Streptococcus sanguis Endocarditis in Rabbits
|
|
|
- Sophie Robinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANTIMICROBIAL AGNTS AND CHMOTHRAPY, Feb. 1984, p /84/ $02.00/O Copyright 1984, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 25, No. 2 Role of Granulocytes in the Prevention and Therapy of xperimental Streptococcus sanguis ndocarditis in Rabbits M. J. M. MDDNS, J. THOMPSON, H. MATTI, AND R. VAN FURTH* Department of Infectious Diseases, University Hospital, 2333AA Leiden, The Netherlands Received 15 March 1983/Accepted 28 September 1983 The contributions of granulocytes to the prevention and therapy of Streptococcus sanguis endocarditis with procaine benzylpenicillin (PBP) was investigated in rabbits. Depletion of granulocytes by treatment with mechlorethamine appeared to have no significant effect on either the prophylactic or therapeutic activities of PBP. Administration of 3,000 IU of PBP before inoculation with S. sanguis retarded the course of the endocarditis for only 24 h whether granulocytes were normal or depressed in numbers. Prophylaxis with either 15,000 or 30,000 IU of PBP was equally effective in non-granulocytopenic and granulocytopenic rabbits. Treatment of established infections with PBP at doses of 3,000 to 300,000 IU of PBP at 12-h intervals for 48 h was equally effective in rabbits with normal and depressed numbers of granulocytes. The effect of 3,000 IU of PBP was equivalent, however, to that of granulocytes alone, as shown by the fact that the numbers of CFU per gram of vegetation in the granulocytopenic rabbits treated with this dose of PBP and in the non-pbp-treated control rabbits were not significantly different. In an earlier study, we showed that granulocytes have a significant influence on the course of left-sided Streptococcus sanguis endocarditis in rabbits (10). This was investigated by depleting the circulation of these cells by treatment with mechlorethamine (HN2). It was found that granulocytes exerted a protective effect, as indicated by the numbers of streptococci in endocardial vegetation and in the circulatory system during the course of the endocarditis. Other authors have reported a similar effect during rightsided streptococcal endocarditis in rabbits (15). Selective depletion of monocytes had no effect on the induction and course of the S. sanguis endocarditis (13). The present study was performed to find out whether granulocytes play a role in the prevention of S. sanguis endocarditis and the sterilization of infected endocardial vegetation by procaine benzylpenicillin (PBP). MATRIALS AND MTHODS xperimental animals. One hundred and fourteen male chinchilla rabbits, weighing 1.8 to 2.3 kg, raised in the Central Institute for Breeding of Laboratory Animals, Zeist Austerlitz, The Netherlands, were used in this study. In the prophylactic experiments, 30 control and 28 granulocytopenic rabbits were used; in the therapeutic experiments, 31 control and 25 granulocytopenic rabbits were used. Rabbits belonging to the respective experimental groups were numbered randomly (5), and each step in the experimental procedure was carried out in this sequence. Induction of granulocytopenia. Mechlorethamine (HN2, mustine hydrochloride; ACF, Chemie Farma B.V., Maarssen, The Netherlands) was used to induce granulocytopenia as described elsewhere (4, 10). Briefly, 10 mg of HN2 was dissolved in 10 ml of saline just before use. A single dose of 5 mg was injected into a marginal ear vein immediately after catheterization. For monitoring the effect of HN2 on the numbers of blood leukocytes, blood samples (approximately 1 ml) of 14 out of 31 control and 12 out of 28 HN2-treated rabbits used in the therapeutic experiments were taken from * Corresponding author. the central ear artery 1 day before catheterization (i.e., before the injection of the drug), at the time of inoculation of the streptococci, and at each day during infection. These samples were collected in plastic vials containing 10 mg of crystalline potassium DTA and were diluted 1:20 in leukocyte pipettes with Turk solution containing 6% acetic acid. Total leukocyte counts were done in duplicate in a Burker hemocytometer. The total numbers of granulocytes, mopocytes, and lymphocytes per microliter were calculated from the total number of leukocytes per microliter and differential counts of 400 leukocytes in four blood smears. Characteristics of the infecting strain. The strain used in this study, S. sanguis NCTC 7864, was the same as that employed in previous studies (10, 13). Bacteria from an overnight culture in Todd-Hewitt broth were diluted with saline to 105 CFU/ml. The minimal inhibitory concentration of penicillin G for this strain, the lowest penicillin concentration with which no growth was observed after 18 h of culture at 37 C in Isosensitest broth (Oxoid Ltd., London, United Kingdom), was 0.06,ug/ml. The same type of test in broth was carried out for measurement of the minimal bactericidal concentration. The inoculum consisted of 105 CFU/ml, and the test was done in Isosensitest broth too. After incubation for 18 h at 37 C, a standard volume of 10,ul from each tube that did not show growth was cultured on blood agar. The minimal bactericidal concentration was regarded as the concentration at which 99.9% of the bacteria were killed. This value was found to be -16,ug of penicillin per ml. Since the ratio of minimal inhibitory concentration to minimal bactericidal concentration exceeded 1/32, this strain can be regarded tolerant. Induction of endocarditis. Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis was induced by inserting a plastic catheter into the left ventricle via the left carotid artery by the method of Durack and Beeson (2). Three days later, 1 ml of a s-uspension containing 105 CFU of S. sanguis was injected into a marginal ear vein, an inoculum that was found to cause infection in 100% of both control and HN2-treated rabbits (10). The catheter was left in situ during the experiments. Penicillin regimens. For prophylaxis, single doses of 3,000, 15,000, or 30,000 IU of PBP (Depocillin, 300,000 IU/ml of 263
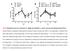
2 264 MDDNS T AL. aqueous suspension, kindly donated by Gist-Brocades N.V., Delft, The Netherlands) was administered subcutaneously 30 min before inoculation of both HN2-treated rabbits and controls. Animals were killed 46 h later, and the vegetations were removed for counting S. sanguis in these lesions. For therapy, four doses of 3,000, 30,000, 100,000, or 300,000 IU of PBP were administered subcutaneously at 12-h intervals starting 20 h after inoculation of the rabbits with streptococci. Animals were killed 12 h after the last injection so that the bacteria in the vegetations could be counted. Monitoring of concentrations of penicillin in blood. Blood samples (25 to 100,ul) collected from the central ear artery at various times during prophylaxis and therapy were added immediately to 200 to 500,ul of sterile distilled water to lyse the blood cells. These samples were tested within 24 h or after storage at -20 C for no more than 4 weeks. Concentrations of penicillin in blood were determined by a cup plate method (3, 7). The test microorganism used was Bacillus stearothermophilus subsp. calidolactis (optimal growth temperature, 56 C). Serial dilutions of a blood sample were compared with a standard in diluted rabbit blood by determining the zone diameter after 18 h of incubation at 56 C (6). The detection limit of this assay is 0.01,ug of penicillin per ml. The concentration was expressed as micrograms of penicillin per milliliter of plasma, after correction for the hematocrit value. Measurement of intensities of bacteremias and heart valve infections. The methods used were generally the same as those described in detail earlier (12). Briefly, endocardial vegetations were isolated aseptically, weighed, and homogenized in 2 ml of glucose broth. Tenfold serial dilutions of this homogenate in saline were made, and 100-,ul samples were plated on sheep blood agar and incubated for 24 to 48 h at 37 C. The degree of infection of the vegetations was expressed as CFU per gram of vegetation. For quantitative blood cultures, 2-ml blood samples were taken from the ear artery or, immediately after the rabbit was killed, from the inferior vena cava. These samples were added to 1 ml of Liquoid (Oxoid; 0.75% [wt/vol] and 0.18 mm para-amino benzoic acid in saline), plated on 5 ml of glucose broth agar, and incubated for 24 to 48 h at 37 C. Bacteremias were expressed as CFU per milliliter