Suprahyoid and Infrahyoid Neck Overview
|
|
|
- Darrell Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10 Imaging Approaches & Indications Neither CT nor MR is a perfect modality for imaging the extracranial H&N. MR is most useful in the suprahyoid neck (SHN) because it is less affected by oral cavity dental amalgam artifact. The SHN tissue is less affected by motion compared with the infrahyoid neck (IHN); therefore, the MR image quality is not degraded by movement seen in the IHN. Axial and coronal T1 fat-saturated enhanced MR is superior to CECT in defining soft tissue extent of tumor, perineural tumor spread, and dural/intracranial spread. When MR is combined with CT of the facial bones and skull base, a clinician can obtain precise mapping of SHN lesions. CECT is the modality of choice when IHN and mediastinum are imaged. Swallowing, coughing, and breathing makes this area a "moving target" for the imager. MR image quality is often degraded as a result. Multislice CT with multiplanar reformations now permits exquisite images of the IHN unaffected by movement. High-resolution ultrasound also has a role. Superficial lesions, thyroid disease, pediatric neck lesions, and nodal evaluation with biopsy are often best done by ultrasonography. Many indications exist for imaging the extracranial H&N. Exploratory imaging, tumor staging, and abscess search comprise 3 common reasons imaging is ordered in this area. Exploratory imaging, an imaging search for any lesion that may be causing the patient's symptoms, is best completed with CECT from skull base to the clavicles. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCCa) staging is best started with CECT, as both the primary tumor and nodes must be imaged, requiring imaging from the skull base to clavicles. MR imaging times and susceptibility to motion artifact make it a less desirable exam in this setting. Instead, MR is best used when specific delineation of exact tumor extent, perineural spread, or intracranial invasion is needed. When the type and cause of H&N infection are sought, CECT is the best exam. CECT can readily differentiate inflammation from abscess. CT can also identify salivary gland ductal calculi, odontogenic infections, mandible osteomyelitis, and intratonsillar abscess as causes of infection. Imaging Anatomy In discussing the extracranial H&N soft tissues, a few definitions are needed. The SHN is defined as deep facial s above the hyoid bone, including parapharyngeal (PPS), pharyngeal mucosal (PMS), masticator (MS), parotid (PS), carotid (CS), retropharyngeal (RPS), danger (DS), and perivertebral (PVS). The IHN soft tissue s are predominantly below the hyoid bone with some continuing inferiorly into the mediastinum or superiorly into the SHN, including the visceral (VS), posterior cervical (PCS), CS, RPS, and PVS. Important SHN anatomic relationships include their interactions with the skull base, oral cavity, and infrahyoid neck. When one thinks about the SHN s and their relationships with the skull base, perhaps the most important consideration is to examine each alone to see what critical structures (cranial nerves, arteries, veins) are at the point of contact between the and the skull base. Space by, the skull base interactions above and IHN extension below are apparent. PPS has bland triangular skull base abutment without critical foramen involved; it empties inferiorly into submandibular (SMS) PMS touches posterior basisphenoid and anterior basiocciput, including foramen lacerum; PMS includes nasopharyngeal, oropharyngeal, and hypopharyngeal mucosal surfaces MS superior skull base interaction includes zygomatic arch, condylar fossa, skull base, including foramen ovale (CNV3), and foramen spinosum (middle meningeal artery); MS ends at inferior surface of body of mandible PS abuts floor of external auditory canal, mastoid tip, including stylomastoid foramen (CNVII); parotid tail extends inferiorly into posterior SMS CS meets jugular foramen (CNIX-XI) floor, hypoglossal canal (CNXII), and petrous internal carotid artery canal; CS can be followed inferiorly to aortic arch; also called poststyloid parapharyngeal RPS contacts skull base along lower clivus without involvement of critical structures; it continues inferiorly to empty into