Physiology Unit 3 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY: THE VASCULAR SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Allen Holt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physiology Unit 3 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY: THE VASCULAR SYSTEM
2 In Physiology Today
3 Hemodynamics F = ΔP/R Blood flow (F) High to low pressure Rate = L/min Pressure (P) Hydrostatic pressure Pressure exerted by blood Generated by contraction of the heart Magnitude varies throughout the system Units of ΔP are mmhg Resistance to blood flow (R) A measure of the friction that impedes flow
4 Hemodynamics F = ΔP/R Resistance is due to: Viscosity Variable Friction between molecules of a flowing fluid > friction = > viscosity Increases as hematocrit increases Length of the vessel Fixed Radius of the vessel Variable F = MAP/R Most important variable in determining resistance in blood vessels
5 Changes in the Radius of a Vessel Effect of vessel radius (r) on resistance (R) Volume of blood is exposed to far more surface friction against the walls of a smaller tube Given the same pressure gradient, flow through a tube decreases 16 fold when the radius is halved
6 Endothelium All blood vessels and the heart are lined with an endothelium Endothelial cells have many functions
7 Pressures in Systemic and Pulmonary Vessels Large arteries serve as low-resistance tubes conducting blood to various organs Act as a pressure reservoir for maintaining blood flow during diastole
8 Arterial Blood Pressure Factors determining pressure in any elastic tube Volume Compliance How easily the structure stretches Compliance = Δ volume/δ pressure Higher the compliance, the easier it stretches Arteries have low compliance. Why? Arteries are resistance vessels Average pressure nearly 100 mmhg
9 Arterial Blood Pressure 1/3 of the stroke volume leaves the arteries during systole The rest of the volume remains in the arteries during systole Distending the walls Raising blood pressure During diastole, arterial walls passively recoil and blood continues to be driven into the arterioles
10 Mean Arteriole Pressure (MAP) Systolic pressure (SP) Diastolic pressure (DP) Pulse pressure PP = SP DP PP = PP = 40 mmhg Mean arteriole pressure Pressure driving blood into the tissues MAP = DP + ⅓(PP) MAP = 80 + ⅓(40) MAP = 93 mmhg Perfusion Pressure
11 Arterioles 2 Major Roles Determine blood flow to organs Major factor in determining MAP Produce the greatest resistance to blood flow Remember flow rate? F = ΔP/R F= MAP/R Vasoconstriction/Vasodilation Intrinsic controls Extrinsic controls Intrinsic tone Spontaneous contractile activity Independent of neural, hormonal or paracrine input
12 Intrinsic Controls Organs and tissues alter their own arteriole resistance Self regulate blood flow Includes Active hyperemia Increased blood flow when tissue metabolic activity inceases Reactive hyperemia Short term increase in blood flow following a brief period of ischemia Local response to injury
13 Intrinsic Controls Endothelial cells secrete paracrine agents that diffuse to adjacent vascular smooth muscle cells Vasodilation/Vasocontriction Nitrous Oxide (NO) Also called endothelium derived relaxing factor (EDRF) Released continuously to maintain vasodilation in the basal state Prostacyclin (PGI 2 ) Eicosanoid
14 Controls of Arteriole Radius
15 Capillaries Low resistance to flow due to large cross-sectional area Movement between plasma and IF Diffusion Vesicle transport Bulk flow Mediated transport (brain) Movement between IF and cytoplasm Diffusion Mediated transport 5% of blood in capillaries
16 Diffusion Gradients Movement of Nutrients and Metabolic End Products Easily diffuse Lipid soluble substances Cellular metabolism creates pressure and concentration gradients O 2, CO 2 Small, water-filled channels in the endothelium Water soluble substances Ions Polar molecules Makes permeability of these substances high
17 Leakiness Movement of Nutrients and Metabolic End Products Due to variations in the size of the water-filled channels Tight capillaries of the brain No clefts Only tight junctions Water-soluble substances only move by carriermediated transport Liver capillaries Large clefts Large holes in the membranes of the endothelial cells Large enough for proteins to pass through
18 Bulk Flow Movement of Protein-Free Fluid Distribution of ECF Bulk flow of proteinfree plasma Remember the capillary wall acts as a filter and proteins typically do not diffuse across Driven by hydrostatic pressure gradients
19 Osmotic Force (π) Protein Concentrations Drive Movement Crystalloids Large amounts of crystalloids in plasma and ICF low-molecular-weight penetrating solutes Na +, Cl -, K + Move with water Colloids Non-penetrating Plasma proteins Concentrations of crystalloids do not change Volume of water and amount of crystalloids do change Increased filtration from plasma to IF Increases volume of IF Decreases volume of plasma [colloid] plasma > [colloid] IF
20 Net Filtration Pressure (NFP) NFP = P c + π IF P IF - π C Opposing forces move protein-free fluid across the capillary wall Filtration (capillary à IF) Absorption (IF à capillary)