of blood. Residual penicillin in homogenates of vegetation or in blood cultures was inactivated by the addition of penicillinase (lot 79D 27, Gist-Brocades N.V.) to a final concentration of 75 IU/ml. Statistical analysis. ffects of HN2 treatment and PBP on the number of CFU per gram of vegetation or per milliliter of blood were compared by a two-sided Student t test. To analyze more than two parameters simultaneously, an analysis of covariance was used. ffects of HN2 and PBP on the incidence of infected vegetations and on the incidence of positive blood cultures were assessed with the chi-square test (1). RSULTS Levels of granulocytopenia and monocytopenia. When HN2 was injected immediately after catheterization, the number of granulocytes per microliter of blood decreased significantly to less than 100 on day 1 (Table 1). The number of granulocytes per microliter of blood in HN2-treated rabbits was significantly lower than that in control rabbits at the time of injection of the streptococci and at all times thereafter. The circulation was depleted of monocytes and lymphocytes simultaneously. Concentration of penicillin in blood. The concentrations of ANTIMICROB. AGNTS CHMOTHR. TABL 1. ffect of HN2 treatment on the number of granulocytes and monocytes in the circulatory system Leukocytes per,ul (mean ± SD) Leukocytes Daya in rabbits': p Control HN2 treated Granulocytes -4 3,086 ± 2,126 2,124 ± ,999 ± 1, ± 291 < ,547 ± 1, ± 28 < ,188 ± 2, ± 59 < ,724 ± 2,314 1,057 ± 757 <0.05 Monocytes ± ± ± 181 7± 9 < ± ± 23 < ± ± ± ± a Day relative to time of inoculation of rabbits with 105 streptococci. b Data are reported for 12 HN2-treated rabbits and 14 controls. Both groups were used in the therapy experiments. penicillin in blood during prophylaxis are given in Fig. 1. The highest concentration was found 30 min after the administration of PBP, i.e., at the time of injection of the streptococci. At no time was there a significant difference between concentrations in control and in HN2-treated rabbits (P > 0.15). The concentrations of penicillin maintained in blood during therapy are given in Fig. 2. Rabbits in which endocarditis was induced received four subcutaneous injections of PBP at 12-h intervals, starting 20 h after the injection of 105 streptococci. Four dosage levels were investigated, as indicated in Fig. 2; concentrations of penicillin in blood were measured at 6-h intervals. These concentrations did not fluctuate significantly at any given dose %4- (U C- C CFU of S.sanguis I I I hours 8 after 30,000 U PBP,15,000 IUPBP,3,000 IUPBP 22 s,c. injection of PBP FIG. 1. Concentrations of penicillin in the blood of 23, 18, and 17 rabbits at various times after injection of 3,000, 15,000, or 30,000 IU of PBP. All data points represent combined data of control and HN2-treated rabbits. Bars show standard errors of the mean. 46
3 VOL. 25, PBP V o q g g c c ro < PBP PBP PBP V V1 V 4." o o- -o-o- /- \4 300,000 IU PBP A hours after iv injection of 105 CFU of S sanguis 6 100,000 iu PBP 30,000 IU PBP -o 0 3,000 IU PBP FIG. 2. Concentrations of penicillin in the blood during therapy of S. sanguis endocarditis in 13, 7, 6, and 9 rabbits given doses between 3,000 and 300,000 IU of PBP. Concentrations at 32, 44, and 56 h were determined before injection of PBP. Concentrations at 26, 38, 50, and 62 h were determined 6 h after dosage. All points represent combined data of control and HN2-treated rabbits. Bars show standard error of the mean. ffect of prophylaxis with PBP in control and HN2-treated rabbits. After the injection of 105 streptococci, the incidences of infected vegetations did not differ significantly between control and HN2-treated rabbits with prophylaxis at any of the dosage levels investigated (Table 2). Also, the number of CFU per gram of vegetation in rabbits that became infected despite prophylaxis with 3,000 IU of PBP did not differ significantly between the control and HN2- treated rabbits. With the higher dosages of PBP, infected vegetations were found only incidentally, which made statistical evaluation of differences impossible. After 3,000 IU of PBP, two HN2-treated rabbits had sterile vegetations, and therefore these animals were excluded from the statistical evaluation of the incidence of positive blood cultures. At 22 h, 3 of 12 control rabbits and 6 of 8 HN2-treated rabbits had positive blood cultures. This difference is significant (X2 = 4.85, P < 0.03). At 46 h, the incidence of positive blood cultures in the two groups of rabbits did not differ significantly (X2 = 0.16, P > 0.5). The number of CFU/ml of blood in the positive blood cultures at 22 h did not differ significantly in the control and HN2- treated rabbits (data not shown; P > 0.8), but at 46 h it was significantly higher in the treated group than in the controls (mean log10 CFU/ml of blood, [n = 6] and [n = 8], respectively; P < 0.05). After prophylaxis with 15,000 or 30,000 IU of PBP, positive blood cultures only occurred occasionally. GRANULOCYTS AND S. SANGUIS NDOCARDITIS 265 ffect of therapy with PBP on infection of the vegetations and intensity of bacteremias. Immediately before the start of PBP therapy, i.e., 20 h after the injection of 105 streptococci, numbers of CFU per gram of vegetation in control and HN2- treated rabbits did not differ significantly. At 68 h, these numbers were significantly higher in HN2-treated animals than in controls (Table 3). After 3,000 IU of PBP, the numbers of CFU per gram of vegetation in the control rabbits were not significantly different from those in the HN2-treated rabbits. At this time, these numbers did not differ significantly from those in the non-pbp-treated control rabbits. In the HN2-treated rabbits, therapy with 3,000 IU of PBP effected a sevenfold difference of the numbers of CFU tper gram of vegetation (P < 0.001). Therapy with higher doses of PBP effected a significant reduction in the numbers of CFU per gram of vegetation (P < 0.001) in both control and HN2-treated rabbits. The magnitude of this reduction was not influenced by either HN2 treatment or the dose of PBP (Table 3). In the non-pbp-treated rabbits and in those treated with 3,000 IU of PBP, the numbers of CFU per milliliter of blood were significantly higher in the HN2-treated rabbits than in the controls at all times (Table 3). There were no significant differences in these numbers in rabbits with or without 3,000 IU of PBP in either the control or HN2 treatment groups (P > 0.20). Therapy with doses ranging from 30,000 to 300,000 IU of PBP led to a significant decrease in the numbers of CFU per milliliter (P < 0.001), but there was no significant difference among the three dosage levels. At 32 h, the combined data for the three dosage levels showed a significantly higher incidence of positive cultures in the HN2- treated rabbits than in the controls, but such a difference was not found at later times (data not shown). DISCUSSION In the present study, administration of HN2 led to both granulocytopenia and monocytopenia. Since an earlier study showed that selective depletion of monocytes has no effect on the induction or course of S. sanguis endocarditis (13), effects of HN2 treatment in the current study may be attributed to the absence of granulocytes. Prophylaxis with PBP was equally effective in non-granulocytopenic and granulocytopenic rabbits. A dose of 3,000 IU of PBP had no effect in either control or granulocytopenic rabbits, and the numbers of bacteria in infected vegetations did not differ significantly between these two groups. The situation at 46 h in rabbits with endocarditis after prophylaxis with 3,000 IU of PBP is similar to that at 20 h in rabbits without prophylaxis, which means that a single dose of 3,000 IU of PBP only retards the course of S. sanguis endocarditis. Compared with 3,000 IU of PBP, prophylaxis with 15,000 IU of PBP resulted in a significantly higher number of rabbits with sterile vegetations, but the incidence of infected vegeta- TABL 2. ffect of prophylaxis with PBP on bacteria in infected vegetations Incidence of infected vegetations Log1o CFU/g of infected vegetations PBP dose (IU) in rabbitsa: X2 p (mean ± SD) in rabbitsb: Control HN2 treated Control HN2 treated 3,000 12/12 9/ > ± ± ,000 0/10 2/ >0.15 Sterile 7.28, ,000 1/8 3/ > ± 2.84 a Number of rabbits with infected vegetations/total number of rabbits investigated after injection of 10' streptococci. b For rabbits given 3,000 IU of PBP for prophylaxis, P > For rabbits given 15,000 and 30,000 IU, numbers with infected vegetations were too small for statistical evaluation.
