2015 Radiology Coding Survival Guide
|
|
|
- Cory Hubbard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2015 Radiology Coding Survival Guide Section II : Diagnostic Radiology (Diagnostic Imaging) Chapter 1 : Head and Neck ( ) The head and neck diagnostic imaging section of CPT includes codes specific to various modalities such as radiography, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance (MR), as well as codes that specify "supervision and interpretation." (See Section I, "Radiology Guidelines" for the definition of "supervision and interpretation.") This section also includes CT angiography codes. In this chapter of the Survival Guide, you'll find answers to many of the questions radiology coders face when coding head and neck diagnostic imaging. Keep Radiograph Coding on Track with Vocabulary Tips You need to know several terms to apply the radiography codes correctly. Here's a rundown of some of the terms you'll see in codes Myelography: Myelography is a radiographic study showing contrast material's passage in the subarachnoid space (around the spinal cord) and nerve roots using fluoroscopy. Example: For the radiological supervision and interpretation of posterior fossa myelography, you should report code (Myelography, posterior fossa, radiological supervision and interpretation). Cisternography: If documentation shows radiography of the brain's basal cistern after subarachnoid injection of contrast, check out (Cisternography, positive contrast, radiological supervision and interpretation). Dacryocystography: When the study visualizes the lacrimal sacs and associated structures with contrast, look for dacryocystography code (Dacryocystography, nasolacrimal duct, radiological supervision and interpretation). Cephalography: Code (Cephalogram, orthodontic) describes a diagnostic study of the patient's skull, jaw, and teeth sometimes called as a cephalometric radiograph to help in planning correction. The patient may have the test repeated over time to show change. Orthopantography: An X-ray film that shows all of the patient's teeth, jaw bones, and nearby structures on a single film is an orthopantogram (70355, Orthopantogram [eg, panoramic x-ray]). (See "Master Radiography Coding with 4 Head and Neck FAQs" in this section for more on this code.) Laryngography: Choose (Laryngography, contrast, radiological supervision and interpretation) for reporting a radiographic contrast study of the larynx (also called the voice box). Sialography: A sialogram (70390, Sialography, radiological supervision and interpretation) involves an X-ray study of the salivary ducts and the related glandular structures.
2 Key Concepts: Master Radiography Coding With 4 Head and Neck FAQs Submitting clean claims requires more than simply matching modality and anatomy to code descriptors. Modifiers, fee schedule indicators, and more all come into play. Read through these head and neck examples to learn some crucial coding essentials that you can apply to the claims you see every day. 1: Match Modifiers to Pre- and Post-Op Imaging Question: Documentation shows one set of X-rays when the patient presents with a suspected mandible fracture and another set of X-rays taken to check for alignment after a surgeon performs closed reduction. How should you code this? Answer: For diagnosing mandibular fractures, most oral and maxillofacial surgeons will use an orthopantogram (70355, Orthopantogram [eg, panoramic x-ray]). If the surgeon requests this form of imaging for both diagnosis and postreduction, you would append modifier 76 (Repeat procedure or service by same physician or other qualified health care professional) to the second orthopantogram code. But if he uses different types of preoperative and postoperative imaging, you can't consider the second X-ray a repeat procedure. 2: Understand Bilateral Indicator '3' for Mastoids Question: How should you report a bilateral service? Answer: Before you report bilateral services, be sure you understand whether your payer considers the code (Radiologic examination, mastoids; less than 3 views per side), to be unilateral or bilateral. What to do: If you check the "Bilat Surg" column in Medicare's Physician Fee Schedule, you'll see a "3" for According to the fee schedule, that means "bilateral payment adjustment does not apply," and you should charge both sides separately at their normal fee. Most services with a "3" are radiology procedures. Resource: You can search the fee schedule online at or download the files at Note that this fee schedule is specific to Medicare, but many private payers adopt Medicare rules. To report the procedure bilaterally, check for your payer's preference. You may need to report the code twice and append modifier 50 (Bilateral procedure) to the second code. Or the payer may have a different preference, such as reporting the procedure as a single line item with 50 appended. Bonus tip: Likely ICD-9 codes for include the following: 383.x Mastoiditis and related conditions 386.x Vertiginous syndromes and other disorders of vestibular system Swelling, mass, or lump in head and neck. 3: Meet Medical Necessity for Question: You perform a three-view X-ray of the facial bones for a patient who suffered facial injuries in a car accident. Does this usually meet the requirements for medical necessity? Answer: You should check with your payer to be positive, but X-rays to assess injuries to the facial bones typically do qualify for reimbursement. You should report the diagnosis with the ICD-9 code supported by your documentation alone. You may also need to report an E code to explain the external cause of the injury, such as E813.0 (Motor vehicle collision with other vehicle, injuring driver of motor vehicle other than motorcycle).
3 CPT considers three views of the facial bones to be a "complete" exam. Because the example states documentation of three views, you should report (Radiologic examination, facial bones; complete, minimum of 3 views). If your documentation reveals fewer than three views, you should report (... less than 3 views). 4: Use Example to Grasp TC/26 Concept Question: An otolaryngologist orders X-rays for two sinus views. How should the radiologist report the services? Answer: You should report (Radiologic examination, sinuses, paranasal, less than 3 views). If your office completes both the professional (modifier 26, Professional component) and the technical component (modifier TC, Technical component), you should not append 26 or TC. Using the global X-ray code (70210 without TC or 26) tells the insurer that the office owns the X-ray equipment and the supplies, and the physician interprets the film and writes a report of his findings. If a facility performs the X-ray, the hospital bills for the technical side, and you should not bill the global X-ray code or the technical component. So the radiologist would report Potential problem: Some ordering physicians want to personally review the films and charge for interpreting the X-ray. If a radiologist performs that portion, the ordering physician should not bill for it also. CCI Spells Out 70120, Bundle Rationale Correct Coding Initiative (CCI) edits spell out which codes Medicare and other payers who adopt these edits bundle together, meaning that if CCI bundles code B into code A, you should report and expect payment for only code A. CCI links a "standard policy statement" to each code pair, and the CCI Coding Policy Manual, Chapter 1 (available at explains the meaning of these standards. For example: You will see the "HCPCS/CPT Procedure Code Definition" policy statement when one code is part of another based on the descriptor language. In many cases, that's because an indented code includes all of the services described by the main entry preceding a semicolon. CCI offers this example: Radiologic examination, mastoids; less than 3 views per side complete, minimum of 3 views per side. For a complete radiologic exam of the mastoids, you should report You don't need to report in addition to if you imaged only one side because the descriptor for (at least three views per side) includes the services described by (less than three views per side). ICD-9: The following diagnosis codes may support medical necessity for sinus views. Check with your payers for their lists of appropriate and payable ICD-9 codes. But choose your ICD-9 code based on the documentation don't choose a code just to get paid: 461.x Acute sinusitis 473.x Chronic sinusitis Headache (includes facial pain and Pain in head NOS) Special Feature: Tackle TMJ Coding Regardless of Modality X-rays: Codes (Radiologic examination, temporomandibular joint, open and closed mouth; unilateral) and ( bilateral), both describe X-rays of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). If the documentation indicates a TMJ X-ray in two projections of one side, one film with the mouth open and one with the
