The Cardiovascular System (Part II)
|
|
|
- Audra Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 黃敏銓 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1
2 Development of veins Three paired veins drain into the tubular heart of a 4-week embryo Vitelline veins: poorly oxygenated blood from yolk sac Umbilical veins: oxygenated blood from the primordial placenta Common cardinal veins: poorly oxygenated blood from the body of the embryo 2
3 Three paired veins Sinus venosus Pharyngeal arch arteries Cardinal veins 26 days Blue color Vitelline vein Umbilical vesicle Umbilical vein (well-oxygenated) 3
4 Three paired veins enter into the sinus venosus Left Right Dorsal view 24 days 4
5 Vitelline veins IVC, Hepatic veins & sinusoids, and portal vein Left Right Hepatic segment of IVC: right vitelline vein Hepatic veins: vitelline veins Hepatic sinusoids Liver Portal vein: vitelline veins Dorsal view (7 weeks) Duodenum 5
6 Umbilical veins Umbilical vein : left umbilical vein Left Right 7th week (Ligamentum venosum) Dorsal view 6
7 7 weeks Anterior cardinal veins Brachiocephalic veins Anastomosis between anterior cardinal veins Left Right 8 weeks Left brachiocephalic vein Right brachiocephalic vein Dorsal view 7
8 Superior vena cava (Oblique vein of left atrium) Indian Pacing Electrophysiol. J. Left Right Superior vena cava Right anterior cardinal vein Right common cardinal vein (Left horn of sinus venosus) Dorsal view 8
9 Left brachiocephalic vein Left superior intercostal vein Oblique vein to coronary sinus
10 Posterior cardinal veins: root of azygos v. and common iliac veins 6 weeks Adult Azygos v. Posterior cardinal vein (mesonephroi) Common iliac veins Right Left 10
11 Subcardinal veins and supracardinal veins replace and supplement posterior cardinal veins Posterior cardinal v. Supracardinal v. Subcardinal v. Right Left 6 weeks 7 weeks 11
12 Subcardinal veins IVC (prerenal seg.) R. suprarenal v. Stem of L. renal v. L. suprarenal v. Subcardinal vein R. gonadal v. L. gonadal v. 6 weeks Right Adult Left 12
13 Supracardinal veins Azygos v. Hemiazygos v. IVC (postrenal seg.) degeneration 8 weeks Right Adult Left Supracardinal vein 13
14 Inferior vena cava (IVC) Left Right IVC (prerenal segment): R. subcardinal v. IVC (renal segment): Subcardinal-supracardinal anastomosis IVC (hepatic segment): R. vitelline vein IVC (postrenal segment): R. supracardinal v. Right Adult Left 14
15 The primordial pulmonary vein develops in the dorsal wall of the left atrium
16 Development of arteries Pharyngeal arch arteries Dorsal aorta Intersegmental arteries Vitelline arteries Umbilical arteries 16
17 Pharyngeal arch arteries (Aortic arches) Intersegmental arteries Dorsal aorta Umbilical artery Pharyngeal arches Aortic sac 4th-5th week (26 days) Vielline artery 17
18 Intersegmental arteries Neck: vertebral arteries Thorax: intercostal arteries Abdomen: lumbar arteries 5th pair: common iliac arteries Sacrum: lateral sacral arteries Caudal end of dorsal aorta: median sacral artery. 18
19 Vitelline arteries Celiac trunk: foregut Superior mesenteric artery: midgut Inferior mesenteric artery: hindgut 19
20 Umbilical arteries Proximal parts Umbilical artery (branch of Internal iliac arteries) Superior vesical arteries Distal parts Medial umbilical ligaments 20
21 Derivatives of pharyngeal arch arteries Pharyngeal arch arteries (Aortic arches) 21
22 Pharyngeal arches and pharyngeal arch arteries Pharyngeal arch arteries 26 days 22
23 Primordial pharyngeal arch arterial pattern is transformed into the final fetal arterial arrangement during the 8 th week (1st, 2nd pairs disappeared) 3 rd, 4 th, and 6 th pharyngeal arch arteries 6 weeks 8 weeks 23
24 Derivatives of the 1st pair pharyngeal arch arteries Maxillary arteries Ears, teeth, muscles of eyes and face External carotid arteries Pharyngeal arch arteries 1st pair of pharyngeal arch arteries 24
25 Derivatives of the 2nd pair pharyngeal arch arteries Stems of the stapedial arteries Stapedial artery: 第 10 週退化 Persistent stapedial artery: 異常 Pharyngeal arch arteries 2nd pair of pharyngeal arch arteries (dorsal part) 25
26 Derivatives of the 3rd pair pharyngeal arch arteries 6 weeks 7 weeks Pharyngeal arch arteries Internal carotid artery Common carotid artery 26
27 Derivatives of the 4th pair pharyngeal arch arteries 1. Right: proximal part of right subclavian artery 2. Left: part of arch of aorta 1 2 Right subclavian artery 1 2 Left subclavian artery Right dorsal aorta 7th intersegmental arteries right left 27
28 Fate of 5th pair of pharyngeal arch arteries 50% embryos: rudimentary vessels no vascular derivatives 50% embryos: no 5th pair arteries develop 28
29 Derivatives of the 6th pair pharyngeal arch arteries Right: Proximal: right pulmonary artery (proximal) Distal: degeneration Left: Proximal: left pulmonary artery (proximal) Distal: ductus arteriosus 29
30 Left recurrent laryngeal nerve hooks around the ligamentum arteriosum and aortic arch 30
31 Why the course of the recurrent laryngeal nerves differs? Pharyngeal arch arteries 6 weeks ductus arteriosus 8 weeks right left Child 31
32 Right and left subclavian artery Arch of aorta Right subclavian artery 2 Left subclavian artery Right dorsal aorta 7th intersegmental arteries right left right left 32
