LIPOFUSCIN, A MARKER OF CELLULAR AGING IN MYOCARDIUM YOUNG PATIENTS AFFECTED BY HIV / AIDS
|
|
|
- Patrick Piers Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5 ARTICOLE ORIGINALE LIPOFUSCIN, A MARKER OF CELLULAR AGING IN MYOCARDIUM YOUNG PATIENTS AFFECTED BY HIV / AIDS Ligia Moldovan, MD, PhD 1 ; Carmen Ardeleanu, Prof. 2 ; Geamai Aysel, PhD 1 1 Th. Burghele University Hospital, Department of Cardiology, Bucharest, Romania 2 Victor Babes National Institute of Research and Development of Pathology and Biomedical Sciences, Bucharest, Romania ABSTRACT Infection with human immunodefi ciency virus HIV is characterized by acquired immunosuppression predisposing the patient to opportunistic infections and malignancies that can affect most organs. Heart, which initially seemed to escape from this rule, it was showed fi rst necroptic, and then clinical and echocardiographic that is affected from the fi rst phase of HIV infection, when patients do not have clinical symptoms, and the disease was revealed only by positive serological tests. The functions of all vital organs begin to decline as aging. Age-related changes occur in all cells, tissues and organs, and they affect the functioning of all systems of the body. With aging, the cells become larger, with less capacity to divide, increasing the amount of pigment, and fatty substances (lipids) within them. Many cells are loosing their ability to function, others begin to function abnormally. Metabolism products accumulate in tissues progressively with aging. A brown pigment called lipofuscin accumulates in many types of tissues together with fat substances. Key words: pigment of wear, aging pigment, lipofuscin, HIV INTRODUCTION HIV infection in the world is expanding impressively smooth. So far, various treatments adopted failed to extend satisfactory the life expectancy of those infected, even if treatment possibilities have been diversified concerning opportunistic infections. Clinical and pathological determinations of respiratory, gastrointestinal, hematological and nervous system are well characterized in HIV infection. Pathological and clinical aspects affecting the cardiovascular system are being evaluated. Experimental clinical and anatomo-pathological trials have shown that all heart structures are affected, showing various structural and functional cardiac changes in relation to the progression and severity of disease and risk of death caused by heart failure. In Romania the first adults case of AIDS in was reported in 1985, and child case in Systematic investigations concerning patients with HIV/AIDS began only after With the AIDS cases in children up representing more than half of all pediatric cases in Europe, Romania was classified with a special position, because most children were infected during the , especially parentheral, caused by improperly sterilized medical and surgical devices, HIV contaminated. The measures introduced since 1990, pediatric infection appears to be under control. After 1995 there were further cases of nosocomial infection. In contrast, in adults, infection is worrying upward slope. Ministry of Health identified the priorities concerning this major health issue, consequently the National AIDS Committee was responsible on developing National Anti-AIDS Health Program (2) Author for correspondence: Ligia Moldovan, MD, Theodor Burghele Clinical Hospital, Cardiology Department, 20 Panduri Av., District 5, Bucharest, Romania geamai_ayfer@yahoo.com 192 REVISTA ROMÂNÅ DE BOLI INFECºIOASE VOLUMUL XIV, NR. 4, AN 2011
2 REVISTA ROMÂNÅ DE BOLI INFECºIOASE VOLUMUL XIV, NR. 4, AN There are no trails concerning the relationship between HIV/AIDS infection and the heart involvement, on adults, in Romania. Heart disease or cardiac involvement as a first sign of HIV infection is rarely reported. Obvious, echocardiographic and anatomo-pathological features are more common than clinical signs. The main reason that led to the choice of this topic is based on real need to obtain data from HIVinfected adult patients regarding the prevalence of cardiac damage in Romania. OBJECTIVES Impact of appearance of lipofuscin-cell aging marker in myocardium of young patients who died from HIV / AIDS. METHODS Pathological changes in cardiac trial were performed on deceased patients with HIV infection on the Hospital for Infectious Diseases and Tropical Diseases Dr. Victor Babes, in Bucharest, during Includes macroscopic and microscopic anatomo-pathological study made by anatomo-pathological evaluation of 16 fragments of myocardium, post mortem collected at random free from the 16 patients died from HIV infection during RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS There were 16 myocardial fragments, histopathologically analyzed, randomly collected from patients who died with HIV infection in at the Hospital Clinic of Infectious and Tropical Diseases Dr. V. Babes, Bucharest. The quality of is determinant for histopathological diagnosis of cardiac lesions. The first and most important moment of the histological methods was the histopathological biopsy. Most important is the rapid sampling to avoid the autolysis. The sampling was made by smooth and sharp devices in order to avoid the crash and damage of the tissues. The samples were various, representative. The targeted tissues had to respect the following criteria: macroscopic changes of the tissue, tissue located on the border, and cardiac normal tissue. The collected fragments were less than 1 cm, with smooth and parallel faces. Drying or crushing was avoided myocardial fragments, quickly fixed in 10% formalin. Formalin fixing goal was to stop the development of cells and tissues in a most close functional status by stopping autolysis. Formaldehyde fixing mechanism is based on its combination with protein molecules in order to form insoluble macromolecules liquid combination used in histological technique. For this reason, cardiac tissue becomes tough and elastic and can be easily cut. The volume of fixative (formalin 10%) should be 50 times over the volume of tissue fragment at room temperature, within 24 hours. The proper fixation of the myocardium fragments was followed by their inclusion in paraffin, in order to achieve a proper consistency of the samples to be cut and allow the application of staining techniques, in order to keeping them. Are required for inclusion in paraffin following stroke: dehydration of the play, clearance, and actual including: Alcohol cannot be mixed with paraffin it is necessary the clearance procedure, consisting by toluene usage during 24 hours. Dehydration procedure uses ethylic alcohol, meaning the alcohol passage of the sample. During the procedure, the alcohol concentration increases gradually, until the water is replaced by pure alcohol. After dehydration and clearance, pieces imbued with toluene were transferred into paraffin baths containing liquid paraffin at a temperature of 54. After paraffin inclusion, the pieces were mounted in paraffin blocks, in order to be subsequently sectioned. Sections of 3-6 microns were attached to slides. The next step was dewaxing and hydration of the sections in order to histological staining. Special stains were performed for evidence of fibrosis and pathogens (fungi, Koch bacillus, bacteria) present in cardiac tissue. Stains used were: Haematoxylin eosin stain: original was used because it allows an efficient nuclei staining with haematoxylin Lie stain Ziehl-Nielsen stain PAS stain van Gieson staining Histological diagnosis of active or borderline myocarditis was defined according to the Dallas criteria; lymphocyte inflammatory infiltrate was considered present in more than 10 lymphocytes per microscope field (magnification x 400).