4 mouth closed, you should report (... unilateral). The bilateral code should be reported only when the documentation shows the TMJ exam on both sides. MRI: Having separate codes for unilateral and bilateral TMJ X-rays distinguishes these services from (Magnetic resonance [e.g., proton] imaging, temporomandibular joint[s]). The term "joint[s]" in the MRI descriptor indicates that you should use this code either for unilateral or bilateral services. Arthrography: Arthrography (70332, Temporomandibular joint arthrography, radiological supervision and interpretation) is a radiographic contrast joint study. The provider injects contrast into the joint, and then takes X-rays in multiple projections. The contrast allows the radiologist to see more details than a conventional X-ray. Tip: You may report the contrast injection separately with (Injection procedure for temporomandibular joint arthrography). You should report and twice (each with modifier RT and LT) if the radiologist performs the procedure on both the right and left sides. CT: Choosing which code to assign for CT views of TM (temporomandibular) joints can be confusing. Although both (Computed tomography, maxillofacial area; without contrast material) and (Computed tomography, head or brain; without contrast material) describe CTs performed on areas of the head, TMJs are a part of the maxillofacial area and so experts consider as a more appropriate code for reporting CT views of TM joints. Protocols for generally do not provide adequate evaluation of the TM joints. If the evaluation includes contrast, you should assign (Computed tomography, maxillofacial area; with contrast material[s]). In addition, if the study was done without contrast followed by contrast, you should report (... without contrast material, followed by contrast material[s] and further sections). ICD-9: A physician may order TMJ services for diagnoses, including the following: TMJ pain (524.62, Arthralgia of temporomandibular joint) TMJ -pain-dysfunction syndrome (524.60, Temporomandibular joint disorders, unspecified) TMJ disc disease (524.63, Articular disc disorder [reducing or non-reducing]) Abnormal sounds, such as clicking noises when opening and closing the jaw (524.64, Temporomandibular joint sounds on opening and/or closing the jaw). Set Speech and Swallowing Study Claims on the Path to Success If you code speech and swallowing studies, be sure you know these radiology codes: Radiologic examination; pharynx or larynx, including fluoroscopy and/ or magnification technique Complex dynamic pharyngeal and speech evaluation by cine or video recording Swallowing function, with cineradiography/videoradiography : You may rarely, if ever, use It describes a radiologic exam using fluoroscopy and/or magnification techniques, but does not include the dynamic elements of the speech evaluation code in which the movements of the mouth and tongue are required : Code describes a radiologic study using cineradiography or video recording for pharyngeal and speech evaluation. Typically, a speech pathologist is present, and the patient repeats sounds to allow for evaluation of the mouth and tongue during speech. Fluoroscopy is used to record how the tongue, palate, and other soft tissues in the mouth function. As the words and sounds are repeated, the speech pathologist and radiologist are able to see where problems may lie : The swallowing function exam described by is used to evaluate the oropharynx, hypopharynx, and upper esophagus. You should report to represent the radiologic supervision and interpretation for a speech language pathologist's performance of the service that (Motion fluoroscopic evaluation of swallowing function by cine or video recording) describes. You may see this study referred to as videofluoroscopic swallow study (VFSS).
5 The procedure includes cineradiography or videoradiography use. Imaging exams included in this procedure include an AP (anteroposterior) film of the barium-distended esophagus from the neck to the diaphragm and right anterior oblique projection to include the neck and thorax. The exam may also include a left anterior oblique projection. Patients who require these tests have often had a stroke and are experiencing dysphagia (438.82, Dysphagia due to cerebrovascular disease). Other diagnosis codes that may justify this procedure include (Malignant neoplasm of esophagus ), (Neoplasm of uncertain behavior of larynx), 787.2x ( dysphagia ), and (Pneumonitis due to inhalation of food or vomitus). Medicare carriers' policies vary, however, so always confirm your payers' guidelines before you perform swallowing studies. Smart move: Because of the potential for confusion between (for swallowing disorders) and (speech evaluation), the radiologist's dictation is vital. You need to know exactly what the radiologist studied and recorded to be able to assign the appropriate code. If you interchange the two codes, you could put your practice at risk. Because payers reimburse you more for 70371, insurers are on the lookout for practices that "upcode" their procedures from If the radiologist's documentation is too vague to determine whether she performed a pharyngeal evaluation or a swallowing study, you should always double check with her. Avoid the temptation to select the correct CPT code based on the diagnoses listed in the report. Some conditions, such as 784.5x (Other speech disturbance ), are specific to pharyngeal/speech evaluations. But as other diagnoses overlap between both procedures, this won't help you select the appropriate code. Stroke (434.91) and throat cancer (149.0), for example, are payable diagnoses for both procedures. Chew on These Edits For a temporal bone CT performed with a head CT, take care how you code. You would typically report a temporal bone CT using either (Computed tomography, orbit, sella, or posterior fossa or outer, middle, or inner ear; without contrast material), (... with contrast material[s]), or (... without contrast material, followed by contrast material[s] and further sections). Take the Pressure Out of 'CT Sinus' Coding When you're coding sinus CTs, look to maxillofacial area codes (Computed tomography, maxillofacial area...). Get a little extra insight into coding these services with these two from-the-trenches scenarios. Scenario 1: A patient undergoes a CT without contrast, and the radiologist focuses his report on the sinuses. You believe the correct code is (... without contrast material). Should you append modifier 52 (Reduced services) because the radiologist doesn't describe the full area in detail? Solution: No need for 52 here. According to the American College of Radiology (ACR), you don't have to code CTs by the slice. Code should be appropriate on its own. Scenario 2: Which CPT code(s) should you report for the following? Your freestanding imaging center performs a sinus CT without contrast. The images and data scans are taken to get computerized data, so a surgeon can use the information to build a 3-D image with the Insta Trak for guidance during surgery. The radiologist dictates his scan findings and labels them as "CT sinuses w/3-d." You have permanent files of the images and can print hard-copy images from the data at any time. Solution: You should report the sinus CT with But fight the urge to report (3D rendering with interpretation and reporting of computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, or other tomographic modality with image postprocessing under concurrent supervision ; not requiring image postprocessing on an independent workstation) or (... requiring image postprocessing on an independent workstation). The AMA's CPT Changes 2006: An Insider's View explains that the 3-D codes describe 3-D rendering with interpretation. CPT and codes descriptor clearly states "require concurrent supervision of image postprocessing 3-D manipulation of volumetric data set and image rendering."
