Infections of the Urine System 366 What causes bladder and kidney infections? 366 Signs and treatment 367
|
|
|
- Marion Kelley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 364 Problems of the Urine System Chapter 23 In this chapter: Infections of the Urine System 366 What causes bladder and kidney infections? 366 Signs and treatment 367 Other Problems of the Urine System 369 Blood in the urine 369 Kidney or bladder stones 369 Need to pass urine often 370 Leaking urine 370 When You Have Problems Passing Stool or Urine 372
2 365 Problems of the Urine System There are 2 kidneys. They make urine by cleaning waste from the blood. The bladder is a bag. It stretches and gets bigger as it fills with urine, and gets small after you pass urine. There are 2 upper urine tubes. They carry the urine from the kidneys to the bladder. When you pass urine, the urine goes down the lower urine tube and comes out a small hole in front of your vagina. This chapter describes the most common problems that affect the urine system. Sometimes these problems are difficult to tell apart. So if your problem seems different from those described here, get medical help. You may need special tests to find out what the problem is. If you can identify the problem, it may be possible to treat the problem at home especially if treatment is started right away. But remember that some serious problems begin with signs that do not seem very bad. These problems can quickly become painful and dangerous. So if you do not feel better within 2 to 3 days, get medical help. Female genital cutting This can damage the urine system and cause serious health problems for a woman all her life. If you have been cut and have problems passing urine, or infections that return again and again, talk to a health worker. You may need surgery to correct the problem. For more information, see the chapter on Female Genital Cutting, page 459.
3 366 Problems of the Urine System Infections of the Urine System A girl or woman of any age even a small baby can get an infection of her urine system. I hope the truck stops soon so I can pass urine. Teach little girls the correct way to wipe after passing stool. There are 2 main kinds of urine system infections. A bladder infection is the most common and the easiest to treat. A kidney infection is very serious. It can lead to permanent damage to the kidney and even death. What causes bladder and kidney infections? Infections of the urine system are caused by germs (bacteria). They get into the body from the outside through the urinary opening near the vagina. Infection is more common in women than in men because a woman s lower urine tube is short. Germs climb more easily up the short tube into the bladder. Germs enter a woman s body or multiply when she: has sex. During sex, germs from the vagina and anus can be pushed up through the urinary opening into the lower urine tube. This is one of the most common causes of a bladder infection in women. To prevent infection, pass urine after having sex. This washes out the urine tube (but does not prevent pregnancy). does not drink enough, especially if she works outside in hot weather and sweats a lot. Germs will start to multiply in the empty bladder. Try to drink at least 8 glasses or cups (2 liters) of liquid a day. When working in the hot sun or in a hot room, drink even more. goes for a long time without urinating (for example, when traveling or working). Not urinating allows germs in the urine system to multiply which can cause an infection. Try to pass urine every 3 to 4 hours. does not keep her genitals clean. Germs from the genitals and especially the anus can get into the urinary opening and cause infection. Try to wash the genitals every day, and always wipe from front to back after passing stool (see page 154). Wiping forward can spread germs from the anus into the urinary opening. Also, try to wash your genitals before having sex. Keep the cloth and pads used for your monthly bleeding very clean between uses. has a disability, especially those from back bone (spinal cord) injuries, or with a loss of feeling in the lower body. For more information, see the books Where There Is No Doctor and A Health Handbook for Women with Disabilities. has HIV infection, which makes it more difficult for the woman to fight infection.
4 Infections of the Urine System 367 Signs and treatment Bladder infection signs: need to pass urine very often. (It may also feel as though some urine is still left inside.) pain or a burning feeling while passing urine pain in the lower belly just after passing urine urine smells bad, or looks cloudy, or has blood or pus in it. (Dark urine can be a sign of hepatitis. See page 277.) urine smells bad Kidney infection signs: any bladder infection signs fever and chills lower back pain, often severe, that can go from the front, around the sides, and into the back nausea and vomiting feeling very ill and weak If you have signs of both a bladder and a kidney infection, you probably have a kidney infection. Don t worry Lihua. I will help you get to the health center. When a woman has a kidney infection, she may be in great pain and feel very ill. This can be very frightening. If this happens to you, try to get a family member or a neighbor to help you get to a health worker or health post. IMPORTANT If your signs are serious, start taking medicine right away. See the next page. Treatment for a bladder infection: Bladder infections can often be treated with home remedies. Start treatment as soon as you notice the signs. A bladder infection can sometimes travel quickly up the urine tubes into the kidneys. Drink a lot of water. Try to drink at least one cup of clean water every 30 minutes. This will make you pass urine often. Sometimes the germs will wash out of your urine system before the infection gets worse. Stop having sex for a few days, or until the signs have gone away. Make a tea from flowers, seeds, and leaves that are known to help cure urine infections.
