Yolo County Health and Human Services
|
|
|
- Osborne Denis Boone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Yolo County Health and Human Services Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 20, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS Agency SUBJECT: January 1, 2018 EMS Protocol & Policy Revisions MEMORANDUM Effective January 1, 2018 the listed Protocols and Policies will go into effect for all Yolo County Providers. The protocol App and website will be updated. It is the responsibility of each agency to ensure that their personnel receive this information. As a reminder, policies and protocols are updated two (2) times a year; January 1 st and July 1 st. Please review the additions and changes thoroughly. If you have any questions, please contact Kristin Weivoda at (530) or kristin.weivoda@yolocounty.org A Message from Dr. Rose: Happy New Year. Highlights 2018 bodes to be an exciting year for Yolo County Emergency Medical Services Agency. We have several new initiatives to be implemented as well as several on the horizon. First off, I wish to thank all of you for your hard work and professional dedication to the patients we serve in Yolo County. I ve worked with many paramedic groups in my career and, without a doubt, those working in Yolo County are some of the best I have encountered in my practice emergency medicine. I personally want to thank each and every one of you for the hard work and dedication you put forth in providing state-of-the-art emergency care to the citizens of Yolo County. We begin this year with our participation in the statewide TXA trial. I m very pleased with the positive feedback and willingness of each paramedic to undertake take this important initiative. I truly believe that administering TXA in the field will benefit our critically injured trauma patients. I was fortunate enough to meet many of you at the trainings. Please be sure to let us know if you find any challenges in following the policy and study protocol. Mountain Valley EMS is finalizing its ketamine protocol for acute pain management. We will be asking to participate in this study. I believe that ketamine is a very useful prehospital agent and adopting it in 137 N. Cottonwood Street, Suite 1300, Woodland, CA (530) Main (530) Fax
2 California is an important step forward. YEMSA will keep you abreast as we move forward with this protocol. I am very excited about our new initiatives this year. The great staff at YEMSA have been working very hard to ensure that we are one of the premier LEMSAs in California. Best of Practice Reminder: We all make mistakes; even the most clinically competent and fully engaged providers can make errors in the field. The key to minimizing the risk of medication errors is to develop a multi-faceted approach. Below are steps you can take to minimize the risk of medication errors: Review common medications used in the field. Utilize reference charts and apps. Be willing to question yourself and others. Contact base or the receiving hospital physician if you are unsure of a medication or dose. Utilize the five (5) rights of safe medication administration: 1. Right Patient 2. Right Medication 3. Right Dose 4. Right Time 5. Right Route Report and document any adverse events, near misses, or unsafe conditions to identify system improvement opportunities and allow for learning. Trial Scope of Practice: We are excited that YEMSA will be live with the TXA trial on January 1, TXA kits will be distributed to your agency. Protocol Updates YEMSA is in the process of re-formatting and organizing all protocols. The goal is to make them more user friendly and incorporate all scope levels into each protocol. Over the next year you will see a complete transition into the new format. In January we are releasing four (4) protocols with the new format. The format combines multiple protocols into a single inclusive protocol. You will notice duplicate protocols in multiple sections during our transition to the new format. For example, adult and pediatric protocols have been combined into shared protocols. Once all of the protocols have been re-formatted, we will organize, rename and renumber all of the protocols at one time. Medical: Allergic Reaction & Anaphylaxis UPDATED/REPLACED: Added Local BLS Scope of Practice: Epinephrine Auto Injectors added BLS, ALS, and (New Format)
3 Altered Level of Consciousness UPDATED/REPLACED: Added BLS Local Scope of Practice: Finger-stick Glucose and Narcan - added BLS, ALS, and (New Format) Ingestion, Overdose and Poisoning UPDATED/REPLACED: Added BLS Local Scope of Practice: Finger-stick Glucose and Narcan - added BLS, ALS, and (New Format) Cardiac Arrest: , , Asystole, Pulseless Electrical Activity, Medical Cardiac Arrest, VF/VT UPDATED/REPLACED: One single Protocol Medical Cardiac Arrest - added BLS, ALS, and (New Format) BLS: & BLS AED, Pulseless Patient & Cardiac Arrest Recitation REPLACED: Medical Cardiac Arrest - added BLS, ALS, and (New Format) : , 8008, Asystole, Pulseless Electrical Activity, Medical Cardiac Arrest, VF/VT UPDATED/REPLACED: One single Protocol Medical Cardiac Arrest - added BLS, ALS, and (New Format) Allergic Reaction & Anaphylaxis UPDATED/REPLACED: Added Local BLS Scope of Practice: Epinephrine Auto Injectors added BLS, ALS, and (New Format) Altered Level of Consciousness UPDATED/REPLACED: Added BLS Local Scope of Practice: Finger-stick Glucose and Narcan - added BLS, ALS, and (New Format) Ingestion, Overdose and Poisoning UPDATED/REPLACED: Added BLS Local Scope of Practice: Finger-stick Glucose and Narcan - added BLS, ALS, and (New Format) Trial: Tranexamic Acid (TXA) Trial Study NEW: TXA Trial Protocol TXA Trial Study Tracking Form NEW: Data collection form for the trial study Tranexamic Acid (TXA) Trial Study Reference Card NEW: Reference Card for the TXA kits Service Provider: Basic Life Support (BLS) Local Scope Policy Revisions
4 NEW: Defines requirements for BLS Local Scope Providers Epinephrine Auto-Injector and Narcan Administration Form NEW: Data collection form for BLS Local Scope Providers Skill Sheets: BLS Local Scope Narcan NEW BLS Local Scope Epinephrine Auto-Injector NEW
5 Medical Revised Date: December 11, 2017 ALLERGIC REACTION & ANAPHYLAXIS Allergic Reaction: Acute onset cutaneous reactions, for example hives, pruritus, flushing, rash, or angioedema not involving the airway. Anaphylaxis: Systemic reaction with one (1) or more of the following symptoms: stridor, wheezing, hoarseness, edema involving the airway, hypotension, airway compromise, decreased level of consciousness. Anaphylaxis (> 30 kg) BLS ABC s Assess VS O 2, titrate SpO 2 to > 94% Assist ventilations as appropriate BLS Local Scope Anaphylaxis (15-30 kg) Epinephrine Auto Injector Epinephrine Auto Injector 0.3 mg IM 0.15 mg IM Inject deep IM into the lateral thigh, Inject deep IM into the lateral thigh, midway between waist and knee midway between waist and knee No repeat No repeat Record time of injection Record time of injection Reassess as needed Reassess as needed ALS Cardiac Monitor, EtCO 2, IV/IO Allergic Reaction Diphenhydramine 1 mg/kg IV/IM/PO Max 50 mg Anaphylaxis Anaphylaxis Epinephrine(1:1,000) 0.3 mg IM Deltoid May repeat x 2 in 10 minutes If no signs of improvement Epinephrine (1:10,000) 0.1 mg (1 ml) IV/IO May Repeat every 10 minutes if SBP < 90 mmhg or stridor Epinephrine (1:1,000) 0.01 mg/kg IM Deltoid or thigh Max 0.3 mg If no signs of improvement Epinephrine (1:10,000) 0.01 mg/kg IV/IO Max single dose 0.1 mg Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 2
6 Medical Revised Date: December 11, 2017 ALS cont Consider Inadequate response to EPI and patient is on Beta Blockers Glucagon 1 mg IV/IO Give over 1 minute Glucagon 1 mg IM/IN If no IV/IO For Wheezing/Bronchospasm Albuterol 5 mg Nebulizer If BP < 90 mmhg For Wheezing/Bronchospasm Albuterol 5 mg Nebulizer If BP < normal range for age (see reference sheet) NS Bolus 20 ml/kg IV/IO NS Bolus 250 ml IV/IO Direction Contact Receiving ED Physician for additional treatment Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 2 of 2
7 Medical Revised Date: December 11, 2017 ALTERED LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS (ALOC) Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is < 15 and etiology unclear. BLS ABC s Assess VS Consider SMR for suspected trauma O 2, titrate SpO 2 to > 94% Temperature Assist ventilations as appropriate Suction as needed Place patient in recovery position If known diabetic with suspected decreased blood sugar, abnormal behavior and pale/moist skin Glucose paste one (1) tube by mouth (PO) or Commercially prepared glucose solution, one (1) bottle by mouth (PO) Do not administer if patient is unconscious, lethargic, or unable to drink fluids. BLS Local Scope Blood Sugar (BS) < 60 mg/dl Refer to BLS treatment If mental status and respiratory effort are depressed and suspected opioid over dose BS < 60 mg/dl Naloxone (Narcan) 2 mg IN May repeat x 1 Max dose 4 mg ½ dose per nare ALS Cardiac Monitor, EtCO 2, IV/IO BS < 60 mg/dl Dextrose 10% 25 gm in 250 ml NS IV/IO Infuse wide open Glucagon 1 mg IM/IN No repeat If no IV/IO Dextrose 10% in 250 ml NS IV (See chart below) If no IV/IO Glucagon 0.5 mg IM/IN No repeat Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 3
