Hip arthroscopy. Introduction. What is an arthroscopy? What happens during the operation? What are the benefits of an arthroscopy?
|
|
|
- Arleen French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Patient information Hip arthroscopy Hip arthroscopy Introduction This leaflet will explain what will happen when you come to the hospital for your operation. It is important that you understand what to expect and feel able to take an active role in your treatment. There will be many different health professionals involved in your care during your stay and there will be a clear plan for any after care when you are discharged from hospital. This leaflet will answer some of your questions but if there is anything you or your family are not sure about then please ask your nurse, doctor or therapist. What is an arthroscopy? Hip arthroscopy is performed under a general anaesthetic (you are asleep) using small cuts through which a camera (to see the joint) and instruments are passed. Using traction (a pulling force) to bring the hip slightly out of joint, your surgeon can get a good view of the hip and any areas that are causing your symptoms. Then, using the appropriate instruments, your surgeon can carry out the necessary procedure(s). What happens during the operation? You will be positioned on a fracture table (special traction table) with a well padded post pressing against the inside of the thigh (very close to the groin) this is used to keep the thigh bones in a good position. Traction is applied to each leg to allow space for the camera to pass into the hip joint. A special X-ray (image intensifier) is used to confirm that the joint is stretched opened enough to allow the camera to pass before starting the operation. X-ray is also used during the operation to help carry out certain procedures. What are the benefits of an arthroscopy? An arthroscopy is much less invasive than previous forms of hip surgery. This means that you have a shorter hospital stay and quicker healing than more traditional surgery. You will also be able to start your rehabilitation earlier. The hip arthroscopy also aims to remove or reduce your symptoms, including pain, instability and stiffness. Hospital stay Your operation can take from 1.5 to 3 hours, depending on how much work needs to be performed. You may need to stay in hospital overnight following your procedure however, Hip arthroscopy April 2017
2 in some cases you may be able to go home on the same day (dependent on the extent of your surgery, and the time the procedure is completed). This may vary depending on your medical history and also on how you are managing to mobilise with help from the physiotherapists. Hip anatomy What conditions can be treated with hip arthroscopy? The four most common conditions are: Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI): This condition involves the head of the thigh bone (femur) and the rim of the socket (acetabulum). It is caused by bumps on the femoral head causing abnormal contact with the socket, which can lead to damage of the cartilage (labrum). This in turn can cause pain. An arthroscopy can be used to reshape the femoral head and socket to prevent this abnormal contact. Labral tear: The hip socket has a rim of fibrous cartilage called the labrum. This can be damaged either through abnormal contact or other causes. Common symptoms of a labral tear include a locking or catching sensation in the hip as well as groin pain. Loose bodies: These are pieces of cartilage that form within the joint. They look like small marbles floating around in the joint space. They can be caused as a result of trauma, sports injury or wear and tear. Articular cartilage injury: Articular cartilage covers the joint surfaces of the head of the femur and inside the socket, allowing for smooth movement. Tears in this cartilage can happen from activities such as running or jumping or as a result of wear and tear. Hip arthroscopy, April
3 After the operation You will need to rest until the effects of the anaesthetic have passed. This may take several hours. Pain You may feel some pain in your hip as well as other areas such as your lower back, buttock or knee. It is important you take your prescribed pain relief in order to help with this pain. You may also notice some swelling around the hip and groin. This is normal and should go down over the first few days. You may find that after the operation you have some pain at the front of your hip, near where the scars are. This area and the area around your hip bone may also feel tender to the touch. This can be due to inflammation of one of the tendons around the hip. Unless there are any contra-indications (reasons why two drugs or procedures should not be used together) we would recommend regular anti-inflammatory tablet usage for the first two weeks after surgery to help with this. Using an ice pack over the area may also help. Your physiotherapist should also be able to recommend some stretches for this area. Walking You may need to stay overnight following your hip arthroscopy. You will be seen by a physiotherapist following your surgery and they will teach you some initial exercises as well as help you to learn to walk with the use of crutches. How much weight you are allowed to put through your operated leg depends on the surgeon s instruction. If your weight bearing is restricted, this can be for up to for 6 weeks but depends on the procedure the surgeon has performed. If you have stairs at home your physiotherapist will show you how to manage these safely. Wound care It is normal for the wound sites to sometimes leak a little bit of blood or fluid in the first few days after your surgery. The nursing staff will discuss taking care of your wound with you. You will need to see a nurse at your doctor s surgery to have the stitches taken out at about days after your surgery. Driving You can drive once you are fully weight bearing and it is comfortable to do so. You must be able to perform an emergency stop without hesitation. It is also a good idea to check the terms of your motor insurance policy with your insurance company to ensure it is valid, as some policies state you must not drive for a certain period of time following an operation. Work You may return to work when the pain has settled and you are confident that you can manage. If your job is not physically demanding, this can be after 1-2 weeks. However, if you have a physically demanding job this can be longer, taking up to 8-12 weeks. An initial sick certificate can be provided by the ward please ask the nurse before you leave the ward. Subsequent certificates will need to be obtained from your GP. Hip arthroscopy, April
4 Sports Return to sports will depend on what you have had done during your hip arthroscopy. You will need to stop doing sports until you are fully weight bearing. Even at this point you should avoid any impact sports or swimming breast stroke. It can take up to 3-6 months before you are able to return to competitive sports. It is important you follow the advice from your surgeon and physiotherapist. Rehabilitation This usually begins within 1-2 weeks of your hip arthroscopy. A physiotherapist will assess you and provide you with some exercises. Depending on the assessment findings your physiotherapist may refer you for hydrotherapy (pool) treatment. However, not every patient requires this. It is very important that you do the prescribed exercises as they will help to build the strength in and around your hip. Your physiotherapist will then continue to review you and progress your exercises as necessary. Follow up appointment You will have an appointment to see the consultant or a member of their team at 6 weeks after your operation. Questionnaires will be sent out electronically for you to complete about how your hip is feeling after the operation. You will also be sent these to complete at 3, 6, and 12 months post operatively. Complications All surgery carries the risk of complications and these will be explained to you before your operation. However, in general, the risk of complications from an arthroscopy is very small. Complications can include: General complications following an anaesthetic such as: inability to pass urine, constipation, blood clot in the leg(s) and/or lungs. Swelling Some swelling is normal following the operation, but if you notice that either your calf or thigh has become very swollen, tender, red and / or hot then it is important that you see your GP or attend the Emergency Department (A&E). Specific complications relating to hip arthroscopy include: Non-improvement / recurrence of symptoms There is a chance that following the arthroscopy your symptoms do not improve. This is more common if the surgeon finds you have arthritis in your hip joint. Cartilage tears can also occur again following your surgery depending on your activity levels. Infection This is very rare following hip arthroscopy. It is important to keep your wounds clean and dry following your operation. If infection occurs it is often superficial and can usually be Hip arthroscopy, April
