Risk Factors That Predispose Patients to Orofacial Pain
|
|
|
- Quentin Carpenter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Risk Factors That Predispose Patients to Orofacial Pain Paul Durham, PhD Distinguished Professor of Cell Biology Director Center for Biomedical & Life Sciences Missouri State University
2 Cluster Headache Migraine TMJ Disorders Allergic Rhinitis Tooth Ache Trigeminal Neuralgia
3 Trigeminal Nerve and Ganglion
4 Trigeminal Ganglion Nerves and Cellular Organization Functional Units Comprised of Neurons and Satellite Glial Cells DAPI Trigeminal Ganglia Ophthalmic Maxillary Mandibular Copyright Gary Carlson. All rights reserved μm 50µm
5 Pseudo-unipolar Neuron Trigeminal Ganglion - Comprised of Neurons and Glia Cell Body Periphery > 90% of cells are glia - glue or slime 2 types of glia in ganglion: 1. Schwann cells - produce myelin 2. Satellite cells - release cytokines - modulate neuronal excitability and activation threshold CNS diseases: - involved in all stages of inflammation & pain - involved in allodynia hyperalgesia CNS
6 Functional Units: Neuronal Cell Bodies and Associated Satellite Glia Cells NF-200 K ir 4.1 DAPI Merged 50 µm
7 Glial Cells Overview Function of Glial Cells Glial cells monitor environment around neurons Decrease excitatory molecules Modulate state of neuronal excitability When glial cells are abnormally activated: release many inflammatory molecules Lower activation threshold cause sensitization Contribute to hyperalgesia and potentially chronic pain CGRP involved in initiating this nociceptive cascade 50µm
8 Neuronal-Glial Cell Interactions in Pain Glial Cells of Peripheral and Central Nervous Systems Role in sensitization/nociception Peripheral Glial Cells (Trigeminal Ganglion) Satellite Glial Cells Central Glial Cells (TNC and other regions of spinal cord and brain) Astrocytes and Microglia Meninges Peripheral sensitization activation of satellite glial cells Trigeminal ganglion neuron Persistent central sensitization and chronic pain are associated with activation of astrocytes and microglia Satellite Glial Cells TNC Astrocytes Microglia
9 Increased S100B Expression in Trigeminal Ganglion Neurons and Glia in Response to Capsaicin S100B: A B Calcium binding protein Expressed in both neurons and glia Secreted role in inflammation Control Capsaicin Capsaicin in TMJ capsule - 2 hrs Thalakoti et al., Headache, 2007 Marker of disease C D E DAPI S100B Merged
10 Trigeminal Neurons and Satellite Glial Cells: Pathway for Pain Transmission Trigeminal Ganglion Neuron Meninges Satellite Glial Cells Orofacial Tissues TMJ and Associated Muscles Trigeminal Nucleus
11 Migraine-TMD-TN Pathology - Increased Expression of Pro-Inflammatory/Nociceptive Signaling Molecules and Increased Neuron-Satellite Glial Cell Communication Tissue Injury Neuronal Cell Body TMJ Muscle Meninges IL-1b, IL-6, NGF PG, ATP, NO Activation/Sensitization of primary afferents Neuropeptide Release Cell Body Trigeminal Neuron Satellite Glia Trigeminal Nucleus Activation of Neurons Astrocytes Microglia Pain
12 Neuronal-Glial Cell Interactions: Possible Role in Initiation and Maintenance of Peripheral Sensitization and Priming Neuronal activation Gap Junctional Communication Release of inflammatory mediators Inflammatory Cycle Initial Glial activation V3 V1 Cytokines, S100B,NO Spreading of Glial activation (via gap junctions, CGRP) Durham, 2016
13 Trigeminal Nerve Pathologies High Comorbidity Increased neuron-glia signaling in ganglion (convergence) may provide explanation for this clinical observation Migraine (V1 activation) Trigeminal Neuralgia Rhinosinusitis (V2 activation) Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMD; V3 activation)
14 Migraine-TMD-TN Pathology Key Role of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) Tissue Injury Neuronal Cell Body TMJ Muscle Meninges IL-1b, IL-6, NGF PG, ATP, NO Activation/Sensitization of primary afferents CGRP Neuropeptide Release CGRP Cell Body Trigeminal Neuron Satellite Glia Trigeminal Nucleus Pain CGRP Activation of Neurons Astrocytes Microglia
15 Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Mechanism for Promoting Neuronal Sensitization PKA = Protein Kinase A Key role In lowering activation threshold of neurons Blocking CGRP receptor activity inhibits trigeminal activation and sensitization
16 CGRP Release from Neuronal Cell Body Promotes Peripheral Sensitization by Initiating an Inflammatory Loop Trigeminal Ganglion CGRP Gene Cytokines NO Glial Cell inos CGRP Receptor CGRP Neuronal Cell
17 Durham, Masterson Headache (1):67-80
18 Durham, Masterson Headache (1):67-80
