1 Access Sites of Percutaneous Procedures
|
|
|
- Milton Potter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Access Sites of Percutaneous Procedures In 1929, Werner Forssman performed the first human cardiac catheterisation by passing a urethral catheter from his left antecubital vein into the right side of his heart (10). Cardiac catheterisation has evolved since then and nowadays is used in a variety of procedures that vary from investigative tests such as angiograms to interventions such as coronary angioplasty and atrial septal defect repairs, thus reducing the need for cardiac surgery (11). These can be referred to as percutaneous coronary procedures, as the heart is accessed by inserting a catheter through the skin into an artery and/or vein, and threading it up to the heart. Access to the arterial system may be via the femoral, brachial or radial artery (5). ADVANTAGES OF PERCUTANEOUS ACCESS The majority of percutaneous coronary investigations and interventions are performed under local anaesthetic, as patients may be asked to cough, hold their breath or move their position during the procedure. Using a local anaesthetic also has the advantage of avoiding the risks associated with general anaesthesia (11). The other advantages that percutaneous coronary procedures offer over cardiac surgery include: Patients are less anxious waiting for a percutaneous procedure than for a surgical procedure (8). A cardiopulmonary bypass machine, if required, and its inherent risks are avoided (8). The hospital stay is shorter. For example, patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) normally stay in hospital for hours, whereas patients undergoing a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) require a stay of 3 7 days (8). Barring complications, the average cost of percutaneous coronary procedures is substantially lower than that of surgery (8). Patients are able to resume their normal life sooner after percutaneous procedures. For example, patients can usually return to work within 7 10 days after a PCI, whereas patients undergoing a CABG return to work within 6 weeks (8). COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
2 2 CARING FOR CARDIAC INTERVENTION PATIENTS Brachial artery Femoral artery Figure 1.1. Introducing a catheter into the brachial or femoral artery. If a patient has a clotting disorder or has recently had thrombolysis, they can be treated in an emergency with PCI (1). SELECTING THE ARTERIAL PUNCTURE The access site is selected by the cardiologist prior to the procedure; however, the femoral artery is the preferred access site to the arterial system for the majority of percutaneous procedures (see Figure 1.1). Although the brachial and radial arteries may be preferred by some cardiologists, they are mainly used if the femoral artery is unavailable, due to peripheral vascular disease, for example, or if the patient is unable to lie flat on their back during the procedure, such as patients with severe heart failure, who would normally sleep with three or four pillows (9). The brachial and radial arteries are smaller than the femoral artery and carry a higher risk of dissection and occlusion. Percutaneous puncture of the brachial artery is more likely to require surgical repair than percutaneous femoral puncture. In addition to this, brachial arteriotomy under direct vision can be technically challenging for the inexperienced operator and is time-consuming (9). Percutaneous radial artery puncture appears safe, but it results in occlusion of the radial artery in around 5% of cases. Although, in such cases, the blood to the hand would be supplied by the ulnar artery, the occluded radial artery would not be available for a CABG surgery if the patient required one in the future (9).
3 ACCESS SITES OF PERCUTANEOUS PROCEDURES 3 FEMORAL ACCESS The most common vascular access site is the femoral artery. It can also be referred to as the Judkin s approach (7). The selected femoral artery is shaved of groin hair in order to reduce infection risk and then the area is liberally cleaned with antiseptic solution (8). Then, a local anaesthetic such as lignocaine is slowly injected into the inguinal area of the groin, as a slow injection of the local anaesthetic is less painful for the patient and produces better tissue infiltration (2). Once the femoral area is anaesthetised, the cardiologist punctures the femoral artery percutaneously by inserting a large cannula containing a removable obturator. The presence of blood flow once the obturator is removed confirms that this cannula is within the lumen of the artery. Once proper placement is established, a guidewire is introduced through the cannula into the artery to the level of the diaphragm. The cannula is then removed and replaced by a valved introducer sheath (known as a femoral sheath) (8). The patient may feel some pushing and tugging at this time. This introducer sheath provides haemostasis and support at the puncture site and reduces potential arterial trauma if multiple catheter exchanges are necessary (8). The femoral vein is accessed in a similar manner if it is required. Venous access is mainly used during electrophysiological studies (EPS) and radio-frequency ablation (RFA). Venous access for temporary pacing is no longer routine during PCI; however, it should be considered for high-risk patients, such as those with acute myocardial infarction (MI) or left bundle branch block needing right coronary artery PCI, or if a rotoblator or thrombus aspiration device is required (6). REMOVING A FEMORAL SHEATH There are several methods of obtaining haemostasis in the femoral puncture site post sheath removal. Closure devices, such as AngioSeal, VasoSeal, Duett and Perclose, allow the removal of the femoral sheath at the end of the procedure, no matter what the anticoagulation status is (9). However, the majority of centres still rely on the compression of the femoral artery using either manual or mechanical compression, or a combination (4). This means that the femoral sheath is usually removed 3 4 hours after the procedure if heparin has been used, such as during PCI (8). As femoral sheaths are usually removed on the ward by nursing staff, it is discussed in more detail in Chapter 2. RADIAL ACCESS The radial artery approach was developed as an alternative to the percutaneous transbrachial approach in an attempt to limit vascular complications. The inherent advantages of the transradial approach are that the hand has a dual arterial supply
4 4 CARING FOR CARDIAC INTERVENTION PATIENTS Palmar arch Ulnar artery Radial artery Figure 1.2. Radial artery anatomy and collateral circulation. connected via the palmar arches and that there are no nerves or veins at the site of puncture (3). The location of the radial artery enables easy access in most people, and it is easier to control bleeding (see Figure 1.2). In addition, prolonged bed rest is unnecessary after the procedure (6). Although using the radial approach is associated with fewer severe access siterelated bleeding complications than the femoral approach, the sheath sizes are smaller. They are usually limited to size 6 or 7 French, and therefore would not be suitable for cases in which larger catheters are required, such as valvuloplasty or rotablation (7). Unfortunately, the radial artery has a propensity to develop spasm, which may make catheter movement difficult or impossible. This can be overcome by the use of vasodilators and long introducer sheaths when appropriate (6). In addition, radial access is only suitable for left-sided heart catheterisation; another approach would be required if the right side of the heart required catheterisation as well (3). Prior to a radial procedure, the clinician must complete an Allen s test to assess the ulnar artery in the arm to be proceeded on. First, the radial and ulnar arteries are occluded simultaneously while the patient makes a fist. Then, when the hand is opened, it appears blanched. The ulnar artery is released and the hand colour should return within 8 10 seconds. Satisfactory ulnar flow can also be documented by pulse oximetry (6). In order to insert the catheter into the radial artery, the selected arm is abducted at a 70 angle on an arm board, and the wrist hyperextended over a gauze roll. It is cleaned liberally with antiseptic. A topical anaesthetic is applied first, as
