Effects of Ketogenic Diet on the Microbiome and Epilepsy. ATPeeps
|
|
|
- Randolf Cornelius Todd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Effects of Ketogenic Diet on the Microbiome and Epilepsy ATPeeps
2 Agenda Background Ketone bodies Ketogenic diet Insulin resistance Gut Microbiota Epilepsy Treatment methods Refractory epilepsy Studies previously done Mice & Human Methods & Results Findings Conclusion
3 Ketone Bodies (KB) Recap: What are ketone bodies? Three water-soluble molecules containing the ketone group that are produced by the liver from fatty acids during periods of low food intake, carbohydrate restricted diets, starvation, prolonged intense exercise, alcoholism, or untreated type 1 diabetes. Not enough insulin = unable to use glucose for energy = breakdown of fat and protein Raised levels of ketone bodies in the body tissues = ketosis 3 main ketone bodies: β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) Acetoacetate (AcAc) Acetone
4 Acetoacetate (AcAc), Acetone and β- hydroxybutyrate (BHB) Acetoacetate principle ketone body produced and utilized during intermediary metabolism other ketone bodies are derived from AcAc Acetone simplest ketone produced by the spontaneous decarboxylation of acetoacetate least abundant ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) In the liver, the BHB-dehydrogenase enzyme reduces AcAc to form BHB BHB is the most prevalent circulating ketone body as cells adapt to carbohydrate restriction BHB is not a technically a ketone due it structure Still considered a ketone because BHB is closely related to AcAc and acetone and affect the body similarly
5 Ketone Bodies Mediate Anti-Seizure Efficacy New data from in vivo and in vitro studies support ketone bodies as having anti-seizure actions Ketones also influence neuronal excitability directly through molecular targets: The mitochondria antioxidant systems, inflammatory mediators, and Histone deacetylation (HDAC) status The anti-seizure efficacy is due to the effects of...
6 Ketogenic Diet (KD) Low carbohydrate, adequate protein, and high-fat diet Body burn fats rather than carbohydrates Diet promotes weight loss though high caloric foods are consumed Ketones fatty acid production decreased glucose uptake
7 Examples of Ketogenic Diet (KD) Foods
8 Ketogenic Diet Used as Treatment Treatment for: Alzheimer s disease Type II Diabetes Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome ASD Epilepsy Insulin resistance mediated by KD is a key player in how the diet can be a used as a treatment for some of these diseases
9 Insulin Resistance KD diet has been found to result in insulin resistance which increases hepatic lipid content Increased diacylglycerol (DAG) content increased protein kinase C(PKCε) activation inhibition of insulin signalling In muscle failure to promote glycogen synthesis: rather promote fatty acid(fa) prod. Increased lipid prod. NAFLD (Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) CAN be fixed with exercise!
10 Recent studies suggest KD may improve insulin sensitivity Insulin resistance leads to a decrease in insulin-stimulated heart muscle and brown adipose tissue(bat) glucose uptake In the heart, it reduces its ketolytic capacity fatty acid oxidation Additionally, 23% reduction of glucagon increase FGF21(regulates energy) Contributes to reduction in fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations Inhibits glucagon secretion from rat pancreatic α-cells Overall, FGF21 has been suggested to play a crucial role in ketogenesis, increases energy expenditure and thermogenic activation of BAT Hepatic expression of FGF21 is implicated in long-term regulation of energy balance and metabolism
11 The microbe(microorganism) population living in our intestine Gut flora or gastrointestinal microbiota ⅓ of out gut microbiota is common to most people and ⅔ are specific to one person Each person/animal has a unique microbiota Even with unique microbiotas they all fulfil physiological functions which impact our health: Helps with digestion Production of some vitamins like B and K Helps with host metabolism and behavior etc. Intermediary in diet and host physiology Composition and function is shaped by diet changing Nutrients available depend on microbial metabolism
12 The microbiota plays an important role in providing materials needed for ketone body synthesis and can affect ketone body synthesis during caloric restriction. Changes are reproducible and persistent lasting impact on host Diet-induced pathologies due to changes in the gut microbiota in mouse models Atherosclerosis = carnitine-rich diet Undernutrition = Malawian diet Abnormal social behavior = maternal high-fat diet KD alters the composition of gut microbiota in mice Ketosis is associated with alterations of gut microbiota association with changes in factors relevant to neurotransmission (neurotransmitter signaling, synaptic protein expression, long-term potentiation, myelination, etc) Changes in host behavior like stress-induced, social, and cognitive behaviors *ketosis = presence of ketone bodies
13 Epilepsy Disorder where nerve cell activity in the brain is disturbed, causing seizures. Symptoms: Fainting, fatigue, muscle spasms, amnesia, anxiety, depression, headaches, temporary paralysis after a seizure, loss of consciousness, etc. 4th most common neurological disorder Affects all ages Also known as "seizure disorder"
14 Epilepsy Epilepsy is a spectrum condition with a wide range of seizure types: Focal - specific place in the brain Without loss of consciousness and with impaired awareness Generalized - all over the brain Absence, tonic, atonic, clonic, myoclonic, tonic-clonic seizures Tonic-clonic seizures: can cause abrupt loss of consciousness, body stiffening and shaking, and sometimes loss of bladder control or biting of the tongue.. Causes: Genetic influences, head trauma, brain conditions, infectious disease, prenatal injury, developmental disorders
15 Current Treatments for Epilepsy Medication Depends on what type of seizures patient has, frequency, age, sex, other medications, and pregnancy Anti-seizure or anticonvulsants Change the way the brain cells work and communicate with each other Nerve stimulation Vagus nerve stimulation Device sends small bursts of electricity through the nerve in chest/abdomen to your brain Medication still may be needed Responsive neurostimulation Device under the scalp, looks for patterns in brain activity that lead to seizure, when pattern detected sends pulse to interrupt it Surgery Resective surgery Part of brain that causes seizures is removed, mostly done when the part is very small with small boundaries, along with controlling important parts like speech, movement, sight, or hearing. Disconnective surgery Instead of removing part of brain, path of nerves involved in the seizures are cut Diet Ketogenic diet
16 Refractory Epilepsy Refractory epilepsy: Condition affecting > ⅓ epileptic individuals, defined by failure to respond to existing anticonvulsant medications A disorder in which nerve cell activity in the brain is disturbed, causing seizures Also known as intractable, or drug-resistant epilepsy. Medicine is NOT bringing seizures under control anti-seizure medication
17 Gut Microbiota Several studies have shown with antibiotic treatment increases the risk of status epilepticus and symptomatic seizures Status epilepticus: repeated seizures one after another without recovery of consciousness between them Acute symptomatic seizures: Clinical seizures occurring at the time of a systemic insult (such as a stroke, traumatic brain injury, subdural hematoma, active CNS infection, active phase of MS, other autoimmune disease, etc.) Hypothesis that gut microbiota (GM) impacts the anti-seizure effects of the KD