19 Summary and Conclusion Our results provide evidence of two distinct mechanisms involved in mediating the stimulated release of CGRP from trigeminal neurons One mechanism occurs via a calcium dependent mechanism that is blocked by the anti-migraine drugs rizatriptan and BoNT-A, while the other mechanism likely involves proton activation of ASICs and increases in intracellular sodium that was not repressed by Rizatriptan or BoNT-A Taken together, our findings provide evidence for a novel mechanism of calcium-independent CGRP release in response to protons that is not blocked by commonly used anti-migraine medications. (Amiloride) Durham and Masterson Headache (2013) Jan;53(1):67-80
20 Neuronal Sensitization and Orofacial Pain TG Activation PAIN Sensitization = Lower threshold of activation Peripheral Sensitization TMJ Ganglion TNC Central Sensitization
21 Migraine and TMD Pathology Can Central Sensitization Promote Peripheral Sensitization? Neuronal Cell Body Central Sensitization Activation/Sensitization of Primary Afferents Cell Body Satellite Glia TMJ or Muscle Dura Trigeminal Neuron Trigeminal Nucleus Activation Of Second Order Neurons Glia Cells
22 CGRP and Receptor Protein RAMP1 are Abundantly Expressed in Medullary Dorsal Horn CGRP RAMP1
23 Can Elevated Levels of CGRP That Mediate Central Sensitization Also Promote Peripheral Sensitization? Trigeminal Ganglion Neuron Nociceptor Terminal Satellite Glial Cells CGRP 500 nm Trigeminal Nucleus
24 Sensitization to Mechanical Stimuli Behavior Experimental Timeline UGO Basile Durham Rat Holder Testing begins Days 1-3 Rest Day 0 Day 1 von Frey test Day 2 Day 3 von Frey test + euthanasia Acclimations Days 4-5 Basal von Frey test Injections + 2 hr von Frey test Day 1 Day 2 von Frey test Day 3
25 Average Number of Nocifensive Responses to 100 g Force (out of 5 applications) CGRP Increases Number of Nocifensive Withdrawal Responses at 2, 24, and 48 Hours Post Injection - Resolution at 72 Hours * * * 0 Basal 2hr D1 D2 D3 Naïve (n=10) IT Saline (n=11) IT CGRP (n=13)
26 Does Bidirectional Signaling Occur in the Trigeminal System? Does CGRP Promote Increased Neuron-Glia Communication in Trigeminal Ganglion Nociceptor Terminal Satellite Glial Cells CGRP Fast Blue Trigeminal Nucleus
27 DAPI Fast Blue is Retrogradely Transported to Cell Body of Trigeminal Neurons and Associated Satellite Glia V1 V2 V3 50 µm 25 µm Enlarged image showing neurons surrounded by satellite glia cells 1000 μm Longitudinal section from rat trigeminal ganglion showing neuronal bands Image showing Fast Blue labeled neurons (vertical arrows) and surrounding satellite glia cells (horizontal arrows)
28 Evidence CGRP Can Promote Peripheral Sensitization Development of a Hypervigilant Trigeminal System CGRP Neuronal Cell Body Central Sensitization Activation/Sensitization of Primary Afferents Cell Body Satellite Glia TMJ or Muscle Dura Cornelison, Hawkins, Durham 2016 Trigeminal Neuron Trigeminal Nucleus Activation of Neurons Astrocytes Microglia
29 Hypervigilant Nervous System Genetic Predisposition and Environmental (Epigenetic) Factors Genetic hyperexcitability Between episodes of migraine During episodes of migraine
30 Risk Factors for Developing TMD Prolonged Opening Neck Muscle Pathology Female Gender NIH funded OPPERA Study
31 Prolonged Opening Promotes Sensitization of Trigeminal Nociceptive Neurons
32 TMD Pathology Involves Activation of Trigeminal System Central Sensitization Hyperalgesia Prolonged Opening Cytokine and MAPK Inflammatory Loop Cell Body Neuronal Cell Body Satellite Glia Cytokine and MAPK Inflammatory Loop TMJ/ Masseter Dysfunction STN Hawkins and Durham J Oral Facial Pain Headache Activation/Sensitization of Primary Afferents Activation/Sensitization of Second Order Neurons and Glia
33 A B C D
34 Protracted Opening Results in a Prolonged Increase in Nocifensive Head Withdrawal Responses to Mechanical Stimulation of V3 Region 5 Average Number of Nocifensive Responses to 100 g Force (Out of 5) Baseline Basal 2hr D3 D7 Naïve (n=10) 100% Opening (n=10) Hawkins and Durham, J Oral Facial Pain Headache 2016
35 Muscle Pathology Leads to Cellular Changes in Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus and Trigeminal Ganglia Sensitization of Trigeminal Nociceptors
36 Neck and Shoulder Muscles Role in TMD Pathology Stress is often cited as trigger of migraine and TMD Stress can manifest as tension in the muscles in the head, face, neck, and shoulders Many TMD sufferers report muscle pain or sensitivity in their head and neck muscles during an attack Trapezius Muscle - common site of neck muscle tension Innervated by C2/C4 DRG that project to laminas I-IV Convergence of sensory stimuli in upper spinal cord
37 Model of Neck Muscle Inflammation and Trigeminal Sensitization Peripheral Sensitization Central Sensitization Muscle inflammation - To test the hypothesis that activation of neurons that provide sensory innervation of the trapezius muscle promote cellular changes in the spinal trigeminal nucleus and trigeminal ganglia implicated in the development of central and peripheral sensitization of trigeminal neurons.
