Migraine is one of the most prevalent neurologic
|
|
|
- Rodger Peters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Concepts in Acute Migraine Management: Clinical and Managed Care Perspectives Maria Lopes, MD, MS; Jeffrey D. Dunn, PharmD, MBA; A. H. Calhoun, MD; and Alan M. Rapoport, MD Specialty Healthcare Benefits Council Migraine is one of the most prevalent neurologic conditions, affecting more than 29.5 million adults in the United States. 1 It is more prevalent than Alzheimer s disease (patients aged >65 years), Parkinson s disease (patients aged >65 years), stroke, and multiple sclerosis combined. 2 Despite its wide prevalence and debilitating nature, migraine is often misdiagnosed and poorly managed by both primary care providers (PCPs) and neurologists. 3-6 The costs of migraine to managed care organizations (MCOs) can be substantial. Inappropriate use of both over-the-counter and prescription medications can lead to increased costs and poor patient outcomes by causing medication overuse headache and unnecessary emergency department (ED) visits. In the United States, total annual migraine-related costs in 2010 were $3.2 billion for outpatient visits, $700 million for ED visits, and $375 million for inpatient hospitalizations. 7 Sixteen percent of first presentations are in the ED. 8 The average total hospital costs are about $1800 per visit. 9 These costs can be substantially higher if imaging is ordered at an average cost of about $2500 for magnetic resonance imaging. 10 One prominent factor correlated with escalating utilization of the ED is opioid use (see clinical recommendations for opioid use in Table 1). A study showed that patients who were dependent on opioids used the ED almost 24 more times per year than those who were not. 15 Few physicians are familiar with International Classification of Headache Disorders II diagnostic criteria (Figure), and although American Headache Society treatment guidelines exist, they are infrequently used by PCPs. 3,6 Inappropriate management of migraine can increase the potential progression from episodic (0 to 14 headache days per month) to chronic migraine (>15 days a month lasting at least 4 hours without treatment), ABSTRACT Migraine is a chronic, prevalent, and disabling neurologic condition, affecting millions of adults in the United States. Inadequate management of and undertreatment of migraine impact patients, payers, providers, and employers and result in increased frequency of attacks, the need for additional medication, and spiraling costs. Although prevention is important, this article highlights treatment challenges in migraine management and explores unmet needs in acute treatment. (Am J Pharm Benefi ts. 2012;4(5): ) Vol. 4, No. 5 The American Journal of Pharmacy Benefi ts 201
2 Lopes Dunn Calhoun Rapoport Table 1. Clinical Recommendations for Classes of Acute Migraine Therapy Drug Class Clinical Recommendations Triptans Early use may prevent central sensitization Less effective after central sensitization develops Triptans contraindicated in patients with ischemic or vasospastic heart disease, stroke, uncontrolled hypertension, and basilar or hemiplegic migraine 11,12 NSAIDs Opioids Butalbital-containing combinations Dihydroergotamine Early use can inhibit neurogenic infl ammation and peripheral sensitization Ability to interrupt established central sensitization when used during later stages of migraine progression Prevention or interruption of cutaneous allodynia Only 1 prescription NSAID (diclofenac potassium for oral solution) is approved by the FDA for acute therapy of migraine 13 Opioids are not FDA approved for acute therapy of migraine Even low-level use of opioids is associated with poor patient outcomes 14 Use of opioids should be limited or discontinued because of their abuse potential and sedative effects Butalbital-containing combinations are not approved by the FDA for acute therapy of migraine and are controversial in this setting Effi cacy in migraine has not been proved in placebo-controlled trials Propensity to cause MOH, dependence, and addiction The US Headache Consortium recommends limited use of these compounds and prescribing only with careful monitoring Rapid-acting therapy that is effective at any stage of migraine Ability to interrupt established central sensitization when used during later stages of migraine progression FDA indicates US Food and Drug Administration; MOH, medication overuse headache; NSAID, nonsteroidal anti-infl ammatory drug. with a pervasive and debilitating impact on quality of life and related increased costs to the payer PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF MIGRAINE PROGRESSION The pathophysiology of migraine is not completely understood. One generally accepted pathway begins with the depolarization of meningeal perivascular trigeminal nerve endings, generally initiated by a wave of cortical spreading depression. 20 Sensitization of central trigeminal pathways (central sensitization) occurs as a result of a barrage of impulses into the brainstem trigeminal nucleus caudalis via the first branch of the trigeminal nerve. 21 The ideal acute treatment of migraine should address both central and peripheral mechanisms of migraine to reduce the risk of developing cutaneous allodynia. A marker for central sensitization, cutaneous allodynia is characterized by pain that is precipitated by normally nonpainful stimuli. 22 Early treatment is a clinical priority, as central sensitization is associated with poor response to therapy and progression to chronic migraine. 22,23 OVERCOMING CHALLENGES IN MIGRAINE TREATMENT Current challenges to optimal migraine treatment include incomplete response to acute therapy (which may increase recurrence), intolerable side effects, medication overuse, poor patient compliance, and frequency of migraine. Poor Response to Acute Therapy Efficacy of acute migraine therapy depends on individual patient response, drug class(es) used, stage of the attack at the time of treatment, time to peak plasma concentrations, and side effects. Poor response may also be due to delayed treatment. Almost half of migraineurs delay taking their medication: reasons include mild pain at the onset of a migraine attack, avoidance of side effects, and fear of expending a limited supply of medications before the end of the month. 24 Compounding the impact of this delay are 2 additional factors: (1) tablet formulations may take 60 minutes or longer to work and (2) gastroparesis, which occurs in the majority of migraineurs, impairs absorption or reduces bioavailability of tablet formulations, resulting in further delay of therapeutic efficacy. 18,25,26 Triptans, due to their specific activity on 5-hydroxytryptamine 1 (5-HT 1 ) receptors, can further exacerbate this problem by delaying gastric emptying times. Liquid preparations and those that act like liquids, on the other hand, are thought to be unaffected by gastroparesis. 27 Intolerance to Triptan Therapy and Headache Recurrence Side effects are a major treatment challenge and may occur in up to 89% of patients taking triptans. 23,28 Although these are often innocuous triptan sensations, their prevalence underscores the need for additional treatment options. Migraine recurrence can result in medication overuse and increased utilization costs, which should be a consideration for both prescribers and payers. 23 The average rate of recurrence for oral sumatriptan is approximately 30%, while it may be as high as 39% for sumatriptan subcutaneous injection. 23,28-30 Diclofenac potassium for oral solution has one of the lowest 24-hour recurrence rates, reported at 14% The American Journal of Pharmacy Benefi ts September/October
