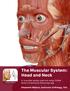
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature
|
|
|
- Jocelyn Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature Introduction The skeletal muscle of the body can be subdivided into: Axial musculature Muscles that position the head and vertebral column Muscles that move the rib cage Appendicular musculature Muscles that stabilize or move the appendicular skeleton The axial muscles can be placed into four groups based on location or function Muscles of the head and neck Muscles of the vertebral column Oblique and rectus muscles Muscles of the pelvic floor Muscles of the Head and Neck Can be subdivided into several different groups Muscles of facial expression Extraocular muscles Muscles of mastication Muscles of the tongue Muscles of the pharynx Muscles of the anterior neck Muscles of Facial Expression (Mouth) Orbicularis oris Zygomaticus major and minor Risorius Mentalis Depressor labii inferioris Depressor anguli oris Levator anguli oris Buccinator Depressor labii superioris Muscles of Facial Expression (Eye) Page 1 of 6 BIOL_218_F_2011_Lecture Outline Ch 10
2 Corrugator supercilii Levator palpebrae superioris Orbicularis oculi Muscles of Facial Expression (Nose) Procerus Nasalis Muscles of Facial Expression (Scalp) Occipitofrontalis Frontal belly (frontalis) Occipital belly (occipitalis) Temporoparietalis Muscles of Facial Expression (Neck) Platysma Extra-ocular Muscles Extrinsic eye muscles (muscles that control eye movement) Medial and lateral rectus muscles Superior and inferior rectus muscles Superior and inferior oblique muscles Extra-ocular Muscles Eye movements Lateral rectus: rotates the eye laterally Medial rectus: rotates the eye medially Superior rectus: rotates the eye upward Inferior rectus: rotates the eye downward Superior oblique: rotates the eye downward and laterally Inferior oblique: rotates the eye upward and laterally Muscles of Mastication Masseter Temporalis Pterygoids Muscles of the Tongue Genioglossus Page 2 of 6 BIOL_218_F_2011_Lecture Outline Ch 10
3 Hyoglossus Palatoglossus Styloglossus Muscles of the Pharynx Pharyngeal constrictors Superior constrictor Middle constrictor Inferior constrictor Muscles of the Pharynx (continued) Laryngeal elevators Palatopharyngeus Stylopharyngeus Muscles of the Pharynx (continued) Palatal muscles Levator veli palatini Tensor veli palatini Anterior Muscles of the Neck Digastric Mylohyoid (deep to the digastric) Geniohyoid (deep to the mylohyoid) Stylohyoid Anterior Muscles of the Neck (continued) Omohyoid Sternohyoid (deep to the omohyoid) Sternothyroid (deep to the sternohyoid) Thyrohyoid (attached to the sternothyroid and hyoid bone) Sternocleidomastoid Muscles of the Vertebral Column Back muscles form three distinct layers Superficial layer (extrinsic back muscles): move the neck Intermediate layer (extrinsic back muscles): move the vertebral column Deep layer (intrinsic back muscles): interconnect the vertebrae Examples of the extrinsic back muscles Page 3 of 6 BIOL_218_F_2011_Lecture Outline Ch 10
4 Superficial layer of extrinsic muscles Trapezius Latissimus dorsi Levator scapulae Rhomboid muscle Example of the extrinsic back muscles Intermediate layer of extrinsic muscles Serratus posterior The Deep Layer (or intrinsic back muscles) Can be further subdivided into: Superficial intrinsic Intermediate intrinsic Deep intrinsic Example of Superficial Intrinsic Back Muscles Splenius muscles Examples of Intermediate Intrinsic Back Muscles Erector spinae (group of three muscles) Spinalis thoracis (most medial of the three) Longissimus thoracis Iliocostalis lumborum (most lateral of the three) Examples of Deep Intrinsic Back Muscles Semispinalis Multifidus Rotatores Interspinales Intertransversarii Spinal Flexors Longus capitis Longus colli The above two muscles rotate or flex the neck Quadratus lumborum Flexes the vertebral column laterally Page 4 of 6 BIOL_218_F_2011_Lecture Outline Ch 10
5 These muscles can be grouped in this manner: Cervical muscles Thoracic muscles Abdominal muscles Cervical oblique muscles Scalene muscles (anterior, middle, and posterior scalenes) Elevate the ribs and also flex the neck Thoracic oblique muscles External intercostals: elevate the ribs Internal intercostals: depress the ribs Transversus thoracis: depresses the ribs Serratus posterior Superior serratus posterior: elevates ribs and enlarges thoracic cavity Inferior serratus posterior: depresses ribs and opposes diaphragm contraction thus decreasing thoracic size Abdominal oblique muscles External oblique: rotates the vertebral column Internal oblique: rotates the vertebral column Transversus abdominis: compresses the abdomen Cervical Rectus Muscles Geniohyoid Omohyoid Sternohyoid Thyrohyoid Thoracic Rectus Muscles Diaphragm muscle Expands the thoracic cavity for inhalation Abdominal Rectus Muscles Rectus abdominis Flexes the vertebral column Divided longitudinally by the linea alba Divided transversally by the tendinous inscriptions Page 5 of 6 BIOL_218_F_2011_Lecture Outline Ch 10