5 treated with antibiotics. In very rare circumstances, if the infection involves the joint it may need further surgical treatment. Numbness The traction applied to the legs to separate the hip joint can result in injury to nerves in the leg. This can manifest itself as numbness in the leg that usually will recover within hours of the surgery; however, occasionally slight loss of feeling over the upper and outer aspect of the thigh can persist for much longer. Occasionally, some patients may experience numbness in the groin; but this is rare and almost always resolves within 24 hours. Failure of the labrum to heal When the labrum is repaired surgically it still then needs to go through a healing process to ensure success. If this is Impaired for whatever reason, there can be a recurrence of symptoms, which may warrant further investigation and treatment. Development of fibrous bands (adhesions) within the joint Over time, this can cause pain and stiffness of the joint. Rehabilitation is the main treatment to prevent/ treat this but sometimes further surgery may be required. Heterotopic ossification New bone formation can occur in the soft tissues around the hip after surgery. This can lead to restricted movement and / or pain. In extreme cases further surgery may be needed. Taking anti-inflammatory medication after surgery (unless contra-indicated) will help to reduce this risk. Vascular complications These are very rare but there is potential for damage to blood vessels causing bleeding. Scars You may always notice the scars from the incision sites. The colour and tenderness of any scars can be minimised by using creams such as E45 or vitamin E oil or Bio-oil. The scars do tend to fade over a period of many months. Progression of degenerative changes (wear and tear) within the joint Hip arthroscopy is part of a spectrum of treatment options for hip problems. Sometimes degenerative changes may progress and other treatments may be necessary including injections or even a hip replacement. Hip arthroscopy, April
6 Initial exercises You will be taught these exercises by your physiotherapist following your operation. You should begin these straight away and do them at least 2 times a day. Only do the ones recommended to you by your physiotherapist. Circulatory exercises Point and bend your ankles. Rotate them in circles. Complete at least 10 of each exercise. Core stability exercise Lying on your back with hips and knees bent and neck and back muscles relaxed. Breathing in - tighten the pelvic floor muscles. Breathing out - lift the pelvic floor and activate deep abdominal muscles. Repeat at least 10 times. Multifidus and core stability exercise Static gluteal contraction Lying face down with your hips over a pillow and back relaxed. Pull the stomach up and in to hollow the lower lateral abdominals. Maintain this abdominal hollow and gently squeeze both buttocks to flatten the low back. Sustain this contraction. Hold for the count of 10. (adpt Sahrmann PhD, PT) Lying face down with your hips over a pillow and back relaxed. Breathing in - tighten the pelvic floor muscles. Breathing out - gently lift the pelvic floor muscles, hollow the lower abdominal area just above the pubic bone and squeeze the lower portion of the buttocks towards the midline. Continue this action until the lower Hip arthroscopy, April
7 buttocks are firmly contracted. Breathing in - slowly and at the same time release the buttocks and abdominal muscle contractions. Breathe out. Static quadriceps contraction Progression - The buttocks contraction can be sustained for two or three breaths. - One side of the buttocks can be exercised whilst the other side remains relaxed. Sit or lie with your legs out in front of you. Bring your toes up towards you and push the back of your knee into the bed by tightening your thigh muscles. Hold for the count of 10. Static hamstrings contraction Static adductor contraction Sit or lie with your legs out in front of you. Pull your toes up towards you. Dig your heel down into the floor / bed. You should feel the muscles at the back of your thigh working hard. Hold for the count of 10. In sitting with feet supported on the floor. Place a ball or rolled up towel between your knees. Squeeze your lower stomach and bottom muscles. Gently squeeze the ball / towel with your knees. You should feel your inner thigh tense. Hold for the count of 10. Hip arthroscopy, April
8 Static abductor contraction Sitting on a chair with feet supported on the floor. Put a rubber exercise band around your knees. Squeeze your lower stomach and bottom muscles. Push your knees apart into the band (there should not be very much movement). Hold for the count of 10 and slowly bring knees back together. 4 point kneeling rocking Kneel on hands and knees with the knees under the hips and the back relaxed in a neutral position. (Feet relaxed). Hip internal rotation Keeping the back flat, slowly rock backwards moving at the hips. Do not let the back bend or arch. Stop after a short distance or before the onset of any pain. Only move backwards as far as the controlled flat back allows. Move slowly and do not stretch. Repeat 10 times (adpt Sahrmann PhD, PT). Kneel on hands and knees with the knees under the hips and hands under the shoulders. Keep the back relaxed in a neutral position. (Feet relaxed). Keeping knees still, take feet apart. Slowly return feet to start position. Alternative position: Sit with knees and feet together. Bring your feet apart with heels leading and toes turned in. Return to starting position. Hip arthroscopy, April
9 Hip external rotation Lying with your knees bent and feet on the floor hip width apart. Turn the soles of your feet to face each other and allow your knees to fall outwards. Feel the stretch in your groin. Keep your back flat on the floor during the exercise. Slowly return knees to start position. Alternative position: Lying on your back with one leg bent. Put one hand on your knee and the other one on your ankle. Rotate your leg outwards, bringing your ankle towards the opposite shoulder. Slowly return leg to start position. Heel slides Hip extension in lying Keeping the hip neutral in rotation, slowly slide the heel along the floor until the leg is straight. Breathing in - maintain abdominal muscle engagement and at the same time bend the hip and knee to slide the leg to the starting position. Help guide the movement with your hands or a towel / belt if it is painful. Breathe out. NB: The lower back should remain neutral and stable throughout. Breathing in as the hip bends enhances lower back stability. Lying face down. Squeeze your lower stomach and bottom muscles (see static gluteal contraction exercise already stated). Lift your leg up behind you towards the ceiling keeping your knee straight. Hold for 10 seconds. Lower your leg slowly. Hip arthroscopy, April
10 Hip abduction in lying Lying on your back. Squeeze your lower stomach and bottom muscles. Slowly take your leg out to the side as far as is comfortable. Slowly bring your leg back into the mid position again. N.B. This exercise can be made easier by placing something shiny / slippery under your heel e.g. a plastic bag or tray. Hip flexion in standing Hip abduction in standing Stand with your hands supported on a firm surface or on your hips if you are able to maintain your balance well. Squeeze your lower stomach and bottom muscles. Raise your operated leg up towards your chest. Do not push into discomfort. Keep stomach and bottom muscles tensed as lower leg. Stand with your hands supported on a firm surface. Keep your body upright and with your hip, knee and foot facing forwards move your operated leg out to the side. Slowly return to the starting position. Hip arthroscopy, April