4 266 MDDNS T AL. ANTIMICROB. AGNTS CHMOTHR. TABL 3. ffect of therapy with PBP on infection of vegetations Incidene of ifectedlogl0 CFU/g (mean ± SD) in Samples vegetations or positive rabbits: pc examined PBP dose (IU)a Time (h) cultures in rabbitsb p Control HN2 Control HN2 Vegetation /6 4/ ± ± 0.99 > /5 6/ ± ± 0.32 <0.03 3, /7 6/ ± ± 0.32 > , /4 3/ ± ± 1.07 > , /4 2/ ± ± , /5 3/ ± ± 0.52 Blood culture /5 5/ ± ± 0.99 < /5 6/ ± ± /5 6/ ± ± , /7 6/ ± ± 0.46 < / 6/ ± ± /7 6/ ± ± 0.19 a Four subcutaneous injections of PBP were given at 12-h intervals, starting 20 h after the injection of 105 streptococci. Vegetations were isolated 12 h after the last PB3P injection. Blood cultures were drawn at the times indicated (at 20 h immediately before the start of therapy). b Number of rabbits with infected vegetations or with positive blood cultures/total number of rabbits investigated. The incidence of infected vegetations was not significantly different in control and HN2-treated rabbits at 20 or 68 h either without PBP or after injection of any dosage (P > 0.50). P values for vegetations in groups without PBP and with 3,000 IU of PBP were obtained by comparing control and HN2-treated rabbits by the Student t test. P values for numbers of bacteria in the blood were obtained by an analysis of covariance using the combined data of control and IN2-treated rabbits at the three time points. In the groups treated with 30,000, 100,000, and 300,000 IU of PBP, the P was obtained from an analysis of covariance using the combined data of control and HN2-treated rabbits at these three dosage levels. tions did not differ significantly between control and granulocytopenic rabbits. Doubling of the dose to 30,000 IU of PBP did not lead to a larger number of rabbits with sterile vegetations in either group. The results of the present study show that during 48 h of therapy with PBP at any of the dosage levels investigated, granulocytes had no effect on the numbers of CFU in the vegetations. Therapy with 3,000 IU of PBP did not significantly reduce the number of streptococci in the vegetations of either control or granulocytopenic rabbits, but doses of 30,000 to 300,000 IU of PBP did. Therapy with 3,000 IU of PBP in granulocytopenic rabbits had an effect on the number of streptococci in the vegetations similar to the effect of granulocytes alone in control rabbits without therapy. However, in the control rabbits, the combination of granulocytes with 3,000 IU of PBP did not further reduce the number of CFU in the vegetations. Apparently, granulocytes are able to keep the number of CFU in check but have difficulty in eradicating them from the vegetations. After 30,000 IU or more of PBP, the number of CFU in the vegetations of granulocytopenic rabbits did not differ significantly from that in control rabbits. This makes an effect of granulocytes in combination with these dosages of PBP unlikely. In contrast to its effect on the vegetations, treatment with 3,000 IU of PBP had no effect on the number of streptococci in the blood of either control or granulocytopenic rabbits. During therapy with the higher dosages of PBP, the streptococci disappeared from the blood, although sterilizing the circulation took a little longer in granulocytopenic rabbits than in controls. This might have been due to the already higher number of streptococci in the circulation of granulocytopenic rabbits at the start of the therapy, or to a longer period of seeding of the streptococci from the vegetations into the circulation. Two explanations can be suggested for the different effects of granulocytes on the numbers of microorganisms in vegetations and in blood during low-dose therapy. Streptococci are continuously seeded from the infected vegetations into the circulation (8-10). These streptococci can resettle on the vegetational surface, become covered by fibrin and platelets, and form new colonies by multiplication. This process might be kept in check by granulocytes, which could phagocytose streptococci on the vegetational surface. It seems likely that during low-dose therapy, altered surface properties (11, 14) would cause fewer streptococci to become attached to the vegetations, and therefore, a protective effect of granulocytes could no longer be measured. Alternatively, as suggested earlier (9, 14), granulocytes might produce and release antibacterial substances that could curb the proliferation of streptococci, but these substances do not potentiate the effect of penicillin, and therefore, their effect on the number of viable bacteria in the vegetations would resemble the effect of low-dose penicillin. Nevertheless, in both situations, streptococci regaining access to the vegetational surface from inside the vegetations would not be retained there by granulocytes in granulocytopenic rabbits (10), which would lead to a more severe bacteremia in these animals than in control rabbits, despite treatment with 3,000 IU of PBP. In summary, an enhancement by granulocytes of the effect of PBP in the prophylaxis or therapy of S. sanguis endocarditis cannot be measured at the level of the vegetations, but at low dosages such a contribution is measurable in the circulatory system. ACKNOWLDGMNTS The skillful technical assistance of W. C. Bauer and R. P. Demeijer is gratefully acknowledged. This investigation was supported by grant from the Dutch Heart Association, The Hague, The Netherlands.
5 VOL. 25, 1984 LITRATUR CITD 1. Armitage, P Statistical methods in medical research. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. 2. Durack, D. T., and P. B. Beeson xperimental bacterial endocarditis. I. Colonization of a sterile vegetation. Br. J. xp. Pathol. 53: Grove, D. C., and W. A. Randall Assay methods of antibiotics. A laboratory manual. Antibiotics monographs, no. 2. Medical ncyclopedia Inc., New York. 4. Herion, J. C., R. I. Walker, W. B. Herring, and J. G. Palmer ffects of endotoxin and nitrogen mustard on leukocyte kinetics. Blood 25: Hewlett-Packard Co Statistics applications. HP-33, p Hewlett-Packard Co., Singapore. 6. Kunst, M. W., and H. Mattie Cefazolin and cephradine: relationship between antibacterial activity in vitro and in mice experimentally infected with scherichia coli. J. Infect. Dis. 137: Mattie, H., W. R. 0. Goslings, and. L. Noach Cloxacillin and nafcillin: serum binding and its relationship to antibacterial effect in mice. J. Infect. Dis. 128: McGowan, D. A., and R. Gillett Scanning electron microscopic observations of the surface of the initial lesion in experimental streptococcal endocarditis in the rabbit. Br. J. xp. Pathol. 61: Meddens, M. J. M., J. Thompson, W. C. Bauer, J. Hermans, and R. van Furth Role of granulocytes and monocytes in GRANULOCYTS AND S. SANGUIS NDOCARDITIS 267 experimental Staphylococcus epidermidis endocarditis. Infect. Immun. 41: Meddens, M. J. M., J. Thompson, F. ulderink, W. C. Bauer, H. Mattie, and R. van Furth Role of granulocytes in experimental Streptococcus sanguis endocarditis. Infect. Immun. 36: Scheld, W. M., 0. Zak, K. Vosbeck, and M. A. Sande Bacterial adhesion in the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis: effect of subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations on streptococcal adhesion in vitro and the development of endocarditis in rabbits. J. Clin. Invest. 68: Thompson, J., F. ulderink, H. Lemkes, and R. van Furth ffect of warfarin on the induction and course of experimental endocarditis. Infect. Immun. 14: Thorig, L., J. Thompson, J. J. meis, and R. van Furth ffects of monocytopenia and anticoagulation in experimental Streptococcus sanguis endocarditis. Br. J. xp. Pathol. 61: Tylewski, S. A., T. Wadstrom, and S. Hjerten The effect of subinhibitory concentrations of penicillin and rifampicin on bacterial cell surface hydrophobicity and on binding to pharyngeal epithelial cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 17: Yersin, B. R., M. P. Glauser, and L. R. Freedman ffect of nitrogen mustard on natural history of right-sided streptococcal endocarditis in rabbits: role for cellular host defenses. Infect. Immun. 35: Downloaded from on May 11, 2018 by guest
Role of Granulocytes in Experimental Streptococcus sanguis Endocarditis
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 1982, p. 325-332 19-9567/82/4325-8$2./ Vol. 36, No. 1 Role of Granulocytes in Experimental Streptococcus sanguis Endocarditis M. J. M. MEDDENS,* J. THOMPSON, F. EULDERINK,
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 1982, p. 325-332 19-9567/82/4325-8$2./ Vol. 36, No. 1 Role of Granulocytes in Experimental Streptococcus sanguis Endocarditis M. J. M. MEDDENS,* J. THOMPSON, F. EULDERINK,
Experimental Staphylococcus epidermidis Endocarditis
