5 Homeostasis and response higher (import)
|
|
|
- Archibald Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5 Homeostasis and response higher (import) Name: Class: Date: Time: 53 minutes Marks: 53 marks Comments: Page of 7
2 Describe how the brain is informed of the image detected by the retina (Total 3 marks) 2 A man hurt his head in an accident. Doctors found that he could not remember anything that had happened on the day of the accident. (a) (i) Name the part of the brain concerned with memory. () (ii) Name one method the doctors could use to find out how much the brain was damaged. () (b) The doctors were worried that the man might also have injured his spine. They touched different areas of his skin with a sharp point. They asked him to tell them each time if he could feel the sharp point. Page 2 of 7
3 (i) Explain how the information about the sharp point touching the skin reaches the man s brain. (6) (ii) The doctors found that the man could feel the sharp point when the point touched his arms but not when the point touched his legs. Suggest what this information could tell the doctors about the damage to the man s spinal cord. Explain your answer. (2) (Total 0 marks) 3 In-vitro fertilisation (IVF) is used to help some women get pregnant. (a) Name the two hormones used in IVF treatment (2) Page 3 of 7
4 (b) The diagram shows the process of IVF. Describe the process of IVF. Use information from the diagram to help you. (4) (Total 6 marks) Page 4 of 7
5 4 The internal body temperature determines how much a person sweats. The graph shows the effect of different internal body temperatures on a person s rate of energy loss by sweating. (a) How much more energy was lost from the body each second by sweating when the body temperature was 37.6 C than when it was 36.6 C? Show clearly how you work out your final answer Amount of energy =... joules per second (2) (b) Explain why a person would feel more thirsty when the body temperature was 37.6 C than when it was 36.6 C (2) Page 5 of 7
6 (c) Explain how sweating helps to control body temperature (3) (Total 7 marks) 5 (a) When a seed starts to grow, the young root grows downwards towards gravity. The young shoot grows upwards, away from gravity. (i) Name this type of plant response to gravity. () (ii) Give two reasons why it is useful for a young root to grow towards gravity (2) (iii) The root grows towards gravity due to the unequal distribution of a substance in the root. Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. This substance is auxin. chlorophyll. sugar. () Page 6 of 7
7 (b) The drawings show some apparatus and materials. Page 7 of 7
8 In this question you will be assessed on using good English, organising information clearly and using specialist terms where appropriate. Describe how the students could use some or all of the apparatus and materials shown in the drawings to investigate the growth response of maize seedlings to light shining from one side. You should include a description of the results you would expect. (6) (Total 0 marks) Page 8 of 7
9 6 The number of cases of Type 2 diabetes in the UK is increasing rapidly. (a) Describe how insulin and glucagon help control the blood sugar concentration in a healthy person. (6) (b) What is Type 2 diabetes? () Page 9 of 7
10 (c) Body mass index (BMI) is a person s body weight divided by the square of his or her height. (i) Graph shows the relationship between BMI and the percentage probability of developing Type 2 diabetes. Graph Percentage probability of developing Type 2 diabetes Suggest an explanation for the relationship between BMI and the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. (2) Page 0 of 7
11 (ii) Graph 2 shows changes in the number of new cases of Type 2 diabetes in the UK. Graph 2 Year Suggest explanations for the trend shown by the data in Graph 2. (3) (Total 2 marks) Page of 7
12 7 A dog runs across the road in front of a car. The driver slams her foot on the brakes. (i) Explain how the nervous system brings about this response (4) (ii) Explain why alcohol consumption would affect the driver s response () (Total 5 marks) Page 2 of 7
13 Mark schemes an impulse or electrical signal accept electrical pulse do not credit message in receptor or neurone of retina accept nerve or rod or cone sent along optic nerve do not credit inverts the image [3] 2 (a) (i) cerebral cortex accept cerebrum / cerebral hemisphere (ii) MRI (scan) allow CAT / CT scan do not accept MIR or electrode stimulation allow electrical stimulation (b) (i) sharp point stimulates (pain) receptor (in the skin) must be in correct order to send (nerve) impulse ignore information and messages via sensory neurone Page 3 of 7
14 (ii) to spinal cord do not accept spine, ignore CNS crosses synapse allow synapse in any correct context to other (relay) neurones / to brain do not accept motor neurone allow explanation in a flow diagram damage must be between arms and legs / below arms accept below the waist since information from nerves in arms still reaches the brain / information from the legs doesn t reach the brain [0] 3 (a) (b) FSH / follicle stimulating hormone allow FHS either order LH / luteinizing hormone any four from: egg(s) collected from ovary (eggs) mixed with sperm or fertilisation occurs allow eggs and sperm put into tube fertilised egg divides embryo formed (embryos) inserted into womb / uterus ignore references to vagina FSH matures egg and LH releases eggs 4 [6] Page 4 of 7
15 4 (a) 345 to 350 ignore working or lack of working use of 355 to 360 and 0 for mark 2 (b) any two from: more sweating (at 37.6 C) more at least once in the first 2 points more water loss or dehydration occurs do not accept prevents dehydration only blood becomes (more) concentrated / (more) salty or need to replace water stimulation of the hypothalamus 2 (c) any three from: evaporation of water do not accept just water loss unqualified cools skin or uses heat from skin cools blood / heat from blood (passing through skin) related to sweating cooling the blood ignore vasodilation 3 [7] 5 (a) (i) gravitropism / geotropism not trophism ignore positive or negative (ii) any two from: anchorage takes in water takes in ions / minerals / salts / correct named example allow nutrients do not accept food 2 Page 5 of 7