18 Mice Microbiota Experiments with Ketogenic Diet
19 The Ketogenic Diet Alters the Gut Microbiota Tested using 6-Hz induced seizure model of refractory epilepsy Mice fed KD exhibit elevated seizure thresholds in response to 6-Hz stimulation KD alters composition of gut microbiota by 4 days postdietary treatment Decreased alpha diversity observed at each time point KD-induced losses of particular bacterial taxa KD increase relative abundance of Akkermansia (Akk) Parabacteroides, Sutterella, and Erysipelotrichaceae increase in KD-fed mice Allobaculum, Bifidobacterium, Desulfovibrio increased in CD(control diet)-fed mice Composition of gut microbiota is rapidly and substantially altered in response to KD
20
21 The GM is Necessary & Sufficient for Anti-Seizure Effects of KD 6-Hz Psychomotor Seizure Assay Experimental groups: Germ free or antibiotic treated mice fed a ketogenic diet Postnatally conventionalized germ free mice fed a ketogenic diet SPF mice fed KD for 14 days exhibited increased seizure thresholds and altered microbiota Gut microbiota is required for KD-mediated increases in seizure protection Actively mediates seizure protection through pathways that are independent of pre-weaning developmental processes Microbial effects on seizure resistance do not correlate with changes in serum BHB or glucose levels Gut microbes modulate seizure susceptibility through mechanisms that do not involve alterations in BHB levels
22
23 The Gut Microbiota Confers Seizure Protection to Mice Fed the Control Diet Study to determine if ketogenic diet-associated gut microbes confer anti-seizure effects in mice fed a control diet: Mice treated with antibiotics were transplanted with the microbiota from specific pathogen free mice and fed either a control diet or ketogenic diet Mice were then evaluated on their susceptibility to 6-Hz seizures after 4 days of dietary treatment Mice transplanted with microbiota from the control diet specimen and fed a ketogenic diet demonstrated an increased seizure threshold Mice fed a control diet demonstrated an increased seizure threshold when transplanted with the microbiota from the ketogenic diet specimen The ketogenic diet microbiota confers seizure protection even in mice fed a control diet
24 The Gut Microbiota Confers Seizure Protection to Mice Fed the Control Diet A confound to these anti-seizure effects arises when specific pathogen free mice and germ free mice treated with antibiotics and fed a control diet demonstrate an increase in seizure threshold To combat this confound: Exogenous bacterial treatment administered to mice fed a control diet Specific pathogen free mice gavaged bi-daily for 28 days with 10^9 colony forming units A. muciniphila and Parabacteroides or with vehicle Treatment increased seizure thresholds in comparison to vehicle gavaged controls Seizure protection not observed in mice treated with A. muciniphila alone Treatment with heat-killed bacteria decreases seizure threshold Persistent exposure to A. muciniphila and Parabacteroides is necessary Fecal transplant of the ketogenic diet microbiota paired with long term bacterial treatment with the ketogenic diet associated taxa confer protection against 6-Hz seizures in mice fed the control diet
25
26
27 KD-Associated Bacteria Mediating Anti- Seizure Effects of the KD -That increase in seizure threshold in SPD CD mice treated with Abx (antibiotics) alone and GF Cd mice relative to SPF (Specific pathogen-free) CD controls caused uncertain results. -Bacterial treatment increased seizure threshold in relation to vehicle-gavaged controls - The Co-administration of A Muciniphilia and Parabacteroides is required for seizure protection.
28
29 Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and SUDE - KD increases A Muciniphilia and parabacteroides in KCNA mice - Decrease in the occurrence of seizures and duration in both KD and CD fed mice. - A. muciniphila and Parabacteroides had a reduced seizure frequency and duration vs vehicle control. - Microbial dietary metabolism regulates secondary metabolites - An impact on the likelihood of a seizure happening
30
31 The Microbiota Modulates Gut, Serum, and Brain Metabolomes Hypothesis: microbial dietary metabolism regulates secondary metabolites that impact seizure susceptibility. Widespread decreases in subsets of ketogenic gamma-glutamylated amino acids Gamma-glutamated forms of the amino acids were particularly affected Gut microbiota modulates gamma-glutamylation itself or selective metabolism of ketogenic GG-amino acids Increased ketogenic GG-amino acids are associated with seizure susceptibility Gut microbiota modulates intestinal and systematic metabolomic responses to KD Association between KD-induced seizure protection and microbiotadependent alterations in levels of ketogenic GG-amino acids
32 What About HUMANS?
33 Ketogenic Diet Treatment in Adults with Refractory Epilepsy KD is used to treat refractory epilepsy mainly FOR CHILDREN Not many studies Untested assumption that adults would not comply with the unpalatable diet
34 Treatment Compliance
35 But KD is still safe! Side Effects Observed in Children Constipation Diarrhea Nausea Vomiting Nephrolithiasis (kidney stones) Metabolic acidosis (excessive quantities of acid) Hyperuricemia (high uric acid) Hypocalcemia (electrolyte imbalance) Hypomagnesemia (low magnesium) Weight loss Hyperlipidemia (too many lipids) Bruising Osteopenia (bone loss)
36 METHODS SUBJECTS Men and women aged with Refractory primary generalized epilepsy (PGE) Localization-related epilepsy (LRE) Failed treatment with 3 antiepileptic drugs & seizure frequency of 1 every 2 months Fast for first hours KD initiated during 4-5 day long hospitalization daily caloric increase (33, 66, 100%) Used 3:1 [fat]:[protein + carbohydrate] ratio by weight, 90% calories derived from fat 4:1 ratio usually used in children
37 (# of people, out of 12) RESULTS (4) (3) (1) (1) (2) (2) (1) (2) No subjects discontinued treatment because of adverse effects SAFE 10/12 subjects improved 6/12 had 50% seizure reduction during the whole treatment 4/12 had 20-50% seizure reduction during the whole treatment 1 did not change 1 worsened Efficacy data in study similar to those from pediatric studies KD may be very effective in proportion of adults
38
39 most
40 most
41 Positive Numbers Percentage of improvement Negative Numbers Percentage of deterioration
42 seizure frequency DID NOT IMPROVE
43
44
45 Adults VS. Children In pediatric studies, antiepileptic effect may persist after KD discontinuation. Previously, adult studies have not evaluated effect of KD on epilepsy after treatment discontinuation. In this study, seizure improvement did NOT outlast KD treatment difference between adult and pediatric responses to KD
46 Conclusion Ketone bodies mediate anti-seizure efficacy of the KD Insulin resistance mediated by KD is a key player in reducing antiseizure effects in epilepsy Effects of a ketogenic diet on epileptic seizures are also mediated by the gut microbiome through their modulation of hippocampal GABA/glutamate ratios Changes in the gut microbiota are required for the anti-seizure effects of the KD Due to previous adaptations in adult gut microbiota, the ketogenic diet affects adult patients ONLY during treatment diet must be continued to have anti-seizure effects
47 References Klein, P., Janousek, J., Barber, A., & Weissberger, R. (2010). Ketogenic diet treatment in adults with refractory epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior, 19(4), Olson, C. A., Vuong, H. E., Yano, J. M., Liang, Q. Y., Nusbaum, D. J., & Hsiao, E. Y. (2018). The gut microbiota mediates the anti-seizure effects of the ketogenic diet. Cell, 173(7), Simeone, Timothy A., et al. "Do ketone bodies mediate the anti-seizure effects of the ketogenic diet?." Neuropharmacology 133 (2018):
