Increased motor unit fibre density in the external
|
|
|
- Evan Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1980, 43, Increased motor unit fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle in ano-rectal incontinence: a single fibre EMG study M E NEILL AND M SWASH From St Mark's Hospital and The London Hospital, London S U M M A R Y The motor unit fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle has been measured in 13 normal subjects aged 18 to 78 years, and in 14 patients with ano-rectal incontinence, aged 17 to 72 years. The mean fibre density in the normal subjects was 1-5±0-16, and in the incontinent subjects it was 2-17±0-28 (p<0001). These findings provide support for the suggestion that ano-rectal incontinence commonly has a neurogenic basis. Investigation of patients with ano-rectal incontinence has relied hitherto on anal pressure studies supported by EMG and more recently, by study of the anal reflex.' Parks, Swash and Urich2 reported histological abnormalities in the voluntary anal sphincter musculature in patients with anorectal incontinence and suggested that the innervation of the external anal sphincter and puborectalis muscles was damaged in these patients. This suggestion has been supported by the observation of abnormalities in small nerves supplying the external anal sphincter muscle itself2 and by quantitative histometric studies of the external anal sphincter, puborectalis and levator ani muscles in a group of patients with anorectal incontinence matched for age with a group of normal subjects.3 4 Conventional EMG studies of the external anal sphincter have not proved useful in clinical practice although they can provide information about the pattern of voluntary control of the external anal sphincter muscle, especially in patients with cauda equina lesions.5 ' In order to study the functional disorder in the external anal sphincter in patients with ano-rectal incontinence we have used single fibre EMG. By this technique a quantitative estimate of the mean number of muscle fibres (from 20 different recordings) belonging to a motor unit within the uptake area of the recording electrode, the motor unit fibre density, may be Address for reprint requests: Dr M Swash, Department of Neurology, The London Hospital, London E1 IBB. Accepted 13 December 1979 obtained. The fibre density may be increased in both neurogenic and myopathic disorders, but in a muscle known not to be affected by a myopathic process an increased fibre density is an index of reinnervation. Other parameters, such as measurement of the neuromuscular jitter and impulse blocking8 9 may also be studied. In this report we describe a method for obtaining single fibre EMG recordings in the external anal sphincter muscle in human subjects. We have used this method to measure the fibre density in this muscle in a group of normal subjects, and in a group of patients with ano-rectal incontinence. The results are consistent with our suggestion2-4 that ano-rectal incontinence can occur from damage to the innervation of the sphincter musculature. Methods Single fibre EMG recordings were made with a Medelec MS6 EMG apparatus, Medelec SF25 single fibre EMG electrodes and low and high frequency filter settings of 500 Hz and 16K Hz. In single fibre EMG recordings in limb muscles a triggering potential is accepted only if its amplitude is greater than 200 [tv, and its rise time is less than 300 ms.8 9 However motor unit action potentials recorded in the external anal sphincter muscle with conventional EMG are smaller than those recorded in other striated muscles; Jesel, Isch-Treussard and Isch6 found a mean amplitude of ,uV, and a maximal amplitude of 343
2 344 3 mv. The low amplitude of motor unit action potentials in the external anal sphincter is due to the small size of the muscle fibres in this muscle. In a histometric study we found that the mean diameter of muscle fibres in the external anal sphincter in normal subjects was less than 30,um.4 We decided, therefore, to accept triggering potentials greater than 150,V in our single fibre EMG studies of this muscle. Technique: In normal subjects the external sphincter muscle shows tonic resting activity, but these potentials are small and show an infrequent and irregular firing pattern. It is difficult to voluntarily activate motor units in the external anal sphincter to a consistency adequate for single fibre EMG recordings to be made. In order to obtain a slight degree of continuous activity in the muscle we have utilised the activating effect of slight traction on the sphincter ring. Each patient was placed in the left lateral position. A Miller-Abbott balloon was inserted into the lower rectum and distended with 30 ml of air and 150 g traction was applied by means of a weighted cord. This proved sufficient to induce a constant, slight amount of activity in the external sphincter muscle. A suitable ground lead was attached to the left thigh. The single fibre EMG electrode was inserted, without anaesthetic, into the external anal sphincter muscle lateral to the anal Table Summary of clinical and EMG data. M E Neill and M Swash margin on either side, and recordings made with the electrode directed both anteriorly and posteriorly in the muscle. Most of the recordings were made in the superficial part of the muscle. As in fibre density measurements in other muscles9 the mean number of single muscle fibre action potentials recorded in 20 different electrode positions was taken as the fibre density. Usually only two skin penetrations were required. The fibre density was measured on both sides