33 Aortic Arch Anomalies Coarctation of Aorta: 10% of CHD Double Aortic Arch Right Arch of Aorta Anomalous Right Subclavian Artery 33
34 Coarctation of Aorta Male : Female 2:1 70% cases : bicuspid aortic valve Juxtaductal coarctation: 90% Postductal coarctation Preductal coarctation Preductal coarctation Postductal coarctation Ductus arteriosus Ductus arteriosus 34
35 Collateral circulation during the fetal period in postductal coarctation 35
36 Preductal coarctation Ductus arteriosus Closure of DA in infant results in hypoperfusion and rapid deterioration Treatment: infusion of prostaglandin E 2 to re-open the ductus arteriosus 36
37 Double Aortic Arch Vascular ring around the trachea and esophagus Large right arch of aorta Small left arch of aorta Normally involutes 37
38 Right arch of aorta Area of abnormal involution Retroesophageal right arch of aorta Right arch of aorta 38
39 Anomalous Right Subclavian Artery Abnormal involution Persistent portion of right dorsal aorta Right subclavian artery Right subclavian artery 39
40 Six primary lymph sacs at the end of embryonic period Begins to develop at the end of the 6th week Head, neck, upper limbs (1) Primordial gut (1) (2) Cystic hygroma 7.5-week embryo (2) Lower trunk, lower limbs 40
41 9-week embryo Right lymphatic duct Right and left thoracic ducts Right Thoracic duct Chyle cistern (cisterna chyli) Left 41
42
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
The Cardiovascular System (Part II)
 The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 1 Aortic arch derivatives Aortic arches 2 Pharyngeal and aortic arches 4 th week 3 (1st, 2nd pairs disappeared) 6 th week (37 days) 4 8th week: transformed into the
The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 1 Aortic arch derivatives Aortic arches 2 Pharyngeal and aortic arches 4 th week 3 (1st, 2nd pairs disappeared) 6 th week (37 days) 4 8th week: transformed into the
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Development of the Great Vessels and Conduc6on Tissue
 Development of the Great Vessels and Conduc6on Tissue Development of the heart fields h:p://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ index.php?6tle=advanced_- _Heart_Fields! 2 Septa6on of the Bulbus Cordis Bulbus
Development of the Great Vessels and Conduc6on Tissue Development of the heart fields h:p://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ index.php?6tle=advanced_- _Heart_Fields! 2 Septa6on of the Bulbus Cordis Bulbus
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries
 Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries Slide 1: In this presentation I am going to describe for you the development of what are known as the great arteries. The great arteries
Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries Slide 1: In this presentation I am going to describe for you the development of what are known as the great arteries. The great arteries
The Cardiovascular System (Part I) 黃敏銓 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所
 The Cardiovascular System (Part I) 黃敏銓 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Congenital heart defects (CHDs) 台灣兒童心臟學會 Sinus venarum Membranous septum Conus arteiosus (infundibulum) Aortic vestibule The Cardiovascular System
The Cardiovascular System (Part I) 黃敏銓 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Congenital heart defects (CHDs) 台灣兒童心臟學會 Sinus venarum Membranous septum Conus arteiosus (infundibulum) Aortic vestibule The Cardiovascular System
Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems. Repetition: Muscle tissue
 Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems Repetition: Muscle tissue Beginning of the cardiovascular system development the 3rd week: Hemangiogenesis (day 15 16) blood islets (insulae
Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems Repetition: Muscle tissue Beginning of the cardiovascular system development the 3rd week: Hemangiogenesis (day 15 16) blood islets (insulae
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Development of the Heart and Vasculature
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Development of the Heart and Vasculature Overview vascular system appears (middle of 3 rd week) when the embryo is not able to satisfy its nutrition by diffusion Heart is the first functional
IN THE NAME OF GOD Development of the Heart and Vasculature Overview vascular system appears (middle of 3 rd week) when the embryo is not able to satisfy its nutrition by diffusion Heart is the first functional
THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES
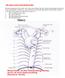 1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
Circumcaval Ureter: Embryology
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 444 448 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Circumcaval Ureter: Embryology Arianna Lesma *, Aldo Bocciardi, Patrizio Rigatti
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 444 448 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Circumcaval Ureter: Embryology Arianna Lesma *, Aldo Bocciardi, Patrizio Rigatti
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY. Guidelines. Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta.
