Blood Pressure Measurement
|
|
|
- Katrina Greer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Blood Pressure Measurement
2 What is blood pressure? Blood pressure refers to the force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels. The pressure of the circulating blood decreases as blood moves through arteries, arterioles, capillaries, and veins. Blood pressure values are reported in millimeters of mercury (mmhg). Blood pressure is recorded as systolic over diastolic e.g. 120/60.
3 What is blood pressure? The systolic arterial pressure is defined as the peak pressure in the arteries, which occurs near the beginning of the cardiac cycle. The diastolic arterial pressure is the lowest pressure (at the resting phase of the cardiac cycle ). Measures of arterial pressure are not static, but undergo natural variations from one heartbeat to another and throughout the day. Blood pressure also changes in response to stress, nutritional factors, drugs, or disease.
4 Systole is the contraction of heart chambers, pushing blood out of the chambers. The chamber valves are closed.
5 Diastole is the period of time when the heart fills with blood after systole (contraction). The chamber valves are open. The heart is at rest.
6 High blood pressure High blood pressure (or hypertension) is defined in an adult as a blood pressure greater than or equal to 140 mm Hg systolic pressure or greater than or equal to 90 mm Hg diastolic pressure. High blood pressure directly increases the risk of coronary heart disease (which leads to heart attack) and stroke, especially when there are other risk factors. High blood pressure is the major preventable cause of premature illhealth.
7 Risk factors for developing hypertension Obesity; Physical inactivity; High consumption of alcohol; High intake of dietary sodium; Low intake of dietary potassium ; Stress; Increasing age; Cigarette smoking; Increased blood cholesterol; Patients with systemic diseases including diabetes mellitus; renal disease; peripheral vascular disease; Family history of hypertension, CHD or stroke.
8 Preparation for measurement The patient should abstain from eating, drinking, smoking and taking drugs that affect the blood pressure one hour before measurement. Instruct your patients to avoid coffee, smoking or any other unprescribed drug with sympathomimetic activity on the day of the measurement.
9 Preparation for measurement Because a full bladder affects the blood pressure, it should be emptied. Painful procedures and exercise should have been avoided one hour prior to the measurement. The patient should have been sitting quietly for about 5 minutes.
10 Preparation for measurement BP is taken in a quiet room and at comfortable temperature, the room temperature and time of the day must be recorded.
11 Taking BP. Main Steps Wash your hands - Handwashing prevents the spread of infection; Prepare all the required equipment: a qualitative stethoscope, an appropriately sized blood pressure cuff, a blood pressure measurement instrument with a manual inflate mode, gloves (if necessary), a cotton pad. Cleanse the ear pieces and the diaphragm of the stethoscope with a spirit cotton pad.
12 Taking BP. Main Steps Explain the purpose and procedure to the patient. Now I would like to take your blood pressure. The blood pressure is an important vital sign. Depending on it, I will prescribe you investigations and treatment. Do you agree? Acum eu Vă voi masura tensiunea arterială. Tensiunea arterială este un parametru important al stării de sanatate, în dependența de nivelui temperaturei eu voi prescri investigațiile necesare și tratament. Sunteți de acord?
13 Taking BP. Main Steps After that, you should explain what you want to do: Please, relax, don t worry, this procedure is safe and not complicated. I will put the BP cuff around your upper arm, the cuff will be inflated, then deflated; after that I will say your BP level, please, don t move and speak during the procedure, it will take about a few minutes. Please, open your shoulder region. Vă rog, nu retrăiți, relaxați-vă, procedura dată este inofensivă, eu Vă voi plasa manșeta tonometrul în regiunea brațului, o voi umfla, apoi dezumfla și voi anunța cifrele TA, Va rog, nu Va mișcați și nu vorbiți în timpul procedurei. Durata este de cîteva minute. Eliberați, Va rog, regiunea brațului.
14 Taking BP. Main Steps The Position of the Patient The patient must sit. The arm and back are supported. The feet should be resting firmly on the floor. The feet should not dangle.
15 Taking BP. Main Steps The Position of the arm The measurements should be made on the right arm whenever possible. The patient s arm should be resting on the desk and raised (by using a pillow). The palm is facing up. The arm should remain bent and completely relaxed.
16 Taking BP. Main Steps The Position of the arm The patient's arm should be slightly flexed at elbow. Push the sleeve up, wrap the cuff around the bare arm. The cuff is applied directly over the skin (the clothes artificially raise the blood pressure ). The cuff lower border should be 2.5 cm above antecubital The centre of the inflatable bladder should be over the brachial artery.
17 Taking BP. Main Steps Feel for a pulse from the artery coursing through the inside of the elbow (antecubital fossa). Turn the thumb-screw. With your left hand place the stethoscope head directly over the artery you have found. Press firmly but not too hard so that not to block the artery.
18 Taking BP. Main Steps Use your right hand to pump the squeeze bulb several times as you listen to the pulse sounds. When the BP cuff has inflated enough to stop the blood flow, you should hear no sounds through the stethoscope and pump up an additional mmhg to the level of suspected Systolic BP. Deflate the cuff slowly at a rate of 2-3 mmhg per second until you can again detect a radial pulse. Listen for auditory vibrations from artery "bump, bump, bump" (Korotkoff)
19 Taking BP. Main Steps Systolic blood pressure is the pressure at which you can first hear the pulse. Diastolic blood pressure is the last pressure at which you can still hear the pulse.
20 Taking BP. Main Steps Avoid moving your hands or the head of the stethescope while you are taking readings as this may produce noise that can obscure the Sounds of Korotkoff. The difference between two arm readings should be within mm Hg. Differences greater than imply differential blood flow. If you wish to repeat the BP measurement, you should allow the cuff to completely deflate, permit any venous congestion in the arm to resolve and then repeat a minute or so later.
21 Taking BP. Main Steps Explain the result to the patient Your Blood pressure level is..., thank you. Nivelul tensiunii arteriale Dvoastră este..., Va mulțumesc Dispose of the equipment properly. Wash your hands.
22 VARIANTA ROMÂNĂ
23 Ce este tensiunea arterială? Blood pressure refers to the force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels. The pressure of the circulating blood decreases as blood moves through arteries, arterioles, capillaries, and veins. Blood pressure values are reported in millimeters of mercury (mmhg). Blood pressure is recorded as systolic over diastolic e.g. 120/60. Tensiunea arterială se referă la forța exercitată de sângele care circulă asupra pereților vaselor de sânge. Presiunea sângelui care circulă scade în timp ce sângele trece prin artere, arteriole, capilare si vene. Valorile tensiunii arteriale sunt raportate în mmhg (milimetri pe coloana de Mercur). Tensiunea arterială este înregistrată ca tensiunea sistolică pe tensiunea diastolică, de exemplu, 120/60.
