PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION
|
|
|
- Sydney Whitehead
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION Description For jumping (basketball, volleyball) or contact sports, Patellar dislocation and subluxation are injuries to the protect the patella with supportive devices, such as elastic kneecap (patella) affecting the joint it forms with the thigh bandages, tape, braces, knee sleeves with a hole for the bone (femur). The patella is a V-shaped convex bone that sits patella and a built-up outer side or straps to pull the patella within a V-shaped concave groove of the femur, known as the inward, or knee pads. trochlea. Patellar dislocation is a condition in which the For sports that require cleats or spikes on the athletic shoe, patella is displaced from its normal position and no longer sits use cleats or spikes of appropriate length for the sport and in the trochlea. Patellar subluxation is a condition in which the turf or field conditions. the patella is not centered within the trochlea, but the joint surfaces still touch; thus the patella is not in normal relationship to the trochlea. This tends to occur in adolescents and With appropriate reduction (repositioning of the joint) and Expected Outcome young adults. treatment, complete healing requires at least 6 weeks. Common Signs and Symptoms Severe pain when attempting to move the knee and a feeling of the knee giving way Tenderness, swelling, and bruising of the knee Numbness or paralysis below the dislocation from pinching, cutting, or pressure on the blood vessels or nerves (uncommon) Often patellar dislocation to the outer side of the knee, causing an obvious deformity; often relocates on its own when the knee is straightened, leaving no deformity; damage is the same in both cases Lump on the inner knee, which is the end of the inner part of the thigh bone (femur) Causes Direct blow to the knee Twisting or pivoting injury to the lower extremity, such as with cutting (rapid change of direction) Powerful muscle contraction Congenital abnormality (you are born with it), such as a shallow or malformed joint surfaces Risk Increases With Participation in contact sports (football, soccer), sports that require jumping and landing (basketball, volleyball), or sports in which cleats are worn on shoes Persons with wide pelvis, knocked knees, or shallow or malformed joint surfaces Previous knee sprains or patellar dislocations Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) Preventive Measures Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or competition. Maintain appropriate conditioning: Thigh, leg, and knee strength Flexibility and endurance Cardiovascual fitness Possible Complications Associated fracture or joint cartilage injury due to the dislocation or reduction (repositioning) of the patella Damage to nearby nerves or major blood vessels (rare) Prolonged healing or recurrent dislocation if activity is resumed too soon Excessive bleeding within the knee due to dislocation Patella pain and giving way, usually due to inadequate or incomplete rehabilitation Unstable or arthritic joint following repeated injury or delayed treatment General Treatment Considerations After immediate reduction (repositioning of the bones of the joint), treatment consists of ice and medications to relieve pain. Reduction can be performed without surgery, although surgery may be necessary to remove loose fragments of bone or cartilage caused by the dislocation or reduction or to help prevent further dislocation. Elevating the injured knee at or above heart level helps in reducing swelling. Your doctor may drain the blood from your knee. Immobilization by splinting, casting, or bracing without immobilization for up to 6 weeks is may be recommended to protect the joint while the tissues heal. After immobilization, stretching and strengthening of the injured, stiff, and weakened joint and surrounding muscles (due to immobilization and the injury) are necessary. These may be done with or without the assistance of a physical therapist or athletic trainer. Medication Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, such as aspirin and ibuprofen (do not take within 7 days before surgery), or other minor pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, are often recommended. Take these as directed by your physician. Contact your physician immediately if any bleeding, stomach upset, or signs of an allergic reaction occur. Strong pain relievers may be prescribed as necessary. Use only as directed and only as much as you need. 518
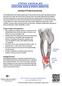
2 PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION 519 Heat and Cold Cold is used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation for acute and chronic cases. Cold should be applied for 10 to 15 minutes every 2 to 3 hours for inflammation and pain and immediately after any activity that aggravates your symptoms. Use ice packs or an ice massage. Heat may be used before performing stretching and strengthening activities prescribed by your physician, physical therapist, or athletic trainer. Use a heat pack or a warm soak. Notify Our Office If Pain, tenderness, or swelling worsens despite treatment You experience pain, numbness, or coldness in the foot Blue, gray, or dusky color appears in the toenails Any of the following signs of infection occur after surgery: fever, increased pain, swelling, redness, drainage, or bleeding in the surgical area New, unexplained symptoms develop (drugs used in treatment may produce side effects) Femur Patella Knee joint Fibula Tibia Figure 1 Dislocated patella
3 520 RANGE OF MOTION AND STRETCHING EXERCISES Patellar Dislocation and Subluxation Phase I First Time Dislocations: For up to 6 weeks after an initial (first time) patella dislocation or subluxation you may be placed in a knee immobilizer so that the injured tissues can begin to heal. This type of immobilizer will usually keep your knee completely straight. Sometimes your physician will allow some motion in a brace that has hinges or he or she will allow you to come out of your brace to bend and straighten your knee. If this is the case, follow your physician s specific instructions. Once you are allowed to start moving your knee, these are some of the initial exercises you may start your rehabilitation program with until you see your physician, physical therapist, or athletic trainer again or until your symptoms are resolved. Chronic or Repeated Dislocations or Subluxations: The person with a patella that suffers from chronic or repeated dislocations or subluxations will often not be placed in an immobilizer. This individual is often allowed to begin to bend and straighten his or her knee as much as is comfortable. Please remember: Flexible tissue is more tolerant of the stresses placed on it during activities. Each stretch should be held for 20 to 30 seconds. A gentle stretching sensation should be felt. RANGE OF MOTION Knee Flexion and Extension 1. Sit on the edge of a table or chair. 2. Use the uninjured/unaffected leg to straighten (extend) and bend (flex) the injured/affected leg. 3. Flexion Cross your ankles, placing the uninjured or unaffected leg on top of the injured/affected leg. Pull your heel(s) backward under the surface you are sitting on to increase the amount you can bend your knee. 4. Extension Cross your ankles, placing the uninjured or unaffected leg under the injured/affected leg. Pull your heel(s) backward under the surface you are sitting on to increase the how much you can straighten your knee. RANGE OF MOTION Knee Flexion 1. Lie on your back with your legs out straight. 2. Slowly slide your heel toward your buttocks. Bend your knee as far as is comfortable to get a stretching sensation. 3. Hold for seconds. 4. Return your leg to the starting position. RANGE OF MOTION Gravity Knee Flexion 1. Lie on the floor as shown with your toes/foot lightly touching the wall. 2. Allow your toes/foot to slide down the wall, allowing gravity to bend your knee for you. 3. Obtain a comfortable stretching sensation. 4. Hold this position for seconds. Then return the leg to the starting position.