8 Medical Revised Date: December 11, 2017 Mental status and respiratory effort is depressed ALS cont. Mental status and respiratory effort is depressed Naloxone (Narcan) 2 mg IV/IO/IM Naloxone (Narcan) 2 mg IN ½ dose per nare Naloxone (Narcan) 0.1 mg/kg IV/IO/IM Max single dose 2 mg May repeat x 2 every 2-3 minutes Naloxone (Narcan) 0.1 mg/kg IN Max single dose 2 mg ½ dose per nare May repeat x 1 Dextrose 10% in 250 ml Infusion Chart AGE WEIGHT VOLUME D 10% 25 gm Preemie 2 kg 10 ml Newborn 3 kg 15 ml 3 months 5 kg 25 ml 6 months 7 kg 35 ml 1-2 years 11 kg 55 ml 3-4 years 15 kg 75 ml 5-6 years 19 kg 95 ml 7-8 years 24 kg 120 ml 9-10 years 31 kg 155 ml years 40 kg 200 ml Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 2 of 3
9 Medical Revised Date: December 11, 2017 ALS cont. Consider Consider diabetic related complications (hypoglycemia/diabetic Ketoacidosis [DKA]) Consider Carbon Monoxide (CO) toxicity Consider 12-Lead Electrocardiogram (EKG) AEIOU-TIPS Alcohol Epilepsy/Endocrine/Electrolytes/Exocrine Insulin/Infection Overdose/Oxygen deprivation Uremia Trauma/Temperature Psychosis/Porphyria/Poison Stroke/Shock/Sepsis/Space occupying lesion/subarachnoid hemorrhage Refer to appropriate treatment protocol Direction Contact Receiving ED Physician for additional treatment Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 3 of 3
10 Medical Revised Date: December 11, 2017 INGESTION, OVERDOSE AND POISONING BLS Consider calling Poison Control ABC s Assess Vital Signs (VS) O 2, titrate SpO 2 > 94% Assist respirations as needed BLS Local Scope Blood Sugar (BS) < 60 mg/dl or un-measurable Glucose paste one (1) tube by mouth (PO) or Commercially prepared glucose solution, one (1) bottle by mouth (PO) Do not administer if patient is unconscious, lethargic, or unable to drink fluids. If mental status and respiratory effort are depressed and suspected opioid over dose Naloxone (Narcan) 2 mg IN May repeat x 1 ½ dose per nare ALS Cardiac Monitor, SpO 2, EtCO 2 IV/IO Suspected Opiates Suspected Opiates Mental status and respiratory effort is depressed Naloxone (Narcan) 2 mg IV/IO/IM Naloxone (Narcan) 2 mg IN ½ dose per nare Glucagon 1 mg IV/IO Beta Blockers Mental status and respiratory effort is depressed Naloxone (Narcan) 0.1 mg/kg IV/IO/IM Max single dose 2 mg May repeat x 2 every 2-3 minutes Naloxone (Narcan) 0.1 mg/kg IN ½ dose per nare May repeat x 1 If no IV/IO Glucagon 1 mg IM/IN Atropine 0.5 mg IV/IO May repeat every 5 minutes up to 3 mg max SBP < 70 mmhg Epinephrine (1:10,000) 0.1 mg (1 ml) IV/IO Repeat until SBP > 90 mmhg BS < 60 mg/dl or un-measurable Dextrose 10% in 250 ml NS IV (See chart below) Infuse wide open If no IV/IO Glucagon 0.5 mg IM/IN No repeat Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 2
11 Medical Revised Date: December 11, 2017 Tricyclic Antidepressants If any other following are present: SBP < 90 mmhg, QRS > 0.12 seconds and/or seizures Sodium Bicarbonate 1 meq/kg IV/IO ALS cont. Dextrose 10% in 250 ml Infusion Chart AGE WEIGHT VOLUME D 10% 25 gm Calcium Channel Blockers SBP < 90 mmhg Calcium Chloride 10% 10 ml IV/IO 1 ml per minute May repeat every 5 minutes, total 4 doses Organophosphate or Carbamate Pesticides HR < 50 BPM Preemie 2 kg 10 ml Newborn 3 kg 15 ml 3 months 5 kg 25 ml 6 months 7 kg 35 ml 1-2 years 11 kg 55 ml 3-4 years 15 kg 75 ml 5-6 years 19 kg 95 ml Atropine 2 mg IV/IO May repeat every 3 minutes Hydrofluoric Acid Calcium Chloride 10% 10 ml IV/IO Contact Receiving ED Physician for additional treatment. Direction 7-8 years 24 kg 120 ml 9-10 years 31 kg 155 ml years 40 kg 200 ml Overdose/poisoning in the pediatric population is dynamic and requires rapid transport. Contact Receiving ED Physician for additional treatment. Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 2 of 2
12 Cardiac Arrest Revised Date: December 12, 2017 MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST BLS Follow the 2015 American Heart Guidelines for CPR, C-A-B Continuous chest compressions at a rate of one hundred (100) to one hundred and twenty (120) per minute with a depth of two to two point four (2-2.4 ) inches Place one (1) oropharyngeal airway (OPA) Bag-Valve Mask (BVM) one (1) breath every six (6) to eight (8) seconds (10 breaths per minute) Apply Automated External Defibrillator (AED) Follow command prompts, shock if indicated by AED Continue CPR for two (2) minutes or five (5) cycles Avoid Interruptions, do not interrupt CPR to administer medications or perform any procedures ALS Place on the Cardiac Monitor & Defib Pads Place an NG/OG Tube Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) Shockable Rhythm: - Shock with a Defibrillator per manufacturers energy dose Epinephrine (1:10,000) 1mg IV/IO repeat q 3-5 minutes Amiodarone 300 mg SIVP/IO (flush tubing with 20 ml NS) Amiodarone 150 mg SIVP/IO Repeat 3-5 minutes after 1 st dose (flush tubing with 20 ml NS) Hypothermia Epinephrine (1:10,000) 1mg IV/IO repeat q 3-5 minutes Shockable Rhythm Shock with a Defibrillator at 2 J/kg, subsequent shocks at 4 J/kg Epinephrine (1:10,000) 0.01 mg/kg, IV/IO repeat q 3-5 minutes Resume BLS CPR for two (2) minutes Re-assess rhythm Asystole Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) Amiodarone 5 mg/kg SIVP/IO Max single dose 300 mg May repeat x 1 q 5 minutes Address Reversible Causes Hypoglycemia Tension Hypoxia Tamponade cardiac Hypo/Hyperkalemia Trauma Hypovolemia Toxins Hydrogen Ion (acidosis) Thrombosis Epinephrine (1:10,000) 0.01 mg/kg, IV/IO repeat q 3-5 minutes Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 2
13 Cardiac Arrest Revised Date: December 12, 2017 ALS cont Direction Termination of Resuscitation (TOR) if there is no response to the resuscitation efforts after twenty (20) minutes) See Termination of Resuscitation (TOR) protocol If ROSC is achieved See ROSC Protocol Transmit Code Report via Physio Control Monitor Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 2 of 2
14 Basic Life Support Revised Date: December 12, 2017 MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST BLS Follow the 2015 American Heart Guidelines for CPR, C-A-B Continuous chest compressions at a rate of one hundred (100) to one hundred and twenty (120) per minute with a depth of two to two point four (2-2.4 ) inches Place one (1) oropharyngeal airway (OPA) Bag-Valve Mask (BVM) one (1) breath every six (6) to eight (8) seconds (10 breaths per minute) Apply Automated External Defibrillator (AED) Follow command prompts, shock if indicated by AED Continue CPR for two (2) minutes or five (5) cycles Avoid Interruptions, do not interrupt CPR to administer medications or perform any procedures ALS Place on the Cardiac Monitor & Defib Pads Place an NG/OG Tube Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) Shockable Rhythm: - Shock with a Defibrillator per manufacturers energy dose Epinephrine (1:10,000) 1mg IV/IO repeat q 3-5 minutes Amiodarone 300 mg SIVP/IO (flush tubing with 20 ml NS) Amiodarone 150 mg SIVP/IO Repeat 3-5 minutes after 1 st dose (flush tubing with 20 ml NS) Hypothermia Epinephrine (1:10,000) 1mg IV/IO repeat q 3-5 minutes Shockable Rhythm Shock with a Defibrillator at 2 J/kg, subsequent shocks at 4 J/kg Epinephrine (1:10,000) 0.01 mg/kg, IV/IO repeat q 3-5 minutes Resume BLS CPR for two (2) minutes Re-assess rhythm Asystole Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) Amiodarone 5 mg/kg SIVP/IO Max single dose 300 mg May repeat x 1 q 5 minutes Address Reversible Causes Hypoglycemia Tension Hypoxia Tamponade cardiac Hypo/Hyperkalemia Trauma Hypovolemia Toxins Hydrogen Ion (acidosis) Thrombosis Epinephrine (1:10,000) 0.01 mg/kg, IV/IO repeat q 3-5 minutes Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 2
15 Basic Life Support Revised Date: December 12, 2017 ALS cont Direction Termination of Resuscitation (TOR) if there is no response to the resuscitation efforts after twenty (20) minutes) See Termination of Resuscitation (TOR) protocol If ROSC is achieved See ROSC Protocol Transmit Code Report via Physio Control Monitor Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 2 of 2
16 Revised Date: December 12, 2017 MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST BLS Follow the 2015 American Heart Guidelines for CPR, C-A-B Continuous chest compressions at a rate of one hundred (100) to one hundred and twenty (120) per minute with a depth of two to two point four (2-2.4 ) inches Place one (1) oropharyngeal airway (OPA) Bag-Valve Mask (BVM) one (1) breath every six (6) to eight (8) seconds (10 breaths per minute) Apply Automated External Defibrillator (AED) Follow command prompts, shock if indicated by AED Continue CPR for two (2) minutes or five (5) cycles Avoid Interruptions, do not interrupt CPR to administer medications or perform any procedures ALS Place on the Cardiac Monitor & Defib Pads Place an NG/OG Tube Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) Shockable Rhythm: - Shock with a Defibrillator per manufacturers energy dose Epinephrine (1:10,000) 1mg IV/IO repeat q 3-5 minutes Amiodarone 300 mg SIVP/IO (flush tubing with 20 ml NS) Amiodarone 150 mg SIVP/IO Repeat 3-5 minutes after 1 st dose (flush tubing with 20 ml NS) Hypothermia Epinephrine (1:10,000) 1mg IV/IO repeat q 3-5 minutes Shockable Rhythm Shock with a Defibrillator at 2 J/kg, subsequent shocks at 4 J/kg Epinephrine (1:10,000) 0.01 mg/kg, IV/IO repeat q 3-5 minutes Resume BLS CPR for two (2) minutes Re-assess rhythm Asystole Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) Amiodarone 5 mg/kg SIVP/IO Max single dose 300 mg May repeat x 1 q 5 minutes Address Reversible Causes Hypoglycemia Tension Hypoxia Tamponade cardiac Hypo/Hyperkalemia Trauma Hypovolemia Toxins Hydrogen Ion (acidosis) Thrombosis Epinephrine (1:10,000) 0.01 mg/kg, IV/IO repeat q 3-5 minutes Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 2