24 Ce este tensiunea arterială? The systolic arterial pressure is defined as the peak pressure in the arteries, which occurs near the beginning of the cardiac cycle. The diastolic arterial pressure is the lowest pressure (at the resting phase of the cardiac cycle ) Measures of arterial pressure are not static, but undergo natural variations from one heartbeat to another and throughout the day. Blood pressure also changes in response to stress, nutritional factors, drugs, or disease. Tensiunea arterială sistolică este definită ca presiunea cea mai mare în artere, care apare aproape de începutul ciclului cardiac. Tensiunea arterială diastolică este cea mai mică presiune (în faza de repaus a ciclului cardiac). Măsurile presiunii arteriale nu sunt statice, ci suferă variații naturale de la o bătaie a inimii la alta și pe tot parcursul zilei. Tensiunea arterială se schimbă, de asemenea, ca raspuns la stres, factori nutriționali, medicamente sau boli.
25 Sistola Systole is the contraction of heart chambers, pushing blood out of the chambers. The chamber valves are closed. Sistola este contracția camerelor inimii, forțând sângele din camere. Supapele camerei sunt închise.
26 Diastola Diastole is the period of time when the heart fills with blood after systole (contraction). The chamber valves are open. The heart is at rest. Diastola este perioada de timp când inima se umple cu sânge după sistolă (contracție). Supapele camerei sunt deschise. Inima este în repaus.
27 Tensiune arterială crescută High blood pressure (or hypertension) is defined in an adult as a blood pressure greater than or equal to 140 mm Hg systolic pressure or greater than or equal to 90 mm Hg diastolic pressure. High blood pressure directly increases the risk of coronary heart disease (which leads to heart attack) and stroke, especially when there are other risk factors. High blood pressure is the major preventable cause of premature illhealth. Tensiunea arterială crescută (sau hipertensiunea) este definită la un adult ca o tensiune arteriala mai mare sau egală cu 140 mm Hg a tensiunii arteriale sistolice sau mai mare sau egală cu 90 mm Hg a celei diastolice. Tensiunea arterială mare sporește direct riscul de boli cardiace coronariene (ceea ce duce la atac de cord) si accident vascular cerebral, în special atunci când există și alți factori de risc. Tensiunea arteriala mare este cea mai importantă cauza care poate fi prevenită a problemelor de sanatate premature.
28 Factorii de risc care duc la hipertensiunea arterială Obezitatea; Obesity; Physical inactivity; Lipsa de activitate fizică; High consumption of alcohol; Consumul mare de alcool; High intake of dietary sodium; Aportul crescut de sodiu dietetic; Low intake of dietary potassium ; Aportul scazut de potasiu dietetic; Stress; Stresul; Increasing age; Înaintarea în vârstă; Cigarette smoking; Fumatul; Increased blood cholesterol; Colesterolul marit din sânge; Patients with systemic diseases including diabetes mellitus, renal disease, peripheral vascular disease; Family history of hypertension, CHD or stroke. Pacienții cu boli sistemice care includ diabetul zaharat, boala renală, boli vasculare periferice; Antecedente familiale de hipertensiune, boală coronariană sau accident vascular cerebral.
29 Pregătirea pentru măsurare The patient should abstain from eating, drinking, smoking and taking drugs that affect the blood pressure one hour before measurement. Pacientul ar trebui să se abțină de la mâncare, băutură, fumat și de la primirea medicamentelor care afectează tensiunea arterială cu o oră înainte de măsurare. Instruct your patients to avoid coffee, smoking or any other unprescribed drug with sympathomimetic activity on the day of the measurement. Instruiți pacienții dumneavoastră să evite cafeaua, fumatul sau orice medicamente neprescrise cu activitate simpatomimetică în ziua măsurării.
30 Pregătirea pentru măsurare Because a full bladder affects the blood pressure, it should be emptied. Painful procedures and exercise should have been avoided one hour prior to the measurement. The patient should have been sitting quietly for about 5 minutes. Deoarece vezica urinară plină afectează tensiunea arterială, aceasta ar trebui să fie golită. Procedurile dureroase și exercițiile ar trebui să fie evitate cu o oră înainte de măsurare. Pacientul trebuie să fie așezat liniștit timp de aproximativ 5 minute.
31 Pregătirea pentru măsurare BP is taken in a quiet room and at comfortable temperature, the room temperature and time of the day must be recorded. Tensiunea arterială este măsurată într-o cameră liniștită și la o temperatura confortabilă a camerei, temperatura și timpul zilei trebuie să fie înregistrate.
32 Măsurarea tensiunii arteriale. Etapele principale Wash your hands - Handwashing prevents the spread of infection; Prepare all the required equipment: a qualitative stethoscope, an appropriately sized blood pressure cuff, a blood pressure measurement instrument with a manual inflate mode, gloves (if necessary), a cotton pad. Cleanse the ear pieces and the diaphragm of the stethoscope with a spirit cotton pad. Spălați-vă pe mâini - spălarea mâinilor previne răspândirea infecției; Pregătiți tot echipamentul necesar: un stetoscop calitativ, o manșetă de dimensiuni corespunzătoare, un instrument de măsurare a tensiunii arteriale cu mod de umflare manual, mănuși (dacă este necesar), un tampon de bumbac. Curățiți piesele pentru urechi si diafragma stetoscopului cu un tampon de bumbac.
33 Măsurarea tensiunii arteriale. Etapele principale Explain the purpose and procedure to the patient. Now I would like to take your blood pressure. The blood pressure is an important vital sign. Depending on it, I will prescribe you investigations and treatment. Do you agree? Explicați scopul și procedura pacientului. Acum aș vrea să vă măsor tensiunea arterială. Tensiunea arterială este un semn vital și important. În funcție de aceasta, vă voi prescrie investigații și tratament. Sunteți de acord?
34 Măsurarea tensiunii arteriale. Etapele principale After that, you should explain what you want to do: Please, relax, don t worry, this procedure is safe and not complicated. I will put the BP cuff around your upper arm, the cuff will be inflated, then deflated; after that I will say your BP level, please, don t move and speak during the procedure, it will take about a few minutes. Please, open your shoulder region. După aceea, ar trebui să explicați ceea ce doriți să faceți: Vă rog, relaxați-vă, nu vă faceți griji, această procedură este sigură și nu este complicată. Vă voi pune manșeta in jurul bratului, manșeta va fi umflată, apoi dezumflată; după aceea Vă voi spune care este tensiunea Dvoastră, Vă rog, nu Vă mișcați și nu vorbiți în timpul procedurii, va dura aproximativ câteva minute. Vă rog, deschide-ti regiunea umerilor.
