Fast Calcium Currents in Cut Skeletal Muscle Fibres of the Frogs Rana temporaria and Xenopus laevis
|
|
|
- Darcy Haynes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1988), 7, ! Short communication Fast Calcium Currents in Cut Skeletal Muscle Fibres of the Frogs Rana temporaria and Xenopus laevis M. HENČĽK, D. ZACHAROVÁ and J. ZACHAR Centre of Physiological Sciences. Slovak Academy of Sciences, Vlarska Bratislava. Czechoslovakia Multiple types of voltage-gated Ca channels have been described in a variety of excitable cells (for a review see Tsien et al. 1987). Electrophysiological and biochemical properties of the slow Ca channels in skeletal muscle have been intensively studied during the last decade (for a review see Beaty et ai. 1987; Fosset and Lazdunski 1987). However, recently a fast low threshold Ca 2 + current was reported in rat skeletal muscle cells in culture (Cognard et al. 1986) and in twitch skeletal muscles of Rana montezume (Cola and Stefani 1986) and Rana pipiens (Garcia and Stefani 1987; Areola et al. 1987). The present communication describes fast Ca :+ currents in phasic and tonic muscle fibres of the frogs Rana temporaria and Xenopus laevis and persistence of these currents after denervation. Similarly as in our previous studies of slow Ca channels in normal and denervated phasic and tonic muscle fibres (Henček et al. 1985; Zacharová et al. 1985) the vaseline gap method of Hille and Campbell (1976) was used to record the fast Ca 2+ ionic currents. Muscle segments isolated from m. ileofibularis of R. temporaria or X. laevis were perfused with an internal solution containing (in mmol/1): Cs glutamate 108, MgCl : 6.5, CaCl : 0.069, ATP 5, camp 0.2, EGTA 5 10, Cs Hepes 20, ph 7.4. The external solution contained (in mmol/1): Na + glutamate 110 or the same concentrations of Cs + or TMA glutamate respectively, TEA bromide 110, Ca 2+ glutamate orSr , Cs Hepes 10, and TTX Fig. 1 shows two types of inward ionic currents at two voltage pulses lasting several seconds, recorded from 4 different muscle fibre segments of Rana temporaria. The ionic currents in A were recorded from phasic muscle fibres, those in B, C and D from phasic denervated, tonic, and tonic denervated muscle fibres respectively. At low depolarization a fast activating and non-iractivating current appears as a sole component of the ionic current recorded. At higher depolarizations ( 20 mv in A, B, C; 46 mv in D) a distinct slowly activating and inactivating current component (slow Ca current) becomes apparent. At shorter pulses (Fig. 2A, B) the fast current component appears at wider
2 652 Henček at al. Fig. 1. Fast and slow Ca 2 ' currents recorded in phasic (A), phasic denervated (B), tonic (C) and tonic denervated (D) muscle fibres. Rana temporaria, m ileofibularis. Hi = 90mV {A, B) and - 80 mv (C. D). External solution (in mmol/1): Ca : ' 1.8 (10 in C, D), Na glutamate 110, TTX range of depolarizations. Fig. 2 also reveals that the ionic currents are present both in Ca 2T and Sr 2+ containing salines (A, B) and in absence of Na ions (B, Q, In B and C, TMA and Cs ions were substituted for Na ions respectively. The fast calcium currents in denervated tonic muscle fibres (Fig. 2C) could be recorded over a wider range of depolarizations as a sole component C; this enabled to construct the current-voltage relationship. The slow Ca current appeared in this case only when the pulse duration was prolonged to more than 1000 ms. The current-voltage relationship reveals that at the given conditions (pulse duration: 100ms; holding potential: 80mV) the maximum current is obtained at both 30mV and 20 mv. The threshold ( 60 mv) and maximum values of the fast Ca (Ca f ) current in tonic fibres correlate well with those obtained in phasic fibres of R. temporaria and X. laevis (Fig. 4) as well as with data from other excitable structures under patch-clamp conditions (Bossu et al. 1985; Mitra et Morad 1986; Carbone et Lux 1987; Narahashi et al. 1987). Fast activating and inactivating Ca 2t^ inward currents were frequently observed upon applying ms pulses to phasic muscle fibre segments from Xenopus laevis (Fig. 3A, B, C). The records in the left column were obtained at physiological concentrations of Ca and Na ions (1.8 and 110 mmol/1 respectively). The amplitudes of these Ca' T currents were considerably increased after blocking the K channels with TEA 4 substituted for Na ions. The
3 Fast Calcium Currents in Skeletal Muscle Fibres 653 Fig. 2. Activation of fast (Ca f ) and slow (Ca,) calcium and/or strontium currents. A, B: Phasic fibres. External solution: A: Sr* + 10, Na glutamate 110 ( + TTX 0.001), B: Sr' 5, TMA glutamate 110 ( + TTX); Hi = 90 mv, C: Tonic denervated fibre: Ca" f 10, Cs glutamate 110. Two superimposed records with different time bases: Ca f (100ms), Ca s (1000ms). Inset: Current-voltage relation for a tonic denervated fibre. Hi = 80 mv. tail current in TEA + solution reversed its sign in comparison with that in control solution, where an inward current, most probably the slow Ca 2+ current, started developing. The time constants of activation (r m ) and inactivation (r h ) changed from 1.1 to 1.05 ms and from 17 to 30 ms respectively, and conductance (G) increased from 1.56 to 2.65mS/cm 2. Qualitatively the same changes occurred in solution with Cs ions (Fig. 3B; C increased from 0.6 to 1.4mS/cm 2 ). The calcium nature of this fast calcium current is supported by the effect of calcium blockers, i.e. Ni ions (Fig. 3C). When the inward current was blocked, an outward current appeared, as also observed by Cota and Stefani (1986) who used Mg ions as blockers. On replacing external Na and CI ions with Cs glutamate, transient fast Ca 2+ currents have been observed on several occasions also in twitch muscle fibres of Rana temporaria. Fig. 4 shows that the transient fast Ca 2+ current activated at 60 mv and reached a peak value at 20 mv. The current-voltage relationships of these currents from twitch muscle fibres of R. temporaria correlate very well with those in X. laevis fibre. Table 1 gives selected parameters of these currents.