17 Revised Date: December 12, 2017 ALS cont Direction Termination of Resuscitation (TOR) if there is no response to the resuscitation efforts after twenty (20) minutes) See Termination of Resuscitation (TOR) protocol If ROSC is achieved See ROSC Protocol Transmit Code Report via Physio Control Monitor Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 2 of 2
18 Revised Date: December 11, 2017 ALLERGIC REACTION & ANAPHYLAXIS Allergic Reaction: Acute onset cutaneous reactions, for example hives, pruritus, flushing, rash, or angioedema not involving the airway. Anaphylaxis: Systemic reaction with one (1) or more of the following symptoms: stridor, wheezing, hoarseness, edema involving the airway, hypotension, airway compromise, decreased level of consciousness. Anaphylaxis (> 30 kg) BLS ABC s Assess VS O 2, titrate SpO 2 to > 94% Assist ventilations as appropriate BLS Local Scope Anaphylaxis (15-30 kg) Epinephrine Auto Injector Epinephrine Auto Injector 0.3 mg IM 0.15 mg IM Inject deep IM into the lateral thigh, Inject deep IM into the lateral thigh, midway between waist and knee midway between waist and knee No repeat No repeat Record time of injection Record time of injection Reassess as needed Reassess as needed ALS Cardiac Monitor, EtCO 2, IV/IO Allergic Reaction Diphenhydramine 1 mg/kg IV/IM/PO Max 50 mg Anaphylaxis Anaphylaxis Epinephrine(1:1,000) 0.3 mg IM Deltoid May repeat x 2 in 10 minutes If no signs of improvement Epinephrine (1:10,000) 0.1 mg (1 ml) IV/IO May Repeat every 10 minutes if SBP < 90 mmhg or stridor Epinephrine (1:1,000) 0.01 mg/kg IM Deltoid or thigh Max 0.3 mg If no signs of improvement Epinephrine (1:10,000) 0.01 mg/kg IV/IO Max single dose 0.1 mg Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 2
19 Revised Date: December 11, 2017 ALS cont Consider Inadequate response to EPI and patient is on Beta Blockers Glucagon 1 mg IV/IO Give over 1 minute Glucagon 1 mg IM/IN If no IV/IO For Wheezing/Bronchospasm Albuterol 5 mg Nebulizer If BP < 90 mmhg For Wheezing/Bronchospasm Albuterol 5 mg Nebulizer If BP < normal range for age (see reference sheet) NS Bolus 20 ml/kg IV/IO NS Bolus 250 ml IV/IO Direction Contact Receiving ED Physician for additional treatment Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 2 of 2
20 Revised Date: December 11, 2017 ALTERED LEVEL OF CONSCIOUSNESS (ALOC) Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is < 15 and etiology unclear. BLS ABC s Assess VS Consider SMR for suspected trauma O 2, titrate SpO 2 to > 94% Temperature Assist ventilations as appropriate Suction as needed Place patient in recovery position If known diabetic with suspected decreased blood sugar, abnormal behavior and pale/moist skin Glucose paste one (1) tube by mouth (PO) or Commercially prepared glucose solution, one (1) bottle by mouth (PO) Do not administer if patient is unconscious, lethargic, or unable to drink fluids. BLS Local Scope Blood Sugar (BS) < 60 mg/dl Refer to BLS treatment If mental status and respiratory effort are depressed and suspected opioid over dose BS < 60 mg/dl Naloxone (Narcan) 2 mg IN May repeat x 1 Max dose 4 mg ½ dose per nare ALS Cardiac Monitor, EtCO 2, IV/IO BS < 60 mg/dl Dextrose 10% 25 gm in 250 ml NS IV/IO Infuse wide open Glucagon 1 mg IM/IN No repeat If no IV/IO Dextrose 10% in 250 ml NS IV (See chart below) If no IV/IO Glucagon 0.5 mg IM/IN No repeat Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 3
21 Revised Date: December 11, 2017 Mental status and respiratory effort is depressed ALS cont. Mental status and respiratory effort is depressed Naloxone (Narcan) 2 mg IV/IO/IM Naloxone (Narcan) 2 mg IN ½ dose per nare Naloxone (Narcan) 0.1 mg/kg IV/IO/IM Max single dose 2 mg May repeat x 2 every 2-3 minutes Naloxone (Narcan) 0.1 mg/kg IN Max single dose 2 mg ½ dose per nare May repeat x 1 Dextrose 10% in 250 ml Infusion Chart AGE WEIGHT VOLUME D 10% 25 gm Preemie 2 kg 10 ml Newborn 3 kg 15 ml 3 months 5 kg 25 ml 6 months 7 kg 35 ml 1-2 years 11 kg 55 ml 3-4 years 15 kg 75 ml 5-6 years 19 kg 95 ml 7-8 years 24 kg 120 ml 9-10 years 31 kg 155 ml years 40 kg 200 ml Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 2 of 3
22 Revised Date: December 11, 2017 ALS cont. Consider Consider diabetic related complications (hypoglycemia/diabetic Ketoacidosis [DKA]) Consider Carbon Monoxide (CO) toxicity Consider 12-Lead Electrocardiogram (EKG) AEIOU-TIPS Alcohol Epilepsy/Endocrine/Electrolytes/Exocrine Insulin/Infection Overdose/Oxygen deprivation Uremia Trauma/Temperature Psychosis/Porphyria/Poison Stroke/Shock/Sepsis/Space occupying lesion/subarachnoid hemorrhage Refer to appropriate treatment protocol Direction Contact Receiving ED Physician for additional treatment Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 3 of 3
23 Revised Date: December 11, 2017 INGESTION, OVERDOSE AND POISONING BLS Consider calling Poison Control ABC s Assess Vital Signs (VS) O 2, titrate SpO 2 > 94% Assist respirations as needed BLS Local Scope Blood Sugar (BS) < 60 mg/dl or un-measurable Glucose paste one (1) tube by mouth (PO) or Commercially prepared glucose solution, one (1) bottle by mouth (PO) Do not administer if patient is unconscious, lethargic, or unable to drink fluids. If mental status and respiratory effort are depressed and suspected opioid over dose Naloxone (Narcan) 2 mg IN May repeat x 1 ½ dose per nare ALS Cardiac Monitor, SpO 2, EtCO 2 IV/IO Suspected Opiates Suspected Opiates Mental status and respiratory effort is depressed Naloxone (Narcan) 2 mg IV/IO/IM Naloxone (Narcan) 2 mg IN ½ dose per nare Glucagon 1 mg IV/IO Beta Blockers Mental status and respiratory effort is depressed Naloxone (Narcan) 0.1 mg/kg IV/IO/IM Max single dose 2 mg May repeat x 2 every 2-3 minutes Naloxone (Narcan) 0.1 mg/kg IN ½ dose per nare May repeat x 1 If no IV/IO Glucagon 1 mg IM/IN Atropine 0.5 mg IV/IO May repeat every 5 minutes up to 3 mg max SBP < 70 mmhg Epinephrine (1:10,000) 0.1 mg (1 ml) IV/IO Repeat until SBP > 90 mmhg BS < 60 mg/dl or un-measurable Dextrose 10% in 250 ml NS IV (See chart below) Infuse wide open If no IV/IO Glucagon 0.5 mg IM/IN No repeat Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 2
24 Revised Date: December 11, 2017 Tricyclic Antidepressants If any other following are present: SBP < 90 mmhg, QRS > 0.12 seconds and/or seizures Sodium Bicarbonate 1 meq/kg IV/IO ALS cont. Dextrose 10% in 250 ml Infusion Chart AGE WEIGHT VOLUME D 10% 25 gm Calcium Channel Blockers SBP < 90 mmhg Calcium Chloride 10% 10 ml IV/IO 1 ml per minute May repeat every 5 minutes, total 4 doses Organophosphate or Carbamate Pesticides HR < 50 BPM Preemie 2 kg 10 ml Newborn 3 kg 15 ml 3 months 5 kg 25 ml 6 months 7 kg 35 ml 1-2 years 11 kg 55 ml 3-4 years 15 kg 75 ml 5-6 years 19 kg 95 ml Atropine 2 mg IV/IO May repeat every 3 minutes Hydrofluoric Acid Calcium Chloride 10% 10 ml IV/IO Contact Receiving ED Physician for additional treatment. Direction 7-8 years 24 kg 120 ml 9-10 years 31 kg 155 ml years 40 kg 200 ml Overdose/poisoning in the pediatric population is dynamic and requires rapid transport. Contact Receiving ED Physician for additional treatment. Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 2 of 2
25 Trial Revised Date: December 12, 2017 PURPOSE TRANEXAMIC ACID (TXA) TRIAL STUDY To determine the role of prehospital Tranexamic Acid (TXA) to improve hemorrhagic shock outcomes, prevent massive internal bleeding by stabilizing clot formation, and decrease extravascular bleeding in trauma patients. AUTHORITY Health & Safety Code, Division 2.5, Emergency Medical Services California Code of Regulations, Title 22, Division 9, Prehospital Emergency Medical Services INCLUSION CRITERIA Patients must meet anatomic, physiologic, and/or mechanism of injury trauma triage criteria as established by the Yolo County Emergency Medical Services Agency (YEMSA). Patients meeting the criteria for major trauma should be transported to the closest, most appropriate receiving center in the most expeditious manner. The prehospital use of TXA should be considered for all trauma patients that meet any of the following inclusion criteria: I. s, age greater than or equal to (>) eighteen (18) years old and; II. III. Any sustained blunt or penetrating trauma within three (3) hours and: Patient meets one (1) or more of the following criteria: A. Blunt or penetrating trauma with Signs and Symptoms (Si/Sx) of hemorrhagic shock B. Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) of less than (<) 90 mmhg at scene of injury, during ground medical transport, or on arrival to designated trauma centers C. Patients who are considered to be high risk for significant hemorrhage: 1. Estimated Blood Loss (EBL) of 500 ml in the field and accompanied by a Heart Rate (HR) greater than (>) 120 Beats Per Minute (BPM) 2. Bleeding not controlled by direct pressure or tourniquet 3. Major amputation of any extremity above the wrists or above the ankles CONTRAINDICATIONS I. Any patient < eighteen (18) years of age II. Any patient with an active thromboembolic event (within the last twenty-four [24] hours); i.e., active stroke, myocardial infarction or pulmonary embolism III. Any patient with a hypersensitivity or anaphylactic reaction to TXA IV. Any patient more than three (3) hours post injury V. Traumatic arrest with > five (5) minutes of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) without return of Vital Signs (VS) VI. Penetrating cranial injury VII. Traumatic brain injury with brain matter exposed VIII. Isolated drowning or hanging victims IX. Documented cervical cord injury with motor deficit Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 3