4 PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION 521 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES Patellar Dislocation and Subluxation Phase I These are some of the initial exercises you may start your rehabilitation program with until you see your physician, physical therapist, or athletic trainer again or until your symptoms are resolved. Please remember: Strong muscles with good endurance tolerate stress better. Do the exercises as initially prescribed by your physician, physical therapist, or athletic trainer. Progress slowly with each exercise, gradually increasing the number of repetitions and weight used under their guidance. STRENGTH Quadriceps, 7 Count The quality of the muscle contraction in this exercise is what counts the most, not just the ability to lift your leg! 1. Tighten the muscle in front of your thigh as much as you can, pushing the back of your knee flat against the floor. 2. Tighten this muscle harder. 3. Lift your leg/heel 4 to 6 inches off the floor. 4. Tighten this muscle harder again. 5. Lower your leg/heel back to the floor. Keep the muscle in front of your thigh as tight as possible. 6. Tighten this muscle harder again. 7. Relax. 8. Repeat exercise times, times per day. STRENGTH Quadriceps, Isometrics 1. Lie flat or sit with your leg straight. 2. Tighten the muscle in the front of your thigh as much as you can, pushing the back of your knee flat against the floor. This will pull your kneecap up your thigh, toward your hip. 3. Hold the muscle tight for seconds. 4. Repeat this exercise times, times per day. STRENGTH Hip Extension 1. Lie on your stomach with your legs straight out behind you. 2. Raise your leg up behind you from your hip. Keep your knee straight. Hold this position for seconds. 3. Slowly lower your leg to the starting position. 4. Repeat exercise times, times per day.
5 522 STRENGTH Hip Abduction 1. Lie on your side as shown with the injured/weak leg on top. 2. Bend the bottom knee slightly for balance. Roll your top hip slightly forward. 3. Lift your top leg straight up, leading with your heel. Do not let it come forward. Hold this position for seconds. 4. Slowly lower your leg to the starting position. STRENGTH Hip Adduction 1. Lie on your side as shown with the injured/weak leg on the bottom. 2. Place the foot of your top leg flat on the floor for balance. It may be in front or behind the bottom leg. 3. Lift the bottom leg as shown. Hold this position for seconds. 4. Slowly lower your leg to the starting position. RANGE OF MOTION AND STRETCHING EXERCISES Patellar Dislocation and Subluxation Phase II Phase II begins when you can bend your knee at least 100 to 110 degrees. At this time you are ready to start bending your knee farther and to start stretching your muscles again. These are some of the initial exercises you may start your rehabilitation program with until you see your physician, physical therapist, or athletic trainer again. Progress as your motion and symptoms allow. If you feel too much pulling and that your knee cap is coming out of place, stop them immediately and consult your physician, physical therapist, or athletic trainer. Please remember: Flexible tissue is more tolerant of the stresses placed on it during activities. Each stretch should be held for 20 to 30 seconds. A gentle stretching sensation should be felt. STRETCH Quadriceps, Prone 1. Lie on your stomach as shown. 2. Bend your knee, grasping your toes, foot, or ankle. If you are too tight to do this, loop a belt or towel around your ankle and grasp that. 3. Pull your heel toward your buttock until you feel a stretching sensation in the front of your thigh. 4. Keep your knees together. 5. Hold this position for seconds.