4 654 Henček at al TEA* 01V 40 ms Ci' Fig. 3. The effect of TEA +. Cs 4 and Nr* on Ca, in muscle fibres of Xenopus laevis (three different fibres). A. B. C Left: in control solution Ri (Ca mmol/l, Na glutamate HO + TTX Right: in TEA' bromide 110, Cs ions substituted for Na ions, and after the addition of NiCl, (2mmol 1). Table 1. Conductances and kinetics of transient fast Ca channels in muscle fibres of Xenopus laevis and Rana temporaria External solution (mmol 1) Membrane depolarization (mv) (ms) (ms) G ms enr Na glutamate 110, Caglut Cs glutamate 110 or TEA bromide 110 Ca ± ±0.83
5 Fast Calcium Currents in Skeletal Muscle Fibres 655 i 40 ms i Fig. 4. Transient fast Ca" + currents in muscle fibre segments of Rana temporaria. External solution (in mmol): Ca , Cs glutamate TTX Current-voltage relations: Rana temporaria (circles, triangles), Xenopus laevis (crosses). In conclusion, our experiments provided evidence for two calcium currents, a fast and slow, present in twitch and tonic muscle of the frog R. temporaria and in twitch fiber of ľ. laevis. Both types of Ca channels persist after denervation. The fast Ca 2+ currents inactivated either very slowly, in particular in response to long lasting stimuli, similarly as in muscle fibres of Rana montezume and R. pipiens (Cota and Stefani 1986; Arrecola et al. 1987), or rapidly on shorter lasting depolarizations. Both inactivation states could be seen in the same experiments. In denervated twitch and tonic muscle fibers very slow inactivation was observed. Analysis of the different factors which may play a role in these changes is in progress although it is not sure whether this can be do under voltage clamp conditions. References Arreola J., Calvo J., Garcia M. C, Sanchez J. A. (1987): Modulation of calcium channels of twitch skeletal muscle fibres of the frog by adrenaline and cyclic adenosine monophosphate J. Physiol. 393, Beaty G. N., Cota G., Nicola Siri L., Nicola Síri L Sanchez J. A., Stefani E. (1987): Skeletal Muscle Ca 2+ Channels. In: Structure and Physiology of the Slow Inward Calcium Channel (Eds T Riggle, J. C. Ventor), pp , Alan R Liss, Inc.
6 656 Hcnčck at al Bossu J. L., Feltz A., Thomann J. M. (1985): Depolarization elicits two distinct calcium currents in vertebrate sensory neurones. Pflugers Arch. 403, Cognard Ch., Lazdunski M.. Romey G. (1986): Different types ofca 2, channels in mammalian skeletal muscle in culture. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 83, Carbone E., Lux H. D. (1987): Kinetics and selectivity of a low-voltage-activated calcium current in chick and rat sensory neurones. J. Physiol. 386, Cota G., Stefani E. (1986): A fast-activated inward calcium current in twitch muscle fibres of the frog (Rana montesume). J. Physiol. 370, Fosset M., Lazdunski M. (1987): Biochemical Characterization of the Skeletal Muscle Ca 2 ' Channel. In: Structure and Physiology of the Slow Inward Calcium Channel (Eds. T. Riggle, J. C. Ventor). pp , Alan R. Liss, Inc. Garcia J.. Stefani E. (1987): Appropriate conditions to record activation of fast Ca 2+ channels in frog skeletal muscle (Rana pipiens). Pflúgers Arch. 408, Henček M.. Zacharová D., Zachar J., Karhánek M. (1985): Sodium and calcium currents in denervated phasic muscle fibres of the frog. Physiol. Bohemoslov. 34, 424 Hille B.. Campbell D. T. (1976): An improved vaseline gap voltage clamp for skeletal muscle fibers. J. Gen. Physiol. 67, Mitra, R.. Morad M. (1986): Two types of calcium channels in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 83, Narahashi T.. Tsunoo A., Yoshii M. (1987): Characterization of two types of calcium channels in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J. Physiol. 383, Tsien R. W., Hess P., McCleskey E. W.. Rosenberg R. L. (1987): Calcium Channels: Mechanisms of Selectivity, Permeation, and Block. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 16, Zacharová D.. Henček M., RadzukiewiczT. L., Zachar J., Nasledov G. A. (1985): Calcium currents recorded from segments of normal and denervated frog tonic muscle fibres. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 4, Final version accepted July 11, 1988
Generation of Twitch Tension in Frog Atrial Fibers by Na/Ca Exchange
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1988), 7, 29 38 29 Generation of Twitch Tension in Frog Atrial Fibers by Na/Ca Exchange A. K. FILIPPOV 1, S. M. TERTISHNIKOVA 1, T. I. BOUQUET', V. I. POROTIKOV 1 and V. I. ILYIN
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1988), 7, 29 38 29 Generation of Twitch Tension in Frog Atrial Fibers by Na/Ca Exchange A. K. FILIPPOV 1, S. M. TERTISHNIKOVA 1, T. I. BOUQUET', V. I. POROTIKOV 1 and V. I. ILYIN
The "Pacemaker" Function of the Transient Outward Current in the Rabbit Myocardium
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1988). 7. 235 242 235 The "Pacemaker" Function of the Transient Outward Current in the Rabbit Myocardium R. Z. GAINULLIN 1, N. I. KUKUSHKIN 1, R. E. KISELEVA 2 and E. A. SOSUNOV
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1988). 7. 235 242 235 The "Pacemaker" Function of the Transient Outward Current in the Rabbit Myocardium R. Z. GAINULLIN 1, N. I. KUKUSHKIN 1, R. E. KISELEVA 2 and E. A. SOSUNOV
Pacing Dependence of the Slow Inward Current in Frog Atrial Myocardium
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1982) 1, 307 318 307 Pacing Dependence of the Slow Inward Current in Frog Atrial Myocardium B. NILIUS* and M. HENCEK Institute of Normal and Pathological Physiology, Centre of Physiological
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1982) 1, 307 318 307 Pacing Dependence of the Slow Inward Current in Frog Atrial Myocardium B. NILIUS* and M. HENCEK Institute of Normal and Pathological Physiology, Centre of Physiological
Calcium-Induced and Voltage-Dependent Inactivation of Calcium Channels in Crab Muscle Fibres
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1988), 7, 113 134 113 Calcium-Induced and Voltage-Dependent Inactivation of Calcium Channels in Crab Muscle Fibres Y. MOUNIER, V. STAL and C. GOBLET Laboratoire de Physiologie des
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1988), 7, 113 134 113 Calcium-Induced and Voltage-Dependent Inactivation of Calcium Channels in Crab Muscle Fibres Y. MOUNIER, V. STAL and C. GOBLET Laboratoire de Physiologie des
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 2. THE SODIUM ACTION POTENTIAL Video 2-1: Observations and hypotheses Sodium action potential 1 Observations 2 Patch clamp recording whole-cell configuration
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 2. THE SODIUM ACTION POTENTIAL Video 2-1: Observations and hypotheses Sodium action potential 1 Observations 2 Patch clamp recording whole-cell configuration