5 368 Problems of the Urine System STIs, especially chlamydia, can cause a burning feeling when a woman passes urine. If you do not feel better in 1 to 2 days, stop taking the home remedies and start taking the medicines in the box below. If you do not feel better in 2 more days, see a health worker. You may have an STI rather than a urine system infection (see page 263). IMPORTANT Before taking any of these medicines, especially if you are pregnant or breastfeeding, first read about them in the Green Pages of this book. Medicine Bladder Infection Medicines How much to take cotrimoxazole 2 tablets of 480 mg (160 mg trimethoprim and 800 mg sulfamethoxazole) or nitrofurantoin 100 mg When to take by mouth, 2 times a day for 3 days by mouth, 2 times a day for 5 days If you do not start to feel better in 2 days (48 hours), there may be a resistance to these medicines in your area. If possible, check with a health worker, or take instead cephalexin, 500 mg, by mouth, 2 times a day for 7 days. Treatment for a kidney infection: If you have signs of a kidney infection, home remedies are not enough. Start taking these medicines right away. But if you do not start to feel better after 2 days, see a health worker. Kidney Infection Medicines Medicine ciprofloxacin How much to take 500 mg or cotrimoxazole 2 tablets of 480 mg (160 mg trimethoprim and 800 mg sulfamethoxazole) When to take by mouth, 2 times a day for 10 days by mouth, 2 times a day for 10 days If you cannot swallow medicines because you are vomiting, take: ceftriaxone or gentamicin 1 gram (1000 mg) 80 mg the first time only, then 60 mg each other time IV or IM, once a day IV or IM, 3 times a day When you can swallow medicine again without vomiting, stop injections and continue with the medicine by mouth for kidney infection, until you have taken medicine for a total of 10 days.
6 Other Problems of the Urine System 369 Blood in the urine If your urine has blood in it, and if there are no other signs of a bladder or kidney infection, you may have bladder or kidney stones (see below). Or you may have one of these diseases, if they are common in your community: Bilharzia (blood flukes, schistosomiasis) can cause permanent damage to the urine system if it is not treated early enough. See a health worker trained in problems of the urine system for treatment, and to learn how to prevent bilharzia from happening again. For more information about bilharzia, see Where There Is No Doctor or another general medical book. Tuberculosis (TB) can damage the bladder and kidneys. For more information, see page 387. Other Problems of the Urine System 387 tuberculosis Kidney or bladder stones These are small hard stones that start to grow in the kidney, and then move through the urine system. Signs: Sudden, very bad pain: in the back where the kidneys are, or in the side near the kidneys, or lower down in the urine tubes or bladder. Other signs are: Blood in the urine. This can happen if the stones scratch the inside of the urine system. Difficulty passing urine. This can happen if a stone blocks the tubes. Treatment: Drink large amounts of liquid (at least 1 or 2 cups every 30 minutes). This will help wash the stone out of the kidney and down the urine tube. Take a pain medicine. If the pain is very bad, get medical help. Sometimes the blocked urine tubes become infected. Treat this problem the same way you would treat a kidney infection. 482 medicines for pain
7 370 Problems of the Urine System growths, 380 diabetes, 174 This young woman s husband was embarrassed by the smell of her leaking urine. He made her leave his house. Need to pass urine often This may happen because: the muscles around your bladder and womb have become weak. The squeezing exercise (page 371) may help strengthen these muscles. a growth (like a fibroid) in your abdomen is pushing against the bladder so it cannot hold much urine. you have a bladder infection. you have diabetes. Leaking urine Poor control of urine (incontinence) This is caused by weak or damaged muscles around the bladder. It happens mainly to older women or to women after childbirth. The urine leaks out when a woman puts pressure on the weak muscles in her lower belly during sex, or by laughing, coughing, sneezing, or lifting. The squeezing exercise (page 371) may help. Urine leaking from the vagina (fistula) When a woman leaks urine all the time from the vagina, she may have a hole between her vagina and bladder. (Sometimes the hole is between the rectum and the vagina, and stool leaks out.) This serious problem happens as a result of an obstructed childbirth, when the baby has difficulty getting out. It can happen to women of all ages. The baby s head presses on the skin between the bladder and the vagina (or the rectum and vagina). This causes an opening (fistula) to form between the bladder and the vagina (or the rectum and vagina). The baby is almost always born dead. After the birth, the fistula does not heal on its own and urine or stool leaks out through the vagina all the time. The girl or woman has to clean herself continuously, and if she has extra cloth or a pad, she can wear this to stay dry. If she cannot get help (see the next page), fistulas can cause serious problems for a girl or woman in her daily life. Her husband, family, and friends may avoid her because she smells of urine all the time. It may be difficult for her to earn money if she no longer can work, and she may feel extremely embarrassed and ashamed. Some girls and women get traumatic fistula because of rape or other violent sexual actions such as a weapon being pushed into a vagina. This can cause tears inside the woman that also cause her to leak urine or stool. Girls and women with traumatic fistula will need support and counseling about the sexual violence, as well as surgery to repair the fistula and other damage to their genitals.