16 (iii) auxin (b) Marks awarded for this answer will be determined by the Quality of Communication (QC) as well as the standard of the scientific response. Examiners should also refer to the information on page 5, and apply a best-fit approach to the marking. 0 marks No relevant content. Level ( 2 marks) There is a basic description of a simple method involving seedlings and light. Level 2 (3 4 marks) There is a description of a method involving seedlings in -sided light, and a control, with a correct observation. Level 3 (5 6 marks) There is a description of a method involving groups of seedlings in -sided light, and in control conditions. It includes some correct measurements or observations. examples of Biology points made in the response: use of scissors to cut tips from some shoots / cut hole in box use of forceps for handling seedlings use of ruler to measure lengths of shoots at start and at end other factors controlled eg temperature / water use of lamp + box re. one-sided lighting repetitions each treatment 3 times control in total darkness / all-round light time taken = several hours to a few days sample results: tip exposed to -sided light bend to light, tip removed vertical, control vertical 6 [0] 6 (a) (b) any six from: hormone(s) / named produced by pancreas if blood glucose levels are too high, insulin is produced / released allowing glucose to move from the blood into the cells / named eg liver glucose is converted to glycogen if blood glucose levels fall, glucagon is produced / released glycogen is converted to glucose causing glucose to be released into the blood diabetes that occurs when the body (cells) do not respond / are less responsive to insulin 6 Page 6 of 7
17 (c) (i) higher BMIs due to increase in mass / weight (relative to height) / obesity obesity / being overweight / being fat is a (significant) risk factor for Type 2 diabetes allow causes Type 2 diabetes (ii) any three from: related to described change in diet eg fast foods and less exercise which increases the chance of obesity / increases BMI increased awareness has helped to slow the increase 3 [2] 7 (i) eyes as sense organs/detector/receptors in eye, electrical signals (impulses), to co-ordinator, then to leg muscles/effector for mark each 4 (ii) affects the nervous system and slows down the reactions for mark [5] Page 7 of 7
4-5 Homeostasis and response Biology
 4-5 Homeostasis and response Biology.0 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose (sugar) concentration may rise more than normal.. Which organ in the body monitors this rise in blood sugar? Tick one
4-5 Homeostasis and response Biology.0 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose (sugar) concentration may rise more than normal.. Which organ in the body monitors this rise in blood sugar? Tick one
Chapter 10 Human Nervous System
 Chapter 0 Human Nervous System Name: Class: Date: Time: 07 minutes Marks: 07 marks Comments: Page of 35 (a) List A gives the names of four stimuli. List B gives four parts of the human body. Draw a straight
Chapter 0 Human Nervous System Name: Class: Date: Time: 07 minutes Marks: 07 marks Comments: Page of 35 (a) List A gives the names of four stimuli. List B gives four parts of the human body. Draw a straight
Hormones are involved in controlling the menstrual cycle and fertility. (a) (i) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence.
 Hormones are involved in controlling the menstrual cycle and fertility. (a) (i) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. auxin follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) thalidomide A hormone
Hormones are involved in controlling the menstrual cycle and fertility. (a) (i) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. auxin follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) thalidomide A hormone
4-5 Homeostasis and response Trilogy
 4-5 Homeostasis and response Trilogy.0 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose (sugar) concentration may rise more than normal.. Which organ in the body monitors this rise in blood sugar? Tick one
4-5 Homeostasis and response Trilogy.0 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose (sugar) concentration may rise more than normal.. Which organ in the body monitors this rise in blood sugar? Tick one
A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. the response each type of effector makes.
 This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin. (2) (b) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. (i) There are two
This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin. (2) (b) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. (i) There are two
Y11 Homeostasis & Response
 Key words: 1. Homeostasis: Maintaining a constant internal environment 2. Receptor: Detects a change in the environment 3. Effector: Muscle or gland that carries out a response 4. Stimulus: A change in
Key words: 1. Homeostasis: Maintaining a constant internal environment 2. Receptor: Detects a change in the environment 3. Effector: Muscle or gland that carries out a response 4. Stimulus: A change in
Describe fully how the structures shown in the diagram bring about this reflex action (6)
 Q. A person accidentally touches a hot pan. Her hand automatically moves away from the pan. The diagram shows the structures involved in this action. (a) Describe fully how the structures shown in the
Q. A person accidentally touches a hot pan. Her hand automatically moves away from the pan. The diagram shows the structures involved in this action. (a) Describe fully how the structures shown in the
Y11 Homeostasis & Response
 Key words: 1. Homeostasis: Maintaining a constant internal environment 2. Receptor: Detect a change in the environment 3. Effector: Muscle or gland that carries out a response 4. Stimulus: A change in
Key words: 1. Homeostasis: Maintaining a constant internal environment 2. Receptor: Detect a change in the environment 3. Effector: Muscle or gland that carries out a response 4. Stimulus: A change in
spinal cord P finger Q What is the sequence of nerve cells through which an impulse passes during a reflex action?
