Faecal incontinence. Information for adults. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
|
|
|
- Janis Bond
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Faecal incontinence Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
2 Contents Role of the large intestine.. 3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4 Normal bowel emptying.5 Causes of faecal incontinence.6 Tests for investigating faecal incontinence...8 Managing faecal incontinence...9 Dietary measures...9 Skin care...11 Managing smells and excessive wind...14 Strengthening programme Holding on...15 Treatment for faecal incontinence.. 16 Glossary...17 GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 2
3 Role of the large intestine The large intestine (also known as the colon) is responsible for transforming waste into semi solid stools for excretion. It does this by absorbing fluid from the waste as it moves through. Stool consistency can vary between hard lumps to loose and mushy depending on how long the stools have been in the large intestine and how much water has been reabsorbed from them. Ideally, stools should be formed into soft, smooth sausage shapes which are comfortable to pass. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 3
4 Mass movements in the large intestine The descending colon and the rectum are the storage tank at the end of the large intestine Normally the rectum is relatively empty, although some stool enters the rectum regularly However, most stool arrives all at once in the rectum as a result of mass movements, which happen from time to time, especially before the need to go to the toilet is experienced These mass movements are major waves of pressure which are capable of moving the stool through the whole length of the colon, like toothpaste being squeezed along a tube. What causes these mass movements? Food arriving in the stomach when you eat a meal sets off a pressure wave in the colon a few minutes later. This is why people often need to empty the bowel, sometimes urgently, soon after eating. This is also why, for many people, the bowel is relatively quiet at night The first meal of the day, along with the physical activity of getting ready in the morning, stimulates contractions in the colon and mass movements. Thus many people experience the urge to evacuate their bowels shortly after breakfast. The rate of movement through the digestive system is highly variable. Depending on what you have eaten, food USUALLY takes an average of 1-3 days to be processed. 90% of this time is spent in the colon. Normal bowel function varies between different people Some people move their bowels 3 times a day while others move their bowels once every 3 days. Anything in between this is normal. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 4
5 Normal bowel emptying When stool enters the rectum, the internal anal sphincter muscle automatically relaxes to open up the anal canal. This allows stool to enter the upper anal canal. Here, very sensitive nerve cells figure out whether there is wind, diarrhoea or normal stool present. Most people know that stool is in the rectum without really having to think about it. The external anal sphincter is a much thicker ring of muscle wrapping around the outside of the internal anal sphincter. We have voluntary control of this muscle this means that you can deliberately squeeze / use this muscle, just like you could with a muscle in the arm or leg. If a normal stool is sensed and it is NOT convenient for you to find a toilet at that time, you can DELAY bowel emptying by squeezing the external anal sphincter. Stool will be pushed back up and out of the anal canal. Most people do this without even thinking about it. Thus the urge to empty the bowel is resisted and will wear off. The external sphincter can relax, and stool will not enter the anal canal again until the next mass movement action. When this occurs, you will feel another urge to empty your bowels. These urges will continue at intervals until the bowel is emptied. Continually resisting the urge to empty your bowel or ignoring the urge to empty the bowel can lead to constipation. This is because the stool is forced to GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 5
6 spend a longer amount of time in the colon, allowing more fluid to be reabsorbed. The stool will become harder and more difficult to pass. Causes of faecal incontinence Faecal incontinence is the inability to control wind or faeces from the bowel. It is a common but often silent affliction. For some people there is a single straight forward cause for the symptom of faecal incontinence. For others, a number of factors will combine to determine whether the person is continent or incontinent. For example, a woman might sustain some injury to the anal sphincter during childbirth, but still be continent. However, later in life after she develops irritable bowel syndrome or has anal surgery or reaches menopause, these added factors might push her over the edge, and she will become incontinent. Primary problem Anal sphincter or pelvic floor damage Common cause Obstetric trauma Previous surgery (haemorrhoidectomy, anal stretch, lateral sphincterotomy, gynaecological surgery) Idiopathic degeneration Direct trauma or injury (eg impalement) Congenital abnormality GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 6
7 Anorectal pathology Rectal prolapse Anal or recto vaginal fistula Haemorrhoids or skin tags Gut motility or stool consistency Neurological disease Impaction with overflow diarrhoea Infection Inflammatory bowel disease Irritable bowel syndrome Pelvic irradiation Diet Psychological state eg anxiety Spinal cord injury Multiple sclerosis Spina bifida / sacral agenesis (these people will have constipation, and secondary overflow faecal incontinence) Alzheimer s disease Institutionalised or immobile elderly people Severely constipated children GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 7
8 Lifestyle and environmental factors Poor toilet facilities Inadequate care / non available assistance Drugs with gut side effects Frailty and dependence Tests for investigating constipation Which investigations you and your doctor decide on will depend on your symptoms, family history and age. Medical history The doctor may ask you to describe your faecal incontinence, particularly how long you have been incontinent, how often your bowel movements are, consistency of stools, presence of blood and your bowel habits. A record of eating habits, medication, and level of physical activity or exercise will also help the doctor determine the cause of constipation. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 8
