15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications
|
|
|
- Lenard Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing fluid intake help prevent UTI recurrence? In recent years there has been great emphasis on functional abnormalities of the lower urinary tract, reflected by the presence of poor voiding habits as risk factors for recurrence of urinary tract infection (UTI). 278 It has also been shown that such abnormalities may be associated with bowel movement disorders, such that constipation and/or encopresis could increase the risk of recurrent UTI. 279 Therefore, improving or normalising such dysfunctions could lead to prevention of UTI and its consequences, such as kidney damage and morbidity associated with UTI. Another intervention that may promote prevention could be increasing fluid intake, which may promote more regular evacuation of the bladder and prevent bacterial multiplication. 280 Below is evidence taken from the NICE CPG 11 as well as additional studies that were found. A study conducted in Switzerland evaluated the presence of various risk factors (family history of UTI, infrequent voiding, low fluid intake, functional constipation, inadequate anogenital hygiene and bathroom habits) in 90 girls (median age 8.4 years, range years) with a history of recurrent UTI ( 3 UTIs) compared with 45 girls without a history of UTI (median age 7.3 years, range 4-14 years). The study found significant differences in the risk factors in girls with recurrent UTI compared to those girls without urinary infection: family history of UTI (42% vs 11%, P<0.001), infrequent voiding of urine (54% vs 24%, P<0.001), low fluid intake (53% vs 16%, P<0.001) and functional constipation (30% vs 13%, P<0, 05). However, no differences related to inadequate anogenital hygiene or bathroom habits were found comparing the cases (14%) and controls (13%). 11 study 2 + A study in the Philippines evaluated the association between bathroom habits and cleanliness (washing frequency: daily versus less than once a day, cleaning after urination, cleaning after defecation; cleaning direction, use of soap during cleaning) as well as voiding habits (frequency of urination: less than 5 times a day, or more than 5 times a day; retention of urine during the day; permission to urinate in school) with the risk of UTI in 23 children with UTI, compared to 23 children with no history of UTI (age range 6-12 years). The study found no association between any of the variables and the increased risk of UTI. 11 study 2-153
2 A US study compared the prevalence of dysfunctional elimination syndrome (DES) in a cohort of children diagnosed with UTI before 2 years of age (115 girls and 8 boys, mean age 7.3 years, range years) compared to a cohort of children with no history of UTI (120 girls and 5 boys, mean age 7 years, range years) to establish whether UTI encourages the development of DES. The study found no differences in the prevalence of DES among girls and boys with UTI (22%) and without UTI (21%), P=0.82. Within the UTI cohort, there was no difference in the prevalence of DES among those with VUR (18%) and those without VUR (25%), P=0.52. The study also evaluated the prevalence of various risk factors (encopresis, DES, VUR) in the subgroup of patients with recurrent UTI (n=31) and found that encopresis was the only statistically significant risk factor associated with recurrent UTI: encopresis (OR 2.5, 95% CI ; P=0.03), DES (OR 2.2, 95% CI ; P=0.05), VUR (OR 2.2, 95% CI ; P=0.07). 11 A retrospective US study analysed the incidence of recurrent UTI and associated risk factors in patients diagnosed with first UTI before 6 months of age without radiographic abnormalities at the time of diagnosis (n=84, 52 girls and 32 boys; mean age 4.8 years, range years), during a mean follow-up period of 4.4 years (range years). None of the patients received prophylactic antibiotics after the radiological study. A total of 16 patients (19%) had recurrences. No risk factor studied by univariate analysis (P>0.05) was significantly related with the onset of recurrence. These included age at which toilet training was taught (before or after 2 years), daytime urinary continence and history of constipation (less than 3 bowel movements per week). 122 Cohort study Cohort study SNS CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
3 A Belgian study investigated the possible relationship between recurrent UTI and possible risk factors; among them, learning to control the bowels. It questioned 4,332 families with school age children (2,215 boys and 2,117 girls, mean age 11.5±0.56 years). The study found that the prevalence of a single UTI in girls and boys was 13% and 4.4%, respectively, and recurrent UTI, 5% and 1% respectively; these differences were statistically significant (18% vs 5.4%, P<0.001). Regarding the rest of variables studied they found a higher prevalence of recurrent UTI in children with daytime urinary incontinence (with or without enuresis; P<0.001); in children with 10 or more voids per day (P<0.02); and in children with nocturia at least once a week (P<0.001). Regarding the learning to control the bowels they found that it was earlier (before 18 months of age) in the group of children without UTI than in the group with recurrent UTI (P<0.05). Teaching methods and reactions to voiding failures were different between families, such that, for example, families of children with recurrent UTI were forcing children to stay longer on the toilet (P<0.001), encouraging pushing (P<0.001) or opening the water tap (P<0.001). Among children with recurrent UTI, they found that 9.1% had encopresis, compared to 2.5% without recurrent UTI. 11 A Danish study investigated the relationship between voiding habits, the prevalence of daytime urinary leakage and the presence of UTI in children (median age 7 years, range 6-9 years) in 1,557 families by questionnaire. It found a prevalence of UTI of 9.4% in girls and 2.8% in boys. For girls, the symptoms suggestive of voiding difficulties were more frequent in those with previous UTI than those with no history of UTI: bedwetting (25.3% vs 12.4%, P<0.002); daytime urinary incontinence (29.3% vs 12.9%, P<0.0002); not reaching the bathroom (40% vs 27.9%, P<0.03); prolonged voiding (33.3% vs 17.8%, P<0.002); poor urine flow (29.3% vs 15.8%, P<0.003); ability to void again (32% vs 17.3%, P<0.002); manual compression of the abdomen (17.3% vs 7.3%, P<0.003); and encopresis (13.3% vs 6.0%, P<0.03). By logistic regression, the symptoms that correlated with UTI in girls were squatting (OR 4.6, 95% CI ) and encopresis (OR 6.1, 95% CI ). Due to the small number of boys with UTI, conclusions about voiding habits and UTI could not be drawn. There were no significant differences in the frequency of daily urination for those with and without UTI. 11 Cross-sectional study 3 Cross-sectional study 3 155