6 You may use the 3-D rendering codes with 70486, but only when your service meets those requirements, and in the above scenario description, the radiologist neither supervises the creation of 3-D images nor interprets them. For more on proper use of and see "Ace 3-D Coding with 5 Can't-Miss Rules" in Chapter 12, "Other Procedures ( )." Case Study: Knock Out Neck CT Questions with This How-To Guide Start by analyzing the report (in the gray box below) from an imaging center, and decide which CPT, ICD-9, and HCPCS codes you would report on the center's global service claim. Size Up Your CPT Solution For this exam, you should report (Computed tomography, soft tissue neck; with contrast material[s]). You can't automatically depend on the "Neck CT with contrast" header to choose your code, but the report describes neck anatomy and intravenous contrast, confirming that the neck CT with contrast code is correct. Beware: The report says that "sagittal and coronal computer reconstruction images were also obtained." You should not report (3D rendering with interpretation and reporting of computed tomography...) because converting an axial scan into the coronal or sagittal plane is 2-D reformatting. CPT guidelines specify that you may not report 2-D formatting separately. Exam: CT neck with contrast Indication: Left vocal cord paralysis Technique: Axial CT cuts were obtained from the top of the orbits down to the thoracic inlet using 100 cc of Isovue mm axial CT cuts were also obtained through the larynx. Sagittal and coronal computer reconstruction images were also obtained. Indications for use of non-ionic contrast: None reported Findings: No mass lesion within the posterior nasopharynx or oropharynx. There are multifocal punctuate calcifications in the right palatine tonsil. The submandibular and parotid glands are unremarkable. There are subcentimeter anterior cervical and left submandibular lymph nodes. There are subcentimeter left internal jugular lymph nodes. The left pyriform sinus is slightly larger than the right, and there is dilatation of the left laryngeal ventricle. There is probably atrophy of the left true vocal cord best seen on the 1.3-mm thick images. The left arytenoid cartilage has a more medial position than the right. The thyroid glands are unremarkable. The visualized upper mediastinum is unremarkable. Impression: 1. Left vocal cord paralysis 2. No cervical mass or adenopathy Follow These ICD-9 Accuracy Tips You'll have to overcome a few obstacles to choose the most accurate diagnosis code for this service, which includes the finding of "left vocal cord paralysis." ICD-9 limits your vocal cord paralysis choices to 478.3x (Paralysis of vocal cords or larynx ). Problem: The radiologist documented that the vocal cord paralysis was left side only, but to choose the most specific code, you also need to know whether the paralysis is partial or complete. Solution: If you can't get a confirmed diagnosis from the ordering physician, you should report the unspecified code: (Unspecified paralysis of vocal cords). Don't Miss These Contrast Unit Tips
7 To achieve the "with contrast" portion of this exam, the provider administered 100 cc of Isovue 300 (non-ionic contrast) intravenously. If you bear the drug's cost, then you should report the contrast with Q9967 (Low osmolar contrast material, mg/ml iodine concentration, per ml). The descriptor says to report the code "per ml," so you should report 100 units for the 100 cc administered. Why: One milliliter (ml) equals one cubic centimeter (cc). Remember: CPT defines "with contrast" for imaging as contrast administered intravascularly, intra-arterially, or intrathecally. If the patient received only oral or rectal contrast, you would not choose a "with contrast" imaging code option. Note: The report says, "Indications for use of non-ionic contrast: None reported." But this missing information isn't an issue. The restrictive criteria for LOCM (low osmolar contrast material) went away a few years ago. Special Feature: Keep Sight of Anatomic Site to Select CTA Code As with computed tomography (CT) scan codes, CPT breaks the CT angiography (CTA) codes down according to anatomic site. If your documentation is unclear regarding the specific site (for instance, abdomen versus pelvis), always ask the physician to select the most accurate CPT code rather than just choosing one that you believe to be "close." Good news: CTA codes got a 2008 facelift aimed at bolstering your right to report CTAs without modifier 52 (Reduced services). The lowdown: The phrase "without contrast material(s), followed by contrast material(s) and further sections" in pre CTA codes led many auditors to claim that if the physician didn't perform imaging without contrast, coders had to append modifier 52 to the CTA code. But the codes' original intent was to include non-contrast imaging when performed not to require it. The revision clarifies that you can report these CTA codes even without documentation of non-contrast imaging. This coding concept applies to multiple CTA codes, such as the following: Computed tomographic angiography, head, with contrast material(s), including noncontrast images, if performed, and image postprocessing Computed tomographic angiography, neck, with contrast material(s), including noncontrast images, if performed, and image postprocessing Computed tomographic angiography, chest (noncoronary), with contrast material(s), including noncontrast images, if performed, and image postprocessing Computed tomographic angiography, pelvis, with contrast material(s), including noncontrast images, if performed, and image postprocessing Computed tomographic angiography, lower extremity, with contrast material(s), including noncontrast images, if performed, and image postprocessing Computed tomographic angiography, abdomen, with contrast material(s), including noncontrast images, if performed, and image postprocessing Computed tomographic angiography, abdominal aorta and bilateral iliofemoral lower extremity runoff, with contrast material(s), including noncontrast images, if performed, and image postprocessing. Catch These Head and Neck MRI Coding Opportunities CPT 's organization of radiology codes by anatomic regions is handily self-explanatory until you come across imaging of an area that codes don't name explicitly or have two studies of the same area. Use this FAQ to keep your head and neck MRI coding on track.
8 1: Look to for Brachial Plexus MRI Question: What code should you report if you perform a brachial plexus MRI to the thyroid gland level to diagnose head and neck cancers? Answer: You should choose the appropriate code from (Magnetic resonance [e.g., proton] imaging, orbit, face and/or neck...), according to the February 2001 ACR Bulletin. The American College of Radiology (ACR) maintains that you should use for orbit, face, and neck MRIs, but also "for reporting an MRI of the brachial plexus, when the study is performed to the level of the thyroid gland for diagnosing head and neck cancers." Remember: Medical specialty societies offer a wealth of invaluable technical knowledge, but don't forget their coding opinions are nonbinding. If CMS or the AMA offers guidelines, those trump nonbinding opinions may become the standards an insurance audit holds providers to. Is for Face Alone OK? Tip: In 2007, CPT changed the descriptors for from "and" to "and/or." Reason: The "and" inaccurately suggested that you had to image all of the sites face, head, and neck to report one of the codes, according to the AMA's CPT Changes The "and/or" clarifies that you also may use the codes if the patient has imaging performed on just the face, just the orbits, or just the neck. 2: Count Brain and IAC MRIs as 1, Usually Question: What is the appropriate way to bill MRI of the brain and IACs? If two studies are performed, is it appropriate to bill MRI of the brain two times? Answer: You may report two brain MRIs ( , Magnetic resonance [e.g., proton] imaging, brain [including brain stem]...) only if the physician performs and documents separate and distinct exams for the brain and IACs (internal auditory canals) with separate and distinct indications for each. Watch for: You should not consider a few additional sequences of the IACs to be a separate exam. And even if you meet the separate-and-distinct requirements, your payer is unlikely to cover the second service. Some payers may suggest appending modifier 22 (Increased procedural services) if you take extra images just remember that the extra work required and the extra scrutiny modifier 22 brings, may not be worth the trouble. Careful: Some practices document the IAC scan separately and use orbit, face, and neck MRI codes 70540, 70542, and for the IAC. But you shouldn't use these codes for this service unless your payer instructs you in writing to do so. Reason: Brain MRI codes are appropriate for IACs because the inner ear and eighth nerve are part of the brain stem, according to the AMA 2003 coding symposium. Bonus tip: The AMA cited the same reasoning for instructing you to report (Magnetic resonance [eg, proton] imaging, brain [including brain stem] ) for pituitary studies. 3: Dig Into Codes for DTI Question: Does CPT offer codes other than (Magnetic resonance [e.g., proton] imaging, brain [including brain stem]...) for diffusion tensor imaging? Answer: No. You should stick to for diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), which evaluates the direction and amount of water diffusion within the body. The same holds true for two other special brain MRI techniques: Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), which evaluates water diffusion within the body Perfusion imaging, including perfusion weighted imaging, which evaluates microscopic blood flow levels. Head Off MRA Blunders With This Guide