6 Muscles of the Perineum and Pelvic Diaphragm Main functions Support the organs of the pelvic cavity Flex the joints of the sacrum and coccyx Control the movement of material through the urethra and anus The Perineum (pelvic floor) Divided into two triangles Urogenital triangle Anal triangle The two triangles are separated by: Superficial transverse perineal muscle Muscles of the Pelvic Floor Superficial urogenital triangle area Superficial transverse perineal Ischiocavernosus Bulbospongiosus Superficial anal triangle area Superficial transverse perineal Gluteus maximus External anal sphincter Muscles of the Pelvic Floor Deep urogenital triangle area Deep transverse perineal Deep anal triangle area Coccygeus Iliococcygeus Pubococcygeus Page 6 of 6 BIOL_218_F_2011_Lecture Outline Ch 10
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Anatomy and Physiology app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Anatomy and Physiology app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES A. Watch the video 13.1 Muscular System Overview and observe
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Anatomy and Physiology app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES A. Watch the video 13.1 Muscular System Overview and observe
Lab Activity 11: Group I
 Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
The Muscular System Part A
 10 The Muscular System Part A Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Organization of the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 10.1 Describe the general function of the body s axial and
10 The Muscular System Part A Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Organization of the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 10.1 Describe the general function of the body s axial and
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book
 Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46484 1 Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end
OpenStax-CNX module: m46484 1 Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end
The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk
 The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk Dr. Nabil Khouri Dr. Nabil Khouri MD MSc, PhD Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk Dr. Nabil Khouri Dr. Nabil Khouri MD MSc, PhD Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor. Zygomaticus major Buccinator
 Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
SKELETAL MUSCLES. Objectives
 Objectives Body Wall Muscles Remember the pattern Hypaxial Muscle Overview Cervical body wall muscles Hypaxial Muscle Overview Thoracic body wall muscles Hypaxial Muscle Overview Abdominal body wall muscles
Objectives Body Wall Muscles Remember the pattern Hypaxial Muscle Overview Cervical body wall muscles Hypaxial Muscle Overview Thoracic body wall muscles Hypaxial Muscle Overview Abdominal body wall muscles
5/21/2013. Muscle Anatomy. Thursday January, 24 th, Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle
 Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Module 6 - The Muscular System Introduction to the Muscular System and Muscles of the Head, Neck and Shoulder
 Module 6 - The Muscular System Introduction to the Muscular System and Muscles of the Head, Neck and Shoulder There will be three modules to cover the muscle anatomy of the body. The first module will
Module 6 - The Muscular System Introduction to the Muscular System and Muscles of the Head, Neck and Shoulder There will be three modules to cover the muscle anatomy of the body. The first module will
Bone Practical. Labs Muscle Labs. Final Practical. Divisions of the Muscular System. Quiz format
 Bone Practical Labs 17 + 18 Muscles Wed 7/11 @ 8am 40 50 stations About half axial, half appendicular bones Disarticulated bones: Skulls, partial skulls, vertebrae, ribs, skeletons, arm bones, leg bones,
Bone Practical Labs 17 + 18 Muscles Wed 7/11 @ 8am 40 50 stations About half axial, half appendicular bones Disarticulated bones: Skulls, partial skulls, vertebrae, ribs, skeletons, arm bones, leg bones,
function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of