3 194 REVISTA ROMÂNÅ DE BOLI INFECºIOASE VOLUMUL XIV, NR. 4, AN 2011 Anatomo-pathological processing material harvested from heart of 16 patients deceased with HIV infection conducted in: Hospital Pathology Laboratory of Infectious Diseases and Tropical Diseases Dr. V. Babes Bucharest Pathology Laboratory of Hospital Th. Burghele Bucharest National Research Development of Pathology and Biomedical Sciences; Dr. V. Babes Bucharest Demographic characteristics and anatomopathological diagnosis of the study group (16 people) post-mortem heart fragments samples are shown in Table 1. Table 1. Clinical aspects and anatomopathological diagnosis Nr. Name Gender Age (years) Macroscopic diagnose Microscopic diagnose 1 I-V M 38 - Subendocardium fi brosis (+) with recent necrosis areas. Interstitial oedema. Rare microbial colonies. Regenerative type nucleus. Hyperaemia and interstitial oedema. 2 G-P M 52 Dilatative cardiomiopathy, left ventricle hypertrophy Diffuse interstitial fi brosis (+++)and arteriosclerosis with narrowing of arteriolar lumen eccentric Regenerative type nucleus. 3 M-M M 40 Dilatative cardiomiopathy Diffuse interstitial fi brosis (++). Arteriosclerosis with narrowing of arteriolar lumen (~30% remaining). 4 C-R F 36 Dilatative cardiomiopathy Diffuse interstitial fi brosis (+)and microvascular fi brosis, lipofuscin in myocardium fiber (++) 5 T-V M 34 Miocarditis Serous pericarditis Marked hyperaemia and the presence of red blood cells in rolls. Parietal thrombus with micelles. Without myocardial fi brosis. 6 V-E F 53 Myocardium dystrophy Discreet interstitial fi brosis(+). Hyperaemia (+). Large, hipercrom nucleus, (regenerative aspect). Rich pigment of lipofuscin (+++). Cryptococcus. 7 C-I M 39 Left ventricle hypertrophy. Serous pericarditis Interstitial moderate fi brosis (+ +) without vascular narrowing. Moderate hyperaemia (++). Regenerative nuclei. Lipofuscin pigment (+++). 8 D-C M 65 - Massive diffuse interstitial fi brosis (+++), without narrowing the lumen. Discreet lymphoid interstitial infl ammatory infi ltrate(+). Discrete hyperaemia (+). Large, very numerous hipercromi nucleus, large. Atrophy of muscle fi bers. 9 D-O F 52 - Moderate fi brosis (+ +). discreet hyperaemia (+). Lipofuscin (++). Discrete interstitial infl ammatory infi ltrate (lymphoid). Cryptococcus. Regenerative nuclei 10 I-C F 28 - Fibrosis (+++) with narrowing of the vascular wall. Lipofuscin (+). Discreet lymphoid interstitial infl ammatory infi ltrate (+) Regenerative nuclei 11 I-I F 36 Metastasis in myocardium. Left ventricle hypertrophy Marked fi brosis without narrowing (+++). Important swelling with narrowing of the fi bers; rare hypertrophic nuclei. Rare infl ammatory elements. Important hyperaemia. Many hypertrophic nuclei. Fungal thrombus. 12 D-C M 35 - Moderate fi brosis (+ +) without vascular damage. Moderate oedema. Lipofuscin (++); rare infl ammatory elements. Marked hyperaemia. Many hypertrophic nuclei. Fungal thrombus. 13 C-M F 31 Haemorrhage pericarditis Fibrosis (+) without vascular damage. Edema and moderate hyperemia. Lipofuscin (++); discrete chronic infl ammation. Parietal thrombus fungal and fungal interstitial deposits. 14 G-F M 18 Dilatative cardiomiopathy Reduced fi brosis (+) without vascular damage. Important oedema. Moderate hyperaemia. Lipofuscin (++). Moderate chronic infl ammation. Small deposits of small venous vessels such fungi. Fibrin thrombi in small vessels.