35 Măsurarea tensiunii arteriale. Etapele principale Poziția pacientului The patient must sit. The arm and back are supported. The feet should be resting firmly on the floor. The feet should not dangle. Pacientul trebuie să fie așezat. Brațul și spatele sunt susținute. Picioarele trebuie sa se sprijine ferm pe podea. Picioarele nu ar trebui să se legene.
36 Măsurarea tensiunii arteriale. Etapele principale Poziția brațului The measurements should be made on the right arm whenever possible. The patient s arm should be resting on the desk and raised (by using a pillow). The palm is facing up. The arm should remain bent and completely relaxed. Măsurările trebuie efectuate pe brațul drept de fiecare dată când este posibil. Brațul pacientului trebuie sa fie pe masă și ridicat (prin utilizarea unei perne). Palma este orientată în sus. Brațul trebuie să rămână îndoit și complet relaxat.
37 Măsurarea tensiunii arteriale. Etapele principale Poziția brațului The patient's arm should be slightly flexed at elbow. Push the sleeve up, wrap the cuff around the bare arm. The cuff is applied directly over the skin (the clothes artificially raise the blood pressure ). The cuff lower border should be 2.5 cm above antecubital The centre of the inflatable bladder should be over the brachial artery. Brațul pacientului trebuie să fie ușor flexat la cot. Împingeți manșonul în sus, înfășurați manșeta în jurul brațului gol. Manșeta se aplică direct pe piele (hainele ridică în mod artificial tensiunea arterială). Marginea inferioară a manșetei trebuie să fie 2,5 cm deasupra antecubital Centrul balonului gonflabil ar trebui să fie peste artera brahială.
38 Măsurarea tensiunii arteriale. Etapele principale Feel for a pulse from the artery coursing through the inside of the elbow (antecubital fossa). Turn the thumb-screw. With your left hand place the stethoscope head directly over the artery you have found. Press firmly but not too hard so that not to block the artery. Simțiți pulsul de pe artera care trece prin interiorul cotului (fossa antecubital). Rotiți șurubul cu cap striat. Cu mâna stângă puneți capul stetoscopului direct peste artera care ați găsit-o. Apăsați ferm, dar nu prea tare, astfel încât să nu blocați artera.
39 Măsurarea tensiunii arteriale. Etapele principale Use your right hand to pump the squeeze bulb several times as you listen to the pulse sounds. When the BP cuff has inflated enough to stop the blood flow, you should hear no sounds through the stethoscope and pump up an additional mmhg to the level of suspected Systolic BP. Deflate the cuff slowly at a rate of 2-3 mmhg per second until you can again detect a radial pulse. Listen for auditory vibrations from artery "bump, bump, bump" (Korotkoff) Folosiți mâna dreaptă pentru a pompa balonul parcă stoarcându-l de mai multe ori în timp ce ascultați sunetele pulsului. Atunci când manșeta este umflată suficient pentru a opri fluxul de sânge, nu ar trebui să auziți nici un sunet prin stetoscop și mai pompați încă mmhg până la nivelul suspectat de tensiune sistolică. Dezumflați manșeta încet, la o viteză de 2-3 mmhg pe secundă până când puteți detect din nou pulsul radial. Ascultați vibrațiile auditive de pe artera "bump, bump, bump" (Korotkoff)
40 Măsurarea tensiunii arteriale. Etapele principale Systolic blood pressure is the pressure at which you can first hear the pulse. Tensiunea arterială sistolică este tensiunea la care se poate auzi prima dată pulsul. Diastolic blood pressure is the last pressure at which you can still hear the pulse. Tensiunea arterială diastolică este ultima tensiune la care se poate încă auzi pulsul.
41 Măsurarea tensiunii arteriale. Etapele principale Avoid moving your hands or the head of the stethoscope while you are taking readings as this may produce noise that can obscure the Sounds of Korotkoff. The difference between two arm readings should be within mm Hg. Differences greater then imply differential blood flow. If you wish to repeat the BP measurement you should allow the cuff to completely deflate, permit any venous congestion in the arm to resolve and then repeat a minute or so later. Evitați să mișcați mâinile sau capul stetoscopului în timp ce citiți valorile deoarece acest lucru poate produce zgomot care poate să acopere sunetele Korotkoff. Diferența dintre valorile celor două brațe ar trebui să fie în limita a mm Hg. Diferențe mai mari de implică fluxul sanguin diferențial. Dacă doriți să repetați măsurarea tensiunii arteriale, ar trebui să lăsați manșeta să se dezumfle complet, să permiteți ca orice congestie venoasă în braț să fie soluționată și apoi repetați circa un minut mai târziu.
42 Măsurarea tensiunii arteriale. Etapele principale Explain the result to the patient Your Blood pressure level is..., thank you. Dispose of the equipment properly. Wash your hands. Explicați rezultatul pacientului Nivelul tensiunii arteriale a Dvoastră este..., Va mulțumesc. Aranjați echipamentul corespunzător. Spălați-vă pe mâini.
To maintain the ideal homeostasis; The rate of chemical reactions in body is regulated by the temperature; If the temperature is too high or too low,
 To maintain the ideal homeostasis; The rate of chemical reactions in body is regulated by the temperature; If the temperature is too high or too low, the body s fluid balance is also affected. 1. The Core
To maintain the ideal homeostasis; The rate of chemical reactions in body is regulated by the temperature; If the temperature is too high or too low, the body s fluid balance is also affected. 1. The Core
LAB: Blood Pressure Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System!
