Urinary incontinence in women & men
|
|
|
- Elfreda Phillips
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Urinary incontinence in women & men Dr. Blayne Welk Assistant Professor, Western University, London, ON, Canada Part 1: INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN Urinary incontinence is common. About 1 in 4 young women, and almost half of older women, experience urinary incontinence. Incontinence is not diagnosed or treated in many of these women. Some are not bothered by it and choose not to get help from their doctor. However, we know that incontinence is linked to falls and fractures in the elderly, skin breakdown because of the constant irritation of wearing wet pads, depression, more frequent visits to the doctor, and a lower quality of life. Incontinence affects all areas of life, including physical, mental and social life. In fact, the quality of life with incontinence has been shown to be lower than with some chronic diseases, such as heart disease, arthritis and diabetes. Urinary incontinence has a large economic impact. Research suggests that $16 billion is spent on incontinence in the United States. This number includes personal, healthcare and medication-related expenses, but 70% of this money is spent on routine management (the purchase of items such as pads and diapers, laundry and dry cleaning). Because of these costs, women spend on average $750/year to manage their incontinence. The body parts involved in urinary control are shown in Figure 1. There are 2 types of incontinence: Urethra Figure 1. The bladder stores the urine made by the kidneys. It sits between your pubic bone and vagina.the urine exits the body through the urethra.the urethra is surrounded by a muscle, called the urinary sphincter, which controls the urine flow. Behind the vagina are the rectum and the anus, which are responsible for bowel movements. Bladder Uterus Vagina Rectum 1. Stress incontinence: This type of incontinence happens if urine leaks when you move, sneeze, cough or laugh. 2. Urgency incontinence: This type of incontinence happens if urine leaks at the same time as you get the urge to go to the bathroom. This is usually part of an overactive bladder (OAB). With OAB, you urinate more frequently (day and night) and you get an immediate urge to go to the bathroom (without the normal warnings); so you end up having to rush and find a bathroom. About 1 in 3 people with OAB have urgency incontinence. 92
2 Many women have a mix of these two types this is called mixed incontinence. Even in these cases, most women find that one type of urinary leakage (either stress or urgency) is more common. There are also less common causes of urinary incontinence: overflow incontinence, when a person cannot empty their bladder properly; and continuous incontinence, when there is an abnormal connection between your bladder and vagina. This is a rare complication, but can happen when you have surgery on your bladder, uterus or vagina. The first thing to do is to determine the type of incontinence that you have; there are different treatments for different types. There are many reasons why women develop urinary incontinence. It is mostly seen in older women, although a large number of younger women also experience incontinence. Reasons why women develop urinary incontinence Being overweight; a woman of average height (5 4, or 1.6 m) who weighs more than 180 lbs (or 82 kg) has twice the risk of urinary incontinence. Women who have had vaginal deliveries are at a higher risk. A large part of a woman s risk of incontinence is inherited from her parents. Specific medications and neurologic conditions (such as spinal cord injury, previous strokes, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson s disease and dementia) are associated with incontinence. The reasons why a woman develops incontinence depends on the type of incontinence. Stress incontinence usually occurs because of a weakness in the supports of the urethra. The urethra is a 4-cm tube that caries urine out of the bladder. Wrapped around this tube is the urinary sphincter, the muscle that controls urinary flow. Usually a combination of weak tissues holding the urethra in place and a weak urinary sphincter leads to stress incontinence. Urgency incontinence occurs because of changes in the bladder muscle, the bladder lining or in the nerves that control the bladder. These changes cause the bladder muscle to contract without the usual signal from the brain. This causes a sudden urge to go to the bathroom. What to expect when seeing a doctor for incontinence Your family doctor may refer you to a specialist to evaluate your incontinence, or may suggest some treatment options before considering a referral. Usually urologists or gynecologists are the specialists that deal with urinary incontinence. They may suggest operations to treat certain types of incontinence. Topics your doctor will ask you about: Previous health Medications Allergies 93
3 To help your doctor determine the type of urinary incontinence that you have, you should keep track of what you are doing when you experience incontinence. You should be able to describe to your doctor how much urine leaks and how this bothers you and affects your life. Questions your doctor may ask you: How frequently do you urinate (day and night)? Do you have urinary urgency (which is when you have the sudden urge to urinate that you can t easily put off)? Do you have trouble with your urinary stream (such as a slow stream)? Do you feel like you empty your bladder well? Many doctors will ask you to fill out a form called a voiding diary (Figure 2). Completing this form will help you and your doctor see exactly what your urinary habits are like. An average person urinates up to eight times a day and 0 1 time overnight. The normal amount of urine passed with each urination is ml (7 14 ounces). Your doctor may also ask you about your urinary history, your drinking habits (especially caffeinated beverages or alcohol), new neurological symptoms (double vision, muscle weakness, tingling or numbness) and pelvic pain. The pelvic exam You will likely have a pelvic exam. The doctor will assess for any vaginal prolapse when the bladder, uterus or rectum bulge into the vagina. Many women have mild pelvic organ prolapse that usually does not require treatment, however more severe cases may require a pessary (a device inserted to support your uterus or vagina) or surgery. During the pelvic exam the doctor may ask you to perform a Kegel. This is the name of the exercise where the pelvic floor is contracted. This is the same muscle that you would use to stop your urination. Some people aren t able to control this muscle very well, and may benefit from strengthening it. Finally, it is important to see if there is urinary leakage. This can be done with a cough test. You should have a full bladder, and then the doctor will ask you to cough or strain, and observe. It may have to be done in different positions to demonstrate the incontinence. At the same time, the amount of movement of the urethra is observed. If there is movement of the urethra, it is termed hypermobility. Urine tests Figure 2. An example of a voiding diary.this is used to keep track of your urinary habits over 24 hours.you can get a blank form at /VoidingDiary_en.PDF Most women will be asked for urine tests to see if there is infection or blood in the urine. If there is blood in the urine, you should be evaluated by a urologist. If there is a urine infection, you should be treated to make sure that the infection isn t causing some of your symptoms. 94