of the circular external anal sphincter muscle, but most of the recordings were made on the dependent left side. All the potentials were recorded for subsequent analysis. Patients: Thirteen subjects, eight of whom were women, served as controls. These volunteer patients were attending St Mark's Hospital for treatment of disorders not affecting the perineum, anus or rectum, such as inguinal hernia, carcinoma of the colon and cholecystitis. Their ages ranged from 18 to 78 years (mean 51 yr). Examination of the perineum, anus and rectum before single fibre EMG revealed no abnormality, and there was no clinical evidence of disease of the lumbosacral spine or nerve roots. Fourteen patients with ano-rectal incontinence were studied. All these patients were women. Their ages ranged from 17 to 72 years (mean 42 yr). Clinical details are given in the table. Case Sexl Type Duration Defecation Rectal Perineal Obstetric history para. Other clinicalfeatures Singlefibre EMG no age of FI of FI straining prolapse descent (yr) (yr) Fibre Mean MUAP density duration (ms) I Ff17 Loose Father has myotonic dystrophy 2 F/21 Solid Rectopexy F/36 Solid Precipitate delivery Long history incontinence began constipation after childbirth (2nd) 4 F/38 Solid precipitate delivery Rectopexy post anal repair previously 5 F/40 Solid perineal tear Incontinence worse after each delivery 6 F/41 Loose difficult deliveries F/43 Solid difficult deliveries Crohn's disease F/49 Solid precipitate deliveries Ff50 Solid 2/ severe perineal tears Vaginal repair lumbar laminectomies 10 F/60 Loose Vaginalrepair hysterectomy 11 F/61 Solid normal deliveries Rectopexy history of constipation 12 F/62 Loose caesarian sections Vaginal repair hysterectomy 13 F/65 Solid normal delivery Rectopexy anal pain F/72 Solid prolonged labour Vaginal repair maximal anal dilation Ft=faec s incontinence; =severe; + + =moderate; + =mild; MUAP=motor unit action potential.
3 Increased motor unit fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle Results In the 13 normal subjects the fibre density ranged from 1*3 to 1-8 (mean 15, SD 0-16). The relation between fibre density and age in these subjects is shown in fig 1. There was an increase in fibre density with age, which was most evident after the age of 60 years. In the youngest subject studied, a woman aged 18 years, the fibre density was slightly higher than in two subjects aged 20 to 30 years. A typical pair of potentials recorded from one of these normal subjects is shown in fig 2. The neuromuscular jitter was not measured, but no potential pair showed a jitter greater than 50 ms. All the triggering potentials were greater than 200,uV in amplitude. In the 14 patients with ano-rectal incontinence the fibre density ranged from 1P8 to 2-7 (mean 2-17, SD 0-28). The range of fibre densities in the normal subjects and incontinent patients did not overlap and the mean values in the two groups 1 8 1*7 1-6 Fibre density 1 - Female x Male Age in years x 0 * x 0 x SD Fig 1 The relation between fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle and age, in 13 normal subjects. I Fig 2 A double potential, showing a normal jitter. Scale: I mv, I ms. were significantly different. (Student's two tailed t test; p<0-001). The fibre densities in the incontinent subjects are shown, compared to the normal values in relation to age, in fig 3. A stable motor unit action potential showing an increased number of single muscle fibre action potentials, without increased jitter or impulse blocking, is shown in fig 4. In some potentials individual spike components showed an increased jitter and impulse blockings were seen in some of these. Rarely, blocking of two components was seen (fig 5), an indication of failure of transmission at an axonal branch in the terminal innervation ex Fibre density Mean 2-1 * 0. Standard deviation! * Age in years Fig 3 Fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle, plotted against age, in 14 patients with ano-rectal incontinence. The data from the normal subjects are shown by the thicker line. Fig 4 A stable motor unit action potential consisting of five separate components recorded in the external anal sphincter muscle of a patient with incontinence (case 3). Scale: I mv, I ms. 345 _
4 346 L Fig 5 A potential with four components. Since the configuration of the second pair of components differs slightly from that of the first pair, this recording is interpreted as representing 'neural blocking' of the second pair of components rather than intermittent double discharges. Scale: I mv, I mis. Discussion In most subjects single fibre EMG assessment of the external anal sphincter is neither difficult nor painful. Some subjects were distressed by their inability to observe the procedure of electrode placement, as in ordinary EMG examinations, but the use of a weighted intra-rectal balloon to induce slight activity in the external anal sphincter made it relatively easy to record enough potentials for fibre density measurements in about 20 minutes. In patients with incontinence it was more difficult to obtain recordings of 20 different motor unit action potentials. We have used a slightly lower amplitude criterion for the triggering potential in our work than was used by Stalberg and Thiele7 in their study of the fibre density in the extensor digitorum communis muscle,7 9 because the mean diameter of muscle fibres in the external anal sphincter muscle is less than half that found in limb muscles of normal subjects.4 Most of the triggering potentials, however, recorded in the external anal sphincter in our subjects were greater than 