11 Hip extension in standing Stand with your hands supported on a firm surface. Keep your body upright and with your hip, knee and foot facing forwards move your operated behind you. Do not arch your back or lean forwards. The following exercises may be added in once your hip is feeling more comfortable. Your physiotherapist will be able to guide you. Clams Bent knee fall outs Lie on your un-operated side with your knees bent. Tighten your buttocks and stomach muscles. Lift your top knee as far as you can, without letting your pelvis rotate forward or back. Keep your feet together and back straight during the exercise. Hold for 10 seconds. Lower your leg slowly. Lie on your back with one leg bent and the heel beside the straight knee. Your back should be flat and your pelvis should be level without any twist. Squeeze your stomach muscles to keep the back flat and slowly let the bent knee lower out to the side. Do not let the pelvis twist or rotate at all. Only move the leg as far as the flat back and level pelvis allow. Slowly return to the start position maintaining control of the pelvis during the return. (adpt Sahrmann PhD, PT). Hip arthroscopy, April
12 Bridging Lying on your back with knees bent. Squeeze your lower stomach and bottom muscles. Lift your bottom off the floor (do not arch your back). Hold for count of 10. Return to starting position. Hip abduction in side lying Lying on your side supporting yourself on your elbow. Roll top hip slightly forward, use top arm to support yourself in front. Keeping top leg straight lift it up towards the ceiling to hip height. Make sure the leg stays in line with your body and toes point forwards. Please note: During the above exercises you should not push into pain but mild discomfort is acceptable. As is usual with any new exercise, your muscles may ache and you may experience new aches and pains for a few days but these should settle. If they do not, try to establish the aggravating exercise and leave this out of your exercise programme for a few days and then try again. Exercise pictures Physio Tools Ltd. Hip arthroscopy, April
13 Stretches Maintaining range of movement at your hip is very important post operatively. To help with maintaining or improving the range of movement at your hip, it is important to perform the following stretches along with your exercises. Anterior hip stretch Stand straight with one knee bent and the foot supported on a stool as shown. Bend your straight leg until a stretch is felt at the front of the thigh on the other leg. Alternative position: Half kneeling. Tighten your stomach muscles to keep your back straight. Rotate the heel behind you outwards while pushing your hip forwards. Quadriceps stretch External rotation stretch Stand holding on to a support with one hand and to your ankle with the other hand. Keeping your knees together, gently pull your ankle towards your bottom. You should feel a stretch down the front of your thigh. Sitting on a chair with your foot on the opposite knee. Gently push your knee towards the floor. Hip arthroscopy, April
14 Adductor stretch Lying with your knees bent and feet on the floor hip width apart. Turn the soles of your feet to face each other and allow your knees to fall outwards. Feel the stretch in your groin. Keep your back flat on the floor during the exercise. Piriformis stretch Sit on the floor with one leg straight and the other leg crossed over it. Bring your knee towards your opposite shoulder. Feel the stretch in your buttock. Hamstring stretch Stand with the leg to be stretched on a footstool. Flex your ankle and push the heel towards the footstool keeping your knee straight. Bend your upper body forwards from your hips keeping your back straight. You should feel the stretching behind your knee and thigh. Alternative position: Lie on the back with both legs straight. Bend one hip to 90 degrees and hold the thigh in this position. The knee should be relaxed. Holding the thigh in position, slowly straighten the knee until a stretch is felt at the back of the thigh. Sustain this stretch. Hip arthroscopy, April
15 Calf stretch Stand in a walking position with the leg to be stretched straight behind you and the other leg bent in front of you. Take support from a wall or chair. Lean your body forwards and down until you feel the stretching in the calf of the straight leg. Exercise pictures Physio Tools Ltd. Stages of rehabilitation Stage 1 Initial phase (Week 1-3) (Improving range of movement) Aims: Reduce pain and swelling. Normalise your walking pattern depending on weight bearing status. Improve hip muscle strength and core strength. Improve movement at your hip, including rotation. Improve your balance. Stage 2 Intermediate phase (Week 3-5) (Strengthening) Aims: Improve muscle strength by functional exercise Step ups/down, static bike etc. Improve core strength (the muscles in your abdomen, back, pelvic floor and hips). Improve balance double leg to single leg. Maintain cardiovascular fitness Swimming no breast stroke, static bike, walking on treadmill (if walking pattern normalised). Improve movement. Complete hydrotherapy; if appropriate. Week 6 Consultant review and completion of HOOS/ functional questionnaires (electronically). Stage 3 Advanced phase (Week 5-12) (Stamina) Aims: Improve muscle endurance. Hip arthroscopy, April
16 Full hip range of movement with stable pelvis. Good core control and stability (have strong and flexible muscles in your core). Improve cardiovascular fitness. Begin plyometric work fast, change of direction exercises useful for sport. Week 12 Consultant review and completion of HOOS/ functional questionnaires (electronically). Stage 4 Sports specific rehab (Week 12+) Aims: Designed for people who want to return to competitive sport. Gradually return to maximal effort Challenge balance. Complete full impact activities. Begin sport training before returning to full competition. Eliminate asymmetries in activities such as running. Goals: Return to full sporting activity. Depending on what procedures were performed on the hip it may not be advisable to return to high impact exercise such as running, rugby etc. Consultant review at 6 months and 1 year Completion of HOOS and functional scores (electronically). Discussion around return to sports/activities. Post operative progress: As listed above you will be reviewed at regular intervals at the Royal Berkshire Hospital by a specialist physiotherapist, who will assess your progress. The most important component of your recovery is your regular attendance at physiotherapy classes where you will be given strict instructions regarding appropriate exercises and the dos and don ts. At certain points before and after your surgery we will be going through one or two questionnaires with you to provide us with information about your functional improvement not only to make sure you are getting better but also to ensure that our surgery has been successful for our own records. Your co-operation in this will be much appreciated. Useful numbers and contacts Redlands Ward: / 7485 RBH Outpatient Physiotherapy: Wokingham Physiotherapy: West Berkshire Physiotherapy: Clinical Admin Team (CAT 5) CAT5@royalberkshire.nhs.uk Hip arthroscopy, April
17 For more information about the Trust visit our website: This document can be made available in other languages and formats upon request. ORTH-P_850 Reviewed: April 2017 by Debbie Burden (Orthopaedic Physiotherapy Specialist), Tony Andrade (Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon), Tom Pollard (Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon). Review due: April 2019 Hip arthroscopy, April
Information and exercises following a proximal femoral replacement
 Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following a proximal femoral replacement Introduction The hip joint is a type known as a ball and socket joint. The cup side of the joint is known as
Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following a proximal femoral replacement Introduction The hip joint is a type known as a ball and socket joint. The cup side of the joint is known as
Physiotherapy Services. Physiotherapy Guide. Hip Replacement
 Physiotherapy Services Physiotherapy Guide to Hip Replacement AGH 01535 293656 Bingley Hospital 01274 563438 Ilkley Coronation Hospital 01943 609666 ext 241 Skipton General Hospital 01756 701726 Settle
Physiotherapy Services Physiotherapy Guide to Hip Replacement AGH 01535 293656 Bingley Hospital 01274 563438 Ilkley Coronation Hospital 01943 609666 ext 241 Skipton General Hospital 01756 701726 Settle
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
What is arthroscopy? Normal knee anatomy
 What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021
 Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis 0496 October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021 This advice and exercise booklet has been produced by senior physiotherapists working for DynamicHealth.
Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis 0496 October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021 This advice and exercise booklet has been produced by senior physiotherapists working for DynamicHealth.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises
 Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw
 Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw Introduction A dynamic hip screw is performed where the neck of femur has been fractured and where there is a good chance
Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw Introduction A dynamic hip screw is performed where the neck of femur has been fractured and where there is a good chance
Lumbar decompression or discectomy
 Information and exercises Lumbar decompression or discectomy Introduction A lumbar decompression or discectomy is done to relieve pressure on the nerves in order to relieve pain and altered sensation.
Information and exercises Lumbar decompression or discectomy Introduction A lumbar decompression or discectomy is done to relieve pressure on the nerves in order to relieve pain and altered sensation.
Low Back Program Exercises
 Low Back Program Exercises Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite
Low Back Program Exercises Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite
Knee Conditioning Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust. Pulmonary Rehabilitation. Exercise programme
 Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Pulmonary Rehabilitation Exercise programme Introduction to exercises Wear sensible shoes and loose clothing. When performing
Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Pulmonary Rehabilitation Exercise programme Introduction to exercises Wear sensible shoes and loose clothing. When performing
FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT
 THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
GENERAL EXERCISES KNEE BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017
 GENERAL EXERCISES KNEE BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only are not to be
GENERAL EXERCISES KNEE BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only are not to be
Developed by: Physiotherapy Department Surrey Memorial Hospital. Printshop #
 Developed by: Physiotherapy Department Surrey Memorial Hospital Printshop # 255171 The following exercises are intended for you to continue at home. Your physiotherapist will teach and mark the exercises
Developed by: Physiotherapy Department Surrey Memorial Hospital Printshop # 255171 The following exercises are intended for you to continue at home. Your physiotherapist will teach and mark the exercises
Physiotherapy following peri acetabular osteotomy (PAO) surgery
 Physiotherapy following peri acetabular osteotomy (PAO) surgery This leaflet explains more about returning to your everyday activities after your peri acetabular osteotomy (PAO). It explains the exercises
Physiotherapy following peri acetabular osteotomy (PAO) surgery This leaflet explains more about returning to your everyday activities after your peri acetabular osteotomy (PAO). It explains the exercises
Knee Conditioning Program
 Knee Conditioning Program Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Knee Conditioning Program Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Knee arthroscopy. Physiotherapy Department. Patient information leaflet
 Knee arthroscopy Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet What is a knee arthroscopy? A knee arthroscopy is a type of keyhole surgery performed through small cuts in the skin. An instrument
Knee arthroscopy Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet What is a knee arthroscopy? A knee arthroscopy is a type of keyhole surgery performed through small cuts in the skin. An instrument
Physiotherapy after your hip arthroscopy
 Physiotherapy after your hip arthroscopy This leaflet gives you advice about recovering from your hip arthroscopy. It explains exercises you should do each day, things to look out for and some general
Physiotherapy after your hip arthroscopy This leaflet gives you advice about recovering from your hip arthroscopy. It explains exercises you should do each day, things to look out for and some general
Knee Replacement Rehabilitation
 Knee Replacement Rehabilitation The following exercises may be given to you to help get you moving and become more independent. Please bring this copy of the exercises with you to hospital. After your
Knee Replacement Rehabilitation The following exercises may be given to you to help get you moving and become more independent. Please bring this copy of the exercises with you to hospital. After your
Physiotherapy. Hip Conditioning Program
 Physiotherapy This is a general hip conditioning program designed to provide you with a wide variety of exercises and strategies to manage your symptoms. Improved hip strength, flexibility and stability
Physiotherapy This is a general hip conditioning program designed to provide you with a wide variety of exercises and strategies to manage your symptoms. Improved hip strength, flexibility and stability
SCIATICA. Contents YOUR GUIDE TO. An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition. What is sciatica?...
 Contents What is sciatica?................................................3 What causes sciatica?............................................3 YOUR GUIDE TO SCIATICA An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises
Contents What is sciatica?................................................3 What causes sciatica?............................................3 YOUR GUIDE TO SCIATICA An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises
GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
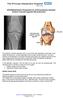 GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Femur ACL Graft Fibula Tibia The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments in the
GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Femur ACL Graft Fibula Tibia The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments in the
Hip Pain. Anatomy of the hip
 Hip Pain Anatomy of the hip The hip is a ball and socket joint, the ball is on the head of femur (the top of the thigh bone) and the socket (acetabulum) is a part of the pelvis. It s surrounded by tendons
Hip Pain Anatomy of the hip The hip is a ball and socket joint, the ball is on the head of femur (the top of the thigh bone) and the socket (acetabulum) is a part of the pelvis. It s surrounded by tendons
Ex Fix Rehab Phase II Strengthening
 Perform repetitions of each exercise, twice daily. Increase to repetitions. Ankle Pumps: With leg resting on bed and knee straight, slowly pump ankle up and down as far as possible. Quad sets: Tighten
Perform repetitions of each exercise, twice daily. Increase to repetitions. Ankle Pumps: With leg resting on bed and knee straight, slowly pump ankle up and down as far as possible. Quad sets: Tighten
General Principles of Stretching. To be effective, stretching must be done slowly, gently and frequently.