6 PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION 523 FLEXIBILITY Hamstrings 1. Lie on your back with your leg bent and both hands holding on to it behind the thigh as shown. 2. Your hip should be bent to 90 degrees and the thigh pointing straight at the ceiling. 3. Straighten out your knee as far as you can. Keep your thigh pointing straight toward the ceiling. 4. Keep the other leg flat on the floor. 5. Hold this position for seconds. ILIOTIBIAL BAND STRETCH 1. Lie on your side as shown. The muscle/iliotibial band to be stretched should be on top. 2. With your hand, grasp your ankle and pull your heel to your buttocks and bend your hip so that your knee is pointing forward as in the top drawing. 3. Rotate your hip up so that your thigh is away from your body as shown and in line with your body. Keep your heel to your buttocks. 4. Bring the thigh back down and behind your body. Do not bend at the waist. Keep your heel pressed to your buttocks. 5. Place the heel of your opposite foot on top of your knee and pull the knee/thigh down farther. You should feel a stretch on the outside of your thigh near your kneecap. 6. Hold this position for seconds. 7. Repeat exercise times, times per day. FLEXIBILITY Hamstrings, Doorway 1. Lie on your back near the edge of a doorway as shown. 2. Place the leg your are stretching up the wall keeping your knee straight. 3. Your buttock should be as close to the wall as possible and the other leg should be kept flat on the floor. 4. You should feel a stretch in the back of your thigh. 5. Hold this position for seconds. PATELLA Self Mobilization, Knee Flexed 1. Sit with your knee bent 75 to 90 degrees and your foot flat on the floor. 2. Place the inside half of your palm (near your thumb) on top of the inside half of your kneecap. 3. Press down on the inside half of your kneecap, attempting to lift the outside edge up, stretching the fibers that are tight. You should feel a slight stretching sensation on the outside edge of your kneecap. 4. Hold this position for seconds.
7 524 STRENGTHENING EXERCISES Patellar Dislocation and Subluxation Phase II These are some of the exercises you may progress to in your rehabilitation program. These exercises are usually done during the second phase of your rehabilitation program. Do not progress to these until you have been authorized to do so by your physician, physical therapist, or athletic trainer. You may continue with all exercises started in Phase I also. Please remember: Strong muscles with good endurance tolerate stress better. Do the exercises as initially prescribed by your physician, physical therapist, or athletic trainer. Progress slowly with each exercise, gradually increasing the number of repetitions and weight used under their guidance. STRENGTH Quadriceps, Step-Ups 1. Use a step or books. 2. Place your foot on the step or books approximately inches in height. Make sure that your kneecap is in line with the tip of your shoe or your second toe. 3. Hold on to a hand rail, chair, wall, or another object for balance if needed. 4. Slowly step up and down. Make sure that the kneecap is always in line with the tip of your shoe or your second toe. Lightly touch the heel of the opposite leg to the floor and return to the starting position. STRENGTH Quadriceps, Short Arcs 1. Lie flat or sit with your leg straight. 2. Place a inch roll under your knee, allowing it to bend. 3. Tighten the muscle in the front of your knee as much as you can, and lift your heel off the floor. 4. Hold this position for seconds. Additional Weights: OK TO USE DO NOT USE!!! If okay d by your physician, physical therapist, or athletic trainer, a pound weight may be placed around your ankle for additional weight. STRENGTH Quadriceps, Wall Slide 1. Stand with your back against the wall. Your feet should be shoulder-width apart and approximately 18 to 24 inches away from the wall. Your kneecaps should be in line with the tip of your shoes or your second toe. 2. Slowly slide down the wall so that there is a degree bend in your knees. (Your physician, physical therapist, or athletic trainer will instruct you how to progress the amount of bend based on your symptoms and diagnosis.) 3. Hold this position for seconds. Stand up and rest for seconds. 4. Repeat exercise times, times per day.
8 PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION 525 STRENGTH Hip Extension 1. Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. 2. Push down, raising your hips/buttocks off the floor. 3. Keep your pelvis level. Do not allow it to turn/rotate. 4. You may do this exercise with both legs together (which is easier) or with just one leg as shown (which is harder). Hold this position for seconds. 5. Slowly lower to the starting position. STRENGTH Isometric Quad/VMO 1. Sit in a chair with your knee bent 75 to 90 degrees as shown in the drawing. 2. With your fingertips, feel the muscle just above the kneecap on the inside half of your thigh. This is the VMO. 3. Push your foot and leg into the floor to cause the thigh muscles to tighten. 4. Concentrate on feeling the VMO tighten. This muscle is important because it helps control the position of your kneecap. 5. Tighten and hold for seconds.
9 Notes: (Up to 4400 characters only) Notes and suggestions
MENISCUS TEAR. Description
 MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE
 TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE Description Preventive Measures A tibial plateau fracture is a complete or incomplete break Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or in the larger of the two leg bones
TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE Description Preventive Measures A tibial plateau fracture is a complete or incomplete break Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or in the larger of the two leg bones
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures)
 METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Expected Outcome. Causes
 Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Knee Pain. Pain in the pressure on. the kneecap. well as being supported (retinaculum) quadricep. Abnormal. to the knee. or dislocate.
