Comparison of Success Rate of Classical Supraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block with and without Nerve Stimulator
|
|
|
- Berniece Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MVP Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol 4(2), , July-December 2017 ISSN (Print) : X ISSN (Online) : DOI: /mvpjms/2017/v4i2/11033 Comparison of Success Rate of Classical Supraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block with and without Nerve Stimulator Sayali Patil 1 and Alka Koshire 2* 1 PG Resident, Department of Anaesthesia, Dr. Vasantrao Pawar Medical College Hospital & Research Centre, Nashik , Maharashtra, India; drsayalip@gmail.com 2 Professor & Head, Department of Anaesthesia, Dr. Vasantrao Pawar Medical College Hospital & Research Centre, Nashik , Maharashtra, India; alkakoshire15@gmail.com Abstract Introduction: Brachial plexus block has now evolved into valuable and safe alternative to general anesthesia for upper limb surgeries. The nerve stimulation technique make use of electric current to elicit motor stimulation of nerves and confirm the proximity of the needle to the nerve, thereby avoiding the discomfort caused due to paresthesia leading to good success rate, even when the pa-tient is uncooperative or uncommunicative. Aim and Objectives: To compare between paresthesia technique and use of nerve locator in performing supraclavicular brachial plexus block with respect to success and complication rate. Materials and Methods: A comparative study was conducted at department of Anesthesia of a tertiary care centre. A total of 100 patients undergoing upper limb elective surgery were included after satisfying inclusion and exclusion criteria. The anesthetic method employed was Brachial plexus block by Supraclavicular Approach: using paresthesia technique (Group A: 50 subjects) and; by using Nerve Stimulator technique (Group B: 50 subjects). Both the groups of patients were studied for performance time, sensory block, and motor block and for success rate. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS ver. 21. Results: Onset of sensory and motor block were significantly faster in nerve stimulator group as compared to paraesthesia group (p<0.05), also the duration of block was more in nerve stimulation group (7.28 vs 6.54 hrs; p-0.057). Failure of block was seen in 22% patients with paraesthesia technique as compared to 14% with nerve stimulation (p-0.44). No difference was observed between the groups on the basis of complication rate (10% vs 2%; p-0.2). Conclusion: Onset of sensory and motor block was shorter and duration of analgesia was longer with nerve stimulation group. Nerve stimulation was found more effective than paraesthesia with respect to degree of success and complication rate. Keywords: Brachial Plexus Block, Nerve Stimulator, Paresthesia 1. Introduction Regional anesthesia has much to offer for the patients, surgeons and anesthesiologists because of its inherent simplicity, preservation of consciousness, avoidance of airway instrumentation, rapid recovery and significant postoperative analgesia. The supraclavicular block is one of the several techniques used to accomplish anesthesia of the brachial plexus. The block is performed at the level of the brachial plexus trunks where the majority of sensory, motor and sympathetic innervations of the upper extremity is carried in just three nerve structures confined to a very small surface area. Consequently, typical features of this block include rapid onset, predictable and dense anesthesia 1,2. Regional blockade at the brachial plexus provides effective and reliable anesthesia and analgesia for upper extremity surgeries. However, success is highly dependent upon the precise localization of neural structures. Historically, this was accomplished through the elicitation of one or more paresthesia. The exclamation, No paresthesia, no anesthesia became the mantra of many (though not all) of our founding fathers 3. Clinicians in opposition to paresthesia techniques often cite an increased risk of neurologic complications postoperatively by proclaiming more the paresthesia, more the dysesthesia. The nerve stimulation technique relies on the use of electric current to elicit motor stimulation of nerves and confirm the proximity of the needle to the nerve. In *Author for Correspondence
2 Comparison of Success Rate of Classical Supraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block with and without Nerve Stimulator addition to a good success rate, there are other advantages in this method 4. A patient need not be subjected to the discomfort of paresthesia when the nerve is stimulated to produce a motor twitch because motor fibers have a lower electrical threshold than sensory fibers. Another point in favour of nerve localization by electrical stimulation is that a satisfactory block may be performed when the patient is uncooperative, or uncommunicative, as a result of a psychotic state, coma, or language barrier and it can be given in any position. Regional block with the aid of a nerve stimulator can also be performed under general anesthesia, especially in children 5. The present study was thus conducted to compare between paresthesia technique and use of nerve locator in performing supraclavicular brachial plexus block with respect to its onset action, duration of action, success rate, performance time onset, immediate complications and post-operative neurological symptoms. 2. Aim and Objectives To compare between paresthesia technique and use of nerve locator in performing supraclavicular brachial plexus block with respect to success and complication rate. 3. Methods A prospective Randomized control study was conducted on 100 patients at the Department of Anesthesia, Medical College and tertiary health care centre for the period of 2 years (Dec 2014 to Dec 2016). Patients scheduled to undergo upper limb surgeries under Brachial Plexus Block were included in the study after fulfilling the inclusion and exclusion criteria. A written and informed consent was taken from all. Each and every patient received pre medication. The anesthetic method employed would be Brachial plexus block by Supraclavicular Approach: Using Paresthesia/ Nerve Stimulator technique. The local anesthetic solution employed was: Lignocaine with Adrenalin 2% 15cc + 2cc NaHCO3 + 5cc of Normal Saline + 20cc Bupivacaine 0.5% Both the groups of patients were studied for success rate, performance time, onset of sensory blockade & motor blockade, duration of sensory & motor blockade and the postoperative complications. In Paresthesia group (P), an intradermal wheal was raised just above the palpating finger with a 24G needle. A 5 cm 22G short bevel needle connected to a syringe was inserted through the skin wheal and advanced slowly Backwards (posteriorly), slightly Inward (Medially) and Downward (caudal) [BID] gradually towards first rib so that the shaft of the needle and syringe are almost parallel to the patient s head. The patient was instructed to say yes when he feels a sensation of tingle or electric shock down the arm and tell verbally where he feels it. Paresthesia was sought in the digits of the hand or wrist, if obtained; after negative aspiration for air and blood, local anaesthetic was injected. If paresthesia was not obtained and needle touched the first rib, we walked the needle posteriorly or towards vertebra to elicit paresthesia. If not, we repeated the procedure. In Nerve Stimulator group (N), Frequency was set at 1 Hz as 2 Hz may cause unpleasant and vigorous muscle twitches. Positive electrode was connected to ECG lead and negative electrode to a port in the needle. The needle used was 50 mm size, fully insulated except at tip. The landmarks, puncture site and direction of the needle were the same as that used in the paresthesia group. We began at 1.5 ma current strength; twitch of the fingers being observed; with the clear motor twitch of all fingers taken as end motor response. As soon as we observed the twitch the current strength was decreased to 0.5 ma with continued observation of twitch. Even at 0.5 ma current if we get a satisfactory twitch of all fingers, the simulator was turned off, and the drug injected with repeated aspiration for blood. If the finger twitch disappeared on decreasing the current strength, needle position was adjusted by one to two millimetres in such a way as to elicit the twitch response and again the procedure repeated. The following parameters were studied. Onset of sensory block. Duration of sensory blockade. Onset of motor block. Duration of motor blockade. Hemodynamic parameters. Side effects and complications. 4. Results Overall majority of the subjects were between years of age (84%) in both the groups. No difference was observed between the groups as per age distribution. 136 Vol 4 (2) July-December MVP Journal of Medical Sciences
