Tachycardia (Fast Heart Rhythm)
|
|
|
- Colin Weaver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tachycardia The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Tachycardia (Fast Heart Rhythm) Registered Charity No
2 Introduction to Catheter Ablation This booklet is intended for use by people who wish to understand more about Tachycardia. The information within this booklet comes from research and previous patients experiences. The booklet offers an explanation of Tachycardia and how it is treated, alongside true life success stories. Additional information can be sourced at the provided websites. This booklet should be used in addition to the information given to you by doctors, nurses and physiologists. If you have any questions about any of the information given in this booklet, please ask your nurse, doctor or cardiac physiologist. Arrhythmia Alliance (A-A) is a coalition of charities, patient groups, patients, carers, medical groups and allied professionals. These groups remain independent. However, work together under the A-A umbrella to promote timely and effective diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias. A-A supports and promotes the aims and objectives of the individual groups.
3 Contents The normal electrical system of the heart Diagram of the heart s electrical system What are Arrhythmias? What happens in the heart to cause an arrhythmia? What can trigger an arrhythmia? How do I know what kind of arrhythmia I have? Electrocardiogram (ECG) Holter monitor Cardiac event monitor Types of Arrhythmia Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) AV Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT) AV Reentry Tachycardia (AVRT) or Wolff- Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) Ventricular fibrillation What treatments are available to me? Medicines Permanent Pacemaker Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation Internal Cardioversion Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Further Information Arrhythmia Alliance patient booklets are reviewed annually. This booklet will be next updated February 2009, if you have any comments or suggestions please contact A-A. Glossary of terms Atrium Top chambers of the heart that receive blood from the body and from the lungs. The right atrium is where the heart s natural pacemaker (sino atrial node) can be found. Arrhythmia An abnormal heart rhythm. Bradycardia A slow heart rate, normally less than 60 beats per minute. Cardiac Arrest When the heart stops beating. Cardioversion The use of a small energy shock to stop fast heart rhythms. Defibrillation The use of a higher energy shock to stop fast heart rhythms. Heart attack Occurs when one of the coronary arteries becomes blocked by a blood clot. The blood supply to part of the heart muscle is blocked, causing part of the heart muscle to die. Tachycardia Fast heart rhythm. Ventricles The two lower chambers of the heart. The right ventricle pumps blood into the lungs and the left ventricle pumps blood around the body. Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) A fast, dangerous heart rhythm which causes the heart to stop pumping. This rhythm needs a shock to stop itand return the heart back to a normal rhythm. A cardiac arrest can soon follow if the rhythm is not treated quickly with a shock. Ventricular Tachycardia A fast rhythm which causes the heart to pump less efficiently, and can lead to dizziness, fainting and unconsciousness. If not treated with medication or an electric shock, the rhythm can lead to ventricular fibrillation.
4 The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout the upper (atria) and lower (ventricles) chambers of the heart to make it beat in a regular, coordinated rhythm. The conduction system consists of two areas called nodes that contain conduction cells and special pathways that transmit the impulse. The normal heartbeat begins when an electrical impulse is fired from the sinus node (SA node), in the right atrium. The sinus node is responsible for setting the rate and rhythm of the heart and is therefore referred to as the heart s pacemaker. The electrical impulse fired from the SA node spreads throughout the atria, causing them to contract and squeeze blood into the ventricles. The electrical impulse then reaches the atrioventricular node (AV node), which acts as a gateway, slowing and regulating the impulses travelling between the atria and the ventricles. As the impulse travels down the pathways into the ventricles the heart contracts and pumps blood around the body. The cycle then begins all over again. The normal adult heart beats in a regular pattern times a minute; this is called sinus rhythm. Diagram of the heart s electrical system Sinus Node Pulmonary Veins Atrium AV Node Ventricule Conducting pathways 2008
5 What are Arrhythmias? Arrhythmias are disorders of your heart s electrical system whereby there is a change in the regular beat of your heart. Sometimes if the conduction pathway is damaged or becomes blocked, or if an extra pathway exists, the heart s rhythm changes. The heart may beat too quickly (tachycardia), too slowly (bradycardia) or irregularly which may affect the heart s ability to pump blood around the body. These abnormal heartbeats are known as arrhythmias. Arrhythmias can occur in the upper chambers of the hear t, (the atria) or in the lower chambers of the heart, (the ventricles). Arrhythmias may occur at any age, and are most often a nuisance rather than a serious problem. What happens in the heart to cause an arrhythmia? Any interruption in the hear t s electrical system can cause an arrhythmia. For example, an irregular heartbeat may begin with an abnormal impulse in a part of the heart other than the normal pacemaker (the sinus node). Or the sinus node may develop an abnormal rate or rhythm. What can trigger an arrhythmia? Common causes of arrhythmias include electrical variations that people are born with, which may only become a problem in adult life. Certain triggers can include stress, caffeine, tobacco, alcohol, diet pills, and cough and cold medicines, but there is usually an underlying physical reason for it. If your heart tissue is damaged as a result of acquired heart disease such as myocardial infarction (heart attack) or congenital heart disease you may also be at risk of developing arrhythmias. In rare cases, it may be that doctors cannot identify a cause of their arrhythmias. How do I know what kind of arrhythmia I have? If your doctor suspects that you may have an arrhythmia, one or more of the following tests may be performed to determine the cause of your symptoms. Electrocardiogram (ECG) An electrocardiogram is a recording of the electrical activity of your hear t. Electrode stickers are placed on your chest and connected by wires to a recording machine. Your hear t s electrical signals produce a pattern on graph paper in the ECG. By analysing the pattern of these waves, your doctor can often determine what type of arrhythmia you have. ECG testing can be done at rest, or while you are exercising on a treadmill.