5 ACCESS SITES OF PERCUTANEOUS PROCEDURES 5 it reduces the amount of lignocaine needed for local infiltration over the radial pulse. Large amounts of lignocaine may obscure the pulse and make cannulation more difficult (6). A small incision is made and an 18-gauge needle is introduced at a 45 angle into the radial artery. A guidewire is inserted first and then a valved introducer sheath. Haemostasis is obtained at the end of the procedure after sheath removal using direct pressure. It is recommended that the arterial puncture site be allowed to bleed for several beats before maintaining direct pressure. The radial pulse should be monitored regularly for several hours after the procedure (3). SHEATH REMOVAL AND POST-PROCEDURE CARE Before the sheath is removed, 1 mg of verapamil is given through the sheath to minimise spasm of the radial artery (6). Although haemostasis can be achieved by applying direct manual pressure over the puncture site, there are several radial haemostat devices available on the market, and their guidelines should be followed. The following is a description of one such device. A plastic bracelet with a pressure pad is placed around the wrist. Gauze is wrapped around the plastic strip to prevent skin injury when the bracelet is tightened. Another folded piece of gauze is placed under the pressure pad over the sheath insertion site. While the operator presses the pad over the puncture site, the sheath is withdrawn gently and the bracelet is tightened. The pad is pressed down and locked over the puncture by tightening of the bracelet bracket. The bracelet should be tight enough to ensure haemostasis but not occlude flow to the hand. The patient is checked 1 2 hours later, and the bracelet is loosened. The patient can be discharged 2 hours later and the bracelet removed at home. The patient should be given instructions about puncture site compression with the fingers if later bleeding occurs (6). BRACHIAL ACCESS There are two methods of obtaining brachial access, but they should be reserved for patients in whom the radial artery cannot be used (6). PERCUTANEOUS BRACHIAL ARTERY PUNCTURE Percutaneous arterial puncture is a safe and effective alternative to brachial artery cut-down, and is normally favoured over the brachial artery cut-down. Although it is similar to femoral arterial puncture, there are several important differences: 1. The brachial artery is smaller (3 5 mm in diameter) than the femoral artery. 2. Because of relatively loose subcutaneous tissues, the course of the brachial artery may change considerably. 3. Spasm can occur easily, with considerable decrease in pulse amplitude, making the puncture more difficult.
6 6 CARING FOR CARDIAC INTERVENTION PATIENTS 4. The artery is more mobile than the femoral artery. 5. The median nerve lies very close to the artery. Accidental touching of the median nerve causes a peculiar electrical shock sensation in the hand. 6. Care should be taken to puncture the artery on the first attempt. Because of the smaller space in the arm, uncontrolled haematoma formation here can readily cause compression syndrome with ischaemia of the forearm and hand (6). The brachial artery can accommodate up to size 8 French sheath in large men. However, in most patients, especially smaller men and women, smaller sheaths (less than or equal to 6 French) are preferred (6). The brachial and radial pulses should be checked prior to attempting a brachial puncture. They should be strong and equal in both arms. The patency of the ulnar artery should be checked by the Allen s test (6). The arterial sheath is removed at the end of the procedure and haemostasis is achieved by applying minutes of manual pressure until the bleeding has stopped. The arm circumference at the site of the puncture should be measured to facilitate the detection of haematoma formation. The patient should be instructed to keep the arm in a relaxed position for 4 6 hours. Although the patient is allowed to sit up in bed, ambulation should be restricted until these 4 6 hours are completed, to ensure haemostasis (6). BRACHIAL CUT-DOWN/SONES PROCEDURE The brachial cut-down procedure is also known as the Sones procedure. This procedure is rarely performed nowadays, as radial access or brachial puncture is favoured over it. Unlike the other procedures, this is not a percutaneous procedure. Once the brachial area is anaesthetised, the brachial artery is accessed by making an incision close to the crease in the elbow. The selected artery is brought to the surface and is used to insert the appropriate catheters for the procedure. Once the procedure is completed, the artery is sutured to prevent bleeding, and then the incision is sutured. If non-absorbable sutures are used on the incision, they will need to be removed in 7 10 days. The wound should be covered with a firm dressing (2). There is no need for the patient to be kept flat or motionless following a brachial cut-down procedure. They may sit up, eat and mobilise to the bathroom. If the patient has a strong radial pulse, they can be discharged home after 4 6 hours observation (2). REFERENCES 1. Al-Obaidi, M., Noble, M. and Siva, A. (2004) Crash Course Cardiology, 2nd edn, London, Mosby. 2. Baim, D. S. (2006) Grossman s Cardiac Catheterisation: Angiography and Intervention, 7th edn, Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
7 ACCESS SITES OF PERCUTANEOUS PROCEDURES 7 3. Braunweld, E., Zipes, D. and Libby, P. (2001) Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine, Vol. 1, 6th edn, London, W.B. Saunders Co. 4. Galli, G. (2005) Ask the experts: Re removing arterial and venous sheaths after PCI, Critical Care Nurse, available online at 5. Julian, D. G., Cowan, J. C. and McLenachan, J. M. (2005) Cardiology, 8th edn, London, Elsevier Saunders. 6. Kern, M. (2003) The Cardiac Catheterisation Handbook, 4th edn, London, Mosby. 7. Montalsecot, G., Andersen, H., Antoniucer, D., Betriu, A., de Boer, M., Grip, L., et al. (2004) Recommendations on percutaneous coronary intervention for the reperfusion of acute ST elevation myocardial infarction, Heart, 90, available online at 8. Morton, P. G., Fontaine, D. K., Hudak, C. M. and Gallo, B. M. (2005) Critical Care Nursing: A Holistic Approach, 8th edn, Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 9. Norell, M. and Perrins, J. (2003) Essential Interventional Cardiology, Philadelphia, PA, W.B. Saunders Co. 10. Rosendorff, C. (2005) Essential Cardiology: Principles and Practice, 2nd edn, Totowa, New Jersey, Humana Press. 11. Swanton, R. H. (2003) Pocket Consultant Cardiology, 5th edn, Oxford, Blackwell Publishing.