9 Physical examination This may include a digital rectal examination, where a gloved, lubricated finger is used to evaluate the tone of the anal sphincter and also detect tenderness, obstruction and blood. In some cases, blood and thyroid tests might be necessary to look for thyroid disease and serum calcium, OR to rule out inflammatory, endocrine, metabolic and other systemic disorders which may be causing your constipation. Special investigations These are usually reserved for people with severe symptoms, for those with sudden changes in number and consistency of bowel movements or blood in the stool and for older adults. Endo-anal ultrasound a small ultrasound probe is placed into the anus, to generate a two dimensional picture of the anatomy. Managing faecal incontinence What can be done depends on the cause, how severe the problem is, as well as the age, health and motivation of the individual who is affected. 1. Dietary measures 2. Skin care 3. Managing smells and excessive wind 4. Strengthening programme Holding on 1. Dietary measures Eat smaller meals at In some people, eating a large meal triggers the urge to have a bowel movement, and sometimes causes diarrhoea. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 9
10 regular and frequent intervals Swallowing air Avoid foods and drinks which cause loose stools Increase fibre Eating smaller and more frequent meals can reduce the frequency of bowel movements. It can also make it easier for your intestines to digest and decrease wind production Having regular meal times prevents the bowel from being empty an empty bowel produces more wind and gurgles! Sometimes the way in which you eat means that you swallow a lot of air with your food. Try eating a little more slowly; chew each mouthful carefully (especially if the food is high in fibre) and try to avoid talking too much while you are actually eating. If you are in a hurry, don t be tempted to wash down half chewed food with a gulp of drink. In fact, eating and drinking at the same time can also increase the amount of air that you swallow, so try drinking before or after food, rather than during. Chewing gum, snoring and sleeping with your mouth open can increase the amount of air you ingest. dairy products (in those who are lactose intolerant) spicy, greasy or fatty foods alcohol caffeinated beverages diet foods or drinks sugar free gum and candy The daily recommended intake of fibre is 30 grams Fibre is found in cereals, grains, legumes, fruit, vegetables and salad vegetables The amount of fibre found in different types of food is shown below fibre increases stool bulk and improves stool consistency You should increase your fibre gradually over a few weeks to reduce the possibility of bloating and gas GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 10
11 2.5g 6.2g 1.6g 1.8g 2g 3.1g 4.1g 0.9g 3g 8.1g 0.5g 0.4g 1.5g 3.8g 2g Fibre supplement eg Normafibe Normafibe reduces the amount of gas production bulks up the motion makes it stick together Makes it all come out in one go to reduce faecal soiling. The correct method of taking Normafibe is 1. Eat a meal 2. Take a sip of water to wet your mouth. 3. Put ½ teaspoon of Normafibe in your mouth and swallow (without chewing) with water 4. Put ½ teaspoon of Normafibe in your mouth and swallow with plenty of water Avoid foods which cause excessive wind production beans (especially baked beans and kidney beans) nuts (especially peanuts) muesli, dried fruit Bran cereal and other high fibre / wholegrain cereals Cabbage, cauliflower, carrots, broccoli Eggs shellfish GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 11
12 Milk and milk products (especially if lactose intolerant) Jacket potato skins, peas, lentils Onions, radishes, leeks, swede and parsnips brown rice or wholemeal pasta Salad (especially cucumber) hot spicy foods and rich fatty foods Fizzy carbonated drinks alcohol especially beer 2. Skin care Why is good skin care important? Anyone who has frequent bowel motions, diarrhoea or faecal incontinence may get sore skin around the back passage from time to time. This can be very uncomfortable and distressing. Occasionally the skin may become so inflamed that it breaks into an open sore. These are then difficult to heal. Taking good care of the skin around your back passage can help to prevent these problems from developing. Why do I get sore? Bowel motions contain chemicals like digestive juices and acid, which break down your food. If you have very fluid bowel motions, the acid and juices can still be present, and irritate any skin it contacts if you have incontinence of bladder and bowel, you will be more likely to get sore, as the urine and faeces react together Severe itching and irritation is called pruritus ani and is treatable Haemorrhoids can cause itching and you may need to use a cream regularly to prevent itching and soreness. With some anal conditions, it is very difficult to wipe your bottom effectively. A little always seems to get left. This stool starts to make your bottom sore GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 12
13 People who are not eating a healthy balanced diet, not drinking enough fluids or not having enough exercise are more prone to soreness as are people who are generally unwell or inactive Some people find that certain food or drink makes them more prone to soreness, especially citrus fruits like oranges. It might be worth cutting these out on a trial basis and more permanently if this helps Tips to prevent soreness After a bowel action, always wipe gently with soft toilet paper or ideally the newer moist toilet paper (available from large pharmacies and some supermarkets!) Discard each piece of paper after one wipe so that you are not re contaminating the area you have just wiped Whenever possible, wash around the anus after a bowel action a bidet is ideal and portable versions are available. If this is not possible, you may be able to use a shower attachment with your bottom over the edge of the bath. OR, use a soft disposable cloth with warm water. Sometimes a little ingenuity is needed; especially if you are not at home. Some people find that a small plant spray, watering can or jug filled with warm water makes washing easy on the toilet or over the edge of the bath Do not be tempted to use disinfectants or antiseptics in the washing water these can sting and many people are sensitive to the chemicals in them, and will develop a reaction. Plain warm water is best Avoid using products with strong perfume e.g. scented soap, talcum powder, deodorants etc Choose a non scented soap or baby soap. Many baby wipes contain alcohol and are best avoided. Wear cotton underwear to allow skin to breathe Barrier creams and pads GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 13
14 Avoid using any creams or lotions on the area, unless advised to do so by a Biofeedback Specialist Nurse regular uses of these recommended creams can prevent sore skin If you do use a barrier cream, use a simple one eg zinc and castor oil and use just a small amount, gently rubbed in. Large amounts can stop the skin from breathing and can make the area sweaty and uncomfortable. Make sure that the old layer of cream is washed off before applying more. Some people are allergic to lanolin, so creams containing this should be avoided. Your Biofeedback Specialist Nurse may suggest using a barrier wipe, which forms a protective film over the skin, especially if you have diarrhoea and are opening your bowels very frequently If you have to wear a pad because of incontinence, try to make sure that no plastic comes into contact with your skin, and that you use a pad with a soft surface If you already have sores Still follow all the above advice on preventing sores Use a barrier cream / ointment as recommended by your Biofeedback Specialist Nurse If drying the skin after washing is difficult / uncomfortable, you may use a hairdryer on a VERY low setting (be careful!) Try not to scratch the anal area, even if it is itchy, because this will make things worse. Wear cotton gloves in bed (from the pharmacy) to stop yourself from scratching in your sleep Try to allow air to get to the anal area for at least part of every day Tell your nurse or doctor that the skin is broken! They can prescribe other products to help treat the symptoms and prevent serious infections 3. Managing smells and excessive wind GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 14