4 Other specialized tests may be performed: A bladder scanner or urinary catheter can be used to see how well you empty your bladder after voiding. A cystoscopy may be performed to evaluate the inside of your bladder or urethra; this involves passing a small telescope into your bladder. Urodynamic testing is a specialized way of measuring how your bladder and urinary sphincter work. A small catheter (only a few millimeters in size) is placed into your bladder, and another one into your vagina or rectum. Your bladder is then filled with fluid, and the pressures in your bladder are measured during filling, and at the end when you are asked to urinate. Non-surgical, mon-medical treatments Some women choose to manage their urinary incontinence with absorptive pads. Either sanitary napkins or minipads can be used, although pads designed specifically for incontinence may work better. See Table 1 for an overview of the things you can do, without surgery or medicine, to help your incontinence. Table 1. Non-medical non-surgical treatment options Pads, liners, diapers Changing the types and amounts of fluids you drink Learning to suppress the sudden urge to void Pelvic floor muscle exercises (Kegel s exercises) Weight loss Vaginal pessaries, urethral plugs or catheters Lifestyle changes can improve urinary incontinence. Examples include: Changing the amount or type of fluid you drink. Changing the number of times you urinate. Decreasing your caffeine intake. Decreasing the amount of fluids you drink in a day. Urinating on a regular schedule helps prevent you from being caught off guard by the sudden urge to urinate, and can help retrain your bladder to function on a more normal schedule. Urge suppression techniques can be used for urgency incontinence: when you feel the sudden urge to urinate you stop, tighten you pelvic floor (with a Kegel), and then wait for the urge to void to lessen. Weight loss has been shown to reduce urinary incontinence in women. In one study, overweight women who lost on average 8 kg (18 lbs) over six months were twice as likely to have an improvement in their incontinence. 95
5 Pelvic floor muscle therapy (or Kegel s exercise) can strengthen your pelvic floor. It can reduce urinary incontinence. These exercises can be used for stress and urgency type incontinence. It is usually recommended that you do at least contractions daily (usually split into 3-5 different sets done throughout the day). Some women have trouble isolating these muscles, and they may benefit from seeing a specialized nurse or physiotherapist who treats pelvic floor disorders (a list of these professions can be found online: Biofeedback is the term used when these exercises are taught with the help of a device that shows you what your muscles are doing to make it easier for you to understand how to control and interpret your muscles. Pessaries are rubber inserts that are placed into the vagina. They can be used for vaginal prolapse, and for urinary incontinence (Figure 3, part a). There are several types available; you need a specialized nurse or physician to help you find the correct fit. Special incontinence pessaries have a knob that sits under the urethra to help support it, and reduce stress incontinence. Urethral inserts are also available. These are short plugs that are inserted into the urethra (Figure 3, part b). They are only used for a short time and then thrown away. They are useful for women who need only a short period of continence, such as during intense physical activity. Catheters are soft plastic tubes that are used to empty the bladder. There are catheters with balloons on the end of them that are held in place in your bladder; these are rarely used to manage urinary incontinence. Temporary catheters (often called clean intermittent catheters or CIC) are inserted into your urethra for a few minutes to empty the bladder, and then they are removed. They may be suggested by your doctor if you have overflow incontinence, and are not able to empty your bladder. A B Figure 3. An example of a urinary incontinence pessary (a) and a urethral insert (b). 96
6 Medical treatments There aren t many effective treatments for stress incontinence. A type of antidepressant called duloxetine may help treat stress urinary incontinence, however it is not officially recognized by Health Canada for this use. Other types of antidepressants may increase the strength of the urinary sphincter and can be used to treat stress or urgency incontinence, although there are not many studies looking at this use. Estrogen was previously used for stress incontinence. However, recently, it has not been shown to be effective. Topical vaginal estrogen may still be recommended for frequent urinary tract infections, as a temporary treatment prior to vaginal surgery, or for symptoms of vaginal dryness or pain with intercourse. Using oral medications Urgency incontinence is usually treated with oral medications. The class of medications that is used is called anticholinergic medications (because of the effect they have on a certain type of receptor found in the body). See Table 2 for the different types of anticholinergic medications. There is a new class of medication that acts on the beta receptor in the bladder, and does not seem to have many of the side effects seen in anticholinergic medications (mirabegron, Table 2). There are no clear differences in the actual effectiveness of these medications. Your doctor can help you choose the right one and make sure it is safe for you. Generally the long-acting forms (which are taken once a day) have less dry mouth compared to the short-acting forms (which are usually taken multiple times a day). Coverage for these medications is different among the provinces in Canada, and may differ among private health plans. You may need to try different medications before you find the right one. Usually the medications should have an effect within one to four weeks. This expected benefit is less urinary urgency, less frequent urinating, and less urinary leakage associated with the feeling of urgency. These medications will not improve stress urinary incontinence. 97
7 Table 2. Examples of types of overactive bladder medications available in Canada. Trade name Generic name Dose Number of times per day Ditropan (also comes as an Oxybutynin extended release pill, and a skin patch) mg Once to three times Detrol LA (also comes as an Tolterodine ER immediate release pill) 2-4 mg Once Enablex Darifenacin mg Once Toviaz Fesoterodine 4-8 mg Once Trosec Tropsium 20 mg Twice Vesicare Solifenacin 5-10 mg Once Myrbetriq Mirabegron mg Once Common side effects for anticholinergic medications: Dry mouth Constipation Blurred vision Dry eyes Headache Upset stomach Not everyone has these side effects. If you experience bothersome dry mouth, you can try alcoholfree mouthwash, oral lubricants or sugar-free lozenges or gum. If constipation becomes a problem, increase your intake of dietary fibre or try over-the-counter laxatives or stool softeners. There may be other side effects that should be discussed with your doctor. These medications should not be taken if you have an untreated closed angle glaucoma of the eye, urinary retention (an inability to empty the bladder properly) or certain stomach problems. Surgery for stress incontinence For your urethral sphincter to work properly, it must be correctly supported by the surrounding tissues, and the sphincter muscle itself must be working properly. The sphincter muscle may not work properly if it s been damaged by previous surgery, or if the sphincter is not properly supported by the tissue of the vagina and pelvis. There are different types of surgery to improve the function of the urethral sphincter by restoring support to the urethral sphincter. Urethral bulking treatments: This is when semi-solid material is injected into the urethra, often through a cystoscope. This material helps the urethral sphincter close. This procedure is not very invasive, and in some women may be the best option. However, the long-term success of this procedure is low, and many patients need multiple treatments over time. Risks from this procedure usually include bleeding, infection, and an inability to urinate after the procedure (which is usually temporary). 98