Neuroscience 201A Problem Set #1, 27 September 2016
 Neuroscience 201A Problem Set #1, 27 September 2016 1. The figure above was obtained from a paper on calcium channels expressed by dentate granule cells. The whole-cell Ca 2+ currents in (A) were measured
Neuroscience 201A Problem Set #1, 27 September 2016 1. The figure above was obtained from a paper on calcium channels expressed by dentate granule cells. The whole-cell Ca 2+ currents in (A) were measured
Differences in ionic currents between canine myocardial and Purkinje cells
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiological Reports ISSN 2051-817X Differences in ionic currents between canine myocardial and Purkinje cells Mario Vassalle & Leonardo Bocchi Department of Physiology and Pharmacology,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Physiological Reports ISSN 2051-817X Differences in ionic currents between canine myocardial and Purkinje cells Mario Vassalle & Leonardo Bocchi Department of Physiology and Pharmacology,
Effects of Chloride Replacement and Chloride Transport Blockade on the Tonic Tension of Frog Atrial Trabeculae
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1986), 5, 113 124 113 Effects of Chloride Replacement and Chloride Transport Blockade on the Tonic Tension of Frog Atrial Trabeculae H. SOUSTRE, A. RAKOTONIRINA and J. LENFANT Laboratoire
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1986), 5, 113 124 113 Effects of Chloride Replacement and Chloride Transport Blockade on the Tonic Tension of Frog Atrial Trabeculae H. SOUSTRE, A. RAKOTONIRINA and J. LENFANT Laboratoire
Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview
 Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview Components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Vascular system Blood Figure 12-1 Plasma includes water, ions, proteins, nutrients, hormones, wastes,
Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview Components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Vascular system Blood Figure 12-1 Plasma includes water, ions, proteins, nutrients, hormones, wastes,
Interaction of Diltiazem with Single L-type Calcium Channels in Guinea-pig Ventricular Myocytes
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1992), 11, 535 543 535 Interaction of Diltiazem with Single L-type Calcium Channels in Guinea-pig Ventricular Myocytes A. ZAHRADNÍKOVÁ and I. ZÁHRADNÍK Institute of Molecular Physiology
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1992), 11, 535 543 535 Interaction of Diltiazem with Single L-type Calcium Channels in Guinea-pig Ventricular Myocytes A. ZAHRADNÍKOVÁ and I. ZÁHRADNÍK Institute of Molecular Physiology
The Effects of Extracellular Calcium Removal on Sino-atrial Node Cells Treated with Potassium-depleted Solutions
 Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 36, 403-409, 1986 The Effects of Extracellular Calcium Removal on Sino-atrial Node Cells Treated with Potassium-depleted Solutions Shun-ichi MIYAMAE
Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 36, 403-409, 1986 The Effects of Extracellular Calcium Removal on Sino-atrial Node Cells Treated with Potassium-depleted Solutions Shun-ichi MIYAMAE
nerves of the toad Bufo marinus and voltage clamped as described by Dodge and Frankenhaeuser (7). Neurotoxins
 BRIEF COMMUNICATION SIMULTANEOUS MODIFICATIONS OF SODIUM CHANNEL GATING BY TWO SCORPION TOXINS GING Kuo WANG AND GARY STRICHARTZ Department ofanesthesia Research Laboratories, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
BRIEF COMMUNICATION SIMULTANEOUS MODIFICATIONS OF SODIUM CHANNEL GATING BY TWO SCORPION TOXINS GING Kuo WANG AND GARY STRICHARTZ Department ofanesthesia Research Laboratories, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Acta Physiologica Sinica
 , 1999 4, 51 (2), 187 192 187 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 1998204222 1998206203 3 (No139500052) 3 3, 221002 3 3 3 3 3 (, 200031) ( Ito), 28 d (H28, 6 h/ d), Ito (16118 4161 6132 1135 pa/ pf, P < 0105),
, 1999 4, 51 (2), 187 192 187 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 1998204222 1998206203 3 (No139500052) 3 3, 221002 3 3 3 3 3 (, 200031) ( Ito), 28 d (H28, 6 h/ d), Ito (16118 4161 6132 1135 pa/ pf, P < 0105),
Lidocaine alters the input resistance and evokes neural activity in crayfish sensory neurons
 20 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (2007), 26, 20 26 Lidocaine alters the input resistance and evokes neural activity in crayfish sensory neurons M. B. Keceli and N. Purali Hacettepe University, Medical Faculty,
20 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (2007), 26, 20 26 Lidocaine alters the input resistance and evokes neural activity in crayfish sensory neurons M. B. Keceli and N. Purali Hacettepe University, Medical Faculty,
Spontaneous contractions commonly occur in denervated mammalian skeletal. respectively.
 Journal of Physiology (1989), 418, 427-439 427 With 8 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain TRANSIENT AND PERSISTENT SODIUM CURRENTS IN NORMAL AND DENERVATED MAMMALIAN SKELETAL MUSCLE BY PETER W. GAGE,
Journal of Physiology (1989), 418, 427-439 427 With 8 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain TRANSIENT AND PERSISTENT SODIUM CURRENTS IN NORMAL AND DENERVATED MAMMALIAN SKELETAL MUSCLE BY PETER W. GAGE,
PLATEAU-GENERATING NERVE CELLS IN HELIX: PROPERTIES OF THE REPOLARIZING VOLTAGE-GATED AND Ca 2+ -ACTIVATED POTASSIUM CURRENTS
 J. exp. Biol. 152, 211-241 (1990) 211 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1990 PLATEAU-GENERATING NERVE CELLS IN HELIX: PROPERTIES OF THE REPOLARIZING VOLTAGE-GATED AND Ca 2+ -ACTIVATED
J. exp. Biol. 152, 211-241 (1990) 211 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1990 PLATEAU-GENERATING NERVE CELLS IN HELIX: PROPERTIES OF THE REPOLARIZING VOLTAGE-GATED AND Ca 2+ -ACTIVATED
CALCIUM CHANNELS OF AMPHIBIAN STOMACH AND
 CALCUM CHANNELS OF AMPHBAN STOMACH AND MAMMALAN AORTA SMOOTH MUSCLE CELLS JOHN M. CAFFREY, RA R. JOSEPHSON,* AND ARTHUR M. BROWN Department ofphysiology and Molecular Biophysics, Baylor College ofmedicine,
CALCUM CHANNELS OF AMPHBAN STOMACH AND MAMMALAN AORTA SMOOTH MUSCLE CELLS JOHN M. CAFFREY, RA R. JOSEPHSON,* AND ARTHUR M. BROWN Department ofphysiology and Molecular Biophysics, Baylor College ofmedicine,
Synaptic Integration
 Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
Introduction to Neurobiology
 Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
7.06 Spring of PROBLEM SET #6
 7.6 Spring 23 1 of 6 7.6 PROBLEM SET #6 1. You are studying a mouse model of hypercholesterolemia, a disease characterized by high levels of cholesterol in the blood. In normal cells, LDL particles in