DS at T3 level PVS touches low clivus, encircles occipital condyles and foramen magnum; PVS continues inferiorly to level into thorax In addition to skull base interactions, the relationships of the SHN s to the fat-filled PPSs are key to analyzing SHN masses. The PPSs are a pair of fat-filled s in the lateral SHN surrounded by the PMS, MS, PS, CS, and RPS. When a mass enlarges in one of these s, it displaces the PPS fat. Larger masses define their of origin based on this displacement pattern. Medial PMS mass displaces PPS laterally More anterior MS mass displaces PPS posteriorly Lateral PS mass displaces PPS medially Posterolateral CS mass displaces styloid process and PPS anteriorly More posteromedial lateral RPS nodal mass displaces PPS anterolaterally The IHN anatomic relationships are defined by their superior and inferior projections. The VS has no SHN, instead projecting only inferiorly into the superior mediastinum. The PCS extends superiorly to the mastoid tip and ends inferiorly at the clavicle. It is predominantly an IHN, however. The CS begins at the floor of jugular foramen and carotid canal and extends inferiorly to the aortic arch. The RPS begins at the ventral clivus superiorly and traverses SHN- IHN to T3 level. The DS is immediately posterior to the RPS but continues beyond T3 level into mediastinum. For imaging purposes, RPS and DS can be considered a single entity. The PVS can be defined from skull base above to clavicle below. The PVS is divided by l slip into prevertebral and paraspinal s. Understanding the deep cervical e (DCF) of the neck can be challenging. However, it is these e that define the very s we use to subdivide neck diseases and construct -specific DDx lists. It is imperative that a clear understanding of these e be grasped by any clinician caring for patients with disease in this area. Many nomenclatures have been used to describe the neck. The following is a practical distillate meant to simplify
2 Common Benign and Malignant Tumors in Spaces of Neck Pharyngeal mucosal Warthin tumor Posterior cervical Pharyngeal SCCa Pharyngeal SCCa nodal metastasis (VA-VB) Tonsillar NHL Glomus vagale paraganglioma NHL nodal disease Masticator Carotid body paraganglioma Differentiated thyroid carcinoma nodes Sarcoma Schwannoma of CNIX-XII Visceral Perineural CNV3 SCCa Retropharyngeal Differentiated thyroid carcinoma Parotid SCCa nodal metastasis Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma Mucoepidermoid carcinoma NHL nodal disease Thyroid NHL Adenoid cystic carcinoma Perivertebral Cervical esophageal carcinoma Malignant nodal metastases Vertebral body systemic metastasis Parathyroid adenoma Benign mixed tumor Brachial plexus schwannoma SCCa = squamous cell carcinoma; NHL = non-hodgkin lymphoma. this challenging subject. There are 3main DCF in the neck. The same names are used in the SHN and IHN. The superficial layer (SL-DCF), the middle layer (ML-DCF), and deep layer of DCF (DL-DCF) are the 3 important in the neck. In the SHN, the SL-DCF circumscribes MS and PS and contributes to the carotid sheath. In the IHN, it "invests" neck by surrounding the infrahyoid strap, sternocleidomastoid, and trapezius muscles, which are derived from the same embryologic origin. It also contributes to the carotid sheath of the CS in the IHN. The ML-DCF in the SHN defines the deep margin of the PMS. It contributes to carotid sheath in both the SHN and IHN. In the IHN, it also circumscribes the VS. In both the SHN and IHN, the DL-DCF surrounds PVS. A slip of DL-DCF dives medially to the transverse process, dividing PVS into prevertebral and paraspinal s. Another slip of DL-DCF, the alar, provides the lateral wall to RPS and DS, as well as the posterior wall to RPS, separating RPS from DS. DL-DCF contributes to carotid sheath, like the SL and ML-DCF. The internal structures of the s of the neck are for the most part responsible for the diseases there. Let us begin by defining the critical contents of the SHN s. PPS contains fat with rare minor salivary glands PMS contains mucosa, lymphatic ring, and minor salivary glands; in nasopharyngeal mucosal, opening of eustachian tube, torus tubarius, adenoids, superior constrictor, and levator palatini muscles can be seen; oropharyngeal mucosal contains