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Blood Vessels. Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels. Veins carry blood toward the heart
 C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
Arteries. Lecture #2
 Arteries Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs and tissues
Arteries Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs and tissues
Mediastinum It is a thick movable partition between the two pleural sacs & lungs. It contains all the structures which lie
 Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Omran Saeed. Mohammad Al-muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE
 TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
Embryology of the Heart
 *Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
*Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
Lab 6: Blood. BIO104 Laboratory Handouts 147. Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics. 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition -
 147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students
 University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet. C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart
 Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Chest and cardiovascular
 Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Circulatory system. Lecture #2
 Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
Heart & vascular system I. Dawei Dong
 Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
Breathing. Heart Rate
 Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels
 REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 10 Dr. Stuart Sumida. Further Development of the Mesoderm (and Endoderm)
 Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 10 Dr. Stuart Sumida Further Development of the Mesoderm (and Endoderm) Further Development: Digestive System Foregut, Midgut, Hindgut Heart and Aortic Arches
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 10 Dr. Stuart Sumida Further Development of the Mesoderm (and Endoderm) Further Development: Digestive System Foregut, Midgut, Hindgut Heart and Aortic Arches
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts
 Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
The Blood Vessels of the Thorax
 5 The Blood Vessels of the Thorax Chapter Outline Large Arteries of the Thorax 78 The Aorta 78 Ascending Aorta and the Pericardium 78 Aneurysm of the Arch of the Aorta 78 Coarctation of the Aorta 78 Trauma
5 The Blood Vessels of the Thorax Chapter Outline Large Arteries of the Thorax 78 The Aorta 78 Ascending Aorta and the Pericardium 78 Aneurysm of the Arch of the Aorta 78 Coarctation of the Aorta 78 Trauma
Posterior Abdominal wall-
 Structures of posterior abdominal wall: o Bony boundaries: 5 lumber vertebra and their intervertebral disc, iliac fossa and iliac crest. o Muscles: psoas major, quadrates lumborum, transversus abdominis,
Structures of posterior abdominal wall: o Bony boundaries: 5 lumber vertebra and their intervertebral disc, iliac fossa and iliac crest. o Muscles: psoas major, quadrates lumborum, transversus abdominis,
1 Right & left Hepatic ducts Gastric Impression of spleen
 Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line
 L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments
 Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid
 Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels
 MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
Figure 10.1A Transparency Master 79
 Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Cardiovascular System. Chapter 22
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Chapter 22 Cardiac Contractions Cardiac cycle consists of alternate periods of contraction and relaxation Contraction is the systolic pressure Blood is ejected into
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Chapter 22 Cardiac Contractions Cardiac cycle consists of alternate periods of contraction and relaxation Contraction is the systolic pressure Blood is ejected into
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum. Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes
 Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
It passes through the diaphragm at the level of the 10th thoracic vertebra to join the stomach
 The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION
 THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Development of the Liver and Pancreas
 Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
SLIDES 6 AND 10 MM PIG SLIDES; TRANSVERSE SECTIONS AND SAGITAL; FETAL PIGS-1-8INCH; HUMAN SAGITAL DIAGRAMS:DRAWINGS OF THE PIG SECTIONS TO BE
 SLIDES 6 AND 10 MM PIG SLIDES; TRANSVERSE SECTIONS AND SAGITAL; FETAL PIGS-1-8INCH; HUMAN SAGITAL SECTION DIAGRAMS:DRAWINGS OF THE PIG SECTIONS TO BE LABELLED, AND FOUR DRAWINGS TO BE MADE. REFERENCES:PATTEN:
SLIDES 6 AND 10 MM PIG SLIDES; TRANSVERSE SECTIONS AND SAGITAL; FETAL PIGS-1-8INCH; HUMAN SAGITAL SECTION DIAGRAMS:DRAWINGS OF THE PIG SECTIONS TO BE LABELLED, AND FOUR DRAWINGS TO BE MADE. REFERENCES:PATTEN:
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Angiology Part 4. Veins. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Angiology Part 4 Veins Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 General introduction of the veins Vessel which return the blood back to atrium No pulsation,veneous blood, metabolic
Systematic Anatomy Angiology Part 4 Veins Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 General introduction of the veins Vessel which return the blood back to atrium No pulsation,veneous blood, metabolic
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46610 1 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the
OpenStax-CNX module: m46610 1 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
11.1 The Aortic Arch General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta
 456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم
 MAY 3, 2012 [POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL] LECTURE 26 ANATOMY Quick Revision: بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم Last time we started with the anterior abdominal wall and said that: 1. Diaphragm is the root of the abdomen.