 LAB: Blood Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System! Lab Objectives. At the completion of the lab, you should be able to: measure pulse or heart rate (HR) and respiratory rate (RR);
LAB: Blood Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System! Lab Objectives. At the completion of the lab, you should be able to: measure pulse or heart rate (HR) and respiratory rate (RR);
BLOOD PRESSURE ASSESSMENT
 BLOOD PRESSURE ASSESSMENT Course Principles of Health Science Unit X Vital Signs Course Health Science Unit VI CPR / AED & First Aid Essential Question How do health care skills help to promote health
BLOOD PRESSURE ASSESSMENT Course Principles of Health Science Unit X Vital Signs Course Health Science Unit VI CPR / AED & First Aid Essential Question How do health care skills help to promote health
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE. MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL (equ04)
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 2/80 7/17 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN, Patient Care Technician Multi-skilled
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 2/80 7/17 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN, Patient Care Technician Multi-skilled
How To Measure Vital Signs
 How To Measure Vital Signs How to Use This Tutorial This tutorial is intended for healthcare providers or students to teach basic vital signs skills Use the navigation buttons below to move through the
How To Measure Vital Signs How to Use This Tutorial This tutorial is intended for healthcare providers or students to teach basic vital signs skills Use the navigation buttons below to move through the
PLANK 1 Direct Care Staff Trained in Accurate BP Measurement
 Direct Care Staff Trained in Accurate BP Measurement 1. 2. 3. 5. 22 to 26 cm Small adult (12X22 cm) 27 to 34 cm Adult (16X30 cm) 35 to 44 cm Large adult (16X36 cm) 45 to 52 cm Adult thigh (16X42 cm) widths
Direct Care Staff Trained in Accurate BP Measurement 1. 2. 3. 5. 22 to 26 cm Small adult (12X22 cm) 27 to 34 cm Adult (16X30 cm) 35 to 44 cm Large adult (16X36 cm) 45 to 52 cm Adult thigh (16X42 cm) widths
Lab #10 Physiology of the Circulatory System
 Lab #10 Physiology of the Circulatory System Introduction The circulatory system functions to deliver oxygen an nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart
Lab #10 Physiology of the Circulatory System Introduction The circulatory system functions to deliver oxygen an nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart
Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse. City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved
 Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved Course Content: Definition of Blood Pressure Normal Blood Pressure Readings Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved Course Content: Definition of Blood Pressure Normal Blood Pressure Readings Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
PART I: HEART ANATOMY
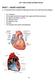 Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
High Blood Pressure Blood Pressure Monitoring at Home -- F...
 Return to Web version High Blood Pressure Blood Pressure Monitoring at Home Why should I measure my blood pressure at home and keep a record of it? Measuring your blood pressure at home and keeping a record
Return to Web version High Blood Pressure Blood Pressure Monitoring at Home Why should I measure my blood pressure at home and keep a record of it? Measuring your blood pressure at home and keeping a record
LAB 9: Metabolic Rates
 LAB 9: Metabolic Rates Introduction: The cardiovascular (circulatory) system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart pumps
LAB 9: Metabolic Rates Introduction: The cardiovascular (circulatory) system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart pumps
science-u.org What affects blood Blood Pressure Directions You Will Need BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME Minutes
 What affects blood pressure? BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME 25-60 Minutes You Will Need Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) Stethoscope Blood pressure cuffs and stethoscopes can be found online
What affects blood pressure? BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME 25-60 Minutes You Will Need Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) Stethoscope Blood pressure cuffs and stethoscopes can be found online
Physiology of the Circulatory System modified from
 Physiology of the Circulatory System modified from http://www.ekcsk12.org/science/aplabreview/aplab10.htm Introduction The circulatory system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth
Physiology of the Circulatory System modified from http://www.ekcsk12.org/science/aplabreview/aplab10.htm Introduction The circulatory system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth
Ambulatory Services Orientation & Skill Review Skill Performance Checklist: Vital Signs. Name: Date:
 Evaluation Levels Behavior Level 3 Met Performed all skills competently. No behaviors omitted. Level 2 Satisfactory Omitted no more than three (3) non-critical behaviors. Level 1 Unsatisfactory Omitted
Evaluation Levels Behavior Level 3 Met Performed all skills competently. No behaviors omitted. Level 2 Satisfactory Omitted no more than three (3) non-critical behaviors. Level 1 Unsatisfactory Omitted
CAMOSUN COLLEGE BIOLOGY 144 (2010) LABS
 LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
Vital Signs Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment
 Vital Signs Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Become a Data Gathering Machine The exam begins as soon as you see the patient o Appearance, demeanor, dress Well groomed, neat, disheveled, work
Vital Signs Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Become a Data Gathering Machine The exam begins as soon as you see the patient o Appearance, demeanor, dress Well groomed, neat, disheveled, work
For instance, it can harden the arteries, decreasing the flow of blood and oxygen to the heart. This reduced flow can cause
 High Blood Pressure Blood pressure is the force of blood against your artery walls as it circulates through your body. Blood pressure normally rises and falls throughout the day, but it can cause health
High Blood Pressure Blood pressure is the force of blood against your artery walls as it circulates through your body. Blood pressure normally rises and falls throughout the day, but it can cause health
Managing Blood Pressure: It Takes a Team
 Managing Blood Pressure: It Takes a Team Module Two How to Take Blood Pressure October 2011 MODULE TWO: How to Take Blood Pressure Module Two: HOW TO TAKE BLOOD PRESSURE Objectives Demonstrate proper technique
Managing Blood Pressure: It Takes a Team Module Two How to Take Blood Pressure October 2011 MODULE TWO: How to Take Blood Pressure Module Two: HOW TO TAKE BLOOD PRESSURE Objectives Demonstrate proper technique
Lecture #3 - Blood Pressure Recording Procedure. Equipment
 Lecture #3 - Blood Pressure Recording Procedure CKiD Blood Pressure Training Equipment Mabis Medic-Kit aneroid sphygmomanometer Mabis Medic-Kit assortment of cuff sizes Stethoscope with bell (pediatric
Lecture #3 - Blood Pressure Recording Procedure CKiD Blood Pressure Training Equipment Mabis Medic-Kit aneroid sphygmomanometer Mabis Medic-Kit assortment of cuff sizes Stethoscope with bell (pediatric
Clinical Research Coordinator Skills Program
 Clinical Research Coordinator Skills Program Vital Signs This Skill Requires Provider direction Standard Precautions Using purell before and after contact with the patient or the patient s environment
Clinical Research Coordinator Skills Program Vital Signs This Skill Requires Provider direction Standard Precautions Using purell before and after contact with the patient or the patient s environment
Protocol 4: Measuring Blood Pressure
 Zool 430L Protocols Page 8 of 12 Protocol 4: Measuring Blood Pressure 4.1 Via Auscultation (listening through stethoscope) The estimate of blood pressure is obtained by cutting off blood flow with a known
Zool 430L Protocols Page 8 of 12 Protocol 4: Measuring Blood Pressure 4.1 Via Auscultation (listening through stethoscope) The estimate of blood pressure is obtained by cutting off blood flow with a known
LEARNING OUTCOME The students will be able to elicit vital signs correctly on human volunteers/patients
 Vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, respiratory rate, pain) are physiological parameters that a healthcare professional requires when dealing with patients. Accurate measurement of vital signs
Vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, respiratory rate, pain) are physiological parameters that a healthcare professional requires when dealing with patients. Accurate measurement of vital signs
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
!"#$ Blood Pressure Monitor. Instruction manual page 1 Gebrauchsanweisung Seite 17 Gebruiksaanwijzing pagina 33
 !"#$ Blood Pressure Monitor Instruction manual page 1 Gebrauchsanweisung Seite 17 Gebruiksaanwijzing pagina 33 Mode d emploi page 49 Manuale de instructone pagina 65 Manual de instrucciones pagina 81 Introduction
!"#$ Blood Pressure Monitor Instruction manual page 1 Gebrauchsanweisung Seite 17 Gebruiksaanwijzing pagina 33 Mode d emploi page 49 Manuale de instructone pagina 65 Manual de instrucciones pagina 81 Introduction
Measuring body temperature, blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate and oxygen saturation
 Vital Signs Measuring body temperature, blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate and oxygen saturation Aims To ensure that students are able to demonstrate the safe and correct technique for setting up
Vital Signs Measuring body temperature, blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate and oxygen saturation Aims To ensure that students are able to demonstrate the safe and correct technique for setting up
Data Collection Worksheet
 Data Collection Worksheet 1. Has a doctor or nurse ever said that you have: High blood pressure or hypertension? [ ] No [ ] Yes [ ] Not Sure 1.a. If Yes, then at what age were you first told this? Age
Data Collection Worksheet 1. Has a doctor or nurse ever said that you have: High blood pressure or hypertension? [ ] No [ ] Yes [ ] Not Sure 1.a. If Yes, then at what age were you first told this? Age