![function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of](/thumbs/74/71276096.jpg) Nerves I. Cranial nerves A. Olfactory (CN I) 1. Olfactory bulb 2. Olfactory tract B. Optic n. (CNII) function - carries visual sensory information from the neural retina to the diencephalon & midbrain
Nerves I. Cranial nerves A. Olfactory (CN I) 1. Olfactory bulb 2. Olfactory tract B. Optic n. (CNII) function - carries visual sensory information from the neural retina to the diencephalon & midbrain
Contents. Preface xv. SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1. SECTION 2: The Bodynamic Psycho-Motor Anatomy 29
 Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
The Back. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
The Muscular System. Part A
 The Muscular System Part A 10 The Muscular System Part A 10 Hold onto your glutes, this is a big one. 10 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
The Muscular System Part A 10 The Muscular System Part A 10 Hold onto your glutes, this is a big one. 10 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The muscular system specifically concerns skeletal muscles and associated connective tissue that make individual muscle organs. B. This chapter discusses how
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The muscular system specifically concerns skeletal muscles and associated connective tissue that make individual muscle organs. B. This chapter discusses how
Main Menu. Trunk and Spinal Column click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Trunk and Spinal Column click here Main Menu K.9 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k9/k9entry.htm[3/27/18, 2:00:55 PM] The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column complex 24 intricate
1 The Trunk and Spinal Column click here Main Menu K.9 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k9/k9entry.htm[3/27/18, 2:00:55 PM] The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column complex 24 intricate
The Muscular System Lab Power Point
 The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives
 1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
2. In regards to the bones of the arm and forearm, which of the following is TRUE?
 Anatomy and Physiology Fall Exam II: Form A Name: 1. Use the following table to answer Question 1. I II III IV V The nasal bone articulates with the frontal process of the maxilla The mastoid process is
Anatomy and Physiology Fall Exam II: Form A Name: 1. Use the following table to answer Question 1. I II III IV V The nasal bone articulates with the frontal process of the maxilla The mastoid process is
1. In regards to the bones of the face, which of the following is NOT TRUE?
 Anatomy and Physiology Fall Exam II: Form B Name: 1. In regards to the bones of the face, which of the following is NOT TRUE? A. The vomer bone articulates with the dorsal surface of the palatine process
Anatomy and Physiology Fall Exam II: Form B Name: 1. In regards to the bones of the face, which of the following is NOT TRUE? A. The vomer bone articulates with the dorsal surface of the palatine process
Muscles of the Face, Head, and Neck
 Muscles of the Face, Head, and Neck 1 How Muscles Are Named Many muscles named using such features as Location Function Shape Direction of fibers Number of heads or divisions Points of attachment Size
Muscles of the Face, Head, and Neck 1 How Muscles Are Named Many muscles named using such features as Location Function Shape Direction of fibers Number of heads or divisions Points of attachment Size
The Back OUTLINE. Vertebral Column (review) Craniovertebral Joints Dorsal Scapular Region(review) Muscles of the Back Suboccipital Region
 The Back OUTLINE Vertebral Column (review) Craniovertebral Joints Dorsal Scapular Region(review) Muscles of the Back Suboccipital Region Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com
The Back OUTLINE Vertebral Column (review) Craniovertebral Joints Dorsal Scapular Region(review) Muscles of the Back Suboccipital Region Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com
Chapter 11: The Muscular System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
3/27/2012. Muscle Classification: Functional Groups. Interactions of Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Naming Skeletal Muscles Direction of Muscle Fibers Action Location Origin & Insertion Skeletal Muscle Size Shape Number Of Origins Direction of Muscle Fibers Relative to the Midline RECTUS = parallel to
Naming Skeletal Muscles Direction of Muscle Fibers Action Location Origin & Insertion Skeletal Muscle Size Shape Number Of Origins Direction of Muscle Fibers Relative to the Midline RECTUS = parallel to
A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract.
 Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
GLOBAL EDITION. Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology ELEVENTH EDITION. Martini Nath Bartholomew
 GLOBAL EDITION Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology ELEVENTH EDITION Martini Nath Bartholomew Spotlight Figures 1 2 Levels of Organization 2 4 Chemical Notation 3 1 Anatomy of a Model Cell 3 7 Protein
GLOBAL EDITION Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology ELEVENTH EDITION Martini Nath Bartholomew Spotlight Figures 1 2 Levels of Organization 2 4 Chemical Notation 3 1 Anatomy of a Model Cell 3 7 Protein
#8 35 ANATOMY MUSCLES OF THE HEAD. Nermeen Sweiti & Sua'dad Al-Ani 8/10/2015. Nabeel Khouri. Page 0 of 24
 #8 35 ANATOMY MUSCLES OF THE HEAD Nermeen Sweiti & Sua'dad Al-Ani 8/10/2015 Nabeel Khouri Page 0 of 24 Today we will start a new topic: MUSCLES o How should we study the muscles: a. Tables (I will add
#8 35 ANATOMY MUSCLES OF THE HEAD Nermeen Sweiti & Sua'dad Al-Ani 8/10/2015 Nabeel Khouri Page 0 of 24 Today we will start a new topic: MUSCLES o How should we study the muscles: a. Tables (I will add
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
1TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE
 TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
The Muscular System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association
 C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association Personal Trainer/Advanced Personal Trainer/ Master Trainer/ Sports Nutritionist/ Martial Arts Strength Trainer/Step & Kickbox Aerobics Instructor/ Health Club Manager/
C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association Personal Trainer/Advanced Personal Trainer/ Master Trainer/ Sports Nutritionist/ Martial Arts Strength Trainer/Step & Kickbox Aerobics Instructor/ Health Club Manager/
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Axial Muscles of the Abdominal Wall, and Thorax *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46485 1 Axial Muscles of the Abdominal Wall, and Thorax * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end
OpenStax-CNX module: m46485 1 Axial Muscles of the Abdominal Wall, and Thorax * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end
The Anatomy Coloring Book Wynn Kapit Lawrence M. Elson Fourth Edition
 The Anatomy Coloring Book Wynn Kapit Lawrence M. Elson Fourth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the
The Anatomy Coloring Book Wynn Kapit Lawrence M. Elson Fourth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the
Muscles of the Upper Limb that are dissected in the Back Region Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery Notes
 Muscles of Upper Limb that are dissected in Back Region Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery Notes floor of thoraco thoraco inserting spines from intertubercular arm nerve (C7,8) a. tendon
Muscles of Upper Limb that are dissected in Back Region Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery Notes floor of thoraco thoraco inserting spines from intertubercular arm nerve (C7,8) a. tendon
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401
 Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 11 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 11 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) The attachment of a muscle s tendon to the stationary bone is called the ; the attachment of the muscle s other tendon to the movable
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 11 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) The attachment of a muscle s tendon to the stationary bone is called the ; the attachment of the muscle s other tendon to the movable
Sports Medicine Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX
 Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan & A. Eastlake, 2008 Muscles of the Upper Limbs In this
Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan & A. Eastlake, 2008 Muscles of the Upper Limbs In this
2/4/2018. Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue. Ch.7 Review. Sternocleidomastoid.
 Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
The Trunk and Spinal Column Kinesiology Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Trunk and Spinal Column Kinesiology Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column 24 articulating vertebrae 31 pairs of spinal nerves Abdominal muscles some
The Trunk and Spinal Column Kinesiology Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column 24 articulating vertebrae 31 pairs of spinal nerves Abdominal muscles some
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
The Biomechanics of the Human Spine. Basic Biomechanics, 6 th edition By Susan J. Hall, Ph.D.