21 Net Filtration Pressure (NFP) NFP = P c + π IF P IF - π C Starling Forces The 4 factors that determine NFP Only difference is capillary pressure Positive NFP favors filtration Arteriole end Negative NFP favors absorption Venule end
22 Veins Factors determining pressure in any elastic tube Volume Compliance Δ volume/δ pressure Higher the compliance, the easier it stretches Veins can hold large amounts of blood with a small increase in pressure Veins have high compliance. Why? Venous pressure average <10 mmhg
23 Venous Pressure Pressure differences between peripheral veins (all veins not within the thoracic cavity) and the right atrium Peripheral veins mmhg Right atrium 0 mmhg Low pressure difference is sufficient because veins offer low resistance to flow Diameters of veins are altered in response to blood volume
24 Venous Pressure and SV 1. Sympathetic PostG neurons release NE Causes contraction of venous smooth muscle Decreases diameter Decreases compliance Raising venous pressure 2. Also respond to hormones and paracrine agents 3. Skeletal muscle pump 4. Respiratory pump Inspiration enhances venous return
25 Lymphatic System Large water-filled channels permeable to all IF constituents IF enters lymphatic capillaries by bulk flow Capillary filtration exceeds capillary absorption by 4 L/day 4 L/day returned to blood via lymphatic system
26 Regulation of Systemic Arterial Pressure Major cardiovascular variable regulated is MAP in systemic circulation MAP in systemic circulation CO x total peripheral resistance (TPR) All changes in MAP must be the result of changes in CO and/or TPR Changes in TPR is normally due to changes in resistance of arterioles
27 Regulation of Systemic Arterial Pressure
28 Regulation of Systemic Arterial Pressure A change in a single variable will produce a change in CO or TPR Any deviation in blood pressure will elicit homeostatic reflexes so that CO and/or TPR will adjust to accommodate the change in arteriole pressure
29 Arterial Baroreceptors Baroreceptors Sensitive to stretch or distortion Degree of wall stretching is directly related to pressure within the artery Carotid sinus Aortic arch baroreceptor Afferent neurons travel from baroreceptors to the cardiovascular control center in the medulla
30 The Baroreceptor Reflex Response to a decrease in arterial blood pressure Net result: Increased CO Increased HR Increased SV Increased TPR Vasoconstriction Return of blood pressure to normal Baroreceptor reflex is a short-term regulator of arterial blood pressure < a few days
31 Cardiovascular Center Medulla Oblongata Primary integrating center for the baroreceptor reflexes Input from baroreceptors regulate activity of: Vagus nerve Sympathetic nerves Heart Arterioles Veins
32 Long-Term Regulation of Arterial Pressure Baroreceptors adapt to prolonged changes in pressure Primary mechanism for long-term regulation is blood volume Blood volume determines arterial pressure by influencing Venous pressure EDV SV CO
33 Other Cardiovascular Reflexes and Responses Increase in blood pressure Decrease arterial [O 2 ] Increase arterial [CO 2 ] Decreased blood flow to the brain Pain in skin Stress Anxiety Anger Walking Decrease in blood pressure Pain in viscera or joints Sleeping Good mood
Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions 14.1 Physical Law Governing Blood Flow and Blood Pressure 1. How do you calculate flow rate? 2. What is the driving force of blood
Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions 14.1 Physical Law Governing Blood Flow and Blood Pressure 1. How do you calculate flow rate? 2. What is the driving force of blood
Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow. Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD
 Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD Outline 1- Physical laws governing blood flow and blood pressure 2- Overview of vasculature 3- Arteries 4. Capillaries and venules
Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD Outline 1- Physical laws governing blood flow and blood pressure 2- Overview of vasculature 3- Arteries 4. Capillaries and venules
Heart. Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node. Lymphatic. system Arteriovenous anastomosis. (exchange vessels)
 Venous system Large veins (capacitance vessels) Small veins (capacitance vessels) Postcapillary venule Thoroughfare channel Heart Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node Lymphatic system Arteriovenous anastomosis
Venous system Large veins (capacitance vessels) Small veins (capacitance vessels) Postcapillary venule Thoroughfare channel Heart Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node Lymphatic system Arteriovenous anastomosis
Cardiovascular System. Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
PHYSIOLOGY WEEK 9. vascular physiology - ED Primary Exam Teaching
 PHYSIOLOGY WEEK 9 vascular physiology - ED Primary Exam Teaching CONCEPTS OF BLOOD FLOW Vascular distensibility - when pressure in the arterioles is increased, this dilates the arterioles and therefore