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 1977, p. 504-509 Copyright 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 17, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Warfarin on the Induction and Course of Experimental Staphylococcus
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 1977, p. 504-509 Copyright 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 17, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Warfarin on the Induction and Course of Experimental Staphylococcus
Natural History of Aortic Valve Endocarditis in Rats
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, JUlY 192, p. 127-131 19-9567/2/7127-5$2./ Vol. 37, No. 1 Natural History of Aortic Valve Endocarditis in Rats ERIC HtRAIEF, MICHEL P. GLAUSER,* AND LAWRENCE R. FREEDMANt Division
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, JUlY 192, p. 127-131 19-9567/2/7127-5$2./ Vol. 37, No. 1 Natural History of Aortic Valve Endocarditis in Rats ERIC HtRAIEF, MICHEL P. GLAUSER,* AND LAWRENCE R. FREEDMANt Division
Experimental Endocarditis
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 1976, p. 1284-1289 Copyright C 1976 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 14, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Warfarin on the Induction and Course of Experimental Endocarditis
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 1976, p. 1284-1289 Copyright C 1976 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 14, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Warfarin on the Induction and Course of Experimental Endocarditis
Effects of tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-pa) on Streptococcus sanguis infected endocardial vegetations in vitro
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1988) 21, 609-620 Effects of tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-pa) on Streptococcus sanguis infected endocardial vegetations in vitro A. G. M. Baiting", J. Thompson',
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1988) 21, 609-620 Effects of tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-pa) on Streptococcus sanguis infected endocardial vegetations in vitro A. G. M. Baiting", J. Thompson',
Experimental Endocarditis Caused by Streptococcus sanguis:
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, July 1981, p. 1-14 66-484/81/71-5$2./ Vol. 2, No. 1 Experimental Endocarditis Caused by Streptococcus sanguis: Single and Combined Antibiotic Therapy MARIA V. VICENTE,
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, July 1981, p. 1-14 66-484/81/71-5$2./ Vol. 2, No. 1 Experimental Endocarditis Caused by Streptococcus sanguis: Single and Combined Antibiotic Therapy MARIA V. VICENTE,
Determination of MIC & MBC
 1 Determination of MIC & MBC Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) are defined as the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial that will inhibit the visible growth of a microorganism after overnight
1 Determination of MIC & MBC Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) are defined as the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial that will inhibit the visible growth of a microorganism after overnight
Interleukin 1 Increases the Susceptibility of Rabbits to Experimental Viridans Streptococcal Endocarditis
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Feb. 2006, p. 947 952 Vol. 74, No. 2 0019-9567/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.74.2.947 952.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Interleukin
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Feb. 2006, p. 947 952 Vol. 74, No. 2 0019-9567/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.74.2.947 952.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Interleukin
Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds
 Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds Yuan Zeng, Bingyu Li, Anwar Kalalah, Sang-Jin Suh, and S.S. Ditchkoff Summary Antibiotic activity of ten commercially available odor eliminating
Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds Yuan Zeng, Bingyu Li, Anwar Kalalah, Sang-Jin Suh, and S.S. Ditchkoff Summary Antibiotic activity of ten commercially available odor eliminating
Rifampin Resistance. Charlottesville, Virginia i0w organisms in Trypticase soy broth (BBL Microbiology
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 1980, p. 658-662 0066-4804/80/04-0658/05$02.00/0 Vol. 17, No. 14 Treatment of Experimental Staphylococcal Infections: Effect of Rifampin Alone and in Combination
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 1980, p. 658-662 0066-4804/80/04-0658/05$02.00/0 Vol. 17, No. 14 Treatment of Experimental Staphylococcal Infections: Effect of Rifampin Alone and in Combination
Biological Consulting Services
 Biological Consulting Services of North Florida/ Inc. May 13, 2009 Aphex BioCleanse Systems, Inc. Dear Sirs, We have completed antimicrobial efficacy study on the supplied Multi-Purpose Solution. The testing
Biological Consulting Services of North Florida/ Inc. May 13, 2009 Aphex BioCleanse Systems, Inc. Dear Sirs, We have completed antimicrobial efficacy study on the supplied Multi-Purpose Solution. The testing
Streptococcus mitis. 11). Reports by Home and Tomasz (11) indicated. that of nine S. sanguis strains tested, all were
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Jan. 1983, P. 67-73 0066-4804/83/010067-07$02.00/0 Copyright C 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 23, No. 1 Penicillin Therapy of Experimental Endocarditis
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Jan. 1983, P. 67-73 0066-4804/83/010067-07$02.00/0 Copyright C 1983, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 23, No. 1 Penicillin Therapy of Experimental Endocarditis
A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci
 J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 231 A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci E. J. L. LOWBURY, A. KIDSON, AND H. A. LILLY From the Medical Research Council
J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 231 A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci E. J. L. LOWBURY, A. KIDSON, AND H. A. LILLY From the Medical Research Council
Xylose-Polyethylene Glycol 400-Hydrogen Peroxide
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGNTS AND CHMOTHRAPY, Sept. 1991, p. 1799-183 66-484/91/91799-5$2./ Copyright C) 1991, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 35, No. 9 In Vitro Studies of Water Activity and Bacterial Growth
ANTIMICROBIAL AGNTS AND CHMOTHRAPY, Sept. 1991, p. 1799-183 66-484/91/91799-5$2./ Copyright C) 1991, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 35, No. 9 In Vitro Studies of Water Activity and Bacterial Growth
THE SENSITIVITY OF STAPHYLOCOCCI AND OTHER WOUND BACTERIA TO ERYTHROMYCIN, OLEANDOMYCIN, AND SPIRAMYCIN
 J. clin. Path. (1959), 12, 163. THE SENSITIVITY OF STAPHYLOCOCCI AND OTHER WOUND BACTERIA TO ERYTHROMYCIN, OLEANDOMYCIN, AND SPIRAMYCIN BY E. J. L. LOWBURY AND L. HURST From the Medical Research Council
J. clin. Path. (1959), 12, 163. THE SENSITIVITY OF STAPHYLOCOCCI AND OTHER WOUND BACTERIA TO ERYTHROMYCIN, OLEANDOMYCIN, AND SPIRAMYCIN BY E. J. L. LOWBURY AND L. HURST From the Medical Research Council
Study on The Inhibition Effect of Nisin
 The Journal of American Science, 1(2), 2005, Li, et al, Study on The Inhibition Effect of Study on The Inhibition Effect of Tiejing Li 1, Jin Tao 2, Fu Hong 1 1. Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin,
The Journal of American Science, 1(2), 2005, Li, et al, Study on The Inhibition Effect of Study on The Inhibition Effect of Tiejing Li 1, Jin Tao 2, Fu Hong 1 1. Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin,
Early oral switch for antibiotic treatment of infective endocarditis
 AEPEI: Association pour l Etude et la Prévention des Endocardites Infectieuses Early oral switch for antibiotic treatment of infective endocarditis Prof. Pierre Tattevin Infectious Diseases & ICU, INSERM
AEPEI: Association pour l Etude et la Prévention des Endocardites Infectieuses Early oral switch for antibiotic treatment of infective endocarditis Prof. Pierre Tattevin Infectious Diseases & ICU, INSERM
Medical Microbiology
 Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
blood culture methods
 J. clin. Path., 1974, 27, 273-279 An experimental assessment of different anaerobic blood culture methods D. C. SHANSON From the Department of Clinical Microbiology, University College Hospital, London
J. clin. Path., 1974, 27, 273-279 An experimental assessment of different anaerobic blood culture methods D. C. SHANSON From the Department of Clinical Microbiology, University College Hospital, London
Efficacy of Ceftaroline Fosamil against Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains in a rabbit meningitis model.