38 Inflammation in Trapezius Muscle Promotes Prolonged Sensitization of Trigeminal Nociceptive Neurons Average Number of Responses (out of 5) Hawkins et al. J of Orofacial Pain, Control CFA 1 0 Baseline Day 1 Day 7 Day 14
39 Pathology in the Neck Muscles Promotes Cellular Changes Associated with Sensitization of the Trigeminal System: A Potential Risk Factor for Migraine and TMD Trigeminal Nociceptor Sensitization CGRP TG STN DRG C2/C4 Trapezius Muscles (Inflammation)
40 Sensitization of Trigeminal Nociceptive Neurons in Response to Prolonged Neck Muscle Inflammation: Risk for TMD and Migraine Pathology
41 Risk Factors and Trigeminal Sensitization Peripheral Sensitization Headache Tree Extract Central Sensitization Neck Muscle Inflammation - Test the hypothesis that sensitization of the trigeminal system prior to activation of TRPA1 receptors by a pungent odor is sufficient to cause nociception and allodynia.
42 Neck Muscle Inflammation Promotes Sensitization of Trigeminal Nociceptors Injection Sites of CFA 2. Sensitization of Spinal Neurons and Glia x x x x x x xx UGO Basile Durham Rat Holder 3. Sensitization of TG Peripheral Nociceptors 1. Sensitization of DRG Peripheral Nociceptors Injection of 10 µl of complete Freund s adjuvant (CFA) in 10 different sites -- heat killed bacteria -- promotes inflammation
43 Nocifensive Responses (out of 5) Minor Neck Muscle A Inflammation Does Not Cause Nociception V V Basal D1 D4 D8 Naïve (n = 9) Saline Muscle (n = 7) CFA Muscle (n = 11)
44 Neck Muscle Inflammation Promotes Increased PKA Expression Naive D1 D4 D8 Evidence of sensitized neurons in spinal cord Lower activation threshold to other stimuli Risk factor for orofacial pain Naïve (n = 3) D1 Post CFA (n = 3) D4 Post CFA (n = 3) D8 Post CFA (n = 3) 1.00 ± ± ± ± 0.10 P = P = P = 0.001
45 Activation of Trigeminal Nerves Via TRPA1: Headache Tree Extract Umbellularia californica Umbellulone Nassini (Geppetti), Brain 2012 Pungent Odors: Trigger for migraine
46 Experimental Design Induction of Muscle Inflammation (Risk Factor) - Complete Freund s adjuvant (CFA) CBL Exposure California Bay Leaf (CBL) Oil Exposure (Trigger) - Oil extract from leaves of the Umbellularia californica tree that acts on TRPA1 receptors in the trigeminovascular system upon inhalation Mechanical Nociception Mechanical Nociception - UGO Basile Durham Rat Holder and von Frey filaments
47 Nocifensive Responses (out of 5) Minor Neck Muscle A Inflammation Promotes Sensitization of Trigeminal Neurons: Activation with Pungent Odor V V3 * # * # Basal D8 2hr Post CBL Naïve + CBL (n = 10) Saline Muscle + CBL (n = 7) CFA Muscle + CBL (n = 15)
48 Risk Factors and Trigeminal Sensitization Peripheral Sensitization Central Sensitization Prolonged Opening Neck Muscle Inflammation - Test the hypothesis that sensitization of the trigeminal system prior to prolonged jaw opening is sufficient to cause chronic nociception (pain) and allodynia.