 1 The diagram represents a simple reflex arc. spinal cord P R pin finger Q muscle What is the sequence of nerve cells through which an impulse passes during a reflex action? PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 2 The
1 The diagram represents a simple reflex arc. spinal cord P R pin finger Q muscle What is the sequence of nerve cells through which an impulse passes during a reflex action? PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 2 The
B5 Quick Revision Questions
 B5 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 Why does body temperature need to be kept constant? Answer 1... of 50 Enzyme action Cellular functions Question
B5 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 Why does body temperature need to be kept constant? Answer 1... of 50 Enzyme action Cellular functions Question
M1. (a) pupils dilated (at B) allow converse for A 1. in dim light / low light levels 1. because circular muscles (in iris) relax 1
 M. (a) pupils dilated (at B) allow converse for A in dim light / low light levels because circular muscles (in iris) relax (and) radial muscles contract (b) figure 2 shows myopia where light does not focus
M. (a) pupils dilated (at B) allow converse for A in dim light / low light levels because circular muscles (in iris) relax (and) radial muscles contract (b) figure 2 shows myopia where light does not focus
Homeostasis. Mark Scheme 1. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Level GCSE (9-1) Exam Board 4.5 Homeostasis and Response. Booklet Mark Scheme 1
 Homeostasis Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.5 Homeostasis and Response Sub-Topic Homeostasis Difficulty Level Silver Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 60 minutes
Homeostasis Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.5 Homeostasis and Response Sub-Topic Homeostasis Difficulty Level Silver Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 60 minutes
1. The diagram below represents the homeostatic control of body temperature. What does the part labelled X represent? D. Hypothalamus (Total 1 mark)
 1. The diagram below represents the homeostatic control of body temperature. What does the part labelled X represent? A. Heart B. Kidney C. Pituitary D. Hypothalamus 2. What is the sequence of operations
1. The diagram below represents the homeostatic control of body temperature. What does the part labelled X represent? A. Heart B. Kidney C. Pituitary D. Hypothalamus 2. What is the sequence of operations
The rate at which blood glucose concentration changes is affected by the food eaten.
 Insulin controls blood glucose concentration. The rate at which blood glucose concentration changes is affected by the food eaten. In an experiment a person who does not have diabetes ate two slices of
Insulin controls blood glucose concentration. The rate at which blood glucose concentration changes is affected by the food eaten. In an experiment a person who does not have diabetes ate two slices of
(Total 4 marks) Q2. The graph shows changes in the levels of three hormones in a menstrual cycle.
 Q1. A woman wants to have a baby. She has been told that her body is not making and releasing eggs. However she has thousands of cells which could develop into them. A possible treatment is to give her
Q1. A woman wants to have a baby. She has been told that her body is not making and releasing eggs. However she has thousands of cells which could develop into them. A possible treatment is to give her
Homeostasis AnswerIT The regulation of the internal conditions of a cell or organism to maintain optimum conditions.
 Homeostasis AnswerIT 1. Define homeostasis. The regulation of the internal conditions of a cell or organism to maintain optimum conditions. 2. Why does homeostasis need to maintain optimal conditions?
Homeostasis AnswerIT 1. Define homeostasis. The regulation of the internal conditions of a cell or organism to maintain optimum conditions. 2. Why does homeostasis need to maintain optimal conditions?
Homeostasis and Response. AQA Biology topic 5
 Homeostasis and Response AQA Biology topic 5 5.1 Homeostasis Homeostasis: An introduction Wow it s hot here! What would happen if I stand here for too long? What would happen if I drank too much water?
Homeostasis and Response AQA Biology topic 5 5.1 Homeostasis Homeostasis: An introduction Wow it s hot here! What would happen if I stand here for too long? What would happen if I drank too much water?
Fact Sheet B2.1 Homeostasis
 Fact Sheet B2.1 Homeostasis Homeostasis What is homeostasis? Why is homeostasis important? State the components that all control systems have. Describe the roles of the above components. Define negative
Fact Sheet B2.1 Homeostasis Homeostasis What is homeostasis? Why is homeostasis important? State the components that all control systems have. Describe the roles of the above components. Define negative
Core 1. Coordination, Response & Homeostasis. page 1.
 Core 1 Coordination, Response & Homeostasis page 1 Core 2 1 1 1. Coordination, Response & Homeostasis page 2 Core 3 Fig. 2 Fig. 2 Coordination, Response & Homeostasis page 3 Alternative to practical 1
Core 1 Coordination, Response & Homeostasis page 1 Core 2 1 1 1. Coordination, Response & Homeostasis page 2 Core 3 Fig. 2 Fig. 2 Coordination, Response & Homeostasis page 3 Alternative to practical 1
Homeostasis. Name (2) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector.
 Homeostasis. Name. Thornton College Q.This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin............. (2) (b) A response is caused when information in the nervous
Homeostasis. Name. Thornton College Q.This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin............. (2) (b) A response is caused when information in the nervous
Draw one line from each contraceptive to the method of preventing pregnancy.