3 Sayali Patil and Alka Koshire Table 1. Distribution of study subjects based on age group Age Group (years) Method of Block Total </= % 12.0% 11.0% % 48.0% 52.0% % 36.0% 32.0% > % 4.0% 5.0% p- value Table 2. Distribution of study subjects based on Gender Gender Method of Block Total Female % 24.0% 25.0% Male % 76.0% 75.0% p- value Male predominance was seen in present study (75%) in both the groups. No difference was observed between the groups as per gender distribution. Table 3. Comparison of mean age between study groups Group Mean SD SEM p- value Paraesthesia PNS Mean age of subjects in Paraesthesia and Nerve stimulator group was years and 37.5 years respectively (p-0.5). Table 4. Comparison of mean duration of block performed between study groups Duration of Block Performed Mean SD SEM p- value (min.) Paraesthesia PNS Mean time required for performing block was more with Paraesthesia technique as compared to Nerve stimulator (11.46 vs mins; p-0.177). The difference however was not significant. Table 5. Comparison of mean time for onset of sensory block between study groups Onset of Sensory Block Method of Block Mean SD SEM p- value Median Paraesthesia <0.01 PNS Radial Paraesthesia <0.01 PNS Ulnar Paraesthesia <0.01 PNS Musculocutaneous Paraesthesia <0.01 PNS Mean onset of sensory block was significantly faster with nerve stimulator technique for all the nerves involved in the block. The time taken through nerve stimulator technique was between minutes for all the nerves while it was between minutes with paraesthesia technique (p<0.01). Table 6. Comparison of mean time for onset of motor block between study groups Onset of Motor Block (min.) Mean SD SEM p- value Paraesthesia <0.01 PNS Mean onset of motor block was also significantly faster with nerve stimulator technique as compared to paraesthesia group (17.42 mins vs mins; p<0.01). Table 7. Comparison of mean duration of block between study groups Duration of Block (hrs.) Mean SD SEM p- value Paraesthesia PNS Total duration of block was more with Nerve stimulator technique as compared to Paraesthesia technique (7.28 hours vs 6.54 hours; p-0.057). The difference however was not significant. Table 8. Distribution of subjects based on failure of block Failure of Block Method of Block Total No % 78.0% 82.0% Yes % 22.0% 18.0% p- value Vol 4 (2) July-December MVP Journal of Medical Sciences 137
4 Comparison of Success Rate of Classical Supraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block with and without Nerve Stimulator Failure of block was seen in 14% patients of nerve stimulator group as compared to 22% in paraesthesia group (p-0.436). Table 9. Distribution of subjects based on complications Complications Method of Block Total No % 90.0% 94.0% Hematoma % 8.0% 4.0% Pneumothorax (PNX) % 2.0% 2.0% p- value Hematoma was seen in 0% and 8% patients while pneumothorax occurred in 2% patients each in nerve stimulator and paraesthesia group respectively (p> 0.05). Table 10. Distribution of subjects based on grade of sensory block Grade of Sensory Block Method of Block Total Normal % 10.0% 9.0% Blunting of Sensation % 12.0% 9.0% Total Sensory loss % 78.0% 82.0% p- value No difference was observed between both the study groups with respect to grade of sensory block achieved. Total sensory loss was seen in 86% and 78% patients of nerve stimulator and paraesthesia group respectively (p- 0.52). Table 11. Distribution of subjects based on grade of motor block Grade of Motor Block Method of Block Total No Blockade % 14.0% 11.0% Elbow level % 6.0% 10.0% Wrist Level % 16.0% 17.0% Finger Level % 64.0% 62.0% p- value No difference was observed between both the study groups with respect to grade of motor block achieved. Motor block till level of fingertips was seen in 60% and 64% patients of nerve stimulator and paraesthesia group respectively (p-0.47). 5. Discussion Peripheral nerve blocks are cost effective anaesthetic techniques used to provide anaesthesia and analgesia while avoiding hemodynamic consequences and airway instrumentation of general anaesthesia. Brachial plexus block is a relatively safe and an easy procedure for upper limb surgeries. Supraclavicular approach has been routinely used in our institution for upper limb surgeries and it has proven to be a safe technique as well. The block is usually given after eliciting paresthesia. Paresthesia technique was used till recently and presently nerve stimulator is made available in our institution. Frequently cited disadvantages of paresthesia technique include mainly patient discomfort while eliciting paresthesia and that its success is highly dependent on the cooperation of the patient. The objectives of this study are to compare between paresthesia technique and use of nerve locator in performing supraclavicular brachial plexus block in terms of performance time, sensory blockade, motor blockade, success rate and associated complications. 5.1 Demography Distribution Male predominance was seen in present study (75%) in both the groups. No difference was observed between the groups as per gender distribution. Mean age of subjects in Paraesthesia and Nerve stimulator group was years and 37.5 years respectively (p-0.5). In a similar study by Sathyam et al 6, there were no clinical or statistically significant differences in the demographic profile of patients in either group. In another such study by Bansal et al. mean age in Paraesthesia and Nerve stimulator group was 46.1 years and 43 years respectively (p>0.05) with males predominance in both groups (M:F - 41/14 and 37/18). Similarly no difference in demographic profile was seen in studies by Liguori et al., 7 Franco et al., 8 and Baranowski et al Time for Performing Block Mean time required for performing block was more with Paraesthesia technique as compared to Nerve stimulator (11.46 minutes vs minutes; p-0.177). The difference however was not significant. Similar observations were also made in the study by Bansal et al, 10 where mean time required for performing block was more with Paraesthesia 138 Vol 4 (2) July-December MVP Journal of Medical Sciences
5 Sayali Patil and Alka Koshire technique as compared to Nerve stimulator (13.0 minutes vs 6.25 minutes; p<0.05). Similar observations were also made by Baranowski et al. where time required by nerve stimulation technique was significantly less (p<0.01) 8. While Sathyam et al., noted no significant difference between the two techniques in the mean duration of performing block Onset of Sensory Block To determine the onset of analgesia and anesthesia, we performed our assessment at the sensory areas of the median, ulnar, radial and musculocutaneous nerves and found that the onset of analgesia and anaesthesia in radial, median and ulnar nerve distributions were shorter in the nerve stimulator group than the paresthesia group. Mean onset of sensory block was significantly faster with nerve stimulator technique for all the nerves involved in the block. The time taken through the nerve stimulator technique was between minutes for all the nerves while it was between minutes with paraesthesia technique (p<0.01). In a study by Sathyam et al., time required for sensory block in paresthesia group was 13.6 minutes and minutes in nerve stimulator group for radial nerve distribution. In median nerve distribution it was minutes in nerve stimulator group and minutes for paresthesia group. Along the distribution of ulnar nerve paresthesia group showed an onset time of minutes and nerve stimulator group minutes (p<0.01 for all) 6. Our results also concurs with study conducted by Carlo D Franco who found anesthesia onset in all four major nerves to be within for nerve stimulation group Onset of Sensory and Motor Block Mean onset of motor block was also significantly faster with nerve stimulator technique as compared to paraesthesia group (17.42 minutes vs minutes; p<0.01). In a study by Sathyam et al. the paresthesia group showed a greater onset time of minutes than nerve stimulator group (17.72 minutes). The difference however was statistically not significant. Liguori et al., also observed slightly greater onset time in paraesthesia