7.6 Spring 23 1 of 6 7.6 PROBLEM SET #6 1. You are studying a mouse model of hypercholesterolemia, a disease characterized by high levels of cholesterol in the blood. In normal cells, LDL particles in
Suppression of calcium release by calcium or procaine in
 3624 Journal of Physiology (1995), 485.2, pp. 437-445 437 Suppression of calcium release by calcium or procaine in voltage clamped rat skeletal muscle fibres J. Garcia and M. F. Schneider * Department
3624 Journal of Physiology (1995), 485.2, pp. 437-445 437 Suppression of calcium release by calcium or procaine in voltage clamped rat skeletal muscle fibres J. Garcia and M. F. Schneider * Department
Calcium current reactivation after flash photolysis of
 Journal of Physiology (1995), 487.1, pp. 51-56 4610 51 Calcium current reactivation after flash photolysis of nifedipine in skeletal muscle fibres of the frog D. Feldmeyer, P. Zollner, B. Pohl and W. Melzer
Journal of Physiology (1995), 487.1, pp. 51-56 4610 51 Calcium current reactivation after flash photolysis of nifedipine in skeletal muscle fibres of the frog D. Feldmeyer, P. Zollner, B. Pohl and W. Melzer
THREE TYPES OF VOLTAGE-DEPENDENT CALCIUM CURRENTS DEVELOPING IN CULTURED HUMAN NEUROBLASTOMA CELLS
 ORIGINAL PAPER Nagoya 1. Med. Sci. 62. 39-45, 1999 THREE TYPES OF VOLTAGE-DEPENDENT CALCIUM CURRENTS DEVELOPING IN CULTURED HUMAN NEUROBLASTOMA CELLS MASAO KITO [, MITSUO MAEHARA 2 and KAZUYOSHI WATANABE
ORIGINAL PAPER Nagoya 1. Med. Sci. 62. 39-45, 1999 THREE TYPES OF VOLTAGE-DEPENDENT CALCIUM CURRENTS DEVELOPING IN CULTURED HUMAN NEUROBLASTOMA CELLS MASAO KITO [, MITSUO MAEHARA 2 and KAZUYOSHI WATANABE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature19102 Supplementary Discussion Benzothiazepine Binding in Ca V Ab Diltiazem and other benzothiazepines inhibit Ca V 1.2 channels in a frequency-dependent manner consistent with pore block
doi:10.1038/nature19102 Supplementary Discussion Benzothiazepine Binding in Ca V Ab Diltiazem and other benzothiazepines inhibit Ca V 1.2 channels in a frequency-dependent manner consistent with pore block
Phys 173 / BGGN 266. LPA Induced Cl - Oscillations in Xenopus Oocytes. Nini Huynh David Marciano Chisa Suzuki
 Phys 173 / BGGN 266 LPA Induced Cl - Oscillations in Xenopus Oocytes Nini Huynh David Marciano Chisa Suzuki If only we hadn t poked these oocytes, how cute would it be! INTRODUCTION Electrophysiology in
Phys 173 / BGGN 266 LPA Induced Cl - Oscillations in Xenopus Oocytes Nini Huynh David Marciano Chisa Suzuki If only we hadn t poked these oocytes, how cute would it be! INTRODUCTION Electrophysiology in
Effects of depolarization and low intracellular ph on charge movement currents of frog skeletal muscle fibers
 J Appl Physiol 90: 228 234, 2001. Effects of depolarization and low intracellular ph on charge movement currents of frog skeletal muscle fibers EDWARD M. BALOG AND ROBERT H. FITTS Department of Biology,
J Appl Physiol 90: 228 234, 2001. Effects of depolarization and low intracellular ph on charge movement currents of frog skeletal muscle fibers EDWARD M. BALOG AND ROBERT H. FITTS Department of Biology,
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #2
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #2 1. (PeiXi) You are performing research on a novel ion channel and want to learn some of its characteristics. a) When you conducted voltage clamp
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN 140 Fall 2016 Problem Set #2 1. (PeiXi) You are performing research on a novel ion channel and want to learn some of its characteristics. a) When you conducted voltage clamp
Relation between Membrane Potential Changes and Tension in Barnacle Muscle Fibers
 Relation between Membrane Potential Changes and Tension in Barnacle Muscle Fibers CHARLES EDWARDS, SHIKO CHICHIBU, and SUSUMU HAGIWARA From the Department of Physiology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis,
Relation between Membrane Potential Changes and Tension in Barnacle Muscle Fibers CHARLES EDWARDS, SHIKO CHICHIBU, and SUSUMU HAGIWARA From the Department of Physiology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis,
Common molecular determinants of local anesthetic, antiarrhythmic, and anticonvulsant block of voltage-gated Na channels
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 93, pp. 9270 9275, August 1996 Pharmacology Common molecular determinants of local anesthetic, antiarrhythmic, and anticonvulsant block of voltage-gated Na channels DAVID
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 93, pp. 9270 9275, August 1996 Pharmacology Common molecular determinants of local anesthetic, antiarrhythmic, and anticonvulsant block of voltage-gated Na channels DAVID
Modified Kinetics and Selectivity of Sodium Channels in Frog Skeletal Muscle Fibers Treated with Aconitine
 Modified Kinetics and Selectivity of Sodium Channels in Frog Skeletal Muscle Fibers Treated with Aconitine DONALD T. CAMPBELL From the Department of Physiology, Yale University School of Medicine, New
Modified Kinetics and Selectivity of Sodium Channels in Frog Skeletal Muscle Fibers Treated with Aconitine DONALD T. CAMPBELL From the Department of Physiology, Yale University School of Medicine, New
Force enhancement in single skeletal muscle fibres on the ascending limb of the force length relationship
 The Journal of Experimental Biology 207, 2787-2791 Published by The Company of Biologists 2004 doi:10.1242/jeb.01095 2787 Force enhancement in single skeletal muscle fibres on the ascending limb of the
The Journal of Experimental Biology 207, 2787-2791 Published by The Company of Biologists 2004 doi:10.1242/jeb.01095 2787 Force enhancement in single skeletal muscle fibres on the ascending limb of the
abolished, the transient outward chloride current normally activated by membrane
 J. Physiol. (1984), 357, pp. 173-183 173 With 7 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain CHLORIDE CURRENT INDUCED BY INJECTION OF CLCIUM INTO XENOPUS OOCYTES BY R. MILEDI ND I. PRKER From the Department of
J. Physiol. (1984), 357, pp. 173-183 173 With 7 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain CHLORIDE CURRENT INDUCED BY INJECTION OF CLCIUM INTO XENOPUS OOCYTES BY R. MILEDI ND I. PRKER From the Department of
NEURONS Chapter Neurons: specialized cells of the nervous system 2. Nerves: bundles of neuron axons 3. Nervous systems
 NEURONS Chapter 12 Figure 12.1 Neuronal and hormonal signaling both convey information over long distances 1. Nervous system A. nervous tissue B. conducts electrical impulses C. rapid communication 2.
NEURONS Chapter 12 Figure 12.1 Neuronal and hormonal signaling both convey information over long distances 1. Nervous system A. nervous tissue B. conducts electrical impulses C. rapid communication 2.