15 Why do I have so much wind? There is no doubt that some food lead to more wind production than others. Often this is foods high in fibre, which the normal bacteria in the bowel digest, producing gas as a by product. However this is very individual food that produces a lot of wind for one person may not do so for someone else. It is worth experimenting to see if eating certain foods make things worse for you, and if avoiding those foods helps. Controlling or disguising smells Try to ensure good ventilation of the room you are in Use an aromatherapy oil burner, scented candle, incense, or potpourri Aerosol air freshener or solid block air fresheners that work all the time Essential oils such as lavender or lemon oil Try striking a match and then blowing it out immediately and allowing the small plume of smoke to drift into the room. Tip: you may like to keep a box of matches and an egg cup for the used match in your bathroom Other products There is almost no scientific research on this, so we cannot actually recommend any products. However, some people find that one or more of the following products reduces wind or reduced the smell from wind: Peppermint oil / peppermint tea Aloe vera capsules / drinks Charcoal tablets Mintec / De gas Yakult / probiotic tablets You could also try going to a health food store and asking about their wind reducing products. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 15
16 4. Strengthening exercises Holding on Programme Currently when you feel an urge to do a bowel motion, you find that you have to rush to the toilet urgently. Your rectum, your sphincter muscles and your confidence need retraining to help you overcome this problem. Stage 1: Next time you need to do a bowel motion, 1. Sit on the toilet 2. Hold on for one minute before you open your bowels 3. Gradually increase this to 5 minutes. Don t worry if you re not able to do this for the first few times. Keep on practising! Stage 2: Once you have mastered Stage 1, it is time to try holding on for TEN MINUTES before opening your bowels. This stage is harder, but remember you re on the toilet and therefore safe. It might helpful to bring something with you to read! Stage 3: Now that you can delay opening your bowel for 10 minutes whilst sitting on the toilet, it is time to begin to move away from the toilet. Now, when you want to open your bowels, sit NEAR the toilet, either on the edge of the bath or on a chair in the bathroom or just outside the toilet area. Now hold on for 5 minutes. Once you can do this, repeat the exercise, holding on for 10 minutes. Stage 4: When you are able to delay opening your bowels for 10 minutes whilst OFF the toilet, you should now gradually move further away. Try shifting to your bedroom. As your muscles are now becoming stronger, you should be able to hold on for 10 minutes and as you feel more confident, increase the distance between you and the toilet. Gradually you will find that you can increase the distance of the time away from the toilet. This may take some time to master, but remember that the more you practice this programme, the sooner this will happen! GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 16
17 Treatment for faecal incontinence Biofeedback This is a program to help the patients sense when their anal muscle is squeezed or relaxed and encouraging them to improve this response until it becomes automatic Surgery Surgery may be performed when a muscle defect is identified, usually as a result of giving birth. Up to 80 90% of patients have a very good response to this type of surgery. Patients usually do not return to perfect continence, as some wind problems still remain. Diversion Some patients have such severe incontinence and problems due to the incontinence there the stream of faeces may need to be diverted to the abdominal wall. This is done by creating a colostomy or ileostomy. This is often considered the last and least popular option, yet it returns the dignity and control to an often chaotic life. Artificial anus formation This is done by implanting a fluid filled prosthesis that squeezes the anal canal closed OR stimulated transplanted muscles. This may be suitable in certain patients with intractabl3e incontinence who are not suitable for muscle repair. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 17
18 Glossary anal sphincter bowel habits continence defaecation incontinence faeces gastrointestinal tract peristalsis A ring of muscle closing off anal canal and allowing you to control WHEN you will defaecate, once faeces arrives in the rectum How often and where one has bowel motions Having voluntary control over urinary and faecal discharge The discharge of faeces from the rectum Inability to voluntarily control one s urinary and faecal discharge Once food is digested, it is transformed into a waste product called faeces to be expelled from the body The tube like organ connecting the mouth to the anus. Along this tract, food is broken down, digested, and converted to faeces to be expelled The muscular contraction / relaxation movements of the gastrointestinal tract which propels the food along the tube GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 18
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet Central Middlesex Hospital Tips on Controlling Wind and Smells Tips on Controlling Wind and Smells Having a bowel problem can sometimes mean that you cannot reliably control
Patient Information Leaflet Central Middlesex Hospital Tips on Controlling Wind and Smells Tips on Controlling Wind and Smells Having a bowel problem can sometimes mean that you cannot reliably control
Biofeedback Program. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
 Biofeedback Program GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Biofeedback Checklist Bristol Stool Form Scale Digestive process 4F s Fibre, Fluid, Fitness,
Biofeedback Program GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Biofeedback Checklist Bristol Stool Form Scale Digestive process 4F s Fibre, Fluid, Fitness,
Bowel Health in Adults
 Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
Bowel Health in Adults Patient Information Contact Details: Bladder and Bowel Specialist Nurse Service First Floor New Alderley House Macclesfield District General Hospital Victoria Road Macclesfield SK10
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
Constipation. Information for adults. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
 Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse
 Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
Delormes Operation for Rectal Prolapse Your Questions Answered What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the rectum become weakened, allowing the muscle of the rectum
Patient Information Leaflet. Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation
 Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
Patient Information Leaflet Treating Rectal Prolapse Delormes Operation Treating Rectal Prolapse - Delormes operation What is a rectal prolapse? A rectal prolapse occurs when the normal supports of the
DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION
 Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services DIETARY ADVICE FOR CONSTIPATION What is constipation? Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints and it can affect people of all ages. Bowel
Dietary advice for people with colostomies
 Dietary advice for people with colostomies Introduction During your surgery, you have had a colostomy formed. Colostomies are formed due to problems in the colon (large bowel). This leaflet is designed
Dietary advice for people with colostomies Introduction During your surgery, you have had a colostomy formed. Colostomies are formed due to problems in the colon (large bowel). This leaflet is designed
Anal sphincter exercises. Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals
 Anal sphincter exercises Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Anal sphincter exercises to help lessen leakage from the bowel Sphincter exercises, when practiced correctly, can build up
Anal sphincter exercises Information for patients Sheffield Teaching Hospitals Anal sphincter exercises to help lessen leakage from the bowel Sphincter exercises, when practiced correctly, can build up
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Bowel Problems after Radiation
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Bowel Problems after Radiation If you have bowel problems after radiation, you may feel embarrassed. Don t let this stop you from asking for help. Sometimes, radiation
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Bowel Problems after Radiation If you have bowel problems after radiation, you may feel embarrassed. Don t let this stop you from asking for help. Sometimes, radiation
Pelvic floor weakness
 Information leaflet for patients Pelvic floor weakness Physiotherapy department You have been referred to this department for treatment and advice because you have one or more of the following symptoms:
Information leaflet for patients Pelvic floor weakness Physiotherapy department You have been referred to this department for treatment and advice because you have one or more of the following symptoms:
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know. A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury
 Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Biofeedback for pouch dysfunction. Brigitte Collins, Lead Nurse BSc (Hons), MSc GI Nursing, Dip/ Hypnotherapy
 Biofeedback for pouch dysfunction Brigitte Collins, Lead Nurse BSc (Hons), MSc GI Nursing, Dip/ Hypnotherapy Objectives Awareness of St Marks biofeedback therapy Strategies that may help pouch dysfunction
Biofeedback for pouch dysfunction Brigitte Collins, Lead Nurse BSc (Hons), MSc GI Nursing, Dip/ Hypnotherapy Objectives Awareness of St Marks biofeedback therapy Strategies that may help pouch dysfunction
Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy
 A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
16 Colostomy. The function of the large bowel (colon) is to absorb water and salts from our food during the process of digestion.
 16 Colostomy Eating and drinking with a colostomy The function of the large bowel (colon) is to absorb water and salts from our food during the process of digestion. If you have an end colostomy then the
16 Colostomy Eating and drinking with a colostomy The function of the large bowel (colon) is to absorb water and salts from our food during the process of digestion. If you have an end colostomy then the
Causes Of Flatulence. How to Stop Farting Fast by Using Natural Remedies for Gas
 How to Stop Farting Fast by Using Natural Remedies for Gas 4.5 (90.23%) 43 votes Gases are a taboo subject and farting is something very personal and quite embarrassing when it happens in a public place
How to Stop Farting Fast by Using Natural Remedies for Gas 4.5 (90.23%) 43 votes Gases are a taboo subject and farting is something very personal and quite embarrassing when it happens in a public place
Stool softeners are medicines like (ducolox - pericolace - senokot). You want the stool to remain soft so it is easier to empty the bowel.
 "Bowel Management" How the Body Works The food you eat and drink provides your body with many nutrients. These nutrients give you energy and help you stay healthy. As food moves through your body it breaks
"Bowel Management" How the Body Works The food you eat and drink provides your body with many nutrients. These nutrients give you energy and help you stay healthy. As food moves through your body it breaks
Dietary advice following Ileostomy
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Dietary advice following Ileostomy An information guide Dietary advice following Ileostomy Stoma nurse... Contact number... Dietician...
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Dietary advice following Ileostomy An information guide Dietary advice following Ileostomy Stoma nurse... Contact number... Dietician...
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
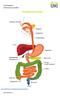 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
Foreword. Bowel Management
 2 Bowel Management Foreword The section on is very similar to that of Bladder Care and Management section, as there are many issues to be addressed. You should always remember that what works for one individual
2 Bowel Management Foreword The section on is very similar to that of Bladder Care and Management section, as there are many issues to be addressed. You should always remember that what works for one individual
Advice for Parents and Carers
 Advice for Parents and Carers 1 2 CONTENTS 4. What is constipation? 4. What is faecal impaction? 5. How common is constipation in children? 5. How to tell if your child may be constipated 6. How constipation
Advice for Parents and Carers 1 2 CONTENTS 4. What is constipation? 4. What is faecal impaction? 5. How common is constipation in children? 5. How to tell if your child may be constipated 6. How constipation
Side Effects from Radiation Treatment to the Prostate
 Canterbury Regional Cancer and Haematology Service Side Effects from Radiation Treatment to the Prostate Your doctor has recommended that you have a course of radiation therapy. This leaflet contains information
Canterbury Regional Cancer and Haematology Service Side Effects from Radiation Treatment to the Prostate Your doctor has recommended that you have a course of radiation therapy. This leaflet contains information
Hemorrhoids. What are hemorrhoids? What is the cause? What are the symptoms?