3 Concepts in Acute Migraine Management Medication Overuse and Medication Overuse Headache Medication overuse headache may occur with overuse of several classes of drugs but is commonly associated with over-thecounter medications, triptans, opioids, and butalbital-containing combinations. 15,31 In March 2012, the US Food and Drug Administration issued a label change for several triptans, highlighting their potential to contribute to medication overuse headache Additional concerns with opioids are tolerance, dependence, and addiction; patients should restrict their use of opioids or avoid them completely. 14 Figure. International Classification of Headache Disorders II Criteria for Migraine Without Aura 16 A. At least 5 headache attacks fulfilling criteria B through D B. Headache attacks lasting 4 to 72 hours (untreated or unsuccessfully treated) C. Headache has at least 2 of the following characteristics: Unilateral location Pulsating quality Moderate or severe pain intensity Aggravation by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity (eg, walking or climbing stairs) D. During headache, at least 1 of the following characteristics: Nausea and/or vomiting Photophobia and/or phonophobia E. Headache cannot be attributed to another disorder Progression to Chronic Migraine The transformation from episodic to chronic migraine can be costly for MCOs. In one study, patients who developed chronic migraine had significantly more outpatient, pain clinic, and ED visits compared with those whose migraine remained episodic. 35,36 While overuse of acute medications (particularly opioids, butalbital-containing combinations, and triptans) is strongly associated with migraine recurrence and the transformation to chronic migraine, about 3% of migraineurs develop chronic migraine each year without medication overuse. 18,28,37 Benefits of Early Treatment With Rapid-Acting Therapy Interrupting migraine progression is a key goal of treatment. Once central sensitization and its clinical correlate cutaneous allodynia occur, the efficacy of triptans is reduced. 22,23 Benefits of early treatment include potentially improved patient outcomes, reduced use of medications, and reduced risk of developing chronic migraine. While triptans and other acute therapies are effective early in the course of migraine, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or dihydroergotamine are preferred therapies in later stages, as they can prevent or reverse central sensitization and cutaneous allodynia Clinical recommendations for classes of migraine drugs are shown in Table 1. THERAPEUTIC AND FORMULARY CONSIDERATIONS Availability of generic triptans and new formulations of migraine drugs may prompt formulary reviews of the migraine category. Products in development include a sumatriptan transdermal patch (Zelrix), a dihydroergotamine mesylate inhalation aerosol (Levadex), a sumatriptan nasal powder device (OptiNose), and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antagonists. Existing products, available since the 7 triptan tablets were approved, include a sumatriptan naproxen sodium fixed-combination tablet (Treximet), a sumatriptan injection needle-free delivery system (Sumavel DosePro), diclofenac potassium for oral solution (Cambia), and onabotulinum toxin A injections (Botox) for prevention of chronic migraine. Sumatriptan Naproxen Sodium Fixed-Combination Tablets. Sumatriptan naproxen sodium fixed-combination tablets are meant to stop migraine in its initial stages and thereby prevent central sensitization. 11,39 The combination is only modestly superior to sumatriptan or naproxen alone, and both components are available generically at a lower price. 39 Sumatriptan Injection Needle-Free Delivery System. The sumatriptan injection needle-free delivery system uses pressurized nitrogen to propel the drug through the skin and into the subcutaneous tissue. Benefits include fast onset of action, even in the presence of gastroparesis. 12 It is bioequivalent to generic sumatriptan injections but is priced higher. Diclofenac Potassium for Oral Solution. Diclofenac potassium for oral solution is a buffered powder that rapidly dissolves in 2 ounces of water and is the only prescription NSAID approved in the United States for the acute treatment of migraine. With demonstrated plasma levels within 5 minutes, it achieves initial analgesic relief within 15 minutes (compared with 60 minutes for tablet diclofenac), delivering peak plasma levels 2 to 4 times higher than those delivered by the tablet. The oral solution was significantly superior in time to onset, efficacy, and duration of response compared with the same dose in tablet formulation. It interrupts the progression Vol. 4, No. 5 The American Journal of Pharmacy Benefi ts 203
4 Lopes Dunn Calhoun Rapoport Table 2. Assessment of Acute Migraine Medication Efficacy 44 Factor to Assess End Point Rapidity of relief Meaningful onset within 1 hour Partial vs total pain relief Total relief within 2 hours Relief of associated symptoms No nausea, vomiting, photophobia, or phonophobia Return to normal function Within 2 hours without sedation Headache recurrence Prevented due to total relief with 1 dose of medication Consistency of response Relief for every headache Adverse effects None or minimal Preference/convenience of formulation Ease of use, acceptable pain or taste considerations, convenience Cost Reasonable, with good effi cacy and return to functionality with minimal disability of peripheral and central sensitization, and is not impacted by gastroparesis. There is no generic equivalent for this formulation, but it is priced higher than generic NSAIDs. 18,41 Onabotulinum Toxin A. Onabotulinum toxin A is indicated for the prevention of chronic migraine and costs an estimated $1000 to $2000 per treatment, including physician fees. 42,43 A recent study on chronic migraine found onabotulinum toxin A has a small to modest benefit in reducing the number of headache days per month but was not associated with fewer migraine attacks per month. 