Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic
|
|
|
- Agnes Caitlin Webster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
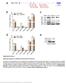
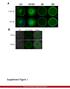
1 Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic density. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection, neurons were immunostained for PSD95 (green). Expression of mir124 did not cause marked changes in neurite structure and density of PSD95 clusters. Bar graph represents Mean ± SE, n = 16 cells, p>0.05, t test. Scale bars = 10 μm (full images), 3 μm (dendrites).
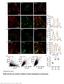
2 Supplementary Figure 2. mir124 does not affect GluA1 expression. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection, neurons were immunostained for GluA1 (green) under permeant conditions. No changes in GluA1 cluster intensity were found in cells expressing mir124. Bar graphs represent Mean ± SE. n = 18 cells, t test. Image scale bar = 10 μm.
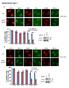
3 Supplementary Figure 3. mir124 BS does not affect total GluA1 expression. Cultured hippocampal neurons were transfected with a mir124-neutralizing sponge BS (containing GFP) at DIV12 and total GluA1 was immunostained 2 d later. GFP was transfected as a control. In cells expressing mir124 BS, the total GluA1 puncta intensity was not affected. Bar graph represents Mean ± SE, n = 10 cells, p>0.05, t test. Image scale bar = 10 μm.
4 Supplementary Figure 4. GluA2-UTR-GFP blocks the mir124-mediated decrease in GluA2 expression. (A) DIV12 cultured hippocampal neurons were co-transfected with mir124 or a scrambled control (both contain DsRed) with GFP, or co-transfected with GluA2-UTR-GFP with mir124. Total GluA2 was immunostained 2 d later under permeant conditions.
5 (B) In cells expressing mir124, GluA2 levels were decreased compared to the scrambled control. However, mir124 did not change GluA2 in neurons expressing GluA2-UTR-GFP. Bar graph represents Mean ± SE, n = 9-10 cells, * = p<0.05, ns = p>0.05, t test. Image scale bars = 10 μm (full images), 3 μm (dendrites).
6 Supplementary Figure 5. Suppression of mir124 does not affect GABAR and NMDAR expression. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with sirna against mir124, together with DsRed. Scrambled sirna (scrna) was used as a control. GABA receptor subunit α1 (α1r) or NMDA receptor subunit GluN1 were immunostained 2 d after transfection. Inhibition of mir124 did not affect the expression of α1r (A and B; n = 10 cells, p>0.05, t test) or GluN1 (C and D; n = 11 cells, p>0.05, t test). Image scale bars = 10 μm.
7 Supplementary Figure 6. mir124-transfected cells show decreased mepsc decay time and typical multiplicative homeostatic scaling. (A) mir124 expressing cells showed a decreased in average mepsc decay time. Bar graph represents Mean ± SE, n = 6 cells, ** = p<0.01, t test. (B) mir124 expression did not change mepsc frequency. Bar graph represents Mean ± SE, n = 6 cells, p>0.05, t test. (C and D) Cumulative probability plots of amplitude (C) and inter-event interval (D) show typical multiplicative scaling by TTX/APV incubation in mir124-transfected cells.
8 Supplementary Figure 7. Neuronal inactivity causes an increase in mir124 expression. Hippocampal neurons were incubated with TTX/APV for 15 hr. The amount of mir124 was measured by qpcr. Neuronal inhibition led to an increase in mir124. (n = 3, p<0.05, t test).
9 Supplementary Figure 8. GluA2 is increased during HSP. Neurons were transfected with mir124 or BS for 1 d, and then incubated with TTX/APV for 15 hr. Immunostaining showed a significant increase in GluA2 puncta intensity in both the non-transfected surrounding cells and the transfected cells (A). The homeostatic increase in GluA2 was blocked by BS (B).
10 Supplementary Figure 9. CP-AMPARs are required for HSP. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 for 1 d, and then incubated with TTX/APV, with or without PhTx, for 12 hr. Application of PhTx abolished HSP expression shown by mepsc recordings. (n = 5-8 cells, * = p<0.05, ** = p < 0.01, *** = p<0.001, ns = p>0.05, t test).