8
Cardiac Catheterization
 Cardiac Catheterization What is cardiac catheterization? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat cardiovascular conditions. During cardiac catheterization, a long thin tube called
Cardiac Catheterization What is cardiac catheterization? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat cardiovascular conditions. During cardiac catheterization, a long thin tube called
Parkland Health & Hospital System Women & Infant Specialty Health
 Parkland Health & Hospital System Women & Infant Specialty Health NS 1700.04 Nursery Services Procedure Manual Arterial Puncture Practice Statement Upon the written order of the provider, the credentialled
Parkland Health & Hospital System Women & Infant Specialty Health NS 1700.04 Nursery Services Procedure Manual Arterial Puncture Practice Statement Upon the written order of the provider, the credentialled
Cardiac Catheterisation and Balloon Coronary Angioplasty
 Cardiac Catheterisation and Balloon Coronary Angioplasty Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Cardiac Catheterisation This process is known as Angiography or Angiogram. It is a test performed under
Cardiac Catheterisation and Balloon Coronary Angioplasty Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Cardiac Catheterisation This process is known as Angiography or Angiogram. It is a test performed under
Cheltenham General Hospital
 Page 1 of 5 Coronary angioplasty Introduction This leaflet provides information for patients undergoing coronary angioplasty also known as PCI (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention). What is coronary artery
Page 1 of 5 Coronary angioplasty Introduction This leaflet provides information for patients undergoing coronary angioplasty also known as PCI (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention). What is coronary artery
Percutaneous coronary intervention (angioplasty) +/- rotablation
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label Why do I need this procedure? If you are coming into hospital for a cardiac procedure
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label Why do I need this procedure? If you are coming into hospital for a cardiac procedure
This leaflet is available in other formats including large print, audio tape, CD and braille, and in languages other than English, upon request.
 Information for inpatients This leaflet is available in other formats including large print, audio tape, CD and braille, and in languages other than English, upon request. Med/304.1 (2012) Page 1 of 8
Information for inpatients This leaflet is available in other formats including large print, audio tape, CD and braille, and in languages other than English, upon request. Med/304.1 (2012) Page 1 of 8
Arterial Line Insertion Pre Reading
 PROCEDURE ACCREDITATION THE CANBERRA HOSPITAL EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT Arterial Line Insertion Pre Reading Indications Requirement for continuous blood pressure monitoring (all patients on pressors, inotropes,
PROCEDURE ACCREDITATION THE CANBERRA HOSPITAL EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT Arterial Line Insertion Pre Reading Indications Requirement for continuous blood pressure monitoring (all patients on pressors, inotropes,
What to expect when having an angiogram
 What to expect when having an angiogram Cardiology Department Patient information leaflet What is coronary artery disease? Coronary artery disease is the narrowing of one or more of the blood vessels that
What to expect when having an angiogram Cardiology Department Patient information leaflet What is coronary artery disease? Coronary artery disease is the narrowing of one or more of the blood vessels that
Vascular Access: Management of Complications. Chris Burrell, South West Cardiothoracic Centre, Plymouth
 Vascular Access: Management of Complications Chris Burrell, South West Cardiothoracic Centre, Plymouth Alternative Vascular Access Sites Femoral Axillary Brachial Radial Ulnar Femoral v Radial Vascular
Vascular Access: Management of Complications Chris Burrell, South West Cardiothoracic Centre, Plymouth Alternative Vascular Access Sites Femoral Axillary Brachial Radial Ulnar Femoral v Radial Vascular
Transradial Artery Approach for Coronary Intervention: Maharat Nakhonratchasima Hospital Experience of The First 20 Cases
 Transradial Artery Approach for Coronary Intervention: Maharat Nakhonratchasima Hospital Experience of The First 20 Cases Pinij Kaewsuwanna M.D. Tongprakob Siriwanij M.D. Cardiovascular Disease Center,
Transradial Artery Approach for Coronary Intervention: Maharat Nakhonratchasima Hospital Experience of The First 20 Cases Pinij Kaewsuwanna M.D. Tongprakob Siriwanij M.D. Cardiovascular Disease Center,
Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
 Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Your doctor has recommended
Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Your doctor has recommended
Cath Lab Essentials : Transradial Cardiac Catheterization
 Cath Lab Essentials : Transradial Cardiac Catheterization Pranav M. Patel, MD, FACC, FSCAI Interim Chief, Division of Cardiology Director, Cardiac Catheterization Lab Associate Professor of Medicine University
Cath Lab Essentials : Transradial Cardiac Catheterization Pranav M. Patel, MD, FACC, FSCAI Interim Chief, Division of Cardiology Director, Cardiac Catheterization Lab Associate Professor of Medicine University
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Procedure (TAVI)
 Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
ANGIOPLASTY SUMMIT 2004 Seoul, South Korea APRIL 29-MAY 2, 2004
 ANGIOPLASTY SUMMIT 2004 Seoul, South Korea APRIL 29-MAY 2, 2004 RESULTS OF STUDIES COMPARING TRANSRADIAL AND FEMORAL ANGIOGRAPHY HOWARD A. COHEN, M.D. UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH MEDICAL CENTER PRESBYTERIAN
ANGIOPLASTY SUMMIT 2004 Seoul, South Korea APRIL 29-MAY 2, 2004 RESULTS OF STUDIES COMPARING TRANSRADIAL AND FEMORAL ANGIOGRAPHY HOWARD A. COHEN, M.D. UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH MEDICAL CENTER PRESBYTERIAN
Percutaneous coronary intervention. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Percutaneous coronary intervention Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the
Percutaneous coronary intervention Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the
Transradial Complications How to predict/prevent and treat
 Transradial Complications How to predict/prevent and treat David Kettles St Dominic s Private and Frere hospitals East London, South Africa Are all complications preventable? NO! Distal embolisation Vessel
Transradial Complications How to predict/prevent and treat David Kettles St Dominic s Private and Frere hospitals East London, South Africa Are all complications preventable? NO! Distal embolisation Vessel
Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures
 Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed after you
Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed after you
1 Description. 2 Indications. 3 Warnings ASPIRATION CATHETER
 Page 1 of 5 ASPIRATION CATHETER Carefully read all instructions prior to use, observe all warnings and precautions noted throughout these instructions. Failure to do so may result in complications. STERILE.
