Incidence and diagnosis of unilateral arterial cerebral infarction in newborn infants *
|
|
|
- Daniella Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J. Perinat. Med. 33 (2005) Copyright by Walter de Gruyter Berlin New York. DOI /JPM Short communication Incidence and diagnosis of unilateral arterial cerebral infarction in newborn infants * Sven Schulzke 1, **, Peter Weber 2, Juerg Luetschg 2 and Hubert Fahnenstich 1 1 Department of Neonatology, University Children s Hospital, Basel, Switzerland 2 Department of Neuropediatrics, University Children s Hospital, Basel, Switzerland Abstract Aims: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is accepted as the gold standard for the diagnosis of arterial cerebral infarction (ACI), but few studies have reported the incidence of neonatal ACI based on MRI findings. We provide new population-based epidemiologic and diagnostic data on all infants diagnosed between 1997 and 2002 in our center with an MRI-confirmed diagnosis of unilateral neonatal ACI. Results: Nine patients were identified, giving an incidence of 1:2300 unilateral ACIs in our inborn population. In all patients the middle cerebral artery was affected. Seven patients showed epileptic seizures, usually starting within the first 3 days of life. EEG was pathologic in all patients. Only three infarctions were diagnosed by ultrasound. Initial MRI established diagnosis of ACI in eight out of nine patients and subsequent MRI described the exact location of infarctions in all patients. Six out of nine patients developed hemiparesis and five had deficits in language development. There is a substantial need for special care facilities and long-term therapeutic interventions. Conclusions: The incidence of neonatal ACI is higher than previously reported. The sensitivity of early cerebral ultrasound for diagnosis of ACI is low. Seizures in the first 3 days of life combined with pathologic EEG findings should lead to MRI, regardless of normal cerebral ultrasound. *A part of the data in this study was presented as a poster at the Pediatric Academic Societies Meeting, May 2003, Seattle, WA, USA. **Corresponding author: Sven Schulzke, MD Department of Neonatology University Children s Hospital Roemergasse 8 CH-4005 Basel/Switzerland Tel.: q , Fax: q sven.schulzke@unibas.ch Keywords: Arterial cerebral infarction; magnetic resonance imaging; newborn infants. Introduction Symptomatic unilateral arterial cerebral infarction (ACI) in newborn infants usually occurs in the territory of a major cerebral artery, most often in the middle cerebral artery (MCA) w1x, with a predominance of the left side w3x. The majority of infants do not suffer from asphyxia, but present with seizures during the very first days of life w7x. Cranial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is accepted as the gold standard for the diagnosis of ACI w8x, while the diagnostic role of cerebral ultrasound is controversial w1, 4, 5x. Few studies have used MRI for diagnosis during the neonatal period w1, 8x and few population-based epidemiologic data exist. Most authors estimate an incidence of 1:4000 ACIs based on a study that used computed tomography (CT) and data from w2, 10x. With neonatal MRI routinely available, we hypothesize that detection rates of ACI should be higher. The objective of this study was to provide current populationbased epidemiologic data on the incidence of unilateral ACI in newborns and to elucidate the diagnostic value of newborn seizures, electroencephalography (EEG), cerebral ultrasound and MRI for the diagnosis of ACI. Methods Patients All newborns born between 1/1/1997 and 12/31/2002 and diagnosed in the University Children s Hospital, Basel with a discharge diagnosis of MRI-proven unilateral ACI were identified using full-text searchable electronic databases of patient records and by hand-searching discharge letters from the Department of Neonatology and the Department of Pediatric Neurology. Population Our perinatal center consists of two major women s hospitals of the two Swiss cantons Basel-Stadt and Basel- Landschaft, with two associated tertiary-care neonatal units of the University Children s Hospital, Basel. The two
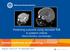
2 Schulzke et al., Arterial cerebral infarction in newborn infants 171 women s hospitals cover 50% of all deliveries in the two cantons and serve as both regional hospitals and referral centers. Inborn newborns were born in the two abovementioned hospitals. In addition, there are four obstetric departments within the two provinces referring ill outborn children, and four hospitals in neighboring provinces that refer critically ill outborn children. Hospitals referring outborn children were free to choose our center for neonatal care or others from neighboring provinces. Therefore, to allow for a well-defined population, incidence was calculated for inborn children only, based on total birth rates from 1997 to 2002 in the two associated women s hospitals. Evaluation of patient data Diagnostic features Seven out of nine patients showed neonatal seizures, and in six patients seizures started within the first 3 days of life. In four patients we observed focal clonic seizures, while three patients presented with generalized seizures consisting of apnea and generalized clonic and tonic convulsions. EEG recordings from all identified neonates were carried out within 48 h of the onset of seizures. All neonatal EEG recordings showed pathologic findings as follows: abnormal lateralized background (5), periodic lateralized epileptiform discharges (1), and focal hypersynchrony (7). In only three of eight patients did cerebral ultrasound show focal echogenic lesions suggesting ACI. Information was obtained from obstetric and pediatric patient records. Patient charts, EEGs, cerebral ultrasounds, MRI images and data on neurodevelopmental follow-up were evaluated retrospectively. Diagnostic procedures All instrumental diagnostic procedures were performed during routine neonatal care. Initial EEGs with a minimum duration of 30 min and cerebral ultrasound studies were recorded in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) within 48 h after the onset of seizures. Ultrasound was carried out by consultant neonatologists and certified pediatric radiologists using Aloka SSD-1700 and Medison Digital Gaia ultrasound scanners with MHz multifrequency sector transducers. MRI was carried out on a 1.0-T Picker system during the neonatal period in all but three patients (numbers 3, 4 and 7), who received their first MRI at the ages of 2, 3 and 8 months of life, respectively. Results Identified patients From 11 patients with MRI-proven ACI, two were excluded because of multiple bilateral infarctions following severe asphyxia. Eight out of nine infants with unilateral ACI were identified during the neonatal period; one boy, who was without pathological findings as a neonate, was admitted to our center at the age of 4 months because of left-sided spasticity. Infants were born between 35 and 42 weeks of gestation. There were 13,901 inborn live births during the study period, and six of the nine identified patients were inborn. This translates to an incidence of 1:2316 unilateral neonatal ACIs. Characteristics and diagnostic details of all patients are shown in Table 1. Figure 1 (A) Axial T1-weighted MRI (day 7) and (B) coronal cerebral ultrasound (day 5) of patient no. 8. MRI shows enhanced signal intensity of the left posterior hemisphere due to ischemic infarction of the left middle cerebral artery, while the cerebral ultrasound is unremarkable.