anterior and posterior tonsillar pillars, palatine, and lingual tonsils MS includes posterior mandibular body and ramus, TMJ, CNV3, masseter, medial and lateral pterygoid and temporalis muscles, and pterygoid venous plexus PS contains parotid, extracranial CNVII, nodes, retromandibular vein, and external carotid artery CS contains CNIX-XII, internal jugular vein, and internal carotid artery RPS has fat and medial and lateral RPS nodes inside Prevertebral PVS contains vertebral body, veins and arteries, and prevertebral muscles (longus colli and capitis); in paraspinal PVS resides posterior elements of vertebra and paraspinal muscles The critical contents of IHN s are defined next. VS contains thyroid and parathyroid glands, trachea, esophagus, recurrent laryngeal nerves, and pretracheal and paratracheal nodes PCS has fat, CNXI, and level V nodes inside CS houses common carotid artery, internal jugular vein, and CNX IHN RPS has no nodes and contains only fat Prevertebral PVS has brachial plexus and phrenic nerve, vertebral body, veins, arteries, and prevertebral and scalene muscles within; paraspinal PVS contains only posterior vertebra elements and paraspinal muscles Approaches to Imaging Issues in SHN and IHN It is crucial that the clinician has a method of analysis when a mass is found in the neck. In the SHN, mass evaluation methodology begins with defining mass of origin (PMS, MS, PS, CS, lateral RPS). When small, this is simple, as the mass is seen within the confines of one. In larger masses, ask, "How does the mass displace the PPS?" Next, utilize a specific DDx list. Match the imaging findings to the diagnoses within this list to narrow your differential. With IHN masses, a similar evaluation methodology can be employed. First, determine what the mass originates in (VS, CS, PCS). Then, review -specific DDx list. Match radiologic findings of your case to this DDx list. The clinical findings will guide a clinician's differential. Lesions of posterior midline s (RPS and PVS) of the neck need different image evaluation. When a lesion is defined here, 1st ask, "How does mass displace prevertebral muscles (PVM)?" In the case of an RPS mass, PVMs are flattened posteriorly or invaded from anterior to posterior. Contrast this imaging appearance to that of the PVS mass in which the PVMs are lifted anteriorly or invaded from posterior to anterior. Since most PVS lesions arise from vertebral body, vertebral body destruction and epidural disease will be linked. The DL-DCF "forces" PVS disease into the epidural. Selected References 1. Harnsberger HR et al: Differential diagnosis of head and neck lesions based on their of origin. 1. the suprahyoid part of the neck. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 157(1):147-54, Smoker WR et al: Differential diagnosis of head and neck lesions based on their of origin. 2. the infrahyoid portion of the neck. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 157(1):155-9,
3 Buccal, retromaxillary fat pad Masticator Pharyngeal mucosal /surface Retropharyngeal Perivertebral, prevertebral Perivertebral, paraspinal Parapharyngeal Parotid Masseter muscle Temporalis muscle Lateral pterygoid muscle Styloid process Internal jugular vein Internal carotid artery Pharyngeal mucosal /surface Retromaxillary fat pad (buccal ) Masticator Parapharyngeal Parotid 12 (Top) Axial graphic depicts the s of the suprahyoid neck. Surrounding the paired fat-filled parapharyngeal s (PPS) are the 4 critical paired s of this region, the pharyngeal mucosal (PMS), masticator (MS), parotid (PS), and carotid s (CS). Retropharyngeal (RPS) and perivertebral s (PVS) are the midline nonpaired s. A PMS mass pushes the PPS laterally, an MS mass pushes the PPS posteriorly, a PS mass pushes the PPS medially, and a CS mass pushes the PPS anteriorly. Lateral RPS mass pushes PPS anteriorly without lifting styloid process. The superficial (yellow line), middle (pink line), and deep (turquoise line) layers of deep cervical outline the s. (Bottom) Axial CECT at the level of the nasopharyngeal suprahyoid neck shows the 4 key s surrounding the PPS: The PMS, MS, PS, and CS. Notice the retropharyngeal fat stripe is not seen in the high nasopharynx between the prevertebral muscles and the pharyngeal mucosal surface.