11 Supplementary Figure 10. Contribution of GluA2-containing AMPARs in HSP. Mir124- transfected neurons were incubated with TTX/APV for 12 hrs to induce HSP. Cells were then recorded in the absence and presence of PhTx. PhTx caused a decrease in mepsc amplitude in mir124-transfected cells under control conditions (2 nd pair of bar graphs). In TTX/APV treated cells, PhTx caused a partial decrease in mepsc amplitude in mir124 transfected cells, but not in the control cells (3 rd and 4 th pairs of bar graphs) (n = 6-9 cells, * = p<0.05, ** = p<0.01, *** = p<0.001, ns = p>0.05, t test).
12 Supplementary Figure 11. Association of EVI1 with mir124 promoter. A ChIP assay shows positive detection of the mir124 promoter sequence in EVI1 immunoprecipitates from cortical neurons. Genomic DNA (gdna) was used as control.
13 Cell lysates IP: HDAC1 IgG Ctrl TTX 1h TTX 2h HDAC1 IP IP: HDAC1 IgG Ctrl TTX 1h TTX 2h Reprobe HDAC1 EVI HDAC Supplementary Figure 12. Co-IP of EVI1 and HDAC1. Neurons were incubated with TTX/APV for 1 or 2 hr. Using the cell lysates, immunoprecipitates of anti-hdac1 antibodies were probed for EVI1. HDAC1-EVI1 association was reduced by neuronal inhibition.
14 Supplemental Figure 13. Full western blots for Figure 1E.
15 Supplemental Figure 14. Full western blots for Figure 2B.
16 Supplemental Figure 15. Full western blots for Figure 3D.
17 Supplemental Figure 16. Full western blots for Figure 7G.
18 Treatment Amplitude (pa) SE Con Basal mir124 Basal Con TTX/APV mir124 TTX/APV Con TTX/APV/PhTx mir124 TTX/APV/PhTx Table 1. mepsc amplitudes from Supplementary Figure 9.
19 Treatment Amplitude (pa) SE Con Basal mir124 Basal Con Basal PhTx mir124 Basal PhTx Con TTX/APV mir124 TTX/APV Con TTX/APV PhTx mir124 TTX/APV PhtX Table 2. mepsc amplitudes from Supplementary Figure 10.
Schwarz et al. Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis
 Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell
 Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Garcia-Alvarez et al. Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1.Expression and RNAi-mediated silencing of STIM1 in hippocampal neurons (DIV, days in vitro).
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Garcia-Alvarez et al. Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1.Expression and RNAi-mediated silencing of STIM1 in hippocampal neurons (DIV, days in vitro).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
Mechanisms for acute stress-induced enhancement of glutamatergic transmission and working memory
 (2011) 16, 156 170 & 2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 1359-4184/11 www.nature.com/mp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mechanisms for acute stress-induced enhancement of glutamatergic transmission
(2011) 16, 156 170 & 2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 1359-4184/11 www.nature.com/mp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mechanisms for acute stress-induced enhancement of glutamatergic transmission
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplemental information Acid-sensing ion channel 1a contributes to hippocampal LTP inducibility through multiple mechanisms
 Supplemental information Acid-sensing ion channel 1a contributes to hippocampal LTP inducibility through multiple mechanisms Ming-Gang Liu, Hu-Song Li, Wei-Guang Li, Yan-Jiao Wu, Shi-Ning Deng, Chen Huang,
Supplemental information Acid-sensing ion channel 1a contributes to hippocampal LTP inducibility through multiple mechanisms Ming-Gang Liu, Hu-Song Li, Wei-Guang Li, Yan-Jiao Wu, Shi-Ning Deng, Chen Huang,
Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C. N. Petrok, J.
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Title: PIP 3 controls synaptic function by maintaining AMPA receptor clustering at the postsynaptic membrane Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Title: PIP 3 controls synaptic function by maintaining AMPA receptor clustering at the postsynaptic membrane Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C.
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the. mutated sequence.
 Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S2
 Supplementary Figure S A) The blots shown in Figure B were qualified by using Gel-Pro analyzer software (Rockville, MD, USA). The ratio of LC3II/LC3I to actin was then calculated. The data are represented
Supplementary Figure S A) The blots shown in Figure B were qualified by using Gel-Pro analyzer software (Rockville, MD, USA). The ratio of LC3II/LC3I to actin was then calculated. The data are represented
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical
 Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical representation using all SNPs (n= 13,515,798) including the region on chromosome 1 including SORT1 which was previously
Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical representation using all SNPs (n= 13,515,798) including the region on chromosome 1 including SORT1 which was previously
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR
 Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
a b c Supplementary Figure 1 R Shrm4 0 -/- -/- GABA B1b Wild type GABA B1a GABA B1a -GABA B1b mean intensity (a.u) Ponceau GABA B
 a b c 200 - H S1 P1 S2 P2 SYN TIF PSD Shrm4 95 - PSD95 34 - Synaptophysin 120-100 - Wil type GABA B1a -/- GABA B1b -/- -GABA B1a -GABA B1b e f 5 μm 10 μm 20 μm 100 - GABA B1a 600 400 200 Ponceau GABA B
a b c 200 - H S1 P1 S2 P2 SYN TIF PSD Shrm4 95 - PSD95 34 - Synaptophysin 120-100 - Wil type GABA B1a -/- GABA B1b -/- -GABA B1a -GABA B1b e f 5 μm 10 μm 20 μm 100 - GABA B1a 600 400 200 Ponceau GABA B
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Bidirectional optogenetic modulation of the tonic activity of CEA PKCδ + neurons in vitro. a, Top, Cell-attached voltage recording illustrating the blue light-induced increase in
Supplementary Figure 1 Bidirectional optogenetic modulation of the tonic activity of CEA PKCδ + neurons in vitro. a, Top, Cell-attached voltage recording illustrating the blue light-induced increase in
NMDAR-dependent Argonaute 2 phosphorylation regulates mirna activity and dendritic spine plasticity
 Article NMDAR-dependent Argonaute 2 phosphorylation regulates mirna activity and dendritic spine plasticity Dipen Rajgor 1, Thomas M Sanderson 2, Mascia Amici 2, Graham L Collingridge 2,3,4 & Jonathan
Article NMDAR-dependent Argonaute 2 phosphorylation regulates mirna activity and dendritic spine plasticity Dipen Rajgor 1, Thomas M Sanderson 2, Mascia Amici 2, Graham L Collingridge 2,3,4 & Jonathan
293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell extracts were subjected
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
Supplementary Figure 1. Rab27a-KD inhibits speed and persistence of HEp3 cells migrating in the chick CAM. (a) Western blot analysis of Rab27a
 Supplementary Figure 1. Rab27a-KD inhibits speed and persistence of HEp3 cells migrating in the chick CAM. (a) Western blot analysis of Rab27a expression in GFP-expressing HEp3 cells. (b) Representative
Supplementary Figure 1. Rab27a-KD inhibits speed and persistence of HEp3 cells migrating in the chick CAM. (a) Western blot analysis of Rab27a expression in GFP-expressing HEp3 cells. (b) Representative
Mossy Fiber-CA3 Synapses Mediate Homeostatic Plasticity in Mature Hippocampal Neurons
 Article Mossy Fiber-CA3 Synapses Mediate Homeostatic Plasticity in Mature Hippocampal Neurons Kea Joo Lee, 1, Bridget N. Queenan, 1,3, Aaron M. Rozeboom, 1 Ryan Bellmore, 1 Seung T. Lim,,3 Stefano Vicini,
Article Mossy Fiber-CA3 Synapses Mediate Homeostatic Plasticity in Mature Hippocampal Neurons Kea Joo Lee, 1, Bridget N. Queenan, 1,3, Aaron M. Rozeboom, 1 Ryan Bellmore, 1 Seung T. Lim,,3 Stefano Vicini,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0110-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0110-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by
How Nicotinic Signaling Shapes Neural Networks
 How Nicotinic Signaling Shapes Neural Networks Darwin K. Berg Division of Biological Sciences University of California, San Diego Nicotinic Cholinergic Signaling Uses the transmitter ACh to activate cation-selective
How Nicotinic Signaling Shapes Neural Networks Darwin K. Berg Division of Biological Sciences University of California, San Diego Nicotinic Cholinergic Signaling Uses the transmitter ACh to activate cation-selective
Supplementary Figure 1. MAT IIα is Acetylated at Lysine 81.
 IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
Control GST GST-RAP. α2-mg. 170 kda. b-actin. 42 kda LRP-1
 % of max Supplementary Figure 1 Control GST GST-RP 17 kda α2-mg 42 kda b-actin Gate: CD11c+ (DCs) Gate: F4/8+ (Mfs) IgG Cd11cCre + Lrp1 fl/fl LRP-1 Supplementary figure 1. () MDCs were pretreated with
% of max Supplementary Figure 1 Control GST GST-RP 17 kda α2-mg 42 kda b-actin Gate: CD11c+ (DCs) Gate: F4/8+ (Mfs) IgG Cd11cCre + Lrp1 fl/fl LRP-1 Supplementary figure 1. () MDCs were pretreated with
Lecture 7: Roles for MAGUKS in Activity-dependent Synaptogenesis MCP
 Lecture 7: Roles for MAGUKS in Activity-dependent Synaptogenesis MCP 9.013 04 Po st -S yn ap (P ti SD c ) De ns it y PSD site en face.25 µm From: Kennedy (2000) Science MEMBRANE ASSOCIATED GUANYLATE KINASES
Lecture 7: Roles for MAGUKS in Activity-dependent Synaptogenesis MCP 9.013 04 Po st -S yn ap (P ti SD c ) De ns it y PSD site en face.25 µm From: Kennedy (2000) Science MEMBRANE ASSOCIATED GUANYLATE KINASES
Dep. Control Time (min)
 aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. PICALM expression in brain capillary endothelium in human brain and in mouse brain.
 Supplementary Figure 1 PICALM expression in brain capillary endothelium in human brain and in mouse brain. a, Double immunostaining for PICALM (red, left) and lectin positive endothelial profiles (blue,
Supplementary Figure 1 PICALM expression in brain capillary endothelium in human brain and in mouse brain. a, Double immunostaining for PICALM (red, left) and lectin positive endothelial profiles (blue,
Psychiatric Risk Factor ANK3/Ankyrin-G Nanodomains Regulate the Structure and Function of Glutamatergic Synapses
 Neuron Article Psychiatric Risk Factor ANK3/Ankyrin-G Nanodomains Regulate the Structure and Function of Glutamatergic Synapses Katharine R. Smith, 1 Katherine J. Kopeikina, 1 Jessica M. Fawcett-Patel,
Neuron Article Psychiatric Risk Factor ANK3/Ankyrin-G Nanodomains Regulate the Structure and Function of Glutamatergic Synapses Katharine R. Smith, 1 Katherine J. Kopeikina, 1 Jessica M. Fawcett-Patel,
Palmitoylation regulates glutamate receptor distributions in postsynaptic densities through control of PSD95 conformation and orientation
 Palmitoylation regulates glutamate receptor distributions in postsynaptic densities through control of PSD95 conformation and orientation Okunola Jeyifous a,b,1, Eric I. Lin a,b,1, Xiaobing Chen b,c, Sarah
Palmitoylation regulates glutamate receptor distributions in postsynaptic densities through control of PSD95 conformation and orientation Okunola Jeyifous a,b,1, Eric I. Lin a,b,1, Xiaobing Chen b,c, Sarah
Dynamic Interaction of Stress Granule, DDX3X and IKK-α Mediates Multiple Functions in
 Dynamic Interaction of Stress Granule, and Mediates Multiple Functions in Hepatitis C Virus Infection Véronique Pène, Qisheng Li#, Catherine Sodroski, Ching-Sheng Hsu, T. Jake Liang# Liver Diseases Branch,
Dynamic Interaction of Stress Granule, and Mediates Multiple Functions in Hepatitis C Virus Infection Véronique Pène, Qisheng Li#, Catherine Sodroski, Ching-Sheng Hsu, T. Jake Liang# Liver Diseases Branch,
Supporting Information
 ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a)
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
An unconventional role for mirna: let-7 activates Toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration
 An unconventional role for mirna: let-7 activates Toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration Sabrina M. Lehmann, Christina Krüger, Boyoun Park, Katja Derkow, Karen Rosenberger, Jan Baumgart, Thorsten
An unconventional role for mirna: let-7 activates Toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration Sabrina M. Lehmann, Christina Krüger, Boyoun Park, Katja Derkow, Karen Rosenberger, Jan Baumgart, Thorsten
Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage response at telomeres that determines cell survival Karolina O. Hain, Didier J. Colin, Shubhra Rastogi, Lindsey
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage response at telomeres that determines cell survival Karolina O. Hain, Didier J. Colin, Shubhra Rastogi, Lindsey
Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation.
 ` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/308/ra4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Antipsychotics Activate mtorc1-dependent Translation to Enhance Neuronal Morphological Complexity Heather Bowling, Guoan
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/308/ra4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Antipsychotics Activate mtorc1-dependent Translation to Enhance Neuronal Morphological Complexity Heather Bowling, Guoan
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Chapter 2. Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit
 15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 SNARE Probes for FRET/2pFLIM Analysis Used in the Present Study. mturquoise (mtq) and Venus (Ven) are in blue and yellow, respectively. The soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 SNARE Probes for FRET/2pFLIM Analysis Used in the Present Study. mturquoise (mtq) and Venus (Ven) are in blue and yellow, respectively. The soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of mir mimics and anti-mirs on DTPs a, Representative fluorescence microscopy images of GFP vector control or mir mimicexpressing parental and DTP
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of mir mimics and anti-mirs on DTPs a, Representative fluorescence microscopy images of GFP vector control or mir mimicexpressing parental and DTP
Kainate receptor activation induces glycine receptor endocytosis through PKC desumoylation
 Received 26 Mar 214 Accepted 13 Aug 214 Published 19 Sep 214 DOI: 1.138/ncomms598 Kainate receptor activation induces glycine receptor endocytosis through PKC desumoylation Hao Sun 1, *, Li Lu 1, *, Yong
Received 26 Mar 214 Accepted 13 Aug 214 Published 19 Sep 214 DOI: 1.138/ncomms598 Kainate receptor activation induces glycine receptor endocytosis through PKC desumoylation Hao Sun 1, *, Li Lu 1, *, Yong
Local Presynaptic Activity Gates Homeostatic Changes in Presynaptic Function Driven by Dendritic BDNF Synthesis
 Article Local Presynaptic Activity Gates Homeostatic Changes in Presynaptic Function Driven by Dendritic Synthesis Sonya K. Jakawich, 1,2 Hassan B. Nasser, 2 Michael J. Strong, 2 Amber J. McCartney, 1,2
Article Local Presynaptic Activity Gates Homeostatic Changes in Presynaptic Function Driven by Dendritic Synthesis Sonya K. Jakawich, 1,2 Hassan B. Nasser, 2 Michael J. Strong, 2 Amber J. McCartney, 1,2
Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development
 Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development 1 Frankie Hang Fung Lee, 1 Ping Su, 1 Yu Feng Xie, 1 Kyle Ethan Wang, 2 Qi Wan and 1,3 Fang Liu 1 Campbell Research Institute, Centre
Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development 1 Frankie Hang Fung Lee, 1 Ping Su, 1 Yu Feng Xie, 1 Kyle Ethan Wang, 2 Qi Wan and 1,3 Fang Liu 1 Campbell Research Institute, Centre
Supplemental Information. Differential Regulation. of Evoked and Spontaneous Release. by Presynaptic NMDA Receptors
 Neuron, Volume 96 Supplemental Information Differential Regulation of Evoked and Spontaneous Release by Presynaptic NMDA Receptors Therése Abrahamsson, hristina You hien hou, Si Ying Li, Adamo Mancino,
Neuron, Volume 96 Supplemental Information Differential Regulation of Evoked and Spontaneous Release by Presynaptic NMDA Receptors Therése Abrahamsson, hristina You hien hou, Si Ying Li, Adamo Mancino,
A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis. Midbrain Forebrain/ Forebrain/ Hindbrain Spinal cord Hindbrain Hindbrain
 A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis NTD Number of embryos % among NTD Embryos Exencephaly 52 74.3% Craniorachischisis 6 8.6% Spina bifida 5 7.1% Microcephaly 7 1% B Normal
A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis NTD Number of embryos % among NTD Embryos Exencephaly 52 74.3% Craniorachischisis 6 8.6% Spina bifida 5 7.1% Microcephaly 7 1% B Normal
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Coordinated Changes in Dendritic Arborization and Synaptic Strength during Neural Circuit Development