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 3 September 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00285-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 1 2 Efficacy
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 3 September 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00285-13 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 1 2 Efficacy
Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis Endocarditis
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Oct. 1978, p. 52-56 0019-9567/78/0022-0052$02.00/0 Copyright X 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 22, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Immunization on Susceptibility to
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Oct. 1978, p. 52-56 0019-9567/78/0022-0052$02.00/0 Copyright X 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 22, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Immunization on Susceptibility to
Changes in the Microflora of Bovine Colostrum During Natural Fermentation
 27 f. Milk Food Techno/. Vol. 39. No. I, Pages 27-31!January, 1976) Copyright 1976, International Association of Milk, Food, and Environmental Sanitarians Changes in the Microflora of Bovine Colostrum
27 f. Milk Food Techno/. Vol. 39. No. I, Pages 27-31!January, 1976) Copyright 1976, International Association of Milk, Food, and Environmental Sanitarians Changes in the Microflora of Bovine Colostrum
Endocarditis in Rats
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Feb. 1987, p. 139-143 0066-4804/87/020139-05$02.00/0 Copyright C) 1987, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 31, No. 2 Continuous-Infusion Ampicillin Therapy of
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Feb. 1987, p. 139-143 0066-4804/87/020139-05$02.00/0 Copyright C) 1987, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 31, No. 2 Continuous-Infusion Ampicillin Therapy of
Commercial in Confidence
 Determination of Bactericidal Activity of Zwiteck Sanitizer using the European Standard Method BS EN 1276:2009 ~ Project Report Prepared for Zwiteck BV Inspiring tomorrow s professionals Determination
Determination of Bactericidal Activity of Zwiteck Sanitizer using the European Standard Method BS EN 1276:2009 ~ Project Report Prepared for Zwiteck BV Inspiring tomorrow s professionals Determination
Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children
 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1108 Nidhi ORIGINAL Gupta, Manohar ARTICLE Bhat Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children 1
10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1108 Nidhi ORIGINAL Gupta, Manohar ARTICLE Bhat Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children 1
Survival of Aerobic and Anaerobic Bacteria in
 APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1968, p. 445-449 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Survival of Aerobic and Anaerobic Bacteria in Chicken Meat During Freeze-Dehydration,
APPLIED MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1968, p. 445-449 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Survival of Aerobic and Anaerobic Bacteria in Chicken Meat During Freeze-Dehydration,
Against Aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Dec. 1979, p. 6-6 0066-0/79/1-06/05$0.00/0 Vol., No. 6 In Vitro Activity of LY17935, a New 1-Oxa Cephalosporin, Against Aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli DENNIS G. DELGADO,
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Dec. 1979, p. 6-6 0066-0/79/1-06/05$0.00/0 Vol., No. 6 In Vitro Activity of LY17935, a New 1-Oxa Cephalosporin, Against Aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli DENNIS G. DELGADO,
Laboratory assessment of physical and chemical methods of preserving urine specimens
 J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 532-536 Laboratory assessment of physical and chemical methods of preserving urine specimens P. G. WATSON AND B. I. DUERDEN' From the Department of Bacteriology, Edinburgh University
J. clin. Path., 1977, 30, 532-536 Laboratory assessment of physical and chemical methods of preserving urine specimens P. G. WATSON AND B. I. DUERDEN' From the Department of Bacteriology, Edinburgh University
Garenoxacin Treatment of Experimental Endocarditis Caused by Viridans Group Streptococci
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 2006, p. 1263 1267 Vol. 50, No. 4 0066-4804/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.50.4.1263 1267.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 2006, p. 1263 1267 Vol. 50, No. 4 0066-4804/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.50.4.1263 1267.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
COAGULATION OF HUMAN PLASMA BY PASTEURELLA PESTIS'
 COAGULATION OF HUMAN PLASMA BY PASTEURELLA PESTIS' DANIEL M. EISLER Naval Biological Laboratory, School of Public Health, University of California, Berkeley, California Received for publication June 27,
COAGULATION OF HUMAN PLASMA BY PASTEURELLA PESTIS' DANIEL M. EISLER Naval Biological Laboratory, School of Public Health, University of California, Berkeley, California Received for publication June 27,
Aciphin Ceftriaxone Sodium
 Aciphin Ceftriaxone Sodium Only for the use of Medical Professionals Description Aciphin is a bactericidal, long-acting, broad spectrum, parenteral cephalosporin preparation, active against a wide range
Aciphin Ceftriaxone Sodium Only for the use of Medical Professionals Description Aciphin is a bactericidal, long-acting, broad spectrum, parenteral cephalosporin preparation, active against a wide range
Silver-Coated Nylon Fiber as an Antibacterial Agent
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGNTS AND CHMOTHRAPY, Jan. 1987, p. 93-99 Vol. 31, No. 1 66-484/87/193-7$2./ Copyright 1987, American Society for Microbiology Silver-Coated Nylon Fiber as an Antibacterial Agent PATRICIA
ANTIMICROBIAL AGNTS AND CHMOTHRAPY, Jan. 1987, p. 93-99 Vol. 31, No. 1 66-484/87/193-7$2./ Copyright 1987, American Society for Microbiology Silver-Coated Nylon Fiber as an Antibacterial Agent PATRICIA
Synergistic Activity of Azithromycin and Pyrimethamine or
 ANTMCROBAL AGNTS AND CHMOTHRAPY, May 199, p. 997-11 66-44/9/5997-5$./ Copyright 199, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 36, No. 5 Synergistic Activity of Azithromycin and Pyrimethamine or Sulfadiazine
ANTMCROBAL AGNTS AND CHMOTHRAPY, May 199, p. 997-11 66-44/9/5997-5$./ Copyright 199, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 36, No. 5 Synergistic Activity of Azithromycin and Pyrimethamine or Sulfadiazine
Influence of Water Diuresis on Antimicrobial
 Influence of Water Diuresis on Antimicrobial Treatment of Enterococcal Pyelonephritis SANDRA P. LEVISON and DONALD KAYE From the Department of Medicine, The Medical College of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia,
Influence of Water Diuresis on Antimicrobial Treatment of Enterococcal Pyelonephritis SANDRA P. LEVISON and DONALD KAYE From the Department of Medicine, The Medical College of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia,
Sensitivity of Gram-negative bacilli to ampicillin
 J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 644-648 Sensitivity of Gram-negative bacilli to ampicillin after six years' clinical use B. SLOCOMBE AND R. SUTHERLAND From Beecham Research Laboratories, Brockham Park, Betchworth,
J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 644-648 Sensitivity of Gram-negative bacilli to ampicillin after six years' clinical use B. SLOCOMBE AND R. SUTHERLAND From Beecham Research Laboratories, Brockham Park, Betchworth,
Ph. Eur. Reference Standard - LEAFLET
 European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) 7, Allée Kastner CS 30026, F-67081 Strasbourg (France) Tel. +33 (0)3 88 41 20 35 Fax. + 33 (0)3 88 41 27
European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) 7, Allée Kastner CS 30026, F-67081 Strasbourg (France) Tel. +33 (0)3 88 41 20 35 Fax. + 33 (0)3 88 41 27
Research Article. The effects of hyaluronic acid on the morphological physiological differentiation of Lactobacillus
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(7):368-372 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The effects of hyaluronic acid on the morphological
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(7):368-372 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The effects of hyaluronic acid on the morphological
Synergism of Fosfomycin-Ampicillin and Fosfomycin-
 ANTIMICROBiAL AGENTS AND CHEMoTHERAPY, May 1978, p. 75-79 66-484/78/13-75$2./ Copyright 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Synergism of Fosfomycin-Ampicillin and Fosfomycin-
ANTIMICROBiAL AGENTS AND CHEMoTHERAPY, May 1978, p. 75-79 66-484/78/13-75$2./ Copyright 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Synergism of Fosfomycin-Ampicillin and Fosfomycin-
International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety, 2012, 1(2): International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety
 International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety, 2012, 1(2): 54-59 International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety Journal homepage: www.modernscientificpress.com/journals/ijfns.aspx ISSN: 2165-896X
International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety, 2012, 1(2): 54-59 International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety Journal homepage: www.modernscientificpress.com/journals/ijfns.aspx ISSN: 2165-896X
Bacterial Survival In Synovial Fluid: Is S. aureus in the Knee Joint Persisting Despite Antibiotic Treatment?
 Bacterial Survival In Synovial Fluid: Is S. aureus in the Knee Joint Persisting Despite Antibiotic Treatment? Sana Dastgheyb 1, Sommer Hammoud 2, Constantinos Ketonis, MD 3, James Purtill, MD 3, Michael
Bacterial Survival In Synovial Fluid: Is S. aureus in the Knee Joint Persisting Despite Antibiotic Treatment? Sana Dastgheyb 1, Sommer Hammoud 2, Constantinos Ketonis, MD 3, James Purtill, MD 3, Michael
Staphylococcus aureus
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Nov. 1993, p. 2318-2322 66-484/93/112318-5$2./ Copyright X 1993, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 37, No. 11 Uptake of Azithromycin by Human Monocytes and Enhanced
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Nov. 1993, p. 2318-2322 66-484/93/112318-5$2./ Copyright X 1993, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 37, No. 11 Uptake of Azithromycin by Human Monocytes and Enhanced
Antimicrobial activity of Terminalia chebula
 , ISSN 2249 4340 Vol. 1, No. 2, pp. 175-179, September 2011 RESEARCH ARTICLE Antimicrobial activity of Terminalia chebula M. Golam MOSTAFA, Mahdia RAHMAN, M. Manjurul KARIM* Department of Microbiology,
, ISSN 2249 4340 Vol. 1, No. 2, pp. 175-179, September 2011 RESEARCH ARTICLE Antimicrobial activity of Terminalia chebula M. Golam MOSTAFA, Mahdia RAHMAN, M. Manjurul KARIM* Department of Microbiology,
INVESTIGATIONS ON RABBITS
 Meningitis THE PASSAGE OF PENICILLINS INTO THE CEREBRO-SPINAL FLUID AND BRAIN IN EXPERIMENTAL MENINGITIS-EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS ON RABBITS THE majority of the experiments were made on adult rabbits.
Meningitis THE PASSAGE OF PENICILLINS INTO THE CEREBRO-SPINAL FLUID AND BRAIN IN EXPERIMENTAL MENINGITIS-EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS ON RABBITS THE majority of the experiments were made on adult rabbits.
Affinity of Doripenem and Comparators to Penicillin-Binding Proteins in Escherichia coli and ACCEPTED
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on February 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.01-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on February 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.01-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Daptomycin versus vancomycin in the treatment of methicillin-resistant. Staphylococcus aureus meningitis in experimental rabbit model.
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 14 January 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01996-12 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Daptomycin
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 14 January 2013 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01996-12 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Daptomycin
THE "REVERSAL," NEUTRALIZATION, AND SELECTIVITY
 THE "REVERSAL," NEUTRALIZATION, AND SELECTIVITY OF GERMICIDAL CATIONIC DETERGENTS' MORTON KLEIN AND ZELMA G. KARDON Department of Bacteriology, School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia
THE "REVERSAL," NEUTRALIZATION, AND SELECTIVITY OF GERMICIDAL CATIONIC DETERGENTS' MORTON KLEIN AND ZELMA G. KARDON Department of Bacteriology, School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia
*Corresponding author: ABSTRACT
 Pathology and Hygiene SUSCEPTIBILITY, RESISTANCE AND ANTIBIOTIC PROFILE OF BACITRACIN AGAINST CLOSTRIDIUM PERFRINGENS STRAINS ISOLATED DURING CLINICAL OUTBREAKS OF EPIZOOTIC RABBIT ENTEROPATHY Richez P.
