PERITONEAL DIALYSIS. Frequently Asked Questions
|
|
|
- Janis Pitts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PERITONEAL DIALYSIS Frequently Asked Questions How will I know if PD is working well? What Problems can happen on PD? What medicines will I need to take? Will I need to be on a special diet or fluid restriction?
2
3 How will I know if PD is working well? Most people, who have been on PD for a few weeks, start to feel quite well again. When you first start PD you may still be passing urine and this will help clear some waste and fluid from your body. Over the first two years on PD your urine output may decline, and your PD prescription may need to be changed. Symptoms such as feeling weak and tired, nausea and lack of appetite may be a sign that you are not receiving enough dialysis. A number of different blood and PD fluid tests can be carried out to assess how well your dialysis is working. What tests will I need to check how well my PD is working? People on PD need to have regular blood tests. Blood tests can tell how well PD is working, how well nourished you are, the state of your bones, how acid your blood is as well as your blood count, and iron level. The substances measured include: Creatinine: Potassium: Urea: Phosphate: Glucose: Bicarbonate: Albumin: This is the waste produced by muscles. A high creatinine level is not harmful, but it is an indicator of other waste in the blood. For an average sized person on PD the target level is below 800 mmols/l. This mineral is normally present in the blood. If the level gets too high or low it can cause the heart to stop. The normal level is mmols/l. Crisis levels are less than 2 or greater than 8, but most Kidney Units prefer you to have a large safety margin! Urea is produced when the food we eat is broken down. The normal level is mmols/l, but in dialysis patients a realistic target to aim for is a urea level of less than 25mmols/l. A high urea level will ften cause sickness. Phosphate is one of the substances in the blood necessary to keep bones healthy. The normal level is mmols/l. The target level on dialysis is less than 1.8 mmols. A high level can cause itching and bone disease. Diet and phosphate binders can help to control the level. The normal level of blood glucose is mmols/l. For diabetics on PD the high glucose in the PD fluid (needed to remove fluid) can cause problems. If patients absorb a lot of glucose from the PD fluid they may put on body weight. This is a measure of the acidity of the blood. If the blood bicarbonate level is low, this means the blood is too acid, and can cause weakness and fatigue. The normal level of bicarbonate in the blood is mmol/l. If the level is lower than normal, the amount of PD may need to be increased to reduce the acid level in the blood, or a bicarbonate supplement may be needed. This is a type of protein, and is an indicator of how well nourished 1
4 Calcium: Haemoglobin: Ferritin: PFT: a person is. The normal level is grams/l. The target level is around 35 grams/l but this varies between Units, as Hospitals use different methods to measure albumin. This mineral is needed to keep bones healthy. The normal level of calcium in the blood is mmol/l. Haemoglobin, or Hb as it is known, is the substance in the blood that carries oxygen around the body. The normal level is g/dl in women, and in men. A low Hb is called anaemia. The target level for people on PD is around 11-12g/dl. Iron supplements and EPO are common treatments for anaemia. Iron is needed to produce red blood cells, and a guide to how much iron is in the body is to do a blood test for ferritin. The target level for ferritin in the blood is above 200 mg/l. A Peritoneal Function Test. In some Units people are asked to collect all the PD fluid that they drain out, along with all the urine they pass in a 24-hour period. The fluid is sampled, tested, and the amount of waste cleared by PD, and by the kidneys (if the person passes urine) is then calculated. This is known as a Peritoneal Function Test (PFT) or Adequacy Test. What are the signs/symptoms of PD not working well? When people are not getting enough dialysis, they are sometimes referred to as under-dialysed. The main symptoms are tiredness, feeling weak, and going off food. However, these symptoms can also be due to other things such as: Anaemia (a low blood count) Stomach Ulcer Constipation A high level of urea in the blood can cause nausea and lack of appetite, leading to a loss of body weight or muscle size. What will happen if my results show my PD is not working well? A number of options can be considered to improve a person s PD. These include: Increasing the volume of the PD bags Doing an extra exchange during the day, or at night with a machine. Using special PD fluid such as Icodextrin. Changing from CAPD to APD. Increasing the time on APD, changing the number of exchanges, or the time each bag remains in the abdomen, or doing additional daytime exchanges. But, sometimes changing the type of PD, the volume or number of bags used, will not 2
5 be sufficient or be acceptable to the person, and the best option might be to change to haemodialysis. What problems can happen on PD? The occurrence of problems on PD and their severity can vary greatly between individuals. The 4 main areas in which problems can occur are listed below: 1. Psychological Problems Anxiety and Depression: As well as all the anxieties felt by most people at some time in their lives, kidney patients also have additional anxieties relating to their condition and their treatment. You will need to understand the reasons for your anxieties and any medical causes that can be treated. Having a better understanding often helps people to cope. It sometimes helps to share anxieties, and identify ways of coping. Many Units have a Renal Social Worker, a psychologist, or members of the Kidney Patient Association as well as doctors and nurses who will have experience of helping people to cope with their anxieties. People on dialysis are as prone to depression as anyone else. Occasionally people will need medical treatment for depression, but quite often, after a period of feeling low, people find ways of coping and adjusting to life on PD. Body image: Some people on PD do not like the way PD affects their appearance. The abdomen tends to get stretched by PD, giving it a rounded appearance. Young people in particular may be very conscious of their body shape, especially if they are slim. Keeping fit and doing exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles will help. The PD catheter can also cause body image problems. People on PD have to come to terms with the fact that they now have a plastic tube permanently protruding from their abdomen. Some people find this very difficult to cope with, feeling that they have been mutilated. They may also worry that the catheter might put off a sexual partner. Some people make a joke or tell a funny story about why the catheter is there when showing it to someone for the first time. It is important to talk about your feelings with your partner, PD nurse or doctor who can refer you to someone who may be able to help you come to terms with your changed body image. People on PD may need to remind themselves, that people who really love them, will continue to do so, regardless of how they look. 2. Infections Peritonitis: This is an infection inside the tummy. The most common reason why people on PD get peritonitis is that they touch the connection between the bag of fluid and the catheter. However, even if PD exchanges are scrupulously clean, infection 3
6 can still enter the abdomen from the outside world through the catheter. People can expect to get on average less than one attack of peritonitis every year. So it is not that common. Indeed, some people never get it. On APD peritonitis is less likely to occur than on CAPD, probably because fewer catheter connections are required. A person will know when they have peritonitis because the dialysis fluid that drains out will be cloudy. This fluid is normally see-through. The signs and symptoms are usually one or more of the following: Cloudy bag Tummy pain Vomiting A raised temperature Peritonitis is treated by adding one or more antibiotics to the fresh dialysis fluid, and by antibiotic tablets. Patients are not usually admitted to hospital when they have peritonitis. Occasionally, a person may get several attacks of peritonitis in a row. The doctor may then decide that an operation to remove the old PD catheter, and put in a new one is needed straight away. Alternatively, the doctor may decide that it is better to delay replacing the catheter and to rest the abdomen by not using it for PD for a period of 4 to 6 weeks. If this happens, the person will usually need to have haemodialysis until PD is resumed. Peritonitis is usually caused by one of two types of bacteria: Staphylococcus epidermidis Staphylococcus aureus Both of the above infections are often known as staph infections. In rare but serious cases, peritonitis is caused by a fungus (usually a type called candida albicans). If peritonitis is caused by a fungus, it will be treated straight away by an operation to remove the PD catheter. Drugs are not very effective against fungi, but the problem soon goes away if the catheter is removed. The catheter can still be replaced at a later date. If a person has many bad attacks of peritonitis, PD may no longer be suitable for them. They will then have to change to haemodialysis as their long-term treatment. Exit Site and Tunnel Infections: This is an infection at the point where the PD catheter comes out through the skin. This causes a red tender area around the exit site, and when someone has this type of infection, squeezing around the exit site may produce some pus. 4