PHYSIOLOGY WEEK 9 vascular physiology - ED Primary Exam Teaching CONCEPTS OF BLOOD FLOW Vascular distensibility - when pressure in the arterioles is increased, this dilates the arterioles and therefore
Veins. VENOUS RETURN = PRELOAD = End Diastolic Volume= Blood returning to heart per cardiac cycle (EDV) or per minute (Venous Return)
 Veins Venous system transports blood back to heart (VENOUS RETURN) Capillaries drain into venules Venules converge to form small veins that exit organs Smaller veins merge to form larger vessels Veins
Veins Venous system transports blood back to heart (VENOUS RETURN) Capillaries drain into venules Venules converge to form small veins that exit organs Smaller veins merge to form larger vessels Veins
BIOL 219 Spring Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System
 1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
3/10/2009 VESSELS PHYSIOLOGY D.HAMMOUDI.MD. Palpated Pulse. Figure 19.11
 VESSELS PHYSIOLOGY D.HAMMOUDI.MD Palpated Pulse Figure 19.11 1 shows the common sites where the pulse is felt. 1. Temporal artery at the temple above and to the outer side of the eye 2. External maxillary
VESSELS PHYSIOLOGY D.HAMMOUDI.MD Palpated Pulse Figure 19.11 1 shows the common sites where the pulse is felt. 1. Temporal artery at the temple above and to the outer side of the eye 2. External maxillary
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Chapter 9. Body Fluid Compartments. Body Fluid Compartments. Blood Volume. Blood Volume. Viscosity. Circulatory Adaptations to Exercise Part 4
 Body Fluid Compartments Chapter 9 Circulatory Adaptations to Exercise Part 4 Total body fluids (40 L) Intracellular fluid (ICF) 25 L Fluid of each cell (75 trillion) Constituents inside cell vary Extracellular
Body Fluid Compartments Chapter 9 Circulatory Adaptations to Exercise Part 4 Total body fluids (40 L) Intracellular fluid (ICF) 25 L Fluid of each cell (75 trillion) Constituents inside cell vary Extracellular
Physiology of Circulation
 Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
Anatomy 36 Study Guide Unit 3
 Anatomy 36 Study Guide Unit 3 Chapter 11 Amine hormones Peptide hormones Steroid hormones 11 4 Hormones of the adrenal cortex 11 6 Hormones of the gonads Categories of hormones Table 11 2 Hormone receptors
Anatomy 36 Study Guide Unit 3 Chapter 11 Amine hormones Peptide hormones Steroid hormones 11 4 Hormones of the adrenal cortex 11 6 Hormones of the gonads Categories of hormones Table 11 2 Hormone receptors
Cardiovascular system
 BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp , , , I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System
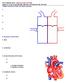 P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide
 Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
I. Cardiac Output Chapter 14
 10/24/11 I. Cardiac Output Chapter 14 Cardiac Output, Blood Flow, and Blood Pressure Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cardiac
10/24/11 I. Cardiac Output Chapter 14 Cardiac Output, Blood Flow, and Blood Pressure Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cardiac
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Cardiac Output 1 Fox Chapter 14 part 1
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Cardiac Output 1 Fox Chapter 14 part 1 T. Houpt, Ph.D. Regulation of Heart & Blood Pressure Keep Blood Pressure constant if too low, not enough blood (oxygen, glucose) reaches tissues
Vert Phys PCB3743 Cardiac Output 1 Fox Chapter 14 part 1 T. Houpt, Ph.D. Regulation of Heart & Blood Pressure Keep Blood Pressure constant if too low, not enough blood (oxygen, glucose) reaches tissues
Cardiovascular system
 Cardiovascular system L-4 Blood pressure & special circulation Dr Than Kyaw 27 February 2012 Blood Pressure (BP) Pressure generation and flow Blood is under pressure within its closed system. Pressure
Cardiovascular system L-4 Blood pressure & special circulation Dr Than Kyaw 27 February 2012 Blood Pressure (BP) Pressure generation and flow Blood is under pressure within its closed system. Pressure
Collin County Community College
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 6 Blood Vessels 1 Anatomy of Blood Vessels Walls of blood vessels contain 3 distinct layers : Tunica intima innermost layer includes
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 6 Blood Vessels 1 Anatomy of Blood Vessels Walls of blood vessels contain 3 distinct layers : Tunica intima innermost layer includes
Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR
 Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
The Cardiovascular system: physiology of circulation
 Chapter 21 The Cardiovascular system: physiology of circulation blood vessel structure and function physiology of circulation: blood flow, blood pressure, and resistance blood flow the amount of blood
Chapter 21 The Cardiovascular system: physiology of circulation blood vessel structure and function physiology of circulation: blood flow, blood pressure, and resistance blood flow the amount of blood
Circulation. Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications. Venous Return. Arterial flow. Regulation of Cardiac Output.
 Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Arteries AWAY. Branch. Typically oxygenated.
 Arteries AWAY Branch Typically oxygenated. Capillaries Smallest. Most abundant. 10 billion. Huge surface area. Exchange Veins TOWARDS Converge. Typically deoxygenated. 3 Layers of the Vascular Wall Tunica
Arteries AWAY Branch Typically oxygenated. Capillaries Smallest. Most abundant. 10 billion. Huge surface area. Exchange Veins TOWARDS Converge. Typically deoxygenated. 3 Layers of the Vascular Wall Tunica
Physiology of Circulation. Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 16/12/2018
 Physiology of Circulation Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 16/12/2018 Overview of the circulation The function of the circulation is to: 1. transport nutrients to the body tissues 2. transport waste products away 3. conduct
Physiology of Circulation Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 16/12/2018 Overview of the circulation The function of the circulation is to: 1. transport nutrients to the body tissues 2. transport waste products away 3. conduct
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2
 Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2 Blood Pressure Main factors influencing blood pressure: Cardiac output (CO) Peripheral resistance (PR) Blood volume Peripheral resistance is a major factor
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2 Blood Pressure Main factors influencing blood pressure: Cardiac output (CO) Peripheral resistance (PR) Blood volume Peripheral resistance is a major factor
Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate
 Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Blood pressure. Formation of the blood pressure: Blood pressure. Formation of the blood pressure 5/1/12
 Blood pressure Blood pressure Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Ø Blood pressure means the force exerted by the blood against the vessel wall Ø ( or the force exerted by the blood against any unit area
Blood pressure Blood pressure Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Ø Blood pressure means the force exerted by the blood against the vessel wall Ø ( or the force exerted by the blood against any unit area
The Cardiovascular System. The Structure of Blood Vessels. The Structure of Blood Vessels. The Blood Vessels. Blood Vessel Review
 The Cardiovascular System The Blood Vessels The Structure of Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Review Arteries carry blood away from the heart Pulmonary trunk to lungs Aorta to everything else Microcirculation
The Cardiovascular System The Blood Vessels The Structure of Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Review Arteries carry blood away from the heart Pulmonary trunk to lungs Aorta to everything else Microcirculation
Peripheral Circulation and Regulation
 Peripheral Circulation and Regulation Functions of Peripheral Circulation 1. Contain the blood 2. Exchange nutrients, waste products, and gases with tissues 3. Transport 4. Regulate blood pressure, along
Peripheral Circulation and Regulation Functions of Peripheral Circulation 1. Contain the blood 2. Exchange nutrients, waste products, and gases with tissues 3. Transport 4. Regulate blood pressure, along
Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output. Blood Vessels
 Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Made of smooth muscle, elastic and fibrous connective tissue Cells are not electrically coupled Blood Vessels Arteries arterioles
Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Made of smooth muscle, elastic and fibrous connective tissue Cells are not electrically coupled Blood Vessels Arteries arterioles
Blood Pressure Regulation. Slides 9-12 Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = 1/3 systolic pressure + 2/3 diastolic pressure
 Sheet physiology(18) Sunday 24-November Blood Pressure Regulation Slides 9-12 Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = 1/3 systolic pressure + 2/3 diastolic pressure MAP= Diastolic Pressure+1/3 Pulse Pressure CO=MAP/TPR
Sheet physiology(18) Sunday 24-November Blood Pressure Regulation Slides 9-12 Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = 1/3 systolic pressure + 2/3 diastolic pressure MAP= Diastolic Pressure+1/3 Pulse Pressure CO=MAP/TPR
Blood Vessels. Over view. We have about 60,000 miles of blood vessels!
 Blood Vessels Over view 3 types of blood vessels arteries - carry blood away from heart "branch", "diverge", and "fork" veins - carry blood toward heart "join", "merge", and "converge" capillaries - site
Blood Vessels Over view 3 types of blood vessels arteries - carry blood away from heart "branch", "diverge", and "fork" veins - carry blood toward heart "join", "merge", and "converge" capillaries - site
Properties of Pressure
 OBJECTIVES Overview Relationship between pressure and flow Understand the differences between series and parallel circuits Cardiac output and its distribution Cardiac function Control of blood pressure
OBJECTIVES Overview Relationship between pressure and flow Understand the differences between series and parallel circuits Cardiac output and its distribution Cardiac function Control of blood pressure
Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well
 Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well describe the factors which regulate cardiac output describe the sympathetic and parasympathetic control of heart
Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well describe the factors which regulate cardiac output describe the sympathetic and parasympathetic control of heart
PHYSIOLOGY MeQ'S (Morgan) All the following statements related to blood volume are correct except for: 5 A. Blood volume is about 5 litres. B.