42 Formulary Management of Acute Migraine Medications When reviewing a product or class of migraine drugs, clinical considerations such as efficacy, safety, Table 3. Formulary Management Provisions for Acute Migraine Therapies Tiered copayments Generic triptans placed on tier 1 More expensive, branded triptans on a higher copayment tier Brands without generic equivalents on tier 2 or tier 3 with ancillary fees applied Step-therapy edits Depends on perceived benefi ts of therapy and appropriate use Step edits that require a patient to fail the same class of drug more than once may be a hindrance to successfully managing migraine Quantity limits Can help control the overuse of medications, including triptans, barbiturates, and opioids May lead some patients to hoard prescription medications and overuse OTCs, potentially increasing ED utilization and costs Prior authorizations Meant to ensure appropriate diagnosis or prior use of therapy based on formulary policy Often required for high-cost treatments or therapy with questionable clinical effi cacy ED indicates emergency department; OTC, over the counter. tolerability, mechanism of action, formulation, and onset of analgesic effect are paramount. Efficacy parameters should be specific to the migraine category, including data across multiple end points (Table 2). Various formulary management strategies are utilized for migraine therapies (Table 3). Economic considerations include the relative cost of care, currently available therapeutic options, appropriate use/place in therapy, and the potential for abuse or overutilization. Appropriate pharmacologic management of migraine can reduce outpatient visits, ED visits, diagnostic scans, and hospitalizations. Proactive Case Management Plan To proactively manage migraine, healthcare providers should do the following: Review the American Headache Society guidelines. Initiate an effective treatment plan that recommends the right treatment the first time and deters medication overuse and hoarding, as well as the use of less effective medications. Consider the complementary use of a generic triptan and migraine-indicated NSAID to attack both peripheral and central components of migraine. Consider fast-acting medicines to reduce the need for rescue therapy. Educate patients to help them discover and avoid migraine triggers. Refer patients not responding to their current treatment to headache specialists. Ensure that case managers probe long-term and increased use of prescription opioids, overuse of over-the-counter medications, and incidence of medication overuse headache. 204 The American Journal of Pharmacy Benefi ts September/October
5 Concepts in Acute Migraine Management SUMMARY The misdiagnosis, undertreatment, and inappropriate management of migraine can lead to medication overuse, increased attack frequency, and progression to chronic migraine. Treatment should be initiated early with rapid-acting therapy that has the potential to address the central and peripheral mechanisms of migraine, reduce the risk of cutaneous allodynia and medication overuse headache, and minimize recurrence. The pharmacy and therapeutics committee class review of migraine therapies should include economic, pathophysiologic, and clinical considerations. The availability of multiple therapeutic options for acute migraine treatment may improve patient outcomes and reduce costs. Author Affiliations: From AMC Health (ML), Cresskill, NJ; SelectHealth (JDD), Murray, UT; Carolina Headache Institute (AHC), Chapel Hill, NC; Department of Anesthesiology, Department of Psychiatry (AHC), University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC; The David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA (AMR), Los Angeles, CA. Funding Source: None. Author Disclosures: Dr Dunn reports receiving consultancies from Nautilus. Dr Calhoun reports board membership and consultancies from GlaxoSmithKline, Map Pharmaceuticals, Nautilus, and Zogenix advisory boards, and also reports receiving grants from GlaxoSmithKline and lecture fees from GlaxoSmithKline, Nautilus, and Zogenix. Dr Rapoport reports receiving consultancies from Allergan, Map Pharmaceuticals, Impax, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and lecture fees from Allergan and Nautilus. Dr Lopes reports no relationship or financial interest with any entity that would pose a conflict of interest with the subject matter of this article. Authorship Information: Concept and design (ML, JDD, AHC, AMR); acquisition of data (AMR); analysis and interpretation of data (ML, JDD, AMR); drafting of the manuscript (ML, JDD, AHC, AMR); and critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content (ML, JDD, AHC, AMR). Address correspondence to: Maria Lopes, MD, MS, Chief Medical Officer, AMC Health, 117 Truman Dr, Cresskill, NJ REFERENCES 1. National Headache Foundation. Migraine. Accessed May 29, Hirtz D, Thurman DJ, Gwinn-Hardy K, Mohamed M, Chaudhuri AR, Zalutsky R. How common are the common neurologic disorders? Neurology. 2007;68(5): Diamond S, Bigal ME, Silberstein S, Loder E, Reed M, Lipton RB. Patterns of diagnosis and acute and preventive treatment for migraine in the United States: results from the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention study. Headache. 2007;47(3): Dodick DW, Lipsy RJ. Advances in migraine management: implications for managed care organizations. Manag Care. 2004;13(5): Holmes WF, MacGregor EA, Sawyer JP, Lipton RB. Information about migraine disability infl uences physicians perceptions of illness severity and treatment needs. Headache. 2001;41(4): Lipton RB, Hamelsky SW, Dayno JM. What do patients with migraine want from acute migraine treatment? Headache. 2002;42(suppl 1): Insinga RP, Ng-Mak DS, Hanson ME. Costs associated with outpatient, emergency room and inpatient care for migraine in the USA. Cephalalgia. 2011;31(15): Maizels M. Headache evaluation and treatment by primary care physicians in an emergency department in the era of triptans. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(16): Friedman D, Feldon S, Holloway R, Fisher S. Utilization, diagnosis, treatment and cost of migraine treatment in the emergency department. Headache. 2009; 49(8): CostEvaluation.com. How much does an MRI cost? Accessed May 30, Treximet [prescribing information]. Research Triangle Park, NC: GlaxoSmith- Kline; Sumavel DosePro [prescribing information]. San Diego, CA: Zogenix, Inc; Cambia [prescribing information]. Bedminster, NJ: Nautilus Neurosciences, Inc; Rothrock JF. Opiate and opioid ( narcotic ) therapy for acute migraine headache. Headache. 2010;50(7): Buse DC, Pearlman SH, Reed ML, Serrano D, Ng-Mak DS, Lipton RB. Opioid use and dependence among persons with migraine: results of the AMPP study. Headache. 2012;52(1): Headache Classifi cation Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classifi cation of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia. 2004;24(suppl 1): Silberstein SD. Chronic daily headache: classifi cation, epidemiology, and risk factors. Adv Stud Med. 2006;6(9C):S885-S les/articlefi les/pdf/asim_6_9c_p885_890.pdf. Accessed July 12, Kahn K. Cambia (diclofenac potassium for oral solution) in the management of acute migraine. US Neurology. 2011;7(2): Lipton RB, Stewart WF, Diamond S, Diamond ML, Reed M. Prevalence and burden of migraine in the United States: data from the American Migraine Study II. Headache. 2001;41(7): Bolay H, Reuter U, Dunn AK, Huang Z, Boas DA, Moskowitz MA. Intrinsic brain activity triggers trigeminal meningeal afferents in a migraine model. Nat Med. 2002;8(2): Jakubowski M, Levy D, Goor-Aryeh I, Collins B, Bajwa Z, Burstein R. Terminating migraine with allodynia and ongoing central sensitization using parenteral administration of COX1/COX2 inhibitors. Headache. 2005;45(7): Lipton RB, Bigal ME, Ashina S, et al; American Migraine Prevalence Prevention Advisory Group. Cutaneous allodynia in the migraine population. Ann Neurol. 2008;63(2): Krymchantowski AV. Acute treatment of migraine. Breaking the paradigm of monotherapy. BioMed Central website. Accessed April 9, Foley KA, Cady R, Martin V, et al. Treating early versus treating mild: timing of migraine prescription medications among patients with diagnosed migraine. Headache. 2005;45(5): Thomsen LL, Dixon R, Lassen LH, et al. 311C90 (Zolmitriptan), a novel centrally and peripheral acting oral 5-hydroxytryptamine-1D agonist: a comparison of its absorption during a migraine attack and in a migraine-free period. Cephalalgia. 