4 Submandibular Pharyngeal mucosal /surface Retropharyngeal Danger Alar Masticator Posterior belly, digastric muscle Parapharyngeal Parotid Perivertebral, prevertebral Perivertebral, paraspinal Posterior cervical Platysma muscle Submandibular gland Pharyngeal mucosal Sternocleidomastoid muscle Trapezius muscle Retropharyngeal/danger Jugulodigastric node Parotid (tail) Prevertebral, perivertebral Posterior cervical Perivertebral Paraspinal, perivertebral (Top) Axial graphic shows the suprahyoid neck s at the level of the oropharynx. The superficial (yellow line), middle (pink line), and deep (turquoise line) layers of deep cervical outline the suprahyoid neck s. Notice the lateral borders of the RPS and danger s are called the alar, which represents a slip of the deep layer of deep cervical. The CS has a tricolored l representation for the carotid sheath. This is because all 3 layers of deep cervical contribute to the carotid sheath. (Bottom) In this image, through the low oropharynx, the PMS and the PVS have been outlined. The between them is the RPS. The alar that makes up the lateral borders of the RPS is not shown. 13
5 Anterior cervical Retropharyngeal Danger Visceral Carotid sheath Perivertebral, prevertebral touches transverse process Perivertebral, paraspinal Posterior cervical Cricoid cartilage Platysma muscle Sternocleidomastoid muscle External jugular vein Anterior scalene muscle Middle scalene muscle Esophagus Levator scapulae muscle Trapezius muscle Anterior cervical Thyroid gland Visceral Prevertebral, perivertebral Posterior cervical Paraspinal, perivertebral (Top) Axial graphic depicts the and s of the infrahyoid neck. The 3 layers of deep cervical are present in the suprahyoid and infrahyoid neck. The carotid sheath is made up of all 3 layers of deep cervical (tricolor line around CS). Notice the deep layer (turquoise line) completely circles the PVS, diving in laterally to divide it into prevertebral and paraspinal s. The middle layer (pink line) circumscribes the visceral, while the superficial layer (yellow line) "invests" the neck deep tissues. (Bottom) In this axial CECT, the middle layer of deep cervical is drawn to delineate the margins of the visceral. The visceral contains the high-density thyroid gland, the upper cervical esophagus, and the cricoid cartilage. The CS are lateral to the visceral, while the RPS and PVS are posterior. 14
6 Anteromedial tip, petrous internal carotid artery Zygomatic arch Foramen lacerum Basisphenoid Nasopharyngeal mucosal Suprazygomatic masticator CNV3 in foramen ovale Anterior parotid Parapharyngeal Oropharyngeal mucosal Infrazygomatic masticator Sublingual Submandibular Submandibular Hyoid bone Visceral Trachea Esophagus Retropharyngeal Danger Perivertebral, paraspinal Perivertebral, prevertebral T3 vertebral body Fascial "trap door" (Top) Coronal graphic shows suprahyoid neck s as they interact with the skull base. The MS has the largest area of abutment with the skull base, including CNV3. The PMS abuts the basisphenoid and foramen lacerum. The foramen lacerum is the cartilage-covered floor of the anteromedial petrous internal carotid artery canal. (Bottom) Sagittal graphic depicts longitudinal spatial relationships of the infrahyoid neck. Anteriorly, the visceral is seen surrounded by middle layer of deep cervical (pink line). Just anterior to the vertebral column, the RPS and danger run inferiorly toward the mediastinum. Notice the l "trap door" found at the approximate level of T3 vertebral body that serves as a conduit from the RPS to the danger. RPS infection or tumor may access the mediastinum via this route of spread. 15
Head and Neck Image 頭頸部放射影像學
 Head and Neck Image 頭頸部放射影像學 陳家媛 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 cychen@wanfang.gov.tw Normal Suprahyoid neck: the old way Nasopharynx Oropharynx Oral cavity Staging of SCC Spaces of Suprahyoid Neck: a New Way Deep
Head and Neck Image 頭頸部放射影像學 陳家媛 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 cychen@wanfang.gov.tw Normal Suprahyoid neck: the old way Nasopharynx Oropharynx Oral cavity Staging of SCC Spaces of Suprahyoid Neck: a New Way Deep
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
"The Space Between Us:" A Radiographic Review of Common and Uncommon Pathologic Findings within the Deep Spaces of the Neck
 "The Space Between Us:" A Radiographic Review of Common and Uncommon Pathologic Findings within the Deep Spaces of the Neck Poster No.: C-2457 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. K.