7 Some people get exit site infections regularly, whereas others may never get them. Keeping the catheter taped down to the skin will help reduce the likelihood of an exit site infection, especially when the catheter is new. Most Units advise people to put a clean dressing over their exit site each day, after they have showered. Exit site infections respond well to antibiotics, usually given either as tablets or creams. Sometimes, a single intravenous injection of an antibiotic called vancomycin is needed. There is usually no need to remove the PD catheter. Occasionally, an exit site infection spreads down the catheter tunnel (the route taken by the catheter through the tummy wall). This type of infection is called a tunnel infection. Antibiotics are not always effective when someone has a tunnel infection. An operation to remove the catheter will then be necessary. It may be possible to insert a new catheter at the same operation, but this will depend on how extensive the infection is (there is a risk that the new catheter could also get infected). 3. Catheter/Drain Problems Leak of PD fluid: In most people, the seal around the catheter exit site (where the catheter leaves the abdomen) works properly. PD fluid drains in and out of the abdomen through the tube without any leakage. However, in some people, the PD fluid leaks out around the catheter, wetting the dressing over the exit site. If a leaking catheter is rested (not used for dialysis) for 2 to 4 weeks, it will usually seal up again, and become watertight. Occasionally, however, a leak may recur even if the catheter is rested. It may then be necessary to have an operation to take out the leaking catheter. A new catheter, at a different site, is usually put in during the same operation. In some men on PD, fluid leaks into the scrotum, or into the vagina in women and causes swelling. If this type of leak occurs, PD must be stopped temporarily until the leak has healed. A test can be carried out to check the location and size of a leak, and whether surgery is needed to repair it. A special dye is put down the catheter and x-rays show where the dye goes - known as a peritonealogram. Drainage Problems: One of the most common problems with PD - especially when people first start PD is poor drainage of the dialysis fluid. The most common reason for poor drainage is constipation. If a person becomes constipated, the bowels press against the catheter and make the dialysis fluid drain very slowly. The fluid may also get trapped in pockets of bowel, preventing it from draining properly. So it is very important to avoid constipation, perhaps by taking regular laxatives. The PD catheter may become blocked with a substance called fibrin, which is a form of protein. It looks like tiny strands of cotton wool and is completely harmless. A patient may be able to clear the catheter simply by squeezing the tubing to dislodge 5
8 the fibrin. Alternatively, a nurse will be able to clear the catheter by injecting water, saline (a salt solution) or a de-clotting agent called heparin, down the catheter. This is a simple procedure and will not need an operation. Some patients have to inject a small quantity of heparin into a single bag each day (usually the overnight bag) to dissolve any fibrin that accumulates in the peritoneum and hence keep the catheter clear. Another reason for poor drainage is that the catheter is in the wrong position. Sometimes a displaced catheter will float back into the right position naturally. If this does not happen, then an operation may be required to correct the position of the catheter. Blood in PD fluid: Sometimes when PD fluid is drained out at the end of an exchange it may look slightly red or pinkish in colour. This happens if any of the small blood vessels in the peritoneum are broken. This can be caused by lifting something heavy or can happen while playing sport. In females, red or pink bags can occur during their period (menstruation). People are advised to contact their Unit if the bags don t clear up in a few days, or if the fluid in the bags look very bloody, and not just stained red or pink. 4. Physical Problems Fluid overload: The amount of used fluid that is drained out of the body after PD is about 1 to 1.5 litres per day more than the amount of fresh dialysis fluid that is put in. This extra fluid is in effect, the PD person s urine. It does not increase in quantity however much the patient drinks. This means that people on PD have to restrict their drinking to avoid problems due to fluid overload, particularly when they stop passing urine. Fluid overload leads to an increase in body weight, high blood pressure, swollen ankles and shortness of breath. Constipation: Many people on PD are prone to constipation. There are several reasons for this. People on PD (like many others who are not on dialysis!) do not have enough fibre (roughage) in their diet. Wholemeal or brown bread, fresh fruit and vegetables are good sources of fibre. Restrictions on fluid intake, certain fruit (patients on a potassium restriction), and decreased level of activity can all contribute to constipation. Constipation can cause problems with poor drainage of PD fluid. It is therefore important to avoid constipation, by taking regular laxatives, such as lactulose and senokot (senna). Hernia: A hernia occurs when a wall of muscle weakens and lets an organ or tissue out from inside. Hernias can cause difficulties for people on PD. If a person has a hernia before the PD catheter is put in, it can become more of a problem afterwards. The daily draining of PD fluid into and out of the abdomen can cause the hernia to become 6
9 bigger (and more painful). If nothing is done, the bowel can become stuck inside the hernia, thereby blocking the bowel. This will require an emergency operation. If an existing hernia is noticed by the surgeon during an operation to insert a PD catheter, it will be repaired during the same operation to prevent it causing problems in the future. If a hernia develops months or years after the catheter insertion, an operation is needed to repair it. Itching: The normal level of phosphate in the blood is 0.8 to 1.4 mmol/l. On PD, people sometimes have a raised blood phosphate level. It is thought that a high phosphate level causes itching. Blood phosphate levels can be controlled by taking phosphate binders, and reducing phosphate intake in the diet. Sometimes medications such as hydroxyzine or chlorpheniramine (piriton) are used to relieve itching until the blood phosphate level is reduced. Iron deficiency and anaemia can also cause itching. Pain and discomfort: Some people find PD is uncomfortable, or even painful, particularly when they first start treatment. Most people will get used to having fluid in their abdomen, but sometimes small people will be unable to tolerate more than litres of fluid. A feeling of fullness or of being bloated after eating is quite common. People with back problems may be unable to tolerate CAPD and switch to APD (using smaller volumes of fluid by day, and larger volumes when lying down at night) or haemodialysis. Cramp or Restless legs at night: Cramps and restless legs at night affect some people on PD. An imbalance in the levels of water and salt in the blood may be a factor in cramp. Stretching and massaging the limb can help. Quinine sulphate taken at bedtime helps prevent cramp. Restless leg syndrome (an irresistible urge to move the legs at night) can occur in kidney failure. It can be very stressful as it disrupts sleep, leading to tiredness during the day. A tablet called Clonazepam is sometimes used to treat this problem. It may also help the person to sleep. What medicines will I need to take? The most common types of medicines that patients on PD need to take are: Phosphate binders to reduce bone disease Iron, and Erythropoietin to reduce anaemia (low blood count) Anti-hypertensive medicines to control high blood pressure Laxatives to prevent constipation Phosphate binders When the kidneys are working properly they get rid of excess phosphate from the body. Phosphate, which is found in dairy products, nuts and meat, is needed to keep bones healthy. If phosphate levels become too high in kidney failure this can damage bones and blood vessels. Medications such as Calcium carbonate, Calcichew, or Alucaps, if 7