49 TMD Pathology Involves Activation of Trigeminal System Central Sensitization Hyperalgesia/Allodynia Prolonged Opening Cytokine and MAPK Inflammatory Loop Cell Body Neuronal Cell Body Satellite Glia Cytokine and MAPK Inflammatory Loop TMJ/ Masseter Dysfunction Activation/Sensitization of Primary Afferents Sensitization of Second Order Neurons and Glia STN Neck Muscle Inflammation
50 Novel Model of TMD Pathology to Study Role of Risk Factors - Female Gender and Neck Muscle Inflammation CFA model: All injections were performed under 5% isoflurane Injection Sites of CFA Muscle inflammation: 100 microliter total of complete Freund s adjuvant (CFA) was injected into the neck muscle bilaterally at ten different areas x x x x x xx CFA is a composed of inactivated and dried mycobacteria (usually M. tuberculosis) Naïve animals did not receive any treatment
51 Novel Model of TMD Pathology to Study Role of Risk Factors - Prolonged Near Maximal Opening opening: A mouth retractor is placed in between the upper and lower incisors and the retractor arms were then separated till the desired amount is reached. It is measured with the help of Vernier calipers Animals were under 3% isoflurane for 20 mins Maximum opening in males is 22 mm Maximum opening in females is 20 mm
52 D0 D8 Timeline Acclimations Basal von Frey+ Muscle Injection D8 von Frey Reading + Opening 2 hr Post Opening D1 D3 D5 D7 D14 D21 D28 D1-3
53 Scoring of Nocifensive Response Normal/Mild: 0-2 Moderate: 2 4 Severe: 4 6 Unresponsive to mechanical stimulation (most severe pain state): Some animals went into a unresponsive state where no nocifensive withdrawal was observed even to the 180 g filaments These animals were given a score of 6
54 Prolonged Opening In Sensitized Animals Leads to Sustained Allodynia Over Masseter Region -- Males Severe 4 to 6 * * * * * Moderate 2 to 4 * Normal/ Mild 0 to 2 Basal D8 Pre- 2hr Post D1 Post D3 Post D5 Post D7 Post D14 Post D21 Post D28 Post
55 Prolonged Opening In Sensitized Animals Leads to Sustained Allodynia Over Masseter Region -- Females Severe 4 to 6 * * * * * * Moderate 2 to 4 Normal/ Mild 0 to 2 Basal D8 Pre- 2hr Post D1 Post D3 Post D5 Post D7 Post D14 Post D21 Post D28 Post
56 Summary - Neck Muscle Pathology and Prolonged Opening Males Females * * * * * * * * * * Naïve(n=8) M+J(n=9) M(n=9) J(n=8) * * * * * Basal D8 Pre- 2hr Post D1 Post D3 Post D5 Post D7 Post D14 Post D21 Post D28 Post Basal D8 Pre- 2hr Post D1 Post D3 Post D5 Post D7 Post D14 Post D21 Post D28 Post Severe 4 to 6 Moderate 2 to 4 Normal/ Mild 0 to 2
57 Summary of Risk Factors Involved in Promoting Transition from Acute to Chronic Pain States 1. An existing orofacial pain condition high comorbidity 2. Increased levels of CGRP in STN (nicotine, early life stress) 3. Neck muscle inflammation 4. Prolonged jaw opening 5. Female gender 6. Sleep deprivation Multiple risk factors increase likelihood of developing a maladaptive chronic pain state
58 CBLS LAB
Impact of Sleep Deprivation Stress in Promoting Sensitization of the Trigeminal System
 Impact of Sleep Deprivation Stress in Promoting Sensitization of the Trigeminal System Functions of Sleep Fatigue reversal - allows individual to recover and reenergize Biochemical refreshment - promotes
Impact of Sleep Deprivation Stress in Promoting Sensitization of the Trigeminal System Functions of Sleep Fatigue reversal - allows individual to recover and reenergize Biochemical refreshment - promotes
Epigenetics Role in Pain Chronification
 Epigenetics Role in Pain Chronification Evolution of Migraine in Adults Fortunately most people have episodic migraine Most self-manage migraine Gender distribution changes to approximately 6:1 (F:M) for
Epigenetics Role in Pain Chronification Evolution of Migraine in Adults Fortunately most people have episodic migraine Most self-manage migraine Gender distribution changes to approximately 6:1 (F:M) for
Clinically Relevant Model of Temporomandibular Disorder
 BearWorks Institutional Repository MSU Graduate Theses Spring 2017 Clinically Relevant Model of Temporomandibular Disorder Neelima Chelliboina As with any intellectual project, the content and views expressed
BearWorks Institutional Repository MSU Graduate Theses Spring 2017 Clinically Relevant Model of Temporomandibular Disorder Neelima Chelliboina As with any intellectual project, the content and views expressed
Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Good for Other Head and Face Pain? Disclosures BoNT/A for non- CM Botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) in clinical use for headache >20
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Good for Other Head and Face Pain? Disclosures BoNT/A for non- CM Botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) in clinical use for headache >20 years Efficacy of BoNT type A (onabotulinumtoxina,
1 2 3 4 5 6 Is OnabotulinumtoxinA Good for Other Head and Face Pain? Disclosures BoNT/A for non- CM Botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) in clinical use for headache >20 years Efficacy of BoNT type A (onabotulinumtoxina,
Virtually everyone has experienced pain in one