 PHYSIOLOGY MeQ'S (Morgan) Chapter 5 All the following statements related to capillary Starling's forces are correct except for: 1 A. Hydrostatic pressure at arterial end is greater than at venous end.
PHYSIOLOGY MeQ'S (Morgan) Chapter 5 All the following statements related to capillary Starling's forces are correct except for: 1 A. Hydrostatic pressure at arterial end is greater than at venous end.
Chapter 21: Cardiovascular System: Peripheral Circulation and Regulation
 Chapter 21: Cardiovascular System: Peripheral Circulation and Regulation I. General Features of Blood Vessel Structure A. General Pattern of Circulation 1. Ventricles pump blood into 2. These arteries
Chapter 21: Cardiovascular System: Peripheral Circulation and Regulation I. General Features of Blood Vessel Structure A. General Pattern of Circulation 1. Ventricles pump blood into 2. These arteries
Physiology of Circulation
 Physiology of Circulation Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. 12/8/2005 1 PHYSIOLOGY OF CIRCULATION BLOOD FLOW THROUGH THE CAPILLARIES LYMPHATIC SYSTEM BLOOD PRESSURE 12/8/2005 2 1 Fig.21.08 12/8/2005 3 The Blood Pressure
Physiology of Circulation Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. 12/8/2005 1 PHYSIOLOGY OF CIRCULATION BLOOD FLOW THROUGH THE CAPILLARIES LYMPHATIC SYSTEM BLOOD PRESSURE 12/8/2005 2 1 Fig.21.08 12/8/2005 3 The Blood Pressure
Blood Pressure Regulation. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
2402 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology Hemo Dynamics and Blood Vessels I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 721 through 734. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is
Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology Hemo Dynamics and Blood Vessels I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 721 through 734. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is
Microcirculation and Edema. Faisal I. Mohammed MD, PhD.
 Microcirculation and Edema Faisal I. Mohammed MD, PhD. Objectives: Point out the structure and function of the microcirculation. Describe how solutes and fluids are exchang in capillaries. Outline what
Microcirculation and Edema Faisal I. Mohammed MD, PhD. Objectives: Point out the structure and function of the microcirculation. Describe how solutes and fluids are exchang in capillaries. Outline what
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21)
 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
(D) (E) (F) 6. The extrasystolic beat would produce (A) increased pulse pressure because contractility. is increased. increased
 Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes. Pulmonary Circulation H E A R T. Systemic Circulation
 The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes 1. Overview of Blood Circulation A. Pulmonary Circulation Lung Arterioles Pulmonary Artery Capillaries Pulmonary Circulation Venules Pulmonary Veins H E A
The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes 1. Overview of Blood Circulation A. Pulmonary Circulation Lung Arterioles Pulmonary Artery Capillaries Pulmonary Circulation Venules Pulmonary Veins H E A
Microcirculation. Lecture Block 11 (contributions from Brett Burton)
 Lecture Block 11 (contributions from Brett Burton) Elements of Arterioles, capillaries, venules Structure and function: transport Fluid balance Lymph system Vessels of the Circulatory System Diameter Aorta
Lecture Block 11 (contributions from Brett Burton) Elements of Arterioles, capillaries, venules Structure and function: transport Fluid balance Lymph system Vessels of the Circulatory System Diameter Aorta
Chapter 21! Blood Vessels and Circulation! SECTION 21-1! Blood vessels differ in size, structure, and functional properties!