6 Holter monitor A Holter monitor shows changes in your heart rhythm over the course of a 24-hour period that may not be detected during a resting or exercise ECG. If your doctor wants you to have this test, you will be asked to go about your daily activities as usual (except for showering or bathing) while you wear a small, portable recorder that connects to electrode stickers on your chest. You will be asked to come back to the hospital the next day so that the information can be retrieved and analysed. Cardiac event monitor If your doctor feels you need to be monitored for several days or weeks, you may need to have a cardiac event monitor. Your doctor may use this type of recording device if your arrhythmias are infrequent. This device is about the size of a large pager, and can be clipped to your belt or waistband or carried in your purse or pocket. When you feel symptoms, you simply hold the recorder against your chest and press a button; the device then records up to 70 seconds of ECG readings. Types of Arrhythmia Arrhythmias that occur in the atria (the top chambers of the heart) are either atrial or supraventricular (above the ventricles) in origin whereas ventricular arrhythmias start in the ventricles (the lower chambers of the heart). While some arrhythmias are merely a nuisance, others can be life-threatening. A doctor will determine which type of arrhythmia you may have and treat your symptoms accordingly. In general, ventricular arrhythmias caused by hear t disease are the most serious kind, and require prompt medical attention. Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) This type of arrhythmia commonly occurs in young, healthy people. Doctors often refer to supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) as re-entry tachycardias as the electrical impulse does not fade out as with the normal hear tbeat but continues to move in a rapid circle within the conduction system. This is due to an extra electrical pathway which can form a shor t circuit within the hear t s conduction system. SVT is usually a rapid, regular rhythm. The two most common types of SVT are AV-node re-entry tachycardia (AVNRT). AV Nodal Re-entry Tachycardia (AVNRT) This type of arrhythmia occurs when a problem arises in the way the electrical impulses pass through the AV node. Normally, the AV node acts as a gateway slowing and regulating the impulses as they travel between the atria and the
7 ventricles. In AV Nodal re-entry Tachycardia (AVNRT) there are two pathways, known as dual conduction pathways, that can pass impulses to and from the AV node. This type of arrhythmia usually starts following an early beat (ectopic). An electrical short circuit then occurs whereby the electrical impulse rotates around the circuit and with each cycle passes to the ventricles resulting in a very fast heartbeat. AV Re-entry Tachycardia (AVRT) and/or Wolff-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) In AVRT an extra electrical pathway exists that bypasses the normal conduction system. The pathway directly connects the atria (top chambers of the heart) to the ventricles (the bottom chambers of the heart). This extra pathway is known as an accessory pathway. This can be a concealed pathway, meaning there is no evidence of the extra pathway on your ECG, or in WPW. The electrical impulses travel along the accessory pathway thereby bypassing the atrioventricular node. The tissue in the pathway does not slow the impulse down, as in the AV node. Therefore the electrical impulses reach the ventricles before the normal electrical impulse (this is known as pre-excitation). An ECG recording of a patient with WPW syndrome will often show a delta wave which shows the existence of an extra electrical pathway. Very fast heart rates may occur as the electrical impulse bounces between the atria and ventricles. Atrial Fibrillation Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the most common types of arrhythmia. Atrial fibrillation occurs in the atria, in the upper chambers of the hear t. The electrical impulse normally originates at the SA node. However in atrial fibrillation, many electrical impulses are fired rapidly and at random throughout the atria down to the ventricles. The resulting heartbeat is irregular and usually fast. Because the atria are beating rapidly and irregularly (fibrillating), they are unable to completely empty all the blood they receive into the ventricles and this can cause blood clots to form. Therefore, if you are at an increased risk of stroke you may be treated with an anticoagulant (blood thinner) called warfarin. Atrial Flutter Atrial flutter also occurs in the atria (the upper chambers of the heart). In atrial flutter the electrical impulses fire rapidly but the resulting rhythm is regular and organised. The rhythm is due to a re-entry circuit within the atria, whereby the electrical impulse travels in circles leaving and arriving back at the same point. There are several types of atrial flutter, the most common being typical right atrial flutter.