4 REVISTA ROMÂNÅ DE BOLI INFECºIOASE VOLUMUL XIV, NR. 4, AN Nr. Name Gender Age (years) Macroscopic diagnose Microscopic diagnose 15 S-E F 35 Dilatative cardiomiopathy Fibrosis (-). Marked hyperaemia and oedema. Chronic subepicardial infl ammation with fungi. Vasa vasorum thrombosis, relatively frequent hypertrophic nuclei. 16 F-M F 35 - Fibrosis (++). Hyperaemia. Moderate interstitial infl ammatory infi ltrate. Koch bacillus. Macroscopic pathological changes were present on 10 cases (table 1). The average age is years, 8 cases are men and 8 cases are women. Figure 1. Macroscopic lesions The macroscopic described lesions Dilatative cardiomyopathy present in 5 cases; 4 cases of dilated cardiomyopathy associated with fibrosis in various degrees. Pericarditis 3 cases, 1 case pericarditis is associated with myocarditis. Pericardial effusion in low quantity serocitrin aspect (2 cases) haemorrhagic aspect (1 case). Neoplasia: 1 case of cardiac metastasis 1 case with hypertrophy and left ventricular dilatation. The microscopic histopathological lesions Present in all 16 cases (100%), including cases in which macroscopically was not described any heart lesion (Figure 2). Lanjewar (1) and collaborators are describing histopathological changes in 92.30% of subjects. Thus: lymphocytic myocarditis is present at 55.76% myocardial fibrosis is present at 13.46% Cryptococcus neoformans is identified at 3.84%. The histopatological lesions of our trial are presented in Figure 2. Thus: Pigment-lipofuscin wear is described as being present in 8 cases (50%). Pigment wear in all these cases is described as being present in high quantities. 6 of the 8 cases showing lipofuscin are aged between years. Myocardial fibrosis in varying degrees-formation is detected in a total of 14 cases (87.5%). Depending on the degree of fibrosis, is described: reduced fibrosis, described in 5 cases moderate fibrosis described in 5 cases pronounced fibrosis described in 4 cases Myocarditis lymphocytic interstitial described in 3 cases (18.75%). Interstitial oedema is present in 7 cases (43.75%) Large nuclei, hypertrophic hipercromi with regenerative aspect are present in 9 cases. Candida albicans is described to histopathological in a total of 7 cases (43.75%) Cryptococcus neoformans is described in 1 case (6.25%) Figure 2. Histopathological lesions
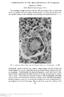
5 196 REVISTA ROMÂNÅ DE BOLI INFECºIOASE VOLUMUL XIV, NR. 4, AN 2011 Myocardial tuberculosis, Koch bacillus, is viewed histologically in 1 case (6.25%) Atherosclerotic ischemic lesions are present in 2 cases (12.5%) Myocardial necrosis is present in 2 cases (12.5%). We present some aspects of aging pigment lipofuscin present in the myocardium of patients infected and deceased from HIV / AIDS at young ages. Images no. 4, 5, 6 reveal the presence of myocardial fiber sarcoplasm wear pigment lipofuscin in high quantity. Fragments were taken from a woman of 28 years. Figure 4. PAS coloration, OB 20X CONCLUSIONS Figure 3. PAS coloration, OB 40X We did not found this comment in the literature. Support the assumption that human immunodeficiency virus HIV is that which would cause wear pigment accumulation in myocardial fibers of young patients (3-5) where normally there should not be. Currently it is known (8) that lipofuscin accumulation in the nervous system results in a functional and structural damage to neurons. This seems to be true for the formation and accumulation of lipofuscin deposits in myocardis at the young ages. Figure 5. PAS coloration Ob 40X High levels of lipofuscin in miocardic fibers
6 REVISTA ROMÂNÅ DE BOLI INFECºIOASE VOLUMUL XIV, NR. 4, AN The result is a functional and structural damage of myocites. (6,7). It is likely that the accumulation of lipofuscin pigment in myocardial fibers is harmful phenomenon. It raises the suspicion that human immunodeficiency virus HIV is the pigment that determines the accumulation of wear in myocardial fibers. (6,7). In the literature we found no references or joint regarding on the presence of pigment in the myocites of the patients deceased by HIV infection. It seems that HIV could induct lipofuscin accumulation and formation of deposits in myocardial fibers. The presence of lipofuscin in myocardium cells suggests the direct action of myocardial infection with HIV virus and multiple extrinsic factors (inflammation, catecholamine, and adrenergic sympathetic activity), myocardial cells undergo autophagy and apoptosis involved in ventricular remodeling and heart failure development. REFERENCES 1. Lanjewar D.N., Katdase G.A., Jain P.P., Hira S.K. Pathology of the heart in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Indian Heart J. 1998; 50: Ministery of Health from Romania Anti-HIV National Committee Moldovan L., Ardelean C., Teodorescu M., Ştefănescu-Winterlik A., Câmpeanu A. Modificări anatomo-patologice cardiace în infecţia cu virusul HIV. Al 41-lea Congres Naţional de Cardiologie, Moldovan L., Stănescu C., Streinu A. Modificări ecocardiografice în infecţia cu virusul HIV. Al XVII-lea Simpozion Naţional de Ecocardiografie, Bucureşti, mai Moldovan L., Brînzan O., Ardeleanu C., Teodorescu M., Ştefănescu- Winterlik A., Câmpeanu A. Aspecte cardiace anatomo-patologice macroscopice şi microscopice în infecţia cu virusul imunodeficienţei umane. Premiul I. Al IV-lea Congres Naţional privind Infecţia HIV/SIDA octombrie 2006, Bucureşti 6. Moldovan L., Ardeleanu C., Teodorescu M., Ştefănescu A., Mischie S., Câmpeanu A. Determinări histopatologice cardiace în infecţia cu virusul HIV. Al XXXII-lea Simpozion Naţional de Morfologie Normală şi Patologică. Bucureşti 7-9.XI Ligia Moldovan, E. Ceauşu, Carmen Ardeleanu, Maria Teodorescu, Ştefănescu-Winterlik A., Geamai Ayfer Lipofuscina în infecţia HIV/ SIDA ; Revista Română de Boli Infecţioase, Riga D., Riga S. Lipofuscin and ceroid pigments in aging and brain pathology. A review of biochemical and morphological properties. Rom. J. Neurol. Psychiat. 1995, 33.2., p