Page 1 of 5 ASPIRATION CATHETER Carefully read all instructions prior to use, observe all warnings and precautions noted throughout these instructions. Failure to do so may result in complications. STERILE.
Central Venous Line Insertion
 Central Venous Line Insertion Understand the indications and risks of CVC insertion Understand and troubleshoot the seldinger technique Understand available sites and select the appropriate site for clinical
Central Venous Line Insertion Understand the indications and risks of CVC insertion Understand and troubleshoot the seldinger technique Understand available sites and select the appropriate site for clinical
Angiogram, angioplasty and stenting
 Angiogram, angioplasty and stenting Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet is for people who are having: an angiogram angioplasty (with or without a stent) An angiogram (also called an arteriogram or angiography)
Angiogram, angioplasty and stenting Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet is for people who are having: an angiogram angioplasty (with or without a stent) An angiogram (also called an arteriogram or angiography)
Golden Jubilee National Hospital Cardiac catheterisation or coronary angioplasty/stenting
 Golden Jubilee National Hospital NHS National Waiting Times Centre Cardiac catheterisation or coronary angioplasty/stenting Patient information guide Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000
Golden Jubilee National Hospital NHS National Waiting Times Centre Cardiac catheterisation or coronary angioplasty/stenting Patient information guide Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000
2. Need for serial arterial blood gas determinations. 2. Anticipation of the initiation of thrombolytic therapy
 I. Subject: Arterial Cannulation II. Policy: Arterial cannulation will be performed upon a physician's order by Cardiopulmonary and Respiratory Therapy personnel certified in the arterial catheterization
I. Subject: Arterial Cannulation II. Policy: Arterial cannulation will be performed upon a physician's order by Cardiopulmonary and Respiratory Therapy personnel certified in the arterial catheterization
Cath Conference Kintur Sanghvi MD March 15, 2007
 Cath Conference Kintur Sanghvi MD March 15, 2007 Case 1: 75 yr old female admitted with chest pain and abnormal stress test t Case 2: 70 yr F with typical exertional angina and HTN, dyslipidemia. Trans
Cath Conference Kintur Sanghvi MD March 15, 2007 Case 1: 75 yr old female admitted with chest pain and abnormal stress test t Case 2: 70 yr F with typical exertional angina and HTN, dyslipidemia. Trans
Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction
 Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) occurs as a result of prolonged myocardial ischemia Atherosclerosis leads to endothelial rupture or erosion that
Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) occurs as a result of prolonged myocardial ischemia Atherosclerosis leads to endothelial rupture or erosion that
Competency Title: Caring for a patient with an arterial line
 Appendix 2 Competency Title: Caring for a patient with an arterial line Aims and objectives Following completion of this competency document the practitioner will be able to: Discuss the indications for
Appendix 2 Competency Title: Caring for a patient with an arterial line Aims and objectives Following completion of this competency document the practitioner will be able to: Discuss the indications for
Electrophysiology Studies and Catheter Ablation. Electrophysiology Studies and Catheter Ablation
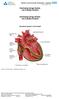 Electrophysiology Studies Cardiac Conduction System. Mdmedicine.wordpress.com Patient Information Leaflet for: Electrophysiology Studies Available via Trust Docs Version: 6 Trust Docs ID: 10 Page 1 of
Electrophysiology Studies Cardiac Conduction System. Mdmedicine.wordpress.com Patient Information Leaflet for: Electrophysiology Studies Available via Trust Docs Version: 6 Trust Docs ID: 10 Page 1 of
Arterial Access for Diagnosis and Intervention T-Woei Tan, MD, FACS
 Arterial Access for Diagnosis and Intervention T-Woei Tan, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Vascular Endovascular Surgery Louisiana State University Health - Shreveport Disclosures None Objective
Arterial Access for Diagnosis and Intervention T-Woei Tan, MD, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgery Vascular Endovascular Surgery Louisiana State University Health - Shreveport Disclosures None Objective
Radial Access and PAD Treatment. Janak Bhavsar, MD June 16, 2016
 Radial Access and PAD Treatment Janak Bhavsar, MD June 16, 2016 Disclosures No relevant disclosures No Actual or Potential Conflict of Interest in this Presentation Acknowledgements Terumo Medical Cook
Radial Access and PAD Treatment Janak Bhavsar, MD June 16, 2016 Disclosures No relevant disclosures No Actual or Potential Conflict of Interest in this Presentation Acknowledgements Terumo Medical Cook
Access Site Complications. Nick Cheshire MD FRCS, Professor of Vascular Surgery Imperial College Healthcare St Mary s Hospital Campus
 Access Site Complications Nick Cheshire MD FRCS, Professor of Vascular Surgery Imperial College Healthcare St Mary s Hospital Campus Surgeons & Cardiologists Interventional Cardiology 2008 Eye of a Hawk,
Access Site Complications Nick Cheshire MD FRCS, Professor of Vascular Surgery Imperial College Healthcare St Mary s Hospital Campus Surgeons & Cardiologists Interventional Cardiology 2008 Eye of a Hawk,
Chapter 14: Arterial Puncture Procedures
 Objectives Chapter 14: Arterial Puncture Procedures 1. Define the key terms and abbreviations listed at the beginning of this chapter. 2. State the primary reason for performing arterial punctures and
Objectives Chapter 14: Arterial Puncture Procedures 1. Define the key terms and abbreviations listed at the beginning of this chapter. 2. State the primary reason for performing arterial punctures and
Patient Information Coronary Angiogram
 Patient Information Coronary Angiogram Cardiac Suite Cardiology Department What is a coronary angiogram? A coronary angiogram is an invasive investigation to detect signs of heart disease, such as narrowing
Patient Information Coronary Angiogram Cardiac Suite Cardiology Department What is a coronary angiogram? A coronary angiogram is an invasive investigation to detect signs of heart disease, such as narrowing
Effective Date: Approved by: Laboratory Executive Director, Ed Hughes (electronic signature)
 1 Policy #: 407 (PLH-407-02) Effective Date: NA Reviewed Date: 2/1/2008 Subject: ARTERIAL PUNCTURE PROCEDURE Approved by: Laboratory Executive Director, Ed Hughes (electronic signature) Approved by: Laboratory
1 Policy #: 407 (PLH-407-02) Effective Date: NA Reviewed Date: 2/1/2008 Subject: ARTERIAL PUNCTURE PROCEDURE Approved by: Laboratory Executive Director, Ed Hughes (electronic signature) Approved by: Laboratory
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
 Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Information for patients and carers Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Information for patients and carers Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Booklet
 Aintree University Hospital FT PICC Booklet: a real world example This local booklet is an example used in the NICE medical technology guidance adoption support resource for SecurAcath for securing percutaneous
Aintree University Hospital FT PICC Booklet: a real world example This local booklet is an example used in the NICE medical technology guidance adoption support resource for SecurAcath for securing percutaneous
Radial Access Just another artery? Keith G Oldroyd Department of Cardiology Western Infirmary Glasgow
 Radial Access Just another artery? Keith G Oldroyd Department of Cardiology Western Infirmary Glasgow Brachial access Not just another artery! Femoral access Not just another artery! Incidence of femoral
Radial Access Just another artery? Keith G Oldroyd Department of Cardiology Western Infirmary Glasgow Brachial access Not just another artery! Femoral access Not just another artery! Incidence of femoral
Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures
 Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This booklet describes cardiac catheterization. It also details how to prepare for the procedure and the care needed after it is done. Before You
Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This booklet describes cardiac catheterization. It also details how to prepare for the procedure and the care needed after it is done. Before You
Coronary angiography and PCI
 Coronary arteries Coronary angiography and PCI Samo Granda, Franjo Naji Department of Cardiology Clinical department of internal medicine University clinical centre Maribor Coronary arteries Atherosclerosis
Coronary arteries Coronary angiography and PCI Samo Granda, Franjo Naji Department of Cardiology Clinical department of internal medicine University clinical centre Maribor Coronary arteries Atherosclerosis
St George Hospital Renal Department Internal Only
 RENAL VASCULAR ACCESS CANNULATION POLICY AND PROCEDURE SUMMARY: A functioning arteriovenous fistula (AVF) or arteriovenous graft (AVG) is paramount in the maintenance of regular and optimal haemodialysis
RENAL VASCULAR ACCESS CANNULATION POLICY AND PROCEDURE SUMMARY: A functioning arteriovenous fistula (AVF) or arteriovenous graft (AVG) is paramount in the maintenance of regular and optimal haemodialysis
Coronary angioplasty and stents
 Tests and Procedures Coronary angioplasty and stents By Mayo Clinic Staff Coronary angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee), also called percutaneous coronary intervention, is a procedure used to open clogged heart
Tests and Procedures Coronary angioplasty and stents By Mayo Clinic Staff Coronary angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee), also called percutaneous coronary intervention, is a procedure used to open clogged heart
Tips for Successful Venipuncture
 Page 1 of 5 Patient Positioning Have patient lie or sit down. Never draw blood on a patient who is standing. Make the patient as comfortable as you possibly can. Always watch and ask patient if he/she
Page 1 of 5 Patient Positioning Have patient lie or sit down. Never draw blood on a patient who is standing. Make the patient as comfortable as you possibly can. Always watch and ask patient if he/she
Closing your atrial septal defect without surgery
 Patient information service Bristol Heart Institute Closing your atrial septal defect without surgery Respecting everyone Embracing change Recognising success Working together Our hospitals. What is an
Patient information service Bristol Heart Institute Closing your atrial septal defect without surgery Respecting everyone Embracing change Recognising success Working together Our hospitals. What is an
A guide to coronary angiography and angioplasty
 A guide to coronary angiography and angioplasty Welcome Contents If you have this booklet then, like many other New Zealanders, heart disease has touched your life. Whether it is you or a loved one who
A guide to coronary angiography and angioplasty Welcome Contents If you have this booklet then, like many other New Zealanders, heart disease has touched your life. Whether it is you or a loved one who
Curtiss T. Stinis, M.D., F.A.C.C., F.S.C.A.I. SCRIPPS CLINIC
 Avoiding and Managing Femoral Access Site Complications Curtiss T. Stinis, M.D., F.A.C.C., F.S.C.A.I. Director, Peripheral Interventions Program Director, Interventional Cardiology Fellowship Division
Avoiding and Managing Femoral Access Site Complications Curtiss T. Stinis, M.D., F.A.C.C., F.S.C.A.I. Director, Peripheral Interventions Program Director, Interventional Cardiology Fellowship Division
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hemorrhage Control. Chapter 6
 Chapter 6 The hemorrhage that take[s] place when a main artery is divided is usually so rapid and so copious that the wounded man dies before help can reach him. Colonel H. M. Gray, 1919 Stop the Bleeding!
Chapter 6 The hemorrhage that take[s] place when a main artery is divided is usually so rapid and so copious that the wounded man dies before help can reach him. Colonel H. M. Gray, 1919 Stop the Bleeding!
Section 6 Intra Aortic Balloon Pump
 Section 6 Intra Aortic Balloon Pump The Intra Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP) The balloon is synthetic and is made for single use only. It is threaded into the aorta, usually via a femoral approach. The balloon
Section 6 Intra Aortic Balloon Pump The Intra Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP) The balloon is synthetic and is made for single use only. It is threaded into the aorta, usually via a femoral approach. The balloon
Insertion of a totally implantable vascular access device (TIVAD)
 Insertion of a totally implantable vascular access device (TIVAD) What is a TIVAD? A TIVAD is a long hollow tube that is inserted into one of the large veins in your body. One end of the tube sits in a
Insertion of a totally implantable vascular access device (TIVAD) What is a TIVAD? A TIVAD is a long hollow tube that is inserted into one of the large veins in your body. One end of the tube sits in a
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Treatment for blocked heart arteries DRAFT. What are arteries? How do heart arteries become blocked?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Complex Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Treatment for blocked heart arteries This handout explains complex percutaneous intervention (PCI) treatment of a coronary
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Complex Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Treatment for blocked heart arteries This handout explains complex percutaneous intervention (PCI) treatment of a coronary
Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
SELF-ASSESSMENT- RSPT 2350 Module B: ABG Technique 1. What % of the population will have ABG results that fall outside of the normal range?