48 Bingo Word Bank BHB: B-hydroxybutyrate CFU: colony forming units AcAc: Acetoacetate SPF: Specific pathogen-free KB GF: Germ free KD CD: Control diet ETC: Electron transport chain BF: Bifidobacterium longum HDAC: Histone deacetylase BHI: Brain heart infusion mpt: Mitochondrial permeability transition OTUs: Operational taxonomic units Ac-CoA: Acetyl coenzyme A KO: Knock out GABA: gamma-aminobutyric acid GGT: gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase Akk: Akkermansia muciniphila AU: Absorbance units FISH: Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization EEG Abx: Antibiotics ROS: reactive oxygen species
KETOGENIC DIET ISMAIL HALAHLEH, MSC. نقیب اخصاي یي التغذیة الفلسطینیین
 KETOGENIC DIET ISMAIL HALAHLEH, MSC. نقیب اخصاي یي التغذیة الفلسطینیین INTRODUCTION WHAT IS KETOGENIC DIET???? KETOGENIC DIET The ketogenic diet (KD) is a diet that is high in fat, low in carbohydrate,
KETOGENIC DIET ISMAIL HALAHLEH, MSC. نقیب اخصاي یي التغذیة الفلسطینیین INTRODUCTION WHAT IS KETOGENIC DIET???? KETOGENIC DIET The ketogenic diet (KD) is a diet that is high in fat, low in carbohydrate,
Physiology Unit 1 METABOLISM OF LIPIDS AND PROTEINS
 Physiology Unit 1 METABOLISM OF LIPIDS AND PROTEINS Alternate Fuel Sources When glucose levels are low Proteins and Triglycerides will be metabolized Tissues will use different fuel sources depending on:
Physiology Unit 1 METABOLISM OF LIPIDS AND PROTEINS Alternate Fuel Sources When glucose levels are low Proteins and Triglycerides will be metabolized Tissues will use different fuel sources depending on:
CHY2026: General Biochemistry. Lipid Metabolism
 CHY2026: General Biochemistry Lipid Metabolism Lipid Digestion Lipid Metabolism Fats (triglycerides) are high metabolic energy molecules Fats yield 9.3 kcal of energy (carbohydrates and proteins 4.1 kcal)
CHY2026: General Biochemistry Lipid Metabolism Lipid Digestion Lipid Metabolism Fats (triglycerides) are high metabolic energy molecules Fats yield 9.3 kcal of energy (carbohydrates and proteins 4.1 kcal)
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 27 Fatty Acid Degradation Dietary Lipid (Triacylglycerol) Metabolism - In the small intestine, fat particles are coated with bile
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 27 Fatty Acid Degradation Dietary Lipid (Triacylglycerol) Metabolism - In the small intestine, fat particles are coated with bile
There are several types of epilepsy. Each of them have different causes, symptoms and treatment.
 1 EPILEPSY Epilepsy is a group of neurological diseases where the nerve cell activity in the brain is disrupted, causing seizures of unusual sensations, behavior and sometimes loss of consciousness. Epileptic
1 EPILEPSY Epilepsy is a group of neurological diseases where the nerve cell activity in the brain is disrupted, causing seizures of unusual sensations, behavior and sometimes loss of consciousness. Epileptic
HISTORY OF THE KETOGENIC DIET
 Laura Roche RD Horizon Health Authority May 29, 2018 AGENDA History of the Ketogenic Diet Diet Pathophysiology Side Effects Pros and Cons How and Why the Diet works Ketogenic Diet for Type 2 Diabetes Ketogenic
Laura Roche RD Horizon Health Authority May 29, 2018 AGENDA History of the Ketogenic Diet Diet Pathophysiology Side Effects Pros and Cons How and Why the Diet works Ketogenic Diet for Type 2 Diabetes Ketogenic
Oxidation of Long Chain Fatty Acids
 Oxidation of Long Chain Fatty Acids Dr NC Bird Oxidation of long chain fatty acids is the primary source of energy supply in man and animals. Hibernating animals utilise fat stores to maintain body heat,
Oxidation of Long Chain Fatty Acids Dr NC Bird Oxidation of long chain fatty acids is the primary source of energy supply in man and animals. Hibernating animals utilise fat stores to maintain body heat,
The Anti-Seizure Effects of Ketone Bodies. Glia Club - Dennis T., Ella O., Erika P, Subathra R.
 ia The Anti-Seizure Effects of Ketone Bodies Glia Club - Dennis T., Ella O., Erika P, Subathra R. Overview 1. Introduction a. Epilepsy b. What is the Ketogenic diet? c. Ketone bodies 2. Potential mechanisms
ia The Anti-Seizure Effects of Ketone Bodies Glia Club - Dennis T., Ella O., Erika P, Subathra R. Overview 1. Introduction a. Epilepsy b. What is the Ketogenic diet? c. Ketone bodies 2. Potential mechanisms
INTRODUCTION TO NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE. Learning in Retirement: Epilepsy
 INTRODUCTION TO NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE Learning in Retirement: Epilepsy Lesson Overview Seizures VS Epilepsy What Causes Seizures? Types of Seizures Epilepsy Pathology General Cellular Molecular Diagnosis
INTRODUCTION TO NEUROLOGICAL DISEASE Learning in Retirement: Epilepsy Lesson Overview Seizures VS Epilepsy What Causes Seizures? Types of Seizures Epilepsy Pathology General Cellular Molecular Diagnosis
Understanding Ketogenic Diet with Rodent Epilepsy Models. Do-Young Kim Barrow Neurological Institute Phoenix, Arizona, USA
 Understanding Ketogenic Diet with Rodent Epilepsy Models Do-Young Kim Barrow Neurological Institute Phoenix, Arizona, USA Causes of Epilepsy The most common causes of epilepsy include: Brain infection,
Understanding Ketogenic Diet with Rodent Epilepsy Models Do-Young Kim Barrow Neurological Institute Phoenix, Arizona, USA Causes of Epilepsy The most common causes of epilepsy include: Brain infection,
Chapter 7- Metabolism: Transformations and Interactions Thomson - Wadsworth
 Chapter 7- Metabolism: Transformations and Interactions 2008 Thomson - Wadsworth Simple Overview of Energy Metabolism The sum of all chemical reactions that go on in living cells Introduction Energy Heat-
Chapter 7- Metabolism: Transformations and Interactions 2008 Thomson - Wadsworth Simple Overview of Energy Metabolism The sum of all chemical reactions that go on in living cells Introduction Energy Heat-
- biochemical principles - practical applications
 The ketogenic diet in pediatric neurology practice - biochemical principles - practical applications Some points from history 1921-1928: «The efficiency of fasting» and being free of seizures 1921-1970:
The ketogenic diet in pediatric neurology practice - biochemical principles - practical applications Some points from history 1921-1928: «The efficiency of fasting» and being free of seizures 1921-1970:
Lipid Metabolism. Remember fats?? Triacylglycerols - major form of energy storage in animals
 Remember fats?? Triacylglycerols - major form of energy storage in animals Your energy reserves: ~0.5% carbs (glycogen + glucose) ~15% protein (muscle, last resort) ~85% fat Why use fat for energy? 1 gram
Remember fats?? Triacylglycerols - major form of energy storage in animals Your energy reserves: ~0.5% carbs (glycogen + glucose) ~15% protein (muscle, last resort) ~85% fat Why use fat for energy? 1 gram
Energy Metabolism. Chapter Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
 Energy Metabolism Chapter 7 Introduction Energy Heat, mechanical, electrical, and chemical Metabolism How the body uses foods to meet its needs Chemical Reactions in the Body Energy metabolism How body
Energy Metabolism Chapter 7 Introduction Energy Heat, mechanical, electrical, and chemical Metabolism How the body uses foods to meet its needs Chemical Reactions in the Body Energy metabolism How body
Epilepsy. Presented By: Stan Andrisse