 Contraceptives are used to prevent pregnancy. (a) Draw one line from each contraceptive to the method of preventing pregnancy. Contraceptive device Method of preventing pregnancy Contains hormones to stop
Contraceptives are used to prevent pregnancy. (a) Draw one line from each contraceptive to the method of preventing pregnancy. Contraceptive device Method of preventing pregnancy Contains hormones to stop
Chapter 5 Homeostasis and Control
 Homeostasis is the regulation of internal conditions in the body. Necessary to maintain optimal conditions for body functioning. The control systems involved in homeostasis are automatic they happen regardless
Homeostasis is the regulation of internal conditions in the body. Necessary to maintain optimal conditions for body functioning. The control systems involved in homeostasis are automatic they happen regardless
Human nervous system
 Human nervous system Question Paper 1 Level GCSE (9-1) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.5 Homeostasis and Response Sub-Topic Human nervous system Difficulty Level Bronze Level Booklet Question Paper
Human nervous system Question Paper 1 Level GCSE (9-1) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.5 Homeostasis and Response Sub-Topic Human nervous system Difficulty Level Bronze Level Booklet Question Paper
Q1.A man hurt his head in an accident. Doctors found that he could not remember anything that had happened on the day of the accident.
 Q1.A man hurt his head in an accident. Doctors found that he could not remember anything that had happened on the day of the accident. (a) (i) Name the part of the brain concerned with memory. (1) (ii)
Q1.A man hurt his head in an accident. Doctors found that he could not remember anything that had happened on the day of the accident. (a) (i) Name the part of the brain concerned with memory. (1) (ii)
convert information to impulse allow send impulse to sensory neurones / brain
 Page of 8 Mark schemes detect changes in surroundings or detect stimuli allow any named stimulus for skin convert information to impulse allow send impulse to sensory neurones / brain (i) muscle contract(ion)
Page of 8 Mark schemes detect changes in surroundings or detect stimuli allow any named stimulus for skin convert information to impulse allow send impulse to sensory neurones / brain (i) muscle contract(ion)
Nerves and Hormones. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Subject Biology (4401) Exam Board. Page 1. Score: /59.
 Nerves and Hormones Question Paper Level IGCSE Subject Biology (4401) Exam Board AQA Unit B1 Topic Nerves and Hormones Booklet Question Paper Time Allowed: 59 minutes Score: /59 Percentage: /100 Grade
Nerves and Hormones Question Paper Level IGCSE Subject Biology (4401) Exam Board AQA Unit B1 Topic Nerves and Hormones Booklet Question Paper Time Allowed: 59 minutes Score: /59 Percentage: /100 Grade
Part 1- Biology Paper 2 Homeostasis and Response Knowledge Questions
 Part 1- Biology Paper 2 Homeostasis and Response Knowledge Questions AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.5 Homeostasis and response Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe what homeostasis is
Part 1- Biology Paper 2 Homeostasis and Response Knowledge Questions AQA TRILOGY Biology (8464) from 2016 Topic T4.5 Homeostasis and response Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe what homeostasis is
Control and Coordination
 CHAPTER 7 Control and Coordination Living organisms respond and react to various stimuli like heat, light, cold, touch, pressure etc. Plants and animals both respond to stimuli but in different manner.
CHAPTER 7 Control and Coordination Living organisms respond and react to various stimuli like heat, light, cold, touch, pressure etc. Plants and animals both respond to stimuli but in different manner.
14 Coordination and response
 oordination and response Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 14 oordination and response ooklet Question Paper 2 Time llowed: 30 minutes Score: /25
oordination and response Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 14 oordination and response ooklet Question Paper 2 Time llowed: 30 minutes Score: /25
(2) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. the two different types of effector
 NERVOUS SYSTEM. NAME.. Q.This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin. A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector.
NERVOUS SYSTEM. NAME.. Q.This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin. A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector.