 1. What % of the population will have ABG results that fall outside of the normal range? 5% 2. Name four factors that affect oxygenation A. Age B. Barometric Pressure/Altitude C. FiO 2 D. Body Position
1. What % of the population will have ABG results that fall outside of the normal range? 5% 2. Name four factors that affect oxygenation A. Age B. Barometric Pressure/Altitude C. FiO 2 D. Body Position
Peripheral and Cardiology Coder 2018
 Peripheral and Cardiology Coder 2018 Cardiovascular Services and Procedures Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing A Division of MedLearn Media, Inc. 445 Minnesota Street, Suite 514 St. Paul, MN
Peripheral and Cardiology Coder 2018 Cardiovascular Services and Procedures Prepared and Published By: MedLearn Publishing A Division of MedLearn Media, Inc. 445 Minnesota Street, Suite 514 St. Paul, MN
Home Health Foundation, Inc. To create more permanent IV access for patients undergoing long term IV therapy.
 PROCEDURE ORIGINAL DATE: 06/99 Revised Date: 09/02 Home Health Foundation, Inc. SUBJECT: PURPOSE: MIDLINE CATHETER INSERTION To create more permanent IV access for patients undergoing long term IV therapy.
PROCEDURE ORIGINAL DATE: 06/99 Revised Date: 09/02 Home Health Foundation, Inc. SUBJECT: PURPOSE: MIDLINE CATHETER INSERTION To create more permanent IV access for patients undergoing long term IV therapy.
Άγγελος Παπανικολάου MD, Ειδικευόμενος Καρδιολογίας, A Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική, ΓΝΑ Ιπποκράτειο
 Άγγελος Παπανικολάου MD, Ειδικευόμενος Καρδιολογίας, A Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική, ΓΝΑ Ιπποκράτειο Endovascular access & closure Seldinger SI. Catheter replacement of the needle in percutaneous
Άγγελος Παπανικολάου MD, Ειδικευόμενος Καρδιολογίας, A Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική, ΓΝΑ Ιπποκράτειο Endovascular access & closure Seldinger SI. Catheter replacement of the needle in percutaneous
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement
 Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Ambulatory Services Orientation & Skill Review Skill Performance Checklist: Vital Signs. Name: Date:
 Evaluation Levels Behavior Level 3 Met Performed all skills competently. No behaviors omitted. Level 2 Satisfactory Omitted no more than three (3) non-critical behaviors. Level 1 Unsatisfactory Omitted
Evaluation Levels Behavior Level 3 Met Performed all skills competently. No behaviors omitted. Level 2 Satisfactory Omitted no more than three (3) non-critical behaviors. Level 1 Unsatisfactory Omitted
Arch Angiography. Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered
 Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This leaflet has been prepared to tell you about arch angiography. It will explain what will happen during this procedure and we hope that it will answer some
Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered This leaflet has been prepared to tell you about arch angiography. It will explain what will happen during this procedure and we hope that it will answer some
CRT Implantation Techniques 부천세종병원순환기내과박상원
 Cardiac Venous System and CRT Implantation Techniques 부천세종병원순환기내과박상원 Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) Goal: Atrial synchronous biventricular pacing Transvenous approach for left ventricular lead
Cardiac Venous System and CRT Implantation Techniques 부천세종병원순환기내과박상원 Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) Goal: Atrial synchronous biventricular pacing Transvenous approach for left ventricular lead
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients
 Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Vascular Access Safety Training: The VAST Agenda
 Vascular Access Safety Training: The VAST Agenda Mitchell W. Krucoff MD, FACC Professor of Medicine / Cardiology Duke University Medical Center Director, Cardiovascular Devices Unit Duke Clinical Research
Vascular Access Safety Training: The VAST Agenda Mitchell W. Krucoff MD, FACC Professor of Medicine / Cardiology Duke University Medical Center Director, Cardiovascular Devices Unit Duke Clinical Research
All about your anaesthetic
 Patient information leaflet All about your anaesthetic Regional anaesthesia 4 and associated risks For patients having a surgical procedure at a Care UK independent diagnostic and treatment entre This
Patient information leaflet All about your anaesthetic Regional anaesthesia 4 and associated risks For patients having a surgical procedure at a Care UK independent diagnostic and treatment entre This
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21543 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dharma, Surya Title: Perspectives in the treatment of cardiovascular disease :
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21543 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dharma, Surya Title: Perspectives in the treatment of cardiovascular disease :
CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY
 CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY What is Coronary Angioplasty? Coronary angioplasty is a procedure to remove the obstruction caused by plaque or fatty build up on the inner walls of the arteries to your heart. It
CORONARY ANGIOPLASTY What is Coronary Angioplasty? Coronary angioplasty is a procedure to remove the obstruction caused by plaque or fatty build up on the inner walls of the arteries to your heart. It
Information for patients, parents and guardians. Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation.
 Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Your Angiogram/ Angioplasty and Stenting
 Your Angiogram/ Angioplasty and Stenting Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Your Angiogram/ Angioplasty and Stenting Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING
 ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
TRANSRADIAL CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION. Amanda Ryan, DO, Interventional Cardiologist Heart Care Centers of Florida April 13, 2013
 TRANSRADIAL CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION Amanda Ryan, DO, Interventional Cardiologist Heart Care Centers of Florida April 13, 2013 TOPICS Historical perspective and current trends Rationale Bleeding for the
TRANSRADIAL CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION Amanda Ryan, DO, Interventional Cardiologist Heart Care Centers of Florida April 13, 2013 TOPICS Historical perspective and current trends Rationale Bleeding for the
Coming in for angioplasty and stent. Information and advice for patients Jim Shahi Unit Tel:
 Coming in for angioplasty and stent Information and advice for patients Jim Shahi Unit Tel: 0118 322 6502 This booklet has been produced by the staff to help answer some of the questions you may have about
Coming in for angioplasty and stent Information and advice for patients Jim Shahi Unit Tel: 0118 322 6502 This booklet has been produced by the staff to help answer some of the questions you may have about
Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE)
 Service: Imaging Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions The team delivering your healthcare want to encourage you to become as involved as possible
Service: Imaging Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions The team delivering your healthcare want to encourage you to become as involved as possible
Spinal anaesthesia for hip and knee joint replacement surgery. Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet
 Spinal anaesthesia for hip and knee joint replacement surgery Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Spinal anaesthesia for hip and knee joint replacement surgery For many operations patients
Spinal anaesthesia for hip and knee joint replacement surgery Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Spinal anaesthesia for hip and knee joint replacement surgery For many operations patients
Cardiology. Renal Denervation
 Cardiology Renal Denervation Cardiology services are provided in the Specialist Outpatient Clinic, Emergency Department, Intensive Care Unit and as an inpatient service. A full spectrum of care is provided
Cardiology Renal Denervation Cardiology services are provided in the Specialist Outpatient Clinic, Emergency Department, Intensive Care Unit and as an inpatient service. A full spectrum of care is provided
Graft for Hemodialysis
 St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Kidney and Urinary Program Graft for Hemodialysis What is a graft? A graft is a man-made tube that joins an artery and a vein in your arm. The graft is called an access.
St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Kidney and Urinary Program Graft for Hemodialysis What is a graft? A graft is a man-made tube that joins an artery and a vein in your arm. The graft is called an access.
Overview of Trasradial Approach for Coronary Angiography and Intervention. A/Prof. Phạm Mạnh Hùng, MD.FACC., FESC
 Overview of Trasradial Approach for Coronary Angiography and Intervention A/Prof. Phạm Mạnh Hùng, MD.FACC., FESC Outline Historical perspective and current trends Rationale for the radial approach Bleeding
Overview of Trasradial Approach for Coronary Angiography and Intervention A/Prof. Phạm Mạnh Hùng, MD.FACC., FESC Outline Historical perspective and current trends Rationale for the radial approach Bleeding
Heart catheterization for adults with congenital heart disease
 Heart catheterization for adults with congenital heart disease What is a heart catheterization? It is a procedure that provides details about your heart function and circulation. It helps your doctor make
Heart catheterization for adults with congenital heart disease What is a heart catheterization? It is a procedure that provides details about your heart function and circulation. It helps your doctor make
Research Article Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Radial Artery Cannulation with Conventional Palpation Technique
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ANAESTHESIA Research Article Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Radial Artery Cannulation with Conventional Palpation Technique Amna 1 *, Saira Mehboob 2, Waqas Alam 3, Amna Gulraze 4
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ANAESTHESIA Research Article Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Radial Artery Cannulation with Conventional Palpation Technique Amna 1 *, Saira Mehboob 2, Waqas Alam 3, Amna Gulraze 4
Fistula for Hemodialysis
 St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Kidney and Urinary Program Fistula for Hemodialysis What is a fistula? A fistula is the joining of an artery and a vein by a surgeon. The fistula is called an access. It
St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Kidney and Urinary Program Fistula for Hemodialysis What is a fistula? A fistula is the joining of an artery and a vein by a surgeon. The fistula is called an access. It
RadRx Your Prescription for Accurate Coding & Reimbursement Copyright All Rights Reserved.
 Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of June 4, 2018 Thrombolysis, Thrombectomy & Angioplasty
Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of June 4, 2018 Thrombolysis, Thrombectomy & Angioplasty
Arterial Puncture. Purpose. Scope. Audience. Physician's Orders Indications Contraindications. Goals
 PROCEDURE - Page 1 of 5 Purpose Scope Audience Physician's Orders Indications Contraindications Goals Arterial blood gas sampling by puncture is accomplished by aseptic technique with a needle and heparinized
PROCEDURE - Page 1 of 5 Purpose Scope Audience Physician's Orders Indications Contraindications Goals Arterial blood gas sampling by puncture is accomplished by aseptic technique with a needle and heparinized
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Table S1. Patient Selection Codes, CIED Generator Procedures Code Type Code Description ICD9 Proc 00.51 Implantation of cardiac resynchronization defibrillator, total system [CRT-D]
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Table S1. Patient Selection Codes, CIED Generator Procedures Code Type Code Description ICD9 Proc 00.51 Implantation of cardiac resynchronization defibrillator, total system [CRT-D]
Trans-catheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) work up
 Trans-catheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) work up You have been referred for an assessment known as a TAVI work up because you have been diagnosed with aortic stenosis. This factsheet explains the
Trans-catheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) work up You have been referred for an assessment known as a TAVI work up because you have been diagnosed with aortic stenosis. This factsheet explains the
Collection of Blood Specimens. To provide instructions on correctly collecting blood specimens via vacutainer.