Pathology and Hygiene SUSCEPTIBILITY, RESISTANCE AND ANTIBIOTIC PROFILE OF BACITRACIN AGAINST CLOSTRIDIUM PERFRINGENS STRAINS ISOLATED DURING CLINICAL OUTBREAKS OF EPIZOOTIC RABBIT ENTEROPATHY Richez P.
aureus."' Previous studies from this laboratory have shown that this agent despite the availability of antimicrobial agents that are effective against
 RICHARD E. DIXON* Department of Medicine, JAY S. GOODMAN * * George Vanderbilt Hunter University Laboratory, School of Medicine, M. GLENN KOENIG*** Nashville, Tennessee 3723 LYSOSTAPHIN: AN ENZYMATIC APPROACH
RICHARD E. DIXON* Department of Medicine, JAY S. GOODMAN * * George Vanderbilt Hunter University Laboratory, School of Medicine, M. GLENN KOENIG*** Nashville, Tennessee 3723 LYSOSTAPHIN: AN ENZYMATIC APPROACH
RICINOLEATE UPON BACTERIA
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE ACTION OF SODIUM RICINOLEATE UPON BACTERIA From the Division of Laboratories and Research, New York State Department of Health, Albany Received for publication, May 14, 1928
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE ACTION OF SODIUM RICINOLEATE UPON BACTERIA From the Division of Laboratories and Research, New York State Department of Health, Albany Received for publication, May 14, 1928
Hassan Pyar Kok-Khiang Peh *
 Isolation of probiotics Lactobacillus acidophilus from commercial yoghurt Hassan Pyar Kok-Khiang Peh * School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University Sains Malaysia, 11800 Minden, Penang, Malaysia. Telephone
Isolation of probiotics Lactobacillus acidophilus from commercial yoghurt Hassan Pyar Kok-Khiang Peh * School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University Sains Malaysia, 11800 Minden, Penang, Malaysia. Telephone
Effect of Clindamycin, Erythromycin, Lincomycin, and Tetracycline on Growth and Extracellular Lipase Production by Propionibacteria In Vitro
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Jan. 1982, p. 39-43 0066-4804/82/010039-05$02.00/0 Vol. 21, No. 1 Effect of Clindamycin, Erythromycin, Lincomycin, and Tetracycline on Growth and Extracellular Lipase
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Jan. 1982, p. 39-43 0066-4804/82/010039-05$02.00/0 Vol. 21, No. 1 Effect of Clindamycin, Erythromycin, Lincomycin, and Tetracycline on Growth and Extracellular Lipase
Specificity and Mechanism of Tetracycline
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Feb., 1966 Vol. 91, No. 2 Copyright 1966 American Society for Microbiology Printed In U.S.A. Specificity and Mechanism of Resistance in a Multiple Drug Resistant Strain of Escherichia
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Feb., 1966 Vol. 91, No. 2 Copyright 1966 American Society for Microbiology Printed In U.S.A. Specificity and Mechanism of Resistance in a Multiple Drug Resistant Strain of Escherichia
UTI : A NEW APPROACH TO ITS DIAGNOSIS
 Abstract UTI : A NEW APPROACH TO ITS DIAGNOSIS Pages with reference to book, From 126 To 129 S. Hafiz, N. Lyall ( Department of Microbiology, The Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi. ) The incidence
Abstract UTI : A NEW APPROACH TO ITS DIAGNOSIS Pages with reference to book, From 126 To 129 S. Hafiz, N. Lyall ( Department of Microbiology, The Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi. ) The incidence
The Action of Chloroform -killed Suspensions of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli on Ligated Rabbit -gut Segments
 J. gm. nghobioi. (i966), 4, 898 Printed in Great Britain 9 The Action of Chloroform killed Suspensions of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli on Ligated Rabbit gut Segments BY JOAN TAYLOR AND K. A. BETTELHEIM
J. gm. nghobioi. (i966), 4, 898 Printed in Great Britain 9 The Action of Chloroform killed Suspensions of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli on Ligated Rabbit gut Segments BY JOAN TAYLOR AND K. A. BETTELHEIM
CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS
 CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS 8.1 INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are the backbone of traditional medicine and
CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS 8.1 INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are the backbone of traditional medicine and
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page:
 Research Article CODEN: AJPAD7 ISSN: 2321-0923 Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page: www.ajpamc.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF HERBAL WASH FOR NASAL HEALTH
Research Article CODEN: AJPAD7 ISSN: 2321-0923 Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page: www.ajpamc.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF HERBAL WASH FOR NASAL HEALTH
The Effect of Fragaria x ananassa Infusum on Salivary Mutans Streptococci
 The Effect of Fragaria x ananassa Infusum on Salivary Mutans Streptococci Harun.A Gunawan.,AR. Putri.,H.Widodo., S Mangundjaja Department of Oral Biology Faculty of Dentistry Universitas Indonesia Jakarta
The Effect of Fragaria x ananassa Infusum on Salivary Mutans Streptococci Harun.A Gunawan.,AR. Putri.,H.Widodo., S Mangundjaja Department of Oral Biology Faculty of Dentistry Universitas Indonesia Jakarta
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis. Objectives. Disclosure 8/27/2018. Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN
 Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
Heart on Fire: Infective Endocarditis Mary McGreal DNP, RN, ANP-c, CCRN Objectives Discuss the incidence of infective endocarditis? Discuss the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis? Discuss clinical
Bacterial Interference in Chick Embryos *
 Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 46, No. 3, 1967 Bacterial Interference in Chick Embryos * JOHN C. RIBBLE t AND HENRY R. SHINEFIELD (From the Department of Medicine, The New York Hospital-Cornell
Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 46, No. 3, 1967 Bacterial Interference in Chick Embryos * JOHN C. RIBBLE t AND HENRY R. SHINEFIELD (From the Department of Medicine, The New York Hospital-Cornell
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THROAT CULTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES. Upon completion of this exercise, the participant should be able to:
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THROAT CULTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon completion of this exercise, the participant should be able to: distinguish three types of hemolysis produced by bacterial colonies. discuss
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THROAT CULTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon completion of this exercise, the participant should be able to: distinguish three types of hemolysis produced by bacterial colonies. discuss
INTRODUCTION PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
 INTRODUCTION Mycoplasma are known as important contaminants of biological products derived from cell lines in the biopharmaceutical industry affecting every parameter of a cell culture system. Contaminated
INTRODUCTION Mycoplasma are known as important contaminants of biological products derived from cell lines in the biopharmaceutical industry affecting every parameter of a cell culture system. Contaminated
P. A. AKPAN AND J. T. ABRAHAM
 GLOBAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED SCIENCES VOL 16, NO. 4 2010: 381-389 COPYRIGHT BACHUDO SCIENCE CO. LTD PRINTED IN NIGERIA. ISSN 1118-0579 www.globaljournalseries.com; Email: info@globaljournalseries.com
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED SCIENCES VOL 16, NO. 4 2010: 381-389 COPYRIGHT BACHUDO SCIENCE CO. LTD PRINTED IN NIGERIA. ISSN 1118-0579 www.globaljournalseries.com; Email: info@globaljournalseries.com
Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Microbiology Volume 7 Number 1 Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials T Wadhwani, K Desai, D Patel, D Lawani,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Microbiology Volume 7 Number 1 Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials T Wadhwani, K Desai, D Patel, D Lawani,
Screening of bacteria producing amylase and its immobilization: a selective approach By Debasish Mondal
 Screening of bacteria producing amylase and its immobilization: a selective approach By Debasish Mondal Article Summary (In short - What is your article about Just 2 or 3 lines) Category: Bacillus sp produce
Screening of bacteria producing amylase and its immobilization: a selective approach By Debasish Mondal Article Summary (In short - What is your article about Just 2 or 3 lines) Category: Bacillus sp produce
EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLOSIS
 EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLOSIS INTRACELLULAR GROWTH OF Salmonella enteritidis INGESTED IN MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES OF MICE, AND CELLULAR BASIS OF IMMUNITY SUSUMU MITSUHASHI, ICHIEI SATO, AND TOKUMITSU TANAKA
EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLOSIS INTRACELLULAR GROWTH OF Salmonella enteritidis INGESTED IN MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES OF MICE, AND CELLULAR BASIS OF IMMUNITY SUSUMU MITSUHASHI, ICHIEI SATO, AND TOKUMITSU TANAKA
ANTIBACTERIAL TOOTHPASTE: DO NOT SWALLOW
 ANTIBACTERIAL TOOTHPASTE: DO NOT SWALLOW Sarah McCuaig BACKGROUND, PURPOSE, HYPOTHESES Market statistics indicate a significant increase in the use of antibacterial products in North American households.