4 A Swiss study evaluated the role of family history, infrequent voiding, low fluid intake, constipation and poor hygiene or bathroom habits in a sample of 141 girls (median age 6.5 years, range years) with a history of recurrent UTI ( 3 episodes of symptomatic UTI). There was a total of 212 functional and behavioural abnormalities in 86% (121) of the girls: infrequent voiding (45%), low fluid intake (43%), constipation (21%), poor hygiene (19%), dysfunctional emptying (18%) and overactive bladder (5%). A total of 66 girls had more than 1 anomaly concurrently. 11 A Canadian study in girls (n=47, mean age 8.2±2.5 years) of functional constipation (with a large faecal reservoir), bladder instability (uninhibited bladder contractions) and recurrent UTI without anatomical abnormalities of the urinary tract found that treatment of functional constipation using enemas prevented recurrence in 93.6% of cases. Among girls affected by enuresis (68%), enema treatment led to the end of enuresis in 69% and improvement in 22% of girls.. Similarly, enema treatment resolved 95% of the cases among the 45% of the girls who suffered from encopresis. 281 Another Canadian study described the presence of uninhibited bladder contractions and rectal dilatation in 16 girls and 1 boy (mean age 6.24±2.2 years) with a history of recurrent UTI and VUR. Clinically, 10 patients had enuresis and 5 also had encopresis. Rectal manometry confirmed the existence of functional constipation in all patients. 282 A US study in 143 patients (105 girls and 38 boys) with a history of UTI and primary VUR under antibiotic treatment until resolution of VUR (surgical or spontaneous), described the prevalence and influence of the bladder or gastrointestinal dysfunction in their history and treatment. It found that 46% of patients had DES (bladder instability, infrequent voiding and constipation), with constipation as the most common symptom (50%), followed by bladder instability (27%) and infrequent bladder emptying (23%). Of the total sample, 49% (70) suffered recurrent UTI during follow up, and 77% (54) of these had DES, compared with the remaining 23% (16) who did not (P< ). Among patients who did not experience recurrent UTI (73), 16% (12) had DES, compared to 84% (61) who did not (P< ). The presence of DES thus increased the risk of recurrent UTI in patients with VUR (OR 17.15, 95% CI ). 283 Cohort study SNS CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
5 A questionnaire-based study in Australia of UTI risk factors at the population level from a sample of 2,856 schoolchildren (1,503 boys and 1,353 girls, mean age 7.3 years, range years) was performed. In the total sample, the prevalence of enuresis was 18.3%; daytime urinary incontinence was 17.3%; encopresis 10.3%; and constipation 5.7%. The prevalence of problems associated with voiding was: 67.4% urgency, 40.1% retention, 32% frequency and 9.2% leakage. Of all the patients with a history of UTI at some point, according to the families (n=362), only in 191 cases a urine culture record could be obtained, from which UTI was confirmed in 103 cases (3.6%). The study found the following as independent variables associated with UTI: renal structure abnormality history (OR 15.7, 95% CI ); daytime urinary incontinence (OR 2.6, 95% CI ); female sex (OR 2.4, 95% CI ); and encopresis (OR 1.9, 95% CI ). The study found no association between constipation and UTI. The risk of UTI in boys with daytime urinary incontinence (OR 8.6, 95% CI ) was higher than in girls with urinary incontinence (OR 2.1, 95% CI 1.2-3, 6). Similarly in older children with kidney problems: over 6 years (OR 25.2, 95% CI ) and over 8 years of age (OR 30.7, 95% CI ), the risk of UTI was higher than in those of a younger age (4-6 years old) with kidney problems. 284 A Swedish study evaluated the residual volume of urine as a possible risk factor in the pathogenesis of lower tract UTI in 29 girls and 10 boys with cystitis (median age 5 years, range 1-14 years), compared with a control of 35 girls and 20 boys (median age 5 years, range 1-12 years). The study found significant differences in residual urine volume (P<0.01). During the acute episode of cystitis, 61% of cases had residues 5mL urine compared to 25% of controls, and 24% of cases had 1 ml residues compared with 62% of controls. 285 A Turkish study evaluated the frequency of nocturnal enuresis, UTI and symptoms of bladder instability in 22 girls and 16 boys (mean age: 5.3±4.25 years) with chronic functional constipation, compared with 16 boys and 15 girls as controls (mean age: 6.8±3.8 years). Significant differences were found regarding the frequency of UTI and urinary urgency. Both situations are more frequent in the group with constipation than in the control group: 42.1% and 26.9% vs 19.4% and 4% (P<0.05), respectively. No significant differences were found between groups for frequency of urinary incontinence (19.2% vs 0%, P=0.051) and nocturnal enuresis (23.1% vs 8%, P> 0.05). 286 study 2 + study 2 - study 2-157
6 A US study of 176 boys and 58 girls (mean age: 9±3 years) with functional constipation and encopresis determined the frequency of UTI and urinary incontinence before and after treatment for constipation over an average 15-month follow-up. The study found an overall incidence of UTI episodes 11% higher in the case of girls (33%) than in boys (3%), P< There was an overall prevalence of 46% urinary incontinence (29% daytime incontinence, 34% nocturnal incontinence and 17% daytime and nocturnal incontinence), without any significant differences in sex or age (P> 0.05). Treatment of constipation led to its resolution in 52% of cases (121). In all cases resolved, there was a significant decrease in the prevalence of urinary incontinence day and night, 23% and 34% before treatment and 2% and 12% after treatment (P<0.05), respectively. In all resolved cases without structural abnormalities of the urinary tract, there was no case of recurrent UTI during follow-up. 287 A Dutch study evaluated the treatment of constipation by colonic enemas in 44 girls and 6 boys (mean age 9.6 years, range years) with constipation, voiding dysfunction and a history of recurrent UTI, who had not responded to previous treatment with oral laxatives and biofeedback. None had anatomical abnormalities of the urinary tract and all received antibiotic prophylaxis. After enema treatment, there was no recurrence of UTI in 84% of cases during a follow-up period of 6 months. 