3 172 Schulzke et al., Arterial cerebral infarction in newborn infants Table 1 Patient characteristics and diagnostic data of infants suffering from unilateral arterial cerebral infarction (ns9) No Place GA Sex Pregnancy CTG Delivery Apgar Neurologic Cerebral EEG MRI Affected of birth score symptoms ultrasound regions (19/59) 1 Inborn 35 M Normal N Spontaneous, 6/10 Day 1 Day 1 N Day 1 background Day 3 Hemisphere cervical focal clonic abnormal, focal infarction Basal ganglia Twisted cord seizures left hypersynchrony mca left Internal capsula left 2 Inborn 41 M Poly- N Spontaneous, 9/10 Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 background Day 11 Hemisphere hydramnion cervical generalized echogenic normal, focal parietooccipital Twisted cord seizures lesion left hypersynchrony bleeding left, left infarction? vascular abnormality? 3 Outborn 41 M Normal N Spontaneous 9/6 Day 1 Day 1, Day 12 background Week 9 Hemisphere generalized day 13 N abnormal, focal infarction Basal ganglia seizures hypersynchrony mca right Internal capsula right 4 Inborn 41 F Normal P Poor 8/9 Day 1 Day 1 N Day 2 background Day 11 Hemisphere progress, generalized Day 2 abnormal, infarction Basal ganglia vacuum seizures echogenic PLEDs left mca left lesion left 5 Inborn 36 F Methadone, N Spontaneous, 6/8 Opiate Day 5 Day 7 background Day 22 Hemisphere nicotine amniotic fluid withdrawal echogenic normal, focal infarction Basal ganglia meconium- syndrome, lesion left hypersynchrony mca left stained No seizures left 6 Inborn 42 M normal N Poor 8/10 Day 2 focal Day 4 N Day 3 background Week 14 Hemisphere progress, clonic normal, focal infarction Basal ganglia vacuum seizures right hypersynchrony mca left left 7 Outborn 40 F Nicotine, P Emergency 9/10 Neonatal period unremarkable, no neonatal 8 months Hemisphere placental c/section diagnostic work-up infarction mca Basal ganglia infarcts 4 months: reduced motor movements left, right Internal capsula beginning spasticity left 6 months: cerebral ultrasound porencephalic cyst right hemisphere 8 months: EEG normal 8 Inborn 41 F Normal N Spontaneous 9/10 Day 3 focal Day 5, Day 4 background Day 7 Hemisphere clonic day 7 N abnormal, focal infarction seizures right hypersynchrony mca left left, sharp/slow waves right
4 Schulzke et al., Arterial cerebral infarction in newborn infants 173 (Table 1 continued) No Place GA Sex Pregnancy CTG Delivery Apgar Neurologic Cerebral EEG MRI Affected of birth score symptoms ultrasound regions (19/59) 9 Outborn 39 F Normal N Non-urgent 9/10 Day 2 focal Day 2, Day 3 background Day 5 Hemisphere c/section clonic day 3 N abnormal, focal infarction seizures right hypersynchrony mca left left GA, gestational age; M, male; F, female; CTG, cardiotocogram; N, normal; P, pathologic; mca, middle cerebral artery; PLED, periodic lateralized epileptic discharges. MRI confirmed the diagnosis of ACI in these three cases. Doppler studies were routinely carried out, but this was never helpful for the diagnosis of ACI. Regarding MRI, a diagnosis of ACI was confirmed in eight out of nine cases after the first MRI scan. In one child, an initial MRI on day 11 showed considerable leftsided bleeding, suggesting hemorrhagic infarction of the left MCA, but bleeding due to a vascular malformation could not be ruled out. After resorption of the hematoma, subsequent MRI scans established the diagnosis of ACI. All patients had unilateral infarction of the middle cerebral artery (Figure 1). Seven out of nine infarctions were leftsided and two were right-sided. For details on the affected cerebral structures, see Table 1. Neurological outcome Six out of nine children developed hemiparesis, while two continued to show epileptic seizures after the neonatal period. Language development was delayed in five out of nine children. There is a substantial need for special care school facilities and long-term therapeutic interventions, as detailed in Table 2. Discussion The incidence of ca. 1:2300 unilateral neonatal ACIs in our population is higher than in another populationbased study w2x in which an incidence of 1:4000 was calculated using cranial CT for confirmation of diagnosis. This discrepancy may be due to the fact that the sensitivity of MRI for diagnosis of ACI is superior to that of CT w6x. Newborn seizures were present in seven out of nine patients, a fact that underlines the value of this clinical condition for the diagnosis of ACI. As helpful as seizures are for initiation of the diagnostic and therapeutic process, two patients were without corresponding neurologic symptoms in the neonatal period. It remains unclear how these patients can be identified at an early date, because there are no predictive markers available. Furthermore, it is not known whether ACIs diagnosed acutely and retrospectively differ in the time of occurrence or pattern of injury w10x. All patients identified during the neonatal period had pathologic EEG recordings. Five out of eight EEG readings showed abnormal lateralizing background activity, indicating poor prognosis regarding the development of hemiparesis w8x. Only one patient showed periodic lateralized epileptiform discharges (PLEDs), known to be pathognomonic for unilateral ACI w9x. We may have missed PLEDs in other patients, as our EEG recordings lasted only min, and were thus of a shorter duration than those reported in recent studies w8, 9x, which used continuous EEG for nearly 2 days.
5 174 Schulzke et al., Arterial cerebral infarction in newborn infants Table 2 Neurological and developmental outcome a of newborn infants suffering from unilateral arterial cerebral infarction (ns9). No Motor Epilepsy Language Age-appropriate School Current Follow Development development communication/ type therapy/ up play behavior support (months) 1 Hemiparesis q Delayed No Special Physio 72 Arm)leg care Speech OT 2 Normal Normal Yes Normal 48 3 Hemiparesis Delayed Yes Normal Physio 48 Leg)arm Speech OT 4 Hemiparesis Delayed No Special Physio 60 Arm)leg care SE, OT 5 Hemiparesis Delayed No Special Physio 48 Leg)arm care SE 6 Hemiparesis q Delayed No Special Physio 42 care OT 7 Hemiparesis Normal Yes b Physio 20 OT 8 Normal Normal Yes b Physio c 24 9 Normal Normal Yes b Physio c 24 SE OT, occupational therapy; SE, special educative therapy. a Based on Griffith s test (F24 months of age) or Denver developmental scale ()24 months of age). b Children are below 3 years of age. c Prophylaxis. We assume that the low sensitivity of cerebral ultrasound results from the timing of the initial ultrasound studies, as they were carried out in the first few days of life. There is evidence from prospective trials showing higher ultrasound sensitivity when carried out at the end of or after the first week of life w4, 8x. Cerebral Doppler studies were not helpful for the diagnosis of ACI in our patients. Some small series have identified transient decreases in cerebral blood-flow velocity ipsilateral to ACI in a proportion of affected infants w11, 12x, while others did not w13x. One reason for this discrepancy could be that some infarctions might be caused by transient vasospasm rather than embolism. In addition, seizures are known to transiently increase blood flow velocity w14x. Furthermore, the inability to show reduced cerebral blood-flow velocities in our study might be due to the timing of the Doppler studies, which were carried out up to 48 h following the onset of seizures. Decreased blood-flow velocity in ACI seems to be significant only within the first 24 h w11x. In general, cerebral blood-flow velocity varies substantially following neonatal seizures due to ACI, and the usefulness of these measurements in ACI has not yet been established w10x. Conventional MRI proved to be very sensitive for the diagnosis of ACI. At a later date, diffusion-weighted imaging was available in our institution (and was used additionally in patients no. 8 and no. 9) and allowed early diagnosis in the first week of life. However, as bleeding due to a vascular malformation could not be ruled out after the first MRI scan in one patient, the possible need for subsequent scans should be kept in mind. Regarding neurological outcome, we found that two-thirds of our patients suffered from hemiparesis and five out of nine children showed delayed language development, mostly because of deficits in expressive language. While the frequency of hemiparesis is consistent with the literature, there are few data on language development after neonatal ACI w10x. The majority of our patients need special care facilities and use multiple therapeutic interventions, such as physiotherapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy and special educative support, which underlines the long-term impact of neonatal ACI on the lives of affected patients and families, as well as healthcare resources. In conclusion, this retrospective case series shows that in our population the incidence of unilateral ACI in newborns is higher than previously reported. The true incidence may even be higher than 1:2300, as not all affected infants have seizures and neurological sequelae. Seizures in the first 3 days of life and pathologic EEG findings should lead to early MRI, regardless of normal cerebral ultrasound, as ACI may be the diagnosis. Acknowledgements We thank Dr. Allison Sommerville for her assistance in preparing the manuscript.