 Chapter 9 The Biomechanics of the Human Spine Structure of the Spine The spine is a curved stack of 33 vertebrae structurally divided into five regions: cervical region - 7 vertebrae thoracic region -
Chapter 9 The Biomechanics of the Human Spine Structure of the Spine The spine is a curved stack of 33 vertebrae structurally divided into five regions: cervical region - 7 vertebrae thoracic region -
Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter Elevates mandible. Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion. Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders
 Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY WORKSHEET Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System Background
 ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY WORKSHEET Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System Background Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by dense regular connective tissue in the form of cord-like tendons or membranous
ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY WORKSHEET Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System Background Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by dense regular connective tissue in the form of cord-like tendons or membranous
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical
 Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Workshop on thoracic diagnostic procedures
 Workshop on thoracic diagnostic procedures SAMM / U. Böhni Kyphosis is in correlation with lordosis of lumbar and cervicle spine 20-40 (Hefti et al. 1997) Extrinsic dorsal muscles superficial layer a.
Workshop on thoracic diagnostic procedures SAMM / U. Böhni Kyphosis is in correlation with lordosis of lumbar and cervicle spine 20-40 (Hefti et al. 1997) Extrinsic dorsal muscles superficial layer a.
3 Movements of the Trunk. Flexion Rotation Extension
 3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
Neck of Condylar. Process. Anterior Border of Ramus. Mandibular. Foramen. Posterior Border of Ramus Incisive Fossa.
 Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
The trunk and spinal column. Functions of Spine. Bones 6/5/2017. Chapter 10. Consider the complexity of functions. 33 bones of the spine
 The trunk and spinal column Chapter 10 Functions of Spine Consider the complexity of functions provides stability to a cylinder permits movement in all directions supports structures of considerable weight
The trunk and spinal column Chapter 10 Functions of Spine Consider the complexity of functions provides stability to a cylinder permits movement in all directions supports structures of considerable weight
List of Muscles and Function. Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows
 List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
Chapter 10. The Muscular System. AP1-Lecture Goodwin College. Introduction. In this chapter we will cover: 4/27/2015
 Chapter 10 The Muscular System AP1-Lecture Goodwin College Introduction In this chapter we will cover: Structural and functional organization of muscles Muscles of the head and neck Muscles of the trunk
Chapter 10 The Muscular System AP1-Lecture Goodwin College Introduction In this chapter we will cover: Structural and functional organization of muscles Muscles of the head and neck Muscles of the trunk
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline Part 1 of 2
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline Part 1 of 2 See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline Part 1 of 2 See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide
 A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
Chapter 11 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Chapter 11 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM 2 Muscle Tissue - refers to all the contractile tissues of the body; skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Muscular System
1 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Chapter 11 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM 2 Muscle Tissue - refers to all the contractile tissues of the body; skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Muscular System
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym!
 Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym! The word FOMO (short for fear of missing out) crops up everywhere, even in the nursery where parents and caregivers race from the one stimulation class to
Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym! The word FOMO (short for fear of missing out) crops up everywhere, even in the nursery where parents and caregivers race from the one stimulation class to
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES
 ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy
 Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
Muscles Built on the Maniken
 Muscles Built on the Maniken Facial Muscle Group 1. Temporalis O temporal fossa I anterior border of the ramus of the mandible A elevates the mandible (bite muscle) and holds jaw while at rest 2. Procerus
Muscles Built on the Maniken Facial Muscle Group 1. Temporalis O temporal fossa I anterior border of the ramus of the mandible A elevates the mandible (bite muscle) and holds jaw while at rest 2. Procerus
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D.
 Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D. Chest cavity - bony structures Chest cavity- bony structures Sternum Ribs True ribs: first seven pairs connect
Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D. Chest cavity - bony structures Chest cavity- bony structures Sternum Ribs True ribs: first seven pairs connect
Lab 5: Myology of the Cat
 Lab 5: Myology of the Cat Objectives 1. To gain an understanding of the muscular system of the cat. 2. To learn the insertions, origins and actions of the muscles you study. 3. To study how the muscles
Lab 5: Myology of the Cat Objectives 1. To gain an understanding of the muscular system of the cat. 2. To learn the insertions, origins and actions of the muscles you study. 3. To study how the muscles
_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come]
![_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come] _CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come]](/thumbs/81/84146690.jpg) 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1 [Half-Title to come] 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 2 THE BACK Lippincott Williams & Wilkins atlas of ANATOMY CHAPTER 1 Plate 1-01 Palpable Structures
10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1 [Half-Title to come] 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 2 THE BACK Lippincott Williams & Wilkins atlas of ANATOMY CHAPTER 1 Plate 1-01 Palpable Structures
Skeleton. The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation.