8 Placing a midurethral sling: This is the most common treatment. These slings are small pieces of mesh that are placed under the urethra by making a small incision in the vagina. They were first used in the mid 1990s. They are passed through the pelvis and either come out through a small incision in the inner thigh, or through a small incision on the lower abdomen. They provide a backstop to help close off the urethra when you are doing anything that involves straining. For some patients with mixed incontinence, they may also relieve symptoms of urinary urgency and urgency incontinence (Figure 4). These procedures are usually done in the operating room and take about minutes. Usually you can go home the same day. You have to limit your physical activity for a few weeks afterwards, while the mesh heals in place. Risks of the surgery may include urinary infection, bleeding, and an inability to urinate afterwards (this requires the temporary placement of a urethral catheter). Other complications include erosion of the mesh into the urethra, or exposure of the mesh in vagina; this is rare, but may require a second surgery to fix. You may also have leg pain (if the sling is passed through the groin muscles) and the new feeling of urinary urgency. Your surgeon will discuss all the risks of this procedure with you before surgery. Figure 4. Examples of the midurethral sling passed through the groin (a, the transobturator sling) or through the lower abdomen (b, retropubic sling). There are also smaller slings, called mini-slings. These are meant to be less invasive than traditional midurethral slings, and allow you a quicker recovery with less discomfort. They may be a reasonable option for some women, as some studies show that they have similar results to the traditional midurethral slings. However, we need more information to make sure these slings are durable, and to determine which patients are best suited for these slings. If you have severe or complicated incontinence, other surgical therapies may be recommended. These were popular surgical options before the invention of midurethral slings, and are still appropriate in certain situations. Slings can be constructed from your own tissue (such as part of your abdominal wall, termed autologous rectus fascial slings). Bladder suspensions (which are done through a lower abdominal incision or using a telescope and small instruments inserted into your abdomen) are another option. 99
9 Surgery for urgency incontinence Surgery is not usually needed. However, certain procedures can treat this type of incontinence. Stimulation of a nerve in the ankle with a small amount of electrical current is called percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation. This is more of a procedure than a surgery. A special needle and machine are used, and the treatment usually lasts for 30 minutes a day, and is done once a week for several weeks. Some people have had good results from this technique, but it requires the long-term use of the machine. Botox is another option if you have severe urgency incontinence. This medication works by decreasing the ability of the bladder muscle to have abnormal contractions. This treatment is often used in patients with a known neurological problem (such as multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injury). This treatment is also temporary, and usually needs to be repeated every 6-9 months. The Botox is injected into the bladder using a small needle and a cystoscope, and is usually done in a procedure or operating room. The main risks are urinary tract infections and not being able to urinate afterwards. If you are unable to urinate after the procedure, you will have to use intermittent catheters to empty your bladder. If this happens, it may take several weeks before your bladder is able to empty properly on its own. Sacral neuromodulation is a procedure where the nerves in the lower back are stimulated to change the way the bladder works. This is usually done in patients who have failed all other treatments. A temporary needle is inserted in the back and connected to a control device. Then your response is followed for a few weeks to see if the treatment works. If it does appear to be working, then a permanent needle and generator are implanted. Only a few centres in Canada currently offer this procedure. Future directions Exciting research is being done in the area of tissue engineering to treat stress urinary incontinence. This includes experimental procedures which take your own muscle stem cells, grow them in a lab, and then inject them into your urethra. This procedure tries to grow back the urethral sphincter, and so far the results are promising. New medications that work on different areas of the bladder are also being developed, and may improve the symptoms of urgency incontinence and overactive bladder. Visit: Women s Bladder Health: The Canadian Continence Foundation 100
10 Part 2: MALE INCONTINENCE Men are less likely to experience urinary incontinence than women because of the prostate, which is located between the base of the bladder and the urinary sphincter (Figure 5). However, men can still experience the same types of incontinence that affect women: 1. Stress incontinence is when urinary leakage occurs with movement or activity, sneezing, coughing, or laughing. In men this mostly happens as a complication of surgery on or near the prostate. 2. Urgency incontinence is when urinary leakage occurs at the same time as the urge to go to the bathroom. Urgency incontinence is often part of the syndrome of overactive bladder (OAB). Up to 10% of older men may experience urgency incontinence. 3. Overflow incontinence can occur in men when they can t empty their bladder well. The bladder stays full, and there is a constant leakage of urine often with small, frequent episodes of urination. This can be the result of a blockage in the urinary flow, often from an enlarged prostate, or scar tissue in the urinary passage. Figure 5. Male anatomy.the bladder stores the urine.the urethra is the tube that drains the urine.the prostate wraps around the first part of the urethra, and just below this is the urinary sphincter, which controls the urinary flow. Causes of urinary incontinence in men: Urinary incontinence becomes more common as men grow older. Up to one in four men will have some urinary incontinence after prostate cancer treatment (with either surgery or radiation therapy) half of these men will consider it a problem. Urinary incontinence usually improves during the first year after surgery. Operations to treat a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate (such as a TURP, which involves resecting the inner portion of the prostate through a telescope), or operations to treat scars in the urinary passageway (urethral strictures) can sometimes cause urinary incontinence. The same neurologic diseases that cause incontinence in women can also cause incontinence in men (such as spinal cord injury, previous strokes, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson s disease and dementia). What to expect from your doctor Your family doctor may refer you to a urologist to evaluate your incontinence, or may suggest some treatment options before considering a referral. 101