2. Measure a subject's blood pressure and heart rate both at rest and during exercise.
 Lab Activity 11 The Cardiovascular System Student Learning Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Define, explain and correctly use the key terms. 2. Measure a subject's blood
Lab Activity 11 The Cardiovascular System Student Learning Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Define, explain and correctly use the key terms. 2. Measure a subject's blood
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
#6 - Cardiovascular III Heart Sounds, Pulse Rate, Hemoglobin Saturation, and Blood Pressure
 #6 - Cardiovascular III Heart Sounds, Pulse Rate, Hemoglobin Saturation, and Blood Pressure Objectives: Observe slide of artery and vein cross-section Auscultate heart sounds using a stethoscope Measure
#6 - Cardiovascular III Heart Sounds, Pulse Rate, Hemoglobin Saturation, and Blood Pressure Objectives: Observe slide of artery and vein cross-section Auscultate heart sounds using a stethoscope Measure
AP Biology Lab 10 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 AP Biology Laboratory Date: Name and Period: AP Biology Lab 10 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. in Exercise 10A you will learn how to measure blood pressure. 2. in
AP Biology Laboratory Date: Name and Period: AP Biology Lab 10 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. in Exercise 10A you will learn how to measure blood pressure. 2. in
MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use What is blood pressure?
 MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents 01... Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use 02... 1. What is blood pressure? 02... 2. Why is it useful measure blood pressure at home?... A. WHO blood pressure
MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents 01... Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use 02... 1. What is blood pressure? 02... 2. Why is it useful measure blood pressure at home?... A. WHO blood pressure
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009
 Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
Home Blood Pressure Log
 Home Blood Pressure Log 2 You or your health care professional may want to monitor your blood pressure at home twice a day for a week or more before appointments to accurately confirm your average blood
Home Blood Pressure Log 2 You or your health care professional may want to monitor your blood pressure at home twice a day for a week or more before appointments to accurately confirm your average blood
Chapter 15: Measuring Height, Weight, and Vital Signs. Copyright 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 15: Measuring Height, Weight, and Vital Signs Height and Weight Weight Baseline measurement at patient s first visit Measured in kg or lbs Common types of scales Balance beam Dial Digital Height
Chapter 15: Measuring Height, Weight, and Vital Signs Height and Weight Weight Baseline measurement at patient s first visit Measured in kg or lbs Common types of scales Balance beam Dial Digital Height
Techniques of Vital Signs. John Gazewood, MD, MSPH Department of Family Medicine
 Techniques of Vital Signs John Gazewood, MD, MSPH Department of Family Medicine Objectives Define normal in several ways. Describe correct technique of measuring vital signs. Describe correct technique
Techniques of Vital Signs John Gazewood, MD, MSPH Department of Family Medicine Objectives Define normal in several ways. Describe correct technique of measuring vital signs. Describe correct technique
Chapter 29 1/8/2018. Vital Signs. Measuring and Reporting Vital Signs. Key Terms
 Chapter 29 Vital Signs Key Terms Blood pressure Body temperature Diastolic pressure Hypertension Hypotension Pulse Pulse rate Respiration Sphygmomanometer Stethoscope Systolic pressure Vital signs Measuring
Chapter 29 Vital Signs Key Terms Blood pressure Body temperature Diastolic pressure Hypertension Hypotension Pulse Pulse rate Respiration Sphygmomanometer Stethoscope Systolic pressure Vital signs Measuring
Section 03: Pre Exercise Evaluations and Risk Factor Assessment
 Section 03: Pre Exercise Evaluations and Risk Factor Assessment ACSM Guidelines: Chapter 3 Pre Exercise Evaluations ACSM Manual: Chapter 3 Risk Factor Assessments HPHE 4450 Dr. Cheatham Purpose The extent
Section 03: Pre Exercise Evaluations and Risk Factor Assessment ACSM Guidelines: Chapter 3 Pre Exercise Evaluations ACSM Manual: Chapter 3 Risk Factor Assessments HPHE 4450 Dr. Cheatham Purpose The extent
Vital Signs. Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment
 Vital Signs Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Become a Data Gathering Machine The exam begins as soon as you see the patient Appearance, demeanor, dress Well groomed, neat, disheveled, work
Vital Signs Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Become a Data Gathering Machine The exam begins as soon as you see the patient Appearance, demeanor, dress Well groomed, neat, disheveled, work
Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations
 ighapmlre33apg269_274 5/12/04 3:10 PM Page 269 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise
ighapmlre33apg269_274 5/12/04 3:10 PM Page 269 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise
M1 Classic. Digital Blood Pressure Monitor. Instruction manual page 1 SYS. mmhg DIA. mmhg. PULSE/min
 1 Classic Digital Blood Pressure onitor Instruction manual page 1 1 Classic English Introduction The ORON 1 Classic measures your blood pressure and pulse simply and quickly from the arm, without the use
1 Classic Digital Blood Pressure onitor Instruction manual page 1 1 Classic English Introduction The ORON 1 Classic measures your blood pressure and pulse simply and quickly from the arm, without the use
AS OCR PHYSICAL EDUCATION The Vascular System
 AS OCR PHYSICAL EDUCATION The Vascular System Learning Objectives: - Distribution of Cardiac output at rest and during exercise - Role of the Vasomotor centre, arterioles and pre-capillary sphincters -
AS OCR PHYSICAL EDUCATION The Vascular System Learning Objectives: - Distribution of Cardiac output at rest and during exercise - Role of the Vasomotor centre, arterioles and pre-capillary sphincters -
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
How to Measure Vital Signs
 How to Measure Vital Signs Caregiving Series: Volume 10 Objectives Upon completion of this training, participants will understand: The definitions of temperature, pulse, respiration and blood pressure
How to Measure Vital Signs Caregiving Series: Volume 10 Objectives Upon completion of this training, participants will understand: The definitions of temperature, pulse, respiration and blood pressure
UNDERSTANDING BLOOD PRESSURE
 UNDERSTANDING BLOOD PRESSURE A HANDY GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING WHAT BLOOD PRESSURE IS, HOW IT AFFECTS YOU, AND HOW TO MEASURE IT AT HOME Authored by the Texas Department of State Health Services Health Promotion
UNDERSTANDING BLOOD PRESSURE A HANDY GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING WHAT BLOOD PRESSURE IS, HOW IT AFFECTS YOU, AND HOW TO MEASURE IT AT HOME Authored by the Texas Department of State Health Services Health Promotion