group, the difference was not significant Total Duration of Block Total duration of block was more with Nerve stimulator technique as compared to Paraesthesia technique (7.28 hours vs 6.54 hours; p-0.057). The difference however was not significant. We found a longer duration of analgesia using nerve stimulator. This is probably due to the fact that nerve locator allowed more precise and closer deposition of local anaesthetic around the nerve. The duration of analgesia has not been compared in many of the studies. Mean duration of blockade in paresthesia group was comparable to the studies by Sathyam et al., 6 and Carlo D Franco et al Grade of Sensory and Motor Block In present study, both the groups i.e., paraesthesia and nerve stimulation, were comparable with respect to grade of sensory and motor block achieved. In a study by Baranowski et al., comparison was made between brachial plexus block by one of three techniques; insertion of a catheter into the brachial plexus sheath (n = 25), use of paraesthesia (n = 50) or use of the nerve stimulator (n = 25) to localise the plexus. They observed no difference between the groups with regard to grade of sensory and motor block achieved. Similar results were also observed by Bansal et al Failure of Block Failure of block was seen in 14% patients of nerve stimulator group as compared to 22% in paraesthesia group (p-0.436). In a study by Bansal et al., the failure rate was seen in 6.3% patients of nerve stimulator group as compared to 12.8% in paraesthesia group (p> 0.05). Study by Baranowski et al., also does not demonstrate a statistical difference between the failure rates of the two groups 10. However, Sathyam et al., observed that failure of block and conversion to general anaesthesia occurred more frequently in the paresthesia group Complications In present study, there was no neurological complications following peripheral nerve blocks i.e., post block neuralgia in any of the group. Sathyam et al., also observed no incidence of any neurological injury in any of the group 6. Bansal et al., observed neurological injury in 2 and 1 patient (out of 55 each) in nerve stimulator and paraesthesia group respectively (p> 0.05). Liguori et al., observed the incidence of Postoperative Neurologic symptoms (PONV) using the NS technique as 10.1% (11/109), whereas the incidence with the MP technique was 9.3% (10/108) (not significant) 7. Fear of pneumothorax limits the use of supraclavicular technique. The incidence of pneumothorax with the classic supraclavicular technique ranges from 0.5% to 6% 11. In present study, pneumothorax occurred in 1 Vol 4 (2) July-December MVP Journal of Medical Sciences 139
6 Comparison of Success Rate of Classical Supraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block with and without Nerve Stimulator patient each in nerve stimulator and paraesthesia group respectively (p> 0.05). Many authors have studied the anatomy of brachial plexus and analysed methods to prevent pneumothorax. These include use of several modifications of supraclavicular block such as modified lateral technique 6 or plumb bob approach. We believe that avoidance of supraclavicular block for fear of pneumothorax is detrimental to our patients because this technique provides an unrivalled rapid onset of predictable upper extremity anaesthesia, which is an advantage in a busy surgical practice. In our study, Hematoma was seen in 0% and 8% patients in nerve stimulator and paraesthesia groups respectively. This finding is supported by Niazi Gazani Masoud et al 11. He found that hematoma prevalence is more in paraesthesia technique due to instances of multiple insertions and there was a significant relationship between times of insertion and hematoma development. Similar results were also observed by Sathyam et al., 6 and Franco et al Conclusion From our study it was concluded that onset of sensory and motor block was shorter in nerve stimulator group. Also duration of analgesia was longer with nerve stimulator group. No difference was observed between the groups with respect to degree of success and complication rate. We therefore advocate the use of the nerve stimulator technique for routine brachial plexus blockade. 7. References 1. Moore D. Supraclavicular approach for block of the brachial plexus. Moore D, editor. Regional block. A handbook for use in the clinical practice of medicine and surgery. 4th ed. Springfield: Charles C Thomas Publisher; 1981.p Labat G. Regional anaesthesia. Its technic and clinical application. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company; Winnie AP. Historical consideration. Plexus Anaesthesia. 1984; 1:43 116, Liguori GA, Zayas VM, Ya Deau JT. Nerve localisation techniques for interscalene brachial plexus blockade: A prospective, randomised comparison of mechanical paresthesia versus elec-trical stimulation. 5. Chapman GM. Regional nerve block with the aid of a nerve stimulator. Anesthesia. 1972; 27: org/ /j tb08195.x 6. Sathyan N, Hedge H, Padmanabha S, Anish KA. Brachial plexus Block: A Comparison of Nerve locator versus paraesthesia technique. Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences. 2014; 13(1): Liguori GA, Zayas VM, YaDeau JT, Kahn RL, Paroli L, Buschiazzo V, Wu A. Nerve localiza-tion techniques for interscalene brachial plexus blockade: A prospective, randomized comparison of mechanical paresthesia versus electrical stimulation. Anesthesia and Analgesia Sep 1; 103(3): ane f PMid: Franco CD, Vieira ZE. 1,001 subclavian perivascular brachial plexus blocks: Success with a nerve stimulator. Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine Feb 29; 25(1): Baranowski AP, Pither CE. A comparison of three methods of axillary brachial plexus anaesthe-sia. Anaesthesia May 1; 45(5): tb14776.x PMid: Bansal P, et al. Comparison of interscalene brachial plexus blockade by eliciting multiple point paresthesia and electrical nerve stimulation techniques: a prospective, randomized trial. The In-ternet Journal of Anesthesiology. 2009; 23(2): Masoud NG, Taghi MM, Reza MG, Maarouf A, Seyedabolhasan S, Naser G. Complications of supraclavicular block of brachial plexus using compound classic and perivascular techniques. Rawal Med J Jan; 32: Vol 4 (2) July-December MVP Journal of Medical Sciences
Brachial Plexus Block, a Comparison of Nerve Locator versus Paresthesia Technique
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. X. (Feb. 2014), PP 06-10 Brachial Plexus Block, a Comparison of Nerve Locator versus
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. X. (Feb. 2014), PP 06-10 Brachial Plexus Block, a Comparison of Nerve Locator versus
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly -
 1 SUBCLAVIAN PERIVASCULAR BRACHIAL PLEXUS BLOCK ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 156 19 th OCTOBER 2009 Dr. Martin Herrick Department of Anaesthesia, Addenbrooke s Hospital, Cambridge, U.K. Correspondence
1 SUBCLAVIAN PERIVASCULAR BRACHIAL PLEXUS BLOCK ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 156 19 th OCTOBER 2009 Dr. Martin Herrick Department of Anaesthesia, Addenbrooke s Hospital, Cambridge, U.K. Correspondence
Dexamethasone Improves Outcome Of Infraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block
 Tanta Medical Journal Vol. (6), April 2008 Original Article ABSTRACT Dexamethasone Improves Outcome Of Infraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block Mohamed Samy Seddik Department of Anesthesia & Intensive Care,
Tanta Medical Journal Vol. (6), April 2008 Original Article ABSTRACT Dexamethasone Improves Outcome Of Infraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block Mohamed Samy Seddik Department of Anesthesia & Intensive Care,
Research Article A Comparative Study of Interscalene and Supraclavicular Approach of Brachial Plexus Block on Upper Limb Surgeries
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ANAESTHESIA Research Article A Comparative Study of Interscalene and Supraclavicular Approach of Brachial Plexus Block on Upper Limb Surgeries Susmita Bhattacharyya, KalyanBrata Mandal,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ANAESTHESIA Research Article A Comparative Study of Interscalene and Supraclavicular Approach of Brachial Plexus Block on Upper Limb Surgeries Susmita Bhattacharyya, KalyanBrata Mandal,
ASSESSMENT OF THE ROLE OF DEXAMETHASONE AS AN ADJUVANT IN SUPRACLAVICULAR BLOCK FOR UPPER LIMB SURGERIES