288 A Canadian study of 29 girls and 16 boys (range 6 months-14 years) with a history of UTI and abnormal bowel habits (hard stools with difficulty in expulsion, no daily bowel movements, rectal bleeding due to anal fissures, prolonged use of laxatives and/or suppositories, large stools and encopresis) found that after initial treatment for improvement of constipation, it resolved in 80% of cases. During the first year of monitoring, there was recurrent UTI in only 20% of cases, which were the ones that had not responded to the initial constipation treatment. After further corrective treatment, there was recurrent UTI at 3 years in only 2 cases with new onset of constipation. 289 When making the recommendations, the GDG considered the consistency of the results, which showed an association between constipation, encopresis, low fluid intake or DES and UTI, especially among the higher level evidence-based studies. 11,284 A certain consistency in the results was seen in the lack of association between anogenital hygiene and the presence of UTI. 11 The GDG considered the preventive measures necessary to improve voiding habits, adequate fluid intake or correction of constipation were shown to be clinically harmless and inexpensive, and could be included in so-called lifestyle changes or healthy habits acquisition. Evidence summary Girls with recurrent UTI had a higher prevalence of infrequent voiding (54% vs 24%, P<0.001), low fluid intake (53% vs 16%, P<0.001) and functional constipation (30% vs 13%, P<0.05) than girls who had never had UTI SNS CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
7 3 No association was seen between inadequate anogenital hygiene and/or inappropriate bathroom habits with the presence of recurrent UTI. 11 DES is associated with an increased risk of recurrent UTI (OR 2.2, 95% CI , P=0.05). 11 Encopresis is associated with an increased risk of UTI (OR 1.9, 95% CI ) 284 or recurrent UTI (OR 2.5, 95% CI ). 11 Daytime urinary incontinence is associated with an increased risk of UTI (OR 2.6, 95% CI ). 284 A correction in constipation for children with functional constipation and/or encopresis with no urinary tract abnormalities prevents or reduces the occurrence of future UTI recurrence.281, Recommendations C D Preventive measures aimed at reducing recurrences of UTI should be tailored according to the pattern of urinary tract dysfunction or urinary habits of the patient, and directed to achieve adequate fluid intake. It is recommended to investigate and address any constipation in children with UTI and/or signs of lower urinary tract dysfunction to prevent recurrence of UTI. 159
Physiology & Neurophysiology of lower U.T.
 Physiology & Neurophysiology of lower U.T. Classification of voiding dysfunction Evaluation of a child with voiding dysfunction Management Storage Ø Adequate volume of urine Ø At LOW pressure Ø With NO
Physiology & Neurophysiology of lower U.T. Classification of voiding dysfunction Evaluation of a child with voiding dysfunction Management Storage Ø Adequate volume of urine Ø At LOW pressure Ø With NO
16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children
 16. UTI prognosis 16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children Key question: What is the risk of recurrent UTI in children with no known structural or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract with a first
16. UTI prognosis 16.1 Risk of UTI recurrence in children Key question: What is the risk of recurrent UTI in children with no known structural or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract with a first
Medical Management of childhood UTI and VUR. Dr Patrina HY Caldwell Paediatric Continence Education, CFA 15 th November 2013
 Medical Management of childhood UTI and VUR Dr Patrina HY Caldwell Paediatric Continence Education, CFA 15 th November 2013 Terminology According to the current ICCS terminology guidelines Bladder and
Medical Management of childhood UTI and VUR Dr Patrina HY Caldwell Paediatric Continence Education, CFA 15 th November 2013 Terminology According to the current ICCS terminology guidelines Bladder and
Appendix F: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation. Audience: For Front-line Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010
 Appendix F: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation Audience: For Front-line Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010 Objectives Address individual needs and preferences with respect
Appendix F: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation Audience: For Front-line Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010 Objectives Address individual needs and preferences with respect
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum
 The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Robinson, J, et al. and the Canadian Pediatric Society. Urinary tract infection in infants and children: Diagnosis and management. Pediatr Child Health 2014;
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Robinson, J, et al. and the Canadian Pediatric Society. Urinary tract infection in infants and children: Diagnosis and management. Pediatr Child Health 2014;
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
INCONTINENCE. Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation TYPES OF INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE 11/08/2015
 INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction (BBD) Naida Kalloo, MD Pediatric Urology Children s National
 Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction (BBD) Naida Kalloo, MD Pediatric Urology Children s National What is Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction? Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and bowel movement disorders Majority
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction (BBD) Naida Kalloo, MD Pediatric Urology Children s National What is Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction? Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and bowel movement disorders Majority
case Prof. Dr.J.Vande Walle Feb Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent 1
 case Prof. Dr.J.Vande Walle Feb 2012 1 A boy, 10 years old! Bedwetting 5/7days! nocturia! wet pants! Frequency 5 x/day! constipation! adhd! URI/ uropathie 2 Urological symptoms* /ALARMSYMPTOMS Yes Leakages
case Prof. Dr.J.Vande Walle Feb 2012 1 A boy, 10 years old! Bedwetting 5/7days! nocturia! wet pants! Frequency 5 x/day! constipation! adhd! URI/ uropathie 2 Urological symptoms* /ALARMSYMPTOMS Yes Leakages