 Knee Pain in Children and Adolescents Description Pain in the knee can occur from various causess but is usually from increased pressure on the kneecap (patella) or abnormal motion. Softening of the cartilage
Knee Pain in Children and Adolescents Description Pain in the knee can occur from various causess but is usually from increased pressure on the kneecap (patella) or abnormal motion. Softening of the cartilage
Patella Instability in Children and Adolescents
 Patella Instability in Children and Adolescents Description Patella Instability is an injury to the kneecap (patella) affecting the joint it forms with the thigh bone (femur) Patella Instability can occur
Patella Instability in Children and Adolescents Description Patella Instability is an injury to the kneecap (patella) affecting the joint it forms with the thigh bone (femur) Patella Instability can occur
WRIST SPRAIN. Description
 WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS
 SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT
 ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg)
 MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
tibial tubercle of the to 19 Compared pulling on inferior pole patella Cause subsequent pain The injury knee that is
 Osgood-Schlatter Disease Description Osgood Schlatter disease is an inflammatory injury of the growth plate on the tibia (shin bone) just below the level of the knee at the tibial tubercle This disease
Osgood-Schlatter Disease Description Osgood Schlatter disease is an inflammatory injury of the growth plate on the tibia (shin bone) just below the level of the knee at the tibial tubercle This disease
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome
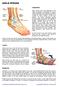
 Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE. Description
 Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON RUPTURE
 POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Posterior tibial tendon rupture is a complete tear of the posterior tibial tendon. This structure is the tendon attachment of leg muscles (posterior
POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Posterior tibial tendon rupture is a complete tear of the posterior tibial tendon. This structure is the tendon attachment of leg muscles (posterior
Spondylolisthesis DESCRIPTION EXPECTED OUTCOME POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS COMMON SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS GENERAL TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS CAUSES
 DESCRIPTION is the slippage of one or more vertebrae, the bones of the spine. Many causes of slippage of the vertebra are possible; these include stress fracture (spondylolysis), which is often seen in
DESCRIPTION is the slippage of one or more vertebrae, the bones of the spine. Many causes of slippage of the vertebra are possible; these include stress fracture (spondylolysis), which is often seen in
Knee Conditioning Program
 Knee Conditioning Program Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Knee Conditioning Program Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
How do you do exercises for patellar tracking disorder?
 To print: Use your web browser's print feature. Close this window after printing. Patellar Tracking Disorder: Exercises Table of Contents Patellar Tracking Disorder: Exercises Patellar Tracking Disorder:
To print: Use your web browser's print feature. Close this window after printing. Patellar Tracking Disorder: Exercises Table of Contents Patellar Tracking Disorder: Exercises Patellar Tracking Disorder:
Spondylolysis DESCRIPTION EXPECTED OUTCOME POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS COMMON SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS GENERAL TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS CAUSES
 DESCRIPTION is a stress or fatigue fracture of the bones of the spine (vertebrae) that does not involve the main weight-bearing part of those bones, the body of the vertebra. Instead, it involves an area
DESCRIPTION is a stress or fatigue fracture of the bones of the spine (vertebrae) that does not involve the main weight-bearing part of those bones, the body of the vertebra. Instead, it involves an area
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash)
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY
 Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain
 What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE
 ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints)
 MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints) Description Expected Outcome Shin splints is a term broadly used to describe pain in the lower extremity brought on by exercise or athletic activity. Most commonly
MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints) Description Expected Outcome Shin splints is a term broadly used to describe pain in the lower extremity brought on by exercise or athletic activity. Most commonly
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
 What is patellofemoral pain syndrome? Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain behind the kneecap. It has been given many names, including patellofemoral disorder, patellar malalignment,
What is patellofemoral pain syndrome? Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain behind the kneecap. It has been given many names, including patellofemoral disorder, patellar malalignment,
KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM
 KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM These exercises are specifically designed to rehabilitate the muscles of the hip and knee by increasing the strength and flexibility of the involved leg. This exercise program
KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM These exercises are specifically designed to rehabilitate the muscles of the hip and knee by increasing the strength and flexibility of the involved leg. This exercise program
Knee Conditioning Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
BICEPS TENDON TENDINITIS (PROXIMAL) AND TENOSYNOVITIS
 BICEPS TENDON TENDINITIS (PROXIMAL) AND TENOSYNOVITIS Description Proximal biceps tendon tendinitis and tenosynovitis is characterized by pain at the front of the shoulder and upper arm caused by inflammation
BICEPS TENDON TENDINITIS (PROXIMAL) AND TENOSYNOVITIS Description Proximal biceps tendon tendinitis and tenosynovitis is characterized by pain at the front of the shoulder and upper arm caused by inflammation
Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella)
 Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella) Patellar Tendinitis The most common tendinitis about the knee is irritation of the patellar tendon.
Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella) Patellar Tendinitis The most common tendinitis about the knee is irritation of the patellar tendon.
What is arthroscopy? Normal knee anatomy
 What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment
 Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment Suprascapular nerve entrapment is an uncommon nerve condition in the shoulder, causing pain and weakness. It involves compression of the suprascapular nerve at the top or
Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment Suprascapular nerve entrapment is an uncommon nerve condition in the shoulder, causing pain and weakness. It involves compression of the suprascapular nerve at the top or
Low-Back Strain DESCRIPTION POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS COMMON SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS GENERAL TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS CAUSES FACTORS THAT INCREASE RISK
 Page Number: 0 Date:13/6/11 Time:20:10:06 Low-Back Strain DESCRIPTION POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS Low-back strain is an injury to the muscles and tendons of the lower back. These muscles require great force
Page Number: 0 Date:13/6/11 Time:20:10:06 Low-Back Strain DESCRIPTION POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS Low-back strain is an injury to the muscles and tendons of the lower back. These muscles require great force
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
LOW BACK STRAIN. Description
 LOW BACK STRAIN Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description
LOW BACK STRAIN Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description
Iliotibial Band Tendinitis (Runner s Knee)
 Iliotibial Band Tendinitis (Runner s Knee) ANATOMY The iliotibial band (or tract) is a thick band of tissue that starts on the pelvis and upper thigh and passes along the outside of the knee and attaches
Iliotibial Band Tendinitis (Runner s Knee) ANATOMY The iliotibial band (or tract) is a thick band of tissue that starts on the pelvis and upper thigh and passes along the outside of the knee and attaches
HERNIATED DISK (Ruptured Disk)
 HERNIATED DISK (Ruptured Disk) Description Expected Outcome Sudden or gradual break in the supportive ligaments surrounding a spinal disk. The disk functions like a cushion between the bony vertebrae (bony
HERNIATED DISK (Ruptured Disk) Description Expected Outcome Sudden or gradual break in the supportive ligaments surrounding a spinal disk. The disk functions like a cushion between the bony vertebrae (bony
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow)
 EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
Ex Fix Rehab Phase II Strengthening
 Perform repetitions of each exercise, twice daily. Increase to repetitions. Ankle Pumps: With leg resting on bed and knee straight, slowly pump ankle up and down as far as possible. Quad sets: Tighten
Perform repetitions of each exercise, twice daily. Increase to repetitions. Ankle Pumps: With leg resting on bed and knee straight, slowly pump ankle up and down as far as possible. Quad sets: Tighten
Ellipse Rehab Phase 2 Strengthening
 Strengthening Perform reps of each exercise, twice daily. Increase to reps Ankle Pumps: With leg resting on bed and knee straight, slowly pump ankle up and down as far as possible. Quad sets: Tighten thigh
Strengthening Perform reps of each exercise, twice daily. Increase to reps Ankle Pumps: With leg resting on bed and knee straight, slowly pump ankle up and down as far as possible. Quad sets: Tighten thigh
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis
 Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
Home Exercise Program for Knee Conditioning
 Prepared for: Prepared by: Instructions: Home Exercise Program for Knee Conditioning Before beginning the conditioning program, warm up the muscles by riding a stationary bicycle or jogging for 10 minutes.