Myocardial Infarction
 Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Pathology of Hypertension
 2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV
 Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV Prabhakar Rajiah, MBBS, MD, FRCR Associate Professor of Radiology Associate Director, Cardiac CT and MRI University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, USA
Cardiovascular manifestations of HIV Prabhakar Rajiah, MBBS, MD, FRCR Associate Professor of Radiology Associate Director, Cardiac CT and MRI University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, USA
THROMBOSIS. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan
 THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI).
 1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.
 المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
The basis of Disease
 General Curriculum The basis of Disease ZHOU REN 周韧 Prof., M.D., Ph.D. Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine Department of Pathology & Patho-physiology Zhenjiang University Judicial Evidence & Evaluation
General Curriculum The basis of Disease ZHOU REN 周韧 Prof., M.D., Ph.D. Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine Department of Pathology & Patho-physiology Zhenjiang University Judicial Evidence & Evaluation
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease
 Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Jessi Smith, MD Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University Slides courtesy of Stacy Rissing, MD Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Jessi Smith, MD Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University Slides courtesy of Stacy Rissing, MD Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used
Extracellular degeneration
 Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock. Richard A. McPherson, M.D.
 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease
 Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Stacy Rissing, MD! Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University! Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used for each indication Pathophysiology
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Stacy Rissing, MD! Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University! Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used for each indication Pathophysiology
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
Cardiovascular Pathology
 Cardiovascular Pathology Duration: 03 Weeks (15 days) Concepts Objectives Activity Time Department Comments 3/SBM-3/01 Introduction to ischaemia, infarction, thrombosis stenosis / occlusion, embolism Atherosclerosis
Cardiovascular Pathology Duration: 03 Weeks (15 days) Concepts Objectives Activity Time Department Comments 3/SBM-3/01 Introduction to ischaemia, infarction, thrombosis stenosis / occlusion, embolism Atherosclerosis
Contributions to Anatomic Pathology, over the years
 Contributions to Anatomic Pathology, over the years Anatomic Pathology, part 1 G.B. Morgagni Xavier Bichat Rudolf Wirchow Anatomic Pathology, part 1 Anatomic pathology materials: morphological samples
Contributions to Anatomic Pathology, over the years Anatomic Pathology, part 1 G.B. Morgagni Xavier Bichat Rudolf Wirchow Anatomic Pathology, part 1 Anatomic pathology materials: morphological samples
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART. I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine
 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine Acute myocardial infarction coagulative necrosis subendocardialy 2 hyperemic layer 3 normal myocard 4 epicard Acute myocardial
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF THE HEART I. practical training 3 rd year General Medicine Acute myocardial infarction coagulative necrosis subendocardialy 2 hyperemic layer 3 normal myocard 4 epicard Acute myocardial
Cardiac Ischemia (is-kē-mē-uh)
 Chapter 21 Cardiac Ischemia (is-kē-mē-uh) By: Alejandra & Lindsay I. Cardiac Ischemia =the most common cause of death in Western Culture ~35% of deaths. -Suddenly from acute coronary occlusion or fibrillation
Chapter 21 Cardiac Ischemia (is-kē-mē-uh) By: Alejandra & Lindsay I. Cardiac Ischemia =the most common cause of death in Western Culture ~35% of deaths. -Suddenly from acute coronary occlusion or fibrillation
HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION
 HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION Learning Objectives Define congestion and hyperemia Differentiate between the two with regard to: Mechanisms / underlying causes Appearance (gross and histologic) Effects Differentiate
HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION Learning Objectives Define congestion and hyperemia Differentiate between the two with regard to: Mechanisms / underlying causes Appearance (gross and histologic) Effects Differentiate
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I. A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin.
 EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
HISTOPATHOLOGY OF MYOCARDIAL DAMAGE IN EXPERIMENTAL FLUOROSIS IN RABBITS
 Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 1 43-50 2001 Research Report 43 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF MYOCARDIAL DAMAGE IN EXPERIMENTAL FLUOROSIS IN RABBITS A Shashi, a SP Thapar b Patiala, India Summary: Young albino rabbits were administered
Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 1 43-50 2001 Research Report 43 HISTOPATHOLOGY OF MYOCARDIAL DAMAGE IN EXPERIMENTAL FLUOROSIS IN RABBITS A Shashi, a SP Thapar b Patiala, India Summary: Young albino rabbits were administered
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE
 APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
Pathophysiology of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction
 Pathophysiology of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction Cheol Woong Yu, MD, PhD Cardiology Department Division of Internal Medicine Korea University Anam Hospital. Etiologies of Chest Pain without obstructive
Pathophysiology of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction Cheol Woong Yu, MD, PhD Cardiology Department Division of Internal Medicine Korea University Anam Hospital. Etiologies of Chest Pain without obstructive
Blood and Circulation Module Year 3 Semester 1
 Blood and Circulation Module Year 3 Semester 1 Duration: 03 Weeks (15 days) Concepts Objectives Activity Time Department 1. 2006-3/SBM-3/01 Introduction to ischaemia, infarction, thrombosis stenosis /
Blood and Circulation Module Year 3 Semester 1 Duration: 03 Weeks (15 days) Concepts Objectives Activity Time Department 1. 2006-3/SBM-3/01 Introduction to ischaemia, infarction, thrombosis stenosis /
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
2
 1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated)
 Carl Christennsen, PhD Chap. 19, 20, & 21 - Circulatory System Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy HEART 1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated) Where does this blood come from?
Carl Christennsen, PhD Chap. 19, 20, & 21 - Circulatory System Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy HEART 1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated) Where does this blood come from?
Prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease: A Tertiary Care Hospital Based Autopsy Study
 Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
A Histological Autopsy Study of the Thyroid gland in HIV infected Adults at the University Teaching Hospital in Lusaka, Zambia
 Original Article A Histological Autopsy Study of the Thyroid gland in HIV infected Adults at the University Teaching Hospital in Lusaka, Zambia 1 1 2 S. Muwowo, V. Mudenda, C. Marimo 1 Department of Pathology
Original Article A Histological Autopsy Study of the Thyroid gland in HIV infected Adults at the University Teaching Hospital in Lusaka, Zambia 1 1 2 S. Muwowo, V. Mudenda, C. Marimo 1 Department of Pathology
Epidemiology and Laboratory Diagnosis of Fungal Diseases
 Medical Mycology (BIOL 4849) Summer 2007 Dr. Cooper Epidemiology of Mycoses Epidemiology and Laboratory Diagnosis of Fungal Diseases Mycosis (pl., mycoses) - an infection caused by a fungus Two broad categories
Medical Mycology (BIOL 4849) Summer 2007 Dr. Cooper Epidemiology of Mycoses Epidemiology and Laboratory Diagnosis of Fungal Diseases Mycosis (pl., mycoses) - an infection caused by a fungus Two broad categories
Mass Histology Service
 Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart
 AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
4/11/2017. Cardiomyopathy. John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart. Disclosures. No Conflicts. Cardiomyopathy. WHO Classification
 Cardiomyopathy John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart Disclosures No Conflicts Cardiomyopathy WHO Classification Anatomy & physiology of the LV 1. Dilated Enlarged Systolic dysfunction 2. Hypertrophic Thickened
Cardiomyopathy John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart Disclosures No Conflicts Cardiomyopathy WHO Classification Anatomy & physiology of the LV 1. Dilated Enlarged Systolic dysfunction 2. Hypertrophic Thickened
Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one
 Necrosis Necrosis Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one or more, small, clearly defined areas of necrosis. Diffuse necrosis- term used
Necrosis Necrosis Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one or more, small, clearly defined areas of necrosis. Diffuse necrosis- term used
27-year-old professionnal rugby player: asymptomatic
 27-year-old professionnal rugby player: asymptomatic Benefits and limits of cardiac MRI in the young athlete with a suspected heart disease. Philippe PAULE Service de Cardiologie, HIA Clermont Tonnerre,
27-year-old professionnal rugby player: asymptomatic Benefits and limits of cardiac MRI in the young athlete with a suspected heart disease. Philippe PAULE Service de Cardiologie, HIA Clermont Tonnerre,
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Heyam Awad
 number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
Disturbances of Circulation. Histopathology Lab #2 (Web)
 Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
Avian Pathology. Bacterial diseases: histo slides. ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN
 Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
MI Acute occlusion of the proximal left anterior descending (LAD) artery is the cause of 40% to 50% of all MIs. *
 MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
Coronary Atherosclerosis In Jammu Region - A Random Postmortem Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Coronary Atherosclerosis In Jammu Region - A Random Postmortem Study Sindhu Sharma, Jagriti Singh, P. Angmo, Chavi, K.K. Kaul Abstract Atherosclerosis is a complex and common disease contributing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Coronary Atherosclerosis In Jammu Region - A Random Postmortem Study Sindhu Sharma, Jagriti Singh, P. Angmo, Chavi, K.K. Kaul Abstract Atherosclerosis is a complex and common disease contributing
5 DISTURBANCES IN CIRCULATION. Congestion / Hyperemia Haemorrhage Thrombosis Embolism Ischemia Infarction Oedema Shock Sludged blood Model Questions
 5 DISTURBANCES IN CIRCULATION Congestion / Hyperemia Haemorrhage Thrombosis Embolism Ischemia Infarction Oedema Shock Sludged blood Model Questions CONGESTION/ HYPEREMIA Hyperemia is increased amount of