 Chapter 21! Blood Vessels and Circulation! SECTION 21-1! Blood vessels differ in size, structure, and functional properties! 2 1! Major Vessel Types! Arteries - carry blood away from the heart Higher pressure
Chapter 21! Blood Vessels and Circulation! SECTION 21-1! Blood vessels differ in size, structure, and functional properties! 2 1! Major Vessel Types! Arteries - carry blood away from the heart Higher pressure
Microcirculation and Edema- L1 L2
 Microcirculation and Edema- L1 L2 Faisal I. Mohammed MD, PhD. University of Jordan 1 Objectives: Point out the structure and function of the microcirculation. Describe how solutes and fluids are exchanged
Microcirculation and Edema- L1 L2 Faisal I. Mohammed MD, PhD. University of Jordan 1 Objectives: Point out the structure and function of the microcirculation. Describe how solutes and fluids are exchanged
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Six main classes of blood vessels (on handout) Wall structure of arteries and veins (on handout) Comparison: Arteries vs. Veins (on handout)
 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY
 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
Physiology lecture 15 Hemodynamic
 Physiology lecture 15 Hemodynamic Dispensability (D) : proportional change in volume per unit change in pressure D = V/ P*V It is proportional (divided by the original volume). Compliance (C) : total change
Physiology lecture 15 Hemodynamic Dispensability (D) : proportional change in volume per unit change in pressure D = V/ P*V It is proportional (divided by the original volume). Compliance (C) : total change
Blood Pressure Fox Chapter 14 part 2
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Blood Pressure Fox Chapter 14 part 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. 1 Cardiac Output and Blood Pressure How to Measure Blood Pressure Contribution of vascular resistance to blood pressure Cardiovascular
Vert Phys PCB3743 Blood Pressure Fox Chapter 14 part 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. 1 Cardiac Output and Blood Pressure How to Measure Blood Pressure Contribution of vascular resistance to blood pressure Cardiovascular
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Chapter 21! Chapter 21 Blood Vessels and Circulation! Blood Vessels and Circulation!
 Chapter 21! Blood Vessels and Circulation! SECTION 21-1! Blood vessels differ in size, structure, and functional properties! 2 Major Vessel Types! Arteries - carry blood away from the heart Higher pressure
Chapter 21! Blood Vessels and Circulation! SECTION 21-1! Blood vessels differ in size, structure, and functional properties! 2 Major Vessel Types! Arteries - carry blood away from the heart Higher pressure
Chapter 21 Peripheral circulation and Regulation
 Chapter 21 Peripheral circulation and Regulation I. Blood vessel structure A. Blood flows from large arteries to small capillaries 1. Large arteries contain large amounts of elastic tissue and little smooth
Chapter 21 Peripheral circulation and Regulation I. Blood vessel structure A. Blood flows from large arteries to small capillaries 1. Large arteries contain large amounts of elastic tissue and little smooth
Types of Blood Vessels
 Chapter 21 Peripheral Circulation and Regulation 21-1 Types of Blood Vessels Capillaries: site of exchange with tissue Arteries in dif. Types & sizes Elastic Muscular Arterioles Veins: thinner walls than
Chapter 21 Peripheral Circulation and Regulation 21-1 Types of Blood Vessels Capillaries: site of exchange with tissue Arteries in dif. Types & sizes Elastic Muscular Arterioles Veins: thinner walls than
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
Structure. Arteries. 21_01d 4/18/12. The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Hemodynamics. Dr Badri Paudel GMC
 Goal of the Cardiovascular System: deliver blood to all parts of the body The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Hemodynamics Dr Badri Paudel GMC Does so by using different types of tubing, attached
Goal of the Cardiovascular System: deliver blood to all parts of the body The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Hemodynamics Dr Badri Paudel GMC Does so by using different types of tubing, attached
Chapter 9, Part 2. Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise
 Chapter 9, Part 2 Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise Electrical Activity of the Heart Contraction of the heart depends on electrical stimulation of the myocardium Impulse is initiated in the right
Chapter 9, Part 2 Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise Electrical Activity of the Heart Contraction of the heart depends on electrical stimulation of the myocardium Impulse is initiated in the right
Blood Pressure and its Regulation
 Blood Pressure and its Regulation Blood pressure in your blood vessels is closely monitored by baroreceptors; they send messages to the cardio regulatory center of your medulla oblongata to regulate your
Blood Pressure and its Regulation Blood pressure in your blood vessels is closely monitored by baroreceptors; they send messages to the cardio regulatory center of your medulla oblongata to regulate your
BIOLOGY 2060 LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) VESSELS P1 OF 7
 BIOLOGY 2060 LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) VESSELS P1 OF 7 1. Blood vessels a. Tubes through which the heart pumps blood. b. 3 major types of blood vessels: arteries, capillaries,
BIOLOGY 2060 LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) VESSELS P1 OF 7 1. Blood vessels a. Tubes through which the heart pumps blood. b. 3 major types of blood vessels: arteries, capillaries,
The circulatory system
 Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 הלב עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 הלב עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1. Adi Mizrahi Textbook Chapter 12
 Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) הלב Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) הלב Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