Coordination and Responses Nervous System (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Coordination and Responses Nervous System (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Nervous System Nervous system Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Brain Spinal Cord Nerves and neurones
Coordination and Responses Nervous System (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Nervous System Nervous system Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Brain Spinal Cord Nerves and neurones
Adaptation 22 Reproduction 24 Cloning and genetic engineering 26 Extinction and evolution 28 Natural selection 30 Pollution 32 Global warming 34
 Contents Exam board specification map iv Introduction vi Topic checker * Topic checker answers * Biology Unit B1a Human Biology The nervous system 2 Hormones 4 Controlling reproduction 6 Diet and exercise
Contents Exam board specification map iv Introduction vi Topic checker * Topic checker answers * Biology Unit B1a Human Biology The nervous system 2 Hormones 4 Controlling reproduction 6 Diet and exercise
Year 10 Biology booklet Topic 1 homeostasis Name:
 Year 10 Biology booklet Topic 1 homeostasis Name: Homeostasis Give a definition for each of these key words: Homeostasis Nervous system Sensory neurone Relay neurone Motor neurone Reflex action Endocrine
Year 10 Biology booklet Topic 1 homeostasis Name: Homeostasis Give a definition for each of these key words: Homeostasis Nervous system Sensory neurone Relay neurone Motor neurone Reflex action Endocrine
Part 1- Biology Paper 2 Homeostasis and Response Application Questions Triple Science
 Part 1- Biology Paper 2 Homeostasis and Response Application Questions Triple Science AQA Biology (8461) from 2016 Topic B4.5 Homeostasis and response Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe what homeostasis
Part 1- Biology Paper 2 Homeostasis and Response Application Questions Triple Science AQA Biology (8461) from 2016 Topic B4.5 Homeostasis and response Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe what homeostasis
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015
 Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Biology Duration: 3.00 Hours Part 1 Index No:- Choose the correct or most appropriate answer and underline them 1) When
Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Biology Duration: 3.00 Hours Part 1 Index No:- Choose the correct or most appropriate answer and underline them 1) When
(b) (i) (at first) large / rapid (loss / change of body mass) 1
 M2.(a) (i) idea of normal food / diet e.g. the same as usual or the same as before allow balanced diet allow none of the slimming programmes ignore healthy diet for comparison accept to show the test is
M2.(a) (i) idea of normal food / diet e.g. the same as usual or the same as before allow balanced diet allow none of the slimming programmes ignore healthy diet for comparison accept to show the test is
Hearing Balance of the body. (b) Eyes : Photoreceptors Seeing (c) Skin : Thermoreceptors
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Control and coordination are provided by nervous and muscular tissues. Nervous tissue is made up of an organized network of nerve cells or neurons, and is specialized for conducting information
NERVOUS SYSTEM Control and coordination are provided by nervous and muscular tissues. Nervous tissue is made up of an organized network of nerve cells or neurons, and is specialized for conducting information
GraspIT AQA GCSE Homeostasis and response - Answers
 A. Homeostasis 1. The body has two automatic control systems; these systems may involve nervous responses or chemical responses. Compare the structure and mode of action of the two control systems. (4)
A. Homeostasis 1. The body has two automatic control systems; these systems may involve nervous responses or chemical responses. Compare the structure and mode of action of the two control systems. (4)
Control And Coordination 49
 7 All the living organisms respond and react to changes in the environment around them. The changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli such as light, heat, cold,
7 All the living organisms respond and react to changes in the environment around them. The changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli such as light, heat, cold,
thebiotutor.com 2J Coordination Time: 1 hour 5 minutes Total marks available: 65 Total marks achieved: Andy Todd
 thebiotutor.com 2J Coordination Time: 1 hour 5 minutes Total marks available: 65 Total marks achieved: Q1. (a) Complete the table to show the characteristic features of the three groups of organisms. Use
thebiotutor.com 2J Coordination Time: 1 hour 5 minutes Total marks available: 65 Total marks achieved: Q1. (a) Complete the table to show the characteristic features of the three groups of organisms. Use
Homeostasis involves maintaining the volume, chemical make up and other factors of blood and tissue fluid within restricted limits and set-points.
 = The maintenance of a constant internal environment Homeostasis involves maintaining the volume, chemical make up and other factors of blood and tissue fluid within restricted limits and set-points. The
= The maintenance of a constant internal environment Homeostasis involves maintaining the volume, chemical make up and other factors of blood and tissue fluid within restricted limits and set-points. The
PMT. Mark Scheme (Results) November GCSE Biology 5BI1F/01
 Mark Scheme (Results) November 2011 GCSE Biology 5BI1F/01 Edexcel is one of the leading examining and awarding bodies in the UK and throughout the world. We provide a wide range of qualifications including
Mark Scheme (Results) November 2011 GCSE Biology 5BI1F/01 Edexcel is one of the leading examining and awarding bodies in the UK and throughout the world. We provide a wide range of qualifications including
Grade 10 IGCSE_ Biology Term 1 Final Exam _ Study Guide. The exam lasts 120 minutes and will include:
 The exam lasts 120 minutes and will include: multiple Choice questions short-answers questions Alternative to practical Chapter 14 Coordination and response, P: 161-174 14.1 Nervous control in humans Describe
The exam lasts 120 minutes and will include: multiple Choice questions short-answers questions Alternative to practical Chapter 14 Coordination and response, P: 161-174 14.1 Nervous control in humans Describe
Church of England School Headteacher: Mr A J W ilcock MA (Cantab)
 B I S H O P R A M S E Y Church of England School Headteacher: Mr A J W ilcock MA (Cantab) 2 nd November 2017 Dear Parent/Carer, Test Results for Biology B10 and B11 Recently your son/daughter completed
B I S H O P R A M S E Y Church of England School Headteacher: Mr A J W ilcock MA (Cantab) 2 nd November 2017 Dear Parent/Carer, Test Results for Biology B10 and B11 Recently your son/daughter completed
GraspIT AQA GCSE Homeostasis and response - Answers
 A. Homeostasis 1. The body has two automatic control systems; these systems may involve nervous responses or chemical responses. Compare the structure and mode of action of the two control systems. (4)
A. Homeostasis 1. The body has two automatic control systems; these systems may involve nervous responses or chemical responses. Compare the structure and mode of action of the two control systems. (4)
Downloaded from
 CHAPTER 7-CONTROL AND COORDINATION Stimulus:-The change in the environment to which an organism respond and react is called stimulus. Control & co-ordination in animals takes place by :-a) Nervous system)
CHAPTER 7-CONTROL AND COORDINATION Stimulus:-The change in the environment to which an organism respond and react is called stimulus. Control & co-ordination in animals takes place by :-a) Nervous system)
Name Class Date. Read the words in the box. Read the sentences. Fill in each blank with the word or phrase that best completes the sentence.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: The Nervous System TWO SYSTEMS WITHIN A SYSTEM 1. What does the nervous system do? a. pump blood b. gather and interpret information c. digest food d. eliminate
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: The Nervous System TWO SYSTEMS WITHIN A SYSTEM 1. What does the nervous system do? a. pump blood b. gather and interpret information c. digest food d. eliminate
Class X: Biology. Chapter 2: Control and coordination.