9 Medicare supplies you with a national coverage determination (NCD) for magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), but that doesn't mean coding these services is cut-and- dried. Make sure you're making the grade with this in-depth look at head MRA coding. Don't Fall Prey to the 'With Contrast' Trap CPT lists the following head MRA codes: Magnetic resonance angiography, head; without contrast material(s) with contrast material(s) without contrast material(s), followed by contrast material(s) and further sequences. Key: Do not report with for head MRA without contrast followed by head MRA with contrast. Report only (Magnetic resonance angiography, head; without contrast material(s), followed by contrast material(s) and further sequences) for these services. Be sure you use the latest contrast supply codes when your facility bears the cost of the contrast. For example, HCPCS 2008 deleted Q9952 (Injection, gadolinium-based magnetic resonance contrast agent, per ml) and created a new gadolinium code, A9579 (Injection, gadolinium-based magnetic resonance contrast agent, not otherwise specified [NOS], per ml), in the "Administrative, Miscellaneous and Investigational" section. Remember: CPT guidelines state that "with contrast" in a code descriptor means "contrast material administered intravascularly, intra-articularly, or intrathecally." You should not consider a study to be "with contrast" if the patient only receives oral and/or rectal contrast. In other words, don't think that just because you report contrast code Q9954 (Oral magnetic resonance contrast agent, per 100 ml) you should report "with contrast" MRA code You can't count oral contrast as "with contrast," according to CPT. Tip: If HCPCS doesn't have a code for the contrast used, you should report A4641 (Radiopharmaceutical, diagnostic, not otherwise classified). Check Out What the MRA NCD Reveals The MRA NCD describes covered conditions but does not list covered ICD-9 codes. The NCD states: All of the following criteria must apply in order for Medicare to provide coverage for MRA of the head and neck: MRA is used to evaluate the carotid arteries, the circle of Willis, the anterior, middle or posterior cerebral arteries, the vertebral or basilar arteries or the venous sinuses; MRA is performed on patients with conditions of the head and neck for which surgery is anticipated and may be found to be appropriate based on the MRA. These conditions include, but are not limited to, tumor, aneurysms, vascular malformations, vascular occlusion, or thrombosis. Within this broad category of disorders, medical necessity is the underlying determinant of the need for an MRA in specific diseases. The medical records should clearly justify and demonstrate the existence of medical necessity; and MRA and contrast angiography (CA) are not expected to be performed on the same patient for diagnostic purposes prior to the application of anticipated therapy. Only one of these tests will be covered routinely unless the physician can demonstrate the medical need to perform both tests. Crucial: Diagnosis codes that payers cover for MRA may differ, but you should never choose a diagnosis code based on coverage. Stick to coding the diagnosis your physician's documentation supports. Check it out: You can find the MRA NCD by searching the Medicare NCD database available at Payers may consider head MRA services ( ) medically necessary for the following: Vascular dementia (290.40) Hemiplegia (342.90)
10 Migraine (346.90) Trigeminal nerve disorders (350.9) Occlusion and stenosis Visual disturbances (368.9) Paralytic strabismus (378.50) Cerebral thrombosis or embolism (434.0x/434.1x) Fracture Subdural or extradural hemorrhage following injury (852.2x/852.4x) Arterial or venous injury (904.9) Example: The physician documents a head MRA without/with contrast for a patient diagnosed with cerebral thrombosis, so you report and a code from the 434.0x range (Cerebral thrombosis...). Should You Switch Codes for Vein MRA? When the radiologist interprets magnetic resonance venography of the brain, you should use the same codes you would use for magnetic resonance imaging of the brain arteries: Helpful: "Angiography" refers to imaging of the blood vessels. The term is not specific to only arteries or only veins. An "arteriogram" is artery imaging, and a "venogram" is vein imaging. You'll find a general consensus that if the radiologist performs MRA of the veins and arteries at the same session, you should report only one brain MRA. Key Concepts: Use This MRI Example to Remember Order Rules Here's What the and fmri Rules Mean for You CPT guidelines lay down the law that you can't report "unless is performed." This section explains how you should apply this rule and when you're most likely to need these codes for your radiology claims. The service: Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) measures the tiny metabolic changes that take place in an active part of the brain. The codes: For fmri, you need to know the following codes: Magnetic resonance imaging, brain, functional MRI; including test selection and administration of repetitive body part movement and/or visual stimulation, not requiring physician or psychologist administration requiring physician or psychologist administration of entire neurofunctional testing Neurofunctional testing selection and administration during noninvasive imaging functional brain mapping, with test administered entirely by a physician or psychologist, with review of test results and report. See if 1 Claim Must Show 70555/96020 CPT designed and to be used together but not necessarily on the same claim form. Code is the testing code, and is the actual imaging code. One physician could do one procedure, and another physician could do the other. For example: Neurosurgeons and neurologists use functional brain mapping as a noninvasive way to help predict the potential for neurological problems that tumor growths, surgical interventions, or other factors might cause. Conducting the test helps the physician and patient make informed decisions concerning surgery or other appropriate treatments. If a neurosurgeon performs the testing, but you're coding for the radiologist who performed the MRI, then you should report and the neurosurgeon should report
11 Note: You won't find technical component payment for or on the Medicare physician fee schedule. Providers rarely if ever perform these services in an office. Physicians who perform the test in the office setting rather than a facility must negotiate with the carrier for reimbursement. Key Phrases Explain the 70554/96020 Ban Sometimes a technologist or physicist instead of a physician or psychologist performs the MRI and the testing. In that case, is appropriate. You should not report with Here's why: The codes conflict because of physician involvement. Code 70554's descriptor states, "not requiring physician or psychologist administration," while states, "with test administered entirely by a physician or psychologist." Also, the and services overlap. Both the testing methodology and the imaging are encompassed in Match fmri With Proper Diagnosis Some payers are creating policies that explain when they find fmri medically necessary. For example, payers may look for the following conditions: 1. The fmri is part of a preoperative evaluation for a planned craniotomy. 2. The fmri is required to localize areas of the brain such as those responsible for speech, language, motor function, and senses, which a proposed surgery might put at risk. ICD-9: Diagnoses you might see associated with functional brain mapping include the following: Arteriovenous malformations, 747.x (Other congenital anomalies of circulatory system) Epilepsy, 345.x (Epilepsy and recurrent seizures) Traumatic brain injury, 854.xx (Intracranial injury of other and unspecified nature)parkinson's disease, 332.x (Parkinson's disease) Schizophrenia, 295.xx (Schizophrenic disorders) Huntington's disease, (Huntington's chorea). - Published on
Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services:
 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Explanation of services: Known
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Explanation of services: Known
Deborah K. Mann & Jennifer Bash. Coding Documentation and Education Managers
 Deborah K. Mann & Jennifer Bash Coding Documentation and Education Managers OBJECTIVES Review the basics of Diagnostic, CT, & MRI documentation Risk areas in radiology associated with Diagnostic, CT, &
Deborah K. Mann & Jennifer Bash Coding Documentation and Education Managers OBJECTIVES Review the basics of Diagnostic, CT, & MRI documentation Risk areas in radiology associated with Diagnostic, CT, &
screening; including image post processing CT, heart; without contrast material; with Requires authorization
 0042T Cerebral perfusion analysis using CT; with ; including of parametric maps with determination of cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood volume, and mean transit time 74263 Computed tomographic (CT) colonography,
0042T Cerebral perfusion analysis using CT; with ; including of parametric maps with determination of cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood volume, and mean transit time 74263 Computed tomographic (CT) colonography,
Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services:
 computed tomography Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Known
computed tomography Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Known
MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF MICHIGAN PRIOR AUTHORIZATION / PRE-SERVICE REVIEW GUIDE IMAGING CODES REQUIRING PRIOR AUTHORIZATION EFFECTIVE 1/1/2014
 70336 MRI MRI, temporomandibular joint(s) 70450 CT/CTA CT, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 CT/CTA CT, head or brain; with contrast material(s) 70470 CT/CTA CT, head or brain; without contrast
70336 MRI MRI, temporomandibular joint(s) 70450 CT/CTA CT, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 CT/CTA CT, head or brain; with contrast material(s) 70470 CT/CTA CT, head or brain; without contrast
Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013
 Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013 Modality and CT Head CTA Head: Cerebrovascular MRI Head MRA Head: Cerebrovascular Functional
Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013 Modality and CT Head CTA Head: Cerebrovascular MRI Head MRA Head: Cerebrovascular Functional
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) AND COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY (CT) SCAN SITE OF CARE
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Utilization Review Guideline MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) AND COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY (CT) SCAN SITE OF CARE Guideline Number: URG-13.01 Effective Date: February 1, 2019 Table
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Utilization Review Guideline MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) AND COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY (CT) SCAN SITE OF CARE Guideline Number: URG-13.01 Effective Date: February 1, 2019 Table
AIM 2014 CPT Radiology & Cardiac Codes Requiring Review
 AIM 2014 CPT Radiology & Cardiac Codes Requiring Review Modality Body Part CT Head 1 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast 1 CT Head 1 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT
AIM 2014 CPT Radiology & Cardiac Codes Requiring Review Modality Body Part CT Head 1 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast 1 CT Head 1 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology
 Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 93451 Right heart catheterization 93452 Left heart catheterization 93453 Combined right and left
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 93451 Right heart catheterization 93452 Left heart catheterization 93453 Combined right and left
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology
 Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Product Category CPT Code CPT Code Description Radiology MR 70336 MRI Temporomandibular Joint(s), (TMJ) Radiology CT 70450 CT Head or
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Product Category CPT Code CPT Code Description Radiology MR 70336 MRI Temporomandibular Joint(s), (TMJ) Radiology CT 70450 CT Head or
2015 Radiology Coding Survival Guide
 2015 Radiology Coding Survival Guide Chapter 3: Spine and Pelvis (72010-72295) In addition to learning the X-ray, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance codes for the spine and pelvis, you should
2015 Radiology Coding Survival Guide Chapter 3: Spine and Pelvis (72010-72295) In addition to learning the X-ray, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance codes for the spine and pelvis, you should
High Tech Imaging Quick Reference Guide
 High Tech Imaging Quick Reference Guide 1 High Tech Imaging Authorizations may now be requested through our secure provider portal, BlueAccess. Getting Started Step 1: Log into BlueAccess from www.bcbst.com
High Tech Imaging Quick Reference Guide 1 High Tech Imaging Authorizations may now be requested through our secure provider portal, BlueAccess. Getting Started Step 1: Log into BlueAccess from www.bcbst.com
Radiology Codes Requiring Authorization*
 70336 Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s) 70450 Computed tomography, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 Computed tomography, head or brain; with contrast material(s)
70336 Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s) 70450 Computed tomography, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 Computed tomography, head or brain; with contrast material(s)
ADI Procedure Codes. August 2016 Revised April 2017 Page 1 of 7 ADI Procedure Codes
 Code Description 70450 CT Head without contrast 70460 CT Head with contrast 70470 CT Head with & without contrast 70480 CT Orbit, et al without contrast 70481 CT Orbit, et al with contrast 70482 CT Orbit,
Code Description 70450 CT Head without contrast 70460 CT Head with contrast 70470 CT Head with & without contrast 70480 CT Orbit, et al without contrast 70481 CT Orbit, et al with contrast 70482 CT Orbit,
2012 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana
 2012 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana CT Head 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o CT Head 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT Head 70482
2012 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana CT Head 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o CT Head 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT Head 70482
05/02/ CPT Preauthorization Groupings Effective May 2, Computerized Tomography (CT) Abdomen 6. CPT Description SEGR CT01
 Computerized Tomography (CT) 6 & 101 5 Upper Extremity 11 Lower Extremity 12 Head 3 Orbit 1 Sinus 2 Neck 4 7 Cervical Spine 8 Thoracic Spine 9 Lumbar Spine 10 Colon 13 CPT Preauthorization Groupings CPT
Computerized Tomography (CT) 6 & 101 5 Upper Extremity 11 Lower Extremity 12 Head 3 Orbit 1 Sinus 2 Neck 4 7 Cervical Spine 8 Thoracic Spine 9 Lumbar Spine 10 Colon 13 CPT Preauthorization Groupings CPT
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
2014 CPT Radiology Codes Requiring Review
 CT Head 1 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast 1 CT Head 1 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast CT Head 1 70482 followed by
CT Head 1 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast 1 CT Head 1 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast CT Head 1 70482 followed by
AMERICAN IMAGING MANAGEMENT
 2012 CPT Codes Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by Chest 71250 CT thorax; w/o 71260 CT thorax; with 71270
2012 CPT Codes Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by Chest 71250 CT thorax; w/o 71260 CT thorax; with 71270
AMERICAN IMAGING MANAGEMENT
 2010 BCBS of Georgia CPT Codes With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast 74170 CT abdomen; w/o contrast
2010 BCBS of Georgia CPT Codes With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast 74170 CT abdomen; w/o contrast
Coding Companion for Neurosurgery/Neurology. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Neurosurgery/Neurology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2011 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Skin...1 Repair...5 General Musculoskeletal...27
Coding Companion for Neurosurgery/Neurology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2011 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Skin...1 Repair...5 General Musculoskeletal...27
2017 Coding and Reimbursement Survival Guide
 2017 Coding and Reimbursement Survival Guide Chapter 14: Otolaryngology CPT 2017: Latest CPT Edition Offers New Code for Injection Laryngoplasty Changes could impact your reimbursement. The New Year is
2017 Coding and Reimbursement Survival Guide Chapter 14: Otolaryngology CPT 2017: Latest CPT Edition Offers New Code for Injection Laryngoplasty Changes could impact your reimbursement. The New Year is
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire
 Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies
 Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies MRI CT South Jersey Radiology Associates The purpose of this general guide is to assist you in choosing the appropriate imaging test to best help your
Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies MRI CT South Jersey Radiology Associates The purpose of this general guide is to assist you in choosing the appropriate imaging test to best help your
HONG KONG COLLEGE OF RADIOLOGISTS. Higher Training (Radiology) Subspecialty Training in Computed Tomography
 HONG KONG COLLEGE OF RADIOLOGISTS Higher Training (Radiology) Subspecialty Training in Computed Tomography [The following guidelines should be read in conjunction with the General Guidelines on Higher
HONG KONG COLLEGE OF RADIOLOGISTS Higher Training (Radiology) Subspecialty Training in Computed Tomography [The following guidelines should be read in conjunction with the General Guidelines on Higher
Diagnostic Imaging Prior Review Code List 2 nd Quarter 2018
 Computerized Tomography (CT) Abdomen 6 Abdomen/Pelvis Combination 101 Service 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by 74176 Computed tomography, abdomen and pelvis;
Computerized Tomography (CT) Abdomen 6 Abdomen/Pelvis Combination 101 Service 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by 74176 Computed tomography, abdomen and pelvis;
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire
 Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
Coding Companion for Plastics/OMS/Dermatology. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Plastics/OMS/Dermatology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2011 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Skin...1 Nails...30 Pilonidal Cyst...34
Coding Companion for Plastics/OMS/Dermatology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2011 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Skin...1 Nails...30 Pilonidal Cyst...34
What is head and neck cancer? How is head and neck cancer diagnosed and evaluated? How is head and neck cancer treated?
 Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that start in the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, salivary glands, nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses. They usually begin
Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that start in the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, salivary glands, nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses. They usually begin
SAMPLE. Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS ICD-10. Cross Coder
 Cross Coder www.optumcoding.com Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS 2017 a ICD-10 A full suite of resources including the latest code set, mapping products, and expert training
Cross Coder www.optumcoding.com Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS 2017 a ICD-10 A full suite of resources including the latest code set, mapping products, and expert training
Radiology Coding. Copyright. Today s Goal 8/17/2010. Answer your questions! Melody W. Mulaik CODING
 Radiology Coding Tips & Traps Melody W. Mulaik 1 877 6 CODING melody.mulaik@codingstrategies.com The material contained in this presentation and handout are distributed under copyright by Coding Strategies,
Radiology Coding Tips & Traps Melody W. Mulaik 1 877 6 CODING melody.mulaik@codingstrategies.com The material contained in this presentation and handout are distributed under copyright by Coding Strategies,
NEURO PROTOCOLS MRI NEURO PROTOCOLS (SIEMENS SCANNERS)
 Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Head and Neck Cancer. What is head and neck cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that usually originate in the squamous cells that line the mouth, nose and throat. Typical symptoms include a persistent
Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that usually originate in the squamous cells that line the mouth, nose and throat. Typical symptoms include a persistent
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (NCD 220.2)
 Policy Number 220.2 Approved By UnitedHealthcare Medicare Committee Current Approval Date 05/14/2014 IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT THIS REIMBURSEMENT POLICY This policy is applicable to UnitedHealthcare Medicare
Policy Number 220.2 Approved By UnitedHealthcare Medicare Committee Current Approval Date 05/14/2014 IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT THIS REIMBURSEMENT POLICY This policy is applicable to UnitedHealthcare Medicare
HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST
 HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST Outpatient Radiology utilization call Carecore at 1-877-773-6964 Modality CPT CODE Description CT SCANS 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST CT SCANS 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN
HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST Outpatient Radiology utilization call Carecore at 1-877-773-6964 Modality CPT CODE Description CT SCANS 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST CT SCANS 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION
 FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 70544 Magnetic resonance angiography, head; without contrast material(s) 70545 with contrast material(s)
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 70544 Magnetic resonance angiography, head; without contrast material(s) 70545 with contrast material(s)
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION
 FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 71250 Computed tomography, thorax; without contrast material 71260 with contrast material(s) 71270 without
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 71250 Computed tomography, thorax; without contrast material 71260 with contrast material(s) 71270 without
CPT 2015: Prepare Your Coding Practice For New Codes As Technology Makes An Advance
 2015 Radiology Coding Survival Guide Section X : 2015 Coding Updates CPT 2015: Prepare Your Coding Practice For New Codes As Technology Makes An Advance Watch for changes in Vertebral fracture assessment,
2015 Radiology Coding Survival Guide Section X : 2015 Coding Updates CPT 2015: Prepare Your Coding Practice For New Codes As Technology Makes An Advance Watch for changes in Vertebral fracture assessment,
Coding Companion for Ophthalmology. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Ophthalmology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2015 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i General Integumentary/Skin...1 Introduction...8
Coding Companion for Ophthalmology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2015 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i General Integumentary/Skin...1 Introduction...8
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
Icd 10 code for ct pelvis with contrast
 Icd 10 code for ct pelvis with contrast November 16, 2009. How to Code for CT Angiography. By Anthony McCallum, CPC, CCS, CIRCC, CPC-I Radiology Today Vol. 10 No. 18 P. 12. CT. procedure code and description
Icd 10 code for ct pelvis with contrast November 16, 2009. How to Code for CT Angiography. By Anthony McCallum, CPC, CCS, CIRCC, CPC-I Radiology Today Vol. 10 No. 18 P. 12. CT. procedure code and description
Codes Requiring Authorization from MedSolutions (MSI): Updated 3/2014
 s Requiring Authorization from MedSolutions (): Updated 3/2014 0042T Cerebral Perfusion Analysis using CT with contrast 0159T CAD, including computer algorithm analysis, BREAST MRI 0195T prepare interspace,
s Requiring Authorization from MedSolutions (): Updated 3/2014 0042T Cerebral Perfusion Analysis using CT with contrast 0159T CAD, including computer algorithm analysis, BREAST MRI 0195T prepare interspace,
Neuroradiology Subspecialty Exam Study Guide
 Neuroradiology Subspecialty Exam Study Guide The exam will consist of three equal parts; Brain, Spine and Head & Neck. Pediatric cases are included within each exam section. Each section will consist of
Neuroradiology Subspecialty Exam Study Guide The exam will consist of three equal parts; Brain, Spine and Head & Neck. Pediatric cases are included within each exam section. Each section will consist of
HIP RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LISTS
 EFFECTIVE OCTOBER 1, 2012 70336 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING TMJ 70450 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITHOUT 70460 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITH 70470 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITHOUT AND WITH
EFFECTIVE OCTOBER 1, 2012 70336 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING TMJ 70450 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITHOUT 70460 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITH 70470 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITHOUT AND WITH
Brain Tumors. What is a brain tumor?
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group. Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer. Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i & 11-1C-106i
 Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Medtronic ENT Transnasal Endoscopic Procedures Coding Guide. Effective January 1, 2009
 Medtronic ENT Transnasal Endoscopic Procedures Coding Guide Transnasal Esophagoscopy Laryngeal Sensory Testing FEES FEEST Transnasal Fiberoptic Laryngoscopy Stroboscopy Disposable Sheaths Effective January
Medtronic ENT Transnasal Endoscopic Procedures Coding Guide Transnasal Esophagoscopy Laryngeal Sensory Testing FEES FEEST Transnasal Fiberoptic Laryngoscopy Stroboscopy Disposable Sheaths Effective January
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
Reimbursement Information for Diagnostic Ultrasound and Ultrasound-guided Vascular Procedures 1
 GE Healthcare Reimbursement Information for Diagnostic Ultrasound and Ultrasound-guided Vascular Procedures 1 January, 2013 www.gehealthcare.com/reimbursement This overview addresses coding, coverage,
GE Healthcare Reimbursement Information for Diagnostic Ultrasound and Ultrasound-guided Vascular Procedures 1 January, 2013 www.gehealthcare.com/reimbursement This overview addresses coding, coverage,
Best Practices for Diagnostic Radiology Documentation. Presented by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, CIRCC, RCC President & Senior Consultant.