Prepared for: Prepared by: Instructions: Home Exercise Program for Knee Conditioning Before beginning the conditioning program, warm up the muscles by riding a stationary bicycle or jogging for 10 minutes.
Lesson Sixteen Flexibility and Muscular Strength
 Lesson Sixteen Flexibility and Muscular Strength Objectives After participating in this lesson students will: Be familiar with why we stretch. Develop a stretching routine to do as a pre-activity before
Lesson Sixteen Flexibility and Muscular Strength Objectives After participating in this lesson students will: Be familiar with why we stretch. Develop a stretching routine to do as a pre-activity before
Low Back Pain Home Exercises
 Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Heel Slides. Isometric Quad. For Appointments call:
 For Appointments call: 612-672-7100 Login ptrx.org/en/fv2d6ekjsq Exercise Prescription Date May 11, 2017 Assigning Provider Shannon Kelly PT, OCS Prescription Description - Post-op Phase 1 & 2 Heel Slides
For Appointments call: 612-672-7100 Login ptrx.org/en/fv2d6ekjsq Exercise Prescription Date May 11, 2017 Assigning Provider Shannon Kelly PT, OCS Prescription Description - Post-op Phase 1 & 2 Heel Slides
Posterior Total Hip Replacement
 Posterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
Posterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
Trochanteric Bursitis: Exercises
 Trochanteric Bursitis: Exercises Your Kaiser Permanente Care Instructions Here are some examples of typical rehabilitation exercises for your condition. Start each exercise slowly. Ease off the exercise
Trochanteric Bursitis: Exercises Your Kaiser Permanente Care Instructions Here are some examples of typical rehabilitation exercises for your condition. Start each exercise slowly. Ease off the exercise
PATELLA INSTABILITY AND REALIGNMENT
 Daniel P. Duggan, D.O. The Sports Clinic 23961 Calle de la Magdalena, Suite 229 Laguna Hills, CA 92653 Phone: (949) 581-7001 Fax: (949) 581-8410 http://orthodoc.aaos.org/danielduggando PATELLA INSTABILITY
Daniel P. Duggan, D.O. The Sports Clinic 23961 Calle de la Magdalena, Suite 229 Laguna Hills, CA 92653 Phone: (949) 581-7001 Fax: (949) 581-8410 http://orthodoc.aaos.org/danielduggando PATELLA INSTABILITY
STRETCHING. Low Back Rotation. Double Leg Pull. Single Leg Pull. Core Home Exercise Program
 Core Home Exercise Program Seth L. Sherman, M.D. Tamara L. Young, ATC, OTC, M.Ed Department of Sports Medicine STRETCHING Low Back Rotation While lying on your back with both of your knees bent. Rotate
Core Home Exercise Program Seth L. Sherman, M.D. Tamara L. Young, ATC, OTC, M.Ed Department of Sports Medicine STRETCHING Low Back Rotation While lying on your back with both of your knees bent. Rotate
GENERAL EXERCISES KNEE BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017
 GENERAL EXERCISES KNEE BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only are not to be
GENERAL EXERCISES KNEE BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only are not to be
Hip Conditioning Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Anterior Shoulder Instability
 Anterior Shoulder Instability Anterior shoulder instability typically results from a dislocation injury to the shoulder joint when the humeral head (ball) of the humerus (upper arm bone) is displaced from
Anterior Shoulder Instability Anterior shoulder instability typically results from a dislocation injury to the shoulder joint when the humeral head (ball) of the humerus (upper arm bone) is displaced from
ANKLE SPRAINS. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 ANKLE SPRAINS Explanation Ankle sprains occur when ligaments in the ankle are partially or completely torn due to sudden stretching, either laterally or medially, or when the ankle is suddenly twisted
ANKLE SPRAINS Explanation Ankle sprains occur when ligaments in the ankle are partially or completely torn due to sudden stretching, either laterally or medially, or when the ankle is suddenly twisted
Southern Sports & Orthopaedics
 Knee conditioning program This knee conditioning program is designed to help you rehabilitate from your knee injury. In some cases, the program is being used as pre-habilitation, that is strengthening
Knee conditioning program This knee conditioning program is designed to help you rehabilitate from your knee injury. In some cases, the program is being used as pre-habilitation, that is strengthening
FLOOR EXERCISES for. strengthening your hip and knee INTERMEDIATE LEVEL
 FLOOR EXERCISES for strengthening your hip and knee INTERMEDIATE LEVEL THIGH STRENGTHENING 3 HIP STRENGTHENING ON YOUR SIDE 5 HIP STRENGTHENING ON YOUR BACK 8 ALL 4 S WITH LEG LIFT 10 When you have pain
FLOOR EXERCISES for strengthening your hip and knee INTERMEDIATE LEVEL THIGH STRENGTHENING 3 HIP STRENGTHENING ON YOUR SIDE 5 HIP STRENGTHENING ON YOUR BACK 8 ALL 4 S WITH LEG LIFT 10 When you have pain
Standing Shoulder Internal Rotation with Anchored Resistance. Shoulder External Rotation Reactive Isometrics
 Standing Shoulder Row with Anchored Resistance Begin standing upright, holding both ends of a resistance band that is anchored in front of you at chest height, with your palms facing inward. Pull your
Standing Shoulder Row with Anchored Resistance Begin standing upright, holding both ends of a resistance band that is anchored in front of you at chest height, with your palms facing inward. Pull your
General Principles of Stretching. To be effective, stretching must be done slowly, gently and frequently.