 Epilepsy Presented By: Stan Andrisse What Is Epilepsy Chronic Neurological Disorder Characterized by seizures Young children or elderly Developing countries Famous Cases Socrates Muhammad Aristotle Joan
Epilepsy Presented By: Stan Andrisse What Is Epilepsy Chronic Neurological Disorder Characterized by seizures Young children or elderly Developing countries Famous Cases Socrates Muhammad Aristotle Joan
Carbohydrates. Three Types of Carbs Fiber. Does not impact the blood sugar. Cleaners Controllers May be eaten on a Ketogenic diet
 The Keto Challenge Carbohydrates Carbohydrates Three Types of Carbs STARCHES (complex carbs) Take a little longer to digest b Slower rise in blood glucose levels Trigger the Fat Truck (Slower, but still
The Keto Challenge Carbohydrates Carbohydrates Three Types of Carbs STARCHES (complex carbs) Take a little longer to digest b Slower rise in blood glucose levels Trigger the Fat Truck (Slower, but still
23.1 Lipid Metabolism in Animals. Chapter 23. Micelles Lipid Metabolism in. Animals. Overview of Digestion Lipid Metabolism in
 Denniston Topping Caret Copyright! The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 23 Fatty Acid Metabolism Triglycerides (Tgl) are emulsified into fat droplets
Denniston Topping Caret Copyright! The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 23 Fatty Acid Metabolism Triglycerides (Tgl) are emulsified into fat droplets
Hompes Method Lesson 29 Organic Acids Part One
 Hompes Method Lesson 29 Organic Acids Part One Health for the People Ltd not for reuse without expressed permission Organic Acids - Introduction The ultimate tool for laboratory evaluations in nutritional
Hompes Method Lesson 29 Organic Acids Part One Health for the People Ltd not for reuse without expressed permission Organic Acids - Introduction The ultimate tool for laboratory evaluations in nutritional
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM. Triacylglycerol and Fatty Acid Metabolism
 ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM II. Triacylglycerol synthesis A. Overall pathway Glycerol-3-phosphate + 3 Fatty acyl-coa à Triacylglycerol + 3 CoASH B. Enzymes 1. Acyl-CoA synthase 2. Glycerol-phosphate
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM II. Triacylglycerol synthesis A. Overall pathway Glycerol-3-phosphate + 3 Fatty acyl-coa à Triacylglycerol + 3 CoASH B. Enzymes 1. Acyl-CoA synthase 2. Glycerol-phosphate
Integrative Metabolism: Significance
 Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
THE GLUCOSE-FATTY ACID-KETONE BODY CYCLE Role of ketone bodies as respiratory substrates and metabolic signals
 Br. J. Anaesth. (1981), 53, 131 THE GLUCOSE-FATTY ACID-KETONE BODY CYCLE Role of ketone bodies as respiratory substrates and metabolic signals J. C. STANLEY In this paper, the glucose-fatty acid cycle
Br. J. Anaesth. (1981), 53, 131 THE GLUCOSE-FATTY ACID-KETONE BODY CYCLE Role of ketone bodies as respiratory substrates and metabolic signals J. C. STANLEY In this paper, the glucose-fatty acid cycle
Applied Nutritional Medicine. Supplement Categories. E.I.Nu.M.
 Supplement Categories In this section, we will begin to explain the Metabolomic Academy method of Nutritional Medicine. The step taken by metabolomic studies was to identify seven categories of major nutritional
Supplement Categories In this section, we will begin to explain the Metabolomic Academy method of Nutritional Medicine. The step taken by metabolomic studies was to identify seven categories of major nutritional
LESSON 2.4 WORKBOOK. Part two: Glucose homeostasis in the blood Un-Storing energy
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Fasting A state of abstinence from all food or drinks that provide calories. For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. LESSON 2.4 WORKBOOK Part two: Glucose homeostasis
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Fasting A state of abstinence from all food or drinks that provide calories. For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. LESSON 2.4 WORKBOOK Part two: Glucose homeostasis
WHY? 26/2/2010. Shimomura Y, Harris RA. J Nutr. 2006;136(1 suppl):232s-233s. BCAA buffer excessive amounts of Glutamate by converting it to Glutamine.
 Branched Chain Amino Acids as Adjunctive Therapy to Ketogenic Diet Athanasios Evangeliou MD 4th Department of Pediatrics of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki Papageorgiou Hospital Thessaloniki E-mail:
Branched Chain Amino Acids as Adjunctive Therapy to Ketogenic Diet Athanasios Evangeliou MD 4th Department of Pediatrics of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki Papageorgiou Hospital Thessaloniki E-mail:
Introduction. 1 person in 20 will have an epileptic seizure at some time in their life
 Introduction 1 person in 20 will have an epileptic seizure at some time in their life Epilepsy is diagnosed on the basis of two or more epileptic seizures. Around 450,000 people in the UK have epilepsy
Introduction 1 person in 20 will have an epileptic seizure at some time in their life Epilepsy is diagnosed on the basis of two or more epileptic seizures. Around 450,000 people in the UK have epilepsy
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetyl CoA oxidation of in postpartum period, 287 Acidifying feeds in transition dairy cow management, 374 Adipose tissues derivatives of, 307
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetyl CoA oxidation of in postpartum period, 287 Acidifying feeds in transition dairy cow management, 374 Adipose tissues derivatives of, 307
Roles of Lipids. principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular
 Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
ACUTE & CHRONIC ETHANOL EFFECTS An Overview
 ACUTE & CHRONIC ETHANOL EFFECTS An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Clinical Biochemistry: PBL Seminar MBBS Yr 4 VJ Temple
ACUTE & CHRONIC ETHANOL EFFECTS An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Clinical Biochemistry: PBL Seminar MBBS Yr 4 VJ Temple
BASIC SCIENCES & BIOCHEMISTRY FOR BETZPAENIC BRIMBLERS
 BASIC SCIENCES & BIOCHEMISTRY FOR BETZPAENIC BRIMBLERS Lymphatic Vessels One main lymph vessel receives lymph from the right upper arm and the right side of the head and the thorax and empties into the
BASIC SCIENCES & BIOCHEMISTRY FOR BETZPAENIC BRIMBLERS Lymphatic Vessels One main lymph vessel receives lymph from the right upper arm and the right side of the head and the thorax and empties into the
Why Talk about Alcohol? Lecture 14: Alcohol. Consuming Alcohol in Moderation
 Lecture 14: Alcohol Why Talk about Alcohol? Energy source Interferes with metabolism Interferes with nutrient absorption Promotes health problems Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Alcohol is a term used
Lecture 14: Alcohol Why Talk about Alcohol? Energy source Interferes with metabolism Interferes with nutrient absorption Promotes health problems Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Alcohol is a term used
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 1 PBL SEMINAR ACUTE & CHRONIC ETHANOL EFFECTS An Overview Sites
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 1 PBL SEMINAR ACUTE & CHRONIC ETHANOL EFFECTS An Overview Sites
Protein & Amino Acid Metabolism
 Pathophysiology 101-823 Unit 4 Metabolism & Metabolic Disease Protein & Amino Acid Metabolism Paul Anderson FALL 2008 Learning Objectives 1. List the metabolic functions of proteins & amino acids. 2. Explain
Pathophysiology 101-823 Unit 4 Metabolism & Metabolic Disease Protein & Amino Acid Metabolism Paul Anderson FALL 2008 Learning Objectives 1. List the metabolic functions of proteins & amino acids. 2. Explain
The molecule that serves as the major source of readily available body fuel is: a. fat. b. glucose. c. acetyl CoA. d. cellulose.