5 DISTURBANCES IN CIRCULATION Congestion / Hyperemia Haemorrhage Thrombosis Embolism Ischemia Infarction Oedema Shock Sludged blood Model Questions CONGESTION/ HYPEREMIA Hyperemia is increased amount of
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology. Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta )
 Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION. Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta
 DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta COMPLICATION OF DIABETES Susceptibility to infections including tuberculosis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and mucocutaneous
DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta COMPLICATION OF DIABETES Susceptibility to infections including tuberculosis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and mucocutaneous
Disturbance of Circulation Hemodynamic Disorder
 Disturbance of Circulation Hemodynamic Disorder 2/17/2017 By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1 Thrombosis Definition: Thrombosis is the formation of solid or semisolid blood clot within
Disturbance of Circulation Hemodynamic Disorder 2/17/2017 By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1 Thrombosis Definition: Thrombosis is the formation of solid or semisolid blood clot within
Cardiac Sarcoidosis. Millee Singh DO Non Invasive Cardiology First Coast Heart and Vascluar
 Cardiac Sarcoidosis Millee Singh DO Non Invasive Cardiology First Coast Heart and Vascluar Introduction Multisystem granulomatous disease of unknown etiology characterized by noncaseating granulomas in
Cardiac Sarcoidosis Millee Singh DO Non Invasive Cardiology First Coast Heart and Vascluar Introduction Multisystem granulomatous disease of unknown etiology characterized by noncaseating granulomas in
BIOLOGY 2290 Pathophysiology I (Health Sciences III ) Sept 2010 Instructor : Dr. Paul S. Sunga, Rm A359a, , Introduction
 BIOLOGY 2290 Pathophysiology I (Health Sciences III ) Sept 2010 Instructor : Dr. Paul S. Sunga, Rm A359a, 323-5251, psunga@langara.bc.ca Introduction This course is designed to provide students with insights
BIOLOGY 2290 Pathophysiology I (Health Sciences III ) Sept 2010 Instructor : Dr. Paul S. Sunga, Rm A359a, 323-5251, psunga@langara.bc.ca Introduction This course is designed to provide students with insights
Epidemiology of Fungal Diseases
 Lecture 2 Epidemiology of Fungal Diseases Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner,
Lecture 2 Epidemiology of Fungal Diseases Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner,
Saluki heart pathology study
 Heart conditions by MaryDee Sist, DVM Originally published in Baraka Book, Autumn-Winter 2001 For the last decade I have been involved in Saluki heart research. Ouroriginalgoalwastoexaminethe incidence
Heart conditions by MaryDee Sist, DVM Originally published in Baraka Book, Autumn-Winter 2001 For the last decade I have been involved in Saluki heart research. Ouroriginalgoalwastoexaminethe incidence
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial
 An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Alfonso López. Cardiac Hypertrophy and Dilation
 Cardiac Hypertrophy and Dilation Alfonso López Professor of Anatomic Pathology Dept. Pathology and Microbiology Atlantic Veterinary College University of Prince Edward Island Canada Jan 23, 2012 Compensatory
Cardiac Hypertrophy and Dilation Alfonso López Professor of Anatomic Pathology Dept. Pathology and Microbiology Atlantic Veterinary College University of Prince Edward Island Canada Jan 23, 2012 Compensatory
Cellular Injury. Intracellular degeneration. By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall /20/2018 1
 Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2014, 55(3):773 779 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Ultrasound and histopathological features of myocardial involvement in HIV
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2014, 55(3):773 779 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Ultrasound and histopathological features of myocardial involvement in HIV
Mechanisms of Cell Injury
 Causes of Cell Injury 1- oxygen deprivation (anoxia) 2- physical agents 3- chemical agents 4- infections agents 5- immunologic reactions 6- genetic defects 7- nutritional imbalances Mechanisms of Cell
Causes of Cell Injury 1- oxygen deprivation (anoxia) 2- physical agents 3- chemical agents 4- infections agents 5- immunologic reactions 6- genetic defects 7- nutritional imbalances Mechanisms of Cell
ARTERIES IN COALWORKERS
 THE RIGHT VENTRICLE AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN COALWORKERS BY ARTHUR J. THOMAS AND W. R. L. JAMES From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals) and the Department of Pathology, Welsh National
THE RIGHT VENTRICLE AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN COALWORKERS BY ARTHUR J. THOMAS AND W. R. L. JAMES From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals) and the Department of Pathology, Welsh National
HEMODYNAMIC DISORDERS
 HEMODYNAMIC DISORDERS Normal fluid homeostasis requires vessel wall integrity as well as maintenance of intravascular pressure and osmolarity within certain physiologic ranges. Increases in vascular volume
HEMODYNAMIC DISORDERS Normal fluid homeostasis requires vessel wall integrity as well as maintenance of intravascular pressure and osmolarity within certain physiologic ranges. Increases in vascular volume
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH
 CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
Cordis EXOSEAL Vascular Closure Device
 to receive our latest news and key activities. Cordis EXOSEAL Vascular Closure Device Polyglycolic Acid Plug (PGA) Material Absorption and Tissue Reaction Assessment 3 Days* 14 Days* 60 Days* LinkedIn
to receive our latest news and key activities. Cordis EXOSEAL Vascular Closure Device Polyglycolic Acid Plug (PGA) Material Absorption and Tissue Reaction Assessment 3 Days* 14 Days* 60 Days* LinkedIn
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Dr. Sami Zaqout The circulatory system Circulatory system Blood vascular systems Lymphatic vascular systems Blood vascular systems Blood vascular systems The circulatory system Circulatory
The Circulatory System Dr. Sami Zaqout The circulatory system Circulatory system Blood vascular systems Lymphatic vascular systems Blood vascular systems Blood vascular systems The circulatory system Circulatory
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies?
 Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Jung Han Kim, PhD Project 1 Project 2
 Jung Han Kim, PhD Professor Joan C Edwards School of Medicine at Marshall University 1700 3 rd Ave, 435 BBSC Huntington, WV 25755 Tel: (304) 696-3873 Email: kimj@marshall.edu My long-term research interest
Jung Han Kim, PhD Professor Joan C Edwards School of Medicine at Marshall University 1700 3 rd Ave, 435 BBSC Huntington, WV 25755 Tel: (304) 696-3873 Email: kimj@marshall.edu My long-term research interest
Annals of RSCB Vol. XV, Issue 1
 AFFECTION OF SANGUINE VESSELS AND BILIARY DUCTS IN CHRONIC INTERSTITIAL FIBROUS HEPATITIS CAUSED BY MIGRATION OF ASCARIS SUUM LARVAE THROUGH PIGLETS LIVER A. F. Gal, V. Miclăuş, C. Cătoi, V. Rus, L. Oana,
AFFECTION OF SANGUINE VESSELS AND BILIARY DUCTS IN CHRONIC INTERSTITIAL FIBROUS HEPATITIS CAUSED BY MIGRATION OF ASCARIS SUUM LARVAE THROUGH PIGLETS LIVER A. F. Gal, V. Miclăuş, C. Cătoi, V. Rus, L. Oana,
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co.
 Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Arterioles of Kidney and Pancreas in Cases
 Arterioles of Kidney and Pancreas in Cases of Cardiac Hypertrophy of Undetermined Causation By HAROLD A. FERRIS, JR., M.D. The arterioles in the kidneys and pancreas in 50 consecutive necropsy cases of
Arterioles of Kidney and Pancreas in Cases of Cardiac Hypertrophy of Undetermined Causation By HAROLD A. FERRIS, JR., M.D. The arterioles in the kidneys and pancreas in 50 consecutive necropsy cases of
INFLAMMATION. 5. Which are the main phases of inflammation in their "sequence": 1. Initiation, promotion, progression.
 INFLAMMATION 1. What is inflammation: 1. Selective anti-infective pathological reaction. 2. Pathological process, typical for vascularized tissues. 3. Self-sustained pathological condition. 4. Disease
INFLAMMATION 1. What is inflammation: 1. Selective anti-infective pathological reaction. 2. Pathological process, typical for vascularized tissues. 3. Self-sustained pathological condition. 4. Disease
Blood & Immunity. Blood
 Blood & Immunity Blood Plasma Watery portion (90% water) of blood About 55% of the blood Contains many proteins including antibodies and albumin Cells Comprise about 45% of blood Erythrocytes (red blood
Blood & Immunity Blood Plasma Watery portion (90% water) of blood About 55% of the blood Contains many proteins including antibodies and albumin Cells Comprise about 45% of blood Erythrocytes (red blood
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS
 CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
Clinical Manifestations of HIV
 HIV Symptoms Diane Havlir, MD Professor of Medicine and Chief, HIV/AIDS Division University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) WorldMedSchool; July 2, 2013 1 Clinical Manifestations of HIV! Result from
HIV Symptoms Diane Havlir, MD Professor of Medicine and Chief, HIV/AIDS Division University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) WorldMedSchool; July 2, 2013 1 Clinical Manifestations of HIV! Result from
CT for Myocardial Characterization of Cardiomyopathy. Byoung Wook Choi, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea
 CT for Myocardial Characterization of Cardiomyopathy Byoung Wook Choi, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea Cardiomyopathy Elliott P et al. Eur Heart J 2008;29:270-276 The European Society
CT for Myocardial Characterization of Cardiomyopathy Byoung Wook Choi, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea Cardiomyopathy Elliott P et al. Eur Heart J 2008;29:270-276 The European Society
Bacterial, viral, protoozal and fungal infections of the CNS
 Bacterial, viral, protoozal and fungal infections of the CNS Prof. Isidro Ferrer, Institut Neuropatologia, Servei Anatomia Patològica, IDIBELL-Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge, Universitat de Barcelona,
Bacterial, viral, protoozal and fungal infections of the CNS Prof. Isidro Ferrer, Institut Neuropatologia, Servei Anatomia Patològica, IDIBELL-Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge, Universitat de Barcelona,
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
HISTOPATHOLOGIC CHANGES OF THE SMALL INTESTINE MUCOSAE IN PIGLETS WITH ANOXIA AND PARTURITION HYPOXIA
 HISTOPATHOLOGIC CHANGES OF THE SMALL INTESTINE MUCOSAE IN PIGLETS WITH ANOXIA AND PARTURITION HYPOXIA Olga-Alina RADA 1, Liliana VASILE 3, H. SĂRĂNDAN 2, H. CERNESCU 2, Diana BREZOVAN 2, Mihaela OSTAN
HISTOPATHOLOGIC CHANGES OF THE SMALL INTESTINE MUCOSAE IN PIGLETS WITH ANOXIA AND PARTURITION HYPOXIA Olga-Alina RADA 1, Liliana VASILE 3, H. SĂRĂNDAN 2, H. CERNESCU 2, Diana BREZOVAN 2, Mihaela OSTAN
Cardiovascular System. Chapters 11, 12
 Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Apparent hypoxic changes in pulmonary arterioles
 J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 481-485 Apparent hypoxic changes in pulmonary arterioles and small arteries in infancy S. R. KENDEEL AND J. A. J. FERRIS' From the Department ofpathology, University of Newcastle
J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 481-485 Apparent hypoxic changes in pulmonary arterioles and small arteries in infancy S. R. KENDEEL AND J. A. J. FERRIS' From the Department ofpathology, University of Newcastle