"The Space Between Us:" A Radiographic Review of Common and Uncommon Pathologic Findings within the Deep Spaces of the Neck Poster No.: C-2457 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. K.
The Neck. BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat
 The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Director of Head and Neck Imaging Weill Cornell Medical Center NewYork Presbyterian Hospital
 C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Director of Head and Neck Imaging Weill Cornell Medical Center NewYork Presbyterian Hospital Objectives Review basics of head and neck imaging Discuss our spatial approach
C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Director of Head and Neck Imaging Weill Cornell Medical Center NewYork Presbyterian Hospital Objectives Review basics of head and neck imaging Discuss our spatial approach
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Head & Neck Contouring
 Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
Head&Neck Imaging. ssregypt.com. Parapharyngeal Spaces. Mamdouh mahfouz MD
 Head&Neck Imaging Parapharyngeal Spaces ssregypt.com Mamdouh mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com Definitio n Fat filled triangular space lateral the pharynx Extends from the skull base to the oropharynx Parapharyngeal
Head&Neck Imaging Parapharyngeal Spaces ssregypt.com Mamdouh mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com Definitio n Fat filled triangular space lateral the pharynx Extends from the skull base to the oropharynx Parapharyngeal
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Tympanic Bulla Temporal Bone. Digastric Muscle. Masseter Muscle
 Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
 Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
 CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
The following images were all acquired using a CTI Biograph
 Positron Emission Tomography/ Computed Tomography Imaging of Head and Neck Tumors: An Atlas Michael M. Graham, MD, PhD, and Yusuf Menda, MD Department of Radiology, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA. Address
Positron Emission Tomography/ Computed Tomography Imaging of Head and Neck Tumors: An Atlas Michael M. Graham, MD, PhD, and Yusuf Menda, MD Department of Radiology, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA. Address
Objectives. Thoracic Inlet. Thoracic Inlet Boundaries. Thoracic Inlet Sagittal View ANTERIOR SCALENE ANTERIOR SCALENE
 Objectives Thoracic Inlet Deborah L. Reede M.D. SUNY Downstate Medical Center Learn the anatomy of the thoracic inlet (TI) Review the clinical and radiographic findings of common lesions encountered in
Objectives Thoracic Inlet Deborah L. Reede M.D. SUNY Downstate Medical Center Learn the anatomy of the thoracic inlet (TI) Review the clinical and radiographic findings of common lesions encountered in
Parotid Gland. Parotid Gland. Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible. Medial pterygoid.
 Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 [ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
[ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
THYROID & PARATHYROID. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy
 THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
Chapter 28: The neck. Fascia of the neck
 Chapter 28: The neck Fascia of the neck The superficial fascia is a fatty areolar layer between the skin and the more obvious deep fascia. It contains the platysma muscles and the external jugular veins
Chapter 28: The neck Fascia of the neck The superficial fascia is a fatty areolar layer between the skin and the more obvious deep fascia. It contains the platysma muscles and the external jugular veins
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5)
 Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
General Anatomic Layout
 General Anatomic Layout 2 Core Messages At the start of the dissection exercise, we must take a panoramic look for orientation. We then establish the limits of the area of operation and the main landmarks.