26 Trial Revised Date: December 12, 2017 GENERAL TREATMENT I. If patient meets anatomic and/or physiologic criterion of the inclusion criteria listed above: A. Begin immediate transport Code 3 if feasible. B. Establish two (2) large bore Intravenous/Intraosseous (IV/IO) Normal Saline (NS) C. Administer NS boluses two hundred-fifty to five hundred milliliters ( ml) D. If SBP < 90 mmhg, consider administering TXA, refer to Procedure below E. After each two hundred fifty (250) ml bolus, recheck VS F. If Altered Level of Consciousness (ALOC), consider medical etiology. G. Refer to YEMSA Protocol Altered Level of Consciousness (ALOC) Syncope H. Refer to YEMSA Protocol General Medical Care I. Refer to YEMSA Protocol Ingestion Overdoses & Poisoning J. Consider tourniquet use if appropriate refer to YEMSA Protocol External Hemorrhage Control. K. Splint fractures and dress wounds only if time permits L. Notify Trauma Center ASAP! II. If patient meets mechanism criterion only: A. May transport Code 2 at the Paramedic s discretion B. May establish one (1) large bore Intervenous/Interossous (IV/IO) Normal Saline (NS) at Paramedic s discretion C. Splint fractures and dress wounds D. Notify Trauma Center ASAP! PROCEDURE If patient meets inclusion criteria listed above: I. Administer TXA 1 gram (gm) in fifty to one hundred (50-100) milliliters (ml) of NS via IV/IO Bolus drip over ten (10) minutes A. (Do not administer IVP This will cause hypotension) II. Follow IV fluid resuscitation, III. Place the approved neon green wristband on patient prior to transporting patient to a Trauma Center IV. Trauma Hospital contact is mandatory. Advise Trauma Hospital of: A. Patient assessment B. VS C. EBL and condition D. TXA administration V. Upon transfer of care at the receiving Trauma Center, obtain a signature of receiving clinician on the TXA Trail Study Tracking Form, retain a copy to be scanned into the epcr, and ensure the form remains with the patient Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 2 of 3
27 Trial Revised Date: December 12, 2017 ADVERSE EFFECTS I. Thromboembolism A. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) B. Pulmonary Embolism (PE) II. Gastrointestinal effects including: A. Nausea B. Vomiting C. Diarrhea III. Headache IV. Fatigue V. Dizziness VI. Visual Disturbance DOCUMENTATION REQUIREMENTS I. Documentation must include: A. Meets trauma triage criteria B. Age C. Weight D. Date/time of injury onset of symptoms E. Mechanism of injury F. Initial SBP and VS G. EBL, both pre and post TXA administration H. Blunt or penetrating trauma location and description of injuries I. VS including Glasgow Coma Scale and temperature: pre, during and post TXA administration J. Any fluid administration K. Date/time TXA was started L. Past medical history M. Allergies N. Race/ethnicity O. Gender P. Any first response agency or transport service defined questions related to TXA CROSS REFERENCES Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 3 of 3
28 YOLO COUNTY EMS AGENCY TXA TRIAL STUDY TRACKING FORM EMS DATA POINTS Incident Date: Incident Time: Incident #: Patient Name: Gender: Male Female Other Patient Age: Patient Weight: Time of Injury: Primary Impression: Dose of TXA Administration: Mechanism of Injury: Time of TXA Administration: Pre TXA Vital Signs HR: RR: BP: Cap Refill: sec Temp: F/C Skin Signs: GCS: Est. Total Blood Loss: ml Post TXA Vital Signs Narrative Details: HR: RR: BP: Cap Refill: sec Temp: F/C Skin Signs: GCS: Est. Total Blood Loss: ml Received by: Print Name: Signature: Date: TRAUMA CENTER DATA POINTS Incident Date: Incident Time: Medical Record #: Receiving Hospital: Mechanism of Injury: Date to Operating Room: ICD 10 Code: Procedure Performed: Time to Operating Room: Disposition (Outcome): Complications: Serious Adverse Effects: Mortality: Yes xx No xx Cause of Death: Discharge Diagnosis: Transfused Blood Products: Yes xx No xx Blood Type: Hospital Days: Ventilator Use: Yes xx No xx Blood Product: Yes xx No xx Number of Units Given: ICU Days: Or Use:
29 Trial Revised Date: December 12, 2017 TRANEXAMIC ACID (TXA) TRIAL STUDY REFERENCE CARD Tranexamic Acid (TXA) Inclusion Criteria 1. Meets YEMSA Anatomic, Physiologic, and/or Mechanism Trauma Triage Criteria and; years of age or older and; 3. Victim of blunt or penetrating trauma within 3 hours of injury and; 4. Patient meets 1 or more of the following criteria: Blunt or penetrating trauma with signs and symptoms of hemorrhagic shock SBP < 90 mmhg at any time during patient care Patients who are high risk for significant hemorrhage: o Estimated blood loss of 500 ml or more with a HR > 120 BPM o Bleeding not controlled by direct pressure or tourniquet o Major amputation of any extremity above the wrist or ankle Pale clammy skin Altered mentation Pulse > 100 Narrowing pulse pressure SBP < 90 (late sign) Signs and Symptoms of Hemorrhagic Shock Contraindications Any patient < 18 years of age Any patient with an active thrombolytic event within the last 24 hours (stroke, myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis) Any patient with hypersensitivity to TXA Any patient that is more than 3 hours post injury Traumatic arrest with > 5 minutes of CPR without return of vital signs Penetrating cranial injury Traumatic brain injury with brain matter exposed Isolated drowning or hanging Cervical cord injury with motor deficits Procedure 1. TXA 1 gram in 100 ml Normal Saline (NS) IV/IO drip over 10 minutes ml NS bolus titrate to SBP of 90 mmhg 3. Place the green wrist band on the patient and document time 4. Advise the trauma hospital of TXA administration 5. Complete the EMS section of TXA Trail Study Form and obtain a signature from the receiving clinician (scribe nurse or physician) Pink Copy scanned into EPCR Yellow and white copy to trauma hospital Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 1
30 Yolo County Emergency Medical Services Agency Service Provider Revised Date: December 12, 2017 PURPOSE BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (BLS) LOCAL SCOPE To establish the requirements and responsibilities for a Yolo County Emergency Medical Services Agency (YEMSA) BLS Service Provider Agency to perform BLS Local Scope. The BLS Local Scope skills in YEMSA are: I. Administration of Epinephrine by auto-injector for suspected anaphylaxis. II. Administration of Naloxone (Narcan) for suspected narcotic overdose. III. Perform finger stick blood glucose testing. AUTHORITY California Code of Regulations, Title 22, Division 9, Chapter 2, Article 2, POLICY Any BLS Service Provider Agency wishing to utilize any of the BLS Local Scope skills for BLS employees shall meet all the requirements set forth by the State law, regulations, and YEMSA policy. I. BLS Local Scope Training Requirements and Responsibilities: A. Only individuals working for a BLS Service Provider Agency within Yolo County may practice BLS Local Scope skills and must be approved by their employer. B. BLS Service Provider Agencies shall provide bi-annual training, skills verification and shall: 1. Utilize the YEMSA approved Skills Verification Form. 2. Utilize instructors qualified by education or experience to teach the required curriculum. The Instructor shall be a Physician (MD), Registered Nurse (RN), Physician s Assistant (PA), Paramedic or Advanced EMT, licensed or certified in California or a MD licensed in another state. An EMT trained in the Local Scope Skill may assist in demonstration of competency and training of that skill, but cannot sign-off on the skill. II. Records/Data Collection: A. A YEMSA BLS Local Scope Medication Administration form shall be completed for each patient on whom Epinephrine or Narcan were administered if the Service Provider Agency is not using a NEMSIS 3.4 compliant system. 1. BLS Local Scope Medication Administration Forms shall be submitted to YEMSA within twenty-four (24) hours of medication administration. 2. Forms may be submitted via to yemsa@yolocounty.org or mailed to 137 N. Cottonwood Street, Suite 1300, Woodland, CA B. A verbal or written report shall be given to the transporting ALS crew at time of transfer of patient care. C. Service Provider Agencies shall notify YEMSA, in writing, of any medication errors or adverse events utilizing the Occurrence Incident Reporting Form. Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 1