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASSESSMENT OF THE ROLE OF DEXAMETHASONE AS AN ADJUVANT IN SUPRACLAVICULAR BLOCK FOR UPPER LIMB SURGERIES Priyesh Bhaskar, Mamta Harjai (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print: 2348-6805
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASSESSMENT OF THE ROLE OF DEXAMETHASONE AS AN ADJUVANT IN SUPRACLAVICULAR BLOCK FOR UPPER LIMB SURGERIES Priyesh Bhaskar, Mamta Harjai (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print: 2348-6805
(Senior Resident, Dept of Anaesthesia, Dr. D. Y. Patil Medical College, Dr. D. Y. Patil Vidyapeeth [DPU], Pune)
![(Senior Resident, Dept of Anaesthesia, Dr. D. Y. Patil Medical College, Dr. D. Y. Patil Vidyapeeth [DPU], Pune) (Senior Resident, Dept of Anaesthesia, Dr. D. Y. Patil Medical College, Dr. D. Y. Patil Vidyapeeth [DPU], Pune)](/thumbs/82/85649280.jpg) IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. IX (April. 2017), PP 25-29 www.iosrjournals.org To Compare the Efficacy of Dexamethasone
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. IX (April. 2017), PP 25-29 www.iosrjournals.org To Compare the Efficacy of Dexamethasone
Brachial plexus blockade within the interscalene groove involves local anesthetic
 Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block- How I do it. Part 1 of a 2 part discussion on technique. Stuart Grant Professor of Anesthesiology Duke University Medical Center Durham NC Brachial plexus blockade within
Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block- How I do it. Part 1 of a 2 part discussion on technique. Stuart Grant Professor of Anesthesiology Duke University Medical Center Durham NC Brachial plexus blockade within
Ultrasound Guided Regional Nerve Blocks
 Ultrasound Guided Regional Nerve Blocks In the country of the blind the one eyed man is King -Deciderius Erasmus (1466-1536) Objectives Benefits of Regional Anesthesia Benefits of US guidance Role of ultrasound
Ultrasound Guided Regional Nerve Blocks In the country of the blind the one eyed man is King -Deciderius Erasmus (1466-1536) Objectives Benefits of Regional Anesthesia Benefits of US guidance Role of ultrasound
Original article: Supraclavicular block with 0.5% levobupivacaine and 0.5% ropivacainecomparative
 Original article: Supraclavicular block with 0.5% levobupivacaine and 0.5% ropivacainecomparative study Dr.V.Sai Dilip 1, Dr.G.Chandra Sekhar 1, Dr.Gopala Krishna Murthy 1, Dr.A.S.Kameswara Rao 1, Dr.K.Sivaji
Original article: Supraclavicular block with 0.5% levobupivacaine and 0.5% ropivacainecomparative study Dr.V.Sai Dilip 1, Dr.G.Chandra Sekhar 1, Dr.Gopala Krishna Murthy 1, Dr.A.S.Kameswara Rao 1, Dr.K.Sivaji
The Upper Limb III. The Brachial Plexus. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Upper Limb III The Brachial Plexus Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Brachial plexus Network of nerves supplying the upper limb Compression of the plexus results in motor & sensory changes
The Upper Limb III The Brachial Plexus Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Brachial plexus Network of nerves supplying the upper limb Compression of the plexus results in motor & sensory changes
DOI: / Page. 1 Dr. Seetharamaiah.S., 2 Dr. G.R.Santhilatha, 3 Dr. T.Venugopala rao, 4 Dr. Venugopalan.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. VII (Sep. 2015), PP 44-48 www.iosrjournals.org To evaluate the efficacy of Inj. Dexmedetomidine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. VII (Sep. 2015), PP 44-48 www.iosrjournals.org To evaluate the efficacy of Inj. Dexmedetomidine
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly
 PERIPHERAL NERVE BLOCKS GETTING STARTED ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 134 PUBLICATION DATE 18/05/09 Dr Kim Russon, Consultant Anaesthetist Dr Helen Findley, ST3 Anaesthetics Dr Zoe Harclerode, ST3 Anaesthetics
PERIPHERAL NERVE BLOCKS GETTING STARTED ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 134 PUBLICATION DATE 18/05/09 Dr Kim Russon, Consultant Anaesthetist Dr Helen Findley, ST3 Anaesthetics Dr Zoe Harclerode, ST3 Anaesthetics
Interscalene brachial plexus blocks in the management of shoulder dislocations
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1989, 6, 199-204 Interscalene brachial plexus blocks in the management of shoulder dislocations T. J. UNDERHILL, A. WAN & M. MORRICE Accident and Emergency Department, Derbyshire
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1989, 6, 199-204 Interscalene brachial plexus blocks in the management of shoulder dislocations T. J. UNDERHILL, A. WAN & M. MORRICE Accident and Emergency Department, Derbyshire
Regional Anesthesia. procedure if required. However, many patients prefer to receive sedation either during the
 1 Regional Anesthesia Regional anaesthesia (or regional anesthesia) is anesthesia affecting only a large part of the body, such as a limb or the lower half of the body. Regional anaesthetic techniques
1 Regional Anesthesia Regional anaesthesia (or regional anesthesia) is anesthesia affecting only a large part of the body, such as a limb or the lower half of the body. Regional anaesthetic techniques
Regional Anaesthesia of the Thoracic Limb
 Regional Anaesthesia of the Thoracic Limb Trauma and inflammation cause sensitization of the peripheral nervous system and the subsequent barrage of nociceptive input (usually by surgery) produces sensitization
Regional Anaesthesia of the Thoracic Limb Trauma and inflammation cause sensitization of the peripheral nervous system and the subsequent barrage of nociceptive input (usually by surgery) produces sensitization
International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN Volume 3, Issue 2, Mar-Apr 2015.
 Anesthesiology Original Research International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 3, Issue 2, Mar-Apr 2015. Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. COMPARISON OF DEXMEDETOMIDINE
Anesthesiology Original Research International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 3, Issue 2, Mar-Apr 2015. Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. COMPARISON OF DEXMEDETOMIDINE
USRA OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY
 USRA OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY Christian R. Falyar, DNAP, CRNA Department of Nurse Anesthesia Virginia Commonwealth University Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Christian Falyar, DO NOT have a
USRA OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY Christian R. Falyar, DNAP, CRNA Department of Nurse Anesthesia Virginia Commonwealth University Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Christian Falyar, DO NOT have a
Surgery Under Regional Anesthesia
 Surgery Under Regional Anesthesia Jean Daniel Eloy, MD Assistant Professor Residency Program Director Rutgers-New Jersey Medical School Rutgers The State University of New Jersey Peripheral Nerve Block
Surgery Under Regional Anesthesia Jean Daniel Eloy, MD Assistant Professor Residency Program Director Rutgers-New Jersey Medical School Rutgers The State University of New Jersey Peripheral Nerve Block
Dr. Georgi Valchev Fellow in regional anaesthesia UZ Leuven
 Dr. Georgi Valchev Fellow in regional anaesthesia UZ Leuven 55 years old woman Latarjetprocedure ASA-1, 49 kg. NKDA Informed consent for RA ISB with catheter uneventful throughout, rate 4/4/60 according
Dr. Georgi Valchev Fellow in regional anaesthesia UZ Leuven 55 years old woman Latarjetprocedure ASA-1, 49 kg. NKDA Informed consent for RA ISB with catheter uneventful throughout, rate 4/4/60 according
Comparison Of 0.5%Bupivacaine And 0.5% Bupivacaine Plus Buprenorphine in Brachial Plexus Block
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (Jan. 2016), PP 01-08 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison Of 0.5%Bupivacaine And 0.5%
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (Jan. 2016), PP 01-08 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison Of 0.5%Bupivacaine And 0.5%
Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks in the emergency department
 Full Text Online @ www.onlinejets.org Case Series DOI: 10.4103/0974-2700.58655 Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks in the emergency department Sanjeev Bhoi, Amit Chandra 1, Sagar Galwankar 2 Department of Emergency
Full Text Online @ www.onlinejets.org Case Series DOI: 10.4103/0974-2700.58655 Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks in the emergency department Sanjeev Bhoi, Amit Chandra 1, Sagar Galwankar 2 Department of Emergency
Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions.
 Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
Dr Kelly Jones Anesthesiologist at Northwest Orthopedics
 Dr Kelly Jones Anesthesiologist at Northwest Orthopedics Decrease narcotic use in the immediate post operative period. Better Pain Control Less side effects then General Anesthesia Sedation Post operative
Dr Kelly Jones Anesthesiologist at Northwest Orthopedics Decrease narcotic use in the immediate post operative period. Better Pain Control Less side effects then General Anesthesia Sedation Post operative
PERIPHERAL REGIONAL BLOCKS. by Mike DeBroeck, DNP, CRNA
 PERIPHERAL REGIONAL BLOCKS by Mike DeBroeck, DNP, CRNA Why am I bothering with this topic at all? Do CRNAs REALLY even do peripheral regional anesthetics? YES!!!!!!! TOPICS GENERAL INFO SUCCESS RATES
PERIPHERAL REGIONAL BLOCKS by Mike DeBroeck, DNP, CRNA Why am I bothering with this topic at all? Do CRNAs REALLY even do peripheral regional anesthetics? YES!!!!!!! TOPICS GENERAL INFO SUCCESS RATES
Patient consent for peripheral nerve blocks
 Patient consent for peripheral nerve blocks 1 Membership of Working Party Dr Anand Sardesai Dr James French Dr Amit Pawa Consultant Anaesthetist, Cambridge, UK Consultant Anaesthetist, Nottingham, UK Consultant
Patient consent for peripheral nerve blocks 1 Membership of Working Party Dr Anand Sardesai Dr James French Dr Amit Pawa Consultant Anaesthetist, Cambridge, UK Consultant Anaesthetist, Nottingham, UK Consultant
CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE BLOCK Author John Hyndman
 Questions CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE BLOCK Author John Hyndman Web Editor Kirsten Fehrmann - kirstenfehrmann@hotmail.com 1) Why does a LA solution containing Epinephrine cause pain on injection and what can
Questions CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE BLOCK Author John Hyndman Web Editor Kirsten Fehrmann - kirstenfehrmann@hotmail.com 1) Why does a LA solution containing Epinephrine cause pain on injection and what can
GUIDELINES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE / PLEXUS BLOCK CATHETER MANAGEMENT DEPARTMENT OF ANAESTHESIOLOGY AND INTENSIVE CARE HOSPITAL KUALA LUMPUR
 GUIDELINES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE / PLEXUS BLOCK CATHETER MANAGEMENT DEPARTMENT OF ANAESTHESIOLOGY AND INTENSIVE CARE HOSPITAL KUALA LUMPUR INTRODUCTION Regional block provides superior pain relief, compared
GUIDELINES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE / PLEXUS BLOCK CATHETER MANAGEMENT DEPARTMENT OF ANAESTHESIOLOGY AND INTENSIVE CARE HOSPITAL KUALA LUMPUR INTRODUCTION Regional block provides superior pain relief, compared
Comparison of ultrasound-guided supraclavicular block according to the various volumes of local anesthetic
 Clinical Research Article Korean J Anesthesiol 2013 June 64(6): 494-499 http://dx.doi.org/10.4097/kjae.2013.64.6.494 Comparison of ultrasound-guided supraclavicular block according to the various volumes
Clinical Research Article Korean J Anesthesiol 2013 June 64(6): 494-499 http://dx.doi.org/10.4097/kjae.2013.64.6.494 Comparison of ultrasound-guided supraclavicular block according to the various volumes
Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular block
 THE JOURNAL OF NEW YORK SCHOOL J u l y 2009 V o l u m e OF REGIONAL ANESTHESIA 1 3 Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular block Arthur Atchabahian, MD Department of Anesthesiology, St. Vincent Medical Center,
THE JOURNAL OF NEW YORK SCHOOL J u l y 2009 V o l u m e OF REGIONAL ANESTHESIA 1 3 Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular block Arthur Atchabahian, MD Department of Anesthesiology, St. Vincent Medical Center,
Guidance for Multiple Injection Axillary Brachial Plexus Block
 A Prospective, Randomized Comparison between Ultrasound versus Ultrasound with Nerve Stimulation Guidance for Multiple Injection Axillary Brachial Plexus Block Mostafa Muhammed Sabra, Ali Fotoh Ali El
A Prospective, Randomized Comparison between Ultrasound versus Ultrasound with Nerve Stimulation Guidance for Multiple Injection Axillary Brachial Plexus Block Mostafa Muhammed Sabra, Ali Fotoh Ali El
JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES
 JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES Singh R, Bisoi P, Mohanty SN, Debata PC. Study On Effect of Dexmedetomidine When Added To Bupivacaine On The Onset Time And Duration Of Block In Supraclavicular
JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES Singh R, Bisoi P, Mohanty SN, Debata PC. Study On Effect of Dexmedetomidine When Added To Bupivacaine On The Onset Time And Duration Of Block In Supraclavicular
Diana Mathioudakis DEAA EDIC AFRCA. consultant paediatric cardiac anaesthetist Intensivist(D/NL) emergency physician(d)
 & Diana Mathioudakis DEAA EDIC AFRCA consultant paediatric cardiac anaesthetist Intensivist(D/NL) emergency physician(d) Anatomy Probe handling Sonoanatomy Tips and Tricks Literature For ultrasound guided
& Diana Mathioudakis DEAA EDIC AFRCA consultant paediatric cardiac anaesthetist Intensivist(D/NL) emergency physician(d) Anatomy Probe handling Sonoanatomy Tips and Tricks Literature For ultrasound guided
An evaluation of brachial plexus block using a nerve stimulator versus ultrasound guidance: A randomized controlled trial
 Original Article An evaluation of brachial plexus block using a nerve versus ultrasound guidance: A randomized controlled trial Shivinder Singh, Rakhee Goyal, Kishan Kumar Upadhyay, Navdeep Sethi, Ram
Original Article An evaluation of brachial plexus block using a nerve versus ultrasound guidance: A randomized controlled trial Shivinder Singh, Rakhee Goyal, Kishan Kumar Upadhyay, Navdeep Sethi, Ram
Australian and New Zealand Registry of Regional Anaesthesia (AURORA)
 Australian and New Zealand Registry of Regional Anaesthesia (AURORA) Overview of Results First 4000 procedures recorded to - www.anaesthesiaregistry.org June 1st 2011 to February 2012 Background Australian
Australian and New Zealand Registry of Regional Anaesthesia (AURORA) Overview of Results First 4000 procedures recorded to - www.anaesthesiaregistry.org June 1st 2011 to February 2012 Background Australian
ASA Closed Claims Project: Regional Anesthesia Claims 1990 or later Lorri A. Lee MD Department of Anesthesiology University of Washington, Seattle, WA
 ASA Closed Claims Project: Regional Anesthesia Claims 1990 or later Lorri A. Lee MD Department of Anesthesiology, Seattle, WA OVERVIEW 1. Closed Claims Project 2. Peripheral Nerve Blocks 3. Neuraxial Claims
ASA Closed Claims Project: Regional Anesthesia Claims 1990 or later Lorri A. Lee MD Department of Anesthesiology, Seattle, WA OVERVIEW 1. Closed Claims Project 2. Peripheral Nerve Blocks 3. Neuraxial Claims
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Demonstrates Lack of Precision in Needle Placement by the Infraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block Described by Raj Et Al.
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Demonstrates Lack of Precision in Needle Placement by the Infraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block Described by Raj Et Al. Øivind Klaastad, MD*, Finn G. Lilleås, MD, Jan S. Røtnes,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Demonstrates Lack of Precision in Needle Placement by the Infraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block Described by Raj Et Al. Øivind Klaastad, MD*, Finn G. Lilleås, MD, Jan S. Røtnes,
increasing pressure registered in kilograms was applied until the subject began to feel a sensation of pain. With an intelligent person the responses
 VARIATIONS IN THE SENSIBILITY TO PRESSURE PAIN CAUSED BY NERVE STIMULATION IN MAN. BY R. C. SHAWE. (From the Royal Infirmary, Manchester.) IN a previous paper (Brit. Journ. Surgery, Jan. 1922) I have given
VARIATIONS IN THE SENSIBILITY TO PRESSURE PAIN CAUSED BY NERVE STIMULATION IN MAN. BY R. C. SHAWE. (From the Royal Infirmary, Manchester.) IN a previous paper (Brit. Journ. Surgery, Jan. 1922) I have given
Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent Option For Day Care Surgeries
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 2 Ver. III. (Feb. 2014), PP 09-13 Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 2 Ver. III. (Feb. 2014), PP 09-13 Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome)
 A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
Somatic neurotomal distribution of the lower extremity. (Reprinted from Brown DL. Atlas of Regional Anesthesia [1]).
![Somatic neurotomal distribution of the lower extremity. (Reprinted from Brown DL. Atlas of Regional Anesthesia [1]). Somatic neurotomal distribution of the lower extremity. (Reprinted from Brown DL. Atlas of Regional Anesthesia [1]).](/thumbs/93/112807563.jpg) Continuous Sciatic Nerve Block André P Boezaart MD, PhD Department of Anesthesia, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA Director of the Regional Anesthesia Study Center of Iowa (RASCI) Introduction Due to
Continuous Sciatic Nerve Block André P Boezaart MD, PhD Department of Anesthesia, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA Director of the Regional Anesthesia Study Center of Iowa (RASCI) Introduction Due to
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides
 The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
The Brachial Plexus and Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
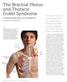 The Brachial Plexus and Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Understanding Signs and Symptoms By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC The brachial plexus of nerves and the subclavian/axillary artery and vein comprise a neurovascular
The Brachial Plexus and Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Understanding Signs and Symptoms By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC The brachial plexus of nerves and the subclavian/axillary artery and vein comprise a neurovascular
S Kannan, Prem Kumar. Assistant Professor, Saveetha Medical College and Hospital, Chennai.