 The molecule that serves as the major source of readily available body fuel is: a. fat. b. glucose. c. acetyl CoA. d. cellulose. Dietary fats are important because: a. they keep blood pressure normal.
The molecule that serves as the major source of readily available body fuel is: a. fat. b. glucose. c. acetyl CoA. d. cellulose. Dietary fats are important because: a. they keep blood pressure normal.
Ketogenic diet and other dietary therapies in epilepsy. Randa Jarrar, MD
 Ketogenic diet and other dietary therapies in epilepsy Randa Jarrar, MD Ketogenic diet: History What is involved Efficacy Complications How does it work Variations: MCT ketogenic diet Low glycemic index
Ketogenic diet and other dietary therapies in epilepsy Randa Jarrar, MD Ketogenic diet: History What is involved Efficacy Complications How does it work Variations: MCT ketogenic diet Low glycemic index
It Takes Guts to Grow a Brain. Josef Neu, M.D. University of Florida
 It Takes Guts to Grow a Brain Josef Neu, M.D. University of Florida neuj@peds.ufl.edu The Versatile Intestine: The intestine is not only a digestive-absorptive organ Largest immune organ of the body. Harbors
It Takes Guts to Grow a Brain Josef Neu, M.D. University of Florida neuj@peds.ufl.edu The Versatile Intestine: The intestine is not only a digestive-absorptive organ Largest immune organ of the body. Harbors
1/31/2009. Paroxysmal, uncontrolled electrical discharge of neurons in brain interrupting normal function
 Paroxysmal, uncontrolled electrical discharge of neurons in brain interrupting normal function In epilepsy abnormal neurons undergo spontaneous firing Cause of abnormal firing is unclear Firing spreads
Paroxysmal, uncontrolled electrical discharge of neurons in brain interrupting normal function In epilepsy abnormal neurons undergo spontaneous firing Cause of abnormal firing is unclear Firing spreads
Week 3 The Pancreas: Pancreatic ph buffering:
 Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Carbohydrate Lipid and Protein! Metabolism! In the catabolism of carbohydrates, glycolysis converts glucose into pyruvate, which is then metabolized into acetyl CoA. Prepared
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Carbohydrate Lipid and Protein! Metabolism! In the catabolism of carbohydrates, glycolysis converts glucose into pyruvate, which is then metabolized into acetyl CoA. Prepared
E. Haritov, E. Angeleska and N. Boyadjieva Department of pharmacology and toxicology, Medical Faculty, Medical University So a
 :.,..,, KETOGENIC DIET AND EPILEPSY: THE ROLE OF KETONE BODIES IN THE INFLUENCE N NEURONAL EXCITABILITY E. Haritov, E. Angeleska and N. Boyadjieva Department of pharmacology and toxicology, Medical Faculty,
:.,..,, KETOGENIC DIET AND EPILEPSY: THE ROLE OF KETONE BODIES IN THE INFLUENCE N NEURONAL EXCITABILITY E. Haritov, E. Angeleska and N. Boyadjieva Department of pharmacology and toxicology, Medical Faculty,
The Glucose Ketone Index Calculator: A Simple Tool to Monitor Therapeutic. Efficacy for Metabolic Management of Brain Cancer
 Nutrition & Metabolism (in press) The Glucose Ketone Index Calculator: A Simple Tool to Monitor Therapeutic Efficacy for Metabolic Management of Brain Cancer Joshua J. Meidenbauer, Purna Mukherjee and
Nutrition & Metabolism (in press) The Glucose Ketone Index Calculator: A Simple Tool to Monitor Therapeutic Efficacy for Metabolic Management of Brain Cancer Joshua J. Meidenbauer, Purna Mukherjee and
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department
 Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department Cardiac Fuels [Sources of energy for the Cardiac muscle] Intended learning outcomes of the lecture: By the end of this lecture you would be able to:-
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department Cardiac Fuels [Sources of energy for the Cardiac muscle] Intended learning outcomes of the lecture: By the end of this lecture you would be able to:-
LIPID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
Paediatric Epilepsy Update N o r e e n Te a h a n canp C o l e t t e H u r l e y C N S E p i l e p s y
 Paediatric Epilepsy Update 2018 N o r e e n Te a h a n canp C o l e t t e H u r l e y C N S E p i l e p s y Epilepsy Service CUH ~550 children New diagnosis-education, support, clinic follow up Epilepsy
Paediatric Epilepsy Update 2018 N o r e e n Te a h a n canp C o l e t t e H u r l e y C N S E p i l e p s y Epilepsy Service CUH ~550 children New diagnosis-education, support, clinic follow up Epilepsy
Chemistry 1120 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chemistry 1120 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 12 12.1 Identify and differentiate between macronutrients (lipids, amino acids and saccharides) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). Master Tutor Section
Chemistry 1120 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 12 12.1 Identify and differentiate between macronutrients (lipids, amino acids and saccharides) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). Master Tutor Section
Nutrients. Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation
 Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS & OTHER NEUROLOGICAL DISEASES
 How Nutrition Changes the Aging Brain MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS & OTHER NEUROLOGICAL DISEASES Nafisa Jadavji, PhD nafisa.jadavji@carleton.ca Outline for Lecture Topics from Lecture #5 Multiple Sclerosis Parkinson
How Nutrition Changes the Aging Brain MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS & OTHER NEUROLOGICAL DISEASES Nafisa Jadavji, PhD nafisa.jadavji@carleton.ca Outline for Lecture Topics from Lecture #5 Multiple Sclerosis Parkinson
These factors should be taken into consideration when addressing fatigue or low energy because each factor will be approached slightly differently.