8 Other Problems of the Urine System 371 Treatment: After the birth, if you are leaking urine or stool, talk with a health worker as soon as possible to find out if she or he knows of a hospital where the fistula can be repaired. You should go to the hospital as soon as possible. If you are leaking urine and cannot get to the hospital quickly, the health worker may know how to put in a plastic or rubber tube (catheter) through the urine hole into the bladder (see page 373). This tube will drain the urine and may help the fistula heal. But you must still go to the hospital. When you get there, the doctor will examine you to see if you need an operation to repair the fistula. Do not despair. The problem can often be made better. IMPORTANT To help prevent infection while the tube is in, drink a lot of fluid (at least 10 to 12 cups a day). This will make you pass urine often and flush out germs. Prevention: Avoid marriage and pregnancy until a girl is 18 years old. All women should deliver their babies with a trained midwife or health worker. Women with extra risks should give birth at a hospital. Do not have babies too close together, so your muscles can get strong again in between births (see page 197). If you have leaking urine or stool after giving birth, seek medical help right away. 72 pregnancy The squeezing exercise This exercise can help strengthen weak muscles that cause you to pass urine often or to leak urine. First practice while you are passing urine. As the urine comes out, stop it by tightly squeezing the muscles in your vagina. Count to 10, then relax the muscles to let the urine come out. Repeat this several times whenever you urinate. Once you know how, practice the squeezing exercise at other times during the day. No one will know. Try to practice at least 4 times a day, squeezing your muscles 5 to 10 times each time. Some women may need surgery to help control leaking urine. If you leak urine and this exercise does not help, get advice from a health worker trained in women s health. The squeezing exercise is good for all women to do every day. It helps keep muscles strong and can prevent problems later in life. I m doing my squeezing exercise and Amana doesn t even know.
9 372 Problems of the Urine System When You Have Problems Passing Stool or Urine If possible, lie on your left side. Many women (and men) do not have normal control over when they pass stool or urine (especially persons who are near death, or who have a spinal cord injury, or a disability that affects the muscles of the lower body). This can be inconvenient and embarrassing. It can also cause skin problems and dangerous infections, so it is important to stay clean, dry, and healthy. Bowel control This information will help those persons who have hard stools (constipation) or who have difficulty passing stool. You can learn to help the stool come out when it is easiest for you. The bowels work best when you are sitting rather than lying, so try to remove the stool when you are sitting on a toilet or pot. If you cannot sit, try to do it lying on your left side. How to remove stool: 1. Cover your hand with a plastic or rubber glove, or a plastic bag. Put oil on your pointing (index) finger (vegetable or mineral oil both work well). To keep your finger clean, use a thin rubber glove, or fingercot, or a plastic bag. 2. Put your oiled finger into the anus about 2 cm (1 inch). Gently move the finger in circles for about 1 minute, until the muscle relaxes and the stool pushes out. 3. If the stool does not come out by itself, remove as much as you can with your finger. 4. Clean the anus and the skin around it well, and wash your hands. To prevent hard stools: drink lots of water every day. keep a regular bowel program. eat foods that are high in fiber. exercise or move your body every day. catheter Bladder control Sometimes it is necessary to remove urine from the bladder by using a rubber or plastic tube called a catheter. Never use a catheter unless it is absolutely necessary. Even careful use of a catheter can cause infection of the bladder and kidneys. So it should be used only if someone has a: very full, painful bladder and cannot pass urine. fistula (see page 370). disability or injury, and cannot feel the muscles that control passing urine.
