C. R. Rardin, MD, P. L. Rosenblatt, MD, N. Kohli, MD,J. R. Miklos, MD, M. Heit, MD, and V. R. Lucente, MD
|
|
|
- Gervase Chambers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C. R. Rardin, MD, P. L. Rosenblatt, MD, N. Kohli, MD,J. R. Miklos, MD, M. Heit, MD, and V. R. Lucente, MD OBJECTIVE: To report our experience with surgical release of tension-free vaginal tape (IVT) for the treatment of persistent post- TVT voiding dysfunction. METHODS: A total of 1175 women underwent TVT placement for treatment of genuine stress urinary incontinence and/or intrinsic sphincter deficiency over a 2-year period. Additional procedures and vaginal repairs were perfonned as indicated. AInong these patients, 23 women (1.9/) had persistent voiding dysfunction (urinary retention, incomplete bladder emptying, or severe urgency or urge incontinence) refractory to conservative management. This cohort underwent a simple vaginal TVT release procedure, performed on an outpatient basis. Preoperative characteristics, intraoperative, and postoperative details were assessed by review of operative notes, medical records, and office notes. Continence status was assessed using subjective and objective information. RESULTS: Mean age was 67 years (range years), and the mean interval between TVT placement and release was 17.3 weeks (range 2-69 weeks; median 8.6 weeks). For die release procedure, dlere were no intraoperative complications, and all patients were discl1arged on die day of surgery. All cases of impaired emptying were completely resolved, and all cases of irritative symptoms were resolved (3%) or improved (7%) by 6 weeks. Fourteen (61%) patients remained continent 6 weeks after the release procedure, six (26%) were improved over baseline, and three patients (13%) had recurrence of stress incontinence. CONCLUSION: Refractory voiding dysfunction after TVT is a relatively uncommon situation and can be successfully managed with a simple midline release procedure. hi most cases, the release procedure does not compromise overall improvement in symptoms of stress incontinence. (Obstet Gynecol 22 by The Alnerican College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.) From the Mount Auburn Hospital, Harvard Medical Sdwol, Cambridge, MaIsathwettr; ](ort/uide Hospital, Alp/iaretta, Georgia; Atlanta Center.for Lo/JaroscopU Uro.g)l1lCcolog)', Atltmta, Georgia; UniversiIJ oflouiwide Medical Center, LouiwiOe, Kentucky; and Lehigh Valley Hospital, AOentown, Pt'7Inrylvania. Since 197, when Yon Giordano described a technique of suturing gracilis muscle flaps beneath the urethra,l suburethral slings have been one of the mainstays of treatment for genuine stress urinary incontinence. A wide variety of procedures have been described, and many have enjoyed favorable success rates, but complications and untoward side effects have been rdatively common. Tension-free vaginal tape (I'VI), a minimally invasive variation on the suburethral sling, has shown great promise in increasing success rates while reducing operative times and complication rates. However, as with all slings, surgical correction of stress urinary incontinence can be associated with persistent voiding dysfunction, including prolonged urinary retention, incomplete bladder emptying, or the development of de novo detrusor instability or overactive bladder. As use oftvr grows, more of these complications are likely to be encountered. As with all surgical procedures, the devdopment and refinement of methods of managing complications is an important process. To that end, we report our experiences with the surgical management of persistent and refractory post- TVT voiding dysfunction and urethral obstruction. MATERIALS AND METHODS Women included in this analysis underwent TVr placement for treatment of genuine stress urinary incontinence over a 28-month period (May 1998 through September 2), by six fellowship-trained urogynecologists, at four US centers. Patients were assessed preoperatively using detailed histories, physical examination with pelvic organ prolapse quantification assessment, and multichannel urodynamic testing. Patient counseling and informed consent procedures were carried out in the usual manner. Additional surgical procedures and vaginal repairs were performed at the time of TVr placement as indicated. Perioperative and postoperative 898 VOL. 1, NO.5, PART I, NOVEMBER 22 by The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Published by Elsevier Science Inc /21$22. PII (2)2279-2
2 management were perfonned according to each individual surgeon's routine. In cases in which impaired bladder emptying (complete urinary retention or incomplete bladder emptying) or severe irritative symptoms (urge incontinence, urgency/frequency, or nocturia) occurred postoperatively, conservative management was employed according to the surgeon's clinical judgment. These measures included continued bladder drainage, urethral dilatation, use of timed voiding protocols, pelvic muscle exercises, and initiation of anticholinergic or a-antagonist medications where appropriate. Subjective information, physical examination, bladder scan and/or postvoid residual determinations were carried out in these patients; repeat pelvic organ prolapse quctntification assessment or urodynamic evaluations were not performed as a matter of routine. In cases where conservative measures proved insufficient, the patient was offered TVT release. Patients who responded satisfactorily to these conservative measures, or who had TVT removed for any other reason (eg, pain or erosion) were not included in this analys~. Mter release, patients were seen at 2 and 6 weeks. Outcomes assessed included subjective and objective improvement in impaired bladder emptying, overactive bladder symptoms, and continence status. Postoperative examinations, including assessment of bladder emptying (bladder scan or catheterization), were performed according to the surgeon's judgment. After TVT release, continence status was assessed. Patients were considered "continent" if they denied stress urinary incontinence and had negative cough stress tests. "hnproved" patients were patients whose incontinence persisted, but were subjectively improved from baseline. Patients were considered "incontinent" if they reported no improvement above baseline, if objective incontinence was noted, or if additional procedures were deemed necessary. Changes in irritative symptoms were assessed subjectively. Office and hospital records were reviewed retrospectively to retrieve demographic, operative, and outpatient information. Tension-free vaginal tape release procedures were performed under general or local anesthesia, according to the surgeon's discretion. Patients were placed in dorsolithotomy position, and a Foley catheter was inserted into the urethra. A small midline incision was made, and the suburethral portion of the 1Vf material was identified by palpation agains the catheter. The tape was then minimally undermined (Figure 1) and either transected in the midline, or segmentally excised. More extensive urethrolysis was carried out only at the surgeon's discretion, and cystourethroscopy was carried out when extensive scar tissue or difficult dissection was encountered. Standardized intraoperative measurements of urethral mobility were not performed; the only uniform goal of Figure 1. Tension-free vaginal tape material, revealed and undermined, before transection. Note fibrous ingrowth into mesh interstices. Digital image, captured from video. Rardin. TvT Rek4Iefor Voiding Dy;l/imction. Obortet Gyneco122. the procedure was complete division of the tape material. Postoperative assessments of bladder emptying (voiding trials) were carried out in routine fashion. The procedure was performed on an outpatient basis. RESULTS During the 2-year study period, 1175 women underwent Tv!' procedures by the ~ix urogynecologic surgeons. Among these patients, 23 (1.9%) women were assessed as having persistent voiding dysfunction (urinary retention, incomplete bladder emptying, or severe urgency or urge incontinence) attributed to the TVT, and refractory to conservative management. Of these 23 patients, 13 (571) had a pre-lyf diagnosis of genuine stress incontinence with urethral hypermobility, five (22%) had intrinsic sphincter deficiency without urethral hypermobility, and five (22%) had intrinsic sphincter deficiency with Urethral hypermobility. Intrinsic sphincter deficiency was defined by urodynamic parameters, including maximal urethral closure pressure of less than 2 an H2O, or Valsalva leak point pressure of less than 6 cm H2O. Eight (35/) had undergone previous anti-incontinence or prolapse surgery in the past (fable 1), and 15 (65%) patients had undergone other pelvic reconstructive surgery at the time oflyf placement (fable 2). Three of the 23 patients had experienced perioperative complications: bladder perforation was noted during the 1vr placement in two patients, and one patient had a postoperative wound hematoma. Twenty patients experienced impaired bladder emptying after the TV!' procedure, three had severe irritative symptoms, and seven had both (fable 3). The mean VOL. 1, NO.5, PART 1, NOVEMBER 22 Rardin el al TVT Release for Voiding Dysfunction 899