8 Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) Ventricular tachycardia (VT) occurs when the electrical impulses arise in the ventricles, the bottom chambers of the heart. The ventricles start beating at an abnormally fast, regular rate. Because the ventricles are beating rapidly the heart does not work as efficiently. This can cause symptoms of weakness, dizziness, chest pain, shortness of breath or even collapse. There are several different types of ventricular tachycardia (VT) and the seriousness of the condition can vary. However, ventricular tachycardia (VT) can be a potentially life threatening hear t rhythm as it can progress to ventricular fibrillation and cause the heart to stop beating (cardiac arrest). There are a number of reasons why people may develop ventricular tachycardia (VT). For example, in people who have had a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), the area of the heart muscle damaged by the heart attack forms scar tissue and this can make the heart susceptible to abnormal heart rhythms. Other people who may experience ventricular tachycardia (VT) are patients with cardiomyopathy, previous corrective congenital heart surgery or inherited arrhythmias. There is also a small group of people who have VT with a structurally normal heart where the VT may be well tolerated. Ventricular fibrillation Ventricular fibrillation occurs in the ventricles, in the bottom chambers of the heart. In Ventricular fibrillation, the electrical impulses are fired from multiple sites in the ventricles in a very fast and irregular way, causing the heart to quiver rather than to beat and pump blood. Ventricular fibrillation is an extremely dangerous hear t rhythm and prompt emergency care must be provided to get the heart pumping again, or death can occur. What treatments are available to me? The results of the tests you have had will determine the type and seriousness of your arrhythmia and your doctor will then discuss with you the treatment options available. You and your doctor will then decide which one is right for you. Remember, many patients with arrhythmias require no further treatment. The most important aspect of any initial evaluation is to determine the significance of the arrhythmia and the need for any type of intervention. Medicines There are a number of drugs that can be used to treat your arrhythmia. Antiarrhythmic drugs are medicines that change the electrical signals in your heart and help prevent irregular or rapid hear t rhythms (please refer to our drug treatment for hear t rhythm disorders booklet).
9 Permanent Pacemaker If you have a slow heart rate your doctor may recommend you have a pacemaker. A pacemaker is a small device used to treat slow heart rhythms, it is implanted beneath the skin below the collarbone and connected to a pacing wire placed inside the hear t. The pacemaker delivers a small electrical impulse to stimulate the heart to beat when it is going too slowly. Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation If you have an extra electrical pathway or group of cells your doctor may advise you to have a radiofrequency catheter ablation. A catheter ablation blocks the area of extra electrical activity causing the arrhythmias, providing relief for those of you who may not have responded well to medications or, for whatever reason, would rather not or cannot take medications. This technique has a high percentage of successfully curing many types of arrhythmias. Internal Cardioversion Internal cardioversion is a low energy electrical shock delivered inside the heart. Two catheters are inserted into a vein in your groin and a small electrode pad applied to your chest. Your Electrophysiologist performs this procedure in the EP lab. During the internal cardioversion, you will be given a short acting sedative to make you sleepy. Internal cardioversion is performed when medications and external cardioversion have been unsuccessful in returning a patient s rhythm back to a normal sinus rhythm. Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator This is a device for people who are at risk of life threatening heart rhythms. It is slightly larger than a pacemaker and usually implanted beneath the skin below the collarbone. It is connected to defibrillation/pacing wire(s) positioned inside the heart via a vein. It has the ability to determine and stop fast ventricular arrhythmias by using extra paced beats, or delivering an electric shock to the heart. It is also capable of pacing the heart to stop it from going too slowly.
10 Useful Websites A list of useful sites can be found at:- This list is not exhaustive and it is constantly evolving. If we have excluded anyone, please accept our sincerest apologies and be assured that as soon as the matter is brought to the attention of the Arrhythmia Alliance, we will quickly act to ensure maximum inclusiveness in our endeavours. If you wish to contact us direct please phone on or hear trhythm@stars.org.uk Further Reading This is the list of Arrhythmia Alliance Patient booklets available by website or ing. Arrhythmia Checklist - Could your hear t rhythm problem be dangerous? Atrial Fibrillation (AF) AF Checklist Blackout Checklist Bradycardia (Slow Hear t Rhythm) CRT/ICD Catheter Ablation Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation Drug Treatment for Heart Rhythm Disorders (Arrhythmias) Electrophysiology Studies Exercising with an ICD FAQs Heart Rhythm Charity Highlighting the Work of the Arrhythmia Alliance ICD Implantable Loop Recorder Long QT Patient Information National Service Framework Chapter 8 CRT/Pacemaker Pacemaker Palpitation Checklist Remote Monitoring for ICDs Sudden Cardiac Arrest Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Tachycardia (Fast Hear t Rhythm) Testing Using Drug Injections to Investigate the Possibility of a Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death Tilt-Test Please feel free to discuss any concerns at all with the doctors, physiologists or your specialist nurse at any time.