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Circulatory System Learning Outcomes State the type of tissue the heart is made of State the function of the heart State the number of chambers in the heart Know how the blood flows
The Circulatory System Circulatory System Learning Outcomes State the type of tissue the heart is made of State the function of the heart State the number of chambers in the heart Know how the blood flows
Understanding Blood Pressure. A handy guide to understanding what blood pressure is, how it affects you, and how to measure it at home
 Understanding Blood Pressure A handy guide to understanding what blood pressure is, how it affects you, and how to measure it at home Acknowledgments page Special thanks to the following individuals and
Understanding Blood Pressure A handy guide to understanding what blood pressure is, how it affects you, and how to measure it at home Acknowledgments page Special thanks to the following individuals and
MX3 Plus English. Introduction. Table of contents. 1 How to obtain meaningful blood pressure readings
 X3 Plus English X3 Plus Introduction The ORON X3 Plus measures your blood pressure and pulse simply and quickly from the arm, without the use of an inflation bulb or stethoscope. The measurement values
X3 Plus English X3 Plus Introduction The ORON X3 Plus measures your blood pressure and pulse simply and quickly from the arm, without the use of an inflation bulb or stethoscope. The measurement values
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
lyondellbasell.com Managing Hypertension
 Managing Hypertension Managing Hypertension There is a growing evidence that the good health of your heart and circulation will help you to age more successfully. A man is as old as his arteries Thomas
Managing Hypertension Managing Hypertension There is a growing evidence that the good health of your heart and circulation will help you to age more successfully. A man is as old as his arteries Thomas
SECTION 16: BLOOD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE IN CHILDREN COHORT STUDY SECTION 16: BLOOD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT 16.1 OVERVIEW OF BLOOD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT This section describes the procedures that are to be performed to obtain
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE IN CHILDREN COHORT STUDY SECTION 16: BLOOD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT 16.1 OVERVIEW OF BLOOD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT This section describes the procedures that are to be performed to obtain
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF SLEEP TECHNOLOGISTS TECHNICAL GUIDELINE FOR PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND VITAL SIGNS MEASUREMENT AND DOCUMENTATION
 AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF SLEEP TECHNOLOGISTS TECHNICAL GUIDELINE FOR PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND VITAL SIGNS MEASUREMENT AND DOCUMENTATION SUMMARY: Sleep technologists observe and monitor physical signs and
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF SLEEP TECHNOLOGISTS TECHNICAL GUIDELINE FOR PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND VITAL SIGNS MEASUREMENT AND DOCUMENTATION SUMMARY: Sleep technologists observe and monitor physical signs and
Crucial Signs כל הזכויות שמורות למד"א מרחב ירושלים
 Crucial Signs Dan Drory, MDA Paramedic and Instructor, 2011 What are Signs? Sign Objective, measurable Symptom Subjective, evaluated by the patient ( Chest Pain, Difficulties Breathing, Headache ) Signs
Crucial Signs Dan Drory, MDA Paramedic and Instructor, 2011 What are Signs? Sign Objective, measurable Symptom Subjective, evaluated by the patient ( Chest Pain, Difficulties Breathing, Headache ) Signs
Blood Pressure Competency Training
 Blood Pressure Competency Training WORKBOOK Table of Contents 3..... Introduction 4..... Background 6..... Equipment Accurate blood pressure What impacts a patient s blood pressure Strategies for proper
Blood Pressure Competency Training WORKBOOK Table of Contents 3..... Introduction 4..... Background 6..... Equipment Accurate blood pressure What impacts a patient s blood pressure Strategies for proper
Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure
 Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure Dr Gari Clifford Adapted from slides by Prof. Lionel Tarassenko Blood pressure Blood is pumped around the body by the heart. It makes its way around the body
Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure Dr Gari Clifford Adapted from slides by Prof. Lionel Tarassenko Blood pressure Blood is pumped around the body by the heart. It makes its way around the body
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
HIGH BLOOD. PRESSURE What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US
 HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US What is Blood Pressure We all need blood pressure to stay alive. Without it, blood can t flow through our bodies to supply
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US What is Blood Pressure We all need blood pressure to stay alive. Without it, blood can t flow through our bodies to supply
FOUNDATIONS OF NUTRITION Hypertension. Research Paper. By Jessica Richardson S A L T L A K E C O M M U N I T Y C O L L E G E
 FOUNDATIONS OF NUTRITION 1020-055 Hypertension Research Paper By Jessica Richardson 2011 S A L T L A K E C O M M U N I T Y C O L L E G E In researching my family health history I have found there is a
FOUNDATIONS OF NUTRITION 1020-055 Hypertension Research Paper By Jessica Richardson 2011 S A L T L A K E C O M M U N I T Y C O L L E G E In researching my family health history I have found there is a
SMALL GROUP SESSION 18A January 17th or January 19th. Groups 1-12: VS and Chest Exam and Harvey Stethophone Session
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 18A January 17th or January 19th Groups 1-12: VS and Chest Exam and Harvey Stethophone Session Readings: Complete the cardiac examination web module. Mosby s Physical Examination, 4
SMALL GROUP SESSION 18A January 17th or January 19th Groups 1-12: VS and Chest Exam and Harvey Stethophone Session Readings: Complete the cardiac examination web module. Mosby s Physical Examination, 4
Webinar Logistics. Now What Do I Need To Do? Blood Pressure in Kids January NC Department of Health and Human Services Division of Public Health
 NC Department of Health and Human Services Division of Public Health Now What Do I Need To Do? Blood Pressure in Kids January 2018 Gerri Mattson, MD, MSPH, FAAP Pediatric Medical Consultant Children and
NC Department of Health and Human Services Division of Public Health Now What Do I Need To Do? Blood Pressure in Kids January 2018 Gerri Mattson, MD, MSPH, FAAP Pediatric Medical Consultant Children and
Blood Pressure Laboratory
 Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR
 Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
AP Biology Lab 10 Physiology of the Circulatory System Lab Activity Student Study Guide
 TM AP Biology Lab 10 Physiology of the Circulatory System Lab Activity Student Study Guide BACKGROUND Some of your arteries and veins are as big around as your thumb, and some are almost too small to see.