3 Table 1. Patient Characteristics Patients undergoing TVT release (n = 23) Characteristics Mean age (range) Mean vaginal parity (range) Pre-1Vf data, n (%) Previous anti-incontinence surgery Previous prolapse surgery Diagnosis of GSUI Urethral hypermobility ISD Both TVf incontinence; ISD = intrinsic sphincter deficiency. 67 (46-86) 3 (-7) 6 (26) 13 (57) = tension-free vaginal tape; GSUI = genuine stress urinary interval between TVf placement and release was 17.3 weeks (range 2-69 weeks; median 8.6 weeks). Two patients had been hospitalized with pyelonephritis after TVf; bod! had experienced multiple urinary tract infections associated wid! urinary retention. Attempts at conservative treatment varied; seven patients (3%) underwent urethral dilatation after TVf placement, with one patient demonstrating partial improvement. Twelve patients were started on medications (anticl1olinergics or a-antagonists) in the treatment of these symptoms; four had partial relief (fable 3). All cases of urinary retention or incomplete emptying were noted immediately after the 1Vf procedure, whereas symptoms of urgency or urge incontinence were often delayed (four of nine sucl1 cases were delayed by at least 6 weeks). Ten (43%) of the TVf release procedures were performed under general anesthesia; the remaining 13 were performed with local anesthetic injection and intravenous sedation as needed. One release procedure was performed under local anesthesia in the office. In addition to the tape transection as described above, two of these patients also underwent some degree of urethrolysis (sharp dissection of the paraurethral tissue), and four Table 2. Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Placement Procedure Mean estimated blood loss (ml) Anesthesia, n (Oto) Local Regional General Concurrent surgery, n (Oto) Anterior repair Vaginal vault suspension (abdominal) Vaginal vault suspension (vaginal) Posterior repair/perineorrhaphy Colpocleisis/co lpectom y Complications, n (Oto) Bladder perforation Wound infcction 93 (:tl2) 1 (43) 1 (43) 7 (3) 7 (3) 1 (4) Patients may have undergone multiple concurrent surgeries at me time of tension-free vaginal tape placemcnt. Table 3. Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Placement-to-Release Interval Mean duration of interval (wk) 17.3 (:t 2) (range 2-69; median 8.6) Presenting symptoms, n (%) Retention (complete) 18 (78) mcomplete bladder emptying Urgency/frequency 1 (43) Medications initiated, n (%) 11 (48) With improvement 3 Dilatation attempted, n (%) 7 (3) ~ili improvement 1 Patients may have presented with multiple symptoms and may have had more than one therapy attempted. patients underwent some degree of tape excision, with segments ranging from 2 to 11 mm. Average estimated blood loss for the rdease procedure was less than 25 ml, and mean operative time was 23 (:t 17) minutes. One patient underwent concurrent umbilical hernia repair, and three patients underwent cystoscopy concurrently. There were no intraoperative complications, and all patients were discharged to home on the same day. All patients were sent home without urinary catheters, with the exception of one patient who requested a suprapubic tube because of her dislike of urethral catheters. That patient resumed normal voiding immediatdy, and me tube was removed within 4 days. Outcomes of the rdease procedure are presented in Table 4. Iinpaired bladder emptying was resolved in all cases immediately after the release procedure. Irritative symptoms (urge incontinence or urgency/frequency) were improved in all cases, and were completely resolved in Table 4. Results of Release Procedure Rdid of impaired bladder emptying (n = 2), n (%) Complete Partial No improvement Relief of urge incontinence or urgency/frequency (n = 1), n (%) Complete Partial No improvement Continence status compared with pre-1vtbascline (n = 23), n (/) Cure Improvement. Failuret 1Vf = tension-free vaginal tape. * Persistent stress 2 wk 6 wk 2 (1) 4 (4) 6 (6) 14 (61) 7 (3) 2 (1) 3 (3) 7 (7) 14 (61) 6 (26) incontinence that was subjectively improved over baseline status, or urge-related incontinence in the absence of stress incontinence. t No improvement in conrinence status compared with baseline and con6mled objectively, or in any case where additional anti-incontinence procedures were requested or oltered. 9 Rardin et al TVT Release for Voiding Dysfunction OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
4 three of ten cases (3%) at 6 weeks. Of note, among the seven patients who experienced some degree of persistent urgency and frequency after the release procedure, three (43%) had demonstrated clinical and urodynamic evidence of detrusor instability before TVr placement Mter the release procedure, 14 patients (61%) remained continent. Six patients (26%) reported partial recurrence of stress incontinence or some degree of urge incontinence in the absence of stress incontinence, and were considered improved after the release procedure. In four of these six patients, incontinence was attributed to detrusor instability, and three of diese four were noted to have some degree of detrusor instability before the primary 1VT procedure. Mter rdease, three patients (13%) reported complete. recurrence of stress incontinence equal to or worse than their initial baseline. Two of these patients had!:lad the 1VT placement performed under general anesthesia, and had concurrent pelvic reconstructive surgery. Two of these patients underwent a simple tape transection, and the other had a 2-mm segment of tape excised. None of these three patients underwent true urethrolysis. Of these three patients, two chose to proceed with additional surgical procedures (one with repeat 1Vf, one with periurethral bulking injection), with good results in both cases. Findings at 6 weeks correlated with those at 2 weeks in nearly all cases; one patient noted partial recurrence of urgency, frequency and/or urge incontinence between 2 and 6 weeks, and one patient experienced deterioration in stress incontinence between die two visits. DISCUSSION All anti-incontinence surgery bears ilie risk of postoperative voiding dysfunction. In most cases, iliese scenarios may be successfully treated willi conservative measures: temporary bladder drainage, timed voiding, biofeedback, and pdvic muscle exercises, or ilie short-tenn use of medica. tions. However, a small minority of patients will have persistent symptoms refractory to conservative therapies, and may require surgical revision of the anti-incontinence procedure. Estimates of the incidence of this complication in patients receiving subureiliral slings range from 1f to 2% of patients.2 The American Urological Association's comprehensive review concluded that the incidence of permanent urinary retention is probably higher among patients with subureiliral slings as compared with oilier procedures, but does not exceed 5%.3 Urinary retention is only one of ilie ways in which urethral obstruction can be manifest. Cross et al describe 39 patients who underwent surgical reversal, or urethrolysis, after Burch procedures, pubovaginal slings, or bladder neck suspensions.4 All patients