10 taken before meals can bind with phosphate in the food you eat so that the phosphate is not absorbed into the body and the level in the blood becomes lower. There are several different types of phosphate binder medication, your doctor and renal dietician will be able to discuss which one might suit you best. Iron and Erythropoietin Healthy kidneys produce a substance called Erythropoietin (known as EPO for short). EPO is used in the bone marrow to help produce red blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen around the body and, if the level is low, it is called anaemia. If EPO is injected into the body (using a small needle) this can help produce red blood cells. EPO is usually given 1-3 times a week. People on EPO will use up Iron quickly making red blood cells, and they may need an iron supplement. This can be given by tablet (eg Ferrous sulphate or Pregaday) or by injection. Anti-hypertensive medicines High blood pressure (hypertension) is fairly common in people with kidney problems. Blood pressure is affected by the amount of fluid in the body as well as the width of the vessels (arteries) that the blood flows through. It is therefore important for people on PD to control the level of fluid in their blood. This is done by balancing what fluid goes in with what comes out. Often one or more medications are needed to control blood pressure. Laxatives Constipation causes drainage problems on PD and it is therefore important to avoid becoming constipated. Lactulose is a liquid, which can be taken daily to prevent constipation: it works by softening the faeces in the bowel. Senokot (senna) can also be used daily to prevent constipation: it works by stimulating the bowel to move. Both drugs can cause stomach cramps in some people. It is important to let the pharmacist know that you are on dialysis if you are buying other laxatives, as some are not suitable for people with kidney failure. Will I need to be on a special diet or fluid restriction? Why are some foods restricted? Many people on PD are able to enjoy a normal diet without too many restrictions. This is because PD is a continuous form of dialysis, and waste from the food digested is continuously being removed. Dietary restrictions of certain foods are usually stricter in the period leading up to needing dialysis (pre dialysis patients). The foods that are sometimes restricted are those which are high in potassium, or phosphate. It is important to discuss your blood results with the doctor or dietician, before restricting your intake of potassium, phosphate, or calcium. If your blood levels are too low this can be harmful too. 8
11 The normal level of potassium in the blood is mmols/l. A very high or low level of potassium can cause the heart to stop. Your Dietician will advise you if you need to increase or decrease your potassium intake. Phosphate (normal level mmol/l) and calcium (normal level mmol/l) levels in the blood need to be kept around normal limits to help prevent bone disease or damage to blood vessels. A combination of diet, dialysis and drugs is usually the best way to keep calcium and phosphate levels normal. Why do I need to eat more protein? Protein is an essential nutrient, which enables the body to build muscles and repair itself. The main sources in the diet are meat, fish, dairy products, and pulses (such as beans and lentils). The normal level of a protein called albumin is around g/l. People on PD lose protein along with the waste they drain out when they do an exchange. Quite often people are advised to eat extra protein, and some people are prescribed drinks or powders that contain extra protein. it is important to discuss your blood test results with the doctor or dietician before changing your intake of protein. 9
12 The National Kidney Federation cannot accept responsibility for information provided. The above is for guidance only. Patients are advised to seek further information from their own doctor National Kidney Federation (NKF) All rights reserved Last Reviewed October 2017
Peritoneal Dialysis. Choosing your logo. V2.0 logos. information. you can trust. Certified Member. The Information Standard
 Use of The Information Standard s Member Logos Peritoneal Dialysis Patient Information Choosing your logo The Information Standard has four logo versions for its members. They are designed to fit neatly
Use of The Information Standard s Member Logos Peritoneal Dialysis Patient Information Choosing your logo The Information Standard has four logo versions for its members. They are designed to fit neatly
INTRODUCTION TO HAEMODIALYSIS
 INTRODUCTION TO HAEMODIALYSIS Why do I need dialysis? What is dialysis? How does haemodialysis work? Where will I have my treatment? Will dialysis cure my kidney failure? Will dialysis keep me well? I
INTRODUCTION TO HAEMODIALYSIS Why do I need dialysis? What is dialysis? How does haemodialysis work? Where will I have my treatment? Will dialysis cure my kidney failure? Will dialysis keep me well? I
Peritoneal dialysis. Overview. Preparing for dialysis. Links to sections in topic Other topics available on website
 Peritoneal dialysis This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. Visit www.infokid.org.uk to find more topics about conditions, tests & diagnosis, treatments and supporting
Peritoneal dialysis This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. Visit www.infokid.org.uk to find more topics about conditions, tests & diagnosis, treatments and supporting
Managing Fluid, Diet and Medications
 Managing Fluid, Diet and Medications This lesson covers: Fluid and body weight Managing your diet Understanding your medications It is important that you feel comfortable with the information and procedures
Managing Fluid, Diet and Medications This lesson covers: Fluid and body weight Managing your diet Understanding your medications It is important that you feel comfortable with the information and procedures
HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL. Living well with Kidney Disease
 HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL Living well with Kidney Disease KIDNEY DISEASE CAN AFFECT ANYONE! 1 HEALTHYSTART PROGRAMME HEALTHYSTART is a lifestyle management programme to assist you to remain healthy
HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL Living well with Kidney Disease KIDNEY DISEASE CAN AFFECT ANYONE! 1 HEALTHYSTART PROGRAMME HEALTHYSTART is a lifestyle management programme to assist you to remain healthy
Haemodialysis. Patient Information. Working together for better patient information. Health & care information you can trust. The Information Standard
 Haemodialysis Patient Information Health & care information you can trust The Information Standard Certified Member Working together for better patient information Haemodialysis (HD) helps to remove the
Haemodialysis Patient Information Health & care information you can trust The Information Standard Certified Member Working together for better patient information Haemodialysis (HD) helps to remove the
Your Kidney Health. Your Choices. Chronic Kidney Disease
 Your Kidney Health Your Choices Your doctor may have told you that you have chronic kidney disease (CKD or advanced kidney disease; or, you may be in kidney failure, and may have to make a decision about
Your Kidney Health Your Choices Your doctor may have told you that you have chronic kidney disease (CKD or advanced kidney disease; or, you may be in kidney failure, and may have to make a decision about
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Peritoneal Dialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. There are 2 types of PD: continuous ambulatory
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peritoneal Dialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and basic principles of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). 2.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peritoneal Dialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and basic principles of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). 2.