1996;16(4): Volans GN. The effect of metoclopramide on the absorption of effervescent aspirin in migraine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1975;2(1): Tfelt-Hansen P. Gastric emptying in migraine. Headache. 2007;47(6): Dahlöf CG. How does sumatriptan perform in clinical practice? Cephalalgia. 1995;15(suppl 15): Bates D, Ashford E, Dawson R, et al; Sumatriptan Aura Study Group. Subcutaneous sumatriptan during the migraine aura. Neurology. 1994;44(9): Diener HC, Tfelt-Hansen P, de Beukelaar F, et al; Study Group. The effi cacy and safety of sc alniditan vs. sc sumatriptan in the acute treatment of migraine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Cephalalgia. 2001;21(6): Bigal ME, Lipton RB. Overuse of acute migraine medications and migraine chronifi cation. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2009,13(4): US Food and Drug Administration. Safety. Imitrex (sumatriptan) nasal spray and tablets. Accessed May 29, US Food and Drug Administration. Safety. Amerge (naratriptan) tablets. Accessed May 29, Vol. 4, No. 5 The American Journal of Pharmacy Benefi ts 205
6 Lopes Dunn Calhoun Rapoport 34. US Food and Drug Administration. Safety. Treximet (sumatriptan/naproxen) tablets. Accessed May 29, Goldberg LD. The cost of migraine and its treatment. Am J Manag Care. 2005;11(2)(suppl):S62-S Halpern MT, Lipton RB, Cady RK, Kwong WJ, Marlo KO, Batenhorst AS. Costs and outcomes of early versus delayed migraine treatment with sumatriptan. Headache. 2002;42(10): Rothrock JF. Migraine chronifi cation : what you can do. Headache. 2009; 49(1): Goadsby PJ. The Act when Mild (AwM) study: a step forward in our understanding of early treatment in acute migraine. Cephalalgia. 2008;28(suppl 2): Burstein R, Collins B, Jakubowski M. Defeating migraine pain with triptans: a race against the development of cutaneous allodynia. Ann Neurol. 2004;55(1): Cady R, Biondi D. An update on migraine pathophysiology and mechanismbased pharmacotherapeutics for migraine. Postgrad Med. 2006;Spec No: Diener HC, Montagna P, Gács G, et al. Effi cacy and tolerability of diclofenac potassium sachets in migraine: a randomized, double-blind, cross-over study in comparison with diclofenac potassium tablets and placebo. Cephalalgia. 2006; 26(5): Jackson JL, Kuriyama A, Hayashino Y. Botulinum toxin A for prophylactic treatment of migraine and tension headaches in adults. JAMA. 2012;307(16): Singer N. Botox shots approved for migraine. The New York Times, October 6, Accessed May 15, Mueller LL. Diagnosing and managing migraine headache. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2007;107(10)(suppl 6):ES10-ES The American Journal of Pharmacy Benefi ts September/October
Adult & Pediatric Patients. Stanford Health Care, Division Pain Medicine
 Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients Theresa Mallick Searle, MS, RN BC, ANP BC Disclosures Speakers Bureau: Allergan, Depomed Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients
Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients Theresa Mallick Searle, MS, RN BC, ANP BC Disclosures Speakers Bureau: Allergan, Depomed Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines
 Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Faculty Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Acute Treatment Strategies
 WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Acute Treatment Strategies Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Acute Treatment Strategies Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
The use of combination therapies in the acute management of migraine
 REVIEW The use of combination therapies in the acute management of migraine Abouch Valenty Krymchantowski Headache Center of Rio, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; Outpatient Headache Unit of the Instituto de Neurologia
REVIEW The use of combination therapies in the acute management of migraine Abouch Valenty Krymchantowski Headache Center of Rio, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; Outpatient Headache Unit of the Instituto de Neurologia
An Overview of MOH. ALAN M. Rapoport, M.D. Clinical Professor of Neurology The David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, California
 An Overview of MOH IHS ASIAN HA MASTERS SCHOOL MARCH 24, 2013 ALAN M. Rapoport, M.D. Clinical Professor of Neurology The David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, California President-Elect
An Overview of MOH IHS ASIAN HA MASTERS SCHOOL MARCH 24, 2013 ALAN M. Rapoport, M.D. Clinical Professor of Neurology The David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, California President-Elect
Page: 1 of 5. Sumatriptan Tablets and Nasal Spray (Imitrex) / sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan (Imitrex / Treximet) Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 12, 2014 Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan (Imitrex / Treximet) Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 12, 2014 Sumatriptan
...SELECTED ABSTRACTS...
 The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on migraine management, were selected for their relevance to this Special Report supplement. Two Sumatriptan Studies Two double-blind
The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on migraine management, were selected for their relevance to this Special Report supplement. Two Sumatriptan Studies Two double-blind
TABLE 1. Current Diagnostic Criteria for Migraine Without Aura 2 A. At least 5 attacks fulfilling criteria B-D B. Headache attacks lasting 4-72 hours
 ANSWERS CONCISE TO FREQUENTLY REVIEW ASKED QUESTIONS FOR CLINICIANS ABOUT MIGRAINE Answers to Frequently Asked Questions About Migraine IVAN GARZA, MD, AND JERRY W. SWANSON, MD Migraine is a common primary
ANSWERS CONCISE TO FREQUENTLY REVIEW ASKED QUESTIONS FOR CLINICIANS ABOUT MIGRAINE Answers to Frequently Asked Questions About Migraine IVAN GARZA, MD, AND JERRY W. SWANSON, MD Migraine is a common primary
Sumatriptan Injection (Imitrex / Alsuma / Sumavel / Zembrace)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.11 Subject: Sumatriptan Injection Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Sumatriptan Injection
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.11 Subject: Sumatriptan Injection Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Sumatriptan Injection
MEASURE #1: MEDICATION PRESCRIBED FOR ACUTE MIGRAINE ATTACK Headache
 MEASURE #1: MEDICATION PRESCRIBED FOR ACUTE MIGRAINE ATTACK Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of migraine who were prescribed a guideline recommended
MEASURE #1: MEDICATION PRESCRIBED FOR ACUTE MIGRAINE ATTACK Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of migraine who were prescribed a guideline recommended
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT
 ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
Migraine Management. Roger Cady, MD Headache Care Center Springfield, MO
 Migraine Management Roger Cady, MD Headache Care Center Springfield, MO Disclosures Objectives The evolution of migraine From benign episodic (benign) headache to potentially a devastating chronic disease
Migraine Management Roger Cady, MD Headache Care Center Springfield, MO Disclosures Objectives The evolution of migraine From benign episodic (benign) headache to potentially a devastating chronic disease