complained of urge incontinence, whereas 51 % had incomplete bladder emptying, 36% reported irritative symptoms, and only 13% were in complete retention. All patients also had physical examinations consistent with hypersuspension of the bladder neck. This distribution of symptomatology was corroborated by Carr and Webster.5 Based on our data, the rate of ~tent and refractory voiding dysfunction after 1VT is low (less than 2%); however, the burgeoning popujarity of the procedure will likely make these Scenarios more common. We describe our experience with variations on a simple release procedure whidi, in all cases, resulted in improvement or complete relief of obstiuctive symptoms. There were no complications, operative times and blood loss estimates were acceptably low, and all cases were performed on an outpatient basis. ill addition, the majority of patients remained continent, or improved above baseline. Romanzi and Blaivas describe a case of urinary retention requiring urethrolysis after TVT placement.6 This case was notable for "excessive" blood loss at the time of TVr placement (2 ml), marked tissue edema postoperatively, and a dramatic overcorrection in urethral mobility (post-tv[ cotton-swab angle of -3 degrees, both resting and sb"aining). The releasing procedure described involved removal of a total of 6 cm of tape material, followed by bilateral dissection above the pubic rami (urethrolysis). This patient experienced a return to normal voiding and remained continent. Another case was reported by Koelle et al, who described a teclurique of intelposition of synthetic mesh between transected ends, in a process of tape dongation.7 Klutke relates his experience with post- TVf urinary retention and obstruction, describing a 2.8% incidence of such voiding dysfunction, as well as similar results of outpatient transvaginal rdease to those we describe here.8 ill the Aus-' trian registry, 39 of 2795 patients (1.4%) required reoperation because of voiding dysfunction.9 A much broader body of literature exists with regard to urethrolysis after standard suburethral slings. Brubaker describes both a simple vaginal incisional release of sling material and an abdomirul1 technique of releasing the rectus fascia attachments of the sling arms.io Carr and Webster,describe vaginal, retropubic, and infrapubic approaches to urethrolysis,5 whereas Petrou et al descnoe a suprameatal approach, II McLennan and Bent describe a technique of tissue interposition (vaginal wall or fascia lata) at the time of urethrolysis to address the rate of urethrolysis failure (reported in other sources between 5-16%),2 and indeed, all four of the patients included in their data did have relief of symp-.th f " I2 A. toms, WI one recurrence mcontlnence. senes f urethrolysis procedures after suburethral sling, reported by Amundsen et al outlines a material-specific technical VOL. 1, NO.5, PART NOVEMBER 22 Rardin et al TVT Release for Voiding Dysfunction 91
5 approam.13 In cases where fascia (autologous or allograft) had been used, the sling was incised in the midline, and, when necessary, retropubic and infrapubic dissection wasperfomled to restore adequate urethral mobility.1n cases of synthetic slings, the material was removed in its entirety. In that study, 93% of patients experienced restoration of normal bladder emptying, and 67% had resolution of urge incontinence. Nine percent of patients had recurrence of stress incontinence, compared with 84% who reported that incontinence was improved from baseline. The optimal evaluation of the patient with postoperative voiding dysfunction after anti-incontinence surgery is not entirely clear. In theory, pressure flow studies help to distinguish between patients with outflow obstruction and those with compromised detrusor function. Urodynamic studies may, however, be misleading. Carr and Webster found no consistency in urodynamic.parameters among patients who benefited from urethrolysis.5 As a result, these authors relied on a clear temporal relationship between the original surgery and the onset of voiding dysfunction in selecting patients for urethrolysis. Petrou et al came to similar conclusions regarding the limited utility of urodynamics in selecting patients for urethrolysis.11 Cystoscopy should be considered to rule out mesh erosion as a cause of irritative symptoms. The data presented here represent the clinical experience of six urogynecologists at different pelvic reconstructive surgery centers in the United States. Each of the surgeons had, at the time of this study, perfomled between 15 and 4 TVT procedures. Although limited by its descriptive and retrospective nature, and by a lack of formal standardization of prerelease evaluation and release techniques, this article represents a large-scale assessment of clinical considerations and outcomes with regard to postoperative voiding dysfunction after TVT and the clinical results of a simple releasing procedure. At the time of this writing, complete data on the 1152 patients who did not require surgical revision are not available, and thus no conclusions regarding risk factors for postoperative voiding dysfunction after Tvr can be made. Evaluation of the long-term outcomes of these patients is ongoing. With future study, it may be possible to identify patients who are at particular risk for obstructive symptoms after Tvr, or to identify those patients who are most Iikdy to benefit from a releasing procedure. Other surgical interventions, sum as "stretcl1ii1g" of the tape, may have their place, particularly in the immediate postoperative period; however, at this point, evidence supporting other interventions is lacking. In the meantime, refractory voiding dysfunction after Tvr can be successfully managed with a simple transvaginal releasing procedure. In most cases, the release procedure does not compromise overall improvement in symptoms of stress incontinence. In light of these benefits, this intervention may be considered in cases of persistent post- TVr voiding dysfunction. REFERENCES 1. Hohenfellner R, Petrie E. Sling procedures in surgery. In: Stanton SL, Tanagho E, eds. Surgery of female incontinence. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1986: Goldman HB, Rackley RR, Appell RA. The efficacy of ured1rolysis without re-suspension for iatrogenic urethral obstruction.} Uro11999;161 : Leach GE, Dmochowski RR, Appell RA, Blaivas ]G, Hadley HR, Luber KM, et al. Female stress urinary incontinence clinical guidelines panel: Summary report on surgical management of female stress urinary incontinence. ] UroI1997;158: Cross CA, Cespedes RD, English SF, McGuire E]. Transvaginal urethrolysis for urethral obstruction after antiincontinence surgery.] UroI1998;159: Carr LK, Webster GD. Voiding dysfunction following incontinence surgery: Diagnosis and treatment with retropubic or vaginal urethrolysis.] UroI1997;157: Romanzi L], Blaivas ]G. Protracted urinary retention necessitation urethrolysis following tension-free vaginal tape surgery.] UroI2;164: Koelle D, Stenz! A, Koebl H, Marth C. Treatment of postoperative urinary retention by elongation of tensionfree vaginal tape. Am] Obstet GynecoI21;185: Klutke C. Urinary retention after tension-frce vaginal tape procedure: hicidence and treatment. Urology 21;58: Tamussino K, Hanzal E, Kolle D, Ralph G, Riss PA Tension-free vaginal tape operation: Results of thc Austrian registry. Obstet GynecoI21;98: Brubaker L. Suburethral sling releasc. Obstet Gynecol 1995;86: II. Petrou SP, Brown]A, Blaivas]G. Suprameatal transvaginal urethrolysis.] UroI1999;161: Md.ennan MT, Bent AE. Sling incision with associated vaginal wall interposition for obstructed voiding secondary to suburethral sling procedure. hit U rogynecol] 1997; 8: Amundsen CL, Guralnick ML, Webster GD. Variations in strategy for the treatment of urethral obstruction after a pubovaginal sling procedure.] UroI2;164: Address reprint requests to: C. R. Rardin, MD, Mount Auburn Hospital, 3 Mount Aubum Street, Suite 32, Cambridge, MA 2138; crardin@earthlink.net. Rec iveddea:mber 28,21. Rec iucd in TeuUcdflnnJune 14, 22. Accepted July 11, Rardin et al TVT Release for Voiding Dysfunction OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Urethrolysis; When, Why & How. M Karram Professor of Ob/Gyn & Urology University of Cincinnati