 General Principles of Stretching To be effective, stretching must be done slowly, gently and frequently. Slowly means that while the exercise is being done the muscle being stretched must be moved slowly
General Principles of Stretching To be effective, stretching must be done slowly, gently and frequently. Slowly means that while the exercise is being done the muscle being stretched must be moved slowly
MENISCUS TEAR. Description
 MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
Patient & Family Guide. Hip Exercises.
 Patient & Family Guide Hip Exercises 2016 www.nshealth.ca Hip Exercises Do your exercises 3 times during the day. Stretching guidelines Before you start your stretching you should: Use heat (e.g. hot pack,
Patient & Family Guide Hip Exercises 2016 www.nshealth.ca Hip Exercises Do your exercises 3 times during the day. Stretching guidelines Before you start your stretching you should: Use heat (e.g. hot pack,
Knee Replacement PROGRAM. Nightingale. Home Healthcare
 Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Exercises to Strengthen Your Back
 Exercises to Strengthen Your Back Your 15 Minute Workout By doing your 15 minute workout 3-5 times per week, you can condition the muscles and joints that support your back and keep it in healthy balance
Exercises to Strengthen Your Back Your 15 Minute Workout By doing your 15 minute workout 3-5 times per week, you can condition the muscles and joints that support your back and keep it in healthy balance
Knee arthroscopy surgery
 Patient information Knee arthroscopy surgery i Important information for all orthopaedic patients undergoing knee arthroscopy surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY
Patient information Knee arthroscopy surgery i Important information for all orthopaedic patients undergoing knee arthroscopy surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY
Copyright Cardiff University
 This exercise programme has been developed by physiotherapists specifically for people with movement disorders. Exercise is not without its risks and this or any other exercise programme has potential
This exercise programme has been developed by physiotherapists specifically for people with movement disorders. Exercise is not without its risks and this or any other exercise programme has potential
Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain
 What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
Rehabilitation. Walkers, Crutches, Canes
 Walkers, Crutches, Canes These devices provide support through your arms to limit the amount of weight on your operated hip. Initially, after a total hip replacement you will use a walker to get around.
Walkers, Crutches, Canes These devices provide support through your arms to limit the amount of weight on your operated hip. Initially, after a total hip replacement you will use a walker to get around.
Do the same as above, but turn your head TOWARDS the side that you re holding on to the chair.
 Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Further information Information on who to contact, i.e. web sites / telephone numbers of other departments / organisations which may be of help. How to contact us Watford General Hospital West Hertfordshire
Further information Information on who to contact, i.e. web sites / telephone numbers of other departments / organisations which may be of help. How to contact us Watford General Hospital West Hertfordshire
Static Flexibility/Stretching
 Static Flexibility/Stretching Points of Emphasis Always stretch before and after workouts. Stretching post-exercise will prevent soreness and accelerate recovery. Always perform a general warm-up prior
Static Flexibility/Stretching Points of Emphasis Always stretch before and after workouts. Stretching post-exercise will prevent soreness and accelerate recovery. Always perform a general warm-up prior
Exercises following Copeland Surface Replacement Arthroplasty (CSRA)
 Physiotherapy patient information Copeland Surface Replacement Arthroplasty Exercises following Copeland Surface Replacement Arthroplasty (CSRA) Introduction The Copeland Surface Replacement as it s name
Physiotherapy patient information Copeland Surface Replacement Arthroplasty Exercises following Copeland Surface Replacement Arthroplasty (CSRA) Introduction The Copeland Surface Replacement as it s name
FLOOR EXERCISES for. strengthening your hip and knee INTERMEDIATE LEVEL
 FLOOR EXERCISES for strengthening your hip and knee INTERMEDIATE LEVEL THIGH STRENGTHENING 3 HIP STRENGTHENING ON YOUR SIDE 5 HIP STRENGTHENING ON YOUR BACK 8 ALL 4 S WITH LEG LIFT 10 When you have pain
FLOOR EXERCISES for strengthening your hip and knee INTERMEDIATE LEVEL THIGH STRENGTHENING 3 HIP STRENGTHENING ON YOUR SIDE 5 HIP STRENGTHENING ON YOUR BACK 8 ALL 4 S WITH LEG LIFT 10 When you have pain
Lesson Sixteen Flexibility and Muscular Strength
 Lesson Sixteen Flexibility and Muscular Strength Objectives After participating in this lesson students will: Be familiar with why we stretch. Develop a stretching routine to do as a pre-activity before
Lesson Sixteen Flexibility and Muscular Strength Objectives After participating in this lesson students will: Be familiar with why we stretch. Develop a stretching routine to do as a pre-activity before
Therapy following a neck of femur fracture
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Therapy following a neck of femur fracture Name of patient: ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Procedure: ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Consultant:
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Therapy following a neck of femur fracture Name of patient: ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Procedure: ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff Consultant:
Reversed geometry shoulder replacement
 Information and exercises Reversed geometry shoulder replacement Introduction The reversed geometry total shoulder replacement is designed for use in shoulders that have a deficient rotator cuff, arthritis
Information and exercises Reversed geometry shoulder replacement Introduction The reversed geometry total shoulder replacement is designed for use in shoulders that have a deficient rotator cuff, arthritis
Above Knee Amputee Home Exercise Program
 An Amputee Associates Clinic Above Knee Amputee Home Exercise Program It is important that you take an active role in your rehabilitation. The following exercises must be done every day to prevent complications.
An Amputee Associates Clinic Above Knee Amputee Home Exercise Program It is important that you take an active role in your rehabilitation. The following exercises must be done every day to prevent complications.
Below Knee Amputee Home Exercise Program
 Below Knee Amputee Home Exercise Program It is important that you take an active role in your rehabilitation. The following exercises must be done every day to prevent complications. After below the knee
Below Knee Amputee Home Exercise Program It is important that you take an active role in your rehabilitation. The following exercises must be done every day to prevent complications. After below the knee
Snow Angels on Foam Roll
 Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
FAQ s: Hip Arthroscopy with Dr. Boyle
 AUT Millennium, 17 Antares Place Telephone: 09 281 6733 Mairangi Bay, Auckland 0632 Fax: 09 479 3805 www.matthewboyle.co.nz office@matthewboyle.co.nz FAQ s: Hip Arthroscopy with Dr. Boyle What is hip arthroscopy?