Disclosures. Triptans for Kids 5/16/13
 5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
Sumatriptan Injection (Imitrex / Alsuma / Sumavel / Zembrace)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.11 Subject: Sumatriptan Injection Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 17, 2017 Sumatriptan Injection
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.11 Subject: Sumatriptan Injection Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 17, 2017 Sumatriptan Injection
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 CGRP Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
CGRP Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
Drug Therapy Guidelines
 Drug Therapy Guidelines Applicable Medical Benefit Effective: 5/1/18 Pharmacy- Formulary 1 x Next Review: 3/19 Pharmacy- Formulary 2 x Date of Origin: 8/29/06 Triptans: almotriptan, Amerge, Axert, Frova,
Drug Therapy Guidelines Applicable Medical Benefit Effective: 5/1/18 Pharmacy- Formulary 1 x Next Review: 3/19 Pharmacy- Formulary 2 x Date of Origin: 8/29/06 Triptans: almotriptan, Amerge, Axert, Frova,
Zomig. Zomig / Zomig-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
The best defense is a good offense. Optimizing the Acute Treatment of Migraine. Disclosures 11/10/2017
 Optimizing the Acute Treatment of Migraine Brian M. Plato, DO, FAHS Norton Neuroscience Institute Louisville, KY Disclosures Speakers Bureau (personal): Allergan, Depomed, Avanir Research Funding (paid
Optimizing the Acute Treatment of Migraine Brian M. Plato, DO, FAHS Norton Neuroscience Institute Louisville, KY Disclosures Speakers Bureau (personal): Allergan, Depomed, Avanir Research Funding (paid
Anti-Migraine Agents
 DRUG POLICY BENEFIT APPLICATION Anti-Migraine Agents Benefit determinations are based on the applicable contract language in effect at the time the services were rendered. Exclusions, limitations or exceptions
DRUG POLICY BENEFIT APPLICATION Anti-Migraine Agents Benefit determinations are based on the applicable contract language in effect at the time the services were rendered. Exclusions, limitations or exceptions
Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description
 Measure Title Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description Percentage of s age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of primary headache who were prescribed
Measure Title Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description Percentage of s age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of primary headache who were prescribed
SUMAVEL DOSEPRO (sumatriptan succinate) solution for injection
 SUMAVEL DOSEPRO (sumatriptan succinate) solution for injection Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit
SUMAVEL DOSEPRO (sumatriptan succinate) solution for injection Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit
medications. This was an openlabel study consisting of patients with migraines who historically failed to respond to oral triptan
 J Headache Pain (2007) 8:13 18 DOI 10.1007/s10194-007-0354-7 ORIGINAL Seymour Diamond Fred G. Freitag Alexander Feoktistov George Nissan Sumatriptan 6 mg subcutaneous as an effective migraine treatment
J Headache Pain (2007) 8:13 18 DOI 10.1007/s10194-007-0354-7 ORIGINAL Seymour Diamond Fred G. Freitag Alexander Feoktistov George Nissan Sumatriptan 6 mg subcutaneous as an effective migraine treatment
Regulatory Status FDA approved indication: Migranal Nasal Spray is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine headaches with or without aura (1).
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Migranal Nasal Spray
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Migranal Nasal Spray
UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA
 SUMATRIPTAN (ALSUMA, IMITREX, SUMAVEL DOSEPRO, ZECUITY ) UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA DRUG CLASS: BRAND (generic) NAME: Serotonin 5-HT1 receptor agonists Imitrex (sumatriptan), Alsuma (sumatriptan),
SUMATRIPTAN (ALSUMA, IMITREX, SUMAVEL DOSEPRO, ZECUITY ) UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA DRUG CLASS: BRAND (generic) NAME: Serotonin 5-HT1 receptor agonists Imitrex (sumatriptan), Alsuma (sumatriptan),
A case of a patient with chronic headache. Focus on Migraine. None related to the presentation Grants to conduct clinical trials from: Speaker bureau:
 Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Zolmitriptan nasal spray provides fast relief of migraine symptoms and is preferred by patients: a Swedish study of preference in clinical practice
 J Headache Pain (2004) 5:237 242 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0132-3 ORIGINAL Carl G.H. Dahlöf Mattias Linde Erika Kerekes Zolmitriptan nasal spray provides fast relief of migraine symptoms and is preferred
J Headache Pain (2004) 5:237 242 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0132-3 ORIGINAL Carl G.H. Dahlöf Mattias Linde Erika Kerekes Zolmitriptan nasal spray provides fast relief of migraine symptoms and is preferred
ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder
 ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache
 MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care. December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary
 Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Richard B Lipton 1, Brian Grosberg 1, Richard P Singer 2, Starr H Pearlman 3, James V Sorrentino 4, John N Quiring 5 and Joel R Saper 6.
 Original Article Efficacy and tolerability of a new powdered formulation of diclofenac potassium for the acute treatment of migraine: Results from the International Migraine Pain Assessment Clinical Trial
Original Article Efficacy and tolerability of a new powdered formulation of diclofenac potassium for the acute treatment of migraine: Results from the International Migraine Pain Assessment Clinical Trial
Zomig. Zomig / Zomig-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache
 MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
What is the Effectiveness of OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox ) in Reducing the Number of Chronic Migraines (CM) in Patients Years Old?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 What is the Effectiveness of OnabotulinumtoxinA
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 What is the Effectiveness of OnabotulinumtoxinA
Abortive Agents. Available Strengths. Formulary Limits. Tablet: 5mg, 10mg ODT: 5mg, 10 mg 25mg, 50mg, 100mg. 5mg/act, 20mg/act
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Migraine Therapy P&T DATE: 9/12/2017 CLASS: Neurological Disorders REVIEW HISTORY 12/16, 9/15, 2/15, 2/10, 5/07 LOB: MCL
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Migraine Therapy P&T DATE: 9/12/2017 CLASS: Neurological Disorders REVIEW HISTORY 12/16, 9/15, 2/15, 2/10, 5/07 LOB: MCL
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centers: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Migraine Diagnosis and Treatment: Results From the American Migraine Study II
 Migraine Diagnosis and Treatment: Results From the American Migraine Study II Richard B. Lipton, MD; Seymour Diamond, MD; Michael Reed, PhD; Merle L. Diamond, MD; Walter F. Stewart, MPH, PhD Objective.
Migraine Diagnosis and Treatment: Results From the American Migraine Study II Richard B. Lipton, MD; Seymour Diamond, MD; Michael Reed, PhD; Merle L. Diamond, MD; Walter F. Stewart, MPH, PhD Objective.
Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines: Migraine Medications
 Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines: Effective: September 18, 2017 Prior Authorization Required Type of Review Care Management Not Covered Type of Review Clinical Review Pharmacy (RX) or Medical (MED)
Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines: Effective: September 18, 2017 Prior Authorization Required Type of Review Care Management Not Covered Type of Review Clinical Review Pharmacy (RX) or Medical (MED)
MIGRAINE UPDATE. Objectives & Disclosures. Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment.
 MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) Inhibitors as Preventive Treatments for Patients with Episodic or Chronic Migraine: Effectiveness and Value
 Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) Inhibitors as Preventive Treatments for Patients with Episodic or Chronic Migraine: Effectiveness and Value Background Draft Background and Scope December 4, 2017
Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) Inhibitors as Preventive Treatments for Patients with Episodic or Chronic Migraine: Effectiveness and Value Background Draft Background and Scope December 4, 2017
Measure Components Numerator Statement
 MEASURE #5: OVERUSE OF OPIOID CONTAINING MEDICATIONS FOR PRIMARY HEADACHE DISORDERS Headache For Quality Improvement Only. Not to be used for Public Reporting or Accountability Measure Description Percentage
MEASURE #5: OVERUSE OF OPIOID CONTAINING MEDICATIONS FOR PRIMARY HEADACHE DISORDERS Headache For Quality Improvement Only. Not to be used for Public Reporting or Accountability Measure Description Percentage
Triptans Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Triptans Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS AND DOSAGE 1-13,14,23,24 Agents Amerge (naratriptan) 1, 2.5 tablets Axert (almotriptan) 6.25, 12.5 tablets migraine attacks with/without
Triptans Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS AND DOSAGE 1-13,14,23,24 Agents Amerge (naratriptan) 1, 2.5 tablets Axert (almotriptan) 6.25, 12.5 tablets migraine attacks with/without
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines
 How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
OH, MY ACHING HEAD! I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING SECONDARY HEADACHES
 1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
10/17/2017 CHRONIC MIGRAINES BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES PATIENT CASE EPIDEMIOLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY
 BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
UNDERSTANDING CHRONIC MIGRAINE. Learn about diagnosis, management, and treatment options for this headache condition
 UNDERSTANDING CHRONIC MIGRAINE Learn about diagnosis, management, and treatment options for this headache condition 1 What We re Going to Cover Today The symptoms and phases of migraine Differences between
UNDERSTANDING CHRONIC MIGRAINE Learn about diagnosis, management, and treatment options for this headache condition 1 What We re Going to Cover Today The symptoms and phases of migraine Differences between
Proposed Project Scope. OPTIMAL USE OnabotulinumtoxinA for the Prevention of Chronic Migraine Clinical Evidence, Policies and Practice
 Proposed Project Scope OPTIMAL USE OnabotulinumtoxinA for the Prevention of Chronic Migraine Clinical Evidence, Policies and Practice May 2018 1. BACKGROUND AND RATIONALE Migraine is a common, debilitating
Proposed Project Scope OPTIMAL USE OnabotulinumtoxinA for the Prevention of Chronic Migraine Clinical Evidence, Policies and Practice May 2018 1. BACKGROUND AND RATIONALE Migraine is a common, debilitating
A new questionnaire for assessment of adverse events associated with triptans: methods of assessment influence the results. Preliminary results
 J Headache Pain (2004) 5:S112 S116 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0123-4 Michele Feleppa Fred D. Sheftell Luciana Ciannella Amedeo D Alessio Giancarlo Apice Nino N. Capobianco Donato M.T. Saracino Walter Di Iorio
J Headache Pain (2004) 5:S112 S116 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0123-4 Michele Feleppa Fred D. Sheftell Luciana Ciannella Amedeo D Alessio Giancarlo Apice Nino N. Capobianco Donato M.T. Saracino Walter Di Iorio
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 CGRP Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
CGRP Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
Diclofenac potassium for oral solution (CAMBIA ) in the acute management of a migraine attack: clinical evidence and practical experience
 684494TAN0010.1177/1756285616684494Therapeutic Advances in Neurological DisordersJoshi and Rapoport research-article2016 Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders Review Diclofenac potassium for oral
684494TAN0010.1177/1756285616684494Therapeutic Advances in Neurological DisordersJoshi and Rapoport research-article2016 Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders Review Diclofenac potassium for oral
Drug List. Improving Outcomes in Episodic Migraine. Learning Objectives
 12:45 2 pm Improving Outcomes in Episodic Migraine SPEAKERS D. Michael Ready, MD Roger K. Cady, MD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: D. Michael
12:45 2 pm Improving Outcomes in Episodic Migraine SPEAKERS D. Michael Ready, MD Roger K. Cady, MD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: D. Michael
ACUTE TREATMENT FOR MIGRAINE. Cristina Tassorelli
 The European Headache School 2012 ACUTE TREATMENT FOR MIGRAINE Cristina Tassorelli Headache Science Centre, IRCCS Neurological Institute C. Mondino Foundation - Pavia University Centre for Adaptive Disorders
The European Headache School 2012 ACUTE TREATMENT FOR MIGRAINE Cristina Tassorelli Headache Science Centre, IRCCS Neurological Institute C. Mondino Foundation - Pavia University Centre for Adaptive Disorders
PHARMACY COVERAGE GUIDELINES ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE DATE: 5/18/17 SECTION: DRUGS LAST REVIEW DATE: 5/17/18 LAST CRITERIA REVISION DATE: ARCHIVE DATE:
 ALLZITAL (butalbital and acetaminophen) 25 mg/325 mg oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific
ALLZITAL (butalbital and acetaminophen) 25 mg/325 mg oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific
RISK FACTORS AND PROGNOSIS OF CHRONIC MIGRAINE
 RISK FACTORS AND PROGNOSIS OF CHRONIC MIGRAINE Gretchen E. Tietjen, MD University of Toledo Toledo, Ohio Learning objectives At the conclusion of this presentation, participants should be able to: 1. Understand
RISK FACTORS AND PROGNOSIS OF CHRONIC MIGRAINE Gretchen E. Tietjen, MD University of Toledo Toledo, Ohio Learning objectives At the conclusion of this presentation, participants should be able to: 1. Understand
Prevent, Treat, Repeat: Getting Ahead of Migraines. Jennifer Bestard MD FRCPC Neurology
 Prevent, Treat, Repeat: Getting Ahead of Migraines Jennifer Bestard MD FRCPC Neurology Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Presenter: Jennifer Bestard Relationships that may introduce potential bias and/or conflict
Prevent, Treat, Repeat: Getting Ahead of Migraines Jennifer Bestard MD FRCPC Neurology Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Presenter: Jennifer Bestard Relationships that may introduce potential bias and/or conflict
Headache. Section 1. Migraine headache. Clinical presentation
 Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation.