11 Topics your doctor will ask you about you: Previous health Medications Allergies Your urologist will carefully look at your history of previous prostate surgery, or other surgery performed by a urologist (especially operations or procedures on the prostate or urethra). These answers will help your doctor determine your type of urinary incontinence (stress, urgency, or overflow). Questions your doctor will ask you: How frequently do you urinate (day and night)? How is your urinary stream is it a slow or weak stream, a stream that starts and stops, or a stream that takes a while to start? Do you have urinary urgency (which is when you have the sudden urge to urinate that you can t easily put off)? Do you feel like you empty your bladder completely? Your doctor may also ask you about your urinary history, your drinking habits (especially caffeinated beverages or alcohol), new neurological symptoms (double vision, muscle weakness, tingling or numbness) and pelvic pain. Your doctor will also check for urinary infections, blood in your urine, your bowel function, and prostate cancer treatment status (such as your most recent prostate-specific antigen level). The physical exam Abdominal exam to see if the bladder can be felt. If so, it may indicate overflow incontinence. A genital exam A rectal exam Other possible tests A urinalysis to check for blood or infection in the urine A uroflow test to measure the speed of your urination (for this test, you will be asked to urinate in a special toilet to measure the speed your urine). Your doctor will compare your value with expected values for your age. A bladder scanner to determine how full your bladder is after you have voided (known as your PVR, or post-void residual). If this is elevated it may indicate a problem with emptying your bladder properly. Cystoscopy is a small flexible telescope placed into your bladder through the urethra to make sure there is no urethral scarring, and to assess the prostate size, and the appearance of the bladder. 102
12 A urodynamics test measures how your bladder and urinary sphincter work. A small catheter (only a few millimeters in size) is placed into your bladder, and another one into your rectum. Your bladder is then filled with fluid, and the pressures in your bladder are measured during filling, and at the end when you are asked to urinate. Non-surgical, non-medical treatments Some men may not be very bothered by their incontinence, and may choose to manage it with pads. See Table 3 for an overview of some things you can do, without medicine or surgery, to help with your incontinence. Table 3. Non-medical non-surgical treatment options Pads, liners, diapers Changing the types and amounts of fluids you drink Pelvic floor muscle exercises (Kegel s exercises) Catheters, condom catheters, penile clamps Some non-operative options to manage urinary incontinence: Various penile clamps can be used to manage stress incontinence. These devices act like a clothespin on the penis, and help stop the urinary leakage. However, they can cause penile and urethral damage, and damage to the skin of the penis. These are best used by men who want to use them only for infrequent, short periods of time (such as a few hours during a weekly golf game). Condom catheters are condoms that are attached to the penis with adhesive, and drain into a catheter bag worn on the leg. These can also cause skin irritation on the penis, but may be appropriate for some men. Catheters may be required for some men with overflow incontinence. These catheters can be left in all the time, (and then changed every four to six weeks). An alternative to a catheter in the bladder all the time is to learn how to pass a catheter into the bladder only when you need to urinate (usually one to four times a day). Doing pelvic floor muscle exercises (or Kegel s exercise) is a good way to strengthen your pelvic floor. They are commonly used in women, and are also appropriate for men. They can be used for both stress and urgency type incontinence. It is usually recommended that you do at least contractions daily (usually split into three to five different sets done throughout the day). If you have trouble with this, see a specialized nurse or physiotherapist who treats pelvic floor disorders (a list of these professions can be found online: Biofeedback is the term used when these exercises are taught with the help of a device that shows you what your muscles are doing in order to make it easier for you to understand how to control and interpret your muscles. You should do these exercises after your prostate surgery to speed up the return of your urinary continence. 103
13 Medical treatments If you have overflow incontinence, you can use the same medications that are used to treat an enlarged prostate. These include alpha blockers (such as tamsulosin or alfuzosin), and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (such as finasteride or dutasteride). Alpha blockers generally work quickly, and should start to help within a few days; they relax the muscle fibres in the prostate. 5-alpha reductase inhibitors take 3-6 months to have an effect; they work by actually shrinking the prostate. If you have urgency type incontinence, you can take anticholinergic medications. There is a small risk these medications cause problems when you empty your bladder. This risk is very low if the residual urine left in the bladder after voiding is small (under 150mL). If you cannot urinate after taking an anticholinergic medication, you will need to be reassessed by your doctor, and may have to stop taking the medication. Surgery for stress incontinence Urethral bulking agents are materials that are injected into the urethra to help the urethral sphincter close. They have been used to treat men with incontinence after radical prostatectomy, however the results are modest. Only a few men are completely cured, and these results are often temporary. Various types of male slings are available. These slings act to either compress the urethra, prevent leakage, or move the urethra into a different position to improve the way the urethral sphincter works (Figure 6). These operations are usually performed for patients with incontinence after prostate surgery. The advantage of these procedures is that they don t need you to press on anything to urinate (unlike the artificial sphincter, which is reviewed later). However, they are not right for all men, and may not work as well for men with a lot of incontinence. Figure 6. An example of the male urethral sling (a) and artificial urinary sphincter (b). 104
14 Risks There are risks to sling surgery for stress incontinence, such as: Not being able to urinate after the surgery (and needing a urinary catheter for a period of time) Bleeding Infection Pain or numbness in the inner thighs or scrotum Failure of the procedure The most common surgery for incontinence after prostate surgery in men is an artificial urinary sphincter (AUS). This device has three parts: 1.A balloon is placed in the lower abdomen, 2.An inflatable cuff is placed around the urethra, and 3.A control pump is placed in the scrotum. The control pump is the only part you have to use: by pushing on the button, the cuff opens and allows urination to occur. After a few minutes, the cuff automatically closes, and is ready for you to use again next time you need to urinate. The AUS has been around for decades, and works well even for severe incontinence. It does have some risks with it. Over time, the device can leak, or stop working; about 1 in 4 men will need to have a second surgery to fix part of the device within 5 years. The device can become infected, or can erode into the urethra (both of which require removal of the device). Over time, the tissue that the cuff presses on can thin out, and the incontinence can return. Surgery for urgency incontinence The same surgical procedures that are used in women can be used in men (please see the section in Part 1 on surgical treatment of urgency incontinence). Future directions Research is continuing to look at ways to decrease the risks of artificial urinary sphincter. One of these ideas is using an antibiotic coating on the device to reduce the risk of infection. New slings for male incontinence are being developed which will increase the types of procedures that can be offered. New medications that work on different areas of the bladder and prostate are also being developed, and these may improve the symptoms of urgency incontinence. Visit: Treatment-Effects/Incontinence 105
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Incontinence. Anatomy The human body has two kidneys. The kidneys continuously filter the blood and make urine.
 Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Incontinence Introduction Urinary incontinence occurs when a person cannot control the emptying of his or her urinary bladder. It can happen to anyone, but is very common in older people. Urinary incontinence
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence. Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa
 Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
Overactive Bladder. When to see a doctor. Normal bladder function
 Overactive Bladder Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder-storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to stop, and overactive bladder may lead to the involuntary
Overactive Bladder Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder-storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to stop, and overactive bladder may lead to the involuntary
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It
 Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It Urogynecology Patient Information Sheet What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for example,
Female Urinary Incontinence: What It Is and What You Can Do About It Urogynecology Patient Information Sheet What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for example,
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence and what causes it? A: When you are not able to hold your urine until you can get to a bathroom, you have what s called urinary incontinence (also called
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence and what causes it? A: When you are not able to hold your urine until you can get to a bathroom, you have what s called urinary incontinence (also called
Overactive bladder. Information for patients from Urogynaecology
 Overactive bladder Information for patients from Urogynaecology An overactive bladder (OAB) is a very common problem. It can cause distressing symptoms that are difficult to control. These can include
Overactive bladder Information for patients from Urogynaecology An overactive bladder (OAB) is a very common problem. It can cause distressing symptoms that are difficult to control. These can include
Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care
 Welcome To Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care Presented by Kamal Masaki, MD Professor and Chair Department of Geriatric Medicine John A. Burns School of Medicine, UH Manoa September 5, 2018 10:00 11:00
Welcome To Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care Presented by Kamal Masaki, MD Professor and Chair Department of Geriatric Medicine John A. Burns School of Medicine, UH Manoa September 5, 2018 10:00 11:00
FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: WHAT IT IS AND WHAT YOU CAN DO ABOUT IT
 URO-GYNECOLOGY PATIIENT IINFORMATIION SHEET FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: WHAT IT IS AND WHAT YOU CAN DO ABOUT IT What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for
URO-GYNECOLOGY PATIIENT IINFORMATIION SHEET FEMALE URINARY INCONTINENCE: WHAT IT IS AND WHAT YOU CAN DO ABOUT IT What is Urinary Incontinence? Stress Incontinence is a leakage of urine that occurs, for
Incontinence. Urinary. In Adults. THIS PUBLICATION IS OUT OF DATE. For most current information:
 Urinary Incontinence In Adults A Patient's Guide r I When you eat and drink, your body absorbs the liquid. The kidneys filter out waste products from the body fluids and make urine. Urine travels down
Urinary Incontinence In Adults A Patient's Guide r I When you eat and drink, your body absorbs the liquid. The kidneys filter out waste products from the body fluids and make urine. Urine travels down
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Some people experience occasional, minor leaks of urine. Others wet their clothes frequently.
 Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence the loss of bladder control is a common and often embarrassing problem. The severity ranges from occasionally leaking urine when you cough or sneeze to having
Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence the loss of bladder control is a common and often embarrassing problem. The severity ranges from occasionally leaking urine when you cough or sneeze to having
Various Types. Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG
 Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN
 Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Incontinence; Lets talk about it. Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery
 Incontinence; Lets talk about it Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Select the most appropriate subtitle for this talk A: Bladders gone wild! B: There s no such thing
Incontinence; Lets talk about it Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Select the most appropriate subtitle for this talk A: Bladders gone wild! B: There s no such thing
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Urinary Incontinence Q: What is urinary incontinence (UI)? A: UI is also known as loss of bladder control or urinary leakage. UI is when urine leaks out before you can get to a bathroom. If you have UI,
Pelvic Support Problems
 AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
Stress incontinence -- occurs during certain activities like coughing, sneezing, laughing, or exercise.