 Urethrolysis; When, Why & How M Karram Professor of Ob/Gyn & Urology University of Cincinnati Anatomy Urethra may be fixed to the pubic bone with dense scar tissue Goal of urethrolysis is to completely
Urethrolysis; When, Why & How M Karram Professor of Ob/Gyn & Urology University of Cincinnati Anatomy Urethra may be fixed to the pubic bone with dense scar tissue Goal of urethrolysis is to completely
Effect of Anesthesia on Voiding Function After Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure
 Effect of Anesthesia on Voiding Function After Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure M. Murphy, MD, M. H. Heit, MD, MSPH, L. Fouts, MD, C. A. Graham, MD, L. Blackwell, RN, and P. J. Culligan, MD OBJECTIVE:
Effect of Anesthesia on Voiding Function After Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure M. Murphy, MD, M. H. Heit, MD, MSPH, L. Fouts, MD, C. A. Graham, MD, L. Blackwell, RN, and P. J. Culligan, MD OBJECTIVE:
This information is intended as an overview only
 This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN THE TREATMENT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE FOR URETHRAL HYPERMOBILITY AND INTRINSIC SPHINCTERIC DEFICIENCY
 Urological Neurology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN SUI Vol. 29 (6): 540-544, November - December, 2003 PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN THE TREATMENT
Urological Neurology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN SUI Vol. 29 (6): 540-544, November - December, 2003 PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN THE TREATMENT
Blue Ridge Urogynecology
 Surgery for Stress Urinary Incontinence Surgery has proved to be a very effective treatment for stress incontinence. The best surgical procedures improve or cure the incontinence in 85 to 90 percent of
Surgery for Stress Urinary Incontinence Surgery has proved to be a very effective treatment for stress incontinence. The best surgical procedures improve or cure the incontinence in 85 to 90 percent of
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence
 A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE
 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 2 What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Urinary
493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 2 What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Urinary
A SIMPLE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TO MINIMIZE POSTOPERATIVE URINARY RETENTION WITH A PUBOVAGINAL SLING
 Urological Neurology Brazilian Journal of Urology Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 27 (3): 275-280, May - June, 2001 A SIMPLE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TO MINIMIZE POSTOPERATIVE URINARY
Urological Neurology Brazilian Journal of Urology Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 27 (3): 275-280, May - June, 2001 A SIMPLE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TO MINIMIZE POSTOPERATIVE URINARY
Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence. Goals of presentation. Preoperative evaluation: Urodynamic Testing? Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D.
 Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence Goals of presentation Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D. Director of Urogynecology The Permanente Medical Group Kaiser, San Francisco Review preoperative care & evaluation
Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence Goals of presentation Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D. Director of Urogynecology The Permanente Medical Group Kaiser, San Francisco Review preoperative care & evaluation
Desara TV and Desara Blue TV
 Desara TV and Desara Blue TV Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Instructions For Use D I Prescription Use only Do not reuse Sterilized using ethylene oxide Available Electronically M Manufactured
Desara TV and Desara Blue TV Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Instructions For Use D I Prescription Use only Do not reuse Sterilized using ethylene oxide Available Electronically M Manufactured
Polypropylene Mesh in Stress Urinary Incontinence. Liqaa R Al-Khuzaee, FICOG
 Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: Iraqi_jms_alnahrain@yahoo.com http://www. colmed-nahrain.edu.iq/ Polypropylene Mesh in Stress Urinary Incontinence Liqaa R Al-Khuzaee,
Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: Iraqi_jms_alnahrain@yahoo.com http://www. colmed-nahrain.edu.iq/ Polypropylene Mesh in Stress Urinary Incontinence Liqaa R Al-Khuzaee,
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566
 Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Tension-free Vaginal Tape for Urodynamic Stress Incontinence
 Long-term Results of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion for Urodynamic Stress Incontinence in Chinese Women at Eight-year Follow-up: a Prospective Study YM CHAN MBBS, MRCOG, FHKAM (O&G), DCG, DCH, DFM,
Long-term Results of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion for Urodynamic Stress Incontinence in Chinese Women at Eight-year Follow-up: a Prospective Study YM CHAN MBBS, MRCOG, FHKAM (O&G), DCG, DCH, DFM,
Risk Factors of Voiding Dysfunction and Patient Satisfaction After Tension-free Vaginal Tape Procedure
 J Korean Med Sci 2005; 20: 1006-10 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Risk Factors of Voiding Dysfunction and Patient Satisfaction After Tension-free Vaginal Tape Procedure
J Korean Med Sci 2005; 20: 1006-10 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Risk Factors of Voiding Dysfunction and Patient Satisfaction After Tension-free Vaginal Tape Procedure
Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence
 Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Effective Date: December 21, 2016 Subject: Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Background: Urinary incontinence (the involuntary
Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Effective Date: December 21, 2016 Subject: Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Background: Urinary incontinence (the involuntary
Sep \8958 Appell Dmochowski.ppt LMF 1
 Surgical Outcomes (How did we get ourselves into this mess?) Roger R. Dmochowski, MD, FACS Department of Urologic Surgery Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville, Tennessee Considerations Evaluation
Surgical Outcomes (How did we get ourselves into this mess?) Roger R. Dmochowski, MD, FACS Department of Urologic Surgery Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville, Tennessee Considerations Evaluation
Desara and Desara Blue
 Desara and Desara Blue Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Instructions For Use D I Prescription Use only Do not reuse Sterilized using ethylene oxide M Manufactured by: Caldera Medical, Inc.
Desara and Desara Blue Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Instructions For Use D I Prescription Use only Do not reuse Sterilized using ethylene oxide M Manufactured by: Caldera Medical, Inc.
When the suburethral sling was first
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUES BY CHERYL IGLESIA, MD, AND MARIA PETTIT CANTER, MD Treating stress urinary incontinence with suburethral slings Recent modifications to suburethral sling procedures have brought them
SURGICAL TECHNIQUES BY CHERYL IGLESIA, MD, AND MARIA PETTIT CANTER, MD Treating stress urinary incontinence with suburethral slings Recent modifications to suburethral sling procedures have brought them
Female Urology. The Results of Grade IV Cystocele Repair Using Mesh. Introduction ZARGAR MA, EMAMI M*, ZARGAR K, JAMSHIDI M
 Urology Journal UNRC/IUA Vol. 1, No. 4, 263-267 Autumn 2004 Printed in IRAN Female Urology The Results of Grade IV Cystocele Repair Using Mesh ZARGAR MA, EMAMI M*, ZARGAR K, JAMSHIDI M Department of Urology,
Urology Journal UNRC/IUA Vol. 1, No. 4, 263-267 Autumn 2004 Printed in IRAN Female Urology The Results of Grade IV Cystocele Repair Using Mesh ZARGAR MA, EMAMI M*, ZARGAR K, JAMSHIDI M Department of Urology,
Pan African Urological Surgeons Association. African Journal of Urology.