 Page 1 of 9 Purpose: To provide instructions on correctly collecting blood specimens via vacutainer. Equipment: Tourniquet-one time use only Vacutainer holder Sterile multi-specimen needle Gauze swab Appropriate
Page 1 of 9 Purpose: To provide instructions on correctly collecting blood specimens via vacutainer. Equipment: Tourniquet-one time use only Vacutainer holder Sterile multi-specimen needle Gauze swab Appropriate
Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy)
 Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy) Basic Information: The insertion and placement of a chest tube into the pleural cavity for the purpose of removing air, blood, purulent drainage, or
Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy) Basic Information: The insertion and placement of a chest tube into the pleural cavity for the purpose of removing air, blood, purulent drainage, or
AV ACESS COMPLICATIONS. Ass. Prof. Dr. Habas
 AV ACESS COMPLICATIONS Ass. Prof. Dr. Habas COMPLICATION AVF IS CONSIDERED A MINOR PROCEDURE INCIDENCE OF COMPLICATION- 20-27% MANY A COMPLICATION LEADS TO FAILURE OF FISTULA LOSS OF SITE AND VEIN FOR
AV ACESS COMPLICATIONS Ass. Prof. Dr. Habas COMPLICATION AVF IS CONSIDERED A MINOR PROCEDURE INCIDENCE OF COMPLICATION- 20-27% MANY A COMPLICATION LEADS TO FAILURE OF FISTULA LOSS OF SITE AND VEIN FOR
The variation of carotid origin, the divergent orientation of common carotid (frequent posterior and left to right direction of right common as
 1 Introduction The access to the common carotid during carotid stenting is very challenging and is responsible of a significant number of embolic complications in the ipsilateral but also in the contralateral
1 Introduction The access to the common carotid during carotid stenting is very challenging and is responsible of a significant number of embolic complications in the ipsilateral but also in the contralateral
Your anaesthetic for heart surgery
 Your anaesthetic for heart surgery Information for patients and carers First Edition 2018 www.rcoa.ac.uk/patientinfo This leaflet gives you information about your anaesthetic for adult heart (cardiac)
Your anaesthetic for heart surgery Information for patients and carers First Edition 2018 www.rcoa.ac.uk/patientinfo This leaflet gives you information about your anaesthetic for adult heart (cardiac)
Patient Information. Peripheral Arterial Disease and the Lutonix 035 Balloon. Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care
 Patient Information Peripheral Arterial Disease and the Lutonix 035 Balloon Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care Contents Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Patient Information Peripheral Arterial Disease and the Lutonix 035 Balloon Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care Contents Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Peripheral Vascular Examination. Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment
 Peripheral Vascular Examination Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Competencies 1. Inspection of upper extremity for: size symmetry swelling venous pattern color Texture nail beds Competencies
Peripheral Vascular Examination Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Competencies 1. Inspection of upper extremity for: size symmetry swelling venous pattern color Texture nail beds Competencies
After the radial artery, the femoral artery is the second most common site for arterial cannulation. One advantage of femoral artery cannulation is
 Arterial Line An arterial line is a thin catheter inserted into an artery. Arterial line placement is a common procedure in various critical care settings. It is most commonly used in intensive care medicine
Arterial Line An arterial line is a thin catheter inserted into an artery. Arterial line placement is a common procedure in various critical care settings. It is most commonly used in intensive care medicine
Images have been removed from the PowerPoint slides in this handout due to copyright restrictions.
 Percutaneous Coronary Intervention https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bssqnhylvma Types of PCI Procedures Balloon Angioplasty Rotational Atherectomy Coronary Stent Balloon Inflation Rotational Atherectomy
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bssqnhylvma Types of PCI Procedures Balloon Angioplasty Rotational Atherectomy Coronary Stent Balloon Inflation Rotational Atherectomy
Access (Antegrade, Retrograde, Pedal)
 Access (Antegrade, Retrograde, Pedal) ARCH St. Louis Craig M. Walker, MD, FACC, FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine Tulane University School of Medicine New Orleans, LA Clinical Professor of Medicine LSU
Access (Antegrade, Retrograde, Pedal) ARCH St. Louis Craig M. Walker, MD, FACC, FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine Tulane University School of Medicine New Orleans, LA Clinical Professor of Medicine LSU
CAMOSUN COLLEGE BIOLOGY 144 (2010) LABS
 LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
Cerebral angiography. Information for families. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust
 Cerebral angiography Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust This leaflet explains about the cerebral angiography procedure and what to expect when your
Cerebral angiography Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust This leaflet explains about the cerebral angiography procedure and what to expect when your
Intravascular Ultrasound
 Scan for mobile link. Intravascular Ultrasound Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) uses a transducer or probe to generate sound waves and produce pictures of the coronary arteries. IVUS can show the entire
Scan for mobile link. Intravascular Ultrasound Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) uses a transducer or probe to generate sound waves and produce pictures of the coronary arteries. IVUS can show the entire
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Definition of electrophysiology study and ablation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Electrophysiology Study and Ablation An electrophysiology, or EP, study is a test of the heart
Definition of electrophysiology study and ablation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Electrophysiology Study and Ablation An electrophysiology, or EP, study is a test of the heart
Catheter Ablation for Atrial Flutter
 Additional Notes Our mission Providing the excellent care we would expect for our own families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Additional Notes Our mission Providing the excellent care we would expect for our own families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
About atrial fibrillation (AFib) Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) What is AFib? What s the danger? Who gets AFib?
 Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
When Aspiration Thrombectomy Does Not Work? A A R O N W O N G N A T I O N A L H E A R T C E N T R E S I N G A P O R E
 When Aspiration Thrombectomy Does Not Work? A A R O N W O N G N A T I O N A L H E A R T C E N T R E S I N G A P O R E Thrombus in STEMI Over 70% of STEMI patients has angiographic evidence of thrombus
When Aspiration Thrombectomy Does Not Work? A A R O N W O N G N A T I O N A L H E A R T C E N T R E S I N G A P O R E Thrombus in STEMI Over 70% of STEMI patients has angiographic evidence of thrombus
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet February 2018 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet February 2018 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used
Vascular Closure Device: A to Z. Owayed M Al Shammeri, MD, FSCAI Interventional Cardiologist AlRayyan Hospital, HMG Riyadh
 Vascular Closure Device: A to Z Owayed M Al Shammeri, MD, FSCAI Interventional Cardiologist AlRayyan Hospital, HMG Riyadh Femoral artery Anatomy Disparities still exist Vascular Closure Devices Suture
Vascular Closure Device: A to Z Owayed M Al Shammeri, MD, FSCAI Interventional Cardiologist AlRayyan Hospital, HMG Riyadh Femoral artery Anatomy Disparities still exist Vascular Closure Devices Suture
PATIENT TEACHING GUIDE FOR PERCUTANEOUS INTERVENTION
 FOR PERCUTANEOUS INTERVENTION Percutaneous Intervention for Coronary Artery and Peripheral Vascular Diseases START TABLE OF CONTENTS OVERVIEW Your Heart and Circulatory System... 3 CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
FOR PERCUTANEOUS INTERVENTION Percutaneous Intervention for Coronary Artery and Peripheral Vascular Diseases START TABLE OF CONTENTS OVERVIEW Your Heart and Circulatory System... 3 CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