What Your Kidneys Do and What Happens When They Fail
 Patient Education Chapter 2 Page 1 What Your Kidneys Do and What Happens When They Fail Objectives: 1. Understand basic kidney functions. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some treatments used for it.
Patient Education Chapter 2 Page 1 What Your Kidneys Do and What Happens When They Fail Objectives: 1. Understand basic kidney functions. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some treatments used for it.
LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR
 LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR Treating Your Hernia with Laparoscopy When You Have a Hernia Anyone can have a hernia. This is a weakness or tear in the wall of the abdomen. It often results from years of wear
LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR Treating Your Hernia with Laparoscopy When You Have a Hernia Anyone can have a hernia. This is a weakness or tear in the wall of the abdomen. It often results from years of wear
Getting Knowledge About Kidney Disease
 Last Reviewed Getting Knowledge About Kidney Disease Have you been told that you have late stage kidney disease? Choose Your Lifestyle On Dialysis There are two kinds of dialysis. Dialysis can be done
Last Reviewed Getting Knowledge About Kidney Disease Have you been told that you have late stage kidney disease? Choose Your Lifestyle On Dialysis There are two kinds of dialysis. Dialysis can be done
Patient Education Kidney Early Education Program (KEEP) Chapter 2 bjectives: Overview 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms
 Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 2 What Your Kidneys Do And what happens when they fail Objectives: 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some ways to treat it. 3. Know the
Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 2 What Your Kidneys Do And what happens when they fail Objectives: 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some ways to treat it. 3. Know the
DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Stage 5 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Stage 5 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
Patient Education Programme. Kidney Options Guiding you when kidneys fail
 Patient Education Programme Kidney Options Guiding you when kidneys fail About the kidneys What do healthy kidneys do? Your two kidneys work more than you realise. The kidneys remove excess body water
Patient Education Programme Kidney Options Guiding you when kidneys fail About the kidneys What do healthy kidneys do? Your two kidneys work more than you realise. The kidneys remove excess body water
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) stages 3b to 5 Overview
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) stages 3b to 5 Overview This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. This leaflet has the overview only. Go to www.infokid.org.uk to find
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) stages 3b to 5 Overview This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. This leaflet has the overview only. Go to www.infokid.org.uk to find
Oxford Kidney Unit. Treatment options for chronic kidney disease A brief overview
 Oxford Kidney Unit Treatment options for chronic kidney disease A brief overview You may feel well at the moment and may not have any symptoms from your kidney disease, but it is important that you understand
Oxford Kidney Unit Treatment options for chronic kidney disease A brief overview You may feel well at the moment and may not have any symptoms from your kidney disease, but it is important that you understand
Treatment Options Not Not access
 Treatment Options Treatment options for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) CKD is a permanent condition. Treatment will: Help the patient feel better Not cure the disease Not make the kidneys start working again
Treatment Options Treatment options for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) CKD is a permanent condition. Treatment will: Help the patient feel better Not cure the disease Not make the kidneys start working again
Haemodialysis Blood Results
 Haemodialysis Blood Results Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient information leaflets.htm Introduction
Haemodialysis Blood Results Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient information leaflets.htm Introduction
What Your Kidneys Do
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What Your Kidneys Do And what happens with kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia. 3. Know the common causes of kidney
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What Your Kidneys Do And what happens with kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia. 3. Know the common causes of kidney
YOUR KIDNEYS AREN T WORKING PROPERLY.
 When you re born, everything works perfectly. Then something goes wrong and you ask: YOUR KIDNEYS AREN T WORKING PROPERLY. What does this mean? How can you stay healthy? HOW DO I DEAL WITH THIS? WHAT ROLE
When you re born, everything works perfectly. Then something goes wrong and you ask: YOUR KIDNEYS AREN T WORKING PROPERLY. What does this mean? How can you stay healthy? HOW DO I DEAL WITH THIS? WHAT ROLE
Appendicitis. Diagnosis and Surgery
 Appendicitis Diagnosis and Surgery What Is Appendicitis? Your side may hurt so much that you called your doctor. Or maybe you went straight to the hospital emergency room. If the symptoms came on quickly,
Appendicitis Diagnosis and Surgery What Is Appendicitis? Your side may hurt so much that you called your doctor. Or maybe you went straight to the hospital emergency room. If the symptoms came on quickly,
Discharge Information following Bowel Surgery
 Discharge Information following Bowel Surgery Here is some information to help with your recovery at home and advice about returning to normal activities following bowel surgery. We hope this will be helpful
Discharge Information following Bowel Surgery Here is some information to help with your recovery at home and advice about returning to normal activities following bowel surgery. We hope this will be helpful
Kidney Disease Treatment Options
 Page 1 Fact sheet The kidneys play a number of important roles in your body such as: extracting excess water to make urine (wee) controlling your blood pressure filtering waste products and toxins from
Page 1 Fact sheet The kidneys play a number of important roles in your body such as: extracting excess water to make urine (wee) controlling your blood pressure filtering waste products and toxins from
Treatment choices for someone with Stage 5 kidney disease are:
 Information for patients about advanced kidney disease Dialysis and non-dialysis treatments DOCUMENT PREPARED FOR This information is to help you understand some key issues about dialysis; it is designed
Information for patients about advanced kidney disease Dialysis and non-dialysis treatments DOCUMENT PREPARED FOR This information is to help you understand some key issues about dialysis; it is designed
Heart failure (Advice for patients)
 Heart failure (Advice for patients) Name----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Date of Birth---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Heart failure (Advice for patients) Name----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Date of Birth---------------------------------------------------------------------------
A VIDEO SERIES. living WELL. with kidney failure WHAT IS KIDNEY FAILURE?