 Urinary incontinence Definition Incontinence is the inability to control the passage of urine. This can range from an occasional leakage of urine, to a complete inability to hold any urine. The three main
Urinary incontinence Definition Incontinence is the inability to control the passage of urine. This can range from an occasional leakage of urine, to a complete inability to hold any urine. The three main
Overactive bladder (OAB) affects approximately 15% of the adult population. Diagnosis is based
 Overactive bladder (OAB) affects approximately 15% of the adult population. Diagnosis is based upon a medical history, and includes a focused physical exam (abdominal, neurological, pelvic in females and
Overactive bladder (OAB) affects approximately 15% of the adult population. Diagnosis is based upon a medical history, and includes a focused physical exam (abdominal, neurological, pelvic in females and
Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider
 Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider Diana J Scott FNP-BC https://youtu.be/gmzaue1ojn4 1 Assessment of Urinary Incontinence Urge Stress Mixed Other overflow, postural, continuous, insensible,
Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider Diana J Scott FNP-BC https://youtu.be/gmzaue1ojn4 1 Assessment of Urinary Incontinence Urge Stress Mixed Other overflow, postural, continuous, insensible,
Management of Female Stress Incontinence
 Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
AgePage. Urinary Incontinence
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
Tension Free vaginal tape. Mrs Ami Shukla, Consultant Urogynaecologist Northampton General Hospital Northampton NN1 5BD
 Tension Free vaginal tape Mrs Ami Shukla, Consultant Urogynaecologist Northampton General Hospital Northampton NN1 5BD What is a TVT procedure? A TVT (Tension Free Vaginal Tape) procedure is an operation
Tension Free vaginal tape Mrs Ami Shukla, Consultant Urogynaecologist Northampton General Hospital Northampton NN1 5BD What is a TVT procedure? A TVT (Tension Free Vaginal Tape) procedure is an operation
Surgery for stress incontinence:
 Surgery for stress incontinence: information for you aashara Published February 2005 by the RCOG Contents Key points About this information What is stress incontinence? Do I need an operation? What operation
Surgery for stress incontinence: information for you aashara Published February 2005 by the RCOG Contents Key points About this information What is stress incontinence? Do I need an operation? What operation
AgePage. Urinary Incontinence
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
National Institute on Aging AgePage Urinary Incontinence Sarah loves to spend time with her friends talking about grandchildren and visiting with neighbors. But lately she s been having a big problem that
Surgery for vaginal vault prolapse. Patient decision aid
 Surgery for vaginal vault prolapse Patient decision aid? i What is vaginal vault prolapse? Vaginal vault prolapse happens when the top of the vagina (the vault) slips from its normal position and sags
Surgery for vaginal vault prolapse Patient decision aid? i What is vaginal vault prolapse? Vaginal vault prolapse happens when the top of the vagina (the vault) slips from its normal position and sags
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE
 IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
IMPROVING URINARY INCONTINENCE INFORMATION FOR OLDER ADULTS, FAMILIES, AND CAREGIVERS READ THIS PAMPHLET TO LEARN: What Urinary Incontinence is. How to Manage Urinary Incontinence. What Pelvic Floor Exercises
Objectives. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence
 Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Overactive Bladder Syndrome
 Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
THE OVER-ACTIVE BLADDER (OAB)
 THE OVER-ACTIVE BLADDER (OAB) Passage of urine is caused by the bladder muscle contracting coordinated with the relaxation of the sphincter muscles, which is controlled by higher centers in the central
THE OVER-ACTIVE BLADDER (OAB) Passage of urine is caused by the bladder muscle contracting coordinated with the relaxation of the sphincter muscles, which is controlled by higher centers in the central
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
Urinary incontinence. Urology Department. Patient Information Leaflet
 Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
Tension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT)
 Page 1 of 7 Tension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Introduction This leaflet will provide you with basic information about the Tension--free Vaginal Tape (TVT) procedure. What is a TVT? TVT is an operation to
Page 1 of 7 Tension-free Vaginal Tape (TVT) Introduction This leaflet will provide you with basic information about the Tension--free Vaginal Tape (TVT) procedure. What is a TVT? TVT is an operation to
Patient Information. Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms. pubic bone. urethra. scrotum. bladder. vaginal canal
 Patient Information English Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is the bladder? pubic bone bladder seminal vesicles prostate rectum The
Patient Information English Basic Information on Overactive Bladder Symptoms The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is the bladder? pubic bone bladder seminal vesicles prostate rectum The
Intermittent self-catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Spinal Injuries
 Intermittent self-catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Spinal Injuries page 2 of 12 What is clean intermittent self-catheterisation (CISC)? Urinary catheterisation is a procedure used to drain
Intermittent self-catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Spinal Injuries page 2 of 12 What is clean intermittent self-catheterisation (CISC)? Urinary catheterisation is a procedure used to drain
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH: Bladder Prolapse Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse Don t Let Bladder Prolapse Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
BLADDER HEALTH: Bladder Prolapse Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse Don t Let Bladder Prolapse Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy
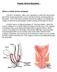 Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
ONE IN THREE WOMEN WHO EVER HAD A BABY WET THEMSELVES EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD DO PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING.
 08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
08 EVERY WOMAN WHO HAS HAD A BABY SHOULD Women who have even just one baby are nearly three times more likely to leak urine and wet themselves, than women who have not had a baby. The more babies you have,
Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy
 A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
A Common problem for Men and women Promoting Continence with Physiotherapy This leaflet contains information about physiotherapy advice and treatment for anyone with bladder and bowel problems. This may
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women
 Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Using Physiotherapy to Manage Urinary Incontinence in Women Bladder control problems are common, and affect people of all ages, genders and backgrounds. These problems are referred to as urinary incontinence
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Definition Prostate gland enlargement is a common condition as men get older. Also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostate gland enlargement can cause bothersome
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Definition Prostate gland enlargement is a common condition as men get older. Also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostate gland enlargement can cause bothersome
Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME
 Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME Introductions Amelia Samuels, Physiotherapist, Active Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Supporting the Continence Foundation of Australia Continence Foundation of Australia
Toning your pelvic floor WELCOME Introductions Amelia Samuels, Physiotherapist, Active Rehabilitation Physiotherapy Supporting the Continence Foundation of Australia Continence Foundation of Australia
Overactive bladder can result from one or more of the following causes:
 Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
DIAPPERS: Transient Causes of Urinary Incontinence and other contributing factors
 DIAPPERS: Transient Causes of Urinary Incontinence and other contributing factors D Delirium Acute confusion alters one s ability to anticipate and meet own needs. Delirium may occur from drugs, surgery,
DIAPPERS: Transient Causes of Urinary Incontinence and other contributing factors D Delirium Acute confusion alters one s ability to anticipate and meet own needs. Delirium may occur from drugs, surgery,
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
IF YOU VE GOT TO GO, WE VE GOT SOLUTIONS.
 IF YOU VE GOT TO GO, WE VE GOT SOLUTIONS. Get the facts about urinary incontinence and get real solutions. HENRY FORD PELVIC HEALTH & CONTINENCE CENTER HENRY FORD WOMEN S HEALTH SERVICES INCONVENIENCE?
IF YOU VE GOT TO GO, WE VE GOT SOLUTIONS. Get the facts about urinary incontinence and get real solutions. HENRY FORD PELVIC HEALTH & CONTINENCE CENTER HENRY FORD WOMEN S HEALTH SERVICES INCONVENIENCE?
Information for Patients. Urinary Incontinence. English
 Information for Patients Urinary Incontinence English Table of contents What is urinary incontinence?... 3 Causes of urinary incontinence... 3 Types of urinary incontinence... 3 Stress urinary incontinence...