 1 2 These factors should be taken into consideration when addressing fatigue or low energy because each factor will be approached slightly differently. 3 4 First we must understand the systems of the body
1 2 These factors should be taken into consideration when addressing fatigue or low energy because each factor will be approached slightly differently. 3 4 First we must understand the systems of the body
Discerning Seizures and Understanding VNS Therapy Delia Nickolaus, CPNP-PC/AC
 O U T R E A C H E D U C A T I O N Discerning and Understanding VNS Therapy Delia Nickolaus, CPNP-PC/AC Program Handouts This information is provided as a courtesy by Children's Health Care System and its
O U T R E A C H E D U C A T I O N Discerning and Understanding VNS Therapy Delia Nickolaus, CPNP-PC/AC Program Handouts This information is provided as a courtesy by Children's Health Care System and its
Nutrition and Energy 1
 Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
Gut Microbiomes of Malawian Twin Pairs Discordant for Kwashiorkor
 Gut Microbiomes of Malawian Twin Pairs Discordant for Kwashiorkor Michelle I. Smith et al. Science 339, 548 (2013) Dept Meeting, 28 May 2013, M. UMEZAKI ABSTRACT. Kwashiorkor, an enigmatic form of severe
Gut Microbiomes of Malawian Twin Pairs Discordant for Kwashiorkor Michelle I. Smith et al. Science 339, 548 (2013) Dept Meeting, 28 May 2013, M. UMEZAKI ABSTRACT. Kwashiorkor, an enigmatic form of severe
Epilepsy: diagnosis and treatment. Sergiusz Jóźwiak Klinika Neurologii Dziecięcej WUM
 Epilepsy: diagnosis and treatment Sergiusz Jóźwiak Klinika Neurologii Dziecięcej WUM Definition: the clinical manifestation of an excessive excitation of a population of cortical neurons Neurotransmitters:
Epilepsy: diagnosis and treatment Sergiusz Jóźwiak Klinika Neurologii Dziecięcej WUM Definition: the clinical manifestation of an excessive excitation of a population of cortical neurons Neurotransmitters:
28. Ketosis and Urea Poisoning
 Module 4 Nutrition Management for Grazing Animals Learning objectives 28. Ketosis and Urea Poisoning On completion of this topic you should be able to: John Nolan Describe the management strategies available
Module 4 Nutrition Management for Grazing Animals Learning objectives 28. Ketosis and Urea Poisoning On completion of this topic you should be able to: John Nolan Describe the management strategies available
THE LIVER AND THE GUT
 THE LIVER AND THE GUT Liver & Gut A quintessential relationship One does not work well without the other There is a continuous bidirectional communication between these organs through the bile, hormones,
THE LIVER AND THE GUT Liver & Gut A quintessential relationship One does not work well without the other There is a continuous bidirectional communication between these organs through the bile, hormones,
Intracranial Studies Of Human Epilepsy In A Surgical Setting
 Intracranial Studies Of Human Epilepsy In A Surgical Setting Department of Neurology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Presentation Goals Epilepsy and seizures Basics of the electroencephalogram
Intracranial Studies Of Human Epilepsy In A Surgical Setting Department of Neurology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Presentation Goals Epilepsy and seizures Basics of the electroencephalogram
Slide 1 THE LIVER AND THE GUT. Slide 2 Liver & Gut. Slide 3 Gut Health For Detoxing
 Slide 1 THE LIVER AND THE GUT Slide 2 Liver & Gut A quintessential relationship One does not work well without the other There is a continuous bidirectional communication between these organs through the
Slide 1 THE LIVER AND THE GUT Slide 2 Liver & Gut A quintessential relationship One does not work well without the other There is a continuous bidirectional communication between these organs through the
Science and Applications of Nutritional Ketosis
 Science and Applications of Nutritional Ketosis Dominic P. D Agostino, PhD Associate Professor Laboratory of Metabolic Medicine University of South Florida, Morsani College of Medicine We Thank Our Sponsors
Science and Applications of Nutritional Ketosis Dominic P. D Agostino, PhD Associate Professor Laboratory of Metabolic Medicine University of South Florida, Morsani College of Medicine We Thank Our Sponsors
Objectives. Amanda Diamond, MD
 Amanda Diamond, MD Objectives Recognize symptoms suggestive of seizure and what those clinical symptoms represent Understand classification of epilepsy and why this is important Identify the appropriate
Amanda Diamond, MD Objectives Recognize symptoms suggestive of seizure and what those clinical symptoms represent Understand classification of epilepsy and why this is important Identify the appropriate
IRON MANGANESE 6/6/2018. Minerals & Performance : Total Performance, Total Performance Plus
 Minerals & Performance : Total Performance, Total Performance Plus June Educational Webinar 2018 Dr Tania Cubitt Performance Horse Nutrition IRON Heme oxygen carrying capacity Iron deficiency rare Iron
Minerals & Performance : Total Performance, Total Performance Plus June Educational Webinar 2018 Dr Tania Cubitt Performance Horse Nutrition IRON Heme oxygen carrying capacity Iron deficiency rare Iron
LILY FOUNDATION. An Introduction to Ketogenic Diets. Susan Wood. Matthew s Friends. Registered Dietitian Adults & Paediatrics
 LILY FOUNDATION An Introduction to Ketogenic Diets Susan Wood Registered Dietitian Adults & Paediatrics Matthew s Friends What is a ketogenic diet? A MEDICAL treatment. Mimics fasting metabolism Alters
LILY FOUNDATION An Introduction to Ketogenic Diets Susan Wood Registered Dietitian Adults & Paediatrics Matthew s Friends What is a ketogenic diet? A MEDICAL treatment. Mimics fasting metabolism Alters
Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism:
 Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism: How Fa8y Acids and Other Fuels Keep Our Bodies Running David M. Koeller, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, CDRC Metabolic Clinic What is Energy? What is Energy? What
Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism: How Fa8y Acids and Other Fuels Keep Our Bodies Running David M. Koeller, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, CDRC Metabolic Clinic What is Energy? What is Energy? What
Energy stores in different organs for a 155 lb male, in Calories
 Energy stores in different organs for a 155 lb male, in Calories Organ Glucose/ Glycogen Triacyl Glycerols* Liver 400 450 400 Brain 8 0 0 Mobile Proteins Muscle 1,200 450 24,000 Adipose Tissue 80 135,000
Energy stores in different organs for a 155 lb male, in Calories Organ Glucose/ Glycogen Triacyl Glycerols* Liver 400 450 400 Brain 8 0 0 Mobile Proteins Muscle 1,200 450 24,000 Adipose Tissue 80 135,000
Intermittent Fasting, Carb Cycling and Weight Management. Brent Agin, MD
 Intermittent Fasting, Carb Cycling and Weight Management Brent Agin, MD CEO/ Founder: Presenter Brent Agin, MD Trim Nutrition, Inc. MyPracticeConnect - Electronic Prescribing Platform & Physician Training