 Original Article CLINICAL COMPARISON OF TWO DIFFERENT VOLUMES OF 0.5% BUPIVACAINE FOR CLAVICULAR SURGERIES USING COMBINED INTERSCALENE AND SUPERFICIAL CERVICAL PLEXUS BLOCK 2 S Kannan, Prem Kumar,2 Assistant
Original Article CLINICAL COMPARISON OF TWO DIFFERENT VOLUMES OF 0.5% BUPIVACAINE FOR CLAVICULAR SURGERIES USING COMBINED INTERSCALENE AND SUPERFICIAL CERVICAL PLEXUS BLOCK 2 S Kannan, Prem Kumar,2 Assistant
Comparison of clonidine adjuvants to ropivacaine in subclavian perivascular approach of supra clavicular brachial plexus block
 Original Research Article Comparison of clonidine adjuvants to ropivacaine in subclavian perivascular approach of supra clavicular brachial plexus block S. Arul Rajan 1, N. Sathyan 2*, T. Murugan 3 1 Assistant
Original Research Article Comparison of clonidine adjuvants to ropivacaine in subclavian perivascular approach of supra clavicular brachial plexus block S. Arul Rajan 1, N. Sathyan 2*, T. Murugan 3 1 Assistant
Comparative Study of Equal Doses of Intrathecal Isobaric Bupivacaine and Isobaric Ropivacaine for Lower Limb Surgeries and Perineal Surgeries
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/229 Comparative Study of Equal Doses of Intrathecal Isobaric Bupivacaine and Isobaric Ropivacaine for Lower Limb Surgeries
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/229 Comparative Study of Equal Doses of Intrathecal Isobaric Bupivacaine and Isobaric Ropivacaine for Lower Limb Surgeries
Presentation Menu. Walk-in Slide. Full Presentation. Access. Site. Needle. Flush. Comfort. Monitor. Removing the EZ-IO catheter.
 Presentation Menu Walk-in Slide Full Presentation Access Site Needle Flush Comfort Monitor Removing the EZ-IO catheter Clinical Support Explore. Discover. Examine. Vidacare Workshop Programmes www.vidacare.com
Presentation Menu Walk-in Slide Full Presentation Access Site Needle Flush Comfort Monitor Removing the EZ-IO catheter Clinical Support Explore. Discover. Examine. Vidacare Workshop Programmes www.vidacare.com
perivascular, sensory and motor effects, 62, side effects, 64 and subfascial hematoma, 221 axillary plexus, 6 7 axonotmesis, 221, 222
 249 Index A abscess, and continuous peripheral nerve block, 244 Achilles tendon rupture, 173 and saphenous nerve block, 208 and sural nerve block, 209 and tibial nerve block, 203, 204, 210, 211 acromion,
249 Index A abscess, and continuous peripheral nerve block, 244 Achilles tendon rupture, 173 and saphenous nerve block, 208 and sural nerve block, 209 and tibial nerve block, 203, 204, 210, 211 acromion,
Comparison of analgesic properties of perineural and systemic dexamethasone in patients undergoing upper limb surgeries under supraclavicular block
 Original Research Article Comparison of analgesic properties of perineural and systemic dexamethasone in patients undergoing upper limb surgeries under supraclavicular block Sathyan Natarajan 1*, Karthikeyan
Original Research Article Comparison of analgesic properties of perineural and systemic dexamethasone in patients undergoing upper limb surgeries under supraclavicular block Sathyan Natarajan 1*, Karthikeyan
Table-2: Fastrack Criteria-According to White and Song
 Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block for Hydrodilatation with Normal Saline in Patients of Frozen Shoulder Divya Srivastav, Anup Chandani, 3 JC Vasava & Assistant Professor, 3 Professor, GMERS, Medical College
Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block for Hydrodilatation with Normal Saline in Patients of Frozen Shoulder Divya Srivastav, Anup Chandani, 3 JC Vasava & Assistant Professor, 3 Professor, GMERS, Medical College
*Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus.
 *Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus. *Vertebral column is formed by the union of 33 sequential vertebrae
*Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus. *Vertebral column is formed by the union of 33 sequential vertebrae
How and why to do an epidural in dogs and cats? Which Indications and which drugs?
 AMVAC/RoSAVA 2014 How and why to do an epidural in dogs and cats? Which Indications and which drugs? Prof. Yves Moens Dipl ECVAA Why do epidurals? A part of a balanced anesthesia A means to provide analgesia
AMVAC/RoSAVA 2014 How and why to do an epidural in dogs and cats? Which Indications and which drugs? Prof. Yves Moens Dipl ECVAA Why do epidurals? A part of a balanced anesthesia A means to provide analgesia
jorapain Original Article ABSTRACT
 Original Article Comparison of Clonidine and Dexmedetomidine 10.5005/jp-journals-10046-0015 as an Adjuvant to 0.5% Ropivacaine Comparison of Clonidine and Dexmedetomidine as an Adjuvant to 0.5% Ropivacaine
Original Article Comparison of Clonidine and Dexmedetomidine 10.5005/jp-journals-10046-0015 as an Adjuvant to 0.5% Ropivacaine Comparison of Clonidine and Dexmedetomidine as an Adjuvant to 0.5% Ropivacaine
Local anaesthetic techniques
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Local anaesthetic techniques Author : CARL BRADBROOK Categories : Vets Date : June 30, 2014 CARL BRADBROOK BVSc, CertVA, DipECVAA,
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Local anaesthetic techniques Author : CARL BRADBROOK Categories : Vets Date : June 30, 2014 CARL BRADBROOK BVSc, CertVA, DipECVAA,
Midazolam with Bupivacaine for Improving Analgesia Quality in Brachial Plexus Block for Upper Limb Surgeries
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Midazolam with Bupivacaine for Improving Analgesia Quality in Brachial Plexus Block for Upper Limb Surgeries Nasreen Laiq 1, Mohammad Naeem Khan 1, Mohammad Arif 1 and Shahid Khan 2 ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Midazolam with Bupivacaine for Improving Analgesia Quality in Brachial Plexus Block for Upper Limb Surgeries Nasreen Laiq 1, Mohammad Naeem Khan 1, Mohammad Arif 1 and Shahid Khan 2 ABSTRACT
Plantar Flexion Seems More Reliable than Dorsiflexion with Labat s Sciatic Nerve Block: A Prospective, Randomized Comparison
 Plantar Flexion Seems More Reliable than Dorsiflexion with Labat s Sciatic Nerve Block: A Prospective, Randomized Comparison Manuel Taboada, MD*, Peter G. Atanassoff, MD, Jaime Rodríguez, MD, PhD*, Joaquín
Plantar Flexion Seems More Reliable than Dorsiflexion with Labat s Sciatic Nerve Block: A Prospective, Randomized Comparison Manuel Taboada, MD*, Peter G. Atanassoff, MD, Jaime Rodríguez, MD, PhD*, Joaquín
A Comparative Evaluation of Techniques in Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block: Conventional blind, Nerve Stimulator Guided and Ultrasound Guided.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.3.16 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 A Comparative Evaluation of Techniques in Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block: Conventional blind, Nerve Stimulator
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.3.16 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 A Comparative Evaluation of Techniques in Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block: Conventional blind, Nerve Stimulator
Power Line to your Line to your Circuit Line to the station neighborhood house breaker living room. Outlet lamp Lamp with socket, Light bulb
 IMC 606 Neuroscience and Behavior Module Dr. Margaret Paroski Analysis of Sensory Lesions You walk into your living room and turn on the lamp. But no light comes on. What would you do? You would probably
IMC 606 Neuroscience and Behavior Module Dr. Margaret Paroski Analysis of Sensory Lesions You walk into your living room and turn on the lamp. But no light comes on. What would you do? You would probably
Comparative Study of Intrathecal Ropivacaine and Levobupivacaine With Fentanyl And Magnesium As Adjuvants For Lower Abdominal Surgeries
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861. Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. II. (May. 214), PP 39-43 Comparative Study of Intrathecal Ropivacaine and Levobupivacaine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861. Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. II. (May. 214), PP 39-43 Comparative Study of Intrathecal Ropivacaine and Levobupivacaine
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Assessment of the Brachial Plexus EMG Course CNSF Halifax Fraser Moore, Canadian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology McGill University
 Assessment of the Brachial Plexus EMG Course CNSF Halifax 2018 Fraser Moore, Canadian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology McGill University Angela Scott, Association of Electromyography Technologists of
Assessment of the Brachial Plexus EMG Course CNSF Halifax 2018 Fraser Moore, Canadian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology McGill University Angela Scott, Association of Electromyography Technologists of