 Transfer of Advances in Sciences into Dental Education Recent Insights into Brainstem Mechanisms Underlying Craniofacial Pain Barry J. Sessle, B.D.S., M.D.S., B.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.S.C., D.Sc. (honorary) Abstract:
Transfer of Advances in Sciences into Dental Education Recent Insights into Brainstem Mechanisms Underlying Craniofacial Pain Barry J. Sessle, B.D.S., M.D.S., B.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.S.C., D.Sc. (honorary) Abstract:
Investigation of Nocifensive and Cellular Effects of Dihydroergotamine in a Model of Chronic Migraine
 BearWorks Institutional Repository MSU Graduate Theses Summer 2015 Investigation of Nocifensive and Cellular Effects of Dihydroergotamine in a Model of Chronic Migraine Jennifer Elise Denson As with any
BearWorks Institutional Repository MSU Graduate Theses Summer 2015 Investigation of Nocifensive and Cellular Effects of Dihydroergotamine in a Model of Chronic Migraine Jennifer Elise Denson As with any
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 The human body contains different types of tissue. The tissue is formed into organs and organ systems.
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 The human body contains different types of tissue. The tissue is formed into organs and organ systems.
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor
 Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
NURSE-UP INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Body s primary communication and control system. Integrates and regulates body function Collects information specialized nervous
NURSE-UP INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Body s primary communication and control system. Integrates and regulates body function Collects information specialized nervous
Chapter 7. The Nervous System
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System General overview of the nervous system functions Sensory input (info travels in along afferent pathways) Integration (information is processed) Sensory neurons Spinal cord
Chapter 7 The Nervous System General overview of the nervous system functions Sensory input (info travels in along afferent pathways) Integration (information is processed) Sensory neurons Spinal cord
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
Man and his environment
 Man and his environment Dr. Elriah M. Makie 0122858517 Nervous Tissue BSc.M.Sc.MBBS Introduction The nervous system is divided into two main parts: The central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain
Man and his environment Dr. Elriah M. Makie 0122858517 Nervous Tissue BSc.M.Sc.MBBS Introduction The nervous system is divided into two main parts: The central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain
Cells of the Nervous System
 Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch
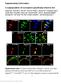 Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Seizure: the clinical manifestation of an abnormal and excessive excitation and synchronization of a population of cortical
 Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
10.1: Introduction. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial cells) Dendrites.
 10.1: Introduction Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial
10.1: Introduction Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Cancer-induced bone pain
 Cancer-induced bone pain Common Prevalent in particular cancers: breast (73%), prostate (68%), thyroid (42%), lung (36%), renal (35%), colon (5%) Correlates with an increased morbidity Reduced performance
Cancer-induced bone pain Common Prevalent in particular cancers: breast (73%), prostate (68%), thyroid (42%), lung (36%), renal (35%), colon (5%) Correlates with an increased morbidity Reduced performance
Sensory coding and somatosensory system
 Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Outline. Animals: Nervous system. Neuron and connection of neurons. Key Concepts:
 Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
Modulation of TRP channels by resolvins in mouse and human
 July 9, 2015, Ion Channel Retreat, Vancouver Ion Channel and Pain Targets Modulation of TRP channels by resolvins in mouse and human Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Pain Research Division Department of Anesthesiology
July 9, 2015, Ion Channel Retreat, Vancouver Ion Channel and Pain Targets Modulation of TRP channels by resolvins in mouse and human Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Pain Research Division Department of Anesthesiology
The Nervous System 7PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART A Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART A Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor
The Nervous System PART A
 7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
Embriologically, The head is formed from the first two cervical segments (except the mandible, which is formed by the third). The first and second
 Embriologically, The head is formed from the first two cervical segments (except the mandible, which is formed by the third). The first and second cervical vertebra are also derived from these two segments.