 African Journal of Urology (2012) 18, 175 179 Pan African Urological Surgeons Association African Journal of Urology www.ees.elsevier.com/afju www.sciencedirect.com Martius flap and anterior vaginal wall
African Journal of Urology (2012) 18, 175 179 Pan African Urological Surgeons Association African Journal of Urology www.ees.elsevier.com/afju www.sciencedirect.com Martius flap and anterior vaginal wall
Management of recurrent stress urinary incontinence and urinary retention following midurethral sling insertion in women
 UROLOGY doi 10.1308/003588412X13373405385610 Management of recurrent stress urinary incontinence and urinary retention following midurethral sling H Hashim 1, TR Terry 2 1 North Bristol NHS Trust, UK 2
UROLOGY doi 10.1308/003588412X13373405385610 Management of recurrent stress urinary incontinence and urinary retention following midurethral sling H Hashim 1, TR Terry 2 1 North Bristol NHS Trust, UK 2
SAFYRE TM : A READJUSTABLE MINIMALLY INVASIVE SLING FOR FEMALE URINARY STRESS INCONTINENCE
 Urological Neurology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology SAFYRE TM - SLING FOR FEMALE SUI Vol. 29 (4): 353-359, July - August, 2003 SAFYRE TM : A READJUSTABLE
Urological Neurology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology SAFYRE TM - SLING FOR FEMALE SUI Vol. 29 (4): 353-359, July - August, 2003 SAFYRE TM : A READJUSTABLE
Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary Retention
 Advances in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 797854, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/797854 Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary
Advances in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 797854, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/797854 Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary
Efficacy and Adverse Effects of Monarc Versus Tension-free Vaginal Tape Obturator: a Retrospective One-year Follow-up Study
 Efficacy and Adverse Effects of Monarc Versus Tension-free Vaginal Tape Obturator: a Retrospective One-year Follow-up Study Yvonne KY CHENG MBChB, MRCOG William WK TO MBBS, M Phil, FRCOG, FHKAM (O&G) HX
Efficacy and Adverse Effects of Monarc Versus Tension-free Vaginal Tape Obturator: a Retrospective One-year Follow-up Study Yvonne KY CHENG MBChB, MRCOG William WK TO MBBS, M Phil, FRCOG, FHKAM (O&G) HX
Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery
 Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery APPLICATION FOR NEW FELLOWSHIP Name of Institution: McGill University Location: Royal Victoria Hospital (Glen Site), St Mary s Hospital Centre Type of Fellowship:
Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery APPLICATION FOR NEW FELLOWSHIP Name of Institution: McGill University Location: Royal Victoria Hospital (Glen Site), St Mary s Hospital Centre Type of Fellowship:
How to Achieve Long-Term Success in the Treatment of Female Urinary Stress Incontinence? Novel Modification on Vaginal Sling
 www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2011.52.3.184 Voiding Dysfunction How to Achieve Long-Term Success in the Treatment of Female Urinary Stress Incontinence? Novel Modification on Vaginal Sling Mahmoud
www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2011.52.3.184 Voiding Dysfunction How to Achieve Long-Term Success in the Treatment of Female Urinary Stress Incontinence? Novel Modification on Vaginal Sling Mahmoud
Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh Repair: A Prospective Study of 105 Cases
 International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
Current Role of Urethrolysis and Partial Excision in Patients Seeking Revision of Anti-Incontinence Sling
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Current Role of Urethrolysis and Partial Excision in Patients Seeking Revision of Anti-Incontinence Sling Alice Drain, MD,* Ekene Enemchukwu, MD, MPH, Nihar Shah, BA,* Raveen Syan, MD,*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Current Role of Urethrolysis and Partial Excision in Patients Seeking Revision of Anti-Incontinence Sling Alice Drain, MD,* Ekene Enemchukwu, MD, MPH, Nihar Shah, BA,* Raveen Syan, MD,*
Postoperative Care for Pelvic Fistulae. Peter Jeppson, MD October 3, 2017
 Postoperative Care for Pelvic Fistulae Peter Jeppson, MD October 3, 2017 No Disclosures Rational for Postoperative Care Intraoperative injury may be managed by: Identification Closure Continuous post-operative
Postoperative Care for Pelvic Fistulae Peter Jeppson, MD October 3, 2017 No Disclosures Rational for Postoperative Care Intraoperative injury may be managed by: Identification Closure Continuous post-operative
Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011
 Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Treatment, Urinary Stress Incontinence, Transurethral Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0359 Revision Date: Code(s): 53860 Transurethral
Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Treatment, Urinary Stress Incontinence, Transurethral Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0359 Revision Date: Code(s): 53860 Transurethral
Burch Colposuspension and Tension-Free Vaginal Tape in the Management of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women
 European Urology European Urology 41 2002) 469±473 Colposuspension and Tension-Free Vaginal Tape in the Management of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women A. Liapis *, P. Bakas, G. Creatsas 2nd Department
European Urology European Urology 41 2002) 469±473 Colposuspension and Tension-Free Vaginal Tape in the Management of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women A. Liapis *, P. Bakas, G. Creatsas 2nd Department
Efficacy and Safety of the TVT-SECUR R and Impact on Quality of Life in Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence: A 2-Year Follow-Up
 www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2011.52.5.335 Voiding Dysfunction Efficacy and Safety of the TVT-SECUR R and Impact on Quality of Life in Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence: A 2-Year Follow-Up Yu
www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2011.52.5.335 Voiding Dysfunction Efficacy and Safety of the TVT-SECUR R and Impact on Quality of Life in Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence: A 2-Year Follow-Up Yu
Urogynaecology. Colm McAlinden
 Urogynaecology Colm McAlinden Definitions Urinary incontinence compliant of any involuntary leakage of urine with many different causes Two main types: Stress Urge Definitions Nocturia: More than a single
Urogynaecology Colm McAlinden Definitions Urinary incontinence compliant of any involuntary leakage of urine with many different causes Two main types: Stress Urge Definitions Nocturia: More than a single
Risk Factors for De Novo Mixed Urinary Incontinence and Stress Urinary Incontinence Following Surgical Removal of a Urethral Diverticulum
 LUTS (2013) 5, 154 158 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk Factors for De Novo Mixed Urinary Incontinence and Stress Urinary Incontinence Following Surgical Removal of a Urethral Diverticulum JaeHeonKIM, 1 Kwang Woo
LUTS (2013) 5, 154 158 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk Factors for De Novo Mixed Urinary Incontinence and Stress Urinary Incontinence Following Surgical Removal of a Urethral Diverticulum JaeHeonKIM, 1 Kwang Woo
A Laparoscopic-Assisted Extraperitoneal Bladder Neck Suspension: An Initial Experience
 Journal Of Laparoendoscopic Surgery Volume 4, Number 5, 1994 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., Publishers A Laparoscopic-Assisted Extraperitoneal Bladder Neck Suspension: An Initial Experience E.D. RIZA, M.D.(1)
Journal Of Laparoendoscopic Surgery Volume 4, Number 5, 1994 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., Publishers A Laparoscopic-Assisted Extraperitoneal Bladder Neck Suspension: An Initial Experience E.D. RIZA, M.D.(1)
To compare intermittent catheterization, sling mobilization and sling transection for treatment of
 1 ABSTRACT: Objective: To compare intermittent catheterization, sling mobilization and sling transection for treatment of urinary retention after mid-urethral sling surgery. Methods: Data registered in
1 ABSTRACT: Objective: To compare intermittent catheterization, sling mobilization and sling transection for treatment of urinary retention after mid-urethral sling surgery. Methods: Data registered in
Current trend in anti-incontinence surgery
 Current trend in anti-incontinence surgery 吳銘斌醫師 (Ming-Ping Wu, M.D., Ph.D.) 奇美醫院婦產部婦女泌尿暨骨盆醫學科主任台北醫學大學醫學院婦產學科副教授成功大學醫學院臨床醫學所博士 Anti-incontinence surgery Bladder buttress operation: Kelly plication Needle
Current trend in anti-incontinence surgery 吳銘斌醫師 (Ming-Ping Wu, M.D., Ph.D.) 奇美醫院婦產部婦女泌尿暨骨盆醫學科主任台北醫學大學醫學院婦產學科副教授成功大學醫學院臨床醫學所博士 Anti-incontinence surgery Bladder buttress operation: Kelly plication Needle
Medium-term follow-up on use of freeze-dried, irradiated donor fascia for sacrocolpopexy and sling procedures
 Int Urogynecol J (2004) 15: 238 242 DOI 10.1007/s00192-004-1146-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mary Pat FitzGerald Æ S. Renee Edwards Æ Dee Fenner Medium-term follow-up on use of freeze-dried, irradiated donor fascia
Int Urogynecol J (2004) 15: 238 242 DOI 10.1007/s00192-004-1146-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mary Pat FitzGerald Æ S. Renee Edwards Æ Dee Fenner Medium-term follow-up on use of freeze-dried, irradiated donor fascia
Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion
 Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes
 Neurourology and Urodynamics 19:127 135 (2000) A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes Asnat Groutz, Jerry G. Blaivas,* and Jarrod E. Rosenthal Weill Medical College,
Neurourology and Urodynamics 19:127 135 (2000) A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes Asnat Groutz, Jerry G. Blaivas,* and Jarrod E. Rosenthal Weill Medical College,
Management of Urethrovaginal Fistulas
 european urology 50 (2006) 1000 1005 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Surgery in Motion Management of Urethrovaginal Fistulas Dmitri Y. Pushkar *, Vladimir V.