6 Schulzke et al., Arterial cerebral infarction in newborn infants 175 References w1x de Vries LS, F Groenendaal, P Eken, IC van Haastert, KJ Rademaker, LC Meiners: Infarcts in the vascular distribution of the middle cerebral artery in preterm and full-term infants. Neuropediatrics 28 (1997) 88 w2x Estan J, P Hope: Unilateral neonatal cerebral infarction in full term infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 76 (1997) F88 w3x Filipek PA, KS Krishnamoorthy, KR Davis, K Kuehnle: Focal cerebral infarction in the newborn: a distinct entity. Pediatr Neurol 3 (1987) 141 w4x Fischer AQ, JC Anderson, R Shuman: The evolution of ischemic cerebral infarction in infancy: a sonographic evaluation. J Child Neurol 3 (1988) 105 w5x Golomb MR, PT Dick, DL MacGregor, DC Armstrong, GA DeVeber: Cranial ultrasonography has a low sensitivity for detecting arterial ischemic stroke in term infants. J Child Neurol 18 (2003) 98 w6x McArdle CB, CJ Richardson, CK Hayden, DA Nicholas, EG Amparo: Abnormalities of the neonatal brain: MR imaging. Part II. Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Radiology 163 (1987) 395 w7x Mercuri E, F Cowan, M Rutherford, D Acolet, J Pennock, L Dubowitz: Ischaemic and haemorrhagic brain lesions in newborns with seizures and normal Apgar scores. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 73 (1995) F67 w8x Mercuri E, M Rutherford, F Cowan, J Pennock, S Counsell, M Papadimitriou, D Azzopardi, G Bydder, L Dubowitz: Early prognostic indicators of outcome in infants with neonatal cerebral infarction: a clinical, electroencephalogram, and magnetic resonance imaging study. Pediatrics 103 (1999) 39 w9x Mercuri E: Early diagnostic and prognostic indicators in full term infants with neonatal cerebral infarction: an integrated clinical, neuroradiological and EEG approach. Minerva Pediatr 53 (2001) 305 w10x Nelson KB, JK Lynch: Stroke in newborn infants. Lancet Neurol 3 (2004) 150 w11x Nishimaki S, K Seki, S Yokota: Cerebral blood flow velocity in two patients with neonatal cerebral infarction. Pediatr Neurol 24 (2001) 320 w12x Perlman JM, NK Rollins, D Evans: Neonatal stroke: clinical characteristics and cerebral blood flow velocity measurements. Pediatr Neurol 11 (1994) 281 w13x Taylor GA: Alterations in regional cerebral blood flow in neonatal stroke: preliminary findings with color Doppler sonography. Pediatr Radiol 24 (1994) 111 w14x Volpe JJ: Neurological evaluation: specialized studies in the neurological evaluation. In: Volpe JJ (ed): Neurology of the Newborn. 3 rd edition, W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia 1994 Received September 3, Revised November 23, Accepted December 1, 2004.
I t is increasingly recognised that arterial cerebral infarction
 F252 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does cranial ultrasound imaging identify arterial cerebral infarction in term neonates? F Cowan, E Mercuri, F Groenendaal, L Bassi, D Ricci, M Rutherford, L de Vries... See end of
F252 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does cranial ultrasound imaging identify arterial cerebral infarction in term neonates? F Cowan, E Mercuri, F Groenendaal, L Bassi, D Ricci, M Rutherford, L de Vries... See end of
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Diagnostic evaluation of a symptomatic cerebrovascular accident in a neonate with focal convulsions
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Diagnostic evaluation of a symptomatic cerebrovascular accident in a neonate with focal convulsions July 2013 2 Anderson S, Rimensberger P, Service de Néonatologie et des Soins
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Diagnostic evaluation of a symptomatic cerebrovascular accident in a neonate with focal convulsions July 2013 2 Anderson S, Rimensberger P, Service de Néonatologie et des Soins
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Neonatal cerebral infarction
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal cerebral infarction May 2002 2 Mann C, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Landeskrankenhaus und Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus Feldkirch, Austria Swiss Society
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal cerebral infarction May 2002 2 Mann C, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Landeskrankenhaus und Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus Feldkirch, Austria Swiss Society
Study of role of MRI brain in evaluation of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
 Original article: Study of role of MRI brain in evaluation of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy *Dr Harshad Bhagat, ** Dr Ravindra Kawade, ***Dr Y.P.Sachdev *Junior Resident, Department Of Radiodiagnosis,
Original article: Study of role of MRI brain in evaluation of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy *Dr Harshad Bhagat, ** Dr Ravindra Kawade, ***Dr Y.P.Sachdev *Junior Resident, Department Of Radiodiagnosis,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
Perlman J, Clinics Perinatol 2006; 33: Underlying causal pathways. Antenatal Intrapartum Postpartum. Acute near total asphyxia
 Perlman J, Clinics Perinatol 2006; 33:335-353 Underlying causal pathways Antenatal Intrapartum Postpartum Acute injury Subacute injury Associated problem Reduced fetal movements Placental insufficiency
Perlman J, Clinics Perinatol 2006; 33:335-353 Underlying causal pathways Antenatal Intrapartum Postpartum Acute injury Subacute injury Associated problem Reduced fetal movements Placental insufficiency
Cranial ultrasound abnormalities in full term infants in a postnatal ward: outcome at 12 and 18 months
 F128 Department of Paediatrics and Neonatal Medicine, Imperial College School of Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London W12 0HS, UK L Haataja E Mercuri FCowan L Dubowitz Correspondence to:
F128 Department of Paediatrics and Neonatal Medicine, Imperial College School of Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London W12 0HS, UK L Haataja E Mercuri FCowan L Dubowitz Correspondence to:
Correlation of Neurodevelopmental Outcome and brain MRI/EEG findings in term HIE infants
 Correlation of Neurodevelopmental Outcome and brain MRI/EEG findings in term HIE infants Ajou University School of Medicine Department of Pediatrics Moon Sung Park M.D. Hee Cheol Jo, M.D., Jang Hoon Lee,
Correlation of Neurodevelopmental Outcome and brain MRI/EEG findings in term HIE infants Ajou University School of Medicine Department of Pediatrics Moon Sung Park M.D. Hee Cheol Jo, M.D., Jang Hoon Lee,
Unilateral neonatal cerebral infarction in full term infants
 F88 Department of Paediatrics, John RadcliVe Hospital, Oxford, OX3 9DU J Estan P Hope Correspondence to: Dr Peter Hope. Accepted 11 December 1996 Unilateral neonatal cerebral infarction in full term infants
F88 Department of Paediatrics, John RadcliVe Hospital, Oxford, OX3 9DU J Estan P Hope Correspondence to: Dr Peter Hope. Accepted 11 December 1996 Unilateral neonatal cerebral infarction in full term infants
Chapter 7. Neuropediatrics 2007; 38 (5): Lara Leijser Alla Vein Lishya Liauw Tzipi Strauss Sylvia Veen Gerda van Wezel-Meijler
 Chapter 7 Prediction of short-term neurological outcome in full-term neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy based on combined use of electroencephalogram and neuro-imaging Lara Leijser Alla Vein
Chapter 7 Prediction of short-term neurological outcome in full-term neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy based on combined use of electroencephalogram and neuro-imaging Lara Leijser Alla Vein
Original Articles NEUROSONOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES IN NEONATES WITH HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
 Original Articles NEUROSONOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES IN NEONATES WITH HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY N.K. Anand A.K. Gupta I.M.S. Lamba ABSTRACT Pattern of neurosonographic (NSG) abnormalities in 150 term
Original Articles NEUROSONOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES IN NEONATES WITH HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY N.K. Anand A.K. Gupta I.M.S. Lamba ABSTRACT Pattern of neurosonographic (NSG) abnormalities in 150 term
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Pediatr Neurol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 October 30.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Pediatr Neurol. 2008 May ; 38(5): 329 334. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2007.12.012. Very Early Arterial Ischemic Stroke in Premature
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Pediatr Neurol. 2008 May ; 38(5): 329 334. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2007.12.012. Very Early Arterial Ischemic Stroke in Premature
RESEARCH BRIEF. Prognostic Value of Resistive Index in Neonates with Hypoxic Ischemic
 RESEARCH BRIEF Prognostic Value of Resistive Index in Neonates with Hypoxic Ischemic A Senthil Kumar, Aparna Chandrasekaran, Rajamannar Asokan and *Kathirvelu Gopinathan From the Department of Neonatology,
RESEARCH BRIEF Prognostic Value of Resistive Index in Neonates with Hypoxic Ischemic A Senthil Kumar, Aparna Chandrasekaran, Rajamannar Asokan and *Kathirvelu Gopinathan From the Department of Neonatology,
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia.
 Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Imaging the Premature Brain- New Knowledge
 Imaging the Premature Brain- New Knowledge Stein Magnus Aukland Haukeland University Hospital University of Bergen NORWAY No disclosure Imaging modalities O Skull X-ray O Computer Tomography O Cerebral
Imaging the Premature Brain- New Knowledge Stein Magnus Aukland Haukeland University Hospital University of Bergen NORWAY No disclosure Imaging modalities O Skull X-ray O Computer Tomography O Cerebral
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia.
 Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Should infants with perinatal thrombosis be screened for thrombophilia and treated by anticoagulants?
 Should infants with perinatal thrombosis be screened for thrombophilia and treated by anticoagulants? Shoshana Revel-Vilk, MD MSc Pediatric Hematology Center, Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Department,
Should infants with perinatal thrombosis be screened for thrombophilia and treated by anticoagulants? Shoshana Revel-Vilk, MD MSc Pediatric Hematology Center, Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Department,
National follow-up program CPUP Pediatric Neurology paper form
 National follow-up program CPUP Pediatric Neurology paper form 110206 1 National Follow-Up program- CPUP Pediatric Neurology Personal nr (unique identifier): Last name: First name: Region child belongs
National follow-up program CPUP Pediatric Neurology paper form 110206 1 National Follow-Up program- CPUP Pediatric Neurology Personal nr (unique identifier): Last name: First name: Region child belongs
Epilepsy in children with cerebral palsy
 Seizure 2003; 12: 110 114 doi:10.1016/s1059 1311(02)00255-8 Epilepsy in children with cerebral palsy A.K. GURURAJ, L. SZTRIHA, A. BENER,A.DAWODU & V. EAPEN Departments of Paediatrics, Community Medicine
Seizure 2003; 12: 110 114 doi:10.1016/s1059 1311(02)00255-8 Epilepsy in children with cerebral palsy A.K. GURURAJ, L. SZTRIHA, A. BENER,A.DAWODU & V. EAPEN Departments of Paediatrics, Community Medicine
Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Neonatal Cranial Ultrasonography
 Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Neonatal Cranial Ultrasonography Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Neonatal Cranial Ultrasonography Guidelines for the Procedure and Atlas of Normal Ultrasound Anatomy With 121 Figures and
Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Neonatal Cranial Ultrasonography Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Neonatal Cranial Ultrasonography Guidelines for the Procedure and Atlas of Normal Ultrasound Anatomy With 121 Figures and
A study of clinico-biochemical profile of neonatal seizure: A tertiary care hospital study
 Original Research Article A study of clinico-biochemical profile of neonatal seizure: A tertiary care hospital study Wakil Paswan 1*, Bankey Behari Singh 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor
Original Research Article A study of clinico-biochemical profile of neonatal seizure: A tertiary care hospital study Wakil Paswan 1*, Bankey Behari Singh 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor
Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury: Ultrasound and Dynamic Color Doppler Sonography perfusion of the Brain and Abdomen with pathologic correlation.
 Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury: Ultrasound and Dynamic Color Doppler Sonography perfusion of the Brain and Abdomen with pathologic correlation. Ricardo Faingold,MD Montreal Children s Hospital Medical
Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury: Ultrasound and Dynamic Color Doppler Sonography perfusion of the Brain and Abdomen with pathologic correlation. Ricardo Faingold,MD Montreal Children s Hospital Medical
Neonatal seizures are an emergency
 VOLUME 46 November - December 2006 NUMBER 11-12 Original Article Neonatal seizures: clinical manifestations and etiology Daisy Widiastuti, Irawan Mangunatmadja, Taralan Tambunan, Rulina Suradi ABSTRACT
VOLUME 46 November - December 2006 NUMBER 11-12 Original Article Neonatal seizures: clinical manifestations and etiology Daisy Widiastuti, Irawan Mangunatmadja, Taralan Tambunan, Rulina Suradi ABSTRACT
Serial 1- and 2-Dimensional Cerebral MRI Measurements in Full-Term Infants after Perinatal Asphyxia
 Original Paper Received: October 27, 2015 Accepted after revision: January 18, 2016 Published online: March 12, 2016 Serial 1- and 2-Dimensional Cerebral MRI Measurements in Full-Term Infants after Perinatal
Original Paper Received: October 27, 2015 Accepted after revision: January 18, 2016 Published online: March 12, 2016 Serial 1- and 2-Dimensional Cerebral MRI Measurements in Full-Term Infants after Perinatal
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Bart s syndrome with severe newborn encephalopathy: a delayed diagnosis
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Bart s syndrome with severe newborn encephalopathy: a delayed diagnosis May 2003 2 Buettiker V, Hogan P, Badawi N, Department of Neonatology (BV, NB), Department of Dermatology
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Bart s syndrome with severe newborn encephalopathy: a delayed diagnosis May 2003 2 Buettiker V, Hogan P, Badawi N, Department of Neonatology (BV, NB), Department of Dermatology
Ischaemic and haemorrhagic brain lesions in
 Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1995; 73: F67-F74 Department of Paediatrics and Neonatal Medicine E Mercuri F Cowan M Rutherford D Acolet L Dubowitz Robert Steiner MRI Unit J Pennock Hammersmith Hospital,
Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1995; 73: F67-F74 Department of Paediatrics and Neonatal Medicine E Mercuri F Cowan M Rutherford D Acolet L Dubowitz Robert Steiner MRI Unit J Pennock Hammersmith Hospital,
P eriventricular leucomalacia (PVL), which is characterised
 F275 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Limitations of ultrasonography for diagnosing white matter damage in preterm infants T Debillon, S N Guyen, A Muet, M P Quere, F Moussaly, J C Roze... See end of article for authors
F275 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Limitations of ultrasonography for diagnosing white matter damage in preterm infants T Debillon, S N Guyen, A Muet, M P Quere, F Moussaly, J C Roze... See end of article for authors
The Clinical Spectrum and Prediction of Outcome in Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy
 Article neurology The Clinical Spectrum and Prediction of Outcome in Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Walter C. Allan, MD* Objectives After completing this article, readers should be able to: 1. List the
Article neurology The Clinical Spectrum and Prediction of Outcome in Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Walter C. Allan, MD* Objectives After completing this article, readers should be able to: 1. List the
Predicting Outcomes in HIE. Naaz Merchant Consultant Neonatologist Beds & Herts Meeting 17/03/2016
 Predicting Outcomes in HIE Naaz Merchant Consultant Neonatologist Beds & Herts Meeting 17/03/2016 Interactive please! Case 1 Term, 3.5 kg Antenatal: Breech Labour/Delivery: Em CS failure to progress, mec
Predicting Outcomes in HIE Naaz Merchant Consultant Neonatologist Beds & Herts Meeting 17/03/2016 Interactive please! Case 1 Term, 3.5 kg Antenatal: Breech Labour/Delivery: Em CS failure to progress, mec