31 644.1 YOLO COUNTY EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR AND NARCAN ADMINISTRATION FORM Date: Incident Location: Agency: Patient Initials: DOB: Male Female Assessment Epinephrine Auto-Injector Naloxone (Narcan) Post Administration Post Administration Signs and Symptoms Signs and Symptoms Assessment Assessment Dose Dose Did patient require 2 nd dose of Narcan Yes No Difficulty speaking or swallowing Difficulty breathing Hives/rash/swelling Flushed or pale skin Rapid weak pulse Blood pressure < 90 mmhg Improved speaking or swallowing Decrease in difficulty breathing Improved skin signs Improved pulse Improved blood pressure No painful stimuli Respirations irregular or absent Pupils pinpoint and non-reactive Pale or cyanotic skin Slow pulse Blood pressure < 90 mmhg Increased level of consciousness Increased respiratory rate Pupils reactive Improved skin signs Improved pulse Improved blood pressure Epinephrine: Additional Information: Administration Times: Narcan 1 st Dose: Narcan 2 nd Dose: Transfer Agency Unit #: Transfer of Care Time: Form Completed by: Signature Date
32 Yolo County Emergency Medical Services Agency Skill Sheets Revised Date: December 5, 2017 SKILLS COMPETENCY VERIFICATION: NARCAN ADMINISTRATION NAME: AGENCY: DATE: EVALUATOR: OBJECTIVE The candidate will demonstrate the ability to correctly identify the indications for Narcan and properly administer the medication. EQUIPMENT Manikin or simulated patient, required medication and administration equipment, Oxygen (O 2 ), stethoscope, pen light, appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). PERFORMANCE CRITERIA AND CONDITIONS The candidate will be presented with a manikin or simulated patient who has Signs and Symptoms (Si/Sx) of an Opioid overdose and is unconscious. The candidate will correctly assemble and administer Narcan. EVENT DOES DOES NOT 1. States the indications for the use of Narcan. Si/Sx of Opioid overdose. o Low BP o Slow weak pulse o No response to painful stimuli o Decreased respiratory rate less than (<) ten (10) beats per minute (BPM) o No breathing (Apnea) o Constricted Pinpoint Pupils o Profuse sweating o Pale or cyanotic skin 2. States the possible side effects of Narcan. Withdrawal symptoms Vomiting 3. States or demonstrates the use of appropriate PPE. 4. Checks medication for damage, proper dose, cloudy or discolored liquid and expiration date. 5. Properly assembles equipment. 6. Properly informs/instructs the patient on medication application and use. 7. Re-assesses patient for effectiveness of treatment and side effects. Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 1
33 Yolo County Emergency Medical Services Agency Skill Sheets Revised Date: December 5, 2017 SKILLS COMPETENCY VERIFICATION: EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR ADMINISTRATION NAME: AGENCY: DATE: EVALUATOR: OBJECTIVE The candidate will demonstrate the ability to correctly identify the indications for Epinephrine and properly administer the medication. EQUIPMENT Manikin or simulated patient, required auto-injector equipment, Oxygen (O 2 ), stethoscope, appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). PERFORMANCE CRITERIA AND CONDITIONS The candidate will be presented with a manikin or simulated patient who has Signs and Symptoms (Si/Sx) of Anaphylaxis and is in severe distress. The candidate will correctly assemble and administer the Epinephrine auto-injector device and properly inform/instruct the patient on its use. 1. States the indications for the use of Epinephrine. Si/Sx of Anaphylaxis. o Low BP o Rapid weak pulse o Difficulty speaking or swallowing o Difficulty breathing o Rash/Hives o Flushed or pale skin o Nausea/Vomiting o Anxiety 2. States the contraindications for the use of Epinephrine. Weight is less than (<) 15 kilograms (kg)/33 pounds (lbs). Si/Sx of an allergic reaction only. 3. States the possible side effects of Epinephrine. Rapid or irregular pulse Anxiety Dizziness Nausea/Vomiting Chest Pain 4. States or demonstrates the use of appropriate PPE. EVENT DOES DOES NOT 5. Checks medication for damage, proper dose, cloudy or discolored liquid and expiration date. 6. Properly assembles equipment. Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 1 of 2
34 Yolo County Emergency Medical Services Agency Skill Sheets Revised Date: December 5, Properly informs/instructs the patient on medication application and use. 8. Re-assesses patient for effectiveness of treatment and side effects. Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Page 2 of 2
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency
 Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services. Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual
 Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02
 PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02 Revision #5 04/19/02 Identify Dysrhythmia DEFIBRILLATE: 2 J/kg, 4 J/kg,
PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02 Revision #5 04/19/02 Identify Dysrhythmia DEFIBRILLATE: 2 J/kg, 4 J/kg,
Johnson County Emergency Medical Services Page 23
 Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies)
 SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY
 COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8061.19 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Decreased Sensorium Last Approved Date: 05/01/17 Effective Date: 05/01/19 Next Review
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8061.19 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Decreased Sensorium Last Approved Date: 05/01/17 Effective Date: 05/01/19 Next Review
ACLS Review. Pulse Oximetry to be between 94 99% to avoid hyperoxia (high oxygen tension can lead to tissue death
 ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
Contra Costa County Emergency Medical Services Drug Reference. Indication Dosing Cautions Comments
 Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
MICHIGAN. Table of Contents. State Protocols. Adult Treatment Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Adult Treatment Protocols Table of Contents 3.1 Altered Mental Status 3.2 Stroke/Suspected Stroke 3.3 Respiratory Distress 3.4 Seizures 3.5 Sepsis
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Adult Treatment Protocols Table of Contents 3.1 Altered Mental Status 3.2 Stroke/Suspected Stroke 3.3 Respiratory Distress 3.4 Seizures 3.5 Sepsis
Resuscitation Checklist
 Resuscitation Checklist Actions if multiple responders are on scene Is resuscitation appropriate? Conditions incompatible with life Advanced decision in place Based on the information available, the senior
Resuscitation Checklist Actions if multiple responders are on scene Is resuscitation appropriate? Conditions incompatible with life Advanced decision in place Based on the information available, the senior
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Naloxone Intranasal EMT OPTIONAL SKILL. Cell Phones and Pagers. Course Outline 09/2017
 EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. Course Outline Introduction and Overview
EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. Course Outline Introduction and Overview
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL
 CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
Pediatric Resuscitation
 Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION. 1. Safe scene, standard precautions. 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness. 3. Quick look (monitor)
 LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
Medical First Responder Program Protocols
 Medical Scene Safety Protocol Verify Scene Safety with Police or Dispatch UNKWN Scene Safe? Enter Continue to Appropriate Protocol Possible to Make Safe Make Safe Then Continue Exit Area and Stage Outside
Medical Scene Safety Protocol Verify Scene Safety with Police or Dispatch UNKWN Scene Safe? Enter Continue to Appropriate Protocol Possible to Make Safe Make Safe Then Continue Exit Area and Stage Outside
table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines
 table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines P1 PEDIATRIC PATIENT CARE...70 P2 APPARENT LIFE-THREATENING EVENT (ALTE)...71 P3 CARDIAC ARREST INITIAL CARE AND CPR...72 73 P4 NEONATAL CARE AND RESUSCITATION...74
table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines P1 PEDIATRIC PATIENT CARE...70 P2 APPARENT LIFE-THREATENING EVENT (ALTE)...71 P3 CARDIAC ARREST INITIAL CARE AND CPR...72 73 P4 NEONATAL CARE AND RESUSCITATION...74
EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY PREHOSPITAL PROTOCOLS
 EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY PREHOSPITAL PROTOCOLS Effective: July 1, 2017 Reviewed: November 9, 2016 Revised: November 9, 2016 EMS Agency Medical Director ALLERGIC REACTION/ANAPHYLAXIS ADULT BLS TREATMENT
EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY PREHOSPITAL PROTOCOLS Effective: July 1, 2017 Reviewed: November 9, 2016 Revised: November 9, 2016 EMS Agency Medical Director ALLERGIC REACTION/ANAPHYLAXIS ADULT BLS TREATMENT
Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off.