SEPARATION OF HYDROGEN ION CURRENTS IN INTACT MOLLUSCAN NEURONES
 J. exp. Biol. 145, 439-454 (1989) 439 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1989 SEPARATION OF HYDROGEN ION CURRENTS IN INTACT MOLLUSCAN NEURONES BY M. P. MAHAUT-SMTTH* Department
J. exp. Biol. 145, 439-454 (1989) 439 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1989 SEPARATION OF HYDROGEN ION CURRENTS IN INTACT MOLLUSCAN NEURONES BY M. P. MAHAUT-SMTTH* Department
CALCIUM-DEPENDENT ACTION POTENTIALS IN THE SECOND-ORDER NEURONES OF COCKROACH OCELLI
 J. exp. Biol. 130, 259-274 (1987) 259 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1987 CALCIUM-DEPENDENT ACTION POTENTIALS IN THE SECOND-ORDER NEURONES OF COCKROACH OCELLI BY MAKOTO MIZUNAMI,
J. exp. Biol. 130, 259-274 (1987) 259 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1987 CALCIUM-DEPENDENT ACTION POTENTIALS IN THE SECOND-ORDER NEURONES OF COCKROACH OCELLI BY MAKOTO MIZUNAMI,
Objectives. Functions of smooth muscle. Smooth muscle. Smooth Muscle Contraction: Mechanism. Latch state. Smooth muscle contraction
 Objectives Functions of smooth muscle Sompol Tapechum,, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj hospital อธ บายล กษณะการหดต วของกล ามเน อเร ยบได อธ บายกลไกและป จจ ยท ม ผลต อการหดต
Objectives Functions of smooth muscle Sompol Tapechum,, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj hospital อธ บายล กษณะการหดต วของกล ามเน อเร ยบได อธ บายกลไกและป จจ ยท ม ผลต อการหดต
The action potential travels down both branches because each branch is a typical axon with voltage dependent Na + and K+ channels.
 BIO 360 - MIDTERM FALL 2018 This is an open book, open notes exam. PLEASE WRITE YOUR NAME ON EACH SHEET. Read each question carefully and answer as well as you can. Point values are shown at the beginning
BIO 360 - MIDTERM FALL 2018 This is an open book, open notes exam. PLEASE WRITE YOUR NAME ON EACH SHEET. Read each question carefully and answer as well as you can. Point values are shown at the beginning
Open- and closed-state fast inactivation in sodium channels Differential effects of a site-3 anemone toxin
 Research paper Channels 5:1, 1-16; January/February 2011; 2011 Landes Bioscience research paper Open- and closed-state fast inactivation in sodium channels Differential effects of a site-3 anemone toxin
Research paper Channels 5:1, 1-16; January/February 2011; 2011 Landes Bioscience research paper Open- and closed-state fast inactivation in sodium channels Differential effects of a site-3 anemone toxin
Nerve. (2) Duration of the stimulus A certain period can give response. The Strength - Duration Curve
 Nerve Neuron (nerve cell) is the structural unit of nervous system. Nerve is formed of large numbers of nerve fibers. Types of nerve fibers Myelinated nerve fibers Covered by myelin sheath interrupted
Nerve Neuron (nerve cell) is the structural unit of nervous system. Nerve is formed of large numbers of nerve fibers. Types of nerve fibers Myelinated nerve fibers Covered by myelin sheath interrupted
The action potential and the underlying ionic currents. Norbert Jost, PhD
 The action potential and the underlying ionic currents Norbert Jost, PhD The propagation of the stimulation in the heart Sinus node Left atria His Bundle Conduction velocity in m/s Time to arrive from
The action potential and the underlying ionic currents Norbert Jost, PhD The propagation of the stimulation in the heart Sinus node Left atria His Bundle Conduction velocity in m/s Time to arrive from
BIONB/BME/ECE 4910 Neuronal Simulation Assignments 1, Spring 2013
 BIONB/BME/ECE 4910 Neuronal Simulation Assignments 1, Spring 2013 Tutorial Assignment Page Due Date Week 1/Assignment 1: Introduction to NIA 1 January 28 The Membrane Tutorial 9 Week 2/Assignment 2: Passive
BIONB/BME/ECE 4910 Neuronal Simulation Assignments 1, Spring 2013 Tutorial Assignment Page Due Date Week 1/Assignment 1: Introduction to NIA 1 January 28 The Membrane Tutorial 9 Week 2/Assignment 2: Passive
Enhancement of synaptic transmission by cyclic AMP modulation of presynaptic I h channels. Vahri Beaumont and Robert S. Zucker
 Enhancement of synaptic transmission by cyclic AMP modulation of presynaptic I h channels Vahri Beaumont and Robert S. Zucker Background I h channels discovered in 1976 (Noma A. and Irisawa H.) Voltage-gated
Enhancement of synaptic transmission by cyclic AMP modulation of presynaptic I h channels Vahri Beaumont and Robert S. Zucker Background I h channels discovered in 1976 (Noma A. and Irisawa H.) Voltage-gated
SimNeuron. Current-and Voltage-Clamp Experiments in Virtual Laboratories. Tutorial
 SimNeuron Tutorial 1 Contents: SimNeuron Current-and Voltage-Clamp Experiments in Virtual Laboratories 1. Lab Design 2. Basic CURRENT-CLAMP Experiments Tutorial 2.1 Action Potential, Conductances and Currents.
SimNeuron Tutorial 1 Contents: SimNeuron Current-and Voltage-Clamp Experiments in Virtual Laboratories 1. Lab Design 2. Basic CURRENT-CLAMP Experiments Tutorial 2.1 Action Potential, Conductances and Currents.
THE EFFECT OF ZINC ON CALCIUM AND HYDROGEN ION CURRENTS IN INTACT SNAIL NEURONES BY M. P. MAHAUT-SMITH*
 /. exp. Biol. 145, 455-464 (1989) 455 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1989 THE EFFECT OF ZINC ON CALCIUM AND HYDROGEN ION CURRENTS IN INTACT SNAIL NEURONES BY M. P. MAHAUT-SMITH*
/. exp. Biol. 145, 455-464 (1989) 455 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1989 THE EFFECT OF ZINC ON CALCIUM AND HYDROGEN ION CURRENTS IN INTACT SNAIL NEURONES BY M. P. MAHAUT-SMITH*
Differences in cardiac atrial and ventricular ion channels
 Differences in cardiac atrial and ventricular ion channels Norbert Jost, PhD Department of Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapy, University of Szeged Division for Cardiovascular Pharmacology, Hungarian Academy
Differences in cardiac atrial and ventricular ion channels Norbert Jost, PhD Department of Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapy, University of Szeged Division for Cardiovascular Pharmacology, Hungarian Academy
depolarization in individual cardiac pacemaker cells (Ca2l current/inward rectiflcation/time- and voltage-dependent K+ current)
 Proc. Nail. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 82, pp. 7796-7800, November 1985 Physiological Sciences Ionic currents that generate the spontaneous diastolic depolarization in individual cardiac pacemaker cells (Ca2l
Proc. Nail. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 82, pp. 7796-7800, November 1985 Physiological Sciences Ionic currents that generate the spontaneous diastolic depolarization in individual cardiac pacemaker cells (Ca2l
Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3e. Chapter 4: The action potential
 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3e Chapter 4: The action potential Introduction Action Potential in the Nervous System Conveys information over long distances Action potential Initiated in the axon
Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3e Chapter 4: The action potential Introduction Action Potential in the Nervous System Conveys information over long distances Action potential Initiated in the axon
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
Original Article Electrophysiology properties of voltage-gated potassium channels in rat peritoneal macrophages
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2013;6(3):166-173 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1301008 Original Article Electrophysiology properties of voltage-gated potassium channels in rat peritoneal macrophages Bao-Ming
Int J Clin Exp Med 2013;6(3):166-173 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1301008 Original Article Electrophysiology properties of voltage-gated potassium channels in rat peritoneal macrophages Bao-Ming