 I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention
 Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention Amanda Janisch, PharmD PGY2 Ambulatory Care Pharmacy Resident MCHS SWMN, Mankato, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No financial interest
Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention Amanda Janisch, PharmD PGY2 Ambulatory Care Pharmacy Resident MCHS SWMN, Mankato, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No financial interest
Drug List. Improving Outcomes in Episodic Migraine. Presenter Disclosure Information. Learning Objectives. Improving Outcomes in Episodic Migraine
 2:15 3:30 pm Improving Outcomes in Episodic Migraine SPEAKERS Brian E. McGeeney, M.D., M.P.H. D. Michael Ready, MD, FAHS Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this
2:15 3:30 pm Improving Outcomes in Episodic Migraine SPEAKERS Brian E. McGeeney, M.D., M.P.H. D. Michael Ready, MD, FAHS Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this
ACUTE MIGRAINE: OLD AND NEW DRUGS JOHN ROBROCK MD FORT WILLIAM FAMILY HEALTH TEAM
 ACUTE MIGRAINE: OLD AND NEW DRUGS JOHN ROBROCK MD FORT WILLIAM FAMILY HEALTH TEAM Conflict of Interest Declaration: Nothing to Disclose Presenter: John Robrock, MD Title of Presentation: Acute Migraine:
ACUTE MIGRAINE: OLD AND NEW DRUGS JOHN ROBROCK MD FORT WILLIAM FAMILY HEALTH TEAM Conflict of Interest Declaration: Nothing to Disclose Presenter: John Robrock, MD Title of Presentation: Acute Migraine:
Headache A Practical Approach
 Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
Clinical case. Clinical case 3/15/2018 OVERVIEW. Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment. Refractory headache.
 OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
Migraine is a very common medical disorder
 MENSTRUALLY RELATED MIGRAINE: IMPLICATIONS FOR EMPLOYERS AND MANAGED CARE * Richard B. Lipton, MD ABSTRACT Migraine is a common disorder, affecting approximately 28 million men and women in the United
MENSTRUALLY RELATED MIGRAINE: IMPLICATIONS FOR EMPLOYERS AND MANAGED CARE * Richard B. Lipton, MD ABSTRACT Migraine is a common disorder, affecting approximately 28 million men and women in the United
Advances in the Treatment of Migraine
 Advances in the Treatment of Migraine C. Philip O Carroll, M.D. Director Neurobehavioral Medicine Hoag Neurosciences Institute Guyuron B Headache, 2015;55:1464-1473 I m sorry your head hurts, sweetie.is
Advances in the Treatment of Migraine C. Philip O Carroll, M.D. Director Neurobehavioral Medicine Hoag Neurosciences Institute Guyuron B Headache, 2015;55:1464-1473 I m sorry your head hurts, sweetie.is
Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017
 Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
Migraine much more than just a headache
 Migraine much more than just a headache Session hosted by Teva UK Limited PUU4 11:15 12:15 UK/NHSS/18/0021b Date of Preparation: August 2018 The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker
Migraine much more than just a headache Session hosted by Teva UK Limited PUU4 11:15 12:15 UK/NHSS/18/0021b Date of Preparation: August 2018 The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. Headache Evaluation and Treatment by Primary Care Physicians in an Emergency Department in the Era of Triptans
 Headache Evaluation and Treatment by Primary Care Physicians in an Emergency Department in the Era of Triptans Morris Maizels, MD ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Background: Despite advances in treatment, patients
Headache Evaluation and Treatment by Primary Care Physicians in an Emergency Department in the Era of Triptans Morris Maizels, MD ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Background: Despite advances in treatment, patients
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital
 Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders
 499788TAN6510.1177/1756285613499788Therapeutic Advances in Neurological DisordersS Landy, R Hoagland 2013499788 Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders Original Research Sumatriptan/naproxen sodium
499788TAN6510.1177/1756285613499788Therapeutic Advances in Neurological DisordersS Landy, R Hoagland 2013499788 Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders Original Research Sumatriptan/naproxen sodium
Management of headache
 Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Drug Class Review Triptans
 Drug Class Review Triptans Preliminary Update Scan #3 February 2014 Last Report: Update #4 (June 2009) The purpose of reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness
Drug Class Review Triptans Preliminary Update Scan #3 February 2014 Last Report: Update #4 (June 2009) The purpose of reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness
Drug Class Review Triptans
 Drug Class Review Triptans April 2013 Last Report: Update #4 (June 2009) The purpose of reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness and harms of different
Drug Class Review Triptans April 2013 Last Report: Update #4 (June 2009) The purpose of reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness and harms of different
Clinical Policy: Sumatriptan Reference Number: CP.CPA.260 Effective Date: Last Review Date: Line of Business: Commercial
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.CPA.260 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Commercial Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.CPA.260 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Commercial Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Migraine headache incurs estimated. The Cost of Migraine and Its Treatment REPORTS. Lawrence D. Goldberg, MD, MBA
 REPORTS The Cost of Migraine and Its Treatment Lawrence D. Goldberg, MD, MBA Abstract Migraine headache incurs estimated annual costs totaling as much as $17 billion in the United States. Most of the direct
REPORTS The Cost of Migraine and Its Treatment Lawrence D. Goldberg, MD, MBA Abstract Migraine headache incurs estimated annual costs totaling as much as $17 billion in the United States. Most of the direct
Migranal Nasal Spray. Migranal Nasal Spray (dihydroergotamine) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 22, 2017 Migranal Nasal Spray
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 22, 2017 Migranal Nasal Spray
An Economic Evaluation of Triptan Products for Migraine
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKVHEValue in Health1098-30152005 ISPOR86647655Original ArticleEconomic Evaluation of TriptansPerfetto et al. Volume 8 Number 6 2005 VALUE IN HEALTH An Economic Evaluation
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKVHEValue in Health1098-30152005 ISPOR86647655Original ArticleEconomic Evaluation of TriptansPerfetto et al. Volume 8 Number 6 2005 VALUE IN HEALTH An Economic Evaluation
A LOOK AT CGRP INHIBITORS FOR MIGRAINE PREVENTION JUNE 2018
 JUNE 2018 Overview: About Migraine WHAT IS MIGRAINE? Migraine is a common, recurrent headache disorder that affects approximately 20% of women and 6-10% of men in the US. Migraine attacks are characterized
JUNE 2018 Overview: About Migraine WHAT IS MIGRAINE? Migraine is a common, recurrent headache disorder that affects approximately 20% of women and 6-10% of men in the US. Migraine attacks are characterized
Outpatient Headache Care Guideline
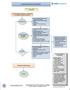 1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
Migraine Treatment What you need to know
