The Healthy Eye Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, pupil and lens. These light rays are
Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public Ray M. Balyeat, MD The Eye Institute Tulsa, Oklahoma The Healthy Eye Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, pupil and lens. These light rays are
MAGNITUDE OF DIABETIC EYE DISEASE IN INDIA
 Dear Doctor This booklet contains information about your role as a physician in preventing blindness in your diabetic patients. You are the first point of contact for your diabetic patients. You see them
Dear Doctor This booklet contains information about your role as a physician in preventing blindness in your diabetic patients. You are the first point of contact for your diabetic patients. You see them
MANAGING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY. <Your Hospital Name> <Your Logo>
 MANAGING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY It s difficult living with Diabetes Mellitus. Ask any diabetic... Their lives are centered around meal plans, glucose levels, and insulin
MANAGING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY It s difficult living with Diabetes Mellitus. Ask any diabetic... Their lives are centered around meal plans, glucose levels, and insulin