 A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure WHAT IS KIDNEY FAILURE? Contents 2 Introduction 11 What is a kidney transplant? 3 What will I learn? 12 What role do diet and medi- 5 Who is on my 7 healthcare
A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure WHAT IS KIDNEY FAILURE? Contents 2 Introduction 11 What is a kidney transplant? 3 What will I learn? 12 What role do diet and medi- 5 Who is on my 7 healthcare
Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery)
 Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Hemodialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. Treatment Options for Kidney Disease
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
Oxford Kidney Unit What do my blood and dialysis results mean? Information for patients
 Oxford Kidney Unit What do my blood and dialysis results mean? Information for patients page 2 If you are on haemodialysis (HD) or peritoneal dialysis (PD) this leaflet is for you. It will provide you
Oxford Kidney Unit What do my blood and dialysis results mean? Information for patients page 2 If you are on haemodialysis (HD) or peritoneal dialysis (PD) this leaflet is for you. It will provide you
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate
 TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
LAPAROSCOPIC GALLBLADDER SURGERY
 LAPAROSCOPIC GALLBLADDER SURGERY Treating Gallbladder Problems with Laparoscopy A Common Problem If you ve had an attack of painful gallbladder symptoms, you re not alone. Gallbladder disease is very common.
LAPAROSCOPIC GALLBLADDER SURGERY Treating Gallbladder Problems with Laparoscopy A Common Problem If you ve had an attack of painful gallbladder symptoms, you re not alone. Gallbladder disease is very common.
Urinary Catheter Passport for patients
 Urinary Catheter Passport for patients Nursing A guide for patients and visitors Contents Why people need a urinary catheter...1 How your bladder and kidneys work...1 What is a catheter?...3 Drainage bags...3
Urinary Catheter Passport for patients Nursing A guide for patients and visitors Contents Why people need a urinary catheter...1 How your bladder and kidneys work...1 What is a catheter?...3 Drainage bags...3
Chronic Kidney Disease: A guide for patients
 Chronic Kidney Disease: A guide for patients our doctor has recently told you that you have chronic kidney disease. Getting this news is an important first step towards taking control of your health. Take
Chronic Kidney Disease: A guide for patients our doctor has recently told you that you have chronic kidney disease. Getting this news is an important first step towards taking control of your health. Take
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~
 Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
Understanding Your Hemodialysis Access Options UNDERSTANDING YOUR PERITONEAL DIALYSIS OPTIONS
 Understanding Your Hemodialysis Access Options UNDERSTANDING YOUR PERITONEAL DIALYSIS OPTIONS HOW THE KIDNEYS WORK Inside each nephron, a special blood vessel called a glomerulus works like a strainer
Understanding Your Hemodialysis Access Options UNDERSTANDING YOUR PERITONEAL DIALYSIS OPTIONS HOW THE KIDNEYS WORK Inside each nephron, a special blood vessel called a glomerulus works like a strainer
TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~
 TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~ To learn about TransUrethral Resection of a Bladder Tumour, you will need to know what these words mean: The bladder stores urine that is made
TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~ To learn about TransUrethral Resection of a Bladder Tumour, you will need to know what these words mean: The bladder stores urine that is made
Shared Decision Making established kidney failure dialysis. Deciding what type of dialysis to choose for established kidney failure
 Shared Decision Making established kidney failure Next clinical review date March 2018 Deciding what type of to choose for established kidney failure This short decision aid is to help you decide what
Shared Decision Making established kidney failure Next clinical review date March 2018 Deciding what type of to choose for established kidney failure This short decision aid is to help you decide what
Signs of a Heart Attack
 Diabetes and Heart Disease Awareness Healthy Living with Diabetes sm and Heart Healthy Living sm Wisconsin Newsletter Spring 2012 Signs of a Heart Attack What are My Risks for Having a Heart Attack? Even
Diabetes and Heart Disease Awareness Healthy Living with Diabetes sm and Heart Healthy Living sm Wisconsin Newsletter Spring 2012 Signs of a Heart Attack What are My Risks for Having a Heart Attack? Even
Blood pressure and kidney disease
 Blood pressure and High blood pressure is the second most common cause of. Your heart pumps your blood through tubes (blood vessels) called arteries and veins. When your blood moves through the blood vessels,
Blood pressure and High blood pressure is the second most common cause of. Your heart pumps your blood through tubes (blood vessels) called arteries and veins. When your blood moves through the blood vessels,
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY
 Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
GASTRECTOMY. Date of Surgery. Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34
 GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS
 Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS Information for Patients and Carers F:\CONTINENCE\Acute Urianary Retention\04-12\005- Indwelling Urinary Cathter Leaflet - A4-13-02-09.doc
Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS Information for Patients and Carers F:\CONTINENCE\Acute Urianary Retention\04-12\005- Indwelling Urinary Cathter Leaflet - A4-13-02-09.doc
Ileal Conduit Diversion Surgery
 Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Hernia surgery in adults
 Page 1 of 9 Hernia surgery in adults Introduction This leaflet will give you information about having hernia surgery. It also answers some of the commonly asked questions and outlines some of the risks
Page 1 of 9 Hernia surgery in adults Introduction This leaflet will give you information about having hernia surgery. It also answers some of the commonly asked questions and outlines some of the risks
Understanding Congestive Heart Failure
 Understanding Congestive Heart Failure Your health care team offers this information to help you and your family cope with congestive heart failure. It defines congestive heart failure, discusses ways
Understanding Congestive Heart Failure Your health care team offers this information to help you and your family cope with congestive heart failure. It defines congestive heart failure, discusses ways
Robot Assisted Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
 Robot Assisted Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy What is a robot assisted total laparoscopic hysterectomy? It is the removal of the uterus, including the cervix, through four small (1/2-1 ) abdominal incisions
Robot Assisted Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy What is a robot assisted total laparoscopic hysterectomy? It is the removal of the uterus, including the cervix, through four small (1/2-1 ) abdominal incisions
Patient & Family Guide. Bowel Surgery.