 1 2 EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. 3 4 5 6 Course Outline Introduction
1 2 EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. 3 4 5 6 Course Outline Introduction
Preparing for your upcoming PALS course
 IU Health PALS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming PALS course UPDATED November 2016 Course Curriculum: 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) AHA
IU Health PALS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming PALS course UPDATED November 2016 Course Curriculum: 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) AHA
MICHIGAN. State Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
Manual Defibrillation. CPR AGE: 18 years LOA: Altered HR: N/A RR: N/A SBP: N/A Other: N/A
 ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
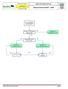 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
 Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
CARDIAC ARREST GENERAL CONSIDERATION
 CARDIAC ARREST GENERAL CONSIDERATION A. Age delineation: Infant CPR guidelines apply to victims less than one year of age; Child CPR guidelines apply to victims one year of age to the onset of adolescence
CARDIAC ARREST GENERAL CONSIDERATION A. Age delineation: Infant CPR guidelines apply to victims less than one year of age; Child CPR guidelines apply to victims one year of age to the onset of adolescence
Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent
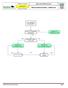 C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
DYSRHYTHMIAS. D. Assess whether or not it is the arrhythmia that is making the patient unstable or symptomatic
 DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
Portage County EMS Patient Care Guidelines. Cardiac Arrest
 Portage County EMS Patient Care Guidelines Cardiac Arrest Note: These guidelines are based on (or adapted from) the current American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency
Portage County EMS Patient Care Guidelines Cardiac Arrest Note: These guidelines are based on (or adapted from) the current American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency
Cardiac Arrest & Therapeutic Hypothermia. Continuing Education May 2012
 Continuing Education May 2012 Cardiac Arrest & Therapeutic Hypothermia Questions/comments on this CE are welcome and should be directed to: Diana Neubecker RN BSN PM NWC EMSS In-Field Coordinator dneubecker@nch.org
Continuing Education May 2012 Cardiac Arrest & Therapeutic Hypothermia Questions/comments on this CE are welcome and should be directed to: Diana Neubecker RN BSN PM NWC EMSS In-Field Coordinator dneubecker@nch.org
Consider Treatable Underlying Causes Early
 Page 1 of 8 Cardiac Arrest Timeout Checklist Assign roles for Pit Crew CPR o Compressors x 2 o Airway o Lead responsible for coordinating team, making decisions o Medications Continuous compressions at
Page 1 of 8 Cardiac Arrest Timeout Checklist Assign roles for Pit Crew CPR o Compressors x 2 o Airway o Lead responsible for coordinating team, making decisions o Medications Continuous compressions at
MICHIGAN. Table of Contents. State Protocols. General Treatment Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Number Protocol Name 1.1 General Pre-hospital Care: Regional Protocol 1.2 Abdominal Pain 1.3 Nausea and Vomiting: Regional
MICHIGAN State Protocols General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Number Protocol Name 1.1 General Pre-hospital Care: Regional Protocol 1.2 Abdominal Pain 1.3 Nausea and Vomiting: Regional
Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
A silent chest is. Pediatrics II Asthma, seizures and cardiac arrest. Children are different. Cough variant asthma. Symptoms of severe distress
 Asthma ~21% of all asthma cases are school aged Pediatrics II Asthma, seizures and cardiac arrest Identify 3 symptoms of an asthma exacerbation Bronchospasm Edema of the bronchi Increased mucus production
Asthma ~21% of all asthma cases are school aged Pediatrics II Asthma, seizures and cardiac arrest Identify 3 symptoms of an asthma exacerbation Bronchospasm Edema of the bronchi Increased mucus production
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult
 Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
PALS Review 2015 Guidelines
 PALS Review 2015 Guidelines BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. 1. Scene Safety 2. Establish Unresponsiveness 3. Check for breathing if absent or agonal (No
PALS Review 2015 Guidelines BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. 1. Scene Safety 2. Establish Unresponsiveness 3. Check for breathing if absent or agonal (No
European Resuscitation Council
 European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY
 COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY. Administration of Naloxone for Opiate Overdose
 SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Administration of Naloxone for Opiate Overdose Disclaimer: Authorization - EMT Optional Skills Only authorized Emergency Medical Technicians (EMT) who
SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Administration of Naloxone for Opiate Overdose Disclaimer: Authorization - EMT Optional Skills Only authorized Emergency Medical Technicians (EMT) who
Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV OBHG Education Subcommittee
 Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV Intravenous and Fluid Therapy Medical Directive Auxiliary Ability to initiate IV access and Ability to administer fluid and fluid boluses in general IV Therapy Actual
Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV Intravenous and Fluid Therapy Medical Directive Auxiliary Ability to initiate IV access and Ability to administer fluid and fluid boluses in general IV Therapy Actual
TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS)
 TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS) Anton Koželj, R.N., B. Sc., lecturer Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Maribor Žitna ulica 15, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia Fact s To know-how to perform basic life
TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS) Anton Koželj, R.N., B. Sc., lecturer Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Maribor Žitna ulica 15, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia Fact s To know-how to perform basic life
EMS Region Medication List 2010
 EMT-B MEDICATIONS Patient Assisted Medications (PAM) and Ambulance Stock Medications Medication Protocol/Use Dose Auto-injector (Epi-pen) Glucose (Oral) Metered-Dose Inhaler (MDI) Allergic/Anaphylactic
EMT-B MEDICATIONS Patient Assisted Medications (PAM) and Ambulance Stock Medications Medication Protocol/Use Dose Auto-injector (Epi-pen) Glucose (Oral) Metered-Dose Inhaler (MDI) Allergic/Anaphylactic
PALS Study Guide 2016
 Mandatory Precourse Self-Assessment at least 70% pass. Bring proof of completion to class. The PALS Provider exam is 50 multiple-choice questions. Passing score is 84%. Student may miss 8 questions. All
Mandatory Precourse Self-Assessment at least 70% pass. Bring proof of completion to class. The PALS Provider exam is 50 multiple-choice questions. Passing score is 84%. Student may miss 8 questions. All
EMT OPTIONAL SKILL. Cell Phones and Pagers. Epinephrine Auto-injector. Course Outline 9/2017
 EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Epinephrine Auto-injector Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. Course Outline Introduction and
EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Epinephrine Auto-injector Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. Course Outline Introduction and
SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY. Administration of Epinephrine Auto-Injector Training
 SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Administration of Epinephrine Auto-Injector Training Disclaimer: Authorization - EMT Optional Skills Only authorized Emergency Medical Technicians (EMT)
SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Administration of Epinephrine Auto-Injector Training Disclaimer: Authorization - EMT Optional Skills Only authorized Emergency Medical Technicians (EMT)
Skills: Recall the incidence of seizures Recall the causes of seizures Describe types of seizures List signs and symptoms of seizure patients
 Medical 1 Resuscitation Describe the morbidity and mortality associated with sudden cardiac arrest List the chain of survival for sudden cardiac arrest as identified by the American Heart Association Discuss
Medical 1 Resuscitation Describe the morbidity and mortality associated with sudden cardiac arrest List the chain of survival for sudden cardiac arrest as identified by the American Heart Association Discuss
ADMINISTRATIVE REQUIREMENT MANUAL EFFECTIVE DATE
 PURPOSE: I. To establish the minimum requirements for a first responder training course in first aid, which all first responders must take, in order to meet the requirements of M.G.L. c. 111, 201 and 105
PURPOSE: I. To establish the minimum requirements for a first responder training course in first aid, which all first responders must take, in order to meet the requirements of M.G.L. c. 111, 201 and 105
ACLS Prep. Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep.