 What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower end of your intestine (rectum) or the anus. The anus is the opening where bowel movements pass out of your body. Hemorrhoids
What are hemorrhoids? Hemorrhoids Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower end of your intestine (rectum) or the anus. The anus is the opening where bowel movements pass out of your body. Hemorrhoids
Diet advice for patients with a stoma
 Diet advice for patients with a stoma There are two different types of stoma; a colostomy or an ileostomy. A colostomy is a stoma that is formed from a part of the large bowel (colon). When undigested
Diet advice for patients with a stoma There are two different types of stoma; a colostomy or an ileostomy. A colostomy is a stoma that is formed from a part of the large bowel (colon). When undigested
Faecal Incontinence Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
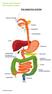 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC)
 Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
ONE IN THREE WOMEN WHO EVER HAD A BABY WET THEMSELVES EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD DO PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING.
 08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
Basic Review of Digestion
 Basic Review of Digestion In the mouth, food is broken down, mixed with saliva, and formed into a bolus. Wave like muscle movements, called peristalsis, push the food throughout the rest of the digestive
Basic Review of Digestion In the mouth, food is broken down, mixed with saliva, and formed into a bolus. Wave like muscle movements, called peristalsis, push the food throughout the rest of the digestive
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate
 TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
 Patient information Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) i Important information for all patients experiencing irritable bowel syndrome. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (:
Patient information Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) i Important information for all patients experiencing irritable bowel syndrome. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (:
Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included.
 Urology Clinic Hospital for Sick Children Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included. Information on bladder retraining, urinary tract infections
Urology Clinic Hospital for Sick Children Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included. Information on bladder retraining, urinary tract infections
Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea
 Patient & Family Guide 2018 Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea www.nscancercare.ca What is diarrhea? Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea Diarrhea
Patient & Family Guide 2018 Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea www.nscancercare.ca What is diarrhea? Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: Diarrhea Diarrhea
Uterus (Womb) Rectum. Another problem could be the sensation of something coming down at the birth canal or back passage (prolapse).
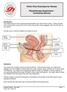 Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Anorectal physiology test
 Anorectal physiology test We hope this factsheet will help to answer some of your questions about having an anorectal physiology test. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don t hesitate
Anorectal physiology test We hope this factsheet will help to answer some of your questions about having an anorectal physiology test. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don t hesitate
Diverticular Disease Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.
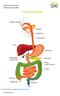 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
MANAGING BLOATING AND WIND
 INFORMATION SHEET MANAGING BLOATING AND WIND INTRODUCTION People with Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), which includes Crohn s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis (UC), often report feeling bloated. Many also
INFORMATION SHEET MANAGING BLOATING AND WIND INTRODUCTION People with Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), which includes Crohn s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis (UC), often report feeling bloated. Many also
A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery)
 Saint Mary s Hospital Newborn Intensive Care Unit Information for Parents A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery) Introduction This information leaflet is designed to help parents and families to care for
Saint Mary s Hospital Newborn Intensive Care Unit Information for Parents A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery) Introduction This information leaflet is designed to help parents and families to care for
Patient information - Constipation
 Preventing constipation Constipation is a common problem. It means either going to the toilet to empty the bowels less often than usual, or passing hard or painful stools. Constipation may be caused by
Preventing constipation Constipation is a common problem. It means either going to the toilet to empty the bowels less often than usual, or passing hard or painful stools. Constipation may be caused by
Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms
 Information for Women Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms SPHERE Bladder and Bowel Service Supporting Pelvic Health through Empowerment Rehabilitation and Education 2 Index Self-managing your urinary
Information for Women Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms SPHERE Bladder and Bowel Service Supporting Pelvic Health through Empowerment Rehabilitation and Education 2 Index Self-managing your urinary
SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health
 SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health 1 Heart Health If you re like most Americans, heart health might be something you don t think about very often. You should. The risk of heart disease increases with age and
SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health 1 Heart Health If you re like most Americans, heart health might be something you don t think about very often. You should. The risk of heart disease increases with age and
Improving Your Bowel Function
 Improving Your Bowel Function EDUCATES, SUPPORTS AND PROMOTES SPECIALIST PHYSIOTHERAPISTS Glossary symptoms - a feeling of a physical change / bothersome change rectum/back passage - where stool / faeces
Improving Your Bowel Function EDUCATES, SUPPORTS AND PROMOTES SPECIALIST PHYSIOTHERAPISTS Glossary symptoms - a feeling of a physical change / bothersome change rectum/back passage - where stool / faeces
Patient Information Leaflet. Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel
 Patient Information Leaflet Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you
Patient Information Leaflet Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Anal Sphincter Exercises for people with leakage from the bowel Introduction Sphincter exercises can help you
Anterior Sphincter Repair Operation
 Anterior Sphincter Repair Operation How will the operation help me? The investigations that you have had indicate that your anal sphincter is damaged or very weak, and this is why you are having trouble
Anterior Sphincter Repair Operation How will the operation help me? The investigations that you have had indicate that your anal sphincter is damaged or very weak, and this is why you are having trouble
Specialist Continence Advisory Service Local Partnerships. Constipation
 Patient Experience Team contact details: Phone: 0115 993 4542 Email: complaints@nottshc.nhs.uk Write to: Patient Experience Team, Moorgreen House, Highbury Hospital, Highbury Vale, Bulwell, Nottingham
Patient Experience Team contact details: Phone: 0115 993 4542 Email: complaints@nottshc.nhs.uk Write to: Patient Experience Team, Moorgreen House, Highbury Hospital, Highbury Vale, Bulwell, Nottingham
Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms
 Information for Men Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms SPHERE Bladder and Bowel Service Supporting Pelvic Health through Empowerment Rehabilitation and Education 2 Index Self-managing your urinary symptoms
Information for Men Self -Managing Your Urinary Symptoms SPHERE Bladder and Bowel Service Supporting Pelvic Health through Empowerment Rehabilitation and Education 2 Index Self-managing your urinary symptoms
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Symptom Management. How to Manage Your Diarrhea
 Symptom Management How to Manage Your Diarrhea This patient guide will help you understand: A What is cancer-related diarrhea?...3 B What causes cancer-related diarrhea?...4 C What can I do to manage diarrhea?...5
Symptom Management How to Manage Your Diarrhea This patient guide will help you understand: A What is cancer-related diarrhea?...3 B What causes cancer-related diarrhea?...4 C What can I do to manage diarrhea?...5
Discharge Information following Bowel Surgery
 Discharge Information following Bowel Surgery Here is some information to help with your recovery at home and advice about returning to normal activities following bowel surgery. We hope this will be helpful
Discharge Information following Bowel Surgery Here is some information to help with your recovery at home and advice about returning to normal activities following bowel surgery. We hope this will be helpful
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet Your Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal
Patient Information Leaflet Your Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal
Chemotherapy effects. your PR.i.VATES.