 Article Coordinated Changes in Dendritic Arborization and Synaptic Strength during Neural Circuit Development Yi-Rong Peng, 1,2 Shan He, 1,2 Helene Marie, 3,4 Si-Yu Zeng, 1,2 Jun Ma, 1 Zhu-Jun Tan, 1,2
Article Coordinated Changes in Dendritic Arborization and Synaptic Strength during Neural Circuit Development Yi-Rong Peng, 1,2 Shan He, 1,2 Helene Marie, 3,4 Si-Yu Zeng, 1,2 Jun Ma, 1 Zhu-Jun Tan, 1,2
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1: Fibroblast-induced elongation of cancer cells requires direct contact with living fibroblasts. A. Representative images of HT29-GFP cultured in the presence
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1: Fibroblast-induced elongation of cancer cells requires direct contact with living fibroblasts. A. Representative images of HT29-GFP cultured in the presence
Activity level controls postsynaptic composition and signaling via the ubiquitin-proteasome system
 Activity level controls postsynaptic composition and signaling via the ubiquitin-proteasome system Michael D. Ehlers 1 1 Department of Neurobiology, Box 3209, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North
Activity level controls postsynaptic composition and signaling via the ubiquitin-proteasome system Michael D. Ehlers 1 1 Department of Neurobiology, Box 3209, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North
Neocortex Zbtb20 / NFIA / Sox9
 Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
F-actin VWF Vinculin. F-actin. Vinculin VWF
 a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
MII. Supplement Figure 1. CapZ β2. Merge. 250ng. 500ng DIC. Merge. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material. GFP-CapZ β2 DNA
 A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
GFP/Iba1/GFAP. Brain. Liver. Kidney. Lung. Hoechst/Iba1/TLR9!
 Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplemental Table I
 Supplemental Table I Cortex Hippocampus Age (weeks) Genotype STE 61 pste 61 STE 61 pste 61 8 100.0 ± 4.4 96.2 ± 6.0 99.8 ± 8.7 167.5 ± 7.8* 100.0 ± 7.0 90.5 ± 13.8 100.0 ± 12.8 260.4 ± 33.9** 12 100.0
Supplemental Table I Cortex Hippocampus Age (weeks) Genotype STE 61 pste 61 STE 61 pste 61 8 100.0 ± 4.4 96.2 ± 6.0 99.8 ± 8.7 167.5 ± 7.8* 100.0 ± 7.0 90.5 ± 13.8 100.0 ± 12.8 260.4 ± 33.9** 12 100.0
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Rapid parallel measurements of macroautophagy and mitophagy in
 Supplemental Figures Rapid parallel measurements of macroautophagy and mitophagy in mammalian cells using a single fluorescent biosensor Sargsyan A, Cai J, Fandino LB, Labasky ME, Forostyan T, Colosimo
Supplemental Figures Rapid parallel measurements of macroautophagy and mitophagy in mammalian cells using a single fluorescent biosensor Sargsyan A, Cai J, Fandino LB, Labasky ME, Forostyan T, Colosimo
Supplementary Figure 1. SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Multiple Autism-Linked Genes Mediate Synapse Elimination via Proteasomal Degradation of a Synaptic Scaffold PSD-95
 Multiple Autism-Linked Genes Mediate Synapse Elimination via Proteasomal Degradation of a Synaptic Scaffold PSD-95 Nien-Pei Tsai, 1,4 Julia R. Wilkerson, 1,4 Weirui Guo, 1 Marina A. Maksimova, 1 George
Multiple Autism-Linked Genes Mediate Synapse Elimination via Proteasomal Degradation of a Synaptic Scaffold PSD-95 Nien-Pei Tsai, 1,4 Julia R. Wilkerson, 1,4 Weirui Guo, 1 Marina A. Maksimova, 1 George
Downregulation of the small GTPase SAR1A: a key event underlying alcohol-induced Golgi fragmentation in hepatocytes
 Downregulation of the small GTPase SAR1A: a key event underlying alcohol-induced Golgi fragmentation in hepatocytes Armen Petrosyan 1*, Pi-Wan Cheng 1,3, Dahn L. Clemens 2,3 & Carol A. Casey 2,3 1 Department
Downregulation of the small GTPase SAR1A: a key event underlying alcohol-induced Golgi fragmentation in hepatocytes Armen Petrosyan 1*, Pi-Wan Cheng 1,3, Dahn L. Clemens 2,3 & Carol A. Casey 2,3 1 Department
A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass
 Supplementary material Figure S1. Interaction between UBL5 and FANCI A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis of UBL5-interacting proteins,