1. Distinguish among the types of blood vessels on the basis of their structure and function.
 Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
The goal of these lectures is to discuss
 Cardiovascular (#2) The goal of these lectures is to discuss basic physiology of the cardiovascular system (heart, vessels, blood pressure, control, hemostasis). This second lecture will discuss blood
Cardiovascular (#2) The goal of these lectures is to discuss basic physiology of the cardiovascular system (heart, vessels, blood pressure, control, hemostasis). This second lecture will discuss blood
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 3
 Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 3 Fluid Shifts Between Capillaries and Tissue Permeable capillaries allow plasma and solutes to pass into interstitial space interstitial or extracellular
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 3 Fluid Shifts Between Capillaries and Tissue Permeable capillaries allow plasma and solutes to pass into interstitial space interstitial or extracellular
Chapters 9 & 10. Cardiorespiratory System. Cardiovascular Adjustments to Exercise. Cardiovascular Adjustments to Exercise. Nervous System Components
 Cardiorespiratory System Chapters 9 & 10 Cardiorespiratory Control Pulmonary ventilation Gas exchange Left heart Arterial system Tissues Right heart Lungs Pulmonary ventilation Cardiovascular Regulation-
Cardiorespiratory System Chapters 9 & 10 Cardiorespiratory Control Pulmonary ventilation Gas exchange Left heart Arterial system Tissues Right heart Lungs Pulmonary ventilation Cardiovascular Regulation-
Control of blood tissue blood flow. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Control of blood tissue blood flow Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives List factors that affect tissue blood flow. Describe the vasodilator and oxygen demand theories. Point out the mechanisms of autoregulation.
Control of blood tissue blood flow Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives List factors that affect tissue blood flow. Describe the vasodilator and oxygen demand theories. Point out the mechanisms of autoregulation.
CVS Hemodynamics. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD.
 CVS Hemodynamics Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD. Objectives point out the physical characteristics of the circulation: distribution of blood volume total cross sectional area velocity blood pressure List the
CVS Hemodynamics Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD. Objectives point out the physical characteristics of the circulation: distribution of blood volume total cross sectional area velocity blood pressure List the
Chapter 19: Blood Vessels. 63 slides
 Chapter 19: Blood Vessels 63 slides 1 Blood Vessels The Blood Vessels are essentially a series of tubes. Three types of blood vessel tubes: Arteries (carry blood away from heart) Arterioles are the smallest
Chapter 19: Blood Vessels 63 slides 1 Blood Vessels The Blood Vessels are essentially a series of tubes. Three types of blood vessel tubes: Arteries (carry blood away from heart) Arterioles are the smallest
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
Blood Pressure Regulation -1
 CVS Physiology Lecture 18 Blood Pressure Regulation -1 Please study the previous sheet before studying this one, even if the first part in this sheet is revision. In the previous lecture we were talking
CVS Physiology Lecture 18 Blood Pressure Regulation -1 Please study the previous sheet before studying this one, even if the first part in this sheet is revision. In the previous lecture we were talking
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1. Resting membrane potential of the ventricular myocardium is: A. -55 to-65mv B. --65 to-75mv C. -75 to-85mv D. -85 to-95 mv E. -95 to-105mv 2. Regarding myocardial contraction:
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1. Resting membrane potential of the ventricular myocardium is: A. -55 to-65mv B. --65 to-75mv C. -75 to-85mv D. -85 to-95 mv E. -95 to-105mv 2. Regarding myocardial contraction:
Circulatory system. Terminology. Ventricles and resistance. Pressure gradients move blood through the heart and vessels.
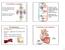 Circulatory system Pressure gradients move blood through the heart and vessels. Pulmonary circulation vs. systemic circulation (to pulmonary circuit) liver head and arms heart aorta diaphragm (from pulmonary
Circulatory system Pressure gradients move blood through the heart and vessels. Pulmonary circulation vs. systemic circulation (to pulmonary circuit) liver head and arms heart aorta diaphragm (from pulmonary
Lecture 10. Circulatory systems; flow dynamics, flow regulation in response to environmental and internal conditions.
 Lecture 10 Circulatory systems; flow dynamics, flow regulation in response to environmental and internal conditions Professor Simchon Influence of P O2 on Hemoglobin Saturation Hemoglobin saturation plotted
Lecture 10 Circulatory systems; flow dynamics, flow regulation in response to environmental and internal conditions Professor Simchon Influence of P O2 on Hemoglobin Saturation Hemoglobin saturation plotted
REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Jonas Addae Medical Sciences, UWI REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Intrinsic Coupling of cardiac and vascular functions - Autoregulation of vessel diameter Extrinsic
REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Jonas Addae Medical Sciences, UWI REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Intrinsic Coupling of cardiac and vascular functions - Autoregulation of vessel diameter Extrinsic
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology. Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta )
 Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System
 AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices. Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont
 Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through two vascular systems
Cardiovascular Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through two vascular systems
CHAPTER 21 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 21 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. One main focus of this chapter considers hemodynamics, the means by which blood flow is altered and distributed and by which blood pressure is regulated. B.