Information for Patients Urinary Incontinence English Table of contents What is urinary incontinence?... 3 Causes of urinary incontinence... 3 Types of urinary incontinence... 3 Stress urinary incontinence...
Information for Patients. Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) English
 Information for Patients Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) English Table of contents What is the bladder?... 3 What are overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 What causes overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 Diagnosis
Information for Patients Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) English Table of contents What is the bladder?... 3 What are overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 What causes overactive bladder symptoms?... 3 Diagnosis
Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients
 Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients This leaflet was written for women who are considering having a TVT operation. If you have any questions that aren't answered by
Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients This leaflet was written for women who are considering having a TVT operation. If you have any questions that aren't answered by
Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence Millions of women experience involuntary loss of urine called urinary incontinence (UI). Some women may lose a few drops of urine while running or coughing. Others may feel a strong,
Urinary Incontinence Millions of women experience involuntary loss of urine called urinary incontinence (UI). Some women may lose a few drops of urine while running or coughing. Others may feel a strong,
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME
 CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control Bladder Prolapse AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is the Bladder? The bladder is a hollow, balloon-like organ made mostly
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence
 Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence This leaflet explains what urge incontinence is and how we can help to reduce and relieve your symptoms. If you have any questions or concerns,
Bladder retraining - treatment for urgency and urge incontinence This leaflet explains what urge incontinence is and how we can help to reduce and relieve your symptoms. If you have any questions or concerns,
Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider.
 Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider. To begin the diary, please choose two days when you will be at home. The two
Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider. To begin the diary, please choose two days when you will be at home. The two
1) What conditions is vaginal mesh used to commonly treat? Vaginal mesh is used to treat two different health issues in women:
 Vaginal Mesh Frequently Asked Questions 1) What conditions is vaginal mesh used to commonly treat? Vaginal mesh is used to treat two different health issues in women: a) stress urinary incontinence (SUI)
Vaginal Mesh Frequently Asked Questions 1) What conditions is vaginal mesh used to commonly treat? Vaginal mesh is used to treat two different health issues in women: a) stress urinary incontinence (SUI)
Returning Home After Prostatectomy
 Returning Home After Prostatectomy Catholic Medical Center in conjunction with Manchester Urology Associates is proud to be one of the few hospitals in the United States to offer Robotic Assisted radical
Returning Home After Prostatectomy Catholic Medical Center in conjunction with Manchester Urology Associates is proud to be one of the few hospitals in the United States to offer Robotic Assisted radical
Bard: Continence Therapy. Stress Urinary Incontinence. Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle.
 Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
Incontinence Patient Information Form
 Incontinence Patient Information Form (To be completed by patient) Before talking with you, the doctor would like some information about your urine leakage. These questions are important for finding out
Incontinence Patient Information Form (To be completed by patient) Before talking with you, the doctor would like some information about your urine leakage. These questions are important for finding out
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men
 Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men (formerly ACPWH) Useful resources Websites Pelvic Obstetric & Gynaecological Physiotherapy - pogp.csp.org.uk Bladder and Bowel Foundation - www.bladderandbowelfoundation.org
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men (formerly ACPWH) Useful resources Websites Pelvic Obstetric & Gynaecological Physiotherapy - pogp.csp.org.uk Bladder and Bowel Foundation - www.bladderandbowelfoundation.org
INCONTINENCE AND OTHER UROLOGICAL DILEMMAS DR. ANNA LAWRENCE UROLOGIST AUCKLAND HOSPITAL 161 UROLOGY
 INCONTINENCE AND OTHER UROLOGICAL DILEMMAS DR. ANNA LAWRENCE UROLOGIST AUCKLAND HOSPITAL 161 UROLOGY COVERING INCONTINENCE BE ON JUST NAPPIES CATHETERS TYPES AVAILABLE AND WHEN TO USE THEM JJ STENTS???
INCONTINENCE AND OTHER UROLOGICAL DILEMMAS DR. ANNA LAWRENCE UROLOGIST AUCKLAND HOSPITAL 161 UROLOGY COVERING INCONTINENCE BE ON JUST NAPPIES CATHETERS TYPES AVAILABLE AND WHEN TO USE THEM JJ STENTS???
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men
 Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men Why are my pelvic floor muscles important? Your pelvic floor muscles are important for bladder and bowel control. These muscles help to keep the bladder
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises and Advice for Men Why are my pelvic floor muscles important? Your pelvic floor muscles are important for bladder and bowel control. These muscles help to keep the bladder
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Pelvic Floor Exercises
 Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
Directorate of Women, Children and Surgical Services Burton and District Urogynaecology Centre A Nationally Accredited Urogynaecology Unit Pelvic Floor Exercises You have been given this leaflet because
Blue Ridge Urogynecology
 Surgery for Stress Urinary Incontinence Surgery has proved to be a very effective treatment for stress incontinence. The best surgical procedures improve or cure the incontinence in 85 to 90 percent of
Surgery for Stress Urinary Incontinence Surgery has proved to be a very effective treatment for stress incontinence. The best surgical procedures improve or cure the incontinence in 85 to 90 percent of
Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy
 Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy Dr Vasudevan has recommended that you have an open radical prostatectomy. This document gives you information on what to expect before, during
Procedure Specific Information Sheet Open Radical Prostatectomy Dr Vasudevan has recommended that you have an open radical prostatectomy. This document gives you information on what to expect before, during
Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems
 If you require this leaflet in any other format, e.g., large print, please telephone 01935 384256 Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems Useful organisations Ms Society Helpline Tel: 0808 800
If you require this leaflet in any other format, e.g., large print, please telephone 01935 384256 Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems Useful organisations Ms Society Helpline Tel: 0808 800
Coping with urges and leaks?
 OAB AND YOU Coping with urges and leaks? Let me help you learn more about overactive bladder (OAB) symptoms and ways to help manage them 1 HOW DOES THE BLADDER WORK? Within the urinary tract, the kidneys
OAB AND YOU Coping with urges and leaks? Let me help you learn more about overactive bladder (OAB) symptoms and ways to help manage them 1 HOW DOES THE BLADDER WORK? Within the urinary tract, the kidneys
Prostate surgery. What is the prostate? What is a TURP? Why is a TURP operation necessary? Deciding to have a TURP operation.