10 When You Have Problems Passing Stool or Urine 373 How to put in a catheter 1. Wash the catheter well with clean, warm water and mild soap. Rinse well with clean, warm water. 2. Wash well with mild soap and clean water the skin around the genitals. Take care to clean the area where urine (pee) comes out and the folds of skin around it (the vulva). If you do not have mild soap, use only clean water. Strong soap can harm your skin. 3. Wash your hands. After washing, only touch things that are sterile or very clean. 4. Sit where your genitals are not touching anything, like on the front of a chair or on a clean toilet seat. If you sit on the ground or another solid surface, put clean cloths under and around the genitals. 5. Wash your hands again with alcohol or with mild soap and clean water, or put on sterile gloves. 6. Cover the catheter with a sterile lubricant (slippery cream) that dissolves in water (not oil or petroleum gel). It helps to protect the soft skin of the genitals and urine tube (urethra). If you do not have any lubricant, make sure the catheter is still wet from the boiled water, and be extra gentle when you put it in. 7. If you put the catheter in by yourself, use a mirror to help you see where the urinary opening is, and use your pointing (index) finger and third finger to hold the skin around the vagina open. The urinary opening is below the clitoris almost at the opening to the vagina. After you have done this a few times, you will be able to feel where the opening is and you will not need to use a mirror. 8. Then, with your middle finger, touch below your clitoris. You will feel a sort of small dent or dimple, and right below that is the urinary opening. Keep your middle finger on that spot, and with your other hand, hold the clean catheter 4 to 5 inches from the end, touch the tip to the end of your middle finger, and gently guide the catheter into the opening until urine starts to come out. Make sure the catheter is in a downward position so that the urine can come out. You will know if the catheter goes into the vagina instead of the urinary opening because it will go in easily, but no urine will come out. Also, when you remove it, the catheter will have discharge (mucus from the vagina) in it. Rinse the catheter in very clean water, and try again. IMPORTANT To avoid infection when using a catheter, it is important for you to be very clean, and to use only a catheter that is very clean (see page 525). If you do get a bladder or kidney infection, talk with a health worker. You may have an infection in your vagina.
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Working for Change 466 Female genital cutting, human rights, and the law 467
 458 Female Genital Cutting Chapter 30 In this chapter: Types of Female Genital Cutting 460 Health Problems Caused by Female Genital Cutting 460 What To Do for Health Problems 461 Heavy bleeding and shock
458 Female Genital Cutting Chapter 30 In this chapter: Types of Female Genital Cutting 460 Health Problems Caused by Female Genital Cutting 460 What To Do for Health Problems 461 Heavy bleeding and shock
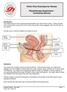
Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC)
 Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Guide for Women
 Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2012 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2012 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING FOR WOMEN STRONG PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLES MEAN GOOD BLADDER AND BOWEL CONTROL WHAT ARE THE PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLES?
 06 STRONG S MEAN WHAT ARE THE S? The floor of the pelvis is made up of layers of muscle and other tissues. These layers stretch like a hammock from the tailbone at the back, to the pubic bone at the front.
06 STRONG S MEAN WHAT ARE THE S? The floor of the pelvis is made up of layers of muscle and other tissues. These layers stretch like a hammock from the tailbone at the back, to the pubic bone at the front.
Uterus (Womb) Rectum. Another problem could be the sensation of something coming down at the birth canal or back passage (prolapse).
 Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Guide for Women
 Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2016 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2016 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate
 TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
Inserting Your Own Urinary Catheter Self-Catheterization Instructions for Women
 CCO/ Clker-Free-Vector-Images/Pixabay.com Inserting Your Own Urinary Catheter Self-Catheterization Instructions for Women Your family practitioner (family doctor or nurse practitioner) has told you that
CCO/ Clker-Free-Vector-Images/Pixabay.com Inserting Your Own Urinary Catheter Self-Catheterization Instructions for Women Your family practitioner (family doctor or nurse practitioner) has told you that
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Guide for Men and Women
 Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Men and Women 1986 2013 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon,
Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Men and Women 1986 2013 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon,
Pelvic floor exercises for women. Information for patients Continence Service
 Pelvic floor exercises for women Information for patients Continence Service page 2 of 8 Why do I need to do pelvic floor exercises? Many women experience pelvic floor problems at some time during their
Pelvic floor exercises for women Information for patients Continence Service page 2 of 8 Why do I need to do pelvic floor exercises? Many women experience pelvic floor problems at some time during their
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME
 CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls
 Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow
CATHETER PASSPORT. Looking after your Urinary Catheter. The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter.
 CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
Chapter 21. In this chapter: How to use this chapter:
 352 Chapter 21 In this chapter: Sudden, Severe Pain in the Abdomen 354 Kinds of 354 During monthly bleeding 354 After childbirth, abortion, or miscarriage 355 With fever 355 With diarrhea 355 During pregnancy
352 Chapter 21 In this chapter: Sudden, Severe Pain in the Abdomen 354 Kinds of 354 During monthly bleeding 354 After childbirth, abortion, or miscarriage 355 With fever 355 With diarrhea 355 During pregnancy
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY
 Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Intermittent self catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Gynaecology
 Intermittent self catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Gynaecology page 2 of 8 What is ISC? Intermittent self catheterisation (ISC) is a simple technique where a narrow tube (catheter) is inserted
Intermittent self catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Gynaecology page 2 of 8 What is ISC? Intermittent self catheterisation (ISC) is a simple technique where a narrow tube (catheter) is inserted
ONE IN THREE WOMEN WHO EVER HAD A BABY WET THEMSELVES EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD DO PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING.