 Patient & Family Guide 2016 Bowel Surgery www.nshealth.ca Bowel Surgery This pamphlet will answer some of your questions about your stay in hospital and care at home. We hope this information will help
Patient & Family Guide 2016 Bowel Surgery www.nshealth.ca Bowel Surgery This pamphlet will answer some of your questions about your stay in hospital and care at home. We hope this information will help
AV Fistula for Dialysis
 AV Fistula for Dialysis Introduction Before starting regular hemodialysis sessions, you must first prepare a vascular access. A vascular access is the site on your body where blood is removed and returned
AV Fistula for Dialysis Introduction Before starting regular hemodialysis sessions, you must first prepare a vascular access. A vascular access is the site on your body where blood is removed and returned
Laparoscopic Bowel Surgery
 Patient & Family Guide Laparoscopic Bowel Surgery 2016 www.nshealth.ca Laparoscopic Bowel Surgery Your surgeon has chosen for you to have laparoscopic bowel surgery instead of open bowel surgery. This
Patient & Family Guide Laparoscopic Bowel Surgery 2016 www.nshealth.ca Laparoscopic Bowel Surgery Your surgeon has chosen for you to have laparoscopic bowel surgery instead of open bowel surgery. This
A VIDEO SERIES. living WELL. with kidney failure HOW KIDNEY FAILURE AFFECTS YOUR BODY
 A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure HOW KIDNEY FAILURE AFFECTS YOUR BODY Contents 2 Introduction 3 What will I learn? 4 How does kidney failure affect my body? 5 How can I protect my heart
A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure HOW KIDNEY FAILURE AFFECTS YOUR BODY Contents 2 Introduction 3 What will I learn? 4 How does kidney failure affect my body? 5 How can I protect my heart
COMMON MEDICINES USED IN CKD CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE 1 This information is intended to help you understand why you need to take your medicines. There are multiple medicines that are used to control the symptoms related to CKD. You
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE 1 This information is intended to help you understand why you need to take your medicines. There are multiple medicines that are used to control the symptoms related to CKD. You
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME
 CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
Diverticular Disease Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.
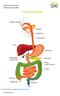 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
Pentostatin (Nipent )
 Pentostatin (Nipent ) Pentostatin (Nipent ) This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. Your treatment will be fully explained by your doctor or nurse, who will be happy to answer any questions.
Pentostatin (Nipent ) Pentostatin (Nipent ) This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. Your treatment will be fully explained by your doctor or nurse, who will be happy to answer any questions.
Know The Facts About Home Dialysis Choices
 Know The Facts About Home Dialysis Choices Fact Sheet www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents What are my choices for dialysis at home?...3 Why consider home hemodialysis?...4 What are the different types of
Know The Facts About Home Dialysis Choices Fact Sheet www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents What are my choices for dialysis at home?...3 Why consider home hemodialysis?...4 What are the different types of
Haemodialysis access with an arteriovenous fistula
 Haemodialysis access with an arteriovenous fistula NHS Logo here Health & care information you can trust The Information Standard Certified Member Working together for better patient information If you
Haemodialysis access with an arteriovenous fistula NHS Logo here Health & care information you can trust The Information Standard Certified Member Working together for better patient information If you
Chapter 6, Part Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99.
 Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99. 2. Your body is made up of,,,, and many other materials.
Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 6, Part 1. 1. Read Activity 6A - Choosing a Meal and orally attempt the procedure and discussion on page 99. 2. Your body is made up of,,,, and many other materials.
A PATIENT S GUIDE. Author: Dr. A. Patel. Editor: Dr. A. Kadri
 A PATIENT S GUIDE Author: Dr. A. Patel Editor: Dr. A. Kadri 1 ACKNOWLEDGMENT I would like to thank all of those individuals involved in producing this educational book for patients. The printing of this
A PATIENT S GUIDE Author: Dr. A. Patel Editor: Dr. A. Kadri 1 ACKNOWLEDGMENT I would like to thank all of those individuals involved in producing this educational book for patients. The printing of this
Diet and nutrition. AL amyloidosis. Living well with. Infosheet Series. AL amyloidosis. Infoline:
 Diet and nutrition This Infosheet explains what a well-balanced diet is, what can make it difficult to maintain when you are an AL amyloidosis patient, when a special diet might be necessary and tips for
Diet and nutrition This Infosheet explains what a well-balanced diet is, what can make it difficult to maintain when you are an AL amyloidosis patient, when a special diet might be necessary and tips for
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse
 Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
Appendix Surgery. (Appendectomy) Your surgery and recovery at home. This booklet belongs to: Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital
 Appendix Surgery (Appendectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets
Appendix Surgery (Appendectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets
Recovering at home. How will I feel when I get home? How should I look after my wound?
 How will I feel when I get home? Following your operation it is normal to have feelings of stress, anxiety or depression. Being affected emotionally is normal. It may help to talk about how you feel with
How will I feel when I get home? Following your operation it is normal to have feelings of stress, anxiety or depression. Being affected emotionally is normal. It may help to talk about how you feel with
Looking After Yourself with Kidney Disease
 Page 1 Fact sheet Looking After Yourself with Kidney disease is called a silent disease as there are often no warning signs. You can lose up to 90 per cent of your kidney function before getting any symptoms.
Page 1 Fact sheet Looking After Yourself with Kidney disease is called a silent disease as there are often no warning signs. You can lose up to 90 per cent of your kidney function before getting any symptoms.