General Anatomic Layout 2 Core Messages At the start of the dissection exercise, we must take a panoramic look for orientation. We then establish the limits of the area of operation and the main landmarks.
PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY
 PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY-
 TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
Salivary ultrasound. Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK
 Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
Head & Neck Radiology (I) Waseem Jerjes
 Head & Neck Radiology (I) Waseem Jerjes Lamboid Suture Frontal Sinus Left Orbit (roof) Left Supraorbital Margin Left Frontozygomatic Suture Left Superior Orbital Fissure Rt Petrous Ridge of Temporal Bone
Head & Neck Radiology (I) Waseem Jerjes Lamboid Suture Frontal Sinus Left Orbit (roof) Left Supraorbital Margin Left Frontozygomatic Suture Left Superior Orbital Fissure Rt Petrous Ridge of Temporal Bone
Lecture 01. The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018
 Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland
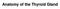 Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Introduction Nomenclature G, thyreos= shield, eidos= like Location Root of the neck ventrally (C5-T1) Function endocrine gland that secretes: Thyroxine (T4) T3 Calcitonin LWW,
Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Introduction Nomenclature G, thyreos= shield, eidos= like Location Root of the neck ventrally (C5-T1) Function endocrine gland that secretes: Thyroxine (T4) T3 Calcitonin LWW,
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Anatomy 2. Parotid bed (V.imp): meaning that gland is sleeping on structures and they are:
 Anatomy 2 Parotid Gland: "refer to previous sheet for extra details." Its pyramidal in shape, apex is toward pharynx. Its Medial surface is divided into Anterio-medial and posterio-medial and its posterio-medial
Anatomy 2 Parotid Gland: "refer to previous sheet for extra details." Its pyramidal in shape, apex is toward pharynx. Its Medial surface is divided into Anterio-medial and posterio-medial and its posterio-medial
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus.
 THYROID GLAND 1 Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus. A small pyramidal lobe projects upwards from the left lobe in 40% of cases. The
THYROID GLAND 1 Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus. A small pyramidal lobe projects upwards from the left lobe in 40% of cases. The
Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group. Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer. Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i & 11-1C-106i
 Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Spine and Neck
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
A pictorial review of the Benign and Malignant Conditions involving the Salivary Glands and Oral Cavity.
 A pictorial review of the Benign and Malignant Conditions involving the Salivary Glands and Oral Cavity. Poster No.: C-2266 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Lavelle, J. F. Gerstenmaier,
A pictorial review of the Benign and Malignant Conditions involving the Salivary Glands and Oral Cavity. Poster No.: C-2266 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Lavelle, J. F. Gerstenmaier,
Clinical evaluation. Imaging Surgical treatment
 Parapharyngeal Space Khalid adhussain AL-Qahtani a MD,MSc,FRCS(c) Assistant Professor Consultant of Otolaryngology Advance Head & Neck Oncology, Thyroid & Parathyroid,Microvascular Reconstruction, ti and
Parapharyngeal Space Khalid adhussain AL-Qahtani a MD,MSc,FRCS(c) Assistant Professor Consultant of Otolaryngology Advance Head & Neck Oncology, Thyroid & Parathyroid,Microvascular Reconstruction, ti and
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck. M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick. Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974.
 Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve. The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions
 Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory fibers to the skin of the clavicular area
 YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY WRITTEN EXAM 2 -- October 10, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Each of the following statements is CORRECT EXCEPT: A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory
YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY WRITTEN EXAM 2 -- October 10, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Each of the following statements is CORRECT EXCEPT: A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Downloaded from by on 02/06/18 from IP address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.205.55 on 02/06/18 from IP address 46.3.205.55. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Imaging of Parapharyngeal Space Lesions: Focus on the
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.205.55 on 02/06/18 from IP address 46.3.205.55. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Imaging of Parapharyngeal Space Lesions: Focus on the
Mohammad Mohtaseb. Nour Hussein. Faisal Nimri
 2 Mohammad Mohtaseb Nour Hussein Faisal Nimri Muscles of the tongue The tongue is a muscular organ and contains intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. The intrinsic muscle contains vertical, oblique, and transverse
2 Mohammad Mohtaseb Nour Hussein Faisal Nimri Muscles of the tongue The tongue is a muscular organ and contains intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. The intrinsic muscle contains vertical, oblique, and transverse
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
HEAD & NECK ANATOMY - MCQ HEAD & NECK ANATOMY
 . ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
. ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
The importance of knowing the lymphatic spread patterns of head and neck cancer for accurate nodal staging on CT: A practical schematic guide
 The importance of knowing the lymphatic spread patterns of head and neck cancer for accurate nodal staging on CT: A practical schematic guide Alba L. Reyes Ortiz, MD Elena Capilla, MD. Lina Cruz Hernández,
The importance of knowing the lymphatic spread patterns of head and neck cancer for accurate nodal staging on CT: A practical schematic guide Alba L. Reyes Ortiz, MD Elena Capilla, MD. Lina Cruz Hernández,
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR
 Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR. Assignment: Head to Toe Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
 Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Thyroid gland. importance. relations and connections. external laryngeal nerves. malformations.
 Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
Bones of the Skull Lateral View
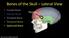 Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
Tumours of Parapharyngeal space
 Tumours of Parapharyngeal space The parapharyngeal spaces (PPS), as the name implies, lie laterally on either side of the pharynx. They are potential spaces, filled with fat and areolar tissue containing
Tumours of Parapharyngeal space The parapharyngeal spaces (PPS), as the name implies, lie laterally on either side of the pharynx. They are potential spaces, filled with fat and areolar tissue containing
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th edition. Lip and Oral Cavity Oropharynx (p16 -) and Hypopharynx Larynx
 AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th edition Lip and Oral Cavity Oropharynx (p16 -) and Hypopharynx Larynx AJCC 7 th edition Lip and Oral cavity Pharynx Larynx KEY CHANGES Skin of head and neck (Vermilion of the lip)
AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th edition Lip and Oral Cavity Oropharynx (p16 -) and Hypopharynx Larynx AJCC 7 th edition Lip and Oral cavity Pharynx Larynx KEY CHANGES Skin of head and neck (Vermilion of the lip)
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD
 Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
The PHARYNX. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D
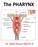 The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
Thyroid INTRODUCTION ANATOMY SUMMARY OF CHANGES
 AJC 7/14/06 1:19 PM Page 67 Thyroid C73.9 Thyroid gland SUMMARY OF CHANGES Tumor staging (T) has been revised and the categories redefined. T4 is now divided into T4a and T4b. Nodal staging (N) has been
AJC 7/14/06 1:19 PM Page 67 Thyroid C73.9 Thyroid gland SUMMARY OF CHANGES Tumor staging (T) has been revised and the categories redefined. T4 is now divided into T4a and T4b. Nodal staging (N) has been
Over the past 18 years, numerous classifications have been proposed to distinguish
 ORGNAL ARTCLE An maging-based Classification for the Cervical Nodes Designed as an Adjunct to Recent Clinically Based Nodal Classifications Peter M. Som, MD; Hugh D. Curtin, MD; Anthony A. Mancuso, MD
ORGNAL ARTCLE An maging-based Classification for the Cervical Nodes Designed as an Adjunct to Recent Clinically Based Nodal Classifications Peter M. Som, MD; Hugh D. Curtin, MD; Anthony A. Mancuso, MD
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy. Raleigh E. Lingeman
 Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy Raleigh E. Lingeman Surgeons doing head and neck surgery must first master the surgical anatomy and technique of doing neck dissection. Neck dissection is either the classic
Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy Raleigh E. Lingeman Surgeons doing head and neck surgery must first master the surgical anatomy and technique of doing neck dissection. Neck dissection is either the classic
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Lips and labial mucosa
 Lips and labial mucosa External portion of the lips: the vermilion border and the skin Vermilion border : the exposed red portion of the lip, covered by mucous membrane, no mucous glands Boundary: the
Lips and labial mucosa External portion of the lips: the vermilion border and the skin Vermilion border : the exposed red portion of the lip, covered by mucous membrane, no mucous glands Boundary: the
Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies. No Disclosures or Conflicts of Interest. Anatomy 10/4/2013
 Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies Daniel G. Deschler, MD Director: Division of Head and Neck Surgery Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary Massachusetts General Hospital Professor Harvard Medical School
Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies Daniel G. Deschler, MD Director: Division of Head and Neck Surgery Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary Massachusetts General Hospital Professor Harvard Medical School
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Neck of Condylar. Process. Anterior Border of Ramus. Mandibular. Foramen. Posterior Border of Ramus Incisive Fossa.
 Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
The Far Lateral Approach to Skull Base: in the Context of Head and Neck Cancer
 Review article The Far Lateral Approach to Skull Base: in the Context of Head and Neck Cancer 1Dr. Jaspreet Singh Badwal, 2 Dr. Upkardeep Singh, 3 Dr. Neha Bharti, 4 Dr.Shivani Garg, 5 Dr.Simarpreet Singh
Review article The Far Lateral Approach to Skull Base: in the Context of Head and Neck Cancer 1Dr. Jaspreet Singh Badwal, 2 Dr. Upkardeep Singh, 3 Dr. Neha Bharti, 4 Dr.Shivani Garg, 5 Dr.Simarpreet Singh
Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Since the first description of the radical neck dissection by George Crile almost a century
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neck Dissection Classification Update Revisions Proposed by the American Head and Neck Society and the American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery K. Thomas Robbins, MD; Garry
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neck Dissection Classification Update Revisions Proposed by the American Head and Neck Society and the American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery K. Thomas Robbins, MD; Garry
STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP STEP 3 SEPARATE PAROTID GLAND FROM SCM STEP 2 IDENTIFICATON OF GREAT AURICULAR NERVE
 STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP Create a modified Blair Figure 1 or facelift incision. Figure 2 Raise a superficial cervico-fascial flap between the Superficial Musculo Aponeurotic System (SMAS)
STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP Create a modified Blair Figure 1 or facelift incision. Figure 2 Raise a superficial cervico-fascial flap between the Superficial Musculo Aponeurotic System (SMAS)
Case Studies in the Skull Base
 Case Studies in the Skull Base Amy C Tsai, MD Neuroradiology Fellow Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah, USA No disclosures related
Case Studies in the Skull Base Amy C Tsai, MD Neuroradiology Fellow Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah, USA No disclosures related
Q&A. Fabulous Prizes. Collecting Cancer Data: Pharynx 12/6/12. NAACCR Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data Pharynx
 Collecting Cancer Data Pharynx NAACCR 2012 2013 Webinar Series Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
Collecting Cancer Data Pharynx NAACCR 2012 2013 Webinar Series Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
University of Palestine. Final Exam 1 st Semester 2014/2015 Total Grade: 60
 Question One: MCQ: 1- The coronal suture joins the a) frontal and parietal bones. b) left and right parietal bones. c) parietal and occipital bones. d) parietal, squamous temporal and greater wing of the
Question One: MCQ: 1- The coronal suture joins the a) frontal and parietal bones. b) left and right parietal bones. c) parietal and occipital bones. d) parietal, squamous temporal and greater wing of the
- Reem Akiely. -Wardeh Al-Swalmeh. - Mohammad Al-Muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 -2 - Reem Akiely -Wardeh Al-Swalmeh - Mohammad Al-Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The palate: * Hard palate * Soft palate the Uvula: is a muscular structure present In the midline of the soft palate (اللهاة) The Hard
-2 - Reem Akiely -Wardeh Al-Swalmeh - Mohammad Al-Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The palate: * Hard palate * Soft palate the Uvula: is a muscular structure present In the midline of the soft palate (اللهاة) The Hard