300,V, and all were greater than 200 tv. The neuromuscular jitter was not measured systematically, but was always less than 50,Ls. In the normal subjects the mean fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle was 15, a value similar to that found in other striated muscles.7 9 No difference was found between men and women of similar age. The fibre density was slightly increased in subjects older than 60 years, as in other muscles.7 " Further, the slightly higher fibre density found in the youngest subject studied (fig 1) is consistent with the higher fibre density found in the extensor digitorum communis in normal subjects less than 10 years of age.9 M E Neill and M Swash The fibre density was increased in the external anal sphincter muscle in all the patients with incontinence. In one patient, aged 17 years (case 1) the fibre density was 1 8, a value the same as that found in an 80 year old normal subject. This patient (case 1) was chronically constipated and was incontinent only for liquid stool. Three other patients (cases 6, 10 and 12) whose fibre densities were 19, 1 85 and 2-0 respectively, were also incontinent only for liquid stool. The other patients, whose fibre densities ranged from 2-0 to 2'7 were incontinent for both liquid and solid faeces. There was thus a relationship between the severity of incontinence and the fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle. No relationship between duration of incontinence and fibre density was observed; this probably reflects the various factors leading to incontinence in these patients. All the patients with incontinence in the present series were women. Nine had a history of abnormal or difficult deliveries with trauma to the pelvic floor musculature, but three had never been pregnant and in two childbirth had been normal. Prolonged and repeated defaecation straining was admitted by nine patients (table), including all those who had not experienced a difficult delivery, or who had not been pregnant. One patient, case 14, became incontinent of faeces after a maximal anal dilatation; this procedure probably damaged the internal anal sphincter, the external sphincter having been injured previously. These patients are thus similar to those studied previously.24 The pathogenesis of idiopathic ano-rectal incontinence is not well understood. Parks and Swash have reported histological evidence of denervation in the external anal sphincter and puborectalis muscles of patients with ano-rectal incontinence2 4 and have suggested that this might result from damage to the pudendal nerves by entrapment beneath the sacrospinous ligaments and perhaps, by stretch injury to the terminal segments of the nerves caused by descent of the perineal floor during defaecation straining.2 3 The finding of an increased motor unit fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle in patients with ano-rectal incontinence is consistent with this hypothesis; an increased fibre density can be correlated with reinnervation, and fibre type grouping is a feature of the histological abnormality in the sphincter musculature in patients with ano-rectal incontinence.24 Myopathic disorders, which may also be associated with an increased fibre density in single fibre EMG recordings" can be excluded as a cause of ano-rectal incontinence by the clinical2 and histological features.24 Further, we have ex-
5 Increased motor unit fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle amined the external anal sphincter muscle by single fibre EMG in two patients with incomplete cauda equina lesions and have found the fibre density to be increased in both patients. Single fibre EMG seems to be a useful technique for study of the functional disorder in the external anal sphincter muscle in patients with incontinence. Since it is a quantitative method it may prove particularly useful for assessing changes in the external anal sphincter muscle occurring during the natural history of perineal disorders or of their treatment. However, comparison of fibre density studies with other techniques such as pressure measurements within the anal canal, both in incontinence and in other ano-rectal disorders will be important before the role of single fibre EMG in the clinical investigation of these disorders can be established. References 1 Henry MM, Swash M. Assessment of pelvic floor disorders and incontinence by electrophysiological recording of the anal reflex. Lancet 1978; 1: Parks AG, Swash M, Urich H. Sphincter denervation in ano-rectal incontinence and rectal prolapse. Gut 1977; 18: Parks AG, Swash M. Denervation of the anal sphincter causing idiopathic ano-rectal incontinence. J R Coll Surg Edinb 1979; 24: Beersiek F, Parks AG, Swash M. Pathogenesis of ano-rectal incontinence, a histometric study of the anal sphincter musculature. J Neurol Sci 1979; 42: Chantrain A, Lloyd K, Swinyard CA. The sphincter ani externus in spina bifida and myelomeningocoele. J Urol 1966; 95: Jesel M, Isch-Treussard C, Isch F. Electrography of striated muscle of anal urethral sphincters. In: Desmedt JE, ed. New Developments in Electromyography and Clinical Neurophysiology. Basel: Karger, 1973: Stalberg E, Thiele B. Motor unit fibre density in the extensor digitorum communis muscle. J Neurol, Neurosurg Psychiatry 1975; 38: Ekstedt J. Human single muscle fibre action potentials. Acta Physiol Scand (Suppl 226) 1964; 61: Stalberg E. Trontelj JV. Single fibre electromyography. London: Mirvalle Press, J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry: first published as /jnnp on 1 April Downloaded from on 13 October 2018 by guest.