Post-Operative Laparoscopic Appendectomy Guide. Dr. Buck Parker, MD FACS Board Certified Surgeon
 Post-Operative Laparoscopic Appendectomy Guide Dr. Buck Parker, MD FACS Board Certified Surgeon www.drbuckparker.com Thanks! Thanks so much for downloading my laparoscopic appendectomy guide! This guide
Post-Operative Laparoscopic Appendectomy Guide Dr. Buck Parker, MD FACS Board Certified Surgeon www.drbuckparker.com Thanks! Thanks so much for downloading my laparoscopic appendectomy guide! This guide
Bowel Resection Surgery (Open Method)
 Bowel Resection Surgery (Open Method) What is a bowel resection? A bowel resection is surgery to remove a part of the large or small intestine. These parts are shown on this diagram. small intestine large
Bowel Resection Surgery (Open Method) What is a bowel resection? A bowel resection is surgery to remove a part of the large or small intestine. These parts are shown on this diagram. small intestine large
About barium meals and swallows. Information for patients Radiology
 About barium meals and swallows Information for patients Radiology What is a barium meal or barium swallow? A barium meal or swallow is a procedure that allows a doctor, called a radiologist, to look at
About barium meals and swallows Information for patients Radiology What is a barium meal or barium swallow? A barium meal or swallow is a procedure that allows a doctor, called a radiologist, to look at
YOUR OPERATION EXPLAINED
 RIGHT HEMICOLECTOMY This leaflet is produced by the Department of Colorectal Surgery at Beaumont Hospital supported by an unrestricted grant to better Beaumont from the Beaumont Hospital Cancer Research
RIGHT HEMICOLECTOMY This leaflet is produced by the Department of Colorectal Surgery at Beaumont Hospital supported by an unrestricted grant to better Beaumont from the Beaumont Hospital Cancer Research
Open Surgery for AAA
 Open Surgery for AAA A Weakened Blood Vessel What does it mean to have an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)? This is a balloon-like bulge in a major blood vessel, the aorta. The bulge forms at a weak place
Open Surgery for AAA A Weakened Blood Vessel What does it mean to have an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)? This is a balloon-like bulge in a major blood vessel, the aorta. The bulge forms at a weak place
Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair
 1 Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair Hernia is a medical condition where a part of the intestine bulges out of the weak abdominal muscles. Inguinal hernia is a type of hernia which occurs in the groin
1 Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair Hernia is a medical condition where a part of the intestine bulges out of the weak abdominal muscles. Inguinal hernia is a type of hernia which occurs in the groin
Limited Bowel Resection. Surgery for Crohn s Disease
 Limited Bowel Resection Surgery for Crohn s Disease What Is Crohn s Disease? Crohn s disease is inflammation (irritation and swelling) of the digestive tract. Crohn s disease occurs anywhere from the mouth
Limited Bowel Resection Surgery for Crohn s Disease What Is Crohn s Disease? Crohn s disease is inflammation (irritation and swelling) of the digestive tract. Crohn s disease occurs anywhere from the mouth
How do I keep healthy?
 Produced July 2016 Page 1 Fact sheet Indigenous health How do I keep healthy? You look after those kidneys and they can look after you It is never too late Smoking, high blood pressure and high sugar levels
Produced July 2016 Page 1 Fact sheet Indigenous health How do I keep healthy? You look after those kidneys and they can look after you It is never too late Smoking, high blood pressure and high sugar levels
LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY INFORMATION LEAFLET
 LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY INFORMATION LEAFLET Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty Page 1 of 8 LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY This leaflet has been written to answers questions that you may have about your operation. If
LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY INFORMATION LEAFLET Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty Page 1 of 8 LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY This leaflet has been written to answers questions that you may have about your operation. If
Mr Sanjeev Sarin MS FRCS. Aortic Aneurysms Patient Information Sheet
 Aortic Aneurysms Patient Information Sheet The aim of this information sheet is to ensure that you understand the nature of the treatment you wish to undertake. Please read it carefully and discuss any
Aortic Aneurysms Patient Information Sheet The aim of this information sheet is to ensure that you understand the nature of the treatment you wish to undertake. Please read it carefully and discuss any
Retropubic Prostatectomy
 2014 Retropubic Prostatectomy Retropubic Prostatectomy What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland that makes a fluid that helps sperm move. It also gives nourishment for the sperm. It is about the size
2014 Retropubic Prostatectomy Retropubic Prostatectomy What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland that makes a fluid that helps sperm move. It also gives nourishment for the sperm. It is about the size
KIDNEY TRANSPLANT - A TREATMENT OPTION
 KIDNEY TRANSPLANT - A TREATMENT OPTION Page 1/5 WHAT IS A KIDNEY TRANSPLANT? When kidney failure becomes very advanced, your kidneys are so damaged they can no longer do their job. A transplant is a treatment
KIDNEY TRANSPLANT - A TREATMENT OPTION Page 1/5 WHAT IS A KIDNEY TRANSPLANT? When kidney failure becomes very advanced, your kidneys are so damaged they can no longer do their job. A transplant is a treatment
Select the dialysis treatment option that is best for you and your family.
 PEP CONNECT PEP Talk Outline P a t i e n t E d u c a t i o n P r o g r a m Your Treatment Options Part 1 Peritoneal Dialysis Select the dialysis treatment option that is best for you and your family. This
PEP CONNECT PEP Talk Outline P a t i e n t E d u c a t i o n P r o g r a m Your Treatment Options Part 1 Peritoneal Dialysis Select the dialysis treatment option that is best for you and your family. This
Fistula for Hemodialysis
 St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Kidney and Urinary Program Fistula for Hemodialysis What is a fistula? A fistula is the joining of an artery and a vein by a surgeon. The fistula is called an access. It
St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Kidney and Urinary Program Fistula for Hemodialysis What is a fistula? A fistula is the joining of an artery and a vein by a surgeon. The fistula is called an access. It
About Your Dialysis Treatment
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Your Dialysis Treatment This information explains dialysis at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK). Your Kidneys and Their Functions Your kidneys are 2 bean-shaped organs
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Your Dialysis Treatment This information explains dialysis at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK). Your Kidneys and Their Functions Your kidneys are 2 bean-shaped organs
Hernia Surgery in Adults
 Page 1 of 7 Hernia Surgery in Adults Introduction This leaflet provides information on hernias in the adult patient and the treatment options available. This leaflet is intended as a guide and is not a
Page 1 of 7 Hernia Surgery in Adults Introduction This leaflet provides information on hernias in the adult patient and the treatment options available. This leaflet is intended as a guide and is not a
Breast Surgery. Breast Surgery
 Words to know... The breast area has many parts: fibrous tissue glandular tissue fat lymph channels and nodes Fibrous tissue anchors the breast to the chest and provides structural support for the breast.
Words to know... The breast area has many parts: fibrous tissue glandular tissue fat lymph channels and nodes Fibrous tissue anchors the breast to the chest and provides structural support for the breast.