 November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
Pediatric advanced life support. Management of decreased conscious level in children. Virgi ija Žili skaitė 2017
 Pediatric advanced life support. Management of decreased conscious level in children Virgi ija Žili skaitė 2017 Life threatening conditions: primary assessment, differential diagnostics and emergency care.
Pediatric advanced life support. Management of decreased conscious level in children Virgi ija Žili skaitė 2017 Life threatening conditions: primary assessment, differential diagnostics and emergency care.
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Name General Pre-hospital Care Abdominal Pain Nausea
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Name General Pre-hospital Care Abdominal Pain Nausea
Cardiac arrest simulation teaching (CASTeach) session
 Cardiac arrest simulation teaching (CASTeach) session Instructor guidance Key learning outcomes Overall aim: Scenarios should be facilitated by the Instructor in such a way that they are performed correctly.
Cardiac arrest simulation teaching (CASTeach) session Instructor guidance Key learning outcomes Overall aim: Scenarios should be facilitated by the Instructor in such a way that they are performed correctly.
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case. VF/Asystole
 Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
What works? What doesn t? What s new? Terry M. Foster, RN
 What works? What doesn t? What s new? Terry M. Foster, RN 2016 Changes Updated every 5 years Last update was 2010 All recommendations have been heavily researched with studies involving large number of
What works? What doesn t? What s new? Terry M. Foster, RN 2016 Changes Updated every 5 years Last update was 2010 All recommendations have been heavily researched with studies involving large number of
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES. -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P
 PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P General: CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES - More often the result and not the cause of acute cardiovascular emergencies - Typically the end result
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P General: CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES - More often the result and not the cause of acute cardiovascular emergencies - Typically the end result
Summary of 2018 Protocol Changes PROTOCOL TITLE PAGE # LINE # ORIGINAL TEXT NEW TEXT
 Important Numbers 3 Regional Programs telephone and fax numbers have been updated. Health Care Facility 5, 14 Calvert Memorial Hospital CalvertHealth Medical Center Health Care Facility 6 Code 239 Frederick
Important Numbers 3 Regional Programs telephone and fax numbers have been updated. Health Care Facility 5, 14 Calvert Memorial Hospital CalvertHealth Medical Center Health Care Facility 6 Code 239 Frederick
Competency Log Professional Responder Courses
 Competency Log Professional Responder Courses Check off each competency once successfully demonstrated. This log may be used as a support tool when teaching a Professional Responder course. Refer to the
Competency Log Professional Responder Courses Check off each competency once successfully demonstrated. This log may be used as a support tool when teaching a Professional Responder course. Refer to the
PALS Case Scenario Testing Checklist Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction
 Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update What s New for 2010? 3 CPR. 4 4 Steps of BLS Survey 5 CPR 6 CPR.
 1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
CSI Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment
 CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
ILS Protocols Content Page
 Altered Mental Status/Coma Asthma Chest Pain CPAP Hypoglycemia Intraosseous Infusion (EZ IO) Adult Intraosseous Infusion (EZIO) Pediatric Poisoning and/or Overdose Seizure Spinal Immob. Decision Tree s
Altered Mental Status/Coma Asthma Chest Pain CPAP Hypoglycemia Intraosseous Infusion (EZ IO) Adult Intraosseous Infusion (EZIO) Pediatric Poisoning and/or Overdose Seizure Spinal Immob. Decision Tree s
Epinephrine Intramuscular (IM) Injection Administration EMT Optional Scope Highlights
 Epinephrine Intramuscular (IM) Injection Administration EMT Optional Scope Highlights Nor-Cal EMS February 2018 version 1 Special Thank You To Seattle / King County EMS NY State Department of Health, Check
Epinephrine Intramuscular (IM) Injection Administration EMT Optional Scope Highlights Nor-Cal EMS February 2018 version 1 Special Thank You To Seattle / King County EMS NY State Department of Health, Check
Supplemental Digital Content 1. Simulation scenarios and critical action checklist for debriefing
 Supplemental Digital Content 1. Simulation scenarios and critical action checklist for debriefing Simulation Scenario #1 I. Title (ACS)-VF-Asystole-ROSC II. Target learner 6-7 medical students per team
Supplemental Digital Content 1. Simulation scenarios and critical action checklist for debriefing Simulation Scenario #1 I. Title (ACS)-VF-Asystole-ROSC II. Target learner 6-7 medical students per team
Portage County EMS Annual Skills Labs
 Portage County EMS Annual Skills Labs Scope: Provide skills labs for all Emergency Medical Responders and First Response EMTs to assure proficiency of skills and satisfy the Wisconsin State approved Operational
Portage County EMS Annual Skills Labs Scope: Provide skills labs for all Emergency Medical Responders and First Response EMTs to assure proficiency of skills and satisfy the Wisconsin State approved Operational
Restore adequate respiratory and circulatory conditions. Reduce pain
 Pre-hospital management of the trauma patient is best performed by an integrated team focused on minimizing the time from injury to definitive care at an appropriate trauma center. Dispatchers, first responders,
Pre-hospital management of the trauma patient is best performed by an integrated team focused on minimizing the time from injury to definitive care at an appropriate trauma center. Dispatchers, first responders,
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes
 Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket
 BLS BASICS: Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket facemask or AMBU bag) Adults call it in, start CPR, get AED Child CPR First, Phone call second
BLS BASICS: Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket facemask or AMBU bag) Adults call it in, start CPR, get AED Child CPR First, Phone call second
COUNTY OF SAN LUIS OBISPO HEALTH AGENCY PUBLIC HEALTH DEPARTMENT
 COUNTY OF SAN LUIS OBISPO HEALTH AGENCY PUBLIC HEALTH DEPARTMENT Michael Hill Health Agency Director Penny Borenstein, MD, MPH Health Officer/Public Health Director SLO County Emergency Medical Services
COUNTY OF SAN LUIS OBISPO HEALTH AGENCY PUBLIC HEALTH DEPARTMENT Michael Hill Health Agency Director Penny Borenstein, MD, MPH Health Officer/Public Health Director SLO County Emergency Medical Services
Emergency Department Guideline. Anaphylaxis
 Emergency Department Guideline Inclusion criteria: 1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to hours) with a AND (b OR c): a. Skin and/or mucosa (pruritus, flushing, hives, angioedema) b. Respiratory compromise
Emergency Department Guideline Inclusion criteria: 1. Acute onset of an illness (minutes to hours) with a AND (b OR c): a. Skin and/or mucosa (pruritus, flushing, hives, angioedema) b. Respiratory compromise
In accordance with protocols, this patient should be transported to which medical facility?