Annex 3. Patient information. Urinary Tract Infection in Children
 Annex 3. Patient information. Urinary Tract Infection in Children Contents Introduction What is urinary tract infection (UTI) and how common is it? What are the signs and symptoms for suspecting UTI? How
Annex 3. Patient information. Urinary Tract Infection in Children Contents Introduction What is urinary tract infection (UTI) and how common is it? What are the signs and symptoms for suspecting UTI? How
Why is the management of UTI so controversial? Kjell Tullus Consultant Paediatric Nephrologist
 Why is the management of UTI so controversial? Kjell Tullus Consultant Paediatric Nephrologist Diagnosing a UTI More difficult then most people realise Contaminating culture Bacterial numbers Confusion
Why is the management of UTI so controversial? Kjell Tullus Consultant Paediatric Nephrologist Diagnosing a UTI More difficult then most people realise Contaminating culture Bacterial numbers Confusion
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
Continence Promotion in
 Everybody s Business- Continence Promotion in Aged Care Melissa O Grady Clinical Nurse Consultant Continence Warning Some graphic images are contained in this presentation Objectives What is Old Age? What
Everybody s Business- Continence Promotion in Aged Care Melissa O Grady Clinical Nurse Consultant Continence Warning Some graphic images are contained in this presentation Objectives What is Old Age? What
Incontinence Patient Information Form
 Incontinence Patient Information Form (To be completed by patient) Before talking with you, the doctor would like some information about your urine leakage. These questions are important for finding out
Incontinence Patient Information Form (To be completed by patient) Before talking with you, the doctor would like some information about your urine leakage. These questions are important for finding out
Diane K. Newman DNP, ANP-BC, PCB-PMD, FAAN
 Diane K. Newman DNP, ANP-BC, PCB-PMD, FAAN Diane K. Newman, DNP is a Biofeedback Certified Continence Specialist. With over 35-years experience, she is an expert in the assessment and management of pelvic-floor
Diane K. Newman DNP, ANP-BC, PCB-PMD, FAAN Diane K. Newman, DNP is a Biofeedback Certified Continence Specialist. With over 35-years experience, she is an expert in the assessment and management of pelvic-floor
Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring
 Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring Yaacov Frishberg, MD Division of Pediatric Nephrology Shaare Zedek Medical Center Jerusalem, ISRAEL UTI - definitions UTI = growth of bacteria
Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring Yaacov Frishberg, MD Division of Pediatric Nephrology Shaare Zedek Medical Center Jerusalem, ISRAEL UTI - definitions UTI = growth of bacteria
 giovanni.montini@aosp.bo.it VD: definition Voiding dysfunction refers to daytime voiding disorders in children who do not have neurologic, anatomic, obstructive, or infectious abnormalities of the urinary
giovanni.montini@aosp.bo.it VD: definition Voiding dysfunction refers to daytime voiding disorders in children who do not have neurologic, anatomic, obstructive, or infectious abnormalities of the urinary
Human Anatomy rectum
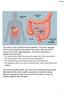 rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
The new ICCS terminology J Urol 176, , 2006
 The new ICCS terminology J Urol 176, 314-324, 2006 The Standardization of Terminology of Lower Urinary Tract Function in Children and Adolescents: Report from the Standardisation Committee of the International
The new ICCS terminology J Urol 176, 314-324, 2006 The Standardization of Terminology of Lower Urinary Tract Function in Children and Adolescents: Report from the Standardisation Committee of the International
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys.
 UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
Appendix E: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation. Audience: For Registered Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010
 Appendix E: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation Audience: For Registered Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010 Objectives Address individual needs and preferences with respect
Appendix E: Continence Care and Bowel Management Program Training Presentation Audience: For Registered Staff Release Date: December 22, 2010 Objectives Address individual needs and preferences with respect
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
CONSTIPATION. Atan Baas Sinuhaji
 CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
CONTINENCE MODULE 1 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMALE LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS
 CONTINENCE MODULE 1 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMALE LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative
CONTINENCE MODULE 1 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMALE LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative
Questionnaire for Incontinent Patients
 Questionnaire for Incontinent Patients Name Date: Date of birth: weight: height: Vaginal deliveries: Caesarean Sections: profession: No Yes Sometimes Yes 50% or more Do you lose urine during sneezing or
Questionnaire for Incontinent Patients Name Date: Date of birth: weight: height: Vaginal deliveries: Caesarean Sections: profession: No Yes Sometimes Yes 50% or more Do you lose urine during sneezing or
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN
 Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Paediatric Urotherapy Training
 Paediatric Urotherapy Training Frances Shit NS, MSc (Hons), ET, Dept. of Surgery, PWH, CUHK HKSAR Urinary Incontinence in Children Urine leakage in a child from 5 years of age Leakage occurs on a regular
Paediatric Urotherapy Training Frances Shit NS, MSc (Hons), ET, Dept. of Surgery, PWH, CUHK HKSAR Urinary Incontinence in Children Urine leakage in a child from 5 years of age Leakage occurs on a regular
URINARY INCONTINENCE. Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
HELPING SCHOOLS MANAGE CONTINENCE PROBLEMS. The Right to
 HELPING SCHOOLS MANAGE CONTINENCE PROBLEMS The Right to Go Continence problems in childhood are common and as a result it is not unusual for schools to have at least one child with a wetting or soiling
HELPING SCHOOLS MANAGE CONTINENCE PROBLEMS The Right to Go Continence problems in childhood are common and as a result it is not unusual for schools to have at least one child with a wetting or soiling
Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider.
 Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider. To begin the diary, please choose two days when you will be at home. The two
Please complete this voiding diary and questionnaire. Bring both of them with you to your next appointment with your provider. To begin the diary, please choose two days when you will be at home. The two
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care
 Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
Continence/Constipation Workshop for RNs in Long-Term Care Slide Presentation Supporting Implementation of the RNAO BPGs: Promoting Continence Using Prompted Voiding and Prevention of Constipation in the
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction. Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield
 GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (community)
 Addressograph label CHI:... Name:... Address:...... Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (community) Past medical history: Is the patient on medications which can affect bladder function? If, please list
Addressograph label CHI:... Name:... Address:...... Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (community) Past medical history: Is the patient on medications which can affect bladder function? If, please list
The involuntary loss of feces in the underwear after. Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence.
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 26;4:67 72 Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, RIJK VAN GINKEL,* HANS A.
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 26;4:67 72 Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, RIJK VAN GINKEL,* HANS A.
Various Types. Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG
 Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Bladder and Bowel Symptoms Troubleshooting Tips
 Bladder and Bowel Symptoms Troubleshooting Tips Unwilling to accept assistance with using the toilet There may be an underlying condition that causes this resistance, or the individual may not understand
Bladder and Bowel Symptoms Troubleshooting Tips Unwilling to accept assistance with using the toilet There may be an underlying condition that causes this resistance, or the individual may not understand
Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I
 Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I 1 Assessment of renal function Clinical manifestations Laboratory tests Urinalysis Urine culture and sensitivity Renal/bladder ultrasound Testicular
Nursing Care for Children with Genitourinary Dysfunction I 1 Assessment of renal function Clinical manifestations Laboratory tests Urinalysis Urine culture and sensitivity Renal/bladder ultrasound Testicular
10. Diagnostic imaging for UTI
 10. Diagnostic imaging for UTI Key question: What is the most effective imaging test for the diagnosis of structural abnormalities of the urinary tract and/or kidney damage in children with UTI? Current
10. Diagnostic imaging for UTI Key question: What is the most effective imaging test for the diagnosis of structural abnormalities of the urinary tract and/or kidney damage in children with UTI? Current
Disease Management. Incontinence Care. Chan Sau Kuen Continence Nurse Consultant United Christian Hospital 14/11/09
 Disease Management in Incontinence Care Chan Sau Kuen Continence Nurse Consultant United Christian Hospital 14/11/09 What is incontinence? Definition of Incontinence - Is the compliant of any involuntary
Disease Management in Incontinence Care Chan Sau Kuen Continence Nurse Consultant United Christian Hospital 14/11/09 What is incontinence? Definition of Incontinence - Is the compliant of any involuntary
Hemorrhoids. Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery
 Hemorrhoids Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery Overview Anatomy Classification Etiology Incidence Symptoms Differential Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management Anatomy Anal canal
Hemorrhoids Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery Overview Anatomy Classification Etiology Incidence Symptoms Differential Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management Anatomy Anal canal
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination
 Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
Dysfunctional voiding
 Dysfunctional voiding The importance of assessment, diagnosis and treatment of dysfunctional voiding and its role in recurrent UTI Dr Dean Wallace Consultant Paediatric Nephrologist RMCH Objectives Development
Dysfunctional voiding The importance of assessment, diagnosis and treatment of dysfunctional voiding and its role in recurrent UTI Dr Dean Wallace Consultant Paediatric Nephrologist RMCH Objectives Development
Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (care home)
 Addressograph label CHI:... Name:... Address:...... Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (care home) Past medical history: Is the patient on medications which can affect bladder function? If, please list
Addressograph label CHI:... Name:... Address:...... Urinary dysfunction assessment tool (care home) Past medical history: Is the patient on medications which can affect bladder function? If, please list
Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS
 Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS OhioHealth, Columbus Ohio Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the role of a pelvic floor therapist in
Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS OhioHealth, Columbus Ohio Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the role of a pelvic floor therapist in
Elimination Disorders Enuresis (primary and secondary) Encopresis (primary and secondary)
 Elimination Disorders Enuresis (primary and secondary) Encopresis (primary and secondary) 1 Elimination disorders Toilet training Developmental milestone Often required for entry into day care Usual sequence:
Elimination Disorders Enuresis (primary and secondary) Encopresis (primary and secondary) 1 Elimination disorders Toilet training Developmental milestone Often required for entry into day care Usual sequence:
 giovanni.montini@aosp.bo.it UTI - EPIDEMIOLOGY INCIDENCE: 1.7/1000 boys/year 3.1/1000 girls/year PREVALENCE: girls 6-7 % (0-6 y) boys 2-2,5 % (Jodal ESPN 2002) Fig 2 Distribution by age (months) and sex
giovanni.montini@aosp.bo.it UTI - EPIDEMIOLOGY INCIDENCE: 1.7/1000 boys/year 3.1/1000 girls/year PREVALENCE: girls 6-7 % (0-6 y) boys 2-2,5 % (Jodal ESPN 2002) Fig 2 Distribution by age (months) and sex
UTI and VUR Practical points and management Kjell Tullus Consultant Paediatric Nephrologist
 UTI and VUR Practical points and management Kjell Tullus Consultant Paediatric Nephrologist Discussion points Diagnosis VUR Radiological investigations 1. Contamination Problems 2. Bacterial numbers 3.