 Class X: Biology Chapter 2: Control and coordination. Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) A system of control and coordination is essential in living organisms so that the different body parts can function
Class X: Biology Chapter 2: Control and coordination. Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) A system of control and coordination is essential in living organisms so that the different body parts can function
Use words from the box to complete the sentences about controlling conditions in our bodies. kidneys liver lungs skin
 HORMONAL COORDINATION IN HUMANS PART I Q1. (a) Use words from the box to complete the sentences about controlling conditions in our bodies. kidneys liver lungs skin (i) (iii) When we breathe out, water
HORMONAL COORDINATION IN HUMANS PART I Q1. (a) Use words from the box to complete the sentences about controlling conditions in our bodies. kidneys liver lungs skin (i) (iii) When we breathe out, water
15-1: How the Nervous System Works. 7 th Grade Life Science
 7 th Grade Life Science Purpose Students will be able to: 1. Identify the functions of the nervous system. 2. Describe the structure of a neuron and the kinds of neurons found in the body. 3. Explain how
7 th Grade Life Science Purpose Students will be able to: 1. Identify the functions of the nervous system. 2. Describe the structure of a neuron and the kinds of neurons found in the body. 3. Explain how
Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism
 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
National 5 - Key Area 1: Cells, Tissues and Organs
 National 5 - Key Area 1: Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. The diagram below shows some of the structures involved in transport in plants. Which line in the table below correctly identifies structures J and
National 5 - Key Area 1: Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. The diagram below shows some of the structures involved in transport in plants. Which line in the table below correctly identifies structures J and
Revision Question Bank. MCQs [Practical Based Questions]
![Revision Question Bank. MCQs [Practical Based Questions] Revision Question Bank. MCQs [Practical Based Questions]](/thumbs/90/104148695.jpg) Revision Question Bank 1. What are phytohormones? 2. Name the part of hindbrain which takes part in regulation of respiration. 3. We suddenly pull our hand when a pin pricks. Name the type of response
Revision Question Bank 1. What are phytohormones? 2. Name the part of hindbrain which takes part in regulation of respiration. 3. We suddenly pull our hand when a pin pricks. Name the type of response
NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Pages
 NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pages 1031-1042 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Communication system that controls metabolism, growth, and development with hormones Maintains homeostasis Hormones: chemical messengers released
NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pages 1031-1042 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Communication system that controls metabolism, growth, and development with hormones Maintains homeostasis Hormones: chemical messengers released
THE HUMAN BODY. study of the structure of living organisms. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: studying the structure of the heart.
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Anatomythe study of the structure of living organisms. Ex: studying the structure of the heart. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: how the heart works to pump blood, etc.
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Anatomythe study of the structure of living organisms. Ex: studying the structure of the heart. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: how the heart works to pump blood, etc.
B5 Homeostasis and Response
 B5 Homeostasis and Response Practice questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 209 minutes Marks: 20 marks Comments: HIGHER TIER Page of 68 Amylase is an enzyme that digests starch. A student investigated the
B5 Homeostasis and Response Practice questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 209 minutes Marks: 20 marks Comments: HIGHER TIER Page of 68 Amylase is an enzyme that digests starch. A student investigated the
GRADE 12 SEPTEMBER 2017 LIFE SCIENCES P1 MARKING GUIDELINE
 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12 SEPTEMBER 2017 LIFE SCIENCES P1 MARKING GUIDELINE MARKS: 150 This marking guideline consists of 7 pages. 2 LIFE SCIENCES P1 (EC/SEPTEMBER 2017) SECTION A QUESTION 1
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE GRADE 12 SEPTEMBER 2017 LIFE SCIENCES P1 MARKING GUIDELINE MARKS: 150 This marking guideline consists of 7 pages. 2 LIFE SCIENCES P1 (EC/SEPTEMBER 2017) SECTION A QUESTION 1
A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. There are two different types of effector.