 General Principles of Stretching To be effective, stretching must be done slowly, gently and frequently. Slowly means that while the exercise is being done the muscle being stretched must be moved slowly
General Principles of Stretching To be effective, stretching must be done slowly, gently and frequently. Slowly means that while the exercise is being done the muscle being stretched must be moved slowly
Routine For: Total Hip Arthroplasty - Standard Precautions
 Standard Hip Precautions TOTAL HIP - 4 Ankle Pump not bend your operative hip beyond a 90 degree angle. not sit with your legs crossed or lie on your back with your operative leg crossed over the other
Standard Hip Precautions TOTAL HIP - 4 Ankle Pump not bend your operative hip beyond a 90 degree angle. not sit with your legs crossed or lie on your back with your operative leg crossed over the other
return to sports after injury IMPROVING STRENGTH, POWER, AND AGILITY
 return to sports after injury IMPROVING STRENGTH, POWER, AND AGILITY This booklet is designed for people recovering from a knee or leg injury who participate in recreational or competitive sports such
return to sports after injury IMPROVING STRENGTH, POWER, AND AGILITY This booklet is designed for people recovering from a knee or leg injury who participate in recreational or competitive sports such
Knee Home Exercise Program Clayton W. Nuelle, MD RANGE OF MOTION
 Knee Home Exercise Program Clayton W. Nuelle, MD RANGE OF MOTION Heel Prop/Quad Isometric While lying flat on a table with knee straight, place heel on a rolled towel. Heel must be high enough so that
Knee Home Exercise Program Clayton W. Nuelle, MD RANGE OF MOTION Heel Prop/Quad Isometric While lying flat on a table with knee straight, place heel on a rolled towel. Heel must be high enough so that
REHABILITATION AFTER ARTHROSCOPIC KNEE SURGERY
 REHABILITATION AFTER ARTHROSCOPIC KNEE SURGERY This protocol is a guideline for your rehabilitation after arthroscopic knee surgery. You may vary in your ability to do these exercises and to progress to
REHABILITATION AFTER ARTHROSCOPIC KNEE SURGERY This protocol is a guideline for your rehabilitation after arthroscopic knee surgery. You may vary in your ability to do these exercises and to progress to
Knee Replacement Rehabilitation
 Knee Replacement Rehabilitation The following exercises may be given to you to help get you moving and become more independent. Please bring this copy of the exercises with you to hospital. After your
Knee Replacement Rehabilitation The following exercises may be given to you to help get you moving and become more independent. Please bring this copy of the exercises with you to hospital. After your
Move your ankle inward toward your other foot and then outward away from your other foot.
 TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT POST OPERATIVE EXERCISES Regular exercises to restore your normal hip motion and strength and a gradual return to everyday activities are important for your full recovery. Dr. Robertson
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT POST OPERATIVE EXERCISES Regular exercises to restore your normal hip motion and strength and a gradual return to everyday activities are important for your full recovery. Dr. Robertson
Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises
 Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises Most athletes (swimmers included) use a combination of controlled movement exercises and specific joint/muscle stretching to improve performance potential. The proposed
Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises Most athletes (swimmers included) use a combination of controlled movement exercises and specific joint/muscle stretching to improve performance potential. The proposed
Knee Arthroscopy: Postoperative Instructions
 Knee Arthroscopy: Postoperative Instructions John P. Woll, MD Knee arthroscopy is a commonly performed procedure that is much less invasive than previous open techniques, but it is still an operation,
Knee Arthroscopy: Postoperative Instructions John P. Woll, MD Knee arthroscopy is a commonly performed procedure that is much less invasive than previous open techniques, but it is still an operation,
Mosaicplasty and OATS Rehabilitation Protocol
 Mosaicplasty and OATS Rehabilitation Protocol PHASE 1: 0 2 weeks after surgery You will go home with crutches, cryocuff cold therapy unit and a CPM machine. GOALS: 1. Protect the cartilage transfer avoid
Mosaicplasty and OATS Rehabilitation Protocol PHASE 1: 0 2 weeks after surgery You will go home with crutches, cryocuff cold therapy unit and a CPM machine. GOALS: 1. Protect the cartilage transfer avoid
Lower Body: General Lower Extremity Exercises Author: Carri A. Dunn, PT
 Lower Body: General Lower Extremity Exercises Author: Carri A. Dunn, PT The following exercises have been prescribed by your physical therapist. They are intended to improve joint flexibility and muscle
Lower Body: General Lower Extremity Exercises Author: Carri A. Dunn, PT The following exercises have been prescribed by your physical therapist. They are intended to improve joint flexibility and muscle
Strength and Balance Exercises
 Strength and Balance Exercises LEG EXTENSIONS Purpose: Strengthen the thigh and leg muscles. Starting Position: Sit tall with your feet flat on floor, shoulderwidth apart. You may hold onto the sides of
Strength and Balance Exercises LEG EXTENSIONS Purpose: Strengthen the thigh and leg muscles. Starting Position: Sit tall with your feet flat on floor, shoulderwidth apart. You may hold onto the sides of
Physical & Occupational Therapy
 In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
Patient & Family Guide. Hip Exercises.