 Best Practices for Diagnostic Radiology Documentation Presented by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, CIRCC, RCC President & Senior Consultant April 11, 2016 AAPC HEALTHCON Agenda Diagnostic Test Orders ACR
Best Practices for Diagnostic Radiology Documentation Presented by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, CIRCC, RCC President & Senior Consultant April 11, 2016 AAPC HEALTHCON Agenda Diagnostic Test Orders ACR
Head and Neck Examination
 Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
Radiography Sep 2004 Page 1 of 5 Version 01.11
 NATIONAL REFERENCE PRICE LIST FOR SERVICES BY RADIOGRAPHERS EFFECTIVE FROM 1 JANUARY 2004 The following reference price list is not a set of tariffs that must be applied by medical schemes and/or providers.
NATIONAL REFERENCE PRICE LIST FOR SERVICES BY RADIOGRAPHERS EFFECTIVE FROM 1 JANUARY 2004 The following reference price list is not a set of tariffs that must be applied by medical schemes and/or providers.
Intro: Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Basic understanding of interventional radiology. Gain knowledge of key terms and phrases
 Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
Coding and Payment Guide for Anesthesia Services. An essential coding, billing, and reimbursement resource for anesthesiology and pain management
 Coding and Payment Guide for Anesthesia Services An essential coding, billing, and reimbursement resource for anesthesiology and pain management Contents Introduction... 1 Coding Systems... 1 Claim Forms...
Coding and Payment Guide for Anesthesia Services An essential coding, billing, and reimbursement resource for anesthesiology and pain management Contents Introduction... 1 Coding Systems... 1 Claim Forms...
Coding Companion for Plastics/OMS/Dermatology. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Plastics/OMS/Dermatology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion... i Skin...1 Nails...28 Pilonidal Cyst...32 Repair...33
Coding Companion for Plastics/OMS/Dermatology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion... i Skin...1 Nails...28 Pilonidal Cyst...32 Repair...33
Diagnostic and interventional venous procedures (lower extremity)
 2017 Coding and Medicare payment guide Diagnostic and interventional venous procedures (lower extremity) All coding, coverage, billing and payment information provided herein by Philips Volcano is gathered
2017 Coding and Medicare payment guide Diagnostic and interventional venous procedures (lower extremity) All coding, coverage, billing and payment information provided herein by Philips Volcano is gathered
2010 Radiology Prior Authorization List for UnitedHealthcare s HealthChoice Members
 70336 MR TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT 70450 CT, HEAD OR BRAIN; WITHOUT MATERIAL 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/ 70470 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O & W/ 70480 CT, ORBIT, SELLA, OR POSTERIOR FOSSA OR OUTER, MID 70481 CT ORBIT W/
70336 MR TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT 70450 CT, HEAD OR BRAIN; WITHOUT MATERIAL 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/ 70470 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O & W/ 70480 CT, ORBIT, SELLA, OR POSTERIOR FOSSA OR OUTER, MID 70481 CT ORBIT W/
2013 Coding Changes. Diagnostic Radiology. Nuclear Medicine
 2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Sample page. Radiology. Cross Coder. Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS
 Cross Coder 2018 Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com. Contents Introduction...
Cross Coder 2018 Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com. Contents Introduction...
Head & Neck Contouring
 Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
and at the same patient encounter. Code has been deleted. For scanning computerized ophthalmic diagnostic imaging of optic nerve and retin
 92227: Remote imaging for detection of retinal disease (eg, retinopathy in a patient with diabetes) with analysis and report under physician supervision, unilateral or bilateral. For Medicare, bill only
92227: Remote imaging for detection of retinal disease (eg, retinopathy in a patient with diabetes) with analysis and report under physician supervision, unilateral or bilateral. For Medicare, bill only
RADIOLOGY PROGRAM TABLE OF CONTENTS. OVERVIEW. . Assessment... and... Certification
 TABLE OF CONTENTS. OVERVIEW............................................................................................. 553..... Assessment............ and..... Certification..........................................................................
TABLE OF CONTENTS. OVERVIEW............................................................................................. 553..... Assessment............ and..... Certification..........................................................................
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis 2017 Edition
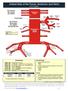 Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
2018 Cerebrovascular Reimbursement Coding Fact Sheet
 The information contained in this document is provided for informational purposes only and represents no statement, promise, or guarantee by Cordis Corporation concerning levels of reimbursement, payment,
The information contained in this document is provided for informational purposes only and represents no statement, promise, or guarantee by Cordis Corporation concerning levels of reimbursement, payment,
CARECORE NATIONAL OUTPATIENT IMAGING SELF-REFERRAL PAYMENT POLICIES PUBLISHED APRIL 2013
 CARECORE NATIONAL OUTPATIENT IMAGING SELF-REFERRAL PAYMENT POLICIES PUBLISHED APRIL 2013 The outpatient imaging self-referral payment policies are designed to promote appropriate use of diagnostic imaging
CARECORE NATIONAL OUTPATIENT IMAGING SELF-REFERRAL PAYMENT POLICIES PUBLISHED APRIL 2013 The outpatient imaging self-referral payment policies are designed to promote appropriate use of diagnostic imaging
Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2014 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Integumentary...1 Arteries and Veins...15 Lymph
Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2014 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Integumentary...1 Arteries and Veins...15 Lymph
CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels
 CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels Objectives Determine specific imaging plane used to acquire or reformat CT scan, i.e. sagittal, coronal, transverse, and offaxis or oblique. Assess and evaluate
CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels Objectives Determine specific imaging plane used to acquire or reformat CT scan, i.e. sagittal, coronal, transverse, and offaxis or oblique. Assess and evaluate
Ultrasound Reimbursement Guide 2015: BioJet Fusion
 Ultrasound Reimbursement Guide 2015: BioJet Fusion Diagnosis codes explain the rationale for a given service and are a key factor in a payer s evaluation of medical necessity and coverage determination
Ultrasound Reimbursement Guide 2015: BioJet Fusion Diagnosis codes explain the rationale for a given service and are a key factor in a payer s evaluation of medical necessity and coverage determination
Analysis of Low-Value Health Services in the Minnesota All Payer Claims Database
 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS AND METHODS SUPPLEMENT Analysis of Low-Value Health Services in the Minnesota All Payer Claims Database MAY 2017 Minnesota Department of Health Health Economics Program 85 E. 7th
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS AND METHODS SUPPLEMENT Analysis of Low-Value Health Services in the Minnesota All Payer Claims Database MAY 2017 Minnesota Department of Health Health Economics Program 85 E. 7th
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
SYLLABUS BDS I PROFESSIONAL GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
0081 Repeat examinations: No reduction 2004.
 NATIONAL REFERENCE PRICE LIST FOR SERVICES BY RADIOGRAPHERS EFFECTIVE FROM 1 JANUARY 26 The following reference price list is not a set of tariffs that must be applied by medical schemes and/or providers.
NATIONAL REFERENCE PRICE LIST FOR SERVICES BY RADIOGRAPHERS EFFECTIVE FROM 1 JANUARY 26 The following reference price list is not a set of tariffs that must be applied by medical schemes and/or providers.