Embriologically, The head is formed from the first two cervical segments (except the mandible, which is formed by the third). The first and second cervical vertebra are also derived from these two segments.
The biochemical origin of pain: The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response: Inflammatory profile of pain syndromes
 The biochemical origin of pain: The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response: Inflammatory profile of pain syndromes 1 Medical Hypothesis 2007, Vol. 69, pp. 1169 1178 Sota Omoigui
The biochemical origin of pain: The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response: Inflammatory profile of pain syndromes 1 Medical Hypothesis 2007, Vol. 69, pp. 1169 1178 Sota Omoigui
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Nervous Tissue. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Nervous Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with
Nervous Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with
211MDS Pain theories
 211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Meyers' A&P February 15, Unit 7. The Nervous System. I. Functions of the Nervous System. Monitors body's internal and external enviornments
 Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
Outline. Neuron Structure. Week 4 - Nervous System. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses
 Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Spinal Cord Injury Pain. Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018
 Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a function of the nervous system? A) sense the internal and external environments B) integrate sensory
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a function of the nervous system? A) sense the internal and external environments B) integrate sensory
Functions of Nervous System Neuron Structure
 Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Pearson Education, Inc.
 13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Warm-Up. Label the parts of the neuron below.
 Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT
 PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
The Nervous System. Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine.
 The Nervous System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine Http://10.10.10.151 Part 1. Summary of the nervous system The Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain + Spinal Cord Peripheral
The Nervous System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine Http://10.10.10.151 Part 1. Summary of the nervous system The Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain + Spinal Cord Peripheral
Introduction to Nervous Tissue
 Introduction to Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Human Histology The Nervous System. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system)
 Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
Index. Dent Clin N Am 51 (2007) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Dent Clin N Am 51 (2007) 275 279 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acupuncture, in persistent facial pain, 269 270 Analgesic systems, sex differences in, 6 8 Anticholinergic
Dent Clin N Am 51 (2007) 275 279 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acupuncture, in persistent facial pain, 269 270 Analgesic systems, sex differences in, 6 8 Anticholinergic
浙江大学医学院基础医学整合课程 各论 III. The Nervous System. Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine
 The Nervous System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine xiongzhang@zju.edu.cn http://10.202.77.12/ 1 Part 1. Summary of the nervous system 2 The Nervous System Central Nervous System
The Nervous System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine xiongzhang@zju.edu.cn http://10.202.77.12/ 1 Part 1. Summary of the nervous system 2 The Nervous System Central Nervous System
! BIOL 2401! Week 5. Nervous System. Nervous System
 Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Chapter Nervous Systems
 The Nervous System Chapter Nervous Systems Which animals have nervous systems? (Which do not) What are the basic components of a NS? What kind of fish performs brain operations? What differentiates one
The Nervous System Chapter Nervous Systems Which animals have nervous systems? (Which do not) What are the basic components of a NS? What kind of fish performs brain operations? What differentiates one
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS. AP Biology Chapter 48
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS AP Biology Chapter 48 Objectives Describe the different types of neurons Describe the structure and function of dendrites, axons, a synapse, types of ion channels, and
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS AP Biology Chapter 48 Objectives Describe the different types of neurons Describe the structure and function of dendrites, axons, a synapse, types of ion channels, and
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization
 Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous system. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Mechanism of Pain Production
 Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007)
 Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Neurons & Impulses
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Neurons & Impulses Organization of the Nervous System: Two Major Portions: The central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS = Brain/Spinal Cord PNS = Nerves-provide
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Neurons & Impulses Organization of the Nervous System: Two Major Portions: The central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS = Brain/Spinal Cord PNS = Nerves-provide
What is pain?: An unpleasant sensation. What is an unpleasant sensation?: Pain. - Aristotle.