Vulnerable Plaque Pathophysiology, Detection, and Intervention. VP: A Local Problem or Systemic Disease. Erling Falk, Denmark
 Vulnerable Plaque Pathophysiology, Detection, and Intervention VP: A Local Problem or Systemic Disease Erling Falk, Denmark Vulnerable Plaque Pathophysiology, Detection, and Intervention VP: A Local Problem
Vulnerable Plaque Pathophysiology, Detection, and Intervention VP: A Local Problem or Systemic Disease Erling Falk, Denmark Vulnerable Plaque Pathophysiology, Detection, and Intervention VP: A Local Problem
Myocarditis in Infants and Children
 in Infants and Children Guideline of the German Society of Pediatric Cardiology Thomas Paul, Carsten Tschöpe, Reinhard Kandolf Children s Heart Center, Georg-August-University, Göttingen Department of
in Infants and Children Guideline of the German Society of Pediatric Cardiology Thomas Paul, Carsten Tschöpe, Reinhard Kandolf Children s Heart Center, Georg-August-University, Göttingen Department of
THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION
 Thorax (1960), 15, 54. THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION AND LYMPHATIC DISTENSION IN LUNG BIOPSIES BY DONALD HEATH AND PETER HICKEN From the Department of Pathology, University of Birmingham
Thorax (1960), 15, 54. THE RELATION BETWEEN LEFT ATRIAL HYPERTENSION AND LYMPHATIC DISTENSION IN LUNG BIOPSIES BY DONALD HEATH AND PETER HICKEN From the Department of Pathology, University of Birmingham
Report Documentation Page
 Clinical and Pathologic Characteristics of Myocarditis as a Cause of Sudden Death Lena Avedissian, Jennifer A. McNear, David A. Appel, Laudino M. Castillo Rojas, J. Edwin Atwood, Lisa A. Pearse, Robert
Clinical and Pathologic Characteristics of Myocarditis as a Cause of Sudden Death Lena Avedissian, Jennifer A. McNear, David A. Appel, Laudino M. Castillo Rojas, J. Edwin Atwood, Lisa A. Pearse, Robert
Acute coronary syndrome. Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA
 Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Bachelor of Chinese Medicine Shock
 BCM Year 2 Dr. Irene Ng Jan 28, 2003 9:30 am 1:00 pm Rm 004 UPB Bachelor of Chinese Medicine 2002 2003 Shock Learning objectives Be able to: know the definition of shock know the classification and causes
BCM Year 2 Dr. Irene Ng Jan 28, 2003 9:30 am 1:00 pm Rm 004 UPB Bachelor of Chinese Medicine 2002 2003 Shock Learning objectives Be able to: know the definition of shock know the classification and causes
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion
 Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
Histopathology Description:
 2013-2-1 CANINE HEART Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION : The Royal Veterinary college, Dept. of Pathology and Biology Signalment: 11-month-old male Border Collie dog (Canis familiaris)
2013-2-1 CANINE HEART Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION : The Royal Veterinary college, Dept. of Pathology and Biology Signalment: 11-month-old male Border Collie dog (Canis familiaris)
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide
 Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV. Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA
 Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA Objectives Review current terminology Identify key histopathologic
Banff-SCT 2017 Towards Uniformity of Terminology for the Pathology of CAV Gerald J. Berry, MD Dept. of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA Objectives Review current terminology Identify key histopathologic
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System. The heart. The heart is a double pump. A quick note on arteries vs. veins. = the muscular pump of the CV system
 Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation.
 As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation. Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood
As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation. Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood
Circulation.notebook March 07, Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Circulatory System p
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
MYCOBACTERIA. Pulmonary T.B. (infect bird)
 MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
3.4. The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System The human circulatory system is made up of the blood, the heart, and the blood vessels. The function of the circulatory system is to transport substances around the body. It moves
The Circulatory System The human circulatory system is made up of the blood, the heart, and the blood vessels. The function of the circulatory system is to transport substances around the body. It moves
Neuropathology Inflammation, Infection, Demyelination in the CNS
 Neuropathology Inflammation, Infection, Demyelination in the CNS PathoBasic 2016-09-20 Jürgen Hench Inflammation in the CNS inflammation generally as a reaction against pathogen, substance, necrotic, or
Neuropathology Inflammation, Infection, Demyelination in the CNS PathoBasic 2016-09-20 Jürgen Hench Inflammation in the CNS inflammation generally as a reaction against pathogen, substance, necrotic, or
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