TM AP Biology Lab 10 Physiology of the Circulatory System Lab Activity Student Study Guide BACKGROUND Some of your arteries and veins are as big around as your thumb, and some are almost too small to see.
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
NHS Health Check Training for Healthy Living Centre Staff and Colleagues. June 2015 Amanda Chappell
 NHS Health Check Training for Healthy Living Centre Staff and Colleagues. June 2015 Amanda Chappell Aim of the session 1. Understanding of the cardiovascular system 2. Describe the most common types of
NHS Health Check Training for Healthy Living Centre Staff and Colleagues. June 2015 Amanda Chappell Aim of the session 1. Understanding of the cardiovascular system 2. Describe the most common types of
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM : (circulatory system) Lab-4
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM : (circulatory system) Lab-4 The Circulatory System: The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) has 3 basic components:- *A muscular pump: heart *Interconnecting tubes: blood
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM : (circulatory system) Lab-4 The Circulatory System: The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) has 3 basic components:- *A muscular pump: heart *Interconnecting tubes: blood
Chapter 15: The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 15: The Cardiovascular System McArdle, W. D., Katch, F. I., & Katch, V. L. (2010). Exercise Physiology: Nutrition, Energy, and Human Performance (7 ed.). Baltimore, MD.: Lippincott Williams and
Chapter 15: The Cardiovascular System McArdle, W. D., Katch, F. I., & Katch, V. L. (2010). Exercise Physiology: Nutrition, Energy, and Human Performance (7 ed.). Baltimore, MD.: Lippincott Williams and
Welcome to the S410. Blood Pressure System. Instruction Manual
 Welcome to the S410 Blood Pressure System Instruction Manual The simulator is to be used as part of an approved educational program for healthcare. It is not a substitute for traditional learning methods
Welcome to the S410 Blood Pressure System Instruction Manual The simulator is to be used as part of an approved educational program for healthcare. It is not a substitute for traditional learning methods
Genetic factors. A number of genetic factors or interactions between genes play a major role in essential hypertension.
 Hypertension Blood pressure is a measurement of the force against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood through your body. Hypertension is another term used to describe high blood pressure.
Hypertension Blood pressure is a measurement of the force against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood through your body. Hypertension is another term used to describe high blood pressure.
Chapter 08. Health Screening and Risk Classification
 Chapter 08 Health Screening and Risk Classification Preliminary Health Screening and Risk Classification Protocol: 1) Conduct a Preliminary Health Evaluation 2) Determine Health /Disease Risks 3) Determine
Chapter 08 Health Screening and Risk Classification Preliminary Health Screening and Risk Classification Protocol: 1) Conduct a Preliminary Health Evaluation 2) Determine Health /Disease Risks 3) Determine
Hypertension Screening and Health Evangelism
 Hypertension Screening and Health Evangelism What You Should Know About Hypertension What Is High Blood Pressure? High blood pressure is present when excessive pressure is present inside blood vessels.
Hypertension Screening and Health Evangelism What You Should Know About Hypertension What Is High Blood Pressure? High blood pressure is present when excessive pressure is present inside blood vessels.
SMALL GROUP SESSION 13 December 1 st or December 3 rd
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 13 December 1 st or December 3 rd Vital Signs/Chest Exam & Clinical Case Discussion Suggested Readings: Complete online physical examination module and quiz. Review Mosby s Guide to
SMALL GROUP SESSION 13 December 1 st or December 3 rd Vital Signs/Chest Exam & Clinical Case Discussion Suggested Readings: Complete online physical examination module and quiz. Review Mosby s Guide to
Medical Advice for Athletes with High or Normal-High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
 Medical Advice for Athletes with High or Normal-High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Created by Dr. Maria-Carmen Adamuz, Consultant Cardiologist. Aug 2017. WHAT IS HYPERTENSION? Blood pressure (BP) is the
Medical Advice for Athletes with High or Normal-High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Created by Dr. Maria-Carmen Adamuz, Consultant Cardiologist. Aug 2017. WHAT IS HYPERTENSION? Blood pressure (BP) is the
PATIENT INFORMATION. Medicine To Treat: H ypertension. Patient Awareness and Self-Care
 PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: H ypertension Patient Awareness and Self-Care WHAT IS BLOOD PRESSURE AND HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE? Blood pressure is the force generated as your heart pumps blood and
PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: H ypertension Patient Awareness and Self-Care WHAT IS BLOOD PRESSURE AND HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE? Blood pressure is the force generated as your heart pumps blood and
Subjects with Elevated CRP Levels and Asymptomatic PAD Prone to Develop Cognitive Impairment
 Subjects with Elevated CRP Levels and Asymptomatic PAD Prone to Develop Cognitive Impairment Pavel Dan Nanu 1, Sanda Maria Deme 1, Ramona Maria Chendereş 1 Abstract: The CRP is an independent predictor
Subjects with Elevated CRP Levels and Asymptomatic PAD Prone to Develop Cognitive Impairment Pavel Dan Nanu 1, Sanda Maria Deme 1, Ramona Maria Chendereş 1 Abstract: The CRP is an independent predictor
Blood Pressure and Exercise Lab
 Blood Pressure and Exercise Lab Rob MacLeod March 9, 2006 1 Purpose and Background Purpose: To learn about external means to measure blood pressure, observe features of venous circulation, and observe
Blood Pressure and Exercise Lab Rob MacLeod March 9, 2006 1 Purpose and Background Purpose: To learn about external means to measure blood pressure, observe features of venous circulation, and observe
BLOOD PRESSURE. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 BLOOD PRESSURE Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration Blood Pressure The force of your blood pushing on the walls of your arteries. How is Blood Pressure Measured? Measured at an artery in the arm and
BLOOD PRESSURE Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration Blood Pressure The force of your blood pushing on the walls of your arteries. How is Blood Pressure Measured? Measured at an artery in the arm and
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History. Chapter 5
 Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Chapter 5 Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Assessment is the most complex skill EMT-Bs learn. During assessment you will: Gather key information. Evaluate
Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Chapter 5 Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Assessment is the most complex skill EMT-Bs learn. During assessment you will: Gather key information. Evaluate
Health Tests for Men & Women What You Need to Know
 Health Tests for Men & Women What You Need to Know Physical Exam / Checkup Detects problems early when they are easier to treat. Promotes having a doctor to discuss health needs with and to keep track
Health Tests for Men & Women What You Need to Know Physical Exam / Checkup Detects problems early when they are easier to treat. Promotes having a doctor to discuss health needs with and to keep track