 08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS
 SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS Topic: Urinary Tract Infection Use the materials in this document to help others learn more about urinary tract infection. LEARNING TOOLS: 1. How to Say it Guide 2. Recognizing
SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS Topic: Urinary Tract Infection Use the materials in this document to help others learn more about urinary tract infection. LEARNING TOOLS: 1. How to Say it Guide 2. Recognizing
Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections Storytelling Activity
 Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections Storytelling Activity Trainer s Tips Make the context and characters in the story culturally relevant.» Choose culturally relevant girls and boys names for the
Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections Storytelling Activity Trainer s Tips Make the context and characters in the story culturally relevant.» Choose culturally relevant girls and boys names for the
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e. For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries
 B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
Bladder Management. Why is a Bladder Program so Important?
 Bladder Management A clear understanding of the principles and skills involved in bladder management will help you prevent complications such as a urinary tract infection. Before your injury, waste products
Bladder Management A clear understanding of the principles and skills involved in bladder management will help you prevent complications such as a urinary tract infection. Before your injury, waste products
21. Getting Tested for HIV
 21. Getting Tested for HIV Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Describe the process of HIV testing. List reasons for getting tested for HIV. Background notes It is not
21. Getting Tested for HIV Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Describe the process of HIV testing. List reasons for getting tested for HIV. Background notes It is not
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care
 Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag
 Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Self-Catheterization for Females
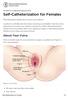 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Self-Catheterization for Females This information explains how to insert your catheter. A catheter is a flexible tube that drains urine from your bladder. Your doctor has
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Self-Catheterization for Females This information explains how to insert your catheter. A catheter is a flexible tube that drains urine from your bladder. Your doctor has
Your Own Teeth and Gums
 Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter
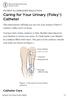 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
Midostaurin (Rydapt )
 Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization. Nova Scotia Rehabilitation Centre
 2014 Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Nova Scotia Rehabilitation Centre Why do I need to do this? Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Your bladder may not empty completely when you go to the
2014 Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Nova Scotia Rehabilitation Centre Why do I need to do this? Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Your bladder may not empty completely when you go to the
Suprapubic and Mitrofanoff Catheter Care
 Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
Stricture guide. Urology department. yeovilhospital.nhs.uk
 Stricture guide Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is a urethral stricture? A urethral stricture is a narrowing or restriction of the urethra (the tube from your bladder through
Stricture guide Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is a urethral stricture? A urethral stricture is a narrowing or restriction of the urethra (the tube from your bladder through
Anterior Sphincter Repair Operation
 Anterior Sphincter Repair Operation How will the operation help me? The investigations that you have had indicate that your anal sphincter is damaged or very weak, and this is why you are having trouble
Anterior Sphincter Repair Operation How will the operation help me? The investigations that you have had indicate that your anal sphincter is damaged or very weak, and this is why you are having trouble
Acute Salpingitis. Fallopian Tubes. Uterus
 Acute Salpingitis Introduction Acute salpingitis is a type of infection that affects the Fallopian tubes. The Fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Acute salpingitis is one of the
Acute Salpingitis Introduction Acute salpingitis is a type of infection that affects the Fallopian tubes. The Fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Acute salpingitis is one of the
Kegel Exercises for Men
 Kegel Exercises for Men The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Kegel Exercises for Men The following information is based on the general experiences of many prostate cancer patients. Your experience may be different. If you have any questions about what prostate cancer
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib )
 Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
Patient Urinary Catheter Passport
 Useful contact details Name Contact Number Produced by Adapted from Worth by Michelle Pickering, Continence Specialist Practitioner Hambleton and Richmondshire Locality Continence Advisory Service and
Useful contact details Name Contact Number Produced by Adapted from Worth by Michelle Pickering, Continence Specialist Practitioner Hambleton and Richmondshire Locality Continence Advisory Service and
Anal sphincter exercises. Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
 Anal sphincter exercises Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Anal sphincter exercises to help lessen leakage from the bowel Sphincter exercises, when practiced correctly, can build up
Anal sphincter exercises Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Anal sphincter exercises to help lessen leakage from the bowel Sphincter exercises, when practiced correctly, can build up