 What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
Y0028_2726_0 File&Use Bladder Control Does Matter
 Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 Bladder Control Does Matter If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Y0028_2726_0 File&Use 04092012 Bladder Control Does Matter If you suffer from urinary incontinence, you re not alone Don t be afraid to raise your hand if you ve been struggling with the embarrassment
Faecal Incontinence Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
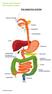 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC)
 Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Patient Information. Tension Free Vaginal/ Obturator Tape (TVT) Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust
 Tension Free Vaginal/Obturator Tape (TVT) Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Tension Free Vaginal/ Obturator Tape (TVT) Reference Number: CW 08 011 003 (version date: September
Tension Free Vaginal/Obturator Tape (TVT) Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Tension Free Vaginal/ Obturator Tape (TVT) Reference Number: CW 08 011 003 (version date: September
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence
 A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence in women
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence in women
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate
 TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises
 INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
INFORMATION FOR WOMEN OF ALL AGES Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises How to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles ASSOCIATION OF CHARTERED PHYSIOTHERAPISTS IN WOMEN S HEALTH This leaflet is supported
PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE CONSULTATION INFORMATION. North Austin, Round Rock and Westlake Main Phone Number
 PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE CONSULTATION INFORMATION North Austin, Round Rock and Westlake Main Phone Number 512-231-1444 www.urologyteam.com Rev June 2017 THE URINARY SYSTEM THE HEALTHY URINARY SYSTEM The urinary
PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE CONSULTATION INFORMATION North Austin, Round Rock and Westlake Main Phone Number 512-231-1444 www.urologyteam.com Rev June 2017 THE URINARY SYSTEM THE HEALTHY URINARY SYSTEM The urinary
Management, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overactive Bladder and Urinary Incontinence
 Management, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overactive Bladder and Urinary Incontinence Arthur Mourtzinos, MD, MBA Co-Vice Chair, Institute of Urology Director, Continence Center Assistant Professor of Urology,
Management, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overactive Bladder and Urinary Incontinence Arthur Mourtzinos, MD, MBA Co-Vice Chair, Institute of Urology Director, Continence Center Assistant Professor of Urology,
Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women. What YOU can do about it...
 Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women What YOU can do about it... www.gynecare.com Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women: It's Common. It's Treatable. Would it surprise you... To learn that more than 13
Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women What YOU can do about it... www.gynecare.com Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women: It's Common. It's Treatable. Would it surprise you... To learn that more than 13
Disease Management. Incontinence Care. Chan Sau Kuen Continence Nurse Consultant United Christian Hospital 14/11/09
 Disease Management in Incontinence Care Chan Sau Kuen Continence Nurse Consultant United Christian Hospital 14/11/09 What is incontinence? Definition of Incontinence - Is the compliant of any involuntary
Disease Management in Incontinence Care Chan Sau Kuen Continence Nurse Consultant United Christian Hospital 14/11/09 What is incontinence? Definition of Incontinence - Is the compliant of any involuntary
 URODYNAMICS Welcome to Chesapeake Urology s Urodynamics Services. Bladder control problems keep millions of people from enjoying a full life, but today, many treatments are available to help. To assist
URODYNAMICS Welcome to Chesapeake Urology s Urodynamics Services. Bladder control problems keep millions of people from enjoying a full life, but today, many treatments are available to help. To assist
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE
 TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE A discussion of the operation and the pre and post operative care You and your doctor have considered the possibility that you have a transurethral resection of
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE A discussion of the operation and the pre and post operative care You and your doctor have considered the possibility that you have a transurethral resection of
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer
 Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women
 The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
The Pelvic Floor Muscles - a Guide for Women This booklet is supported by WWWWW Wellbeing of Women Registered Charity No. 239281 www.wellbeingofwomen.org.uk Introduction Up to a third of all women experience
Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC)
 Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) Name: Age: Reason for visit/referral: Are you referred for or interested in surgery? Yes No Maybe Referring
Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) Name: Age: Reason for visit/referral: Are you referred for or interested in surgery? Yes No Maybe Referring
Stop Coping. Start Living. Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy
 Stop Coping. Start Living Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy Did you know? One in three women will suffer from a pelvic health condition in her lifetime. Four of the most
Stop Coping. Start Living Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy Did you know? One in three women will suffer from a pelvic health condition in her lifetime. Four of the most
Northwest Rehabilitation Associates, Inc.
 Pelvic Health Patient Intake Form Name: Date: Please answer the following questions as honestly and thoroughly as you can. Your responses will help us better understand your condition and provide the best
Pelvic Health Patient Intake Form Name: Date: Please answer the following questions as honestly and thoroughly as you can. Your responses will help us better understand your condition and provide the best
URINARY INCONTINENCE FOR FALLS PREVENTION. by Susan Elms P.T. Elms Physiotherapy
 URINARY INCONTINENCE PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENT FOR FALLS PREVENTION by Susan Elms P.T. Elms Physiotherapy OR How to avoid the mad dash to the bathroom! INCONTINENCE INFORMATION TALK What is incontinence?
URINARY INCONTINENCE PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENT FOR FALLS PREVENTION by Susan Elms P.T. Elms Physiotherapy OR How to avoid the mad dash to the bathroom! INCONTINENCE INFORMATION TALK What is incontinence?
Information for men considering a male sling procedure UHB is a no smoking Trust
 Information for men considering a male sling procedure UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Information for men considering a male sling procedure UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
This information is intended as an overview only
 This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help
 Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help Urogynaecology Introduction This leaflet is produced as a self-help guide for women of East and North Herts that are experiencing issues with continence.
Patient Information Incontinence & Prolapse Self-help Urogynaecology Introduction This leaflet is produced as a self-help guide for women of East and North Herts that are experiencing issues with continence.
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e. For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries
 B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