 Patient & Family Guide Hip Exercises 2016 www.nshealth.ca Hip Exercises Do your exercises 3 times during the day. Stretching guidelines Before you start your stretching you should: Use heat (e.g. hot pack,
Patient & Family Guide Hip Exercises 2016 www.nshealth.ca Hip Exercises Do your exercises 3 times during the day. Stretching guidelines Before you start your stretching you should: Use heat (e.g. hot pack,
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
YOUR FREE COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO HELP RELIEVE LOWER BACK PAIN NATURALLY
 YOUR FREE COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO HELP RELIEVE LOWER BACK PAIN NATURALLY By: helpwithsciatica HTTPS://HELPWITHSCIATICA.COM Table of contents 1 Introduction 2 Exercise: Extensions 3 Exercise: Curl-Ups 4
YOUR FREE COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO HELP RELIEVE LOWER BACK PAIN NATURALLY By: helpwithsciatica HTTPS://HELPWITHSCIATICA.COM Table of contents 1 Introduction 2 Exercise: Extensions 3 Exercise: Curl-Ups 4
Chapter 9: Exercise Instructions
 RESOURCES RESEARCHERS / MEDICAL HOW TO HELP SPONSORS GEHRIG CONNECTION MEDIA TELETHON MDA.ORG search our site Go MDA/ALS Newsmagazine Current Issue Home> Publications >Everyday Life With ALS: A Practical
RESOURCES RESEARCHERS / MEDICAL HOW TO HELP SPONSORS GEHRIG CONNECTION MEDIA TELETHON MDA.ORG search our site Go MDA/ALS Newsmagazine Current Issue Home> Publications >Everyday Life With ALS: A Practical
Anterior Total Hip Replacement
 Anterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
Anterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
Seniors Helping Seniors Stretch Routine TRAINING PEER LEADERS TO SUPPORT SENIORS HEALTH AND WELLNESS
 Seniors Helping Seniors Stretch Routine TRAINING PEER LEADERS TO SUPPORT SENIORS HEALTH AND WELLNESS 2018 - BACK STRETCHES Back Extensions Hold for about 10 seconds Back Flexion Back Rotation, each side
Seniors Helping Seniors Stretch Routine TRAINING PEER LEADERS TO SUPPORT SENIORS HEALTH AND WELLNESS 2018 - BACK STRETCHES Back Extensions Hold for about 10 seconds Back Flexion Back Rotation, each side
ROTATOR CUFF TEAR, SURGERY FOR
 ROTATOR CUFF TEAR, SURGERY FOR Indications (Who Needs Surgery, When, electricity is used to cauterize small capillaries. Electricity or Why, and Goals) a motorized shaver is used to remove the bursa and
ROTATOR CUFF TEAR, SURGERY FOR Indications (Who Needs Surgery, When, electricity is used to cauterize small capillaries. Electricity or Why, and Goals) a motorized shaver is used to remove the bursa and
Lower Extremity Exercises - Knee
 Lower Extremity Exercises - Knee These exercises are to improve joint flexibility and muscle strength. Your therapist will modify the program as needed and provide instructions on doing the exercises correctly.
Lower Extremity Exercises - Knee These exercises are to improve joint flexibility and muscle strength. Your therapist will modify the program as needed and provide instructions on doing the exercises correctly.