Clinical Presentations and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes of Perinatal Stroke in Preterm and Term Neonates: A Case Series
 J Korean Med Sci 2010; 25: 888-94 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.6.888 Clinical Presentations and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes of Perinatal Stroke in Preterm and Term Neonates: A Case Series Perinatal
J Korean Med Sci 2010; 25: 888-94 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.6.888 Clinical Presentations and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes of Perinatal Stroke in Preterm and Term Neonates: A Case Series Perinatal
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain
 DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
Perinatal/Neonatal Case Presentation
 Perinatal/Neonatal Case Presentation & & & & & & & & & & & & & & Bilateral Thalamic Lesions in a Newborn with Intrauterine Asphyxia After Maternal Cardiac Arrest a Case Report with Literature Review Maya
Perinatal/Neonatal Case Presentation & & & & & & & & & & & & & & Bilateral Thalamic Lesions in a Newborn with Intrauterine Asphyxia After Maternal Cardiac Arrest a Case Report with Literature Review Maya
Original article: Evaluation of hypoxic-ischaemic events in preterm neonates using trans cranial ultrasound
 Original article: Evaluation of hypoxic-ischaemic events in preterm neonates using trans cranial ultrasound Priyanka Upadhyay *, Ketki U Patil 1, Rajesh Kuber 2, Vilas Kulkarni 3, Amarjit Singh 4 * Chief
Original article: Evaluation of hypoxic-ischaemic events in preterm neonates using trans cranial ultrasound Priyanka Upadhyay *, Ketki U Patil 1, Rajesh Kuber 2, Vilas Kulkarni 3, Amarjit Singh 4 * Chief
Neuroimaging in Cerebral Palsy Report from North India
 original ARTICLE Neuroimaging in Cerebral Palsy Report from North India How to Cite This Article: Aggarwal A, Mittal H, Debnath SKR, Rai A. Neuroimaging in Cerebral Palsy Report from North India. Iran
original ARTICLE Neuroimaging in Cerebral Palsy Report from North India How to Cite This Article: Aggarwal A, Mittal H, Debnath SKR, Rai A. Neuroimaging in Cerebral Palsy Report from North India. Iran
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods
 Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Cerebral function monitoring in term or near term neonates at MDH: preliminary experience and proposal of a guideline
 Original Article Cerebral function monitoring in term or near term neonates at MDH: preliminary experience and proposal of a guideline Stephen Attard, Doriette Soler, Paul Soler Introduction: Cerebral
Original Article Cerebral function monitoring in term or near term neonates at MDH: preliminary experience and proposal of a guideline Stephen Attard, Doriette Soler, Paul Soler Introduction: Cerebral
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review
 Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Alexopoulou 1, A. Mazioti 1, D. K. Filippiadis 2, C. Chrona
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Alexopoulou 1, A. Mazioti 1, D. K. Filippiadis 2, C. Chrona
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain
 Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Neonatal Brain MRI and Motor Outcome at School Age in Children with Neonatal Encephalopathy: A Review of Personal Experience
 NEURAL PLASTICITY VOLUME 10, NO. 1-2, 2003 Neonatal Brain MRI and Motor Outcome at School Age in Children with Neonatal Encephalopathy: A Review of Personal Experience Eugenio Mercuri and Anna L. Barnett
NEURAL PLASTICITY VOLUME 10, NO. 1-2, 2003 Neonatal Brain MRI and Motor Outcome at School Age in Children with Neonatal Encephalopathy: A Review of Personal Experience Eugenio Mercuri and Anna L. Barnett
Neonatal Seizure. Dr.Nawar Yahya. Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan. Supervised by:
 Neonatal Seizure Supervised by: Dr.Nawar Yahya Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan Objectives: What is neonatal seizure Etiology Clinical presentation Differential diagnosis
Neonatal Seizure Supervised by: Dr.Nawar Yahya Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan Objectives: What is neonatal seizure Etiology Clinical presentation Differential diagnosis
This lecture will provide an overview of the neurologic exam of a neonate in the context of clinical cases.
 A11a Neuro Nuggets from the Trenches Michael D. Weiss, MD Associate Professor Department of Pediatrics, Division of Neonatology University of Florida, Gainesville, FL The speaker has signed a disclosure
A11a Neuro Nuggets from the Trenches Michael D. Weiss, MD Associate Professor Department of Pediatrics, Division of Neonatology University of Florida, Gainesville, FL The speaker has signed a disclosure
White Matter Injury in the Premature Infant: A Comparison between Serial Cranial Sonographic and MR Findings at Term
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:805 809, May 2003 White Matter Injury in the Premature Infant: A Comparison between Serial Cranial Sonographic and MR Findings at Term Terrie E. Inder, Nigel J. Anderson, Carole
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:805 809, May 2003 White Matter Injury in the Premature Infant: A Comparison between Serial Cranial Sonographic and MR Findings at Term Terrie E. Inder, Nigel J. Anderson, Carole
NEONATAL SEIZURES-PGPYREXIA REVIEW
 NEONATAL SEIZURES-PGPYREXIA REVIEW This is a very important Postgraduate topics will few Q asked in undergraduation also. Lets see them in detail. References: 1.Volpe s Neurology of newborn 2.Nelson s
NEONATAL SEIZURES-PGPYREXIA REVIEW This is a very important Postgraduate topics will few Q asked in undergraduation also. Lets see them in detail. References: 1.Volpe s Neurology of newborn 2.Nelson s
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings
 Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
There are several types of epilepsy. Each of them have different causes, symptoms and treatment.
 1 EPILEPSY Epilepsy is a group of neurological diseases where the nerve cell activity in the brain is disrupted, causing seizures of unusual sensations, behavior and sometimes loss of consciousness. Epileptic
1 EPILEPSY Epilepsy is a group of neurological diseases where the nerve cell activity in the brain is disrupted, causing seizures of unusual sensations, behavior and sometimes loss of consciousness. Epileptic
Citation for published version (APA): Roze, E. (2011). Functional development at school age of newborn infants at risk. Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Functional development at school age of newborn infants at risk Roze, Elise IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Functional development at school age of newborn infants at risk Roze, Elise IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Neonatal Seizures: Correlation between Clinico-Etiological Profile and EEG Findings
 BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2014; VOL 38 (1) : 19-23 and EEG Findings RUMA PARVIN 1, AFMSALIM2, MIZANUR RAHMAN 3, KONA CHOWDHURY 4, AZMERI SULTANA 1, SHAFI AHMED 5, K. M. ZIAUR RAHMAN 6 Abstract: Introduction:
BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2014; VOL 38 (1) : 19-23 and EEG Findings RUMA PARVIN 1, AFMSALIM2, MIZANUR RAHMAN 3, KONA CHOWDHURY 4, AZMERI SULTANA 1, SHAFI AHMED 5, K. M. ZIAUR RAHMAN 6 Abstract: Introduction:
MRI Lesions and Infants with Neonatal Encephalopathy. Is the Apgar Score Predictive?