How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery
 Form: D-3251 How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery For patients going home from the Day Surgery Unit at Toronto Western Hospital Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of the Foley
Form: D-3251 How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery For patients going home from the Day Surgery Unit at Toronto Western Hospital Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of the Foley
Surgery for stress incontinence:
 Surgery for stress incontinence: information for you aashara Published February 2005 by the RCOG Contents Key points About this information What is stress incontinence? Do I need an operation? What operation
Surgery for stress incontinence: information for you aashara Published February 2005 by the RCOG Contents Key points About this information What is stress incontinence? Do I need an operation? What operation
PNEUMONIA. Your Treatment and Recovery
 PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~
 TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~ To learn about TransUrethral Resection of a Bladder Tumour, you will need to know what these words mean: The bladder stores urine that is made
TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~ To learn about TransUrethral Resection of a Bladder Tumour, you will need to know what these words mean: The bladder stores urine that is made
Treating your prolapse
 Treating your prolapse This leaflet explains what a prolapse is, and how it can be treated and managed. If you have any questions or concerns, please speak to a doctor or nurse caring for you. What is
Treating your prolapse This leaflet explains what a prolapse is, and how it can be treated and managed. If you have any questions or concerns, please speak to a doctor or nurse caring for you. What is
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises
 INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
After Dental Extractions or Wisdom Teeth Removal
 Patient & Family Guide After Dental Extractions or Wisdom Teeth Removal 2017 Aussi disponible en français : Après l extraction des dents ou l enlèvement des dents de sagesse (FF85-1786) www.nshealth.ca
Patient & Family Guide After Dental Extractions or Wisdom Teeth Removal 2017 Aussi disponible en français : Après l extraction des dents ou l enlèvement des dents de sagesse (FF85-1786) www.nshealth.ca
Everolimus (Afinitor )
 Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
What Is TB? 388 How TB Is Spread 388 How to Know if a Person Has TB 389 How to Treat TB 389 Resistance to TB medicines 390
 386 Chapter 25 In this chapter: What Is TB? 388 How TB Is Spread 388 How to Know if a Person Has TB 389 How to Treat TB 389 Resistance to TB medicines 390 Preventing TB 391 Working for Change 391 387 (TB)
386 Chapter 25 In this chapter: What Is TB? 388 How TB Is Spread 388 How to Know if a Person Has TB 389 How to Treat TB 389 Resistance to TB medicines 390 Preventing TB 391 Working for Change 391 387 (TB)
Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know. A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury
 Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about managing your bladder After SCI, you may
Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about managing your bladder After SCI, you may
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James This handout tells you how to care for your nephrostomy catheter. If you have any questions about this information,
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James This handout tells you how to care for your nephrostomy catheter. If you have any questions about this information,
Urinary Catheter Passport
 Urinary Catheter Passport Catheter Change Record and Looking After Your Urinary Catheter Please take this booklet with you if you are admitted to hospital or have an appointment Patient details Name Address
Urinary Catheter Passport Catheter Change Record and Looking After Your Urinary Catheter Please take this booklet with you if you are admitted to hospital or have an appointment Patient details Name Address
Instruction Guide to Sterile Intermittent Catheterization For Parents of Girls Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
17. Preventing pregnancy
 17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
Open Radical Prostatectomy Surgery
 To learn about radical prostatectomy surgery, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes fluid to help sperm move around. The prostate surrounds the urethra at the neck
To learn about radical prostatectomy surgery, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes fluid to help sperm move around. The prostate surrounds the urethra at the neck
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib )
 Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
In-patient brachytherapy for gynaecological cancer. Cancer Services Information for patients
 In-patient brachytherapy for gynaecological cancer Cancer Services Information for patients i Introduction This booklet provides information about brachytherapy (a type of internal radiotherapy). We hope
In-patient brachytherapy for gynaecological cancer Cancer Services Information for patients i Introduction This booklet provides information about brachytherapy (a type of internal radiotherapy). We hope
My Urinary Catheter Passport Looking after my urinary catheter
 Feedback We welcome your comments. If you have any ideas about how we could do something better or feedback about positive aspects of the service please let us know. If you have a complaint please let
Feedback We welcome your comments. If you have any ideas about how we could do something better or feedback about positive aspects of the service please let us know. If you have a complaint please let
Tips & Tricks for Usage
 Life. Not leaks. BLADDER SUPPORT FOR WOMEN Tips & Tricks for Usage Based on feedback from users and clinicians, here are some questions and answers that might help with using your uresta bladder support
Life. Not leaks. BLADDER SUPPORT FOR WOMEN Tips & Tricks for Usage Based on feedback from users and clinicians, here are some questions and answers that might help with using your uresta bladder support
Hemorrhoids. What are hemorrhoids? What is the cause? What are the symptoms?