11 Please help us to improve services for all those affected by arrhythmias and to save lives by making a donation today. Please complete the donation form below and return to P.O Box 3697 Stratford upon Avon CV37 8YL or click on and click the donate icon. Membership is free to individuals however if you would like to make a DONATION please complete and return. I would like to make a donation to A-A and enclose: I have made donation to A-A via PAYPAL at to the sum of: I have arranged a standing order from my Bank/ Building Society Account to A-A. (min amount 10p.a.) Please tick here if you agree to Gift Aid your subscription/donation Gift Aid Tick here Name of taxpayer:... Address: Postcode:... Please allow Arrhythmia Alliance to claim an extra 28p for every 1 you donate at no cost to you. I want Arrhythmia Alliance to treat all donations I have made since 6 April 2000, and all donations I make from the date of this declaration until I notify you otherwise, as Gift Aid donations. I currently pay an amount of income tax and/or capital gains tax at least equal to the tax that Arrhythmia Alliance reclaims on my donations in the tax year. I may cancel this declaration at any time by notifying A-A. I will notify A-A if I change my address. Please note full details of Gift Aid tax relief are available from your local tax office in leaflet IR 65. If you pay tax at a higher rate you can claim further tax relief in your Self-Assessment tax return. My Bank: Bank Address: Standing Order Authority Please Pay: A-A, Account: Sort Code: , Lloyds TSB Plc, 22 Bridge St, Stratford upon Avon, CV37 6AG The Sum of /E/$: On (1st Date): / / And after this, every: Month / Year (delete) Account No.: Sort Code: Signature: Date: Card Type: Card Number: Name on Card: Please hand this form in to your Bank Credit Card Payment Expiry Date: Amount of /E/$: Address:
12 Executive Committee President Prof A John Camm Dr Phillip Batin Mr Chris Brown Mr Pierre Chauvineau Dr Derek Connelly Dr Campbell Cowan Dr Neil Davidson Dr Wyn Davies Mr Nigel Farrell Dr Adam Fitzpatrick Dr Michael Gammage Mr Steve Gray Mrs Angela Griffiths Mr Robert Hall Dr Guy Haywood Mrs Anne Jolly Mrs Sue Jones Dr Gerry Kaye Dr Nick Linker Mrs Trudie Lobban Ms Nicola Meldrum Prof John Morgan Mrs Jayne Mudd Dr Francis Murgatroyd Dr Richard Schilling Dr Graham Stuart Mrs Jenny Tagney Mr Paul Turner Trustees Mr Chris Brown Dr Derek Connelly Mr Nigel Farrell Dr Adam Fitzpatrick Mrs Trudie Lobban Patrons Prof Hein J J Wellens Prof Silvia G Priori W B Beaumont, OBE Rt. Hon Tony Blair endorsed by Arrhythmia Alliance PO Box 3697 Stratford upon Avon Warwickshire CV37 8YL Tel: info@heartrhythmcharity.org.uk Please remember these are general guidelines and individuals should always discuss their condition with their own doctor. Published 2005 revised February 2008
Electrophysiology Studies (EPS) The Heart Rhythm Charity
 Electrophysiology Studies (EPS) The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Electrophysiology Studies (EPS)
Electrophysiology Studies (EPS) The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Electrophysiology Studies (EPS)
Palpitation Checklist
 Palpitation Checklist Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias Palpitation Checklist Registered Charity No. 1107496 2016 Introduction When
Palpitation Checklist Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias Palpitation Checklist Registered Charity No. 1107496 2016 Introduction When
Tilt test. Tilt test. The Heart Rhythm Charity
 Tilt test The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Tilt test www.aa-za.org Registered Charity No. 1107496
Tilt test The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Tilt test www.aa-za.org Registered Charity No. 1107496
National Service Framework
 National Service Framework The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias National Requirments - Local Implementation
National Service Framework The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias National Requirments - Local Implementation
Drug Treatment for Heart Rhythm Disorders (Arrhythmia)
 Drug Treatment for Heart Rhythm Disorders (Arrhythmia) The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Drug Treatment
Drug Treatment for Heart Rhythm Disorders (Arrhythmia) The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Drug Treatment
What can I do about sudden cardiac arrest?
 The Heart Rhythm Charity What can I do about sudden cardiac arrest? Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for those affected by heart rhythm disorders (cardiac arrhythmias)
The Heart Rhythm Charity What can I do about sudden cardiac arrest? Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for those affected by heart rhythm disorders (cardiac arrhythmias)
Pacemaker Patient Information
 Pacemaker Patient Information The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Pacemaker Patient Information www.heartrhythmcharity.org.uk
Pacemaker Patient Information The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Pacemaker Patient Information www.heartrhythmcharity.org.uk
Sudden Cardiac Arrest. How you can make a difference. Restart The Heart. Arrhythmia Alliance. The Heart Rhythm Charity
 Restart The Heart Arrhythmia Alliance The Heart Rhythm Charity www.heartrhythmcharity.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1107496 2011 Sudden Cardiac Arrest How you can make a difference Everyday, someone like
Restart The Heart Arrhythmia Alliance The Heart Rhythm Charity www.heartrhythmcharity.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1107496 2011 Sudden Cardiac Arrest How you can make a difference Everyday, someone like
The Heart Rhythm Charity
 The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Registered Charity No. 1107496 2007 CRT / Pacemaker Patient Information
The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Registered Charity No. 1107496 2007 CRT / Pacemaker Patient Information
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES
 UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
CRT / ICD Patient Information
 CRT / ICD Patient Information The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias CRT / ICD Patient Information www.heartrhythmcharity.org.uk
CRT / ICD Patient Information The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias CRT / ICD Patient Information www.heartrhythmcharity.org.uk
Genetic testing for inherited cardiac conditions
 Genetic testing for inherited cardiac conditions Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity
Genetic testing for inherited cardiac conditions Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity
Arrhythmias. Pulmonary Artery
 Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Implantable Loop Recorder
 Implantable Loop Recorder Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity No. 1107496 Glossary
Implantable Loop Recorder Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity No. 1107496 Glossary
What is an. arrhythmia?