 MRI Lesions and Infants with Neonatal Encephalopathy. Is the Apgar Score Predictive? E. Mercuri 1,2 M. Rutherford 1 A. Barnett 1 Chr. Foglia 1 L. Haataja 1,3 S. Counsell 4 F. Cowan 1 L. Dubowitz 1 150
MRI Lesions and Infants with Neonatal Encephalopathy. Is the Apgar Score Predictive? E. Mercuri 1,2 M. Rutherford 1 A. Barnett 1 Chr. Foglia 1 L. Haataja 1,3 S. Counsell 4 F. Cowan 1 L. Dubowitz 1 150
Study of correlation severity of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy on MRI brain with clinical findings
 Radiology and Imaging Special Issue December 2017: Vol-7, Issue- 1, P 34-41 Original article: Study of correlation severity of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy on MRI brain with clinical findings *Dr Ramaa
Radiology and Imaging Special Issue December 2017: Vol-7, Issue- 1, P 34-41 Original article: Study of correlation severity of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy on MRI brain with clinical findings *Dr Ramaa
RESEARCH ARTICLE EPILEPSY IN CHILDREN WITH CEREBRAL PALSY
 RESEARCH ARTICLE EPILEPSY IN CHILDREN WITH CEREBRAL PALSY S.Pour Ahmadi MD, M.Jafarzadeh MD, M. Abbas MD, J.Akhondian MD. Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Mashad University of Medical Sciences. Associate
RESEARCH ARTICLE EPILEPSY IN CHILDREN WITH CEREBRAL PALSY S.Pour Ahmadi MD, M.Jafarzadeh MD, M. Abbas MD, J.Akhondian MD. Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Mashad University of Medical Sciences. Associate
Objectives. Birth Depression Management. Birth Depression Terms
 Objectives Birth Depression Management Regional Perinatal Outreach Program 2016 Understand the terms and the clinical characteristics of birth depression. Be familiar with the evidence behind therapeutic
Objectives Birth Depression Management Regional Perinatal Outreach Program 2016 Understand the terms and the clinical characteristics of birth depression. Be familiar with the evidence behind therapeutic
Queen Charlotte Hospital
 Queen Charlotte Hospital Neuroprotection for neonatal encephalopathy Neonatal encephalopathy accounts for 1 million deaths worldwide and even greater numbers of disabled survivors In countries with
Queen Charlotte Hospital Neuroprotection for neonatal encephalopathy Neonatal encephalopathy accounts for 1 million deaths worldwide and even greater numbers of disabled survivors In countries with
ECMUS The Safety Committee of EFSUMB : Tutorial
 Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Screening Cranial Imaging at Multiple Time Points Improves Cystic Periventricular Leukomalacia Detection
 Screening Cranial Imaging at Multiple Time Points Improves Cystic Periventricular Leukomalacia Detection Abhik Das, RTI International John Barks, University of Michigan Subrata Sarkar, University of Michigan
Screening Cranial Imaging at Multiple Time Points Improves Cystic Periventricular Leukomalacia Detection Abhik Das, RTI International John Barks, University of Michigan Subrata Sarkar, University of Michigan
Utility of neuroradiographic imaging in predicting outcomes after neonatal extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
 Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2012) 47, 76 80 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Utility of neuroradiographic imaging in predicting outcomes after neonatal extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Michael D.
Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2012) 47, 76 80 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Utility of neuroradiographic imaging in predicting outcomes after neonatal extracorporeal membrane oxygenation Michael D.
Developmental sequence of periventricular leukomalacia
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1985, 60, 349-355 Developmental sequence of periventricular leukomalacia Correlation of ultrasound, clinical, and nuclear magnetic resonance functions L M S DUBOWITZ,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1985, 60, 349-355 Developmental sequence of periventricular leukomalacia Correlation of ultrasound, clinical, and nuclear magnetic resonance functions L M S DUBOWITZ,
Early instrumental predictors of long term neurodevelopmental impairment in newborns with perinatal asphyxia treated with therapeutic hypothermia
 SIGNA VITAE 218; 14(1): 81-85 Early instrumental predictors of long term neurodevelopmental impairment in newborns with perinatal asphyxia treated with therapeutic hypothermia ALICE MONZANI 1, GIANLUCA
SIGNA VITAE 218; 14(1): 81-85 Early instrumental predictors of long term neurodevelopmental impairment in newborns with perinatal asphyxia treated with therapeutic hypothermia ALICE MONZANI 1, GIANLUCA
Predicting outcome using neonatal MRI in preterm infants. Manon Benders, neonatologist. Summer Conference on Neonatology in Provence
 Predicting outcome using neonatal MRI in preterm infants Manon Benders, neonatologist Summer Conference on Neonatology in Provence Avignon, France, 6 th - 9 th September 2017 the human brain the third
Predicting outcome using neonatal MRI in preterm infants Manon Benders, neonatologist Summer Conference on Neonatology in Provence Avignon, France, 6 th - 9 th September 2017 the human brain the third
Retrospectıve analysıs for newborn ınfants wıth hypoxıc-ıschemıc encephalopathy
 Basic Research Journal of Medicine and Clinical Sciences ISSN 2315-6864 Vol. 1(2) pp. 19-24 September 2012 Available online http//www.basicresearchjournals.org Copyright 2012 Basic Research Journal Full
Basic Research Journal of Medicine and Clinical Sciences ISSN 2315-6864 Vol. 1(2) pp. 19-24 September 2012 Available online http//www.basicresearchjournals.org Copyright 2012 Basic Research Journal Full
The child with hemiplegic cerebral palsy thinking beyond the motor impairment. Dr Paul Eunson Edinburgh
 The child with hemiplegic cerebral palsy thinking beyond the motor impairment Dr Paul Eunson Edinburgh Content Coming to a diagnosis The importance of understanding the injury MRI scans Role of epilepsy
The child with hemiplegic cerebral palsy thinking beyond the motor impairment Dr Paul Eunson Edinburgh Content Coming to a diagnosis The importance of understanding the injury MRI scans Role of epilepsy
Original Research Article
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY INFARCT AND ITS CORRELATION WITH FUNCTIONAL RECOVERY Neethu Tressa Jose 1, Rajan Padinharoot 2, Vadakooth Raman Rajendran 3, Geetha Panarkandy 4 1Junior
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY INFARCT AND ITS CORRELATION WITH FUNCTIONAL RECOVERY Neethu Tressa Jose 1, Rajan Padinharoot 2, Vadakooth Raman Rajendran 3, Geetha Panarkandy 4 1Junior
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Neurology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
What is symptomatic? Neonatal hypoglycemia: how low can you go? Hypoglycemia and MRI. Conflicts. What s the problem? Hypoglycemia and MRI
 Neonatal hypoglycemia: how low can you go? Kristi Watterberg, MD Professor of Pediatrics, UNM What is symptomatic? Jitteriness Cyanosis Poor feeding Weak, high-pitched cry Seizures Apnea Lethargy, low
Neonatal hypoglycemia: how low can you go? Kristi Watterberg, MD Professor of Pediatrics, UNM What is symptomatic? Jitteriness Cyanosis Poor feeding Weak, high-pitched cry Seizures Apnea Lethargy, low
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography
 Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
The NeuroNICU From Concept to Clinical Service. MJ Harbert, MD Co-Director, NeuroNICU Service Rady Children s Hospital San Diego
 The NeuroNICU From Concept to Clinical Service MJ Harbert, MD Co-Director, NeuroNICU Service Rady Children s Hospital San Diego What is a NeuroNICU? Collaboration between Neonatology and Neurology Neonatal
The NeuroNICU From Concept to Clinical Service MJ Harbert, MD Co-Director, NeuroNICU Service Rady Children s Hospital San Diego What is a NeuroNICU? Collaboration between Neonatology and Neurology Neonatal
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level
 Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
Extensive cystic periventricular leukomalacia following early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a very low birth weight infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Extensive cystic periventricular leukomalacia following early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a very low birth weight infant July 2012 2 Berger TM, Caduff JC, Neonatal
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Extensive cystic periventricular leukomalacia following early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a very low birth weight infant July 2012 2 Berger TM, Caduff JC, Neonatal
Neonatal seizures associated with cerebral lesions shown by magnetic resonance imaging
 Archives of Disease in Childhood 1997;77:F105 F110 F105 Neonatal seizures associated with cerebral lesions shown by magnetic resonance imaging H Leth, P B Toft, M Herning, B Peitersen, H C Lou The Danish
Archives of Disease in Childhood 1997;77:F105 F110 F105 Neonatal seizures associated with cerebral lesions shown by magnetic resonance imaging H Leth, P B Toft, M Herning, B Peitersen, H C Lou The Danish
7 Simple Steps to Assess & Document any Neonatal aeeg
 7 Simple Steps to Assess & Document any Neonatal aeeg Created for you by: www.aeegcoach.com How to use the Seven Simple Steps Checklist Hi! It s Kathi Randall here Your aeeg coach. I m so excited to share
7 Simple Steps to Assess & Document any Neonatal aeeg Created for you by: www.aeegcoach.com How to use the Seven Simple Steps Checklist Hi! It s Kathi Randall here Your aeeg coach. I m so excited to share
Continuous EEG monitoring of neonatal seizures: diagnostic and prognostic considerations
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 45-458 Continuous EEG monitoring of neonatal seizures: diagnostic and prognostic considerations J CONNELL, R OOZEER, L DE VRIES, L M S DUBOWITZ, AND V DUBOWITZ
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 45-458 Continuous EEG monitoring of neonatal seizures: diagnostic and prognostic considerations J CONNELL, R OOZEER, L DE VRIES, L M S DUBOWITZ, AND V DUBOWITZ
Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease
 Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease Giuseppe Fariello, Carlo Dionisi-Vici, Cinzia Orazi, Saverio Malena, Andrea Bartuli, Paolo Schingo, Enza Carnevale, Isora Saponara, and Gaetano Sabetta
Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease Giuseppe Fariello, Carlo Dionisi-Vici, Cinzia Orazi, Saverio Malena, Andrea Bartuli, Paolo Schingo, Enza Carnevale, Isora Saponara, and Gaetano Sabetta
Early seizures indicate quality of perinatal care
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1985, 6, 89-813 Early seizures indicate quality of perinatal care R J DERHAM, T G MATTHEWS, AND T A CLARKE Rotunda Hospital, Dublin, Ireland SUMMARY An analysis of antepartum,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1985, 6, 89-813 Early seizures indicate quality of perinatal care R J DERHAM, T G MATTHEWS, AND T A CLARKE Rotunda Hospital, Dublin, Ireland SUMMARY An analysis of antepartum,
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PERINATAL EVENTS AND BRAIN DAMAGE IN SURVIVING CHILDREN BASED ON PAPERS PRESENTED AT AN INTERNATIONA PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : PERINATAL EVENTS AND BRAIN DAMAGE IN SURVIVING CHILDREN BASED ON PAPERS PRESENTED AT AN INTERNATIONA PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 perinatal events and brain damage in surviving
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PERINATAL EVENTS AND BRAIN DAMAGE IN SURVIVING CHILDREN BASED ON PAPERS PRESENTED AT AN INTERNATIONA PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 perinatal events and brain damage in surviving
Provide specific counseling to parents and patients with neurological disorders, addressing:
 Neurology Description: The Pediatric Neurology elective will give the resident the opportunity to learn how to obtain an appropriate history and perform a complete neurologic exam. Four to five half days
Neurology Description: The Pediatric Neurology elective will give the resident the opportunity to learn how to obtain an appropriate history and perform a complete neurologic exam. Four to five half days
Neonatal arterial ischemic stroke was considered an
 Cognitive Outcome at Early School Age in Term-Born Children With Perinatally Acquired Middle Cerebral Artery Territory Infarction Daniela Ricci, MD; Eugenio Mercuri, MD; Anna Barnett, PhD; Rachel Rathbone,
Cognitive Outcome at Early School Age in Term-Born Children With Perinatally Acquired Middle Cerebral Artery Territory Infarction Daniela Ricci, MD; Eugenio Mercuri, MD; Anna Barnett, PhD; Rachel Rathbone,
Hypothermia in Neonates with HIE TARA JENDZIO, DNP(C), RN, RNC-NIC
 Hypothermia in Neonates with HIE TARA JENDZIO, DNP(C), RN, RNC-NIC Objectives 1. Define Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) 2. Identify the criteria used to determine if an infant qualifies for therapeutic
Hypothermia in Neonates with HIE TARA JENDZIO, DNP(C), RN, RNC-NIC Objectives 1. Define Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) 2. Identify the criteria used to determine if an infant qualifies for therapeutic
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Neonatal sinovenous thrombosis
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal sinovenous thrombosis August 2006 2 Hauri-Hohl A, Zeilinger G, Pasquier S, Children s Hospital of Aarau, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas M Berger,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal sinovenous thrombosis August 2006 2 Hauri-Hohl A, Zeilinger G, Pasquier S, Children s Hospital of Aarau, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas M Berger,
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
ultrasonography in preterm infants: association with outcome
 Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1990; 65: 1033-1037 nstitut de la Sante et de la Recherche Medicale (NSERM), Unite 316, Tours, France Philippe Bertrand Francis Gold Sophie Marchand Department of Paediatric
Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1990; 65: 1033-1037 nstitut de la Sante et de la Recherche Medicale (NSERM), Unite 316, Tours, France Philippe Bertrand Francis Gold Sophie Marchand Department of Paediatric
Diagnosing Epilepsy in Children and Adolescents
 2019 Annual Epilepsy Pediatric Patient Care Conference Diagnosing Epilepsy in Children and Adolescents Korwyn Williams, MD, PhD Staff Epileptologist, BNI at PCH Clinical Assistant Professor, Department
2019 Annual Epilepsy Pediatric Patient Care Conference Diagnosing Epilepsy in Children and Adolescents Korwyn Williams, MD, PhD Staff Epileptologist, BNI at PCH Clinical Assistant Professor, Department
Predictive Value of Multimodality Evoked Potentials in Asphyxiated Term Newborns
 Ann Ali Abdel Kader et al. Predictive Value of Multimodality Evoked Potentials in Asphyxiated Term Newborns Ann Ali Abdel Kader 1, Saly El-Kholy 1, Dahlia El-Sebaie 2, Shahira Mostafa 1, Amira El-Gohary
Ann Ali Abdel Kader et al. Predictive Value of Multimodality Evoked Potentials in Asphyxiated Term Newborns Ann Ali Abdel Kader 1, Saly El-Kholy 1, Dahlia El-Sebaie 2, Shahira Mostafa 1, Amira El-Gohary
Adult Neurology Residency Training Program McGill University Objectives of Training and Training Requirements. For Outpatient Neurology Clinics
 Neurology Residency Program Department of Neurology & Neurosurgery Postal address: Montreal Neurological Institute 3801 University Street Montreal, PQ, Canada H3A 2B4 Tel.: (514) 398-1904 Fax: (514) 398-4621
Neurology Residency Program Department of Neurology & Neurosurgery Postal address: Montreal Neurological Institute 3801 University Street Montreal, PQ, Canada H3A 2B4 Tel.: (514) 398-1904 Fax: (514) 398-4621
Is there a way to predict outcome in (near) term neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy based on MR imaging?