Walking/Running Stretch Routine
 Walking/Running Stretch Routine Quadriceps Stretch With left hand grasp your right ankle, gently pull heel toward buttocks until stretch is felt. Repeat on opposite side. Walking/Running Stretch Routine
Walking/Running Stretch Routine Quadriceps Stretch With left hand grasp your right ankle, gently pull heel toward buttocks until stretch is felt. Repeat on opposite side. Walking/Running Stretch Routine
Low Back Program Exercises
 Low Back Program Exercises Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite
Low Back Program Exercises Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite
Developed by: Physiotherapy Department Surrey Memorial Hospital. Printshop #
 Developed by: Physiotherapy Department Surrey Memorial Hospital Printshop # 255171 The following exercises are intended for you to continue at home. Your physiotherapist will teach and mark the exercises
Developed by: Physiotherapy Department Surrey Memorial Hospital Printshop # 255171 The following exercises are intended for you to continue at home. Your physiotherapist will teach and mark the exercises
Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Ridgegate Pkwy., Suite 309 Lone Tree, Colorado Office: Fax:
 ANKLE SPRAIN What is the ATFL? The ankle joint is made up of the tibia, fibula (bones in the lower leg) and the talus (bone below the tibia and fibula). Ligaments in the ankle connect bone to bone and
ANKLE SPRAIN What is the ATFL? The ankle joint is made up of the tibia, fibula (bones in the lower leg) and the talus (bone below the tibia and fibula). Ligaments in the ankle connect bone to bone and
Postoperative Days 1-7
 ACL RECONSTRUCTION REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Postoperative Days 1-7 *IT IS EXTREMELY IMPORTANT THAT YOU WORK ON EXTENSION IMMEDIATELY Goals: * Control pain and swelling * Care for the knee and dressing *
ACL RECONSTRUCTION REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Postoperative Days 1-7 *IT IS EXTREMELY IMPORTANT THAT YOU WORK ON EXTENSION IMMEDIATELY Goals: * Control pain and swelling * Care for the knee and dressing *
Shoulder Dislocation. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms. Treatment. Diagnosis
 Shoulder Dislocation Explanation A dislocated shoulder occurs when the humerus separates from the scapula at the glenohumeral joint, or in simpler terms, the head of the upper arm bone (humerus) is dislodged
Shoulder Dislocation Explanation A dislocated shoulder occurs when the humerus separates from the scapula at the glenohumeral joint, or in simpler terms, the head of the upper arm bone (humerus) is dislodged
Below Knee Amputee Home Exercise Program
 Below Knee Amputee Home Exercise Program It is important that you take an active role in your rehabilitation. The following exercises must be done every day to prevent complications. After below the knee
Below Knee Amputee Home Exercise Program It is important that you take an active role in your rehabilitation. The following exercises must be done every day to prevent complications. After below the knee
Flexibility and Stretching
 Flexibility and Stretching Stretching before exercise prepares the joints for motion, helps avoid injury and increases the range of motion of the area being stretched. After exercise stretching reduces
Flexibility and Stretching Stretching before exercise prepares the joints for motion, helps avoid injury and increases the range of motion of the area being stretched. After exercise stretching reduces
Patellar Instability. OrthoInfo Patella Instability Page 1 of 5
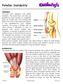 Patellar Instability OVERVIEW You have been diagnosed with patella instability. This means that your knee cap (patella) has been partially or completely going out of place and is not tracking well against
Patellar Instability OVERVIEW You have been diagnosed with patella instability. This means that your knee cap (patella) has been partially or completely going out of place and is not tracking well against
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises. Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
Knee Arthroscopy Exercise Guide
 RECOVERY Knee Arthroscopy Exercise Guide Regular exercise to restore strength and mobility to your knee is important for your full recovery after arthroscopic surgery. Your orthopaedic surgeon or physical
RECOVERY Knee Arthroscopy Exercise Guide Regular exercise to restore strength and mobility to your knee is important for your full recovery after arthroscopic surgery. Your orthopaedic surgeon or physical
Simple Strength, Balance and Flexibility Exercises to Do at Home
 Simple Strength, Balance and Flexibility Exercises to Do at Home For someone with medical problems, or who has been inactive and wants to exercise vigorously, always check with a doctor before beginning
Simple Strength, Balance and Flexibility Exercises to Do at Home For someone with medical problems, or who has been inactive and wants to exercise vigorously, always check with a doctor before beginning
EXERCISE INSTRUCTIONS
 EXERCISE INSTRUCTIONS A/ Strength A01 SQUAT Stand on the Power-Plate with feet shoulder width apart. Keeping the back straight and knees slightly bent, gently squeeze the leg muscles. You should feel tension
EXERCISE INSTRUCTIONS A/ Strength A01 SQUAT Stand on the Power-Plate with feet shoulder width apart. Keeping the back straight and knees slightly bent, gently squeeze the leg muscles. You should feel tension
Prater Chiropractic Wellness Center 903 W. South St. Kalamazoo, MI PH: (269)
 Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following a well-structured conditioning
Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following a well-structured conditioning
Source: Exercise in Arthritis
 Exercise in Arthritis Regular exercise boosts fitness and helps reverse joint stiffness with RA. Decrease Pain, Increase Energy Exercise more to decrease pain and feel more energetic? Hardly seems possible
Exercise in Arthritis Regular exercise boosts fitness and helps reverse joint stiffness with RA. Decrease Pain, Increase Energy Exercise more to decrease pain and feel more energetic? Hardly seems possible
Ankle Program Range of Motion Exercises Stretches:
 Ankle Program Range of Motion Exercises Due to injury, immobilization or a combination of both your ankle has become stiff. These exercises are designed to help regain the motion and strength lost. You
Ankle Program Range of Motion Exercises Due to injury, immobilization or a combination of both your ankle has become stiff. These exercises are designed to help regain the motion and strength lost. You
Snow Angels on Foam Roll
 Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
LOW BACK PAIN. what you can do
 LOW BACK PAIN what you can do Back pain Nearly 80 percent of adults will experience back pain at some point in their life. The good news is that back pain will normally go away within four to six weeks
LOW BACK PAIN what you can do Back pain Nearly 80 percent of adults will experience back pain at some point in their life. The good news is that back pain will normally go away within four to six weeks