 What is an arrhythmia? What is an arrhythmia? Arrhythmia is an umbrella term used to describe a number of conditions where the muscle contraction of the heart is too slow, too fast or irregular because
What is an arrhythmia? What is an arrhythmia? Arrhythmia is an umbrella term used to describe a number of conditions where the muscle contraction of the heart is too slow, too fast or irregular because
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease
 Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
What can I do about sudden cardiac arrest?
 What can I do about sudden cardiac arrest? Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity
What can I do about sudden cardiac arrest? Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity
Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias.
 Long QT Syndrome Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity No. 1107496 Glossary Arrhythmia
Long QT Syndrome Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity No. 1107496 Glossary Arrhythmia
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) patient information
 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) patient information Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) patient information Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered
Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias)
 Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias) Page 1 of 5 The heart needs a small electrical current to pass through the heart in a very set pattern. This is called the heart's conduction system. This leaflet explains
Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias) Page 1 of 5 The heart needs a small electrical current to pass through the heart in a very set pattern. This is called the heart's conduction system. This leaflet explains
What can I do about Sudden Cardiac Arrest?
 What can I do about Sudden Cardiac Arrest? The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias You can make a difference
What can I do about Sudden Cardiac Arrest? The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias You can make a difference
Patient & Primary Care Checklist
 established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Patient & Primary Care Checklist Tel: +44 (0)1789 451 837 Registered Charity Number: 1122442 2011 INTRODUCTION If you have been recently
established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Patient & Primary Care Checklist Tel: +44 (0)1789 451 837 Registered Charity Number: 1122442 2011 INTRODUCTION If you have been recently
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS. A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology MY LIFE HAS TAKEN A TURN FOR THE BETTER. -Emie Bishop ARRHYTHMIAANSWERS.COM AF ANSWERS. A PATIENT EDUCATION HANDBOOK ON ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology MY LIFE HAS TAKEN A TURN FOR THE BETTER. -Emie Bishop ARRHYTHMIAANSWERS.COM AF ANSWERS. A PATIENT EDUCATION HANDBOOK ON ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
About atrial fibrillation (AFib) Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) What is AFib? What s the danger? Who gets AFib?
 Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
ICD Patient Information
 The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Registered Charity No.: 1107406 2005 ICD Patient Information Introduction
The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Registered Charity No.: 1107406 2005 ICD Patient Information Introduction
Patient and primary care checklist
 AF A www.afa.org.uk Patient and primary care checklist Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No.
AF A www.afa.org.uk Patient and primary care checklist Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No.
The heart, the pulse and the electrocardiograph
 AF A www.afa.org.uk The heart, the pulse and the electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
AF A www.afa.org.uk The heart, the pulse and the electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Definition of electrophysiology study and ablation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Electrophysiology Study and Ablation An electrophysiology, or EP, study is a test of the heart
Definition of electrophysiology study and ablation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Electrophysiology Study and Ablation An electrophysiology, or EP, study is a test of the heart
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia PSVT.
 Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
THE HEART, THE PULSE and THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAPH
 www.afa.org.uk Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation THE HEART, THE PULSE and THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAPH Registered Charity No. 1122442
www.afa.org.uk Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation THE HEART, THE PULSE and THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAPH Registered Charity No. 1122442
Information for patients, parents and guardians. Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation.
 Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients Your doctor has determined that you have atrial fibrillation (AF), a common disturbance of the heart s rhythm. This pamphlet will answer many of your
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients Your doctor has determined that you have atrial fibrillation (AF), a common disturbance of the heart s rhythm. This pamphlet will answer many of your
Catheter Ablation. Patient Education
 Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary
 X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
Newer pacemakers also can monitor your blood temperature, breathing, and other factors and adjust your heart rate to changes in your activity.