 Chapter 5 Is there a way to predict outcome in (near) term neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy based on MR imaging? Lishya Liauw Jeroen van der Grond Annette van den Berg-Huysmans Laura Laan
Chapter 5 Is there a way to predict outcome in (near) term neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy based on MR imaging? Lishya Liauw Jeroen van der Grond Annette van den Berg-Huysmans Laura Laan
Hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy: early and late
 Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1996;75:F145-F151 F145 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Department of Paediatrics and Neonatal Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London W12 OHS M Rutherford F Cowan L Dubowitz
Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1996;75:F145-F151 F145 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Department of Paediatrics and Neonatal Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London W12 OHS M Rutherford F Cowan L Dubowitz
Expert opinion on clinical symptoms, management and treatment of infants with congenital cytomegalovirus infection
 Expert opinion on clinical symptoms, management and treatment of infants with congenital cytomegalovirus infection J. Gunkel, J. Nijman, M.A. Maciolek-Verboon, T.F.W. Wolfs, L.S. de Vries Financial disclosure
Expert opinion on clinical symptoms, management and treatment of infants with congenital cytomegalovirus infection J. Gunkel, J. Nijman, M.A. Maciolek-Verboon, T.F.W. Wolfs, L.S. de Vries Financial disclosure
Talking About The Facts: Stroke In Children
 Talking About The Facts: Stroke In Children AWARENESS LEADS TO A QUICKER RESPONSE AND LIFESAVING OUTCOMES FOR CHILDREN. Pediatric Stroke Warriors continues to strengthen communities by providing support
Talking About The Facts: Stroke In Children AWARENESS LEADS TO A QUICKER RESPONSE AND LIFESAVING OUTCOMES FOR CHILDREN. Pediatric Stroke Warriors continues to strengthen communities by providing support
The Encephalopathic Neonate: Choosing the Proper Imaging Technique
 The Encephalopathic Neonate: Choosing the Proper Imaging Technique A. James Barkovich, University of California, San Francisco The central nervous system (CNS) of the neonate may be injured by a number
The Encephalopathic Neonate: Choosing the Proper Imaging Technique A. James Barkovich, University of California, San Francisco The central nervous system (CNS) of the neonate may be injured by a number
Definition พ.ญ.ส ธ ดา เย นจ นทร. Epidemiology. Definition 5/25/2016. Seizures after stroke Can we predict? Poststroke seizure
 Seizures after stroke Can we predict? พ.ญ.ส ธ ดา เย นจ นทร PMK Epilepsy Annual Meeting 2016 Definition Poststroke seizure : single or multiple convulsive episode(s) after stroke and thought to be related
Seizures after stroke Can we predict? พ.ญ.ส ธ ดา เย นจ นทร PMK Epilepsy Annual Meeting 2016 Definition Poststroke seizure : single or multiple convulsive episode(s) after stroke and thought to be related
When? Incidence of neonatal seizures in a NICU population The incidence of seizures is higher in the neonatal period than in any other age group.
 Incidence of neonatal seizures in a NICU population The incidence of seizures is higher in the neonatal period than in any other age group. Standard EEG 2,3% 8.6% Standard EEG + aeeg Scher MS et al; Pediatrics
Incidence of neonatal seizures in a NICU population The incidence of seizures is higher in the neonatal period than in any other age group. Standard EEG 2,3% 8.6% Standard EEG + aeeg Scher MS et al; Pediatrics
MR imaging findings of cerebral damage in infants with
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Liauw I.H. Palm-Meinders J. van der Grond L.M. Leijser S. le Cessie L.A.E.M. Laan B.C. Heeres M.A. van Buchem G. van Wezel-Meijler Differentiating Normal Myelination from Hypoxic-
ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Liauw I.H. Palm-Meinders J. van der Grond L.M. Leijser S. le Cessie L.A.E.M. Laan B.C. Heeres M.A. van Buchem G. van Wezel-Meijler Differentiating Normal Myelination from Hypoxic-
Recent Advances in Neurology Difficult Cases
 Patient X: History Part 1 Recent Advances in Neurology Difficult Cases Heather J. Fullerton, MD, MAS Professor of Neurology & Pediatrics Director, Pediatric Brain Center Previously healthy 14-year old
Patient X: History Part 1 Recent Advances in Neurology Difficult Cases Heather J. Fullerton, MD, MAS Professor of Neurology & Pediatrics Director, Pediatric Brain Center Previously healthy 14-year old
Birth Asphyxia - Summary of the previous meeting and protocol overview
 Birth Asphyxia - Summary of the previous meeting and protocol overview Dr Ornella Lincetto, WHO Geneve Milano, 11June 2007 Vilka är Personality egenskaper med den astrologiska Tvillingarna? Objective of
Birth Asphyxia - Summary of the previous meeting and protocol overview Dr Ornella Lincetto, WHO Geneve Milano, 11June 2007 Vilka är Personality egenskaper med den astrologiska Tvillingarna? Objective of
Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in Please DO NOT mail or fax this form to the CPQCC Data Center. This form is for internal use ONLY.
 Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
/ / / / / / Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA. Participant ID: Hospital Code: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
 Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain in Hypoxic Full-Term Newborns
 42 CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION :42-9 Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain in Hypoxic Full-Term Newborns Aušrelė Kudrevičienė 1, Saulius Lukoševičius 2, Jūratė Laurynaitienė 3, Vitalija
42 CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION :42-9 Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain in Hypoxic Full-Term Newborns Aušrelė Kudrevičienė 1, Saulius Lukoševičius 2, Jūratė Laurynaitienė 3, Vitalija
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Symptomatic congenital CMV infection after recurrent maternal infection
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Symptomatic congenital CMV infection after recurrent maternal infection May 2017 Mack I, Burckhardt MA, Heininger U, Prüfer F, Wellmann S, Department of Pediatric Infectious
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Symptomatic congenital CMV infection after recurrent maternal infection May 2017 Mack I, Burckhardt MA, Heininger U, Prüfer F, Wellmann S, Department of Pediatric Infectious
Introduction. Abstract Objective. Keywords: Neonatal seizure; Clinical type; Etiology; Neuroimaging; Outcome
 original ARTICLE The Etiology, Clinical Type, and Short Outcome of Seizures in Newborns Hospitalized in Besat Hospital/ Hamadan/ Iran How to Cite This Article: Sabzehei MK, Basiri B, Bazmamoun H. The Etiology,
original ARTICLE The Etiology, Clinical Type, and Short Outcome of Seizures in Newborns Hospitalized in Besat Hospital/ Hamadan/ Iran How to Cite This Article: Sabzehei MK, Basiri B, Bazmamoun H. The Etiology,
The tale of global hypoxic ischaemic injury
 The tale of global hypoxic ischaemic injury Poster No.: C-0400 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. M. Zammit, R. Grech ; Paola/MT, Dublin 9/IE Keywords: CNS, CT, MR, Education, Computer
The tale of global hypoxic ischaemic injury Poster No.: C-0400 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. M. Zammit, R. Grech ; Paola/MT, Dublin 9/IE Keywords: CNS, CT, MR, Education, Computer