Ultrasound Reimbursement Information for Anesthesiology 1
 GE Healthcare Ultrasound Reimbursement Information for Anesthesiology 1 January, 2009 www.gehealthcare.com/reimbursement This overview addresses coding, coverage, and for ultrasound guidance with continuous
GE Healthcare Ultrasound Reimbursement Information for Anesthesiology 1 January, 2009 www.gehealthcare.com/reimbursement This overview addresses coding, coverage, and for ultrasound guidance with continuous
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION
 FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 72192 Computed tomography, pelvis; without contrast material 72193 with contrast material(s) 72194 without
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 72192 Computed tomography, pelvis; without contrast material 72193 with contrast material(s) 72194 without
Shadow because the air
 Thyroid Ultrasound Thyroid US examination needs: 1. high frequency transducer 2. extended patient's neck 3. check all the neck area because the swelling could be in areas other than the thyroid such as
Thyroid Ultrasound Thyroid US examination needs: 1. high frequency transducer 2. extended patient's neck 3. check all the neck area because the swelling could be in areas other than the thyroid such as
The Third-Party Reimbursement Process for Orthotics
 The Third-Party Reimbursement Process for Orthotics When the foot hits the ground, everything changes. We know that over 90% of the population suffers with overpronation of their feet. Implementing Foot
The Third-Party Reimbursement Process for Orthotics When the foot hits the ground, everything changes. We know that over 90% of the population suffers with overpronation of their feet. Implementing Foot
Radiation Therapy Services
 Radiation Therapy Services Chapter.1 Enrollment..................................................................... -2.2 Benefits, Limitations, and Authorization Requirements...........................
Radiation Therapy Services Chapter.1 Enrollment..................................................................... -2.2 Benefits, Limitations, and Authorization Requirements...........................
2015 Radiology Coding Survival Guide
 2015 Radiology Coding Survival Guide Chapter 31: Clinical Brachytherapy (77750-77799) Clinical brachytherapy involves applying radioelements into or around a treatment field. CPT guidelines clarify that
2015 Radiology Coding Survival Guide Chapter 31: Clinical Brachytherapy (77750-77799) Clinical brachytherapy involves applying radioelements into or around a treatment field. CPT guidelines clarify that
b. To facilitate the management decision of a patient with an equivocal stress test.
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines EBCT HEART CT & HEART CT CONGENITAL CCTA CPT4 Codes: 75571 EBCT 75572, 75573 Heart CT & Heart CT Congenital 75574 - CCTA LCD ID Number: L33559 J K
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines EBCT HEART CT & HEART CT CONGENITAL CCTA CPT4 Codes: 75571 EBCT 75572, 75573 Heart CT & Heart CT Congenital 75574 - CCTA LCD ID Number: L33559 J K
Ultrasound and Fluoroscopic Paravertebral Facet Joint Injections
 Policy Number FAC06222011RP Ultrasound and Fluoroscopic Approved By UnitedHealthcare Medicare Committee Current Approval Date 06/25/2014 IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT THIS REIMBURSEMENT POLICY This policy is applicable
Policy Number FAC06222011RP Ultrasound and Fluoroscopic Approved By UnitedHealthcare Medicare Committee Current Approval Date 06/25/2014 IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT THIS REIMBURSEMENT POLICY This policy is applicable
Coding Companion for Orthopaedics Upper: Spine & Above. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Orthopaedics Upper: Spine & bove comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2015 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Integumentary...1 Nails...9 Repair...18
Coding Companion for Orthopaedics Upper: Spine & bove comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2015 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Integumentary...1 Nails...9 Repair...18
RADIATION THERAPY SERVICES CSHCN SERVICES PROGRAM PROVIDER MANUAL
 RADIATION THERAPY SERVICES CSHCN SERVICES PROGRAM PROVIDER MANUAL APRIL 2018 CSHCN PROVIDER PROCEDURES MANUAL APRIL 2018 RADIATION THERAPY SERVICES Table of Contents 34.1 Enrollment......................................................................
RADIATION THERAPY SERVICES CSHCN SERVICES PROGRAM PROVIDER MANUAL APRIL 2018 CSHCN PROVIDER PROCEDURES MANUAL APRIL 2018 RADIATION THERAPY SERVICES Table of Contents 34.1 Enrollment......................................................................
The determination of eligible population for this measure requires administrative claims data.
 Overuse of Imaging Measure 6: Ratio of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scans to Computed Tomography Scans for the Evaluation of Children with Atraumatic Headache Description This measure assesses the ratio
Overuse of Imaging Measure 6: Ratio of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scans to Computed Tomography Scans for the Evaluation of Children with Atraumatic Headache Description This measure assesses the ratio
DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY SERVICES CSHCN SERVICES PROGRAM PROVIDER MANUAL
 DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY SERVICES CSHCN SERVICES PROGRAM PROVIDER MANUAL FEBRUARY 2018 CSHCN PROVIDER PROCEDURES MANUAL FEBRUARY 2018 DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY SERVICES Table of Contents 16.1 Enrollment......................................................................
DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY SERVICES CSHCN SERVICES PROGRAM PROVIDER MANUAL FEBRUARY 2018 CSHCN PROVIDER PROCEDURES MANUAL FEBRUARY 2018 DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY SERVICES Table of Contents 16.1 Enrollment......................................................................
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely
Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI Studies should NOT be ordered simultaneously as dual studies (i.e., with and without contrast). Radiation exposure is doubled and both views are rarely
Coding Companion for Podiatry. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Podiatry comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2016 Contents Contents Foot and Toes 28043-28045 [28039, 28041] 28043 28039 28045 28041 Excision, tumor, soft tissue
Coding Companion for Podiatry comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2016 Contents Contents Foot and Toes 28043-28045 [28039, 28041] 28043 28039 28045 28041 Excision, tumor, soft tissue
Any vascular studies performed should be as a result of, or to complement, a thorough patient evaluation and neurological examination.
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines NON-INVASIVE CEREBROVASCULAR ARTERIALS TUDIES Original Date: October 2015 Page 1 of 8 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4 Codes: Please refer to page
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines NON-INVASIVE CEREBROVASCULAR ARTERIALS TUDIES Original Date: October 2015 Page 1 of 8 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4 Codes: Please refer to page
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
BlueAdvantage SM. & BlueChoice SM Radiology Prior Authorization Program Code List CPT /HCPS
 BlueAdvantage SM & BlueChoice SM Radiology Prior Authorization Program Code List CPT /HCPS 70336 MRI TMJ 70450 CT Head Without Contrast 70460 CT Head With Contrast 70470 CT Head Without & With Contrast
BlueAdvantage SM & BlueChoice SM Radiology Prior Authorization Program Code List CPT /HCPS 70336 MRI TMJ 70450 CT Head Without Contrast 70460 CT Head With Contrast 70470 CT Head Without & With Contrast
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Certification Review. Module 28. Medical Coding. Radiology
 Module 28 is the study of x-rays, using radiant energy and other imaging techniques, such as resonance imaging or ultrasound, to diagnose illnesses and diseases. Vocabulary Barium enema (BE): lower gastrointestinal
Module 28 is the study of x-rays, using radiant energy and other imaging techniques, such as resonance imaging or ultrasound, to diagnose illnesses and diseases. Vocabulary Barium enema (BE): lower gastrointestinal
GUIDELINES FOR. Advanced. Imaging Studies
 GUIDELINES FOR Advanced Imaging Studies Locations Herrin Hospital Memorial Hospital of Carbondale St. Joseph Memorial Hospital 201 S 14th Street Herrin, IL 62948 618.942.2171 ext 35400 General Radiography*
GUIDELINES FOR Advanced Imaging Studies Locations Herrin Hospital Memorial Hospital of Carbondale St. Joseph Memorial Hospital 201 S 14th Street Herrin, IL 62948 618.942.2171 ext 35400 General Radiography*
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
MRI and CT of the CNS
 MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