CHAPTER 21 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. One main focus of this chapter considers hemodynamics, the means by which blood flow is altered and distributed and by which blood pressure is regulated. B.
The cardiovascular system is composed of a pump the heart and blood
 5 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Dynamics O B J E C T I V E S 1. To understand the relationships among blood flow, pressure gradient, and resistance 2. To define resistance and describe the main factors
5 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Dynamics O B J E C T I V E S 1. To understand the relationships among blood flow, pressure gradient, and resistance 2. To define resistance and describe the main factors
Physiology - 8 Hemodynamics - 1 M.jafar 24/3/2016 Turquoise Team
 21 Physiology - 8 Hemodynamics - 1 M.jafar 24/3/2016 Turquoise Team Hemodynamics Today we will take about hemodynamics which is the study of the movement of blood and of the forces concerned. Now how the
21 Physiology - 8 Hemodynamics - 1 M.jafar 24/3/2016 Turquoise Team Hemodynamics Today we will take about hemodynamics which is the study of the movement of blood and of the forces concerned. Now how the
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
Cardiac Output (C.O.) Regulation of Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Output (C.O.) Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per minute (5 Litre) Stroke volume: Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per beat. Stroke volume = End diastolic
Cardiac Output (C.O.) Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per minute (5 Litre) Stroke volume: Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per beat. Stroke volume = End diastolic
Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Anatomy of the Heart (See lab handout for terms list) A. Describe the size, shape and location of the heart B. Describe the structure and function of the pericardium
Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Anatomy of the Heart (See lab handout for terms list) A. Describe the size, shape and location of the heart B. Describe the structure and function of the pericardium
Special circulations, Coronary, Pulmonary. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Special circulations, Coronary, Pulmonary Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Describe the control of blood flow to different circulations (Skeletal muscles, pulmonary and coronary) Point out special
Special circulations, Coronary, Pulmonary Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Describe the control of blood flow to different circulations (Skeletal muscles, pulmonary and coronary) Point out special
Chapter 21 (1) An Introduction to Blood Vessels and Circulation
 Chapter 21 (1) An Introduction to Blood Vessels and Circulation Lecture Objectives Compare and contrast the structure of an artery, arteriole, vein, venule, and capillary Discuss the structure and function
Chapter 21 (1) An Introduction to Blood Vessels and Circulation Lecture Objectives Compare and contrast the structure of an artery, arteriole, vein, venule, and capillary Discuss the structure and function
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Blood Vessel Structure
 Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
BIOH122 Session 6 Vascular Regulation
 BIOH122 Session 6 Vascular Regulation To complete this worksheet, select: Module: Distribution Title: Vascular Regulation Introduction 1. a. How do Mean Arterial Blood Pressure (MABP) and Systemic Vascular
BIOH122 Session 6 Vascular Regulation To complete this worksheet, select: Module: Distribution Title: Vascular Regulation Introduction 1. a. How do Mean Arterial Blood Pressure (MABP) and Systemic Vascular
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates. *Ensuring one-way blood. *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction
 *Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
Cardiovascular Physiology III.
 Cardiovascular Physiology III. 43. The microcirculation: capillary solute exchange and fluid dynamics. 44. The microcirculation: lymphatic circulation and edema formation. 45. The characteristics of the
Cardiovascular Physiology III. 43. The microcirculation: capillary solute exchange and fluid dynamics. 44. The microcirculation: lymphatic circulation and edema formation. 45. The characteristics of the
Blood vessels are the tubes through which the heart pumps blood. There are 3 major types of blood vessels: arteries, capillaries, and veins.
 LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) VESSELS P1 OF 1 Blood vessels are the tubes through which the heart pumps blood. There are 3 major types of blood vessels: arteries, capillaries, and
LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II (A. IMHOLTZ) VESSELS P1 OF 1 Blood vessels are the tubes through which the heart pumps blood. There are 3 major types of blood vessels: arteries, capillaries, and
Body Fluids and Fluid Compartments
 Body Fluids and Fluid Compartments Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The chemical reactions of life take place in aqueous solutions. The dissolved substances in a solution are called solutes. In the human body, solutes
Body Fluids and Fluid Compartments Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The chemical reactions of life take place in aqueous solutions. The dissolved substances in a solution are called solutes. In the human body, solutes
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Lecture 1 objectives Explain the basic anatomy of the heart and its arrangement into 4 chambers. Appreciate that blood flows in series through the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
Cardiovascular Physiology Lecture 1 objectives Explain the basic anatomy of the heart and its arrangement into 4 chambers. Appreciate that blood flows in series through the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function
 Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