 What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower end of your intestine (rectum) or the anus. The anus is the opening where bowel movements pass out of your body. Hemorrhoids
What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower end of your intestine (rectum) or the anus. The anus is the opening where bowel movements pass out of your body. Hemorrhoids
Your pelvic floor muscles
 Continence office Ballochmyle Suite, University Hospital Ayr Telephone 019 177 Your pelvic floor muscles Advice and exercise for women Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa
Continence office Ballochmyle Suite, University Hospital Ayr Telephone 019 177 Your pelvic floor muscles Advice and exercise for women Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for women
 Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for women Introduction Many women suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine
Oxford Pelvic Floor Services A guide to the pelvic floor muscles Information for women Introduction Many women suffer from weakness of their pelvic floor muscles. Common symptoms include: leaking urine
Robot Assisted Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
 Robot Assisted Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy What is a robot assisted total laparoscopic hysterectomy? It is the removal of the uterus, including the cervix, through four small (1/2-1 ) abdominal incisions
Robot Assisted Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy What is a robot assisted total laparoscopic hysterectomy? It is the removal of the uterus, including the cervix, through four small (1/2-1 ) abdominal incisions
Healthy Boys POWERFUL BOYS
 Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Patient and Family Education. Bladder Exstrophy. What is bladder exstrophy? How common is bladder exstrophy? What causes bladder exstrophy?
 Patient and Family Education Bladder Exstrophy What is bladder exstrophy? Bladder exstrophy (x-tro-fee) is a bladder that is not formed right. The bladder and genitals are split in half, turned inside
Patient and Family Education Bladder Exstrophy What is bladder exstrophy? Bladder exstrophy (x-tro-fee) is a bladder that is not formed right. The bladder and genitals are split in half, turned inside
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib )
 Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
Stress. incontinence FACTS, ADVICE, AND EXERCISES.
 Stress incontinence FACTS, ADVICE, AND EXERCISES Facts about incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem; one in every four women has problems with some form of leakage. Incontinence can be anything
Stress incontinence FACTS, ADVICE, AND EXERCISES Facts about incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem; one in every four women has problems with some form of leakage. Incontinence can be anything
Managing your suprapubic catheter
 Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
For the Patient: LUPUPE (Carboplatin Option)
 For the Patient: LUPUPE (Carboplatin Option) Other Names: Treatment of Cancer of Unknown Primary Involving the Thorax with Carboplatin and Etoposide LU = LUng PU = Primary Unknown PE = CarboPlatin, Etoposide
For the Patient: LUPUPE (Carboplatin Option) Other Names: Treatment of Cancer of Unknown Primary Involving the Thorax with Carboplatin and Etoposide LU = LUng PU = Primary Unknown PE = CarboPlatin, Etoposide
It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Learn about Respiratory Infections It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Learn about Respiratory Infections It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
Manual: Bowel Ostomy, Ileostomy, Jejunostomy, Colostomy
 RCH@Home Manual: Bowel Ostomy, Ileostomy, Jejunostomy, Colostomy Table of Contents 1. What is a stoma/ostomy?... 2 2. What is a jejeunostomy?... 2 3. What is an ileostomy?... 2 4. What is a colostomy?...
RCH@Home Manual: Bowel Ostomy, Ileostomy, Jejunostomy, Colostomy Table of Contents 1. What is a stoma/ostomy?... 2 2. What is a jejeunostomy?... 2 3. What is an ileostomy?... 2 4. What is a colostomy?...
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Pelvic Floor Exercises Physiotherapy - Woman s Health Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South Tyneside and Sunderland. 2 Introduction Physiotherapists, doctors and nurses know that exercising
Pelvic Floor Exercises Physiotherapy - Woman s Health Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South Tyneside and Sunderland. 2 Introduction Physiotherapists, doctors and nurses know that exercising
Patient Advice for Third & Fourth Degree Tears
 Patient Advice for Third & Fourth Degree Tears Please read this leaflet carefully. It is important that you take note of any instructions or advice given. If you have any questions or problems that are
Patient Advice for Third & Fourth Degree Tears Please read this leaflet carefully. It is important that you take note of any instructions or advice given. If you have any questions or problems that are
Urinary Catheter Care
 Nikki Hardness, DO Aashish Kabra, MD John Logan, MD Jeremy Weiss, DO Elizabeth Kelly McKnight, PA Phone: (303) 388-9321 What is a urinary catheter? Urinary Catheter Care A urinary catheter is a long, hollow,
Nikki Hardness, DO Aashish Kabra, MD John Logan, MD Jeremy Weiss, DO Elizabeth Kelly McKnight, PA Phone: (303) 388-9321 What is a urinary catheter? Urinary Catheter Care A urinary catheter is a long, hollow,
Laparoscopy. What is Laparoscopy? Why is this surgery used? How do I prepare for surgery?