ECG, Blood Pressure, and Exercise Lab
 ECG, Blood Pressure, and Exercise Lab Rob MacLeod March 31, 2006 1 Purpose and Background Purpose: The purpose of the lab is to learn about measuring the ECG and blood pressures and observing the effects
ECG, Blood Pressure, and Exercise Lab Rob MacLeod March 31, 2006 1 Purpose and Background Purpose: The purpose of the lab is to learn about measuring the ECG and blood pressures and observing the effects
Vital Signs and Oxygen Administration
 Vital Signs and Oxygen Administration By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Patient Care and Management (202) May-9-2010 Vital Signs and Oxygen Administration What are the vital signs? Why do we need to know them? How
Vital Signs and Oxygen Administration By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Patient Care and Management (202) May-9-2010 Vital Signs and Oxygen Administration What are the vital signs? Why do we need to know them? How
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Vital Signs. Vital Signs. Pulse. Temperature. Respiration. Blood Pressure
 Vital Signs Jarvis, Chapter 9 Vital Signs Classic Vital Signs TPR/BP Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood Pressure Additional Vital Signs Height Weight BMI (Kg/m2) or (702Xlbs/in2) Supine, orthostatic
Vital Signs Jarvis, Chapter 9 Vital Signs Classic Vital Signs TPR/BP Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood Pressure Additional Vital Signs Height Weight BMI (Kg/m2) or (702Xlbs/in2) Supine, orthostatic
Topic: Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill
 Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill Instructor Guide Session Reference: 1 Topic: Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill Level of Instruction: 2 Time Required: Three Hours Materials
Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill Instructor Guide Session Reference: 1 Topic: Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill Level of Instruction: 2 Time Required: Three Hours Materials
WISEWOMAN UPDATE. December The Importance of Accurate Blood Pressure Measurements
 WISEWOMAN UPDATE December 2005 The Importance of Accurate Blood Pressure Measurements As you know, accurate blood pressure measurement is important! Even a few mmhg can make the difference between a person
WISEWOMAN UPDATE December 2005 The Importance of Accurate Blood Pressure Measurements As you know, accurate blood pressure measurement is important! Even a few mmhg can make the difference between a person
Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and Exercise. Evaluation copy
 Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and Exercise Computer 11 The adaptability of the heart can be observed during exercise, when the metabolic activity of skeletal muscles increases. The cardiovascular system,
Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and Exercise Computer 11 The adaptability of the heart can be observed during exercise, when the metabolic activity of skeletal muscles increases. The cardiovascular system,
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
Living With. Hypertension
 A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Living With Hypertension What Is Hypertension? Hypertension is blood pressure that is too high. Talk to your doctor, use this guide, call 1-800-AHA-USA1 or go to www.americanheart.org,
A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Living With Hypertension What Is Hypertension? Hypertension is blood pressure that is too high. Talk to your doctor, use this guide, call 1-800-AHA-USA1 or go to www.americanheart.org,
The Heart and Cardiovascular System
 The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
Physiological Measurements Training for Care/Nursing & LD Small Group Home Staff
 Physiological Measurements Training for Care/Nursing & LD Small Group Home Staff CONTENTS 1. The National Early Warning Score 2. Respiratory Rate 3. Oxygen Saturations 4. Temperature 5. Blood Pressure
Physiological Measurements Training for Care/Nursing & LD Small Group Home Staff CONTENTS 1. The National Early Warning Score 2. Respiratory Rate 3. Oxygen Saturations 4. Temperature 5. Blood Pressure
Control of Heart Rate
 Control of Heart Rate Control of Heart Rate The beating of your heart is an involuntary movement one that is beyond your direct control. The nerve impulse that causes the heart to beat originates within
Control of Heart Rate Control of Heart Rate The beating of your heart is an involuntary movement one that is beyond your direct control. The nerve impulse that causes the heart to beat originates within
9/27/2016. Adherence and Monitoring of Hypertensive Patients. Conflicts of Interest. Brought to you though a partnership:
 Adherence and Monitoring of Hypertensive Patients. Conflicts of Interest Speaker has no conflicts of interest to disclose I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial
Adherence and Monitoring of Hypertensive Patients. Conflicts of Interest Speaker has no conflicts of interest to disclose I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial
Wellness: Concepts and Applications 8 th Edition Anspaugh, Hamrick, Rosato
 Wellness: Concepts and Applications 8 th Edition Anspaugh, Hamrick, Rosato Preventing Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 2 Cardiovascular Disease the leading cause of death in the U.S. 35.3% of all deaths
Wellness: Concepts and Applications 8 th Edition Anspaugh, Hamrick, Rosato Preventing Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 2 Cardiovascular Disease the leading cause of death in the U.S. 35.3% of all deaths
Vital Signs. (866)
 Vital Signs Obesity, diabetes and sedentary lifestyles may greatly influence a client s abilities during testing procedures in your Occupational Health Services. There has been an increase prevalence in
Vital Signs Obesity, diabetes and sedentary lifestyles may greatly influence a client s abilities during testing procedures in your Occupational Health Services. There has been an increase prevalence in
Chapter 21. Assisting With Assessment. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 21 Assisting With Assessment Vital Signs Vital signs reflect three body processes: Regulation of body temperature Breathing Heart function A person s vital signs: Vary within certain limits Are
Chapter 21 Assisting With Assessment Vital Signs Vital signs reflect three body processes: Regulation of body temperature Breathing Heart function A person s vital signs: Vary within certain limits Are
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE. What is malignant or accelerated hypertension?
 HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE Is high blood pressure important? What is blood pressure? What is high blood pressure? What are the causes of high blood pressure? What are the symptoms of high blood pressure? What
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE Is high blood pressure important? What is blood pressure? What is high blood pressure? What are the causes of high blood pressure? What are the symptoms of high blood pressure? What
14-1: The Body s Transport System. 7 th Grade Life Science
 7 th Grade Life Science Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system, also called circulatory system, is made of your heart blood vessels, and blood. It is like the network of highways on Earth, where
7 th Grade Life Science Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system, also called circulatory system, is made of your heart blood vessels, and blood. It is like the network of highways on Earth, where