 Migraine Treatment What you need to know DR NICOLE LIMBERG ST ANDREWS PLACE SPRING HILL www.migrainespecialist.com.au Migraine what is it? Primary neurobiological condition Waves of reduced brain activity
Migraine Treatment What you need to know DR NICOLE LIMBERG ST ANDREWS PLACE SPRING HILL www.migrainespecialist.com.au Migraine what is it? Primary neurobiological condition Waves of reduced brain activity
Clinical Policy: Sumatriptan Reference Number: CP.HNMC.260 Effective Date: Last Review Date: Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.HNMC.260 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.HNMC.260 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
Early treatment of a migraine attack while pain is still mild increases the efficacy of sumatriptan
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia1468-2982Blackwell Science, 20042411925933Original ArticleEarly treatment of migraine with sumatriptanj Scholpp et al. Early treatment of a migraine attack
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia1468-2982Blackwell Science, 20042411925933Original ArticleEarly treatment of migraine with sumatriptanj Scholpp et al. Early treatment of a migraine attack
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in
 HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
Paediatric headaches. Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services. Brevity, levity, repetition
 Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Risk Factors, Clinical Course, and Barriers to Care in Adults and Pediatrics. Rebecca R. Buttaccio, PA-C Dent Neurologic Institute
 Risk Factors, Clinical Course, and Barriers to Care in Adults and Pediatrics Rebecca R. Buttaccio, PA-C Dent Neurologic Institute Speaker for Avanir Disclosures Learning Objectives 1. Review the risk factors
Risk Factors, Clinical Course, and Barriers to Care in Adults and Pediatrics Rebecca R. Buttaccio, PA-C Dent Neurologic Institute Speaker for Avanir Disclosures Learning Objectives 1. Review the risk factors
Migraine Management. Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital
 Migraine Management Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital Referral Criteria for Migraine Migraine Management Migraine Diagnosis Spot on Health Migraine pathway
Migraine Management Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital Referral Criteria for Migraine Migraine Management Migraine Diagnosis Spot on Health Migraine pathway
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา
 ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
Migraine and hormonal contraceptives
 Migraine and hormonal contraceptives Department of Community Medicine, Systems Epidemiology University of Tromsø, November 2017 Nora Stensland Bugge Medical research student Presentation outline What is
Migraine and hormonal contraceptives Department of Community Medicine, Systems Epidemiology University of Tromsø, November 2017 Nora Stensland Bugge Medical research student Presentation outline What is
Literature Scan: Triptans
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Financial Support: This study was co-funded by OptiNose US, Inc., Yardley, PA, USA, and Avanir Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Aliso Viejo, CA, USA.
 Headache 2015 The Authors. Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/head.12583 Published by Wiley
Headache 2015 The Authors. Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/head.12583 Published by Wiley
Submission for. Reclassification from
 Submission for Reclassification from Prescription Medicine to Pharmacist Only Medicine Zomig (Zolmitriptan) AstraZeneca Limited PO Box 1301 Auckland January 2009 This document is protected by copyright
Submission for Reclassification from Prescription Medicine to Pharmacist Only Medicine Zomig (Zolmitriptan) AstraZeneca Limited PO Box 1301 Auckland January 2009 This document is protected by copyright
Value of postmarketing surveillance studies in achieving a complete picture of antimigraine agents: using almotriptan as an example
 J Headache Pain (2006) 7:27 33 DOI 10.1007/s10194-006-0266-6 ORIGINAL Julio Pascual Hans-Christoph Diener Hélène Massiou Value of postmarketing surveillance studies in achieving a complete picture of antimigraine
J Headache Pain (2006) 7:27 33 DOI 10.1007/s10194-006-0266-6 ORIGINAL Julio Pascual Hans-Christoph Diener Hélène Massiou Value of postmarketing surveillance studies in achieving a complete picture of antimigraine
UPDATE IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT
 UPDATE IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Eric P. Baron, DO Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute Center for Neurological Restoration Headache and Chronic Pain Medicine barone2@ccf.org @Neuralgroover Disclosures
UPDATE IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Eric P. Baron, DO Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute Center for Neurological Restoration Headache and Chronic Pain Medicine barone2@ccf.org @Neuralgroover Disclosures
Treatment Of Medication. Overuse Headache
 7 November 2012 BASH GPwSI Meeting Lecture title... Treatment Of Medication Dr... Overuse Headache Dr Marcus Lewis Dr... The National Migraine Centre International Headache Society Diagnostic criteria
7 November 2012 BASH GPwSI Meeting Lecture title... Treatment Of Medication Dr... Overuse Headache Dr Marcus Lewis Dr... The National Migraine Centre International Headache Society Diagnostic criteria
Maxalt. Maxalt / Maxalt-MLT (rizatriptan) Description. Section: Prescription Drugs Effective Date: April 1, 2016
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Maxalt Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 18, 2016 Maxalt Description Maxalt / Maxalt-MLT (rizatriptan)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Maxalt Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 18, 2016 Maxalt Description Maxalt / Maxalt-MLT (rizatriptan)
Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Truths about Headaches (2017) Most headaches were muscle-tension headaches
 Agenda Case presentation Migraine Morphology Primary and Premonitory Phase Secondary Headache Aura Headache Primer on Pain Medication Overuse Headache Case Presentation RT is a 25 year old woman with daily
Agenda Case presentation Migraine Morphology Primary and Premonitory Phase Secondary Headache Aura Headache Primer on Pain Medication Overuse Headache Case Presentation RT is a 25 year old woman with daily
The Importance of Non-Oral Therapies for Acute Migraine: Addressing Patient Needs
 1 The Importance of Non-Oral Therapies for Acute Migraine: Addressing Patient Needs David W. Dodick, MD Professor Department of Neurology Mayo Clinic Phoenix, Arizona 2 Presentation Objectives Describe
1 The Importance of Non-Oral Therapies for Acute Migraine: Addressing Patient Needs David W. Dodick, MD Professor Department of Neurology Mayo Clinic Phoenix, Arizona 2 Presentation Objectives Describe
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, II. Management of Refractory Headaches
 Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, 2016 II. Management of Refractory Headaches Case presentation 1: A case of intractable daily-persistent headache Keio University School
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, 2016 II. Management of Refractory Headaches Case presentation 1: A case of intractable daily-persistent headache Keio University School