Intermittent Fasting, Carb Cycling and Weight Management Brent Agin, MD CEO/ Founder: Presenter Brent Agin, MD Trim Nutrition, Inc. MyPracticeConnect - Electronic Prescribing Platform & Physician Training
Lehninger 5 th ed. Chapter 17
 Lehninger 5 th ed. Chapter 17 December 26, 2010 Prof. Shimon Schuldiner Email: Shimon.Schuldiner@huji.ac.il Phone: 6585992 CHAPTER 17 Fatty Acid Catabolism Key topics: How fats are digested in animals
Lehninger 5 th ed. Chapter 17 December 26, 2010 Prof. Shimon Schuldiner Email: Shimon.Schuldiner@huji.ac.il Phone: 6585992 CHAPTER 17 Fatty Acid Catabolism Key topics: How fats are digested in animals
The Gut Microbiome: 101 Justin Carlson University of Minnesota
 The Gut Microbiome: 101 Justin Carlson University of Minnesota Where are we now? 360 B.C. 2003 Human Gut Microbes Associated With Obesity Ley et al., Nature. 2006. Consumer Driven Science For Better of
The Gut Microbiome: 101 Justin Carlson University of Minnesota Where are we now? 360 B.C. 2003 Human Gut Microbes Associated With Obesity Ley et al., Nature. 2006. Consumer Driven Science For Better of
Hormonal regulation of. Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Integration & Hormone Regulation
 Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Diet, Microbiome and Health Cindy D. Davis
 Diet, Microbiome and Health Cindy D. Davis davisci@mail.nih.gov OFFICE OF DIETARY SUPPLEMENTS 1 Outline 1.What is the microbiome? 2.How does it vary over the lifespan? 3.What is the evidence that diet
Diet, Microbiome and Health Cindy D. Davis davisci@mail.nih.gov OFFICE OF DIETARY SUPPLEMENTS 1 Outline 1.What is the microbiome? 2.How does it vary over the lifespan? 3.What is the evidence that diet
The impact of the microbiome on brain and cognitive development
 The Gut-Brain Axis The impact of the microbiome on brain and cognitive development Diane Stadler, PhD, RD Oregon Health & Sciences University, Portland, Oregon Lao-American Nutrition Institute With acknowledgements
The Gut-Brain Axis The impact of the microbiome on brain and cognitive development Diane Stadler, PhD, RD Oregon Health & Sciences University, Portland, Oregon Lao-American Nutrition Institute With acknowledgements
MALIGNANT CACHEXIA (CACHEXIA ANOREXIA SYNDROME): Overview
 MALIGNANT CACHEXIA (CACHEXIA ANOREXIA SYNDROME): Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ Temple 1 Cachexia:
MALIGNANT CACHEXIA (CACHEXIA ANOREXIA SYNDROME): Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ Temple 1 Cachexia:
Epilepsy is Seizure Recognition & Response. Epilepsy Facts. Possible Causes of Epilepsy. What happens to the brain during a seizure?
 Epilepsy is Seizure Recognition & Response NOT contagious NOT a mental illness NOT a mental impairment NOT a single disease Epilepsy is A neurological disorder of the brain characterized by the tendency
Epilepsy is Seizure Recognition & Response NOT contagious NOT a mental illness NOT a mental impairment NOT a single disease Epilepsy is A neurological disorder of the brain characterized by the tendency
Hypoglycemia in congenital hyperinsulinism
 How a normal body works: Our body is constantly at work. Our cells need a source of energy, and this source of energy is called glucose. The process is quite simple; think of it like an assembly line.
How a normal body works: Our body is constantly at work. Our cells need a source of energy, and this source of energy is called glucose. The process is quite simple; think of it like an assembly line.
Mark Manary MD. International Symposium on Understanding Moderate Malnutrition in Children for Effective Interventions
 Possible role of the microbiome in the development of acute malnutrition and implications for food-based strategies to prevent and treat acute malnutrition International Symposium on Understanding Moderate
Possible role of the microbiome in the development of acute malnutrition and implications for food-based strategies to prevent and treat acute malnutrition International Symposium on Understanding Moderate
Case 2: Epilepsy A 19-year-old college student comes to student health services complaining of sporadic loss of memory. The periods of amnesia occur
 Case 2: Epilepsy A 19-year-old college student comes to student health services complaining of sporadic loss of memory. The periods of amnesia occur while the student is awake and occasionally in class.
Case 2: Epilepsy A 19-year-old college student comes to student health services complaining of sporadic loss of memory. The periods of amnesia occur while the student is awake and occasionally in class.
Integration Of Metabolism
 Integration Of Metabolism Metabolism Consist of Highly Interconnected Pathways The basic strategy of catabolic metabolism is to form ATP, NADPH, and building blocks for biosyntheses. 1. ATP is the universal
Integration Of Metabolism Metabolism Consist of Highly Interconnected Pathways The basic strategy of catabolic metabolism is to form ATP, NADPH, and building blocks for biosyntheses. 1. ATP is the universal
10/27/2016. Processing in the Large Intestine. The colon of the large intestine is connected to the small intestine
 The hepatic portal vein carries nutrient-rich blood from the capillaries of the villi to the liver, then to the heart The liver regulates nutrient distribution, interconverts many organic molecules, and
The hepatic portal vein carries nutrient-rich blood from the capillaries of the villi to the liver, then to the heart The liver regulates nutrient distribution, interconverts many organic molecules, and
Karin Borges, PhD. October The urgent need for new metabolic (dietary) treatments of epilepsy
 Karin Borges, PhD October 2016 The urgent need for new metabolic (dietary) treatments of epilepsy Epilepsy is a common neurological disease that is characterized by recurrent seizures due to the spontaneous
Karin Borges, PhD October 2016 The urgent need for new metabolic (dietary) treatments of epilepsy Epilepsy is a common neurological disease that is characterized by recurrent seizures due to the spontaneous
for a bright reaching resources
 resources e Glut1 Deficiency Foundation is a non-profit family organization dedicated to improving the lives of those in the Glut1 Deficiency community through its mission of: increased awareness improved
resources e Glut1 Deficiency Foundation is a non-profit family organization dedicated to improving the lives of those in the Glut1 Deficiency community through its mission of: increased awareness improved
Objectives By the end of lecture the student should:
 Objectives By the end of lecture the student should: Discuss β oxidation of fatty acids. Illustrate α oxidation of fatty acids. Understand ω oxidation of fatty acids. List sources and fates of active acetate.
Objectives By the end of lecture the student should: Discuss β oxidation of fatty acids. Illustrate α oxidation of fatty acids. Understand ω oxidation of fatty acids. List sources and fates of active acetate.