 What is pain?: An unpleasant sensation. What is an unpleasant sensation?: Pain. - Aristotle. Nociception The detection of tissue damage or impending tissue damage, but There can be tissue damage without
What is pain?: An unpleasant sensation. What is an unpleasant sensation?: Pain. - Aristotle. Nociception The detection of tissue damage or impending tissue damage, but There can be tissue damage without
The Nervous System. PowerPoint Lecture Slides C H A P T E R 7. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
Nervous system. 1. Neurons :
 Nervous system nervous system is composed of billions of cells, the most essential being the nerve cells or neurons. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system. Two
Nervous system nervous system is composed of billions of cells, the most essential being the nerve cells or neurons. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system. Two
What it Takes to be a Pain
 What it Takes to be a Pain Pain Pathways and the Neurophysiology of pain Dennis S. Pacl, MD, FACP, FAChPM Austin Palliative Care/ Hospice Austin A Definition of Pain complex constellation of unpleasant
What it Takes to be a Pain Pain Pathways and the Neurophysiology of pain Dennis S. Pacl, MD, FACP, FAChPM Austin Palliative Care/ Hospice Austin A Definition of Pain complex constellation of unpleasant
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS
 Lab 14 Introduction to Nervous System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. orbicularis oculi b. sternocleidomastoid c. deltoid d. pectoralis major e. biceps brachii f. rectus
Lab 14 Introduction to Nervous System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. orbicularis oculi b. sternocleidomastoid c. deltoid d. pectoralis major e. biceps brachii f. rectus
Pain. Pain. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Psyc 2906: Sensation--Introduction 9/27/2006
 Pain Pain Pain: One Definition Classic Paths A new Theory Pain and Drugs According to the international Association for the Study (Merskey & Bogduk, 1994), Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience
Pain Pain Pain: One Definition Classic Paths A new Theory Pain and Drugs According to the international Association for the Study (Merskey & Bogduk, 1994), Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience
Nervous system part 1. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015
 EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
April 29, Neurophysiology. Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University,
 April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
Expression of the transient receptor potential channels TRPV1, TRPA1 and TRPM8 in mouse trigeminal primary afferent neurons innervating the dura
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 212 Expression of the transient receptor potential channels TRPV1, TRPA1 and TRPM8 in mouse trigeminal primary afferent
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 212 Expression of the transient receptor potential channels TRPV1, TRPA1 and TRPM8 in mouse trigeminal primary afferent
The Nervous System. Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output
 The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
Neurons Chapter 7 2/19/2016. Learning Objectives. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System
 Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
sensory input receptors integration Human Anatomy motor output Ch. 7 effectors Structural classification
 Human Anatomy Ch. 7 I. The Nervous System A. General characteristics 1. body s control & communication center a. 3 overlapping functions 1) sensory input: receptors monitor stimuli 2) integration: processes,
Human Anatomy Ch. 7 I. The Nervous System A. General characteristics 1. body s control & communication center a. 3 overlapping functions 1) sensory input: receptors monitor stimuli 2) integration: processes,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Teacher Key. Big Idea Different types of neurons compose the nervous tissue that forms the communication system within the body.
 Big Idea Different types of neurons compose the nervous tissue that forms the communication system within the body. Introduction to Neurons An individual s survival and reproductive success depends upon
Big Idea Different types of neurons compose the nervous tissue that forms the communication system within the body. Introduction to Neurons An individual s survival and reproductive success depends upon
Name Biology 125 Midterm #2 ( ) Total Pages: 9
 Name - 1 - Biology 125 Midterm #2 (11-15-07) Part 1: (30 pts) Part 2: (40 pts) Part 3: (6 pts) Part 4: (12 pts) Part 5: (12 pts) Total Pages: 9 Total Score: (100 pts) 1 Name - 2 - Part 1: True or False.
Name - 1 - Biology 125 Midterm #2 (11-15-07) Part 1: (30 pts) Part 2: (40 pts) Part 3: (6 pts) Part 4: (12 pts) Part 5: (12 pts) Total Pages: 9 Total Score: (100 pts) 1 Name - 2 - Part 1: True or False.
The Nervous System -The master controlling and communicating system of the body
 The Nervous System -The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions: -Sensory input -Integration -Motor output Organization of the Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) -Brain
The Nervous System -The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions: -Sensory input -Integration -Motor output Organization of the Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) -Brain
NERVOUS TISSUE. 1. Functional units of the nervous system; receive, process, store and transmit information to other neurons, muscle cells or glands.
 NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
Nervous Tissue and Neurophysiology
 Nervous Tissue and Neurophysiology Objectives Describe the two major divisions of the nervous system and their characteristics. Identify the structures/functions of a typical neuron. Describe the location
Nervous Tissue and Neurophysiology Objectives Describe the two major divisions of the nervous system and their characteristics. Identify the structures/functions of a typical neuron. Describe the location
Unit Three. I. General Functions of the Nervous System. I. General Functions of the Nervous System
 10 Refer to the following URLs. It is a good idea to print them and bring them to class. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/ap.html
10 Refer to the following URLs. It is a good idea to print them and bring them to class. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/ap.html
Nervous System (Part A-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 5 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Introduction Neural Tissue TextBook Readings Pages 388 through 397. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 5 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Introduction Neural Tissue TextBook Readings Pages 388 through 397. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Pathophysiology of Pain
 Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS
 Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
ACUTE TREATMENT FOR MIGRAINE. Cristina Tassorelli
 The European Headache School 2012 ACUTE TREATMENT FOR MIGRAINE Cristina Tassorelli Headache Science Centre, IRCCS Neurological Institute C. Mondino Foundation - Pavia University Centre for Adaptive Disorders
The European Headache School 2012 ACUTE TREATMENT FOR MIGRAINE Cristina Tassorelli Headache Science Centre, IRCCS Neurological Institute C. Mondino Foundation - Pavia University Centre for Adaptive Disorders
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Chapter 10
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei
 Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei General description: nerve tissue nerve cells (neurons): show numerous long processes receive the stimulation make contact with each other, conduct the nerve impulse
Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei General description: nerve tissue nerve cells (neurons): show numerous long processes receive the stimulation make contact with each other, conduct the nerve impulse
Week 7 and 8 Master Worksheet
 The Nervous System Week 7 and 8 Master Worksheet 1. Complete the chart regarding the 3 functions of the nervous system: Sensory input What does it do? Integration Motor output 2. Complete the chart: Component
The Nervous System Week 7 and 8 Master Worksheet 1. Complete the chart regarding the 3 functions of the nervous system: Sensory input What does it do? Integration Motor output 2. Complete the chart: Component
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Lecture 3 (Oct 5 th ): NEURONS AND NERVE IMPULSES Lecture Outline
 Lecture 3 (Oct 5 th ): NEURONS AND NERVE IMPULSES Lecture Outline 1) CNS vs. PNS 2) Structure of Neurons parts of a neuron: soma, dendrites, axons 3) Glial Cells 4) Mitosis and Regeneration in Neurons
Lecture 3 (Oct 5 th ): NEURONS AND NERVE IMPULSES Lecture Outline 1) CNS vs. PNS 2) Structure of Neurons parts of a neuron: soma, dendrites, axons 3) Glial Cells 4) Mitosis and Regeneration in Neurons
General Functions (3) 1.Sensory gathers information 2.Integrative information is brought together 3.Motor responds to signals, homeostasis
 Nervous System Responsible for being aware of the world, coordinating body functions and maintaining homeostasis Information from inside and outside the body is brought to the brain and spinal cord, stimulating
Nervous System Responsible for being aware of the world, coordinating body functions and maintaining homeostasis Information from inside and outside the body is brought to the brain and spinal cord, stimulating
Nervous System. Master controlling and communicating system of the body. Secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
 Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
The Role of Allergies and Sinus Disorders in Headache & Facial Pain
 The Role of Allergies and Sinus Disorders in Headache & Facial Pain Vincent T. Martin, MD Professor of Medicine Co-director of the Headache & Facial Pain Center University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
The Role of Allergies and Sinus Disorders in Headache & Facial Pain Vincent T. Martin, MD Professor of Medicine Co-director of the Headache & Facial Pain Center University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
Fig The C.S. of the Spinal Cord A ganglion is a term for a collection of perikarya located outside of the CNS. In certain regions of the spinal
 Chapter 9 Nervous System The nervous system is divided into two components: The CNS - the brain and spinal cord and the PNS - the nerves emanating from the spinal cord and brain that distribute to other
Chapter 9 Nervous System The nervous system is divided into two components: The CNS - the brain and spinal cord and the PNS - the nerves emanating from the spinal cord and brain that distribute to other
Involvement of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 channel expression in orofacial cutaneous hypersensitivity following tooth pulp inflammation
 8 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 60, No. 1, 8-13, 2018 Original Involvement of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 channel expression in orofacial cutaneous hypersensitivity following tooth pulp inflammation
8 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 60, No. 1, 8-13, 2018 Original Involvement of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 channel expression in orofacial cutaneous hypersensitivity following tooth pulp inflammation
PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus. MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive
 PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
Chapter 34 The Nervous System:
 Chapter 34 The Nervous System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5.3 Responses in the human 1. The nervous system: two-part division into the CNS and the PNS. 2. Neurons, name 3 types, give structure and function
Chapter 34 The Nervous System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5.3 Responses in the human 1. The nervous system: two-part division into the CNS and the PNS. 2. Neurons, name 3 types, give structure and function
NEURAL TISSUE (NEUROPHYSIOLOGY) PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA
 PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
V1-ophthalmic. V2-maxillary. V3-mandibular. motor
 4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