ANTIBACTERIAL TOOTHPASTE: DO NOT SWALLOW Sarah McCuaig BACKGROUND, PURPOSE, HYPOTHESES Market statistics indicate a significant increase in the use of antibacterial products in North American households.
Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials
 The Internet Journal of Microbiology 2009 : Volume 7 Number 1 Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials Teena Wadhwani M.Sc.(semester IV) Nirma
The Internet Journal of Microbiology 2009 : Volume 7 Number 1 Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials Teena Wadhwani M.Sc.(semester IV) Nirma
Calibration Protocols
 Calibration Protocols (1)OD 600 Reference point LUDOX Protocol Materials: 1ml LUDOX CL-X (provided in kit) ddh20 (provided by team) 96 well plate, black with clear flat bottom preferred (provided by team)
Calibration Protocols (1)OD 600 Reference point LUDOX Protocol Materials: 1ml LUDOX CL-X (provided in kit) ddh20 (provided by team) 96 well plate, black with clear flat bottom preferred (provided by team)
Antimicrobial Activity of Ciprofloxacin against Pseudomonas
 ANTMCROBAL AGNTS AND CHMOTHRAPY, Aug. 1985, p. 331-342 Vol. 28, No. 2 66-484/85/8331-12$2./ Copyright C 1985, American Society for Microbiology Antimicrobial Activity of Ciprofloxacin against Pseudomonas
ANTMCROBAL AGNTS AND CHMOTHRAPY, Aug. 1985, p. 331-342 Vol. 28, No. 2 66-484/85/8331-12$2./ Copyright C 1985, American Society for Microbiology Antimicrobial Activity of Ciprofloxacin against Pseudomonas
CHAPTER 6 EVALUATION OF SELECTED PLANT EXTRACTS FOR EVALUATION OF SELECTED PLANT EXTRACTS FOR ANTI-ACNE ACTIVITY
 CHAPTER 6 EVALUATION OF SELECTED PLANT EXTRACTS FOR School of Science, SVKM s NMIMS University Page 119 6. EVALUATION OF SELECTED PLANT EXTRACTS FOR 6.1 MATERIALS AND METHODS 6.1.1 Antimicrobial assays
CHAPTER 6 EVALUATION OF SELECTED PLANT EXTRACTS FOR School of Science, SVKM s NMIMS University Page 119 6. EVALUATION OF SELECTED PLANT EXTRACTS FOR 6.1 MATERIALS AND METHODS 6.1.1 Antimicrobial assays
Loyola ecommons. Loyola University Chicago. Virginia Long Loyola University Chicago. Recommended Citation
 Loyola University Chicago Loyola ecommons Master's Theses Theses and Dissertations 2014 Identification of Clinical Markers That Predict the Outcomes of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infections
Loyola University Chicago Loyola ecommons Master's Theses Theses and Dissertations 2014 Identification of Clinical Markers That Predict the Outcomes of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infections
Effect of Spray Tank Materials on Anti-Bacterial Activities of Sodium Hypochlorite
 Effect of Spray Tank Materials on Anti-Bacterial Activities of Sodium Hypochlorite Jean M. Bonasera and Steven V. Beer Section of Plant Pathology and Plant Microbe Interaction School of Integrative Plant
Effect of Spray Tank Materials on Anti-Bacterial Activities of Sodium Hypochlorite Jean M. Bonasera and Steven V. Beer Section of Plant Pathology and Plant Microbe Interaction School of Integrative Plant
Effect of Vaccine, Route, and Schedule on Antibody
 APPUED MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1969, p. 355-359 Copyright 1969 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 17, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Vaccine, Route, and Schedule on Antibody Response of Rabbits to Pasteurella
APPUED MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1969, p. 355-359 Copyright 1969 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 17, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Vaccine, Route, and Schedule on Antibody Response of Rabbits to Pasteurella
S. O. Oyedemi*, A. I. Okoh, L. V. Mabinya, G. Pirochenva and A. J. Afolayan
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. (7), pp. 120-126, 6 April, 2009 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 164 5315 2009 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper The proposed
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. (7), pp. 120-126, 6 April, 2009 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 164 5315 2009 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper The proposed
Evaluation of Type-Specific and Non-Type-Specific Pseudomonas Vaccine for Treatment of Pseudomonas Sepsis During Granulocytopenia
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 1976, p. 1139-1143 Copyright 1976 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 4 Printed in USA. Evaluation of Type-Specific and Non-Type-Specific Pseudomonas Vaccine for
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Apr. 1976, p. 1139-1143 Copyright 1976 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 4 Printed in USA. Evaluation of Type-Specific and Non-Type-Specific Pseudomonas Vaccine for
Catheter tip cultures on open-heart surgery patients: associations with site of catheter and age of patients
 Catheter tip cultures on open-heart surgery patients: associations with site of catheter and age of patients R FREEMAN, N HJERSING, AND ANITA BURRIDGE From the Department of Microbiology, Freman Hospital,
Catheter tip cultures on open-heart surgery patients: associations with site of catheter and age of patients R FREEMAN, N HJERSING, AND ANITA BURRIDGE From the Department of Microbiology, Freman Hospital,
FIG S1 Replication rates of S. suis strain 10, 10Δsly, and 10cpsΔEF on mono- and virus pre-infected porcine PCLS.
 A strain 10 10cps EF B strain 10 H1N1 + strain 10 10cps EF H1N1 + 10cps EF 10 8 10 sly 10 7 H3N2 + strain 10 H3N2 + 10cps EF CFU/ml media 10 7 10 6 10 5 10 4 CFU/ml media 10 6 10 5 10 4 10 3 0 2 4 8 12
A strain 10 10cps EF B strain 10 H1N1 + strain 10 10cps EF H1N1 + 10cps EF 10 8 10 sly 10 7 H3N2 + strain 10 H3N2 + 10cps EF CFU/ml media 10 7 10 6 10 5 10 4 CFU/ml media 10 6 10 5 10 4 10 3 0 2 4 8 12
Pathogenic organisms in the sputum of patients
 Thorax (1967), 22, 265. Pathogenic organisms in the sputum of patients with chronic bronchitis 0. L. WADE, P. C. ELMES, AND EILEEN BARTLEY From the Department of Therapeutics and Pharmacology and the Department
Thorax (1967), 22, 265. Pathogenic organisms in the sputum of patients with chronic bronchitis 0. L. WADE, P. C. ELMES, AND EILEEN BARTLEY From the Department of Therapeutics and Pharmacology and the Department
THE ROLE OF SPERMINE IN THE INHIBITION
 J. clin. Path. (1951), 4, 360. THE ROLE OF SPERMINE IN THE INHIBITION OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BY HUMAN SEMEN BY J. GUREVITCH, R. ROZANSKY, D. WEBER, A. BRZEZINSKY, AND B. ECKERLING From the Departments
J. clin. Path. (1951), 4, 360. THE ROLE OF SPERMINE IN THE INHIBITION OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BY HUMAN SEMEN BY J. GUREVITCH, R. ROZANSKY, D. WEBER, A. BRZEZINSKY, AND B. ECKERLING From the Departments
Blood culture 壢新醫院 病理檢驗科 陳啟清技術主任
 Blood culture 壢新醫院 病理檢驗科 陳啟清技術主任 A Positive Blood Culture Clinically Important Organism Failure of host defenses to contain an infection at its primary focus Failure of the physician to effectively eradicate,
Blood culture 壢新醫院 病理檢驗科 陳啟清技術主任 A Positive Blood Culture Clinically Important Organism Failure of host defenses to contain an infection at its primary focus Failure of the physician to effectively eradicate,
Infective endocarditis
 Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
Infective endocarditis Today's lecture is about infective endocarditis, the Dr started the lecture by asking what are the most common causative agents of infective endocarditis? 1-Group A streptococci
Experimental endocarditis in the rat secondary to septic arthritis induced by Staphylococcus uureus
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Experimental endocarditis in the rat secondary to septic arthritis induced by Staphylococcus uureus Clin Microbiol Infect 1999; 5: 158-163 Shahin Nozohoor1~2, Jan-Ingrnar Flock 'I2 and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Experimental endocarditis in the rat secondary to septic arthritis induced by Staphylococcus uureus Clin Microbiol Infect 1999; 5: 158-163 Shahin Nozohoor1~2, Jan-Ingrnar Flock 'I2 and
Comparison Between Agar and Broth Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations of Cefamandole, Cefoxitin, and Cefuroxime
 ANTMCROBAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr 1979, p 572-579 0066-4804/79/00572/08$0200/0 Vol 15, No4 Comparison Between Agar and Broth Minimum nhibitory Concentrations of Cefamandole, Cefoxitin, and Cefuroxime
ANTMCROBAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr 1979, p 572-579 0066-4804/79/00572/08$0200/0 Vol 15, No4 Comparison Between Agar and Broth Minimum nhibitory Concentrations of Cefamandole, Cefoxitin, and Cefuroxime
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 March 2007 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi: /aac