Fig. S4. Current-voltage relations of iglurs. A-C: time courses of currents evoked by 100 ms pulses
 Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Calcium Current Restitution in Mammalian Ventricular Myocytes is Modulated by Intracellular Calcium. Gea-Ny Tseng
 468 Calcium Current Restitution in Mammalian Ventricular Myocytes is Modulated by Intracellular Calcium Gea-Ny Tseng Restitution of the conventional L-type calcium current (Ic) was studied in dog or guinea
468 Calcium Current Restitution in Mammalian Ventricular Myocytes is Modulated by Intracellular Calcium Gea-Ny Tseng Restitution of the conventional L-type calcium current (Ic) was studied in dog or guinea
Voltage Gated Ion Channels
 Voltage Gated Ion Channels The Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potential Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Ligand-Gated Ion
Voltage Gated Ion Channels The Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potential Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Ligand-Gated Ion
K Depolarization and Phospholipid Metabolism in Frog Sartorius Muscle
 Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1983), 2, 329 337 329 K Depolarization and Phospholipid Metabolism in Frog Sartorius Muscle I. NOVOTNÝ, F. SALEH and R. NOVOTNÁ Department of General Physiology, Charles University,
Gen. Physiol. Biophys. (1983), 2, 329 337 329 K Depolarization and Phospholipid Metabolism in Frog Sartorius Muscle I. NOVOTNÝ, F. SALEH and R. NOVOTNÁ Department of General Physiology, Charles University,
Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses
 M52_MARI0000_00_SE_EX03.qxd 8/22/11 2:47 PM Page 358 3 E X E R C I S E Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Advance Preparation/Comments Consider doing a short introductory presentation with the following
M52_MARI0000_00_SE_EX03.qxd 8/22/11 2:47 PM Page 358 3 E X E R C I S E Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Advance Preparation/Comments Consider doing a short introductory presentation with the following
Modulation of Cutaneous Cold Receptor Function by Electrolytes, Hormones and Thermal Adaptation
 Physiol. Res. 41: 71-75, 1992 Modulation of Cutaneous Cold Receptor Function by Electrolytes, Hormones and Thermal Adaptation K. SCHAFFER, H. A. BRAUN Institut für Physiologie der Universität, D-3550 Marburg,
Physiol. Res. 41: 71-75, 1992 Modulation of Cutaneous Cold Receptor Function by Electrolytes, Hormones and Thermal Adaptation K. SCHAFFER, H. A. BRAUN Institut für Physiologie der Universität, D-3550 Marburg,
THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION REVISITED: Ca 2+ CHANNELS AND TRANSMITTER RELEASE IN CHOLINERGIC NEURONES IN XENOPUS NERVE AND MUSCLE CELL CULTURE
 exp. Biol. 153, 129-140 (1990) 129 'rinted in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1990 THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION REVISITED: Ca 2+ CHANNELS AND TRANSMITTER RELEASE IN CHOLINERGIC NEURONES IN
exp. Biol. 153, 129-140 (1990) 129 'rinted in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1990 THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION REVISITED: Ca 2+ CHANNELS AND TRANSMITTER RELEASE IN CHOLINERGIC NEURONES IN
Ph.D. THESIS EFFECTS OF THYMOL ON CARDIAC AND SKELETAL MUSCLE NORBERT SZENTANDRÁSSY, M.D.
 Ph.D. THESIS EFFECTS OF THYMOL ON CARDIAC AND SKELETAL MUSCLE NORBERT SZENTANDRÁSSY, M.D. Supervisor: János Magyar M.D., PhD. UNIVERSITY OF DEBRECEN MEDICAL AND HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER MEDICAL SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
Ph.D. THESIS EFFECTS OF THYMOL ON CARDIAC AND SKELETAL MUSCLE NORBERT SZENTANDRÁSSY, M.D. Supervisor: János Magyar M.D., PhD. UNIVERSITY OF DEBRECEN MEDICAL AND HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER MEDICAL SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
MODULATION OF IONIC CURRENTS BY DOPAMINE IN AN INTERNEURONE OF THE RESPIRATORY CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR OF LYMNAEA STAGNALIS
 J. exp. Biol. 189, 37 54 (1994) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1994 37 MODULATION OF IONIC CURRENTS BY DOPAMINE IN AN INTERNEURONE OF THE RESPIRATORY CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR
J. exp. Biol. 189, 37 54 (1994) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1994 37 MODULATION OF IONIC CURRENTS BY DOPAMINE IN AN INTERNEURONE OF THE RESPIRATORY CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR
Intramembrane Charge Movement and L-Type Calcium Current in Skeletal Muscle Fibers Isolated from Control and mdx Mice
 Biophysical Journal Volume 84 January 2003 251 265 251 Intramembrane Charge Movement and L-Type Calcium Current in Skeletal Muscle Fibers Isolated from Control and mdx Mice C. Collet,* L. Csernoch, y and
Biophysical Journal Volume 84 January 2003 251 265 251 Intramembrane Charge Movement and L-Type Calcium Current in Skeletal Muscle Fibers Isolated from Control and mdx Mice C. Collet,* L. Csernoch, y and
Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials Introduction (3:15) This third chapter explains the calcium current triggered by the arrival of the action potential in
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 subtitles Action potentials Introduction (3:15) This third chapter explains the calcium current triggered by the arrival of the action potential in
Summary of Calcium Regulation inside the Cell
 Overview of Calcium Summary of Calcium Regulation inside the Cell Plasma membrane transport a. Influx via receptor & voltage-regulated channels b. Efflux via Ca-ATPase & Na-Ca antiporter ER/SR membrane
Overview of Calcium Summary of Calcium Regulation inside the Cell Plasma membrane transport a. Influx via receptor & voltage-regulated channels b. Efflux via Ca-ATPase & Na-Ca antiporter ER/SR membrane
Schwann cells to express sodium channels is discussed in relation to a recent
 Journal of Physiology (1988), 396, 173-188 173 With 9 text-figures Printed in Great Britain CHANGES IN EXCITABLE MEMBRANE PROPERTIES IN SCHWANN CELLS OF ADULT RABBIT SCIATIC NERVES FOLLOWING NERVE TRANSECTION
Journal of Physiology (1988), 396, 173-188 173 With 9 text-figures Printed in Great Britain CHANGES IN EXCITABLE MEMBRANE PROPERTIES IN SCHWANN CELLS OF ADULT RABBIT SCIATIC NERVES FOLLOWING NERVE TRANSECTION
Question and answers related to the first seven lectures:
 Recitations and Labs # 01, # 02, #3 06 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material for the first test of this course. Info on osmosis, diffusion, metaboism, transport across biological membranes,
Recitations and Labs # 01, # 02, #3 06 The goal of this recitations / labs is to review material for the first test of this course. Info on osmosis, diffusion, metaboism, transport across biological membranes,
Effects of adrenaline on nerve terminals in the superior cervical ganglion of the rabbit
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 331-338. Effects of adrenaline on nerve terminals in the superior cervical ganglion of the rabbit D. D. CHRIST AND S. NISHI Neurophysiology Laboratory, Department of Pharmacology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 331-338. Effects of adrenaline on nerve terminals in the superior cervical ganglion of the rabbit D. D. CHRIST AND S. NISHI Neurophysiology Laboratory, Department of Pharmacology,
CRAYFISH SKELETAL MUSCLE REQUIRES BOTH INFLUX OF EXTERNAL Ca 2+ AND Ca 2+ RELEASE FROM INTERNAL STORES FOR CONTRACTION
 J. exp. Biol. 181, 95 105 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 95 CRAYFISH SKELETAL MUSCLE REQUIRES BOTH INFLUX OF EXTERNAL Ca 2+ AND Ca 2+ RELEASE FROM INTERNAL STORES
J. exp. Biol. 181, 95 105 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 95 CRAYFISH SKELETAL MUSCLE REQUIRES BOTH INFLUX OF EXTERNAL Ca 2+ AND Ca 2+ RELEASE FROM INTERNAL STORES