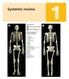 S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back
 Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back Shoulder Muscles Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Major Teres Minor Subscapularis Deltoid (Delts) Function: Raises the upper arm Origin:
Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back Shoulder Muscles Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Major Teres Minor Subscapularis Deltoid (Delts) Function: Raises the upper arm Origin:
The Concise Book of Muscles second edition
 The Concise Book of Muscles second edition Chris Jarmey Lotus Publishing Chichester, England North Atlantic Books Berkeley, California Copyright 2003, 2008 by Chris Jarmey. All rights reserved. No portion
The Concise Book of Muscles second edition Chris Jarmey Lotus Publishing Chichester, England North Atlantic Books Berkeley, California Copyright 2003, 2008 by Chris Jarmey. All rights reserved. No portion
Cat Muscles Flashcards Mt SAC
 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
External Obliques Abdominal muscles that attaches at the lower ribs, pelvis, and abdominal fascia.
 The Core The core is where most of the body s power is derived. It provides the foundation for all movements of the arms and legs. The core must be strong, have dynamic flexibility, and function synergistically
The Core The core is where most of the body s power is derived. It provides the foundation for all movements of the arms and legs. The core must be strong, have dynamic flexibility, and function synergistically
University of Palestine. Final Exam 1 st Semester 2014/2015 Total Grade: 60
 Question One: MCQ: 1- The coronal suture joins the a) frontal and parietal bones. b) left and right parietal bones. c) parietal and occipital bones. d) parietal, squamous temporal and greater wing of the
Question One: MCQ: 1- The coronal suture joins the a) frontal and parietal bones. b) left and right parietal bones. c) parietal and occipital bones. d) parietal, squamous temporal and greater wing of the
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation
 Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Anatomy & Physiology B. Chapter 6: Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology B Chapter 6: Muscles Warm-up What are the three types of muscle tissue? Where are each located? Which are voluntary and which are involuntary? Which are striated which are unstriated?
Anatomy & Physiology B Chapter 6: Muscles Warm-up What are the three types of muscle tissue? Where are each located? Which are voluntary and which are involuntary? Which are striated which are unstriated?
Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8
 Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
HEAD & NECK BY NUMBERS THIRD EDITION Copyright 2013, Anatomy Numbers (Phoenix, AZ) All rights reserved
 HEAD & NECK BY NUMBERS THIRD EDITION Copyright 2013, Anatomy Numbers (Phoenix, AZ) All rights reserved No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic
HEAD & NECK BY NUMBERS THIRD EDITION Copyright 2013, Anatomy Numbers (Phoenix, AZ) All rights reserved No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic
Widens the esophagus during swallowing.
 ANTERO-LATERAL MUSCLES OF THE NECK Suprahyoid muscles: (a)digastricus (Digastric muscle), (b) Mylohyoideus,(c) Stylohyoideus, (d)geniohyoideus During deglutition, they raise the hyoid bone, and with it
ANTERO-LATERAL MUSCLES OF THE NECK Suprahyoid muscles: (a)digastricus (Digastric muscle), (b) Mylohyoideus,(c) Stylohyoideus, (d)geniohyoideus During deglutition, they raise the hyoid bone, and with it
Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column
 Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column Posture Vertebral Alignment Does it really matter? Yes it does! Postural Curves The vertebral column has a series of counterbalancing curves posterior anterior
Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column Posture Vertebral Alignment Does it really matter? Yes it does! Postural Curves The vertebral column has a series of counterbalancing curves posterior anterior
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
The Scalp and Face Protocol. Julie Goodwin, BA, LMT
 The Scalp and Face Protocol Julie Goodwin, BA, LMT The Scalp and Face Protocol Julie Goodwin, BA, LMT Julie Goodwin 2014 2 Agenda Pertinent Anatomy and Physiology Treatment Planning Strokes, Techniques
The Scalp and Face Protocol Julie Goodwin, BA, LMT The Scalp and Face Protocol Julie Goodwin, BA, LMT Julie Goodwin 2014 2 Agenda Pertinent Anatomy and Physiology Treatment Planning Strokes, Techniques
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