Supplementary material Figure S1. Interaction between UBL5 and FANCI A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis of UBL5-interacting proteins,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
PKCλ Is Critical in AMPA Receptor Phosphorylation and Synaptic Incorporation during LTP
 Manuscript EMBO-2012-82900 PKCλ Is Critical in AMPA Receptor Phosphorylation and Synaptic Incorporation during LTP Si-Qiang Ren, Jing-Zhi Yan, Xiao-Yan Zhang, Yun-Fei Bu, Wei-Wei Pan, Wen Yao, Tian Tian
Manuscript EMBO-2012-82900 PKCλ Is Critical in AMPA Receptor Phosphorylation and Synaptic Incorporation during LTP Si-Qiang Ren, Jing-Zhi Yan, Xiao-Yan Zhang, Yun-Fei Bu, Wei-Wei Pan, Wen Yao, Tian Tian
(A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939 (5 µm)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Kidney. Heart. Lung. Sirt1. Gapdh. Mouse IgG DAPI. Rabbit IgG DAPI
 a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
Page 39 of 44. 8h LTA & AT h PepG & AT h LTA
 Page 39 of 44 Fig. S1 A: B: C: D: 8h LTA 8h LTA & AT7519 E: F: 8h PepG G: 8h PepG & AT7519 Fig. S1. AT7519 overrides the survival effects of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and peptidoglycan (PepG). (A) Human
Page 39 of 44 Fig. S1 A: B: C: D: 8h LTA 8h LTA & AT7519 E: F: 8h PepG G: 8h PepG & AT7519 Fig. S1. AT7519 overrides the survival effects of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and peptidoglycan (PepG). (A) Human
Genetic variants in the bipolar disorder risk locus SYNE1 that affect CPG2 expression and protein function
 Molecular Psychiatry https://doi.org/1.138/s4138-18-314-z ARTICLE Genetic variants in the bipolar disorder risk locus SYNE1 that affect CPG2 expression and protein function Mette Rathje 1 Hannah Waxman
Molecular Psychiatry https://doi.org/1.138/s4138-18-314-z ARTICLE Genetic variants in the bipolar disorder risk locus SYNE1 that affect CPG2 expression and protein function Mette Rathje 1 Hannah Waxman
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated
 Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting
 mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Posch et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200912046/dc1 Figure S1. Biochemical characterization of the interaction between
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Posch et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200912046/dc1 Figure S1. Biochemical characterization of the interaction between
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Jewell et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201007176/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. IR Munc18c association is independent of IRS-1. (A and
Supplemental material Jewell et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201007176/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. IR Munc18c association is independent of IRS-1. (A and
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementary Figure S1 12 1 8 6 4 2 1-3 1-2 1-1 1 1 1 1 2 1 3 PF-364422 (µm) U87 (EC 5 = 52.2 ± 8.8 µm) 12 1 8 6 4 2 1-4 1-3 1-2 1-1 1 1 1 1 2 CMPD1 (µm) Primary GM (EC 5 = 1.55 ±.3 µm) U138 (EC 5 = 1.7
Supplementary Figure S1 12 1 8 6 4 2 1-3 1-2 1-1 1 1 1 1 2 1 3 PF-364422 (µm) U87 (EC 5 = 52.2 ± 8.8 µm) 12 1 8 6 4 2 1-4 1-3 1-2 1-1 1 1 1 1 2 CMPD1 (µm) Primary GM (EC 5 = 1.55 ±.3 µm) U138 (EC 5 = 1.7
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT ACTB AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT LCOR
 Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
 open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
pt305-camkii stabilizes a learning-induced increase in AMPA receptors for ongoing memory consolidation after classical conditioning
 Received 6 Nov 213 Accepted 25 Apr 214 Published 3 May 214 pt35- stabilizes a learning-induced increase in AMPA receptors for ongoing memory consolidation after classical conditioning Souvik Naskar 1,,
Received 6 Nov 213 Accepted 25 Apr 214 Published 3 May 214 pt35- stabilizes a learning-induced increase in AMPA receptors for ongoing memory consolidation after classical conditioning Souvik Naskar 1,,