electrical stimulation
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1983;46:67-71 Direct and reflex responses in perineal muscles on electrical stimulation DB VODUSEK, M JANKO, J LOKAR From the Institute for Clinical Neurophysiology,
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1983;46:67-71 Direct and reflex responses in perineal muscles on electrical stimulation DB VODUSEK, M JANKO, J LOKAR From the Institute for Clinical Neurophysiology,
Responses to electrical stimulation of denervated human muscle fibres recorded with single fibre EMG
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1983;46:305-309 Responses to electrical stimulation of denervated human muscle fibres recorded with single fibre EMG JOZE TRONTELJ, ERIK STALBERG From
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1983;46:305-309 Responses to electrical stimulation of denervated human muscle fibres recorded with single fibre EMG JOZE TRONTELJ, ERIK STALBERG From
Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence)
 Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence) What is Accidental Bowel Leakage (ABL)? Accidental bowel leakage is the inability to control solid or liquid stool. This is the inability to control gas and
Accidental Bowel Leakage (Fecal Incontinence) What is Accidental Bowel Leakage (ABL)? Accidental bowel leakage is the inability to control solid or liquid stool. This is the inability to control gas and
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Urodynamic and electrophysiological investigations in neuro-urology
 Urodynamic and electrophysiological investigations in neuro-urology Pr. Gerard Amarenco Neuro-Urology and Pelvic-Floor Investigations Department Tenon Hospital, Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Paris, Er6,
Urodynamic and electrophysiological investigations in neuro-urology Pr. Gerard Amarenco Neuro-Urology and Pelvic-Floor Investigations Department Tenon Hospital, Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Paris, Er6,
Anorectal Diagnostic Overview
 Anorectal Diagnostic Overview 11-25-09 3.11.2010 2009 2010 Anorectal Manometry Overview Measurement of pressures and the annotation of rectal sensation throughout the rectum and anal canal to determine:
Anorectal Diagnostic Overview 11-25-09 3.11.2010 2009 2010 Anorectal Manometry Overview Measurement of pressures and the annotation of rectal sensation throughout the rectum and anal canal to determine:
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR
 LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
Function of the anal sphincters in patients with
 Function of the anal sphincters in patients with intussusception of the rectum B. FRENCKNER AND T. IHRE Gut, 1976,17, 147-151 From the Department of Clinical Physiology and the Department of Surgery, Serafimer
Function of the anal sphincters in patients with intussusception of the rectum B. FRENCKNER AND T. IHRE Gut, 1976,17, 147-151 From the Department of Clinical Physiology and the Department of Surgery, Serafimer
Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists
 Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists Disclosures none Outline Definition Etiologies Exam findings Additional testing Medical management Surgical options What is fecal incontinence? Recurrent
Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists Disclosures none Outline Definition Etiologies Exam findings Additional testing Medical management Surgical options What is fecal incontinence? Recurrent
Perineal Electrophysiologic Tests
 Perineal disorders and emg! Perineal Electrophysiologic Tests Voiding dysfunction Stress Urinary Incontinence urgency OAB Urge Incontinence nocturia Pr. Gerard Amarenco Mixed Incontinence frequency Service
Perineal disorders and emg! Perineal Electrophysiologic Tests Voiding dysfunction Stress Urinary Incontinence urgency OAB Urge Incontinence nocturia Pr. Gerard Amarenco Mixed Incontinence frequency Service
Index of subjects. bilesalt, malabsorption, incontinence in 147
 Index of subjects alcoholism, neuronal damage in 118 Alzheimer dementia, faecal incontinence in 113 anal fissure, manometry in 5 anal retractor, reduction of resting pressure 128 Angelchick prosthesis,
Index of subjects alcoholism, neuronal damage in 118 Alzheimer dementia, faecal incontinence in 113 anal fissure, manometry in 5 anal retractor, reduction of resting pressure 128 Angelchick prosthesis,
MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW
 MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW ANAL MANOMETRY MEASURES PRESSURE ALLOWS INTERPRITATION SENSATION RAIR RECTAL COMPLIANCE MOTIVATION OF THE PATIENT FUNCTION OF THE PUDENDAL NERVE WHEN TO USE ANAL MANOMETRY
MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW ANAL MANOMETRY MEASURES PRESSURE ALLOWS INTERPRITATION SENSATION RAIR RECTAL COMPLIANCE MOTIVATION OF THE PATIENT FUNCTION OF THE PUDENDAL NERVE WHEN TO USE ANAL MANOMETRY
we have recorded decelerating bursts plus complex to quantitate the amount of abnormal EMG activity
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1985;48:1004-1009 Decelerating burst and complex repetitive discharges in the striated muscle of the urethral sphincter, associated with urinary retention
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1985;48:1004-1009 Decelerating burst and complex repetitive discharges in the striated muscle of the urethral sphincter, associated with urinary retention
Fecal Incontinence. Inability to retain feces or bowel movements, resulting in involuntary passage of feces or bowel movements
 Fecal Incontinence (Involuntary Passage of Feces or Bowel Movements) Basics OVERVIEW Inability to retain feces or bowel movements, resulting in involuntary passage of feces or bowel movements GENETICS
Fecal Incontinence (Involuntary Passage of Feces or Bowel Movements) Basics OVERVIEW Inability to retain feces or bowel movements, resulting in involuntary passage of feces or bowel movements GENETICS
Dr Hannah Blakely. Dr Ben Sharp. Ms Julee Binns. Sara Widdowson. 7:15-8:15 Breakfast Session: Oxford Women's Health
 Dr Hannah Blakely Clinical Psychologist Oxford Women's Health Ms Julee Binns Consultant Physiotherapist Oxford Women's Health, Christchurch Sara Widdowson NZ Registered Dietitian Christchurch Public Hospital
Dr Hannah Blakely Clinical Psychologist Oxford Women's Health Ms Julee Binns Consultant Physiotherapist Oxford Women's Health, Christchurch Sara Widdowson NZ Registered Dietitian Christchurch Public Hospital
Pelvic Floor Disorders. Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon
 Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
Surgical Management for Defecation Dysfunction
 Defecatory Dysfunction Surgical Management for Defecation Dysfunction JMAJ 46(9): 378 383, 2003 Tatsuo TERAMOTO Professor, 1st Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Toho University Abstract: Typical
Defecatory Dysfunction Surgical Management for Defecation Dysfunction JMAJ 46(9): 378 383, 2003 Tatsuo TERAMOTO Professor, 1st Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Toho University Abstract: Typical
Viscous Fluid Retention: A New Method for Evaluating Anorectal Function
 Viscous Fluid Retention: A New Method for Evaluating Anorectal Function Michael Srensen, M.D., Tine Tetzschner, M.D., le 0. Rasmussen, M.D., John Christiansen, M.D. From the Department of Surgery D, Glostrup
Viscous Fluid Retention: A New Method for Evaluating Anorectal Function Michael Srensen, M.D., Tine Tetzschner, M.D., le 0. Rasmussen, M.D., John Christiansen, M.D. From the Department of Surgery D, Glostrup
ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION. Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital
 ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital Accidental Bowel Leakage What Gets the Woman into Your Office 67%
ACCIDENTAL BOWEL LEAKAGE: A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO EVALUATION Tristi W. Muir, MD Chair, Department of OB/GYN Houston Methodist Hospital Accidental Bowel Leakage What Gets the Woman into Your Office 67%
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction. Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield
 GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW
 MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW ANAL MANOMETRY MEASURES PRESSURE ALLOWS INTERPRITATION SENSATION RAIR RECTAL COMPLIANCE MOTIVATION OF THE PATIENT FUNCTION OF THE PUDENDAL NERVE WHEN TO USE ANAL MANOMETRY
MCOMPASS ANAL MANOMETRY AN OVERVIEW ANAL MANOMETRY MEASURES PRESSURE ALLOWS INTERPRITATION SENSATION RAIR RECTAL COMPLIANCE MOTIVATION OF THE PATIENT FUNCTION OF THE PUDENDAL NERVE WHEN TO USE ANAL MANOMETRY
Dana Alrafaiah. - Amani Nofal. - Ahmad Alsalman. 1 P a g e
 - 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
- 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
Parameters to quantify. shape of individual MUPs jiggle fullness recruitment (early, reduced) dynamic changes with time (fatigue) 2 normal motor units