AUT Millennium, 17 Antares Place Telephone: 09 281 6733 Mairangi Bay, Auckland 0632 Fax: 09 479 3805 www.matthewboyle.co.nz office@matthewboyle.co.nz FAQ s: Hip Arthroscopy with Dr. Boyle What is hip arthroscopy?
LOW BACK PAIN. Contents What causes Low Back Pain?... 3
 YOUR GUIDE TO LOW BACK PAIN An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition Contents What causes Low Back Pain?....... 3 What treatment can I receive?..... 4 What about exercise?...............
YOUR GUIDE TO LOW BACK PAIN An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition Contents What causes Low Back Pain?....... 3 What treatment can I receive?..... 4 What about exercise?...............
Spine Conditioning Program Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Southern Sports & Orthopaedics
 Knee conditioning program This knee conditioning program is designed to help you rehabilitate from your knee injury. In some cases, the program is being used as pre-habilitation, that is strengthening
Knee conditioning program This knee conditioning program is designed to help you rehabilitate from your knee injury. In some cases, the program is being used as pre-habilitation, that is strengthening
Ellipse Rehab Phase 2 Strengthening
 Strengthening Perform reps of each exercise, twice daily. Increase to reps Ankle Pumps: With leg resting on bed and knee straight, slowly pump ankle up and down as far as possible. Quad sets: Tighten thigh
Strengthening Perform reps of each exercise, twice daily. Increase to reps Ankle Pumps: With leg resting on bed and knee straight, slowly pump ankle up and down as far as possible. Quad sets: Tighten thigh
Arthroscopic capsular release. Information for patients Orthopaedics - Upper Limb
 Arthroscopic capsular release Information for patients Orthopaedics - Upper Limb Introduction The Upper Limb Unit team would like you and your family to understand as much as possible about the operation
Arthroscopic capsular release Information for patients Orthopaedics - Upper Limb Introduction The Upper Limb Unit team would like you and your family to understand as much as possible about the operation
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet This patient information booklet is designed to provide you with information about the Anterior Cruciate Ligament
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet This patient information booklet is designed to provide you with information about the Anterior Cruciate Ligament
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust. Knee Arthroscopy. Issued by the Orthopaedic Department
 Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Knee Arthroscopy Issued by the Orthopaedic Department Introduction This guide has been produced to provide you with information regarding your knee arthroscopy
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Knee Arthroscopy Issued by the Orthopaedic Department Introduction This guide has been produced to provide you with information regarding your knee arthroscopy
Hip Conditioning Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
YOUR FREE COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO HELP RELIEVE LOWER BACK PAIN NATURALLY
 YOUR FREE COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO HELP RELIEVE LOWER BACK PAIN NATURALLY By: helpwithsciatica HTTPS://HELPWITHSCIATICA.COM Table of contents 1 Introduction 2 Exercise: Extensions 3 Exercise: Curl-Ups 4
YOUR FREE COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO HELP RELIEVE LOWER BACK PAIN NATURALLY By: helpwithsciatica HTTPS://HELPWITHSCIATICA.COM Table of contents 1 Introduction 2 Exercise: Extensions 3 Exercise: Curl-Ups 4
Knee Arthroscopy Exercise Programme
 Chester Knee Clinic & Cartilage Repair Centre Nuffield Health, The Grosvenor Hospital Chester Wrexham Road Chester CH4 7QP Hospital Telephone: 01244 680 444 CKC Website: www.kneeclinic.info Email: office@kneeclinic.info
Chester Knee Clinic & Cartilage Repair Centre Nuffield Health, The Grosvenor Hospital Chester Wrexham Road Chester CH4 7QP Hospital Telephone: 01244 680 444 CKC Website: www.kneeclinic.info Email: office@kneeclinic.info
Exercises following arthroscopic (or open) anterior stabilisation
 Physiotherapy patient information Exercises following arthroscopic (or open) anterior stabilisation Introduction The shoulder joint is designed to give a large amount of movement, therefore support from
Physiotherapy patient information Exercises following arthroscopic (or open) anterior stabilisation Introduction The shoulder joint is designed to give a large amount of movement, therefore support from
Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises
 Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises Most athletes (swimmers included) use a combination of controlled movement exercises and specific joint/muscle stretching to improve performance potential. The proposed
Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises Most athletes (swimmers included) use a combination of controlled movement exercises and specific joint/muscle stretching to improve performance potential. The proposed
EXERCISE INSTRUCTIONS
 EXERCISE INSTRUCTIONS A/ Strength A01 SQUAT Stand on the Power-Plate with feet shoulder width apart. Keeping the back straight and knees slightly bent, gently squeeze the leg muscles. You should feel tension
EXERCISE INSTRUCTIONS A/ Strength A01 SQUAT Stand on the Power-Plate with feet shoulder width apart. Keeping the back straight and knees slightly bent, gently squeeze the leg muscles. You should feel tension
Low Back Pain Exercise Guide
 Low Back Pain Exercise Guide Regular exercise is an important adjunct to your treatment that can help restore the strength of your back and allow for a gradual return to your everyday activities. Your
Low Back Pain Exercise Guide Regular exercise is an important adjunct to your treatment that can help restore the strength of your back and allow for a gradual return to your everyday activities. Your
Advice: After the Removal of a Lower Leg Cast
 Advice: After the Removal of a Lower Leg Cast The aim of this leaflet is to give you some understanding of the problems you have with your condition and to provide some advice on how to manage this. It
Advice: After the Removal of a Lower Leg Cast The aim of this leaflet is to give you some understanding of the problems you have with your condition and to provide some advice on how to manage this. It
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises. Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
This Manual is copyright under the Berne Convention. In terms of the Copyright Act 98 of 1978 no part of this leaflet may be reproduced or
 Basic Ball Exercise Manual Train your Core This Manual is copyright under the Berne Convention. In terms of the Copyright Act 98 of 1978 no part of this leaflet may be reproduced or transmitted in any
Basic Ball Exercise Manual Train your Core This Manual is copyright under the Berne Convention. In terms of the Copyright Act 98 of 1978 no part of this leaflet may be reproduced or transmitted in any
ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients
 ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to provide you with advice and guidance on your rehabilitation after reconstruction of your anterior cruciate
ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to provide you with advice and guidance on your rehabilitation after reconstruction of your anterior cruciate
TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE
 TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE Description Preventive Measures A tibial plateau fracture is a complete or incomplete break Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or in the larger of the two leg bones
TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE Description Preventive Measures A tibial plateau fracture is a complete or incomplete break Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or in the larger of the two leg bones
Physiotherapy Following Your Spinal Discectomy
 Physiotherapy Following Your Spinal Discectomy Patient information How to contact us Physiotherapy Department Watford General Hospital West Hertfordshire Hospitals NHS Trust Vicarage Road, Watford, Hertfordshire,
Physiotherapy Following Your Spinal Discectomy Patient information How to contact us Physiotherapy Department Watford General Hospital West Hertfordshire Hospitals NHS Trust Vicarage Road, Watford, Hertfordshire,
KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM
 KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM These exercises are specifically designed to rehabilitate the muscles of the hip and knee by increasing the strength and flexibility of the involved leg. This exercise program
KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM These exercises are specifically designed to rehabilitate the muscles of the hip and knee by increasing the strength and flexibility of the involved leg. This exercise program
Total Hip Replacement Exercise Booklet Cemented Femoral Stem Weight Bearing As Tolerated
 Total Hip Replacement Exercise Booklet Cemented Femoral Stem Weight Bearing As Tolerated Patient Name: Surgeon: Date of Surgery: Physiotherapist: Department of Rehabilitation (416) 967-8650 ext. PR 99506
Total Hip Replacement Exercise Booklet Cemented Femoral Stem Weight Bearing As Tolerated Patient Name: Surgeon: Date of Surgery: Physiotherapist: Department of Rehabilitation (416) 967-8650 ext. PR 99506
Walking/Running Stretch Routine
 Walking/Running Stretch Routine Quadriceps Stretch With left hand grasp your right ankle, gently pull heel toward buttocks until stretch is felt. Repeat on opposite side. Walking/Running Stretch Routine
Walking/Running Stretch Routine Quadriceps Stretch With left hand grasp your right ankle, gently pull heel toward buttocks until stretch is felt. Repeat on opposite side. Walking/Running Stretch Routine
Acute Lower Back Pain. Physiotherapy department
 Acute Lower Back Pain Physiotherapy department Back pain is a common condition and in the UK it affects 7 out of 10 people at some point in their lives. Back pain can be very uncomfortable but it is not
Acute Lower Back Pain Physiotherapy department Back pain is a common condition and in the UK it affects 7 out of 10 people at some point in their lives. Back pain can be very uncomfortable but it is not
Routine For: Total Hip Arthroplasty - Standard Precautions
 Standard Hip Precautions TOTAL HIP - 4 Ankle Pump not bend your operative hip beyond a 90 degree angle. not sit with your legs crossed or lie on your back with your operative leg crossed over the other
Standard Hip Precautions TOTAL HIP - 4 Ankle Pump not bend your operative hip beyond a 90 degree angle. not sit with your legs crossed or lie on your back with your operative leg crossed over the other
STRETCHING. Low Back Rotation. Double Leg Pull. Single Leg Pull. Core Home Exercise Program
 Core Home Exercise Program Seth L. Sherman, M.D. Tamara L. Young, ATC, OTC, M.Ed Department of Sports Medicine STRETCHING Low Back Rotation While lying on your back with both of your knees bent. Rotate
Core Home Exercise Program Seth L. Sherman, M.D. Tamara L. Young, ATC, OTC, M.Ed Department of Sports Medicine STRETCHING Low Back Rotation While lying on your back with both of your knees bent. Rotate
Part A: Running. Max 5 mins. Slow run forwards 5m and return x 2. Hip out x 2. Hip in x 2. Heel Flicks x 2
 Part A: Running. Max 5 mins. Slow run forwards 5m and return x 2 Jog straight to the 20m line. Make sure you keep your upper body straight. Your hip, knee and foot are aligned. Do not let your knee buckle
Part A: Running. Max 5 mins. Slow run forwards 5m and return x 2 Jog straight to the 20m line. Make sure you keep your upper body straight. Your hip, knee and foot are aligned. Do not let your knee buckle
Above Knee Amputation: Positioning and Exercise Program
 Above Knee Amputation: Positioning and Exercise Program The exercises and stretches in this handout will help to prepare you to wear a prosthesis properly. The positioning instructions and exercises in
Above Knee Amputation: Positioning and Exercise Program The exercises and stretches in this handout will help to prepare you to wear a prosthesis properly. The positioning instructions and exercises in
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO REHABILITATION POST KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO REHABILITATION POST KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY Georgia Bouffard Student Physiotherapist Colin Walker Orthopaedic Knee Specialist Frank Gilroy BSc MSCP 1 CONTENTS Anatomy of the knee
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO REHABILITATION POST KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY Georgia Bouffard Student Physiotherapist Colin Walker Orthopaedic Knee Specialist Frank Gilroy BSc MSCP 1 CONTENTS Anatomy of the knee
A patient guide to Hip Impingement Surgical Management
 A patient guide to Hip Impingement Surgical Management Mr Sanjeev Patil Miss Louise Duncan Mr Frank Gilroy Patient Name: Occupation: Operation / Restrictions: Work/Sport: Contents Page: 1 Cover 2 Contents
A patient guide to Hip Impingement Surgical Management Mr Sanjeev Patil Miss Louise Duncan Mr Frank Gilroy Patient Name: Occupation: Operation / Restrictions: Work/Sport: Contents Page: 1 Cover 2 Contents
Hip Arthroscopy Booklet
 Hip Arthroscopy Booklet 2. Hip Anatomy The bones that make up the hip joint are the femur (the thighbone) and the pelvis. At the top end of the femur is a ball called the femoral head. The femoral head
Hip Arthroscopy Booklet 2. Hip Anatomy The bones that make up the hip joint are the femur (the thighbone) and the pelvis. At the top end of the femur is a ball called the femoral head. The femoral head
PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY
 Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
Trochanteric Bursitis: Exercises
 Trochanteric Bursitis: Exercises Your Kaiser Permanente Care Instructions Here are some examples of typical rehabilitation exercises for your condition. Start each exercise slowly. Ease off the exercise
Trochanteric Bursitis: Exercises Your Kaiser Permanente Care Instructions Here are some examples of typical rehabilitation exercises for your condition. Start each exercise slowly. Ease off the exercise
Flexibility and Stretching
 Flexibility and Stretching Stretching before exercise prepares the joints for motion, helps avoid injury and increases the range of motion of the area being stretched. After exercise stretching reduces
Flexibility and Stretching Stretching before exercise prepares the joints for motion, helps avoid injury and increases the range of motion of the area being stretched. After exercise stretching reduces
Prater Chiropractic Wellness Center 903 W. South St. Kalamazoo, MI PH: (269)
 Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following a well-structured conditioning
Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following a well-structured conditioning
Contents. Foreword Bottom to Heels Stretch Knee to Chest Knee Rolls Abdominal Crunches... 7
 Contents Foreword... 3 1. Bottom to Heels Stretch... 4 2. Knee to Chest... 5 3. Knee Rolls... 6 4. Abdominal Crunches... 7 5. Back Extensions... 9 6. Pelvic Tilts... 10 7. Wall Sits... 11 8. Bridging...