 your PR.i.VATES Testicular cancer awareness, advice and support for men in the UK affected by testicular cancer. Chemotherapy effects www.yourprivates.org.uk Chemotherapy effects While the chemotherapy
your PR.i.VATES Testicular cancer awareness, advice and support for men in the UK affected by testicular cancer. Chemotherapy effects www.yourprivates.org.uk Chemotherapy effects While the chemotherapy
Sphincter exercises for people with bowel control problems. Information for patients. Physiotherapy Department
 Sphincter exercises for people with bowel control problems Information for patients Physiotherapy Department 01625 661481 @EastCheshireNHS Leaflet Ref: 11229 Published: June 18 Review: 31/0/5/2021 Page
Sphincter exercises for people with bowel control problems Information for patients Physiotherapy Department 01625 661481 @EastCheshireNHS Leaflet Ref: 11229 Published: June 18 Review: 31/0/5/2021 Page
What Is Constipation?
 CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal act like
Patient Information Leaflet Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal act like
Managing your Bowels. Below is a diagram of the different parts of the digestive system and what they do. The Digestive System:
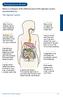 Managing your Bowels Below is a diagram of the different parts of the digestive system and what they do. The Digestive System: 1. Mouth When food is chewed, saliva starts digesting carbohydrates. 2. Oesophagus
Managing your Bowels Below is a diagram of the different parts of the digestive system and what they do. The Digestive System: 1. Mouth When food is chewed, saliva starts digesting carbohydrates. 2. Oesophagus
If follow up test(s) / diagnostic studies ordered: Please see patient to do list/appointment section.
 ERAS CRS DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS Procedure(s) / Surgeries during current admission: *** Discharge to: {Discharge to:220050} If follow up test(s) / diagnostic studies ordered: Please see patient to do list/appointment
ERAS CRS DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS Procedure(s) / Surgeries during current admission: *** Discharge to: {Discharge to:220050} If follow up test(s) / diagnostic studies ordered: Please see patient to do list/appointment
PATIENT INFORMATION Anterior Resection After Care
 PATIENT INFORMATION Anterior Resection After Care Anatomy of your bowel Transverse colon Ascending colon Descending colon Sigmoid colon Rectum Anus Your bowel before your operation The large bowel or colon
PATIENT INFORMATION Anterior Resection After Care Anatomy of your bowel Transverse colon Ascending colon Descending colon Sigmoid colon Rectum Anus Your bowel before your operation The large bowel or colon
Complex Care Hub Manual Bowel Ostomies: Ileostomy, Jejeunostomy, Colostomy
 Complex Care Hub Manual Bowel Ostomies: Ileostomy, Jejeunostomy, Colostomy Table of Contents 1. Overview of the gastrointestinal tract... 2 2. What is a stoma/ostomy?... 2 2.1 What is a Jejeunostomy?...3
Complex Care Hub Manual Bowel Ostomies: Ileostomy, Jejeunostomy, Colostomy Table of Contents 1. Overview of the gastrointestinal tract... 2 2. What is a stoma/ostomy?... 2 2.1 What is a Jejeunostomy?...3
Stricture guide. Urology department. yeovilhospital.nhs.uk
 Stricture guide Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is a urethral stricture? A urethral stricture is a narrowing or restriction of the urethra (the tube from your bladder through
Stricture guide Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is a urethral stricture? A urethral stricture is a narrowing or restriction of the urethra (the tube from your bladder through
Chapter 22. Bowel Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Nutrition and Dietetics Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Diverticular disease Nutrition and Dietetics Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have diverticular disease. It contains information about the disease and
Diverticular disease Nutrition and Dietetics Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have diverticular disease. It contains information about the disease and
Dietary advice for people with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 Dietary advice for people with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Crohn s disease and Ulcerative colitis Information for patients Name Your Dietitian Dietitian contact number: 0118 322 7116 What is Inflammatory
Dietary advice for people with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Crohn s disease and Ulcerative colitis Information for patients Name Your Dietitian Dietitian contact number: 0118 322 7116 What is Inflammatory
Manual: Bowel Ostomy, Ileostomy, Jejunostomy, Colostomy
 RCH@Home Manual: Bowel Ostomy, Ileostomy, Jejunostomy, Colostomy Table of Contents 1. What is a stoma/ostomy?... 2 2. What is a jejeunostomy?... 2 3. What is an ileostomy?... 2 4. What is a colostomy?...