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
SUPRACLAVICULAR REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA REANALYSED: THE CORNISH TECHNIQUE
 THE JOURNAL OF NEW YORK SCHOOL OF REGIONAL ANESTHESIA SUPRACLAVICULAR REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA REANALYSED: THE BY CORHISH PB Author Affiliation: Nelson, New Zealand This essay is based on a project which has
THE JOURNAL OF NEW YORK SCHOOL OF REGIONAL ANESTHESIA SUPRACLAVICULAR REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA REANALYSED: THE BY CORHISH PB Author Affiliation: Nelson, New Zealand This essay is based on a project which has
The relationship of the musculocutaneous nerve to the brachial plexus evaluated by MRI
 DOI 10.1007/s10877-015-9807-3 ORIGINAL RESEARCH The relationship of the musculocutaneous nerve to the brachial plexus evaluated by MRI Trygve Kjelstrup 1,2 Axel R. Sauter 3 Per K. Hol 2,4 Received: 23
DOI 10.1007/s10877-015-9807-3 ORIGINAL RESEARCH The relationship of the musculocutaneous nerve to the brachial plexus evaluated by MRI Trygve Kjelstrup 1,2 Axel R. Sauter 3 Per K. Hol 2,4 Received: 23
Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus nerve block vs procedural sedation for the treatment of upper extremity emergencies
 American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2008) 26, 706 710 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Brief Report Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus nerve vs procedural for the treatment of upper extremity
American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2008) 26, 706 710 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Brief Report Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus nerve vs procedural for the treatment of upper extremity
JUNE 29, 2016 Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Peripheral Nerve Stimulation Shows Promise
 Pain Medicine JUNE 29, 2016 Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Peripheral Nerve Stimulation Shows Promise New Orleans Brian M. Ilfeld, MD, MS, has been involved in more than his fair share of regional anesthesia
Pain Medicine JUNE 29, 2016 Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Peripheral Nerve Stimulation Shows Promise New Orleans Brian M. Ilfeld, MD, MS, has been involved in more than his fair share of regional anesthesia
Peripheral Nerve Problems
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peripheral Nerve Problems How they develop and ways to treat them This handout explains how nerves work, what happens when they are injured, and how peripheral nerve problems
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peripheral Nerve Problems How they develop and ways to treat them This handout explains how nerves work, what happens when they are injured, and how peripheral nerve problems
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. S. S. Liu, 1 J. T. YaDeau, 2 P. M. Shaw, 3 S. Wilfred, 4 T. Shetty 5 and M. Gordon 6
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2044.2011.06619.x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Incidence of unintentional intraneural injection and postoperative neurological complications with ultrasoundguided interscalene and supraclavicular
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2044.2011.06619.x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Incidence of unintentional intraneural injection and postoperative neurological complications with ultrasoundguided interscalene and supraclavicular
Page 1. Results: Both the ultrasound techniques are comparable and better than paracetamol
 ISSN- O: 2458-868X, ISSN P: 2458 8687 Index Copernicus Value: 49. 23 PubMed - National Library of Medicine - ID: 101731606 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.956 International Journal of Medical Science and Innovative
ISSN- O: 2458-868X, ISSN P: 2458 8687 Index Copernicus Value: 49. 23 PubMed - National Library of Medicine - ID: 101731606 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.956 International Journal of Medical Science and Innovative
Review Article Axillary Brachial Plexus Block
 Anesthesiology Research and Practice Volume 2011, Article ID 173796, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/173796 Review Article Axillary Brachial Plexus Block Ashish R. Satapathy and David M. Coventry Department of
Anesthesiology Research and Practice Volume 2011, Article ID 173796, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/173796 Review Article Axillary Brachial Plexus Block Ashish R. Satapathy and David M. Coventry Department of
Eldor Epidural Kit (CSEN 68) Epidural catheter technique
 Eldor Epidural Kit (CSEN 68) Epidural catheter technique Using the epidural needle the epidural space is reached by the loss of resistance technique or the hanging drop technique, while the proximal opening
Eldor Epidural Kit (CSEN 68) Epidural catheter technique Using the epidural needle the epidural space is reached by the loss of resistance technique or the hanging drop technique, while the proximal opening
Peripheral Nerve Problems
 Patient Education Peripheral Nerve Problems How they develop and ways to treat them This handout provides general information about how nerves work, what happens when they are injured, and how peripheral
Patient Education Peripheral Nerve Problems How they develop and ways to treat them This handout provides general information about how nerves work, what happens when they are injured, and how peripheral
Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report
 SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
SHORT REPORT Eur J Anat, 10 (3): 61-66 (2006) Multiple variations involving all the terminal branches of the brachial plexus and the axillary artery a case report K. Ramachandran, I. Kanakasabapathy and
All that tingles is not bends
 All that tingles is not bends Divers are taught to pay attention to any abnormal signs and symptoms after diving. They are instructed to consider them as being possible decompression illness (DCI) until
All that tingles is not bends Divers are taught to pay attention to any abnormal signs and symptoms after diving. They are instructed to consider them as being possible decompression illness (DCI) until
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.28 Comparative Study of Supraclavicular Brachial
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.28 Comparative Study of Supraclavicular Brachial
Regional Anesthesia. Fatiş Altındaş Dept. of Anesthesiology
 Regional Anesthesia Fatiş Altındaş Dept. of Anesthesiology Regional anesthesia - Definition Renders a specific area of the body, e.g. foot, arm, lower extremities insensating to stimulus of surgery or
Regional Anesthesia Fatiş Altındaş Dept. of Anesthesiology Regional anesthesia - Definition Renders a specific area of the body, e.g. foot, arm, lower extremities insensating to stimulus of surgery or
INTRODUCTION. Getting the best scan. Choosing a probe. Choosing the frequency
 Getting the best scan Choosing a probe Select the most appropriate probe for the particular scan required. s vary in their: operating frequency range higher ultrasound frequencies provide better discrimination
Getting the best scan Choosing a probe Select the most appropriate probe for the particular scan required. s vary in their: operating frequency range higher ultrasound frequencies provide better discrimination
A New Anterior Approach for Fluoroscopy-guided Suprascapular Nerve Block
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2012 July; Vol. 25, No. 3: 168-172 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2012.25.3.168 A New Anterior Approach for Fluoroscopy-guided Suprascapular
Original Article Korean J Pain 2012 July; Vol. 25, No. 3: 168-172 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2012.25.3.168 A New Anterior Approach for Fluoroscopy-guided Suprascapular
Ultrasound in Peripheral Nerve Interventions
 Ultrasound in Peripheral Nerve Interventions John L. Lin, M.D. Shepherd Center Assistant Clinical Professor Emory University, School of Medicine Outline Ultrasound basics Nerve blocks in physiatric setting
Ultrasound in Peripheral Nerve Interventions John L. Lin, M.D. Shepherd Center Assistant Clinical Professor Emory University, School of Medicine Outline Ultrasound basics Nerve blocks in physiatric setting
Neural Blocks in Pain Medicine D R M A R G A R E T E B O N E M B C H B F R C A F F P M R C A C O N S U LTA N T I N PA I N M E D I C I N E
 Neural Blocks in Pain Medicine D R M A R G A R E T E B O N E M B C H B F R C A F F P M R C A C O N S U LTA N T I N PA I N M E D I C I N E Stellate Ganglion Block Lumbar Sympathetic Block Requirements Diagnosis