 2 normal motor units STÅLBERG Reinnervated motor unit STÅLBERG STÅLBERG Muscle membrane function - spontaneous Muscle fibre characteristics; diameter MU organisation number of fibres grouping N-M transmission
2 normal motor units STÅLBERG Reinnervated motor unit STÅLBERG STÅLBERG Muscle membrane function - spontaneous Muscle fibre characteristics; diameter MU organisation number of fibres grouping N-M transmission
What is the role for neurophysiology in the evaluation of patients with uro-genito-anal dysfunction?
 London, 2016 What is the role for neurophysiology in the evaluation of patients with uro-genito-anal dysfunction? David B. Vodušek Medical Faculty, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia vodusek.david.b@gmail.com
London, 2016 What is the role for neurophysiology in the evaluation of patients with uro-genito-anal dysfunction? David B. Vodušek Medical Faculty, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia vodusek.david.b@gmail.com
Pelvic Floor Overactivity: Definition and Pathophysiology
 + Pelvic Floor Overactivity: Definition and Pathophysiology WS # 24 The Overactive Pelvic Floor Anna Padoa, MD Urogynecology and Pelvic Floor Service Assaf Harofeh Medical Center + Definition of overactive
+ Pelvic Floor Overactivity: Definition and Pathophysiology WS # 24 The Overactive Pelvic Floor Anna Padoa, MD Urogynecology and Pelvic Floor Service Assaf Harofeh Medical Center + Definition of overactive
2/5/2016. Evolving Surgical Treatment Approaches for Fecal Incontinence in Women: An Evidence and Cased-Based Approach
 Evolving Surgical Treatment Approaches for Fecal Incontinence in Women: An Evidence and Cased-Based Approach Holly E Richter, PhD, MD, FACOG, FACS J Marion Sims Professor Obstetrics and Gynecology Professor
Evolving Surgical Treatment Approaches for Fecal Incontinence in Women: An Evidence and Cased-Based Approach Holly E Richter, PhD, MD, FACOG, FACS J Marion Sims Professor Obstetrics and Gynecology Professor
J. Physiol. (I957) I35, (Received 20 July 1956) The interpretation ofthe experimental results ofthe preceding paper (Matthews
 263 J. Physiol. (I957) I35, 263-269 THE RELATIVE SENSITIVITY OF MUSCLE NERVE FIBRES TO PROCAINE BY PETER B. C. MATTHEWS AND GEOFFREY RUSHWORTH From the Laboratory of Physiology, University of Oxford (Received
263 J. Physiol. (I957) I35, 263-269 THE RELATIVE SENSITIVITY OF MUSCLE NERVE FIBRES TO PROCAINE BY PETER B. C. MATTHEWS AND GEOFFREY RUSHWORTH From the Laboratory of Physiology, University of Oxford (Received
Review Article Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Body Excreta Incontinence and Continence
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS GYNAECOLOGY Review Article Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Body Excreta Incontinence and Continence Abdel Karim M El Hemaly 1 * and Laila ASE Mousa 1 1 Professor of Obstetrics and gynaecology,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS GYNAECOLOGY Review Article Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Body Excreta Incontinence and Continence Abdel Karim M El Hemaly 1 * and Laila ASE Mousa 1 1 Professor of Obstetrics and gynaecology,
Development of the pelvic floor : implications for clinical anatomy Wallner, C.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Development of the pelvic floor : implications for clinical anatomy Wallner, C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Wallner, C. (2008). Development
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Development of the pelvic floor : implications for clinical anatomy Wallner, C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Wallner, C. (2008). Development
Ultrastructural changes in internal anal sphincter in neurogenic faecal incontinence
 Gut, 1988, 29, 1692-1698 Ultrastructural changes in internal anal sphincter in neurogenic faecal incontinence M SWASH, A GRAY, D Z LUBOWSKI, AND R J NICHOLLS From the Sir Alan Parks Physiology Department,
Gut, 1988, 29, 1692-1698 Ultrastructural changes in internal anal sphincter in neurogenic faecal incontinence M SWASH, A GRAY, D Z LUBOWSKI, AND R J NICHOLLS From the Sir Alan Parks Physiology Department,
Summary and conclusion. Summary And Conclusion
 Summary And Conclusion Summary and conclusion Rectal prolapse remain a disorder for which no single ideal treatment was approved for all cases. Complete rectal prolapse (procidentia) is the circumferential
Summary And Conclusion Summary and conclusion Rectal prolapse remain a disorder for which no single ideal treatment was approved for all cases. Complete rectal prolapse (procidentia) is the circumferential
Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives
 Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives 1 Aims of this self assessment competency To equip Midwives with the knowledge and skills to teach pelvic floor
Pregnancy related pelvic floor dysfunction- suggested teaching presentation for Midwives 1 Aims of this self assessment competency To equip Midwives with the knowledge and skills to teach pelvic floor
A70.4 Insertion of neurostimulator electrodes into peripheral nerve Z12.2 Posterior tibial nerve R15.X Faecal incontinence
 The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has issued full guidance to the NHS in England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland on Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS) for
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has issued full guidance to the NHS in England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland on Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS) for
Outlet syndrome: is there a surgical option?'
 Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Volume 77 July 1984 559 Outlet syndrome: is there a surgical option?' M R B Keighley MS FRCS P Shouler FRCS Department of Surgery, General Hospital, Birmingham
Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Volume 77 July 1984 559 Outlet syndrome: is there a surgical option?' M R B Keighley MS FRCS P Shouler FRCS Department of Surgery, General Hospital, Birmingham
New method for the estimation of the number of
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 1195-121 New method for the estimation of the number of motor units in a muscle 2 Duchenne, limb-girdle and facioscapulohumeral, and myotonic
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 1195-121 New method for the estimation of the number of motor units in a muscle 2 Duchenne, limb-girdle and facioscapulohumeral, and myotonic
Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz
 Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz 54 year old female presenting with: Dragging sensation Urinary incontinence Some faecal incontinence HPC Since May 14 had noticed a mass protruding from the vagina when going
Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz 54 year old female presenting with: Dragging sensation Urinary incontinence Some faecal incontinence HPC Since May 14 had noticed a mass protruding from the vagina when going
Functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor and lower urinary tract Stefano Floris, MD, PhD Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
 Functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor and lower urinary tract Stefano Floris, MD, PhD Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Ospedale San Giovanni di Dio, Gorizia, Italy ANATOMY URINARY CONTINENCE
Functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor and lower urinary tract Stefano Floris, MD, PhD Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Ospedale San Giovanni di Dio, Gorizia, Italy ANATOMY URINARY CONTINENCE
Faecal incontinence after childbirth
 Britisb Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology January 1997, Vol. 104, pp. 4650 Faecal incontinence after childbirth *Christine MacArthur Reader (Maternal and Child Epidemiology), *Debra E. Bick Research
Britisb Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology January 1997, Vol. 104, pp. 4650 Faecal incontinence after childbirth *Christine MacArthur Reader (Maternal and Child Epidemiology), *Debra E. Bick Research
EMG; clinical practice. Erik Stålberg
 EMG; clinical practice Erik Stålberg What do we want to express Muscle membrane function - spontaneous Muscle fibre characteristics; diameter MU organisation number of fibres grouping N-M transmission
EMG; clinical practice Erik Stålberg What do we want to express Muscle membrane function - spontaneous Muscle fibre characteristics; diameter MU organisation number of fibres grouping N-M transmission
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Perineum It is the diamond-shaped lower end of the trunk
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Perineum It is the diamond-shaped lower end of the trunk
Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Constipation. Information for adults. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
 Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
Conventional needle electromyography
 3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