RCH@Home Manual: Bowel Ostomy, Ileostomy, Jejunostomy, Colostomy Table of Contents 1. What is a stoma/ostomy?... 2 2. What is a jejeunostomy?... 2 3. What is an ileostomy?... 2 4. What is a colostomy?...
Chapter 19. Assisting With Bowel Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Adult barium enema. X-ray Department Ground Floor, St James Wing. What is a barium enema? Are there alternatives to Barium enema?
 Adult barium enema X-ray Department Ground Floor, St James Wing This information leaflet is for patients who are having a barium enema. It explains the procedure, how to prepare for it and what happens
Adult barium enema X-ray Department Ground Floor, St James Wing This information leaflet is for patients who are having a barium enema. It explains the procedure, how to prepare for it and what happens
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus.
 The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
Gas and Flatulence Prevention Diet
 Gas and Flatulence Prevention Diet Purpose Intestinal gas means different things to different people. Patients may complain of excessive bloating after eating, belching, or rectal gas (flatulence), or
Gas and Flatulence Prevention Diet Purpose Intestinal gas means different things to different people. Patients may complain of excessive bloating after eating, belching, or rectal gas (flatulence), or
Delorme s Operation For Rectal Prolapse
 Delorme s Operation For Rectal Prolapse Patient Information Colorectal Surgery Author ID: NM Leaflet Number: Surg 045 Version: 3.1 Name of Leaflet: Delorme s Operation for Rectal Prolapse Date Produced:
Delorme s Operation For Rectal Prolapse Patient Information Colorectal Surgery Author ID: NM Leaflet Number: Surg 045 Version: 3.1 Name of Leaflet: Delorme s Operation for Rectal Prolapse Date Produced:
Information to Help You Live Life to the Fullest
 Information to Help You Live Life to the Fullest For more information and to join the conversation visit: Prevail.com/LOBC 800-227-3551 CONSUMER EDUCATION 2015 First Quality Products, Inc. All rights reserved.
Information to Help You Live Life to the Fullest For more information and to join the conversation visit: Prevail.com/LOBC 800-227-3551 CONSUMER EDUCATION 2015 First Quality Products, Inc. All rights reserved.
Perineal Tears. Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women & Children s Group
 Perineal Tears Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women & Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
Perineal Tears Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women & Children s Group This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure, and to answer some common queries that
POOP: WHAT S NORMAL & WHAT S NOT
 HEALING LEAKY GUT POOP: WHAT S NORMAL & WHAT S NOT Is my poop normal? Most of us have asked ourselves that at one time or another. When your poop isn t right, it definitely indicates something isn t quite
HEALING LEAKY GUT POOP: WHAT S NORMAL & WHAT S NOT Is my poop normal? Most of us have asked ourselves that at one time or another. When your poop isn t right, it definitely indicates something isn t quite
Managing dietary problems in pancreatic cancer Contents
 13 11 20 Information and support Managing dietary problems in pancreatic cancer Contents Eating after a Whipple procedure Vomiting Diabetes Pancreatic enzyme replacement supplements Nutritional supplements
13 11 20 Information and support Managing dietary problems in pancreatic cancer Contents Eating after a Whipple procedure Vomiting Diabetes Pancreatic enzyme replacement supplements Nutritional supplements
Patient Advice for Third & Fourth Degree Tears
 Patient Advice for Third & Fourth Degree Tears Please read this leaflet carefully. It is important that you take note of any instructions or advice given. If you have any questions or problems that are
Patient Advice for Third & Fourth Degree Tears Please read this leaflet carefully. It is important that you take note of any instructions or advice given. If you have any questions or problems that are
Physiotherapy advice following your third or fourth degree perineal tear
 Further sources of information NHS Choices: www.nhs.uk/conditions Our website: www.sfh-tr.nhs.uk INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Patient Experience Team (PET) PET is available to help with any of your compliments,
Further sources of information NHS Choices: www.nhs.uk/conditions Our website: www.sfh-tr.nhs.uk INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Patient Experience Team (PET) PET is available to help with any of your compliments,
Constipation. AL amyloidosis Infosheet Series. Symptoms and complications. Infoline:
 Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in AL amyloidosis patients, the signs and symptoms, how it is treated and tips for self-management/prevention. What is constipation?
Constipation This Infosheet explains what constipation is, what causes it in AL amyloidosis patients, the signs and symptoms, how it is treated and tips for self-management/prevention. What is constipation?