Neural Blocks in Pain Medicine D R M A R G A R E T E B O N E M B C H B F R C A F F P M R C A C O N S U LTA N T I N PA I N M E D I C I N E Stellate Ganglion Block Lumbar Sympathetic Block Requirements Diagnosis
Assistant Professor, Anaesthesia Department, Govt. General Hospital / Guntur Medical College, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. I (August. 2016), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of 0.25% Ropivacaine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. I (August. 2016), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of 0.25% Ropivacaine
Intraneural injection during nerve stimulator-guided sciatic nerve block at the popliteal fossa
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 102 (6): 855 61 (2009) doi:10.1093/bja/aep097 Advance Access publication May 6, 2009 Intraneural injection during nerve stimulator-guided sciatic nerve block at the popliteal
British Journal of Anaesthesia 102 (6): 855 61 (2009) doi:10.1093/bja/aep097 Advance Access publication May 6, 2009 Intraneural injection during nerve stimulator-guided sciatic nerve block at the popliteal
A Comparative Study of Epidural, Bupivacaine with Buprenorphine and Bupivacaine with Fentanyl in Lower Limb Surgeries
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 12 Ver. III (Dec. 2014), PP 23-28 A Comparative Study of Epidural, Bupivacaine with Buprenorphine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 12 Ver. III (Dec. 2014), PP 23-28 A Comparative Study of Epidural, Bupivacaine with Buprenorphine
Basics of US Regional Anaesthesia. November 2008
 Basics of US Regional Anaesthesia November 2008 Essential Physics HIGH frequency = great resolution but poor penetration LOW frequency = poor resolution but great penetration Potential Advantages of US
Basics of US Regional Anaesthesia November 2008 Essential Physics HIGH frequency = great resolution but poor penetration LOW frequency = poor resolution but great penetration Potential Advantages of US
Axillary block of the brachial plexus
 VOL 17 NO 3 ANESTHESIA JULY 1962 Axillary block of the brachial plexus Guest Faculty Member, Department of Anesthesia Western Reserve University Medical School, Cleveland 6, Ohio The axillary approach
VOL 17 NO 3 ANESTHESIA JULY 1962 Axillary block of the brachial plexus Guest Faculty Member, Department of Anesthesia Western Reserve University Medical School, Cleveland 6, Ohio The axillary approach
Regional Anesthesia and Acute Pain Medicine Fellowship at Wake Forest University
 Regional Anesthesia and Acute Pain Medicine Fellowship at Wake Forest University Fellowship Director: J. Douglas Jaffe, DO Assistant Professor and Member - Section of Regional Anesthesia & Acute Pain Management
Regional Anesthesia and Acute Pain Medicine Fellowship at Wake Forest University Fellowship Director: J. Douglas Jaffe, DO Assistant Professor and Member - Section of Regional Anesthesia & Acute Pain Management
Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries. First Global Conflict Medicine Congress
 Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries Joseph BAKHACH First Global Conflict Medicine Congress Hand & Microsurgery Department American University of Beirut Medical Centre Brachial
Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries Joseph BAKHACH First Global Conflict Medicine Congress Hand & Microsurgery Department American University of Beirut Medical Centre Brachial
Infraclavicular brachial plexus blocks aim at the
 REGIONAL ANESTHESIA AND PAIN MEDICINE SECTION EDITOR DENISE J. WEDEL A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study of Modifications to the Infraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block Øivind Klaastad, MD*, Finn G. Lilleås,
REGIONAL ANESTHESIA AND PAIN MEDICINE SECTION EDITOR DENISE J. WEDEL A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study of Modifications to the Infraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block Øivind Klaastad, MD*, Finn G. Lilleås,
Original Research Article. Kiran Kumar G. V. 1, Rammohan Gurram 1, Gajanan Fultambkar 1 *, Amit Omprakash Gupta 2, Onkar C.
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Kumar KGV et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2018 Jul;6(7):2503-2507 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20182844
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Kumar KGV et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2018 Jul;6(7):2503-2507 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20182844
Interscalene brachial plexus blockade - indications, anatomy, practical performance
 08RC2 Interscalene brachial plexus blockade - indications, anatomy, practical performance Urs Eichenberger Department of Anaesthesiology and Pain Therapy, University Hospital of Bern, Switzerland Saturday,
08RC2 Interscalene brachial plexus blockade - indications, anatomy, practical performance Urs Eichenberger Department of Anaesthesiology and Pain Therapy, University Hospital of Bern, Switzerland Saturday,
Compound Action Potential, CAP
 Stimulus Strength UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Spring, 2013 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition
Stimulus Strength UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Spring, 2013 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition
*the Arm* -the arm extends from the shoulder joint (proximal), to the elbow joint (distal) - it has one bone ; the humerus which is a long bone
 *the Arm* -the arm extends from the shoulder joint (proximal), to the elbow joint (distal) - it has one bone ; the humerus which is a long bone - muscles in the arm : *brachialis muscle *Biceps brachii
*the Arm* -the arm extends from the shoulder joint (proximal), to the elbow joint (distal) - it has one bone ; the humerus which is a long bone - muscles in the arm : *brachialis muscle *Biceps brachii
Safety of Pediatric Regional Anesthesia. Arjunan Ganesh The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
 Safety of Pediatric Regional Anesthesia Arjunan Ganesh The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Disclosure Nothing related to this presentation Objectives Understand the current ASRA/ESRA Practice Advisory
Safety of Pediatric Regional Anesthesia Arjunan Ganesh The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Disclosure Nothing related to this presentation Objectives Understand the current ASRA/ESRA Practice Advisory
3/3/2016. International Standards for the Neurologic Classification of Spinal Cord Injury (ISNCSCI)
 International Standards for the Neurologic Classification of Spinal Cord Injury (ISNCSCI) American Spinal Injury Association International Spinal Cord Society Presented by Adam Stein, MD Chairman and Professor
International Standards for the Neurologic Classification of Spinal Cord Injury (ISNCSCI) American Spinal Injury Association International Spinal Cord Society Presented by Adam Stein, MD Chairman and Professor
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Comparison of three different volumes of mepivacaine in axillary plexus block using multiple nerve stimulation ²
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 91 (4): 519±24 (2003) DOI: 10.1093/bja/aeg215 Comparison of three different volumes of mepivacaine in axillary plexus block using multiple nerve stimulation ² A. Serradell*,
British Journal of Anaesthesia 91 (4): 519±24 (2003) DOI: 10.1093/bja/aeg215 Comparison of three different volumes of mepivacaine in axillary plexus block using multiple nerve stimulation ² A. Serradell*,
REGIONAL/LOCAL ANESTHESIA and OBESITY
 REGIONAL/LOCAL ANESTHESIA and OBESITY Jay B. Brodsky, MD Stanford University School of Medicine Jbrodsky@stanford.edu Potential Advantages Regional compared to General Anesthesia Minimal intra-operative
REGIONAL/LOCAL ANESTHESIA and OBESITY Jay B. Brodsky, MD Stanford University School of Medicine Jbrodsky@stanford.edu Potential Advantages Regional compared to General Anesthesia Minimal intra-operative
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Ultrasound-guided Supraclavicular Nerve Block In-plane Technique: Comparison of Conventional vs Skin Wheal Standoff Technique
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ultrasound-guided Supraclavicular 10.5005/jp-journals-10046-0061 Nerve Block In-plane Technique Ultrasound-guided Supraclavicular Nerve Block In-plane Technique: Comparison of Conventional
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ultrasound-guided Supraclavicular 10.5005/jp-journals-10046-0061 Nerve Block In-plane Technique Ultrasound-guided Supraclavicular Nerve Block In-plane Technique: Comparison of Conventional
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