 Pacemakers & Defibrillators A pacemaker system consists of a battery, a computerized generator and wires with sensors called electrodes on one end. The battery powers the generator, and both are surrounded
Pacemakers & Defibrillators A pacemaker system consists of a battery, a computerized generator and wires with sensors called electrodes on one end. The battery powers the generator, and both are surrounded
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation
 www.afa.org.uk Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation Registered Charity No. 1122442 Copyright
www.afa.org.uk Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation Registered Charity No. 1122442 Copyright
NHS. Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) for arrhythmias. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Issue date: January 2006
 NHS National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Issue date: January 2006 Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) for arrhythmias Understanding NICE guidance information for people with
NHS National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Issue date: January 2006 Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) for arrhythmias Understanding NICE guidance information for people with
Management strategies for atrial fibrillation Thursday, 20 October :27
 ALTHOUGH anyone who has had to run up a flight of steps or has had a frightening experience is quite familiar with a racing heartbeat, for the more than 2 million Americans who suffer from atrial fibrillation
ALTHOUGH anyone who has had to run up a flight of steps or has had a frightening experience is quite familiar with a racing heartbeat, for the more than 2 million Americans who suffer from atrial fibrillation
GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
Diagnostic tests for syncope
 Diagnostic tests for syncope Working together with individuals, families and medical professionals to offer support and information on syncope and reflex anoxic seizures www.stars.org.uk Registered Charity
Diagnostic tests for syncope Working together with individuals, families and medical professionals to offer support and information on syncope and reflex anoxic seizures www.stars.org.uk Registered Charity
PhD FRCP MESC MEAPCI. Consultant Cardiologist SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia. Coronary Arteries
 SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Coronary Arteries Overview LMS Supraventricular tachycardia is defined as an abnormally fast heartbeat. It's a describes a group of arrhythmias which all originate from
SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Coronary Arteries Overview LMS Supraventricular tachycardia is defined as an abnormally fast heartbeat. It's a describes a group of arrhythmias which all originate from
Different indications for pacemaker implantation are the following:
 Patient Resources: ICD/Pacemaker Overview ICD/Pacemaker Overview What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker is a device that uses low energy electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat whenever a pause in the
Patient Resources: ICD/Pacemaker Overview ICD/Pacemaker Overview What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker is a device that uses low energy electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat whenever a pause in the
ICD Implantation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm ICD Implantation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers (the right atrium
Melbourne Heart Rhythm ICD Implantation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers (the right atrium
Arrhythmia Management Joshua M. Cooper, MD, FHRS, FACC
 Arrhythmia Management Joshua M. Cooper, MD, FHRS, FACC Professor of Medicine Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology Temple University Health System Plumbing Electrical System Bradyarrhythmias Sinus Node
Arrhythmia Management Joshua M. Cooper, MD, FHRS, FACC Professor of Medicine Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology Temple University Health System Plumbing Electrical System Bradyarrhythmias Sinus Node
HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland improves the quality of life for people in Scotland affected by chest, heart and stroke illness, through medical research,
HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland improves the quality of life for people in Scotland affected by chest, heart and stroke illness, through medical research,
Diagnosing Arrhythmias
 Diagnosing Arrhythmias Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity No. 1107496 Glossary
Diagnosing Arrhythmias Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity No. 1107496 Glossary
Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances
 Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc.
 Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc. The Miracle of Living February 21, 2018 Matthew Ostrom MD,FACC,FHRS Division of
Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc. The Miracle of Living February 21, 2018 Matthew Ostrom MD,FACC,FHRS Division of
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Patient Information
 Australia www.atrialfibrillation-au.org www.afa-international.org Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Australia www.atrialfibrillation-au.org www.afa-international.org Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Atrial fibrillation. Understanding NICE guidance
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Atrial fibrillation NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Atrial fibrillation NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Which ECG is Right for You?
 Which ECG is Right for You? Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity No. 1107496 Glossary
Which ECG is Right for You? Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity No. 1107496 Glossary
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide
 Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
How does the heart work? The heart is muscle whose main function is a pump; to push blood the rest of your body.
 1 You have a condition called atrial fibrillation. I would like you to learn more about this condition. You should read about it below, and can also watch an Internet program about it. After reading about
1 You have a condition called atrial fibrillation. I would like you to learn more about this condition. You should read about it below, and can also watch an Internet program about it. After reading about
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Patient Information
 AF A Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1122442
AF A Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1122442
Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion
 Page 1 of 10 Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion Introduction This leaflet is to inform you about your planned Direct Current (DC) electrical cardioversion. A cardioversion is an electrical treatment which
Page 1 of 10 Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion Introduction This leaflet is to inform you about your planned Direct Current (DC) electrical cardioversion. A cardioversion is an electrical treatment which
Atrial fibrillation and you. Atrial fibrillation and your treatment options
 Atrial fibrillation and you Atrial fibrillation and your treatment options What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation The Normal Heart Rhythm Electrical System of the Heart The heart pumps blood to