 Q1.This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin............. (2) (b) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. (i)
Q1.This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin............. (2) (b) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. (i)
B1b Topics 3 and 4 Foundation and Higher Tier. Monday 5 March 2012 Morning Time: 20 minutes
 Surname Initial(s) Signature Paper Reference(s) 5006 5026 Edexcel GSE Science (5006) iology (5026) 1b Topics 3 and 4 Foundation and Higher Tier Monday 5 March 2012 Morning Time: 20 minutes Materials required
Surname Initial(s) Signature Paper Reference(s) 5006 5026 Edexcel GSE Science (5006) iology (5026) 1b Topics 3 and 4 Foundation and Higher Tier Monday 5 March 2012 Morning Time: 20 minutes Materials required
Biology Unit Biology B1a (Human Biology)
 Centre Number Candidate Number Surname Other Names Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier and Higher Tier June 2011 Science A Unit Biology B1a (Human Biology) Biology
Centre Number Candidate Number Surname Other Names Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier and Higher Tier June 2011 Science A Unit Biology B1a (Human Biology) Biology
1. The nervous system
 1. The nervous system Our brain, spinal cord and nerves make up your central nervous system. Nerve fibres are made from lots of nerve cells, called neurones. There are three types of neurone: which take
1. The nervous system Our brain, spinal cord and nerves make up your central nervous system. Nerve fibres are made from lots of nerve cells, called neurones. There are three types of neurone: which take
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: ( Division B) Boyceville Invite Dec. 3, 2016 (50pts.)
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: ( Division B) Boyceville Invite Dec. 3, 2016 (50pts.) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following statements
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: ( Division B) Boyceville Invite Dec. 3, 2016 (50pts.) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following statements
Website: Page 1. Page 125»Exercise» Page 126» Question 1:
 Page 125»Exercise» Question 1: Which of the following is a plant hormone? (a) Insulin (b) Thyroxin (c) Oestrogen (d) Cytokinin (d) Cytokinin is a plant hormone. Question 2: The gap between two neurons
Page 125»Exercise» Question 1: Which of the following is a plant hormone? (a) Insulin (b) Thyroxin (c) Oestrogen (d) Cytokinin (d) Cytokinin is a plant hormone. Question 2: The gap between two neurons
B4 Homeostasis and Response
 B4 Homeostasis and Response 35 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 20 Amylase is an enzyme that digests starch. A student investigated the effect of ph on the activity of amylase.
B4 Homeostasis and Response 35 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comments: Page of 20 Amylase is an enzyme that digests starch. A student investigated the effect of ph on the activity of amylase.
Main Function: signal other cells to behave in certain. of communication.
 Main Function: It releases hormones into the blood to signal other cells to behave in certain ways. It is a slow but widespread form of communication. Consists of: Endocrine glands Release hormones into
Main Function: It releases hormones into the blood to signal other cells to behave in certain ways. It is a slow but widespread form of communication. Consists of: Endocrine glands Release hormones into
10th control and co ordination Solved Board questions By JSUNIL
 10th control and co ordination Solved Board questions By JSUNIL 1. All information for our environment is detected by specialised tips of some nerve cells. Mention the name given to such tips and also
10th control and co ordination Solved Board questions By JSUNIL 1. All information for our environment is detected by specialised tips of some nerve cells. Mention the name given to such tips and also
Nervous System. Chapter Structure of the Nervous System. Neurons
 33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Tenth Biology Control and Coordination I. Conceptual Understanding
 Tenth Biology Control and Coordination I. Conceptual Understanding 1. Reaching for a pencil, grasping a doorknob, walking or running, driving etc., involve some movements. What are they? A: Whenever we
Tenth Biology Control and Coordination I. Conceptual Understanding 1. Reaching for a pencil, grasping a doorknob, walking or running, driving etc., involve some movements. What are they? A: Whenever we
Human Biology HBIO4. General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination January Unit 4 Bodies and cells in and out of control
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination January 2012 Question 1 2 Mark
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination January 2012 Question 1 2 Mark
0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/32 Paper 3 Theory (Core), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the March 2016 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/32 Paper 3 Theory (Core), maximum raw mark
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the March 2016 series 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/32 Paper 3 Theory (Core), maximum raw mark
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/21 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
Multicellular Organisms Homework
 Multicellular Organisms Homework NAME: CLASS: Reproduction 1. The diagram shows the parts of a flower. 1a. Name part X (1) 1b. Name the sites of production of both male and female gametes in a flowering
Multicellular Organisms Homework NAME: CLASS: Reproduction 1. The diagram shows the parts of a flower. 1a. Name part X (1) 1b. Name the sites of production of both male and female gametes in a flowering
Exampro GCSE Biology. B2.1 Cells. Name: Class: Foundation tier. Author: Date: Time: 81. Marks: 81. Comments: Page 1 of 27
 Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Lesson 1. Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms
 Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Life Sciences P1 1 FS/September 2016 PREPARATORY EXAMINATION GRADE 12 LIFE SCIENCES P1 SEPTEMBER 2016 MEMORANDUM MARKS: 150
 Life Sciences P1 1 FS/September 2016 PREPARATORY EXAMINATION GRADE 12 LIFE SCIENCES P1 SEPTEMBER 2016 MEMORANDUM MARKS: 150 This memorandum consists of 11 pages. Life Sciences P1 2 FS/September 2016 PRINCIPLES
Life Sciences P1 1 FS/September 2016 PREPARATORY EXAMINATION GRADE 12 LIFE SCIENCES P1 SEPTEMBER 2016 MEMORANDUM MARKS: 150 This memorandum consists of 11 pages. Life Sciences P1 2 FS/September 2016 PRINCIPLES
(2) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. the response each type of effector makes.