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care
 Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
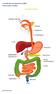 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) consists of a number of symptoms. The most
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) consists of a number of symptoms. The most
Dietary. Ostomists. Advice. National: Scotland:
 Ostomists Dietary Advice www.fittleworth.com DTRY315-1 Opening Hours: 8 am to 8 pm Monday to Friday 9 am to 1 pm Saturday National: 0800 378 846 Scotland: 0800 783 7148 Dietary Advice for Ostomists Giving
Ostomists Dietary Advice www.fittleworth.com DTRY315-1 Opening Hours: 8 am to 8 pm Monday to Friday 9 am to 1 pm Saturday National: 0800 378 846 Scotland: 0800 783 7148 Dietary Advice for Ostomists Giving
Irritable Bowel. Syndrome. Health Promotion Service
 The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
The information in this leaflet is not intended to replace the knowledge or diagnosis of a qualified health practitioner. We encourage you to consult a health professional and ensure your IBS is properly
Radiotherapy to the Prostate. Information for patients
 Radiotherapy to the Prostate Information for patients Northern Centre for Cancer Care Freeman Hospital Introduction Your oncologist has advised you to have a course of radiotherapy to your prostate as
Radiotherapy to the Prostate Information for patients Northern Centre for Cancer Care Freeman Hospital Introduction Your oncologist has advised you to have a course of radiotherapy to your prostate as
Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises
 MALE LUTS/CUP_11_11 Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) include the need to pass water very frequently (frequency)
MALE LUTS/CUP_11_11 Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: Lifestyle Advice, Bladder Training and Pelvic Floor Exercises Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) include the need to pass water very frequently (frequency)
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e. For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries
 B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
Dietary advice when you have a colostomy
 Dietary advice when you have a colostomy Information for patients Name Your Dietitian Dietitian contact number: 0118 322 7116 What is a colostomy? A colostomy is a surgical procedure that brings out the
Dietary advice when you have a colostomy Information for patients Name Your Dietitian Dietitian contact number: 0118 322 7116 What is a colostomy? A colostomy is a surgical procedure that brings out the
Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence
 Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence This leaflet explains what urge incontinence is and how we can help to reduce and relieve your symptoms. If you have any questions or concerns,
Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence This leaflet explains what urge incontinence is and how we can help to reduce and relieve your symptoms. If you have any questions or concerns,
POST-OPERATIVE INSTRUCTIONS FOLLOWING RECTAL OFFICE SURGERY
 POST-OPERATIVE INSTRUCTIONS FOLLOWING RECTAL OFFICE SURGERY 1. KEEP THE RECTAL AREA CLEAN AND DRY. After a bowel movement, clean your bottom with peri-anal cleansing pads (i.e. Tucks or baby-wipes), followed
POST-OPERATIVE INSTRUCTIONS FOLLOWING RECTAL OFFICE SURGERY 1. KEEP THE RECTAL AREA CLEAN AND DRY. After a bowel movement, clean your bottom with peri-anal cleansing pads (i.e. Tucks or baby-wipes), followed
Receiving Radiation Therapy to the Pelvis for Gynaecological Cancers
 Radiation therapy may be recommended for patients with gynaecological cancers: To the pelvis after surgery if margins of surgery were not clear. To the pelvis before surgery to reduce tumour size. This
Radiation therapy may be recommended for patients with gynaecological cancers: To the pelvis after surgery if margins of surgery were not clear. To the pelvis before surgery to reduce tumour size. This
Bladder and Bowel Symptoms Troubleshooting Tips
 Bladder and Bowel Symptoms Troubleshooting Tips Unwilling to accept assistance with using the toilet There may be an underlying condition that causes this resistance, or the individual may not understand
Bladder and Bowel Symptoms Troubleshooting Tips Unwilling to accept assistance with using the toilet There may be an underlying condition that causes this resistance, or the individual may not understand
Health Professional Manual
 Health Professional Manual Session: Healthy Eating COPD and healthy eating General healthy eating advice Getting the most out of every meal Adapted from the Living Well with COPD program (2nd edition),
Health Professional Manual Session: Healthy Eating COPD and healthy eating General healthy eating advice Getting the most out of every meal Adapted from the Living Well with COPD program (2nd edition),
Management and Lifestyle Advice for Adults with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Information for Patients
 Management and Lifestyle Advice for Adults with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Information for Patients 1 This patient information is written to provide patients with information and advice on how to manage
Management and Lifestyle Advice for Adults with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Information for Patients 1 This patient information is written to provide patients with information and advice on how to manage
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE
 IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
A patient s guide to the. management of constipation following surgery
 A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
A patient s guide to the management of constipation following surgery This leaflet has been designed to give you more information about using laxatives after your surgery. What is constipation? After your
American University Of Beirut Medical Center Dietary Department DIET FOR LACTATION
 American University Of Beirut Medical Center Dietary Department Breast Feeding, your best choice WHY? DIET FOR LACTATION Breast milk Is nutritious: it provides your baby with a nutritionally complete feed
American University Of Beirut Medical Center Dietary Department Breast Feeding, your best choice WHY? DIET FOR LACTATION Breast milk Is nutritious: it provides your baby with a nutritionally complete feed
Managing bowel problems after cancer treatment
 Managing bowel problems after cancer treatment Information for cancer survivors Read this pamphlet to learn: What bowel problems are What causes bowel problems What you can do to manage your bowel problems
Managing bowel problems after cancer treatment Information for cancer survivors Read this pamphlet to learn: What bowel problems are What causes bowel problems What you can do to manage your bowel problems
Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury
 Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury A resource for individuals with SCI and their supporters This presentation is based on SCI Model Systems research and was developed with support from the National
Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury A resource for individuals with SCI and their supporters This presentation is based on SCI Model Systems research and was developed with support from the National
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men
 Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men (formerly ACPWH) Useful resources Websites Pelvic Obstetric & Gynaecological Physiotherapy - pogp.csp.org.uk Bladder and Bowel Foundation - www.bladderandbowelfoundation.org
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men (formerly ACPWH) Useful resources Websites Pelvic Obstetric & Gynaecological Physiotherapy - pogp.csp.org.uk Bladder and Bowel Foundation - www.bladderandbowelfoundation.org