Atrial fibrillation and you Atrial fibrillation and your treatment options What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation The Normal Heart Rhythm Electrical System of the Heart The heart pumps blood to
Ventricular Tachycardia in Structurally Normal Hearts (Idiopathic VT) Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Ventricular Tachycardia in Structurally Normal Hearts (Idiopathic VT) Patient Information What is Ventricular Tachycardia? Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an abnormal rapid heart
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Ventricular Tachycardia in Structurally Normal Hearts (Idiopathic VT) Patient Information What is Ventricular Tachycardia? Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an abnormal rapid heart
Atrial Fibrillation: What Should You Know? I (888)
 Atrial Fibrillation: What Should You Know? I was exhausted doing simple tasks because of my AFib. I couldn t walk from the store to my car in the parking lot. Then, I had a MAZE procedure. It was a very
Atrial Fibrillation: What Should You Know? I was exhausted doing simple tasks because of my AFib. I couldn t walk from the store to my car in the parking lot. Then, I had a MAZE procedure. It was a very
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
Atrial Fibrillation. Damage to your heart caused by a heart attack or rheumatic heart disease
 Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information Normal Heart Function The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information Normal Heart Function The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two
Dealing with abnormal Heart rhythms. Michelle White
 Dealing with abnormal Heart rhythms Michelle White ABOUT THE BRITISH HEART FOUNDATION CONTENTS As the nation s heart charity, we have been funding cutting-edge research that has made a big difference to
Dealing with abnormal Heart rhythms Michelle White ABOUT THE BRITISH HEART FOUNDATION CONTENTS As the nation s heart charity, we have been funding cutting-edge research that has made a big difference to
Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph
 AF A The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary
AF A The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary
Electrophysiology Studies and Catheter Ablation. Electrophysiology Studies and Catheter Ablation
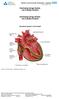 Electrophysiology Studies Cardiac Conduction System. Mdmedicine.wordpress.com Patient Information Leaflet for: Electrophysiology Studies Available via Trust Docs Version: 6 Trust Docs ID: 10 Page 1 of
Electrophysiology Studies Cardiac Conduction System. Mdmedicine.wordpress.com Patient Information Leaflet for: Electrophysiology Studies Available via Trust Docs Version: 6 Trust Docs ID: 10 Page 1 of
Atrial fibrillation (AF) patient information
 AF A www.afa.org.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) patient information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
AF A www.afa.org.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) patient information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
APPROACH TO TACHYARRYTHMIAS
 APPROACH TO TACHYARRYTHMIAS PROF.DR.MD.ZAKIR HOSSAIN PROFESSOR AND HEAD DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE SZMCH TACHYARRYTHMIA Cardiac arrythmia is a disturbance of electrical rhythm of heart. Cardac arrythmia with
APPROACH TO TACHYARRYTHMIAS PROF.DR.MD.ZAKIR HOSSAIN PROFESSOR AND HEAD DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE SZMCH TACHYARRYTHMIA Cardiac arrythmia is a disturbance of electrical rhythm of heart. Cardac arrythmia with
Diagnostic tests for syncope
 Diagnostic tests for syncope Working together with individuals, families and medical professionals to offer support and information on syncope and reflex anoxic seizures www.stars.org.uk Registered Charity
Diagnostic tests for syncope Working together with individuals, families and medical professionals to offer support and information on syncope and reflex anoxic seizures www.stars.org.uk Registered Charity
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias
 Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
Special health. guide. Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding. Atrial Fibrillation WITH
 Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding Atrial Fibrillation WITH Table of Contents Atrial Fibrillation: An Introduction... 1 How AF Affects the Heart... 2 Who Gets AF?...
Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding Atrial Fibrillation WITH Table of Contents Atrial Fibrillation: An Introduction... 1 How AF Affects the Heart... 2 Who Gets AF?...
Direct Current Cardioversion (DCCV)
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is a This is a procedure carried out under a brief anaesthetic, which uses a
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is a This is a procedure carried out under a brief anaesthetic, which uses a
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Todd J. Florin, M.D. Table of Contents The Normal Heart...1 What is Atrial Fibrillation...3 Risks of Afib: Stroke...5 Treatment Options...7 Radiofrequency Ablation...9
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Todd J. Florin, M.D. Table of Contents The Normal Heart...1 What is Atrial Fibrillation...3 Risks of Afib: Stroke...5 Treatment Options...7 Radiofrequency Ablation...9
NEIL CISPER TECHNICAL FIELD ENGINEER ICD/CRTD BASICS
 NEIL CISPER TECHNICAL FIELD ENGINEER ICD/CRTD BASICS OBJECTIVES Discuss history of ICDs Review the indications for ICD and CRT therapy Describe basic lead and device technology Discuss different therapies
NEIL CISPER TECHNICAL FIELD ENGINEER ICD/CRTD BASICS OBJECTIVES Discuss history of ICDs Review the indications for ICD and CRT therapy Describe basic lead and device technology Discuss different therapies
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Implantable cardioverter defibrillators for the treatment of arrhythmias and cardiac resynchronisation therapy for the treatment of heart failure (review
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Implantable cardioverter defibrillators for the treatment of arrhythmias and cardiac resynchronisation therapy for the treatment of heart failure (review
Living with Atrial Fibrillation: RELATIONSHIPS
 www.afa.org.uk Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Living with Atrial Fibrillation: RELATIONSHIPS Registered Charity No. 1122442
www.afa.org.uk Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Living with Atrial Fibrillation: RELATIONSHIPS Registered Charity No. 1122442
Implantation of an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is an Implantable? Your doctor has recommended that you have an Implantable.
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is an Implantable? Your doctor has recommended that you have an Implantable.
Nathan Cade, MD Brandon Fainstad, MD Andrew Prouse, MD
 Nathan Cade, MD Brandon Fainstad, MD Andrew Prouse, MD OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the basic electrophysiology of the four causes of wide complex tachycardia. 2. Develop a simple framework for acute management
Nathan Cade, MD Brandon Fainstad, MD Andrew Prouse, MD OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the basic electrophysiology of the four causes of wide complex tachycardia. 2. Develop a simple framework for acute management
OVERVIEW OF ARRHYTHMIA
 ARRHYTHMIA ABLATION ARRHYTHMIA ABLATION OVERVIEW OF ARRHYTHMIA WHAT IS AN ARRHYTHMIA? There are some people who experience abnormal heart rhythms. The heart rate may be too fast or frequently irregular.