 NOTE: Please select the most appropriate answer based on the Westchester Regional On-Line Medical Control Physician (OLMC) Regional System Overview, as well as current regional and state EMS protocols
NOTE: Please select the most appropriate answer based on the Westchester Regional On-Line Medical Control Physician (OLMC) Regional System Overview, as well as current regional and state EMS protocols
CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health
 CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health Manual Subject Emergency Medical Services Administrative Policies and Procedures Table of Contents
CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health Manual Subject Emergency Medical Services Administrative Policies and Procedures Table of Contents
Sierra Sacramento Valley EMS Agency Policy/Protocol Manual Table of Contents
 SECTION 100 STATE LAW AND REGULATION 100 Index 101 California Health And Safety Code, Division 2.5 Emergency Medical Services 102 California Code Of Regulations, Title 22, Division 9 SECTION 200 LEMSA
SECTION 100 STATE LAW AND REGULATION 100 Index 101 California Health And Safety Code, Division 2.5 Emergency Medical Services 102 California Code Of Regulations, Title 22, Division 9 SECTION 200 LEMSA
2. General Cardiac Arrest Protocol Medical Newborn/Neonatal. Protocol 8-3 Resuscitation 4. Medical Supraventricular
 PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SECTION: Pediatric Cardiovascular Emergencies REVISED: 06/2017 Section 8 1. Cardiac Arrest Unknown Rhythm (i.e. Protocol 8-1 BLS) 2. General Cardiac Arrest Protocol 8-2 3. Medical Newborn/Neonatal
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SECTION: Pediatric Cardiovascular Emergencies REVISED: 06/2017 Section 8 1. Cardiac Arrest Unknown Rhythm (i.e. Protocol 8-1 BLS) 2. General Cardiac Arrest Protocol 8-2 3. Medical Newborn/Neonatal
Sierra Sacramento Valley EMS Agency
 Sierra Sacramento Valley EMS Agency BLS AUTO-INJECTOR EPINEPHRINE ADMINISTRATION OPTIONAL SKILL (UPDATED 08/2017) In order for PSFA, EMR or EMT personnel to administer auto-injector epinephrine, they must:
Sierra Sacramento Valley EMS Agency BLS AUTO-INJECTOR EPINEPHRINE ADMINISTRATION OPTIONAL SKILL (UPDATED 08/2017) In order for PSFA, EMR or EMT personnel to administer auto-injector epinephrine, they must:
HealthCare Training Service
 HealthCare Training Service Advanced Life Support Exam Time: Perusal Time: 20 minutes 5 minutes Total Marks: 25 Instructions: Read each question carefully. Using a pencil, record your response to each
HealthCare Training Service Advanced Life Support Exam Time: Perusal Time: 20 minutes 5 minutes Total Marks: 25 Instructions: Read each question carefully. Using a pencil, record your response to each
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms. Introduction to the Algorithms
 Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Introduction to the Algorithms Cardiac Arrest Algorithms Prehospital Medication Profiles Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Introduction to the Algorithms Cardiac Arrest Algorithms Prehospital Medication Profiles Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate
Toxins and Environmental: HEAT- and COLD-RELATED EMERGENCIES. Accidental Hypothermia/Cold Exposure
 Toxins and Environmental: HEAT- and COLD-RELATED EMERGENCIES Accidental Hypothermia/Cold Exposure Goal: To aid EMS Providers in: the recognition and treatment of systemic effects of accidental hypothermia
Toxins and Environmental: HEAT- and COLD-RELATED EMERGENCIES Accidental Hypothermia/Cold Exposure Goal: To aid EMS Providers in: the recognition and treatment of systemic effects of accidental hypothermia
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac
 Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013
 NUMBERS Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013 Weight in kg = 8 + (age in yrs X 2) Neonate (less than 1 month)
NUMBERS Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013 Weight in kg = 8 + (age in yrs X 2) Neonate (less than 1 month)
3. The signs of Compartment Syndrome are listed in the General Crush Protocol. a. True b. False
 Schoolcraft Medical Control Authority (MCA) Protocol and Procedures Test, February 2015, Version 1 MFR/EMT/SPECIALIST/PARAMEDIC 1. Schoolcraft County Medical Control Protocols and Procedures can be found
Schoolcraft Medical Control Authority (MCA) Protocol and Procedures Test, February 2015, Version 1 MFR/EMT/SPECIALIST/PARAMEDIC 1. Schoolcraft County Medical Control Protocols and Procedures can be found
Michigan Adult Cardiac Protocols TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Asystole Section 2-1 Bradycardia Section 2-2 Cardiac Arrest General Section 2-3 Cardiac Arrest ROSC Section 2-4 Chest Pain Acute Coronary Syndrome
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Asystole Section 2-1 Bradycardia Section 2-2 Cardiac Arrest General Section 2-3 Cardiac Arrest ROSC Section 2-4 Chest Pain Acute Coronary Syndrome
STAYTON FIRE DISTRICT PROTOCOL QUIZ
 STAYTON FIRE DISTRICT PROTOCOL QUIZ Name 1. Please list the appropriate EMS Level for each of the Scope of Practice items below EMR Emergency Medical Responder B Basic Conduct primary and secondary patient
STAYTON FIRE DISTRICT PROTOCOL QUIZ Name 1. Please list the appropriate EMS Level for each of the Scope of Practice items below EMR Emergency Medical Responder B Basic Conduct primary and secondary patient
Unstable: Hypotension/Shock, Fever, Altered Mental Status, Chest discomfort, Acute Heart Failure Saturation <94%, Systolic BP < 90mmHg
 Bradycardia Heart Rate less than 50/min Stable: Monitor Seek expert help Treat Reversible Causes Unstable Signs and Symptoms: chest pain, shortness of breath, altered mental status, weak, Hypotension,
Bradycardia Heart Rate less than 50/min Stable: Monitor Seek expert help Treat Reversible Causes Unstable Signs and Symptoms: chest pain, shortness of breath, altered mental status, weak, Hypotension,
Update of CPR AHA Guidelines
 Update of CPR AHA Guidelines Donald Hal Shaffner Course objective is to have an updated understanding of the American Heart Association s treatment algorithms for the management of cardiac decompensation
Update of CPR AHA Guidelines Donald Hal Shaffner Course objective is to have an updated understanding of the American Heart Association s treatment algorithms for the management of cardiac decompensation
PALS PRETEST. PALS Pretest
 PALS PRETEST 1. A child with a fever, immune system compromise, poor perfusion and hypotension is most likely to be experiencing which type of shock A. cardiogenic B. Neurogenic C. Septic D. Hypovolemic
PALS PRETEST 1. A child with a fever, immune system compromise, poor perfusion and hypotension is most likely to be experiencing which type of shock A. cardiogenic B. Neurogenic C. Septic D. Hypovolemic
ADULT TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 A1 Adult Patient Care A2 Chest Pain / Suspected ACS A3 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR A4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia A5 PEA / Asystole A6 Symptomatic Bradycardia A7 Ventricular
A1 Adult Patient Care A2 Chest Pain / Suspected ACS A3 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR A4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia A5 PEA / Asystole A6 Symptomatic Bradycardia A7 Ventricular
12-LEAD ECG PROCEDURE ALWAYS USE BODY SUBSTANCE ISOLATION PRECAUTIONS
 Oct 1, 2015 draft COUNTY OF MARIN EMS ALS PR 12 12-LEAD ECG PROCEDURE ALWAYS USE BODY SUBSTANCE ISOLATION PRECAUTIONS Patients with a medical history and/ or presenting complaints consistent with Acute
Oct 1, 2015 draft COUNTY OF MARIN EMS ALS PR 12 12-LEAD ECG PROCEDURE ALWAYS USE BODY SUBSTANCE ISOLATION PRECAUTIONS Patients with a medical history and/ or presenting complaints consistent with Acute
Mesa County EMS Protocol Test 2016
 Mesa County EMS Protocol Test 2016 1. Which of the following is incorrect? a. Each EMS and Fire agency should have protocols in place for evaluation of personnel involved in fire suppression operations
Mesa County EMS Protocol Test 2016 1. Which of the following is incorrect? a. Each EMS and Fire agency should have protocols in place for evaluation of personnel involved in fire suppression operations
Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist
 Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist Introduction. Basic Life Support (BLS). Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death
Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist Introduction. Basic Life Support (BLS). Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death
Adult Basic Life Support
 Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all pediatric cardiac arrests. If an arrest is of a known traumatic origin refer to the Dead on
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all pediatric cardiac arrests. If an arrest is of a known traumatic origin refer to the Dead on
PM-03 PED ALLERGY/ANAPHYLAXIS. Protocol SECTION: PM-03 PROTOCOL TITLE: PED ALLERGY/ANAPHYLAXIS REVISED: 01MAY2018
 SECTION: PROTOCOL TITLE: REVISED: 01MAY2018 BLS SPECIFIC CARE: See General Pediatric Care Protocol PM-1 - Determine patient s color category on length based resuscitation tape (Broselow Tape) Epi Pen Protocol
SECTION: PROTOCOL TITLE: REVISED: 01MAY2018 BLS SPECIFIC CARE: See General Pediatric Care Protocol PM-1 - Determine patient s color category on length based resuscitation tape (Broselow Tape) Epi Pen Protocol
Learning Station Competency Checklists
 Learning Station Competency Checklists Cardiac Arrest: Shockable Rhythm Team Dynamics Practice Demonstrates effective team dynamics (see, below) Performs manual maneuvers to open airway* Initiates assisted
Learning Station Competency Checklists Cardiac Arrest: Shockable Rhythm Team Dynamics Practice Demonstrates effective team dynamics (see, below) Performs manual maneuvers to open airway* Initiates assisted
Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies. CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED
 Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED THREE FAMILIAR CARDIAC CONDITIONS Angina Pectoris Acute Myocardial Infarction Congestive Heart Failure ANGINA PECTORIS Chest
Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED THREE FAMILIAR CARDIAC CONDITIONS Angina Pectoris Acute Myocardial Infarction Congestive Heart Failure ANGINA PECTORIS Chest
SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES
 EMS Agency SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES Pediatric Advanced Life Support Policies Emergency Medical Services TITLE: Pediatric Routine Medical Care EMS Policy No. 5800 Pediatric Routine
EMS Agency SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES Pediatric Advanced Life Support Policies Emergency Medical Services TITLE: Pediatric Routine Medical Care EMS Policy No. 5800 Pediatric Routine