Chapter 3 Neurotransmitter release
 NEUROPHYSIOLOGIE CELLULAIRE CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 Neurotransmitter release In chapter 3, we proose 3 videos: Observation Calcium Channel, Ca 2+ Unitary and Total Currents Ca 2+ and Neurotransmitter
NEUROPHYSIOLOGIE CELLULAIRE CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 3 Neurotransmitter release In chapter 3, we proose 3 videos: Observation Calcium Channel, Ca 2+ Unitary and Total Currents Ca 2+ and Neurotransmitter
Supplementary Information
 Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Sodium and Gating Current Time Shifts Resulting from Changes in Initial Conditions
 Sodium and Gating Current Time Shifts Resulting from Changes in Initial Conditions ROBERT E. TAYLOR and FRANCISCO BEZANILLA From the Laboratory of Biophysics, National Institute of Neurological and Communicative
Sodium and Gating Current Time Shifts Resulting from Changes in Initial Conditions ROBERT E. TAYLOR and FRANCISCO BEZANILLA From the Laboratory of Biophysics, National Institute of Neurological and Communicative
The plant alkaloid harmaline blocks the human voltage-gated sodium channel Na v 1.7 expressed in CHO cells: a study using automated patch clamp
 Ernst Moritz Arndt University of Greifswald Institute of Pathophysiology The plant alkaloid harmaline blocks the human voltage-gated sodium channel Na v 1.7 expressed in CHO cells: a study using automated
Ernst Moritz Arndt University of Greifswald Institute of Pathophysiology The plant alkaloid harmaline blocks the human voltage-gated sodium channel Na v 1.7 expressed in CHO cells: a study using automated
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Bernard Katz ( )
 Bernard Katz (1911-2003) German-born biophysicist and neurophysiologist. Studied medicine at the University of Leipzig, then fled to Britain in 1935. Worked at University College London (UCL) under Archibald
Bernard Katz (1911-2003) German-born biophysicist and neurophysiologist. Studied medicine at the University of Leipzig, then fled to Britain in 1935. Worked at University College London (UCL) under Archibald
Supporting Information
 ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
3) Most of the organelles in a neuron are located in the A) dendritic region. B) axon hillock. C) axon. D) cell body. E) axon terminals.
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
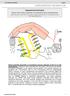 doi: 1.138/nature588 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Information Sensory neuron sodium channel Na v 1.8 is essential for pain at cold temperatures Katharina Zimmermann*, Andreas Leffler*, Alexandru
doi: 1.138/nature588 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Information Sensory neuron sodium channel Na v 1.8 is essential for pain at cold temperatures Katharina Zimmermann*, Andreas Leffler*, Alexandru
High Ca Content of Pacemaker Tissues in the Frog Heart
 Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 34, 1117-1121,1984 High Ca Content of Pacemaker Tissues in the Frog Heart Yasuichiro FUKUDA Department of Physiology II, School of Medicine, Chiba University,
Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 34, 1117-1121,1984 High Ca Content of Pacemaker Tissues in the Frog Heart Yasuichiro FUKUDA Department of Physiology II, School of Medicine, Chiba University,
Physiology sheet #2. The heart composed of 3 layers that line its lumen and cover it from out side, these layers are :
 Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
Effect of hydrogen peroxide on persistent sodium current in guinea pig ventricular myocytes 1
 Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2005 Jul; 26 (7): 828 834 Full-length article Effect of hydrogen peroxide on persistent sodium current in guinea pig ventricular myocytes 1 Ji-hua MA 2, An-tao LUO, Pei-hua ZHANG
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2005 Jul; 26 (7): 828 834 Full-length article Effect of hydrogen peroxide on persistent sodium current in guinea pig ventricular myocytes 1 Ji-hua MA 2, An-tao LUO, Pei-hua ZHANG
Sample Lab Report 1 from 1. Measuring and Manipulating Passive Membrane Properties
 Sample Lab Report 1 from http://www.bio365l.net 1 Abstract Measuring and Manipulating Passive Membrane Properties Biological membranes exhibit the properties of capacitance and resistance, which allow
Sample Lab Report 1 from http://www.bio365l.net 1 Abstract Measuring and Manipulating Passive Membrane Properties Biological membranes exhibit the properties of capacitance and resistance, which allow
Dynamics of calcium regulation of chloride currents in Xenopus oocytes
 Dynamics of calcium regulation of chloride currents in Xenopus oocytes AKINORI KURUMA AND H. CRISS HARTZELL Department of Cell Biology, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia 30322-3030
Dynamics of calcium regulation of chloride currents in Xenopus oocytes AKINORI KURUMA AND H. CRISS HARTZELL Department of Cell Biology, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia 30322-3030
Bay K 8644 is a dihydropyridine that can, among
 Calcium Channel Antagonist Properties of Bay K 8644 in Single Guinea Pig Ventricular Cells 97 Robert W. Hadley and Joseph R. Hume The effects of Bay K 8644 on the high-threshold calcium channel was investigated
Calcium Channel Antagonist Properties of Bay K 8644 in Single Guinea Pig Ventricular Cells 97 Robert W. Hadley and Joseph R. Hume The effects of Bay K 8644 on the high-threshold calcium channel was investigated
K+ current (1K(Ca)), elicited by intracellular Ca2+ injection, reverses near -65 mv,
 J. Physiol. (1985), 362, pp. 131-160 131 With 14 text-figures Printed in Great Britain CALCIUM-INDUCED INACTIVATION OF CALCIUM CURRENT CAUSES THE INTER-BURST HYPERPOLARIZATION OF APL YSIA BURSTING NEURONES
J. Physiol. (1985), 362, pp. 131-160 131 With 14 text-figures Printed in Great Britain CALCIUM-INDUCED INACTIVATION OF CALCIUM CURRENT CAUSES THE INTER-BURST HYPERPOLARIZATION OF APL YSIA BURSTING NEURONES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Voltage-clamp errors cause anomalous interaction between independent ion channels
 AUDITORYAND VESTIBULAR SYSTEMS Voltage-clamp errors cause anomalous interaction between independent ion channels Hamilton E. Farris CA and Anthony J. Ricci Neuroscience Center and Kresge Hearing Labs,
AUDITORYAND VESTIBULAR SYSTEMS Voltage-clamp errors cause anomalous interaction between independent ion channels Hamilton E. Farris CA and Anthony J. Ricci Neuroscience Center and Kresge Hearing Labs,
Cardiac Properties MCQ
 Cardiac Properties MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Cardiac Valves: a- Prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria during
Cardiac Properties MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Cardiac Valves: a- Prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria during
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST)
 Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Structure of the striated muscle general properties
 Structure of the striated muscle general properties Structure of the striated muscle membrane systems 1. Myofibrillum (contractile proteins) 2. Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) longitudinal tubule 3. SR terminal
Structure of the striated muscle general properties Structure of the striated muscle membrane systems 1. Myofibrillum (contractile proteins) 2. Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) longitudinal tubule 3. SR terminal
Neuroscience 201A (2016) - Problems in Synaptic Physiology
 Question 1: The record below in A shows an EPSC recorded from a cerebellar granule cell following stimulation (at the gap in the record) of a mossy fiber input. These responses are, then, evoked by stimulation.