european urology 50 (2006) 1000 1005 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Surgery in Motion Management of Urethrovaginal Fistulas Dmitri Y. Pushkar *, Vladimir V.
Outcomes of Midurethral Slings in Women with Concomitant Preoperative Severe Lower Urinary Tract Voiding Symptoms
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH The Ochsner Journal 15:223 227, 2015 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Outcomes of Midurethral Slings in Women with Concomitant Preoperative Severe Lower Urinary Tract
ORIGINAL RESEARCH The Ochsner Journal 15:223 227, 2015 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Outcomes of Midurethral Slings in Women with Concomitant Preoperative Severe Lower Urinary Tract
Resolution of urge urinary incontinence with midurethral sling surgery in patients with mixed incontinence and low-pressure urethra
 Gynecol Surg (2012) 9:427 432 DOI 10.1007/s10397-012-0735-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Resolution of urge urinary incontinence with midurethral sling surgery in patients with mixed incontinence and low-pressure
Gynecol Surg (2012) 9:427 432 DOI 10.1007/s10397-012-0735-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Resolution of urge urinary incontinence with midurethral sling surgery in patients with mixed incontinence and low-pressure
Rolled Vaginal Wall Flap for The Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence
 African Journal of Urology 1110-5704 Vol. 17, No. 1, 2011 1-5 Original article Rolled Vaginal Wall Flap for The Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence M. Shoukry, M. Hassouna, A. AbdEl-Kerim and S. El-Salmy
African Journal of Urology 1110-5704 Vol. 17, No. 1, 2011 1-5 Original article Rolled Vaginal Wall Flap for The Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence M. Shoukry, M. Hassouna, A. AbdEl-Kerim and S. El-Salmy
Sarah A. Huber, 1 LaChanda Dunlap-Wright, 2 John R. Miklos, 1 and Robert D. Moore Introduction
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2016, Article ID 6180756, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6180756 Case Report Concomitant Laparoscopic Burch Urethropexy and Combined Vaginal-Laparoscopic Mesh Sling
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2016, Article ID 6180756, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6180756 Case Report Concomitant Laparoscopic Burch Urethropexy and Combined Vaginal-Laparoscopic Mesh Sling
Treatment of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence by Trans-Obturaror Tension-Free Vaginal Tape (TVT-O): A Prospecive Controlled Study
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 79, No. 1, June: 267-272, 2011 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Treatment of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence by Trans-Obturaror Tension-Free Vaginal Tape (TVT-O): A
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 79, No. 1, June: 267-272, 2011 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Treatment of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence by Trans-Obturaror Tension-Free Vaginal Tape (TVT-O): A
Desara Blue OV D I. Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence. Instructions For Use
 Desara Blue OV Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Instructions For Use D I Prescription Use only Do not reuse Sterilized using ethylene oxide M Manufactured by: Caldera Medical, Inc. 5171 Clareton
Desara Blue OV Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence Instructions For Use D I Prescription Use only Do not reuse Sterilized using ethylene oxide M Manufactured by: Caldera Medical, Inc. 5171 Clareton
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence. Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations
 The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
Five-Year Outcomes of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure for Treatment of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence
 european urology 50 (2006) 333 338 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Incontinence Five-Year Outcomes of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure
european urology 50 (2006) 333 338 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Incontinence Five-Year Outcomes of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
Tools for Evaluation. Urodynamics Case Studies. Case 1. Evaluation. Case 1. Bladder Diary SUI 19/01/2018
 Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
Overactive bladder symptoms after midurethral sling surgery in women: Risk factors and management
 Received: 4 January 2017 Accepted: 2 May 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23328 REVIEW ARTICLE Overactive bladder symptoms after midurethral sling surgery in women: Risk factors and management Tom Marcelissen Philip
Received: 4 January 2017 Accepted: 2 May 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23328 REVIEW ARTICLE Overactive bladder symptoms after midurethral sling surgery in women: Risk factors and management Tom Marcelissen Philip
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE. Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
Urodynamics in women. Aims of Urodynamics in women. Why do Urodynamics?
 Urodynamics in women Chendrimada Madhu MD, MA, MRCOG Subspecialty Trainee in Urogynaecology Southmead Hospital 2013 Aims of Urodynamics in women n Confirmation of incontinence and its cause n Definition
Urodynamics in women Chendrimada Madhu MD, MA, MRCOG Subspecialty Trainee in Urogynaecology Southmead Hospital 2013 Aims of Urodynamics in women n Confirmation of incontinence and its cause n Definition
AdVance Male Sling System
 AdVance Male Sling System Clinical study summary This document is a compilation and summary of several AdVance Male Sling System peer-reviewed journal articles. The information presented here is taken
AdVance Male Sling System Clinical study summary This document is a compilation and summary of several AdVance Male Sling System peer-reviewed journal articles. The information presented here is taken
Stop Coping. Start Living. Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy
 Stop Coping. Start Living Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy Did you know? One in three women will suffer from a pelvic health condition in her lifetime. Four of the most
Stop Coping. Start Living Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy Did you know? One in three women will suffer from a pelvic health condition in her lifetime. Four of the most
Objectives. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
AGENDA. 8:00 AM 8:30 AM Pelvic Anatomy of the Lower Urinary Tract and the Anatomy and Physiology of Continence/Incontinence Mickey M.
 Thursday, June 12, 2014 Juniper Ballroom 1: Exhibits AGENDA 6:30 AM 8:00 AM Breakfast and Exhibits EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS 8:00 AM 8:30 AM Pelvic Anatomy of the Lower
Thursday, June 12, 2014 Juniper Ballroom 1: Exhibits AGENDA 6:30 AM 8:00 AM Breakfast and Exhibits EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS 8:00 AM 8:30 AM Pelvic Anatomy of the Lower
Post operative voiding dysfunction and the Value of Urodynamics. Dr Salwan Al-Salihi Urogynaecologist Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
 Post operative voiding dysfunction and the Value of Urodynamics Dr Salwan Al-Salihi Urogynaecologist Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Learning objectives: v Pathophysiology of post op voiding dysfunction.