VIDE. Vincristine given via intravenous (IV) infusion over 10 minutes Etoposide & doxorubicin given together via IV infusion over 4 hours
 VIDE VIDE This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may reduce the risk of the cancer coming back, for others it may
VIDE VIDE This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may reduce the risk of the cancer coming back, for others it may
What You Need to Know About Peritoneal Dialysis
 What You Need to Know About Peritoneal Dialysis Getting the Most From Your Treatment 11-10-0511_AboutPeritonealDialysis_V4.indd 1 6/23/06 2:51:01 PM National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes
What You Need to Know About Peritoneal Dialysis Getting the Most From Your Treatment 11-10-0511_AboutPeritonealDialysis_V4.indd 1 6/23/06 2:51:01 PM National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes
Produced by The Kidney Foundation of Canada
 51 HELPFUL TIP There is no standard kidney diet : what you eat may change as your kidney function or your medications change, or if you have other conditions like diabetes. If you re on dialysis, you ll
51 HELPFUL TIP There is no standard kidney diet : what you eat may change as your kidney function or your medications change, or if you have other conditions like diabetes. If you re on dialysis, you ll
Enhanced Recovery Programme Liver surgery
 Enhanced Recovery Programme Liver surgery General Surgery Patient information leaflet Introduction When you are admitted to hospital for your surgery you will be taking part in an enhanced recovery programme.
Enhanced Recovery Programme Liver surgery General Surgery Patient information leaflet Introduction When you are admitted to hospital for your surgery you will be taking part in an enhanced recovery programme.
In-patient brachytherapy for gynaecological cancer. Cancer Services Information for patients
 In-patient brachytherapy for gynaecological cancer Cancer Services Information for patients i Introduction This booklet provides information about brachytherapy (a type of internal radiotherapy). We hope
In-patient brachytherapy for gynaecological cancer Cancer Services Information for patients i Introduction This booklet provides information about brachytherapy (a type of internal radiotherapy). We hope
CATHETER PASSPORT. Looking after your Urinary Catheter. The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter.
 CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
London Strategic Clinical Networks. My AKI. Guidance for patients with, or recovering from, acute kidney injury
 London Strategic Clinical Networks My AKI Guidance for patients with, or recovering from, acute kidney injury Supporting the delivery of equitable, high quality AKI care through collaboration www.londonaki.net
London Strategic Clinical Networks My AKI Guidance for patients with, or recovering from, acute kidney injury Supporting the delivery of equitable, high quality AKI care through collaboration www.londonaki.net
advice on prevention
 Women & Children s Directorate Urinary Tract Infection advice on prevention information for children and their families 2 Urinary tract infection (UTI for short) is one of the commonest bacterial diseases
Women & Children s Directorate Urinary Tract Infection advice on prevention information for children and their families 2 Urinary tract infection (UTI for short) is one of the commonest bacterial diseases
CHRONIC KIDNEY FAILURE
 CHRONIC KIDNEY FAILURE Overview Chronic kidney disease, also called chronic kidney failure, describes the gradual loss of kidney function. Your kidneys filter wastes and excess fluids from your blood,
CHRONIC KIDNEY FAILURE Overview Chronic kidney disease, also called chronic kidney failure, describes the gradual loss of kidney function. Your kidneys filter wastes and excess fluids from your blood,
Expectations and Post Op Instructions: Robotic Cystectomy / Ileal Conduit.
 Expectations and Post Op Instructions: Robotic Cystectomy / Ileal Conduit. You are about to undergo a major operation. The healing process takes time and we would like for you to observe the following
Expectations and Post Op Instructions: Robotic Cystectomy / Ileal Conduit. You are about to undergo a major operation. The healing process takes time and we would like for you to observe the following
Iron treatment for people with chronic kidney disease (CKD)
 Iron treatment for people with chronic kidney disease (CKD) Information for patients Oxford Kidney Unit If you have chronic kidney disease or are receiving peritoneal dialysis (PD) or hospital dialysis
Iron treatment for people with chronic kidney disease (CKD) Information for patients Oxford Kidney Unit If you have chronic kidney disease or are receiving peritoneal dialysis (PD) or hospital dialysis
Hernia Operations. What is a hernia? What does the operation involve? What are the benefits of an operation?
 Hernia Operations Hernia Operations What is a hernia? The abdomen (the medical word for the tummy) contains many organs such as the liver spleen and intestines (the medical word for insides ) and these
Hernia Operations Hernia Operations What is a hernia? The abdomen (the medical word for the tummy) contains many organs such as the liver spleen and intestines (the medical word for insides ) and these
Patient information sheet: BuTrans Patch This information should be read in conjunction with the Taking Opioids for pain information leaflet
 Page 1 of 6 Patient information sheet: BuTrans Patch This information should be read in conjunction with the Taking Opioids for pain information leaflet What type of drug is it? BuTrans transdermal patches
Page 1 of 6 Patient information sheet: BuTrans Patch This information should be read in conjunction with the Taking Opioids for pain information leaflet What type of drug is it? BuTrans transdermal patches
After Your Bariatric Surgery
 After Your Bariatric Surgery Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what problems to look out for how to care for yourself at home about your follow-up appointment who to
After Your Bariatric Surgery Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what problems to look out for how to care for yourself at home about your follow-up appointment who to
Caring for a Nephrostomy and what is Ureteric Stenting
 Useful contacts: Macmillan Cancer Support Tel: 0808 808 00 00 www.macmillan.org.uk Buckinghamshire Healthcare NHS Trust Cancer Education, Information & Support Service Tel: 01296 316954 How can I help
Useful contacts: Macmillan Cancer Support Tel: 0808 808 00 00 www.macmillan.org.uk Buckinghamshire Healthcare NHS Trust Cancer Education, Information & Support Service Tel: 01296 316954 How can I help
The Kidneys. The kidneys are vital organs. Two bean-shaped organs, about the size of a fist
 Kidney Health Coach The Kidneys The kidneys are vital organs Two bean-shaped organs, about the size of a fist Each kidney connects to the bladder by a thin tube called a ureter What do the kidneys do?
Kidney Health Coach The Kidneys The kidneys are vital organs Two bean-shaped organs, about the size of a fist Each kidney connects to the bladder by a thin tube called a ureter What do the kidneys do?
Constipation. What are the signs and symptoms of constipation? Less than three bowel movements per week. Pain or discomfort when opening your bowels
 Infosheet Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is usually diagnosed when your bowels are moving less than three times per week. When you are constipated your bowel movements may be dry, hard
Infosheet Constipation What is constipation? Constipation is usually diagnosed when your bowels are moving less than three times per week. When you are constipated your bowel movements may be dry, hard
Gynaecology Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Vaginal repair Gynaecology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives information about vaginal repair surgery used to treat a vaginal prolapse. The leaflet explains what a
Vaginal repair Gynaecology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives information about vaginal repair surgery used to treat a vaginal prolapse. The leaflet explains what a
Patient Information Leaflet. Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation
 Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