ARRHYTHMIA ABLATION ARRHYTHMIA ABLATION OVERVIEW OF ARRHYTHMIA WHAT IS AN ARRHYTHMIA? There are some people who experience abnormal heart rhythms. The heart rate may be too fast or frequently irregular.
Implantation of a Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy-Defibrillator (CRT-D)
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient Implantation of a Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy-Defibrillator (CRT-D) affix patient label What is
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient Implantation of a Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy-Defibrillator (CRT-D) affix patient label What is
Catheter Ablation for Supra-ventricular Tachycardia
 Additional Notes Our mission To provide the excellent care we would expect for our families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Additional Notes Our mission To provide the excellent care we would expect for our families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Atrial Flutter Patient Information
 AF A Atrial Flutter Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
AF A Atrial Flutter Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
 AF A Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
AF A Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer Turquoise team
 15 physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer 22-3-2016 Turquoise team Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation Today, we are going to talk about the abnormal excitation. As we said before,
15 physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer 22-3-2016 Turquoise team Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation Today, we are going to talk about the abnormal excitation. As we said before,
Catheter Ablation for Atrial Flutter
 Additional Notes Our mission Providing the excellent care we would expect for our own families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Additional Notes Our mission Providing the excellent care we would expect for our own families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
ICD SUPPORT GROUP IRELAND
 www.irishheart.ie ICD SUPPORT GROUP IRELAND The ICD Support Group This is a voluntary group of people, all of whom have ICDs. It was set up in association with the Irish Heart Foundation to help people
www.irishheart.ie ICD SUPPORT GROUP IRELAND The ICD Support Group This is a voluntary group of people, all of whom have ICDs. It was set up in association with the Irish Heart Foundation to help people
RESTORE YOUR RHYTHM. Atrial Fibrillation Information and Treatment Options. To make an appointment, call
 RESTORE YOUR RHYTHM Atrial Fibrillation Information and Treatment Options To make an appointment, call 1-866-847-7194. Managing your AFib? We can help you. Atrial fibrillation is the most common abnormal
RESTORE YOUR RHYTHM Atrial Fibrillation Information and Treatment Options To make an appointment, call 1-866-847-7194. Managing your AFib? We can help you. Atrial fibrillation is the most common abnormal
Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of
Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of
AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 www.irishheart.ie AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Registered charity number CHY 5507 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation This booklet is one of the publications
www.irishheart.ie AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Registered charity number CHY 5507 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation This booklet is one of the publications
X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary Introduction A pacemaker is a device that regulates the heart beat. More than half a million Americans use a pacemaker. If your doctor recommends that you have a pacemaker,
X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary Introduction A pacemaker is a device that regulates the heart beat. More than half a million Americans use a pacemaker. If your doctor recommends that you have a pacemaker,
INFORMATION. Atrial Fibrillation. Summary. Information from the
 1. Information from the For more information contact Heartline 1300 362 787 or www.heartfoundation.com.au Atrial Fibrillation INFORMATION Summary What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is
1. Information from the For more information contact Heartline 1300 362 787 or www.heartfoundation.com.au Atrial Fibrillation INFORMATION Summary What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is
The HeartCheck TM PEN Handheld ECG Is your heartbeat slow, fast, or irregular? Are you at risk? Put your heart health in your own hands
 The HeartCheck TM PEN Handheld ECG Is your heartbeat slow, fast, or irregular? our hands Are you at risk? Put your heart health in your own hands The first FDA-Cleared device that can be unlocked to allow
The HeartCheck TM PEN Handheld ECG Is your heartbeat slow, fast, or irregular? our hands Are you at risk? Put your heart health in your own hands The first FDA-Cleared device that can be unlocked to allow
Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients
 be informed about... Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an abnormal heart rhythm. This pamphlet answers some questions you may have about AF, and gives an overview
be informed about... Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an abnormal heart rhythm. This pamphlet answers some questions you may have about AF, and gives an overview
Case-Based Practical ECG Interpretation for the Generalist
 Case-Based Practical ECG Interpretation for the Generalist Paul D. Varosy, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHRS Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology VA Eastern Colorado Health Care System Associate Professor of Medicine
Case-Based Practical ECG Interpretation for the Generalist Paul D. Varosy, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHRS Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology VA Eastern Colorado Health Care System Associate Professor of Medicine
Paramedic Rounds. Tachyarrhythmia's. Sean Sutton Dallas Wood
 Paramedic Rounds Tachyarrhythmia's Sean Sutton Dallas Wood Objectives At the end of this session, the paramedic will be able to: State the key components of the cardiac conduction pathway, along with the
Paramedic Rounds Tachyarrhythmia's Sean Sutton Dallas Wood Objectives At the end of this session, the paramedic will be able to: State the key components of the cardiac conduction pathway, along with the
EKG Abnormalities. Adapted from:
 EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
Atrial Fibrillaton. Key: RA: right atrium RV: right ventricle PA: pulmonic artery LA: left atrium LV: left ventricle AO: aorta
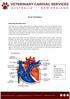 Atrial Fibrillaton How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Atrial Fibrillaton How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material
 1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
Cardiac Cycle. Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time.
 The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