 What is? Laparoscopic surgery is where your doctor uses a thin, lighted camera and small surgical tool placed through a small (1/2 inch) incision usually in the belly button. To help with the surgery,
What is? Laparoscopic surgery is where your doctor uses a thin, lighted camera and small surgical tool placed through a small (1/2 inch) incision usually in the belly button. To help with the surgery,
Table of Contents. Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings
 Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Urinary Catheter Passport for patients
 Urinary Catheter Passport for patients Nursing A guide for patients and visitors Contents Why people need a urinary catheter...1 How your bladder and kidneys work...1 What is a catheter?...3 Drainage bags...3
Urinary Catheter Passport for patients Nursing A guide for patients and visitors Contents Why people need a urinary catheter...1 How your bladder and kidneys work...1 What is a catheter?...3 Drainage bags...3
Patient Information Leaflet. Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel
 Patient Information Leaflet Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you
Patient Information Leaflet Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you
Going home after major gynaecological surgery. Information for patients Gynaecology
 Going home after major gynaecological surgery Information for patients Gynaecology Discharge advice following your surgery You have had a major operation. This booklet gives some useful advice about what
Going home after major gynaecological surgery Information for patients Gynaecology Discharge advice following your surgery You have had a major operation. This booklet gives some useful advice about what
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Hemodialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. Treatment Options for Kidney Disease
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Lu-177
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Lu-177 What is a neuroendocrine tumor? Neuroendocrine cells are mainly found in your bowel, pancreas and lungs.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) Lu-177 What is a neuroendocrine tumor? Neuroendocrine cells are mainly found in your bowel, pancreas and lungs.
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know. A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury
 Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Ileal Conduit Diversion Surgery
 Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Urinary tract infection
 Urinary tract infection Hascombe Ward Patient information leaflet Understanding the urinary tract There are two kidneys, one on each side of the abdomen. They make urine which drains down the ureters into
Urinary tract infection Hascombe Ward Patient information leaflet Understanding the urinary tract There are two kidneys, one on each side of the abdomen. They make urine which drains down the ureters into
Spina Bifida CIC booklet. A practical guide for nurses and health workers to do clean intermittent catheterization (CIC)
 Spina Bifida CIC booklet A practical guide for nurses and health workers to do clean intermittent catheterization (CIC) International Federation for Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus, 2012 Table of Contents
Spina Bifida CIC booklet A practical guide for nurses and health workers to do clean intermittent catheterization (CIC) International Federation for Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus, 2012 Table of Contents
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Pelvic Floor Exercises Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet Up to a third of women experience a problem with their pelvic floor muscles at some point during their life. The muscles can
Pelvic Floor Exercises Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet Up to a third of women experience a problem with their pelvic floor muscles at some point during their life. The muscles can
Continence Promotion. CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS
 Continence Promotion. 1 CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS CHARACTERISTICS OF URINE 2 A liquid excrement consisting of water, salts, and urea, which is made in the kidneys then released through
Continence Promotion. 1 CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS CHARACTERISTICS OF URINE 2 A liquid excrement consisting of water, salts, and urea, which is made in the kidneys then released through
Instruction Guide to Sterile Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Men Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~
 Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
ISC. (Intermittent self-catheterisation) Patient Information. Women and Children Gynaecology
 44 ISC (Intermittent self-catheterisation) Patient Information Women and Children Gynaecology The purpose of this leaflet is to give a brief explanation of what intermittent catheterisation is and how
44 ISC (Intermittent self-catheterisation) Patient Information Women and Children Gynaecology The purpose of this leaflet is to give a brief explanation of what intermittent catheterisation is and how
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer
 Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery Here are general guidelines for home after your surgery. Your doctor may give you other instructions based on your needs
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery Here are general guidelines for home after your surgery. Your doctor may give you other instructions based on your needs
A Stress Urinary Incontinence fact sheet for
 A Stress Urinary Incontinence fact sheet for women and teenagers What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Get to know your gusset - the science bit Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is defined as a sudden
A Stress Urinary Incontinence fact sheet for women and teenagers What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Get to know your gusset - the science bit Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is defined as a sudden
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal act like
Patient Information Leaflet Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal act like
About Intravesical Therapy
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Intravesical Therapy This information explains intravesical (in-tra-ves-i-cal) therapy at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK). It also describes what to expect before and
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Intravesical Therapy This information explains intravesical (in-tra-ves-i-cal) therapy at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK). It also describes what to expect before and
How to Take Care of a Sick Person
 39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. The care a sick person receives is frequently the most important part of his
39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. The care a sick person receives is frequently the most important part of his
Patient Information Leaflet. Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems
 Patient Information Leaflet Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you to improve
Patient Information Leaflet Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Sphincter Exercises for people with Bowel Control Problems Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you to improve
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