UTI and VUR Practical points and management Kjell Tullus Consultant Paediatric Nephrologist Discussion points Diagnosis VUR Radiological investigations 1. Contamination Problems 2. Bacterial numbers 3.
(PDF) PERSISTENT POSTPARTUM URINARY RETENTION: PREVALENCE
 PDF FREQUENT URINATION: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, AND TREATMENT (PDF) PERSISTENT POSTPARTUM URINARY RETENTION: PREVALENCE 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 persistent urge to urinate pdf Frequent urination means having to visit
PDF FREQUENT URINATION: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, AND TREATMENT (PDF) PERSISTENT POSTPARTUM URINARY RETENTION: PREVALENCE 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 persistent urge to urinate pdf Frequent urination means having to visit
Can xanax cause bed wetting
 Can xanax cause bed wetting Search 12-12-2011 I had the Monarc bladder sling surgery a month ago. I am voiding fine, and don't appear to have the stress incontinence anymore; however, I am in constant.
Can xanax cause bed wetting Search 12-12-2011 I had the Monarc bladder sling surgery a month ago. I am voiding fine, and don't appear to have the stress incontinence anymore; however, I am in constant.
OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES
 OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Introduction Mean faecal weight 128 g / cap / day Mean range 51-796 g Absolute range 15-1505 g Main factors affecting mass are caloric intake,
OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Introduction Mean faecal weight 128 g / cap / day Mean range 51-796 g Absolute range 15-1505 g Main factors affecting mass are caloric intake,
Overactive Bladder Syndrome
 Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
Children s Continence Current Awareness Bulletin
 Children s Continence Current Awareness Bulletin November 2018 A number of other bulletins are also available please contact the Academy Library for further details If you would like to receive these bulletins
Children s Continence Current Awareness Bulletin November 2018 A number of other bulletins are also available please contact the Academy Library for further details If you would like to receive these bulletins
encathopedia Volume 5 DIABETES AND THE BLADDER
 encathopedia Volume 5 DIABETES AND THE BLADDER Diabetes (diabetes mellitus, DM) Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has dangerously high blood sugar. This can be either
encathopedia Volume 5 DIABETES AND THE BLADDER Diabetes (diabetes mellitus, DM) Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has dangerously high blood sugar. This can be either
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus.
 The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
Male Symptom Monitor
 Male Symptom Monitor Occupation: Recreational Activities: Presenting problems: 1. 2. When did this start? Please fill out each section that is relevant to your problem Have you had any of the following
Male Symptom Monitor Occupation: Recreational Activities: Presenting problems: 1. 2. When did this start? Please fill out each section that is relevant to your problem Have you had any of the following
Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
Pediatric urinary tract infection. Dr. Nariman Fahmi Pediatrics/2013
 Pediatric urinary tract infection Dr. Nariman Fahmi Pediatrics/2013 objectives EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSATIVE PATHOGENS PATHOGENESIS CATEGORIES OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN pediatrics
Pediatric urinary tract infection Dr. Nariman Fahmi Pediatrics/2013 objectives EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSATIVE PATHOGENS PATHOGENESIS CATEGORIES OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN pediatrics
Voiding and bowel problems. Lise Kay, M.D. Urologist and Surgeon The Danish Society of Polio and Accident Victims
 Voiding and bowel problems Lise Kay, M.D. Urologist and Surgeon The Danish Society of Polio and Accident Victims Topics: Nervous control of voiding and bowel function Other factors with influence on voiding
Voiding and bowel problems Lise Kay, M.D. Urologist and Surgeon The Danish Society of Polio and Accident Victims Topics: Nervous control of voiding and bowel function Other factors with influence on voiding
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy
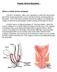 Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e. For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries
 B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
Chapter 18. Assisting With Urinary Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Recurrent Pediatric UTI Revisited 2013
 Recurrent Pediatric UTI Revisited 2013 PIDSP 21.2.2013 Shai Ashkenazi, MD, MSc Medicine changes constantly Some aspects of the standard practice of ~40 years are probably not valid and need to be changed
Recurrent Pediatric UTI Revisited 2013 PIDSP 21.2.2013 Shai Ashkenazi, MD, MSc Medicine changes constantly Some aspects of the standard practice of ~40 years are probably not valid and need to be changed
A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery)
 Saint Mary s Hospital Newborn Intensive Care Unit Information for Parents A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery) Introduction This information leaflet is designed to help parents and families to care for
Saint Mary s Hospital Newborn Intensive Care Unit Information for Parents A guide to Anoplasty (anal surgery) Introduction This information leaflet is designed to help parents and families to care for
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence. Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations
 The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
Summary and conclusions
 Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
encathopedia Volume 7 PARKINSON S AND THE BLADDER
 encathopedia Volume 7 PARKINSON S AND THE BLADDER Parkinson s disease Parkinson s is a progressive neurological condition. In people with Parkinson s, some of the brain cells that create the chemical dopamine
encathopedia Volume 7 PARKINSON S AND THE BLADDER Parkinson s disease Parkinson s is a progressive neurological condition. In people with Parkinson s, some of the brain cells that create the chemical dopamine
Coping with urges and leaks?