MAY 3, 2012 [POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL] LECTURE 26 ANATOMY Quick Revision: بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم Last time we started with the anterior abdominal wall and said that: 1. Diaphragm is the root of the abdomen.
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
Sheet. April/14 th /2013. Introduction to Anatomy. Dr. Maher Hadidi. Muna Abu Hijleh. 1 P a g e
 Sheet Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Muna Abu Hijleh 1 P a g e 29 April/14 th /2013 Superior & Posterior Mediastinum ***Superior mediastinum * is bounded from: -Anterior by manubrium sterni -posterior
Sheet Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Muna Abu Hijleh 1 P a g e 29 April/14 th /2013 Superior & Posterior Mediastinum ***Superior mediastinum * is bounded from: -Anterior by manubrium sterni -posterior
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1
 Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels Outline PART 1: BLOOD VESSEL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 The Cardiovascular System: Blood s Outline PART 1: BLOOD VESSEL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION A. The three major types of blood vessels are, capillaries, and. (p. 699; Fig. 19.1) 1. Arteries carry blood away
The Cardiovascular System: Blood s Outline PART 1: BLOOD VESSEL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION A. The three major types of blood vessels are, capillaries, and. (p. 699; Fig. 19.1) 1. Arteries carry blood away
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong.
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 8: Circulatory System of the Shark Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 8: Circulatory System of the Shark Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how the divisions of the circulatory system relate to one another.
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 8: Circulatory System of the Shark Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how the divisions of the circulatory system relate to one another.
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector. Section I
 Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
Done by: nisreen obeidat
 Sheet: liver and pancreas Done by: nisreen obeidat Embryology of the liver The liver develops in the ventral mesentery of the foregut and divides the ventral mesentery :into 1)lesser omentum (between the
Sheet: liver and pancreas Done by: nisreen obeidat Embryology of the liver The liver develops in the ventral mesentery of the foregut and divides the ventral mesentery :into 1)lesser omentum (between the
The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System
 The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System Jeff Vergales, MD, MS Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Cardiology jvergales@virginia.edu Disclosures I serve as the medical director for
The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System Jeff Vergales, MD, MS Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Cardiology jvergales@virginia.edu Disclosures I serve as the medical director for
The Cardiovascular System
 C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
A. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis. B. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis.
 USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System
 Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
Anatomy of the Blood Vessels
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Blood Vessels References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab:
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Blood Vessels References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab:
The jejunum and the Ileum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
1. Distinguish among the types of blood vessels on the basis of their structure and function.
 Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
Anatomy. Contents Brain (Questions)
 Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
STUDY OF AZYGOS SYSTEM AND ITS VARIATIONS B. Vijaya Nirmala 1, Teresa Rani S 2
 STUDY OF AZYGOS SYSTEM AND ITS VARIATIONS B. Vijaya Nirmala 1, Teresa Rani S 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: B. Vijaya Nirmala, Teresa Rani S. Study of Azygos System and its Variations. Journal of Evolution
STUDY OF AZYGOS SYSTEM AND ITS VARIATIONS B. Vijaya Nirmala 1, Teresa Rani S 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: B. Vijaya Nirmala, Teresa Rani S. Study of Azygos System and its Variations. Journal of Evolution
(2) (1) (3) (4) BLOOD PATHWAY ASSESSMENT RUBRIC
 BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
Major Veins of the Body
 Major Veins of the Body Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Major Veins of the Body Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Contents. Pig Dissection. Contents. External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index
 Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
Chapter 11. The Cardiovascular System. Clicker Questions Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Clicker Questions Oxygen-poor blood is pumped through the venae cavae to the right side of the heart, and then through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs and back
Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Clicker Questions Oxygen-poor blood is pumped through the venae cavae to the right side of the heart, and then through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs and back
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Anatomy II ANAT 302. Course Description
 Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