Question 1: The record below in A shows an EPSC recorded from a cerebellar granule cell following stimulation (at the gap in the record) of a mossy fiber input. These responses are, then, evoked by stimulation.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon?
 Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
depolarizing steps to 0 mv of 3-5 min duration followed by a restoration time at
 Journal of Physiology (1990), 427, pp. 187-209 187 With 11 figures Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECTS OF DIHYDROPYRIDINE DERIVATIVES ON FORCE AND CA2+ CURRENT IN FROG SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBRES BY R. NEUHAUS*,
Journal of Physiology (1990), 427, pp. 187-209 187 With 11 figures Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECTS OF DIHYDROPYRIDINE DERIVATIVES ON FORCE AND CA2+ CURRENT IN FROG SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBRES BY R. NEUHAUS*,
ICa elicited by a subsequent test pulse with half-maximal inactivation occurring for
 Journal of Phy8iology (1988), 401, pp. 201-226 201 With 11 text-figures Printed in Great Britain INACTIVATION, REACTIVATION AND PACING DEPENDENCE OF CALCIUM CURRENT IN FROG CARDIOCYTES: CORRELATION WITH
Journal of Phy8iology (1988), 401, pp. 201-226 201 With 11 text-figures Printed in Great Britain INACTIVATION, REACTIVATION AND PACING DEPENDENCE OF CALCIUM CURRENT IN FROG CARDIOCYTES: CORRELATION WITH
Decreased Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Content Is Responsible for Defective Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Canine Heart Failure
 Decreased Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Content Is Responsible for Defective Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Canine Heart Failure Ion A. Hobai, MD, PhD; Brian O Rourke, PhD Background Altered excitation-contraction
Decreased Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Content Is Responsible for Defective Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Canine Heart Failure Ion A. Hobai, MD, PhD; Brian O Rourke, PhD Background Altered excitation-contraction
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF AXONAL SODIUM CHANNELS IN THE COCKROACH PERIPLANETA AMERICANA L.
 J. exp. Biol. (1979). 83, 49-58 49 With 7 figures Printed in Great Britain PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF AXONAL SODIUM CHANNELS IN THE COCKROACH PERIPLANETA AMERICANA L. II. SLOWING OF SODIUM CURRENT TURN-OFF
J. exp. Biol. (1979). 83, 49-58 49 With 7 figures Printed in Great Britain PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF AXONAL SODIUM CHANNELS IN THE COCKROACH PERIPLANETA AMERICANA L. II. SLOWING OF SODIUM CURRENT TURN-OFF
Spironolactone (SP) is an aldosterone antagonist used in
 Spironolactone and Its Main Metabolite, Canrenoic Acid, Block Human Ether-a-Go-Go Related Gene Channels Ricardo Caballero, BPharm, PhD*; Ignacio Moreno, BPharm*; Teresa González, BSc; Cristina Arias, BSc;
Spironolactone and Its Main Metabolite, Canrenoic Acid, Block Human Ether-a-Go-Go Related Gene Channels Ricardo Caballero, BPharm, PhD*; Ignacio Moreno, BPharm*; Teresa González, BSc; Cristina Arias, BSc;
Interaction of Scorpion -Toxins with Cardiac Sodium Channels: Binding Properties and Enhancement of Slow Inactivation
 Interaction of Scorpion -Toxins with Cardiac Sodium Channels: Binding Properties and Enhancement of Slow Inactivation Haijun Chen and Stefan H. Heinemann From the Research Unit Molecular and Cellular Biophysics,
Interaction of Scorpion -Toxins with Cardiac Sodium Channels: Binding Properties and Enhancement of Slow Inactivation Haijun Chen and Stefan H. Heinemann From the Research Unit Molecular and Cellular Biophysics,
AJP-Heart Articles in PresS. Published on April 11, 2002 as DOI /ajpheart
 AJP-Heart Articles in PresS. Published on April 11, 2002 as DOI 10.1152/ajpheart.01000.2001 MS H-01000-2001/R1 THE ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSE OF RAT ATRIAL MYOCYTES TO ACIDOSIS Kimiaki KOMUKAI, Fabien
AJP-Heart Articles in PresS. Published on April 11, 2002 as DOI 10.1152/ajpheart.01000.2001 MS H-01000-2001/R1 THE ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSE OF RAT ATRIAL MYOCYTES TO ACIDOSIS Kimiaki KOMUKAI, Fabien
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.1933
 The structural basis of open channel block in a prokaryotic pentameric ligand-gated ion channel Ricarda J. C. Hilf, Carlo Bertozzi, Iwan Zimmermann, Alwin Reiter, Dirk Trauner and Raimund Dutzler a GLIC
The structural basis of open channel block in a prokaryotic pentameric ligand-gated ion channel Ricarda J. C. Hilf, Carlo Bertozzi, Iwan Zimmermann, Alwin Reiter, Dirk Trauner and Raimund Dutzler a GLIC
Ca2+ current remained in the mutant.
 J. Physiol. (1984), 351, pp. 397-410 397 With 5 text-figures Printed in Great Britain A MUTATION THAT ALTERS PROPERTIES OF THE CALCIUM CHANNEL IN PARAMECIUM TETRA URELIA BY R. D. HINRICHSEN AND Y. SAIMI
J. Physiol. (1984), 351, pp. 397-410 397 With 5 text-figures Printed in Great Britain A MUTATION THAT ALTERS PROPERTIES OF THE CALCIUM CHANNEL IN PARAMECIUM TETRA URELIA BY R. D. HINRICHSEN AND Y. SAIMI
Introduction. Circulation
 Introduction Circulation 1- Systemic (general) circulation 2- Pulmonary circulation carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs From Lt. ventricle aorta From
Introduction Circulation 1- Systemic (general) circulation 2- Pulmonary circulation carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs From Lt. ventricle aorta From