 1 This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin. (b) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. (i) There are two different
1 This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin. (b) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. (i) There are two different
Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System
 Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System Looking for answers? Visit http://msjadah.weebly.com 1. The Nervous System a) What is the function of nervous system? The nervous system receives,
Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System Looking for answers? Visit http://msjadah.weebly.com 1. The Nervous System a) What is the function of nervous system? The nervous system receives,
Downloaded from
 Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus. It does not involve any thinking. For example, we close our eyes immediately
Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus. It does not involve any thinking. For example, we close our eyes immediately
Reaction time MATERIALS. - Pencil - Chair - Ruler
 Reaction time NAME DATE A hand accidentally touches the hot plate of an oven and is withdrawn immediately. A young child runs out in front of your car and you hammer on the brakes. A lottery ball falls
Reaction time NAME DATE A hand accidentally touches the hot plate of an oven and is withdrawn immediately. A young child runs out in front of your car and you hammer on the brakes. A lottery ball falls
Endocrine system release hormones to regulates physiological process e.g growth, reproduction, metabolism, mentrual cycle, development of secondary
 Endocrine system release hormones to regulates physiological process e.g growth, reproduction, metabolism, mentrual cycle, development of secondary sexual characteristics Consists of endocrine glands which
Endocrine system release hormones to regulates physiological process e.g growth, reproduction, metabolism, mentrual cycle, development of secondary sexual characteristics Consists of endocrine glands which
Control and Coordination. What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
 Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus. It does not involve any thinking. For example,
Control and Coordination Question 1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking? A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus. It does not involve any thinking. For example,
* If a person is badly burnt the hairs on the skin are lost and blisters can cover the surface of the skin.
 Questions Q1. * If a person is badly burnt the hairs on the skin are lost and blisters can cover the surface of the skin. Explain how burns to the skin affect temperature regulation in the human body.
Questions Q1. * If a person is badly burnt the hairs on the skin are lost and blisters can cover the surface of the skin. Explain how burns to the skin affect temperature regulation in the human body.
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Name: Block: Chapter 7: The Nervous System Lesson 1: How the Nervous System Works What is the Role of the Nervous System? Your nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and
Name: Block: Chapter 7: The Nervous System Lesson 1: How the Nervous System Works What is the Role of the Nervous System? Your nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
The Nervous and Endocrine Systems
 Lesson 5 The Nervous and Endocrine Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the nervous and endocrine systems work? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to relate the structures of the nervous and endocrine
Lesson 5 The Nervous and Endocrine Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the nervous and endocrine systems work? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to relate the structures of the nervous and endocrine
09 Coordination and response. #86 The human nervous system
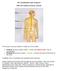 09 Coordination and response #86 The human nervous system The human nervous system is made up of two parts: Central nervous system (CNS) - brain and spinal cord: role of coordination Peripheral nervous
09 Coordination and response #86 The human nervous system The human nervous system is made up of two parts: Central nervous system (CNS) - brain and spinal cord: role of coordination Peripheral nervous
Homeostasis. Achievement Criteria. Excellence Criteria. Demonstrate understanding of how an animal maintains a stable internal environment 10/02/2016
 Homeostasis Demonstrate understanding of how an animal maintains a stable internal environment Biology 3.4 AS91604 Achievement Criteria Explain the purpose of the homeostatic mechanism Be able to explain
Homeostasis Demonstrate understanding of how an animal maintains a stable internal environment Biology 3.4 AS91604 Achievement Criteria Explain the purpose of the homeostatic mechanism Be able to explain
Year 10 AQA GCSE Biology Revision Checklist
 Year 10 AQA GCSE Biology Revision Checklist Use this booklet to help you with your revision in preparation for your year 10 Biology examinations. This is the work that you will have covered by the end
Year 10 AQA GCSE Biology Revision Checklist Use this booklet to help you with your revision in preparation for your year 10 Biology examinations. This is the work that you will have covered by the end
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 4 3 2 5 2 H Signature Paper Reference(s) 4325/2H London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 2H Higher Tier Thursday 15 May 2008 Afternoon Time:
Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 4 3 2 5 2 H Signature Paper Reference(s) 4325/2H London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 2H Higher Tier Thursday 15 May 2008 Afternoon Time:
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
Lesson Overview Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body THINK ABOUT IT The batter slaps a ball to the shortstop, who fields it and throws the ball toward first base. In a single motion, you extend your glove hand, catch the
30.1 Organization of the Human Body THINK ABOUT IT The batter slaps a ball to the shortstop, who fields it and throws the ball toward first base. In a single motion, you extend your glove hand, catch the
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION PREPARATORY EXAMINATION
 GUTENG EPRTMENT OF EUCTION PREPRTORY EXMINTION 2014 2015 10831 FIRST PPER MRKS: 150 Pages 16 TIME: 2½ hours 3 2 GUTENG EPRTMENT OF EUCTION PREPRTORY EXMINTION (First Paper) TIME: 2½ hours MRKS: 150 INSTRUCTIONS
GUTENG EPRTMENT OF EUCTION PREPRTORY EXMINTION 2014 2015 10831 FIRST PPER MRKS: 150 Pages 16 TIME: 2½ hours 3 2 GUTENG EPRTMENT OF EUCTION PREPRTORY EXMINTION (First Paper) TIME: 2½ hours MRKS: 150 INSTRUCTIONS