Contents Foreword... 3 1. Bottom to Heels Stretch... 4 2. Knee to Chest... 5 3. Knee Rolls... 6 4. Abdominal Crunches... 7 5. Back Extensions... 9 6. Pelvic Tilts... 10 7. Wall Sits... 11 8. Bridging...
Exercises for Back Pain Due to Degenerative Disk Disease (Osteoarthritis) and Facet Joint Impingement
 Tel: (905) 886-1212 Email: info@drwilderman.com Exercises for Back Pain Due to Degenerative Disk Disease (Osteoarthritis) and Facet Joint Impingement Aerobic Exercise Recommendations With a disc injury,
Tel: (905) 886-1212 Email: info@drwilderman.com Exercises for Back Pain Due to Degenerative Disk Disease (Osteoarthritis) and Facet Joint Impingement Aerobic Exercise Recommendations With a disc injury,
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
 TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET This leaflet has been produced to help answer some questions you may have following your knee replacement. However if you still have any concerns or queries
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET This leaflet has been produced to help answer some questions you may have following your knee replacement. However if you still have any concerns or queries
Lumbar Decompression GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS HAVING A. Lumbar Decompression
 ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS HAVING A Lumbar Decompression Please stick addresograph
ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS HAVING A Lumbar Decompression Please stick addresograph
EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD
 EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD My exercise goals Name What is my target heart rate? What is the maximum heart rate I should not exceed? What is my target rating of perceived exertion?
EXERCISE AND CYSTIC FIBROSIS: MY EXERCISE RECORD My exercise goals Name What is my target heart rate? What is the maximum heart rate I should not exceed? What is my target rating of perceived exertion?
Pregnancy-related low back pain and pelvic girdle pain (PGP) Information for patients Therapy Services - MSK
 Pregnancy-related low back pain and pelvic girdle pain (PGP) Information for patients Therapy Services - MSK We have written this booklet to answer some of the common questions that women ask about Pregnancy-Related
Pregnancy-related low back pain and pelvic girdle pain (PGP) Information for patients Therapy Services - MSK We have written this booklet to answer some of the common questions that women ask about Pregnancy-Related
Stretching. Knees: Rotate your knees in a circle, keeping them together and bending down slightly.
 Stretching Stretching the Major Muscle Groups Static Stretches Hamstrings: Hang down and try to reach your toes; don t push it. Keep legs and back straight. Just go down to a comfortable level for your
Stretching Stretching the Major Muscle Groups Static Stretches Hamstrings: Hang down and try to reach your toes; don t push it. Keep legs and back straight. Just go down to a comfortable level for your
Presuming all the above symptoms are not present, pain is more likely to be mechanical and caused by a sprain, strain or poor posture.
 Page 1 of 8 View this article online at: patient.info/health/back-pain-exercises Back Pain Exercises Back pain is very common but in most cases is not caused by a serious problem. Most cases of back pain
Page 1 of 8 View this article online at: patient.info/health/back-pain-exercises Back Pain Exercises Back pain is very common but in most cases is not caused by a serious problem. Most cases of back pain
Women s dynamic control physiotherapy class
 Physiotherapy Department Women s dynamic control physiotherapy class This booklet explains what happens in the class and how exercise can help with your back or pelvic pain in pregnancy. It also gives
Physiotherapy Department Women s dynamic control physiotherapy class This booklet explains what happens in the class and how exercise can help with your back or pelvic pain in pregnancy. It also gives
Stretching Exercises for the Lower Body
 Stretching Exercises for the Lower Body Leg Muscles The leg has many muscles that allow us to walk, jump, run, and move. The main muscle groups are: Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching
Stretching Exercises for the Lower Body Leg Muscles The leg has many muscles that allow us to walk, jump, run, and move. The main muscle groups are: Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching
return to sports after injury IMPROVING STRENGTH, POWER, AND AGILITY
 return to sports after injury IMPROVING STRENGTH, POWER, AND AGILITY This booklet is designed for people recovering from a knee or leg injury who participate in recreational or competitive sports such
return to sports after injury IMPROVING STRENGTH, POWER, AND AGILITY This booklet is designed for people recovering from a knee or leg injury who participate in recreational or competitive sports such
34 Pictures That Show You Exactly What Muscles You re Stretching
 By DailyHealthPostJanuary 27, 2016 34 Pictures That Show You Exactly What Muscles You re Stretching Stretching before and after a workout is a great way to promote blood flow to the muscles and increase
By DailyHealthPostJanuary 27, 2016 34 Pictures That Show You Exactly What Muscles You re Stretching Stretching before and after a workout is a great way to promote blood flow to the muscles and increase
Pilates exercises for above-knee amputees
 Pilates exercises for above-knee amputees This booklet includes exercises adapted for people who have had above-knee amputations, and can be used for those who have had bilateral (both sides) amputations.
Pilates exercises for above-knee amputees This booklet includes exercises adapted for people who have had above-knee amputations, and can be used for those who have had bilateral (both sides) amputations.
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Knee arthroscopy surgery
 Patient information Knee arthroscopy surgery i Important information for all orthopaedic patients undergoing knee arthroscopy surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY
Patient information Knee arthroscopy surgery i Important information for all orthopaedic patients undergoing knee arthroscopy surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY
Knee Arthroscopy: Postoperative Instructions
 Knee Arthroscopy: Postoperative Instructions John P. Woll, MD Knee arthroscopy is a commonly performed procedure that is much less invasive than previous open techniques, but it is still an operation,
Knee Arthroscopy: Postoperative Instructions John P. Woll, MD Knee arthroscopy is a commonly performed procedure that is much less invasive than previous open techniques, but it is still an operation,