Post operative voiding dysfunction and the Value of Urodynamics Dr Salwan Al-Salihi Urogynaecologist Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Learning objectives: v Pathophysiology of post op voiding dysfunction.
Surgical treatment of urinary stress incontinence with tension free vaginal tape
 Surgical treatment of urinary stress incontinence with tension free vaginal tape Gynaecology department 01935 384 385 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk Many surgical operations are available for the treatment of
Surgical treatment of urinary stress incontinence with tension free vaginal tape Gynaecology department 01935 384 385 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk Many surgical operations are available for the treatment of
Paravaginal Repair: A Laparoscopic Approach
 44 Paravaginal Repair: A Laparoscopic Approach John R. Miklos and Robert Moore Atlanta Urogynecology Associates, Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.A. Neeraj Kohli Harvard University, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A.
44 Paravaginal Repair: A Laparoscopic Approach John R. Miklos and Robert Moore Atlanta Urogynecology Associates, Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.A. Neeraj Kohli Harvard University, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A.
Guidelines for the Evaluation and Treatment of Recurrent Urinary Incontinence Following Pelvic Floor Surgery
 SOGC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE SOGC Clinical Practice Guideline No. 248, September 2010 (Replaces No. 74, July 1998) Guidelines for the Evaluation and Treatment of Recurrent Urinary Incontinence Following
SOGC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE SOGC Clinical Practice Guideline No. 248, September 2010 (Replaces No. 74, July 1998) Guidelines for the Evaluation and Treatment of Recurrent Urinary Incontinence Following
As more patients express reservations
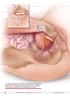 The autologous pubovaginal sling supports the proximal urethra and bladder neck to achieve continence by providing a direct compressive force on the urethra and bladder outlet, or by reestablishing a reinforcing
The autologous pubovaginal sling supports the proximal urethra and bladder neck to achieve continence by providing a direct compressive force on the urethra and bladder outlet, or by reestablishing a reinforcing
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583
 Sacrocolpopexy using mesh to repair vaginal vault prolapse Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583 Your responsibility This guidance represents the view of
Sacrocolpopexy using mesh to repair vaginal vault prolapse Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583 Your responsibility This guidance represents the view of
Brief involuntary urine loss associated with an increase in abdominal pressure. Pathophysiology of Stress Urinary Incontinence Edward J.
 TREATMENT OF SUI Pathophysiology of Stress Urinary Incontinence Edward J. McGuire, MD Department of Urology, University of Michigan Medical Center, Ann Arbor, MI All cases of stress urinary incontinence
TREATMENT OF SUI Pathophysiology of Stress Urinary Incontinence Edward J. McGuire, MD Department of Urology, University of Michigan Medical Center, Ann Arbor, MI All cases of stress urinary incontinence
Sequential Assessment of Urodynamic Findings before and aftertension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Operation for Female Genuine Stress Incontinence
 European Urology European Urology 45 (2004) 362 366 Sequential Assessment of Urodynamic Findings before and aftertension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Operation for Female Genuine Stress Incontinence Long-Yau
European Urology European Urology 45 (2004) 362 366 Sequential Assessment of Urodynamic Findings before and aftertension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Operation for Female Genuine Stress Incontinence Long-Yau
Urethral pressure measurement in stress incontinence: does it help?
 Int Urol Nephrol (2009) 41:491 495 DOI 10.1007/s11255-008-9506-9 UROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Urethral pressure measurement in stress incontinence: does it help? Bassem S. Wadie Æ Ahmed S. El-Hefnawy Received:
Int Urol Nephrol (2009) 41:491 495 DOI 10.1007/s11255-008-9506-9 UROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Urethral pressure measurement in stress incontinence: does it help? Bassem S. Wadie Æ Ahmed S. El-Hefnawy Received:
Patient Information. Tension Free Vaginal/ Obturator Tape (TVT) Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust
 Tension Free Vaginal/Obturator Tape (TVT) Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Tension Free Vaginal/ Obturator Tape (TVT) Reference Number: CW 08 011 003 (version date: September
Tension Free Vaginal/Obturator Tape (TVT) Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Tension Free Vaginal/ Obturator Tape (TVT) Reference Number: CW 08 011 003 (version date: September
John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student
 John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student Prolapse/incontinence You need to know: Pelvic floor anatomy in relation to uterovaginal support and continence The classification of uterovaginal
John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student Prolapse/incontinence You need to know: Pelvic floor anatomy in relation to uterovaginal support and continence The classification of uterovaginal
URINARY INCONTINENCE. Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
9/24/2015. Pelvic Floor Disorders. Agenda. What is the Pelvic Floor? Pelvic Floor Problems
 Management of Pelvic Floor Disorders Doctor, I don t want THAT mesh! Agenda What are pelvic floor disorders (PFDs)? What are the treatment options? Expectant. Conservative. Surgical. How and when are grafts
Management of Pelvic Floor Disorders Doctor, I don t want THAT mesh! Agenda What are pelvic floor disorders (PFDs)? What are the treatment options? Expectant. Conservative. Surgical. How and when are grafts
Outcomes of Surgery of Female Urethral Diverticula Classified Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 european urology 51 (2007) 1664 1670 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Incontinence Outcomes of Surgery of Female Urethral Diverticula Classified
european urology 51 (2007) 1664 1670 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Incontinence Outcomes of Surgery of Female Urethral Diverticula Classified
Management of Female Stress Incontinence
 Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Objective and Subjective Cure Rates after Trans-Obturator Tape (OBTAPE 1 ) Treatment of Female Urinary Incontinence
 european urology 49 (2006) 373 377 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Objective and Subjective Cure Rates after Trans-Obturator Tape (OBTAPE 1 )
european urology 49 (2006) 373 377 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Objective and Subjective Cure Rates after Trans-Obturator Tape (OBTAPE 1 )
Pelvic Prolapse. A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction
 Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women. What YOU can do about it...
 Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women What YOU can do about it... www.gynecare.com Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women: It's Common. It's Treatable. Would it surprise you... To learn that more than 13
Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women What YOU can do about it... www.gynecare.com Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women: It's Common. It's Treatable. Would it surprise you... To learn that more than 13
FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: WHAT IT IS AND WHAT YOU CAN DO ABOUT IT
 URO-GYNECOLOGY PATIIENT IINFORMATIION SHEET FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: WHAT IT IS AND WHAT YOU CAN DO ABOUT IT What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for
URO-GYNECOLOGY PATIIENT IINFORMATIION SHEET FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: WHAT IT IS AND WHAT YOU CAN DO ABOUT IT What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for
Complications from permanent synthetic mesh
 Original Research Symptom Resolution After Operative Management of Complications From Transvaginal Mesh Erin C. Crosby, MD, Melinda Abernethy, MD, MPH, Mitchell B. Berger, MD, PhD, John O. DeLancey, MD,
Original Research Symptom Resolution After Operative Management of Complications From Transvaginal Mesh Erin C. Crosby, MD, Melinda Abernethy, MD, MPH, Mitchell B. Berger, MD, PhD, John O. DeLancey, MD,
Trans-Obturator Tape Operation Using MONARC Technique (Outside-In Technique) --- Revisited Objective and Subjective Assessment
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. I (August. 2016), PP 58-68 www.iosrjournals.org Trans-Obturator Tape Operation Using
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. I (August. 2016), PP 58-68 www.iosrjournals.org Trans-Obturator Tape Operation Using
FDA and Mesh Complications in Vaginal Surgery
 FDA and Mesh Complications in Vaginal Surgery Response to FDA Safety Communication dated July 13, 2011 To Our Patients and Women of the Community: As many of you are aware, on July 13, 2011, the FDA released
FDA and Mesh Complications in Vaginal Surgery Response to FDA Safety Communication dated July 13, 2011 To Our Patients and Women of the Community: As many of you are aware, on July 13, 2011, the FDA released
Cost-effectiveness of urodynamic testing before surgery for women with pelvic organ prolapse and stress urinary incontinence Weber A M, Walters M D
 Cost-effectiveness of urodynamic testing before surgery for women with pelvic organ prolapse and stress urinary incontinence Weber A M, Walters M D Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic
Cost-effectiveness of urodynamic testing before surgery for women with pelvic organ prolapse and stress urinary incontinence Weber A M, Walters M D Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence. Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa
 Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics
 International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics COMMITTEE FOR UROGYNAECOLOGY AND PELVIC FLOOR MEMBER: TSUNG-HSIEN (CHARLES) SU, CHAIR (TAIWAN) DAVID RICHMOND, CO-CHAIR (UK) CHITTARANJAN PURANDARE,
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics COMMITTEE FOR UROGYNAECOLOGY AND PELVIC FLOOR MEMBER: TSUNG-HSIEN (CHARLES) SU, CHAIR (TAIWAN) DAVID RICHMOND, CO-CHAIR (UK) CHITTARANJAN PURANDARE,
Is the role of Burch colposuspension fading away in this epoch for treating female urinary incontinence?
 Int Urogynecol J (2007) 18:937 942 DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0264-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is the role of Burch colposuspension fading away in this epoch for treating female urinary incontinence? SooCheen Ng &
Int Urogynecol J (2007) 18:937 942 DOI 10.1007/s00192-006-0264-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is the role of Burch colposuspension fading away in this epoch for treating female urinary incontinence? SooCheen Ng &
Management of Urinary Incontinence in Older Women. Dr. Cecilia Cheon Department of Obs. & Gyn. Queen Elizabeth Hospital
 Management of Urinary Incontinence in Older Women Dr. Cecilia Cheon Department of Obs. & Gyn. Queen Elizabeth Hospital Epidemiology Causes Investigation Treatment Conclusion Elderly Women High prevalence
Management of Urinary Incontinence in Older Women Dr. Cecilia Cheon Department of Obs. & Gyn. Queen Elizabeth Hospital Epidemiology Causes Investigation Treatment Conclusion Elderly Women High prevalence
Transobturator Tape in Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: It is Time for a New Gold Standard
 Original Article Transobturator Tape in Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: It is Time for a New Gold Standard Navneet Magon, Sanjiv Chopra VSM 1 Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Air Force
Original Article Transobturator Tape in Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: It is Time for a New Gold Standard Navneet Magon, Sanjiv Chopra VSM 1 Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Air Force
Risks and benefits of sling procedures
 Keywords intrinsic sphincter deficiency, midurethral tape, urodynamic stress incontinence, sling procedure, voiding dysfunction Risks and benefits of sling procedures Charlotte Chaliha, Stuart Stanton
Keywords intrinsic sphincter deficiency, midurethral tape, urodynamic stress incontinence, sling procedure, voiding dysfunction Risks and benefits of sling procedures Charlotte Chaliha, Stuart Stanton
Efficacy and safety of a readjustable midurethral sling (Remeex system) for stress urinary incontinence with female voiding dysfunction
 Original Article - Female Urology pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Efficacy and safety of a readjustable midurethral sling (Remeex system) for stress urinary incontinence with female voiding dysfunction
Original Article - Female Urology pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Efficacy and safety of a readjustable midurethral sling (Remeex system) for stress urinary incontinence with female voiding dysfunction
Prediction and prevention of stress urinary incontinence after prolapse surgery van der Ploeg, J.M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prediction and prevention of stress urinary incontinence after prolapse surgery van der Ploeg, J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prediction and prevention of stress urinary incontinence after prolapse surgery van der Ploeg, J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
Prolapse & Stress Incontinence
 Advanced Pelvic Floor Course Prolapse & Stress Incontinence OVERVIEW Day One and morning of Day Two- Pelvic Organ Prolapse The Prolapse component covers the detailed anatomy of POP including the DeLancey
Advanced Pelvic Floor Course Prolapse & Stress Incontinence OVERVIEW Day One and morning of Day Two- Pelvic Organ Prolapse The Prolapse component covers the detailed anatomy of POP including the DeLancey
Bard: Continence Therapy. Stress Urinary Incontinence. Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle.
 Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
Urodynamic findings in women with insensible incontinence
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
Long-Term Outcome of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Female Urinary Incontinence: A 6-Year Follow-Up
 www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.6.409 Voiding Dysfunction Long-Term Outcome of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Female Urinary Incontinence: A 6-Year Follow-Up Jun Hyung Lee, Min Chul
www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.6.409 Voiding Dysfunction Long-Term Outcome of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Female Urinary Incontinence: A 6-Year Follow-Up Jun Hyung Lee, Min Chul
LONG TERM FOLLOW UP OF THE TRANSOBTURATOR TAPE PROCEDURE FOR THE TREATMENT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN A TERTIARY HOSPITAL IN SOUTH AFRICA
 LONG TERM FOLLOW UP OF THE TRANSOBTURATOR TAPE PROCEDURE FOR THE TREATMENT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN A TERTIARY HOSPITAL IN SOUTH AFRICA Dr. A. Chrysostomou MD, FCOG (SA), Mmed (WITS) Senior Specialist,
LONG TERM FOLLOW UP OF THE TRANSOBTURATOR TAPE PROCEDURE FOR THE TREATMENT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN A TERTIARY HOSPITAL IN SOUTH AFRICA Dr. A. Chrysostomou MD, FCOG (SA), Mmed (WITS) Senior Specialist,
Management of Voiding Dysfunction after Prostate Radiotherapy
 Management of Voiding Dysfunction after Prostate Radiotherapy Up to Date Symposium on Uro-Oncology December 7, 2012 Belo Horizonte, Brazil Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial
Management of Voiding Dysfunction after Prostate Radiotherapy Up to Date Symposium on Uro-Oncology December 7, 2012 Belo Horizonte, Brazil Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial
Comparison of bone-anchored male sling and collagen implant for the treatment of male incontinence
 Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722006 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd???2006130012071211Original ArticleComparison of male sling and collagen implant
Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722006 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd???2006130012071211Original ArticleComparison of male sling and collagen implant
Elsevier Editorial System(tm) for Journal de Gynécologie Obstétrique et Biologie de la Reproduction Manuscript Draft
 Elsevier Editorial System(tm) for Journal de Gynécologie Obstétrique et Biologie de la Reproduction Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: JGYN-D-16-00250R1 Title: Vaginocutaneous fistula and buttock abscess
Elsevier Editorial System(tm) for Journal de Gynécologie Obstétrique et Biologie de la Reproduction Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: JGYN-D-16-00250R1 Title: Vaginocutaneous fistula and buttock abscess