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 March 2007 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01000-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 March 2007 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01000-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
Biofilms: Álvaro Pascual MD, PhD Department of Microbiology
 Biofilms: Role on Pathogenesis and Treatment of UTIs. Álvaro Pascual MD, PhD Department of Microbiology University of Seville. Spain. Medical devices-related infections 1. 35 millions/year in USA 2. Most
Biofilms: Role on Pathogenesis and Treatment of UTIs. Álvaro Pascual MD, PhD Department of Microbiology University of Seville. Spain. Medical devices-related infections 1. 35 millions/year in USA 2. Most
LD 60 determinations.-in order to study the resistance of mice to H. RESISTANCE INDUCED AGAINST HISTOPLASMA CAPSULA TUM: QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS*
 RESISTANCE INDUCED AGAINST HISTOPLASMA CAPSULA TUM: QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS* GILBERT A. HILLt AND STANLEY MARCUS From the Department of Bacteriology, College of Medicine, University of Utah, Salt Lake City
RESISTANCE INDUCED AGAINST HISTOPLASMA CAPSULA TUM: QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS* GILBERT A. HILLt AND STANLEY MARCUS From the Department of Bacteriology, College of Medicine, University of Utah, Salt Lake City
Comparison of Anti- Vibrio Activities of Potassium Sorbate, Sodium Benzoate, and Glycerol and Sucrose Esters of Fatty
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1980, p. 1178-1182 0099-2240/80/06-1178/05$02.00/0 Vol. 39, No. 6 Comparison of Anti- Vibrio Activities of Potassium Sorbate, Sodium Benzoate, and Glycerol
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1980, p. 1178-1182 0099-2240/80/06-1178/05$02.00/0 Vol. 39, No. 6 Comparison of Anti- Vibrio Activities of Potassium Sorbate, Sodium Benzoate, and Glycerol
The penetration of erythromycin into human bronchial mucosa
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 24, 179-183 The penetration of erythromycin into human bronchial mucosa H. MAMTIE1, J. J. HOOGETERP1, J. P. G. KAAJAN2* & J. HERMANS3 'Department of Infectious Diseases, 2Department
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 24, 179-183 The penetration of erythromycin into human bronchial mucosa H. MAMTIE1, J. J. HOOGETERP1, J. P. G. KAAJAN2* & J. HERMANS3 'Department of Infectious Diseases, 2Department
Received 26 June 1995/Returned for modification 15 September 1995/Accepted 5 February 1996
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 1996, p. 941 946 Vol. 40, No. 4 0066-4804/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Amoxicillin Dose-Effect Relationship with Streptococcus
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 1996, p. 941 946 Vol. 40, No. 4 0066-4804/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Amoxicillin Dose-Effect Relationship with Streptococcus
Influence of Different Prebiotics and Probiotics on Selective Intestinal Pathogens
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 657-663 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Influence of Different Prebiotics and Probiotics on Selective Intestinal Pathogens Anayata Sharma 1*
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 657-663 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Influence of Different Prebiotics and Probiotics on Selective Intestinal Pathogens Anayata Sharma 1*
International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Life Sciences ISSN Volume 1, Issue 3, Serial 1: November 2012
 In-vitro interactions of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride with different essential mineral salts and its influence on antimicrobial activity (MIC) of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride S. M. Moazzem Hossen 1*, Md.
In-vitro interactions of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride with different essential mineral salts and its influence on antimicrobial activity (MIC) of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride S. M. Moazzem Hossen 1*, Md.
Use of Conductance to Detect Bacteriocin Activity
 772 Journal of Food Protection, Vol. 53, No. 9, Pages 772-776 [September 1990) Copyright International Association of Milk, Food and Environmental Sanitarians Use of Conductance to Detect Bacteriocin Activity
772 Journal of Food Protection, Vol. 53, No. 9, Pages 772-776 [September 1990) Copyright International Association of Milk, Food and Environmental Sanitarians Use of Conductance to Detect Bacteriocin Activity
BIOCHEMISTRY OF BLOOD
 BCH 471 BIOCHEMISTRY OF BLOOD Amal Alamri Experiment 1 Separation of Plasma and Serum from Whole Blood Whole Blood It is living tissue that circulates through the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries
BCH 471 BIOCHEMISTRY OF BLOOD Amal Alamri Experiment 1 Separation of Plasma and Serum from Whole Blood Whole Blood It is living tissue that circulates through the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries
II- Streptococci. Practical 3. Objective: Required materials: Classification of Streptococci: Streptococci can be classified according to:
 Practical 3 II- Streptococci Objective: 1. Use of blood agar to differentiate between,, and hemolytic streptococci. 2. To know Gram reaction, shape and arrangement of streptococci. 3. To differentiate
Practical 3 II- Streptococci Objective: 1. Use of blood agar to differentiate between,, and hemolytic streptococci. 2. To know Gram reaction, shape and arrangement of streptococci. 3. To differentiate
Comparative study of the disinfection capacity of different floor cleaning solutions on ventilated room floor
 Comparative study of the disinfection capacity of different floor cleaning solutions on ventilated room floor M. G. Sanal Kumar, S. Nandakumar, B. Bini & Arya Raj R. S. P.G. & Research Department of Zoology,
Comparative study of the disinfection capacity of different floor cleaning solutions on ventilated room floor M. G. Sanal Kumar, S. Nandakumar, B. Bini & Arya Raj R. S. P.G. & Research Department of Zoology,
Comparison of Colistin-Carbenicillin, Colistin,
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHIEMOTHEIAPY, Jan. 1973, p. 118-124 Copyright 0 1973 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 3, No. 1 Printed in U.SA. Comparison of Colistin-Carbenicillin, Colistin, and Carbenicillin
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHIEMOTHEIAPY, Jan. 1973, p. 118-124 Copyright 0 1973 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 3, No. 1 Printed in U.SA. Comparison of Colistin-Carbenicillin, Colistin, and Carbenicillin
THE EFFECTS OF ACIDITY UPON THE GROWTH OF PNEUMOCOCCUS IN CULTURE MEDIA CONTAINING PROTEINS
 THE EFFECTS OF ACIDITY UPON THE GROWTH OF PNEUMOCOCCUS IN CULTURE MEDIA CONTAINING PROTEINS BY WILLIAM H. KELLEY, M.D. (From the Department of Medicine of the Duke University School of Medicine, Durham,
THE EFFECTS OF ACIDITY UPON THE GROWTH OF PNEUMOCOCCUS IN CULTURE MEDIA CONTAINING PROTEINS BY WILLIAM H. KELLEY, M.D. (From the Department of Medicine of the Duke University School of Medicine, Durham,
Received 30 March 2005; returned 16 June 2005; revised 8 September 2005; accepted 12 September 2005
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 56, 1047 1052 doi:10.1093/jac/dki362 Advance Access publication 20 October 2005 Evaluation of PPI-0903M (T91825), a novel cephalosporin: bactericidal activity,
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 56, 1047 1052 doi:10.1093/jac/dki362 Advance Access publication 20 October 2005 Evaluation of PPI-0903M (T91825), a novel cephalosporin: bactericidal activity,
PNEUMOCOCCUS VALENT LATEX KIT
 PNEUMOCOCCUS 7-10-13-VALENT LATEX KIT Latex particles coated with pneumococcal antiserum raised in rabbits for in vitro diagnostic use Application The Pneumococcus 7-10-13-valent Latex Kit is a ready to
PNEUMOCOCCUS 7-10-13-VALENT LATEX KIT Latex particles coated with pneumococcal antiserum raised in rabbits for in vitro diagnostic use Application The Pneumococcus 7-10-13-valent Latex Kit is a ready to
Activities of Ertapenem, a New Long-Acting Carbapenem, against Penicillin-Sensitive or -Resistant Pneumococci in Experimental Meningitis
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, June 2003, p. 1943 1947 Vol. 47, No. 6 0066-4804/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.6.1943 1947.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, June 2003, p. 1943 1947 Vol. 47, No. 6 0066-4804/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.6.1943 1947.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