Nutritional Demands of Disease and Trauma
 al Demands of Disease and Trauma Lecture 89 Medical School al Requirements Based on needs to support optimal physiological function Are changed by disease or injury metabolism is altered to prevent further
al Demands of Disease and Trauma Lecture 89 Medical School al Requirements Based on needs to support optimal physiological function Are changed by disease or injury metabolism is altered to prevent further
INTRODUCTION TO NUTRITIONAL KETOSIS AND CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
 INTRODUCTION TO NUTRITIONAL KETOSIS AND CLINICAL APPLICATIONS Jeff S. Volek, Ph.D., R.D. Professor Department of Human Sciences Kinesiology Program Columbus, OH 43210 volek.1@osu.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES
INTRODUCTION TO NUTRITIONAL KETOSIS AND CLINICAL APPLICATIONS Jeff S. Volek, Ph.D., R.D. Professor Department of Human Sciences Kinesiology Program Columbus, OH 43210 volek.1@osu.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Transfer of food energy to chemical energy. Includes anabolic and catabolic reactions. The cell is the metabolic processing center
 Metabolism There are a lot of diagrams here. DO NOT, I repeat, DO NOT get overly anxious or excited about them. We will go through them again slowly!! Read the slides, read the book, DO NOT TAKE NOTES.
Metabolism There are a lot of diagrams here. DO NOT, I repeat, DO NOT get overly anxious or excited about them. We will go through them again slowly!! Read the slides, read the book, DO NOT TAKE NOTES.
Biological Immunity Analysis
 Biological Immunity Analysis Indicators Brix Analysis (Sugars/Carbohydrates) Using a refractometer, we are able to measure the line of least resistance for light. Brix is the unit of measurement used to
Biological Immunity Analysis Indicators Brix Analysis (Sugars/Carbohydrates) Using a refractometer, we are able to measure the line of least resistance for light. Brix is the unit of measurement used to
Supplementary Figure 1.
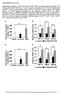 Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
Hompes Method Lesson 29 Organic Acids Part Three
 Hompes Method Lesson 29 Organic Acids Part Three Health for the People Ltd not for reuse without expressed permission Organic Acids - Review Fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids are converted into carboxylic
Hompes Method Lesson 29 Organic Acids Part Three Health for the People Ltd not for reuse without expressed permission Organic Acids - Review Fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids are converted into carboxylic
MICROBIOM AND OBESITY HEINZ GYAKY 2018 BUDAPEST
 MICROBIOM AND OBESITY HEINZ GYAKY 2018 BUDAPEST HUMAN MICROBIOM 10 Billion bacterias are building a 1,5 2 kg heavy human microbiom It is located mainly in the human gut There is a intestinal controlled
MICROBIOM AND OBESITY HEINZ GYAKY 2018 BUDAPEST HUMAN MICROBIOM 10 Billion bacterias are building a 1,5 2 kg heavy human microbiom It is located mainly in the human gut There is a intestinal controlled
Seizure Disorders. Guidelines for assessment of fitness to work as Cabin Crew
 Seizure Disorders Guidelines for assessment of fitness to work as Cabin Crew General Considerations As with all medical guidelines, it is important that each individual case is assessed on its own merits.
Seizure Disorders Guidelines for assessment of fitness to work as Cabin Crew General Considerations As with all medical guidelines, it is important that each individual case is assessed on its own merits.
Intermediary metabolism. Eva Samcová
 Intermediary metabolism Eva Samcová Metabolic roles of tissues Four major tissues play a dominant role in fuel metabolism : liver, adipose, muscle, and brain. These tissues do not function in isolation.
Intermediary metabolism Eva Samcová Metabolic roles of tissues Four major tissues play a dominant role in fuel metabolism : liver, adipose, muscle, and brain. These tissues do not function in isolation.
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
What systems are involved in homeostatic regulation (give an example)?
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and
 Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and Dietetics Tehran University of Medical Sciences Honorary Academic
Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and Dietetics Tehran University of Medical Sciences Honorary Academic
Rumen Fermentation. Volatile Fatty Acids (VFA) Acetate. Acetate utilization. Acetate utilization. Propionate
 Volatile Fatty Acids (VFA) Produced from the fermentation of pyruvate and hind gut Types/ratios depends on diet 3 major VFAs Acetate CH 3 COOH Propionate CH 3 CH 2 COOH Butyrate CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 COOH Cellulose
Volatile Fatty Acids (VFA) Produced from the fermentation of pyruvate and hind gut Types/ratios depends on diet 3 major VFAs Acetate CH 3 COOH Propionate CH 3 CH 2 COOH Butyrate CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 COOH Cellulose
2007 UCB Pharma SA. All rights reserved. GLOSSARY OF TERMS
 2007 UCB Pharma SA. All rights reserved. GLOSSARY OF TERMS Absence Seizure A type of generalised seizure usually seen in children, characterised by transient impairment or loss of consciousness usually
2007 UCB Pharma SA. All rights reserved. GLOSSARY OF TERMS Absence Seizure A type of generalised seizure usually seen in children, characterised by transient impairment or loss of consciousness usually
Gut microbiota, metabolic syndrome, obesity and the nutrient sensor pathways
 Gut microbiota, metabolic syndrome, obesity and the nutrient sensor pathways Department of Gastroenterology, Endocrinology & Metabolism Medical University Innsbruck Herbert Tilg Nothing to disclose Fig.
Gut microbiota, metabolic syndrome, obesity and the nutrient sensor pathways Department of Gastroenterology, Endocrinology & Metabolism Medical University Innsbruck Herbert Tilg Nothing to disclose Fig.
BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 25
 BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 25 General topics for week 14 Session 25 The metabolism of proteins Students are asked to draw the concept map showing all details of protein metabolism 1 Instructions:
BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 25 General topics for week 14 Session 25 The metabolism of proteins Students are asked to draw the concept map showing all details of protein metabolism 1 Instructions:
01/11/2012. Neurological disorders and nutrition. Nutritional and related assessments. Non-nutritional causes: nutritional implications
 Neurological disorders and nutrition General considerations, e.g., dysphagia Main topics and optional Canadian websites: STROKES www.heartandstroke.ca EPILEPSY www.epilepsy.ca PARKINSON S www.parkinson.ca
Neurological disorders and nutrition General considerations, e.g., dysphagia Main topics and optional Canadian websites: STROKES www.heartandstroke.ca EPILEPSY www.epilepsy.ca PARKINSON S www.parkinson.ca
Gut Microbiome Essentials
 CORE COMPONENTS I: Gut Microbiome Essentials 2016 Tom Fabian, PhD Module Outline 1. Microbiome overview: getting a sense of the microbiome, research, what we know 2. Bacteria: features, functions, communities
CORE COMPONENTS I: Gut Microbiome Essentials 2016 Tom Fabian, PhD Module Outline 1. Microbiome overview: getting a sense of the microbiome, research, what we know 2. Bacteria: features, functions, communities
VITAMINS, MINERALS AND THE GUT
 VITAMINS, MINERALS AND THE GUT Nutrients Looking at individual nutrients that are involved with gut health can be misleading This is not about taking individual nutrients It supports more a whole food
VITAMINS, MINERALS AND THE GUT Nutrients Looking at individual nutrients that are involved with gut health can be misleading This is not about taking individual nutrients It supports more a whole food
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 25 Metabolism and Nutrition Metabolic Reactions Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions taking place in the body. Reactions that break
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 25 Metabolism and Nutrition Metabolic Reactions Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions taking place in the body. Reactions that break