 OAB AND YOU Coping with urges and leaks? Let me help you learn more about overactive bladder (OAB) symptoms and ways to help manage them 1 HOW DOES THE BLADDER WORK? Within the urinary tract, the kidneys
OAB AND YOU Coping with urges and leaks? Let me help you learn more about overactive bladder (OAB) symptoms and ways to help manage them 1 HOW DOES THE BLADDER WORK? Within the urinary tract, the kidneys
Implementing Clean Intermittent Catheterisation (CIC)
 Implementing Clean Intermittent Catheterisation (CIC) Julie Dicker (Spina Bifida CNC) Kids Rehab The Children s Hospital at Westmead Reasons for CIC: Neurogenic Bladder CIC is the gold standard for this
Implementing Clean Intermittent Catheterisation (CIC) Julie Dicker (Spina Bifida CNC) Kids Rehab The Children s Hospital at Westmead Reasons for CIC: Neurogenic Bladder CIC is the gold standard for this
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary tract infection: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management of urinary tract infection in children 1.1 Short title
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary tract infection: diagnosis, treatment and long-term management of urinary tract infection in children 1.1 Short title
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE The management of faecal incontinence in adults 1.1 Short title Faecal incontinence 2 Background (a) (b) (c) The National Institute
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE The management of faecal incontinence in adults 1.1 Short title Faecal incontinence 2 Background (a) (b) (c) The National Institute
Mr. GIT KAH ANN. Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
 Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Faecal Incontinence Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
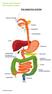 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about faecal incontinence Faecal (or anal) incontinence is the loss of stool, liquid or gas from the bowel at an undesirable time. Males and females of any age may
P. Brandstrom has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve.
 P. Brandstrom has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. Prophylaxis or not? Per Brandström Queen Silvia Children s Hospital Gothenburg
P. Brandstrom has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. Prophylaxis or not? Per Brandström Queen Silvia Children s Hospital Gothenburg
American Pediatric Surgical Nurses Association 111 Deer Lake Rd., Suite 100 Deerfield, IL 60015
 An Innovative Program for Children with Dysfunctional Elimination Kimberly S. Jarczyk, M.S.N., C.P.N.P. Pediatric Continence Program Nemours Children s Clinic Jacksonville, Florida Disclosure Information
An Innovative Program for Children with Dysfunctional Elimination Kimberly S. Jarczyk, M.S.N., C.P.N.P. Pediatric Continence Program Nemours Children s Clinic Jacksonville, Florida Disclosure Information
UTIs in children ( with controversies ) By Dr. Lindokuhle Mahlase
 UTIs in children ( with controversies ) By Dr. Lindokuhle Mahlase Epidemiology By age 7 years, 8 % of girls and 2 % of boys will have had a UTI. Most infections occur in the first 2 years of life ; boys
UTIs in children ( with controversies ) By Dr. Lindokuhle Mahlase Epidemiology By age 7 years, 8 % of girls and 2 % of boys will have had a UTI. Most infections occur in the first 2 years of life ; boys
UWE Bristol. UTI in Children. Angie Green Visiting Lecturer March 2011
 UWE Bristol UTI in Children Angie Green Visiting Lecturer March 2011 Approx 2% children will develop acute febrile UTI Up to 10% girls will develop any kind of UTI Progressive scarring in children with
UWE Bristol UTI in Children Angie Green Visiting Lecturer March 2011 Approx 2% children will develop acute febrile UTI Up to 10% girls will develop any kind of UTI Progressive scarring in children with
Catheter Care & Skin Integrity
 Catheter Care & Skin Integrity Learning outcomes Explain the importance of adequate fluid intake on the effective functioning of a catheter Explain the purpose and function of an indwelling urinary catheter
Catheter Care & Skin Integrity Learning outcomes Explain the importance of adequate fluid intake on the effective functioning of a catheter Explain the purpose and function of an indwelling urinary catheter
Chapter 19. Assisting With Bowel Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
10/6/2016 PEDIATRIC ELIMINATION DISORDERS
 PEDIATRIC ELIMINATION DISORDERS SOPHIA L. THOMAS MN, APRN, FNP-BC, PPCNP-BC, FNAP, FAANP I HAVE NO KNOWN CONFLICTS OR DISCLOSURES Objectives: 1. Define elimination disorders 2. Discuss diagnostic criteria
PEDIATRIC ELIMINATION DISORDERS SOPHIA L. THOMAS MN, APRN, FNP-BC, PPCNP-BC, FNAP, FAANP I HAVE NO KNOWN CONFLICTS OR DISCLOSURES Objectives: 1. Define elimination disorders 2. Discuss diagnostic criteria
Recurrent urinary tract infections
 Recurrent urinary tract infections This booklet is designed to help women understand more about recurrent urinary tract infections and the choices available. Please keep it and take it with you to your
Recurrent urinary tract infections This booklet is designed to help women understand more about recurrent urinary tract infections and the choices available. Please keep it and take it with you to your
Retrospective Analysis of Efficacy and Tolerability of Tolterodine in Children with Overactive Bladder
 European Urology European Urology 45 (2004) 240 244 Retrospective Analysis of Efficacy and Tolerability of Tolterodine in Children with Overactive Bladder A. Raes a,, P. Hoebeke b, I. Segaert a, E. Van
European Urology European Urology 45 (2004) 240 244 Retrospective Analysis of Efficacy and Tolerability of Tolterodine in Children with Overactive Bladder A. Raes a,, P. Hoebeke b, I. Segaert a, E. Van
Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux
 Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux Suzi DEMIRBAG, MD Department of Pediatric Surgery, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, TURKEY Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux Suzi DEMIRBAG, MD Department of Pediatric Surgery, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, TURKEY Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
Urinary tract infection
 Urinary tract infection Hascombe Ward Patient information leaflet Understanding the urinary tract There are two kidneys, one on each side of the abdomen. They make urine which drains down the ureters into
Urinary tract infection Hascombe Ward Patient information leaflet Understanding the urinary tract There are two kidneys, one on each side of the abdomen. They make urine which drains down the ureters into
Is antibiotic prophylaxis of any use in nephro-urology? Giovanni Montini Pediatric Nephrology and Dialysis Unit University of Milan Italy
 Is antibiotic prophylaxis of any use in nephro-urology? Giovanni Montini Pediatric Nephrology and Dialysis Unit University of Milan Italy UTI_VUR Bacteria and Humans: diverse behaviours!! Bacteria Humans
Is antibiotic prophylaxis of any use in nephro-urology? Giovanni Montini Pediatric Nephrology and Dialysis Unit University of Milan Italy UTI_VUR Bacteria and Humans: diverse behaviours!! Bacteria Humans
Female Symptom Monitor
 Female Symptom Monitor Occupation: Recreational Activities: Presenting problems: 1. 2. When did this start? Gynecological History: Please fill out each section that is relevant to your problem What age
Female Symptom Monitor Occupation: Recreational Activities: Presenting problems: 1. 2. When did this start? Gynecological History: Please fill out each section that is relevant to your problem What age
SECTION H: BLADDER AND BOWEL. H0100: Appliances. Item Rationale Health-related Quality of Life. Planning for Care
 SECTION H: BLADDER AND BOWEL Intent: The intent of the items in this section is to gather information on the use of bowel and bladder appliances, the use of and response to urinary toileting programs,
SECTION H: BLADDER AND BOWEL Intent: The intent of the items in this section is to gather information on the use of bowel and bladder appliances, the use of and response to urinary toileting programs,
Urinary Continence & Management Post Stroke
 Urinary Continence & Management Post Stroke Incontinence and Stroke occurs in greater than 50% of acute stroke patients despite the personal, economic and psychosocial impact treatment evidence specific
Urinary Continence & Management Post Stroke Incontinence and Stroke occurs in greater than 50% of acute stroke patients despite the personal, economic and psychosocial impact treatment evidence specific
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
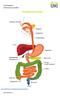 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
Female Symptom Monitor
 Occupation Female Symptom Monitor Presenting problems When did this start? Please fill out each section that is relevant to your problem Gynecological History What age did your period start? Is your cycle
Occupation Female Symptom Monitor Presenting problems When did this start? Please fill out each section that is relevant to your problem Gynecological History What age did your period start? Is your cycle
Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT
 Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study is to find out if there is any relationship between
Occult Chronic Functional Constipation: An Overlooked Cause of Reversible Hydronephrosis in Childhood K Akl ABSTRACT Objective: The aim of this study is to find out if there is any relationship between
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know. A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury
 Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Oncology Patient
 Therapy for the Oncology Patient CARINA SIRACUSA, PT, DPT, WCS OHIOHEALTH PELVIC FLOOR PHYSICAL THERAPIST ONCOLOGY REHABILITATION PROGRAM COORDINATOR What does a pelvic floor therapist treat? Muscles Muscles
Therapy for the Oncology Patient CARINA SIRACUSA, PT, DPT, WCS OHIOHEALTH PELVIC FLOOR PHYSICAL THERAPIST ONCOLOGY REHABILITATION PROGRAM COORDINATOR What does a pelvic floor therapist treat? Muscles Muscles
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Chapter 22. Bowel Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Continence Worksheet Name: Date: Name of Trainer: Name of Company: Clinical Update (NZ) Ltd
 Continence Worksheet Name: Date: Name of Trainer: Name of Company: Clinical Update (NZ) Ltd Segment 1 What is continence? Incontinence is not a but a sign of What organs are involved? and Urine incontinence
Continence Worksheet Name: Date: Name of Trainer: Name of Company: Clinical Update (NZ) Ltd Segment 1 What is continence? Incontinence is not a but a sign of What organs are involved? and Urine incontinence
Constipation- more than Movicol? PATRICK NEARNEY GPSI PAEDIATIRICS
 Constipation- more than Movicol? PATRICK NEARNEY GPSI PAEDIATIRICS Learning Points How to rule out an underlying cause for constipation How to diagnose and treat faecal impaction How to manage encopresis
Constipation- more than Movicol? PATRICK NEARNEY GPSI PAEDIATIRICS Learning Points How to rule out an underlying cause for constipation How to diagnose and treat faecal impaction How to manage encopresis
Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know. A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury
 Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about managing your bladder After SCI, you may
Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about managing your bladder After SCI, you may
Section H Bladder and Bowel
 Instructor Guide Section H Bladder and Bowel Objectives State the intent of Section H Bladder and Bowel. Describe how to conduct the assessment for urinary incontinence. Describe how to conduct the assessment
Instructor Guide Section H Bladder and Bowel Objectives State the intent of Section H Bladder and Bowel. Describe how to conduct the assessment for urinary incontinence. Describe how to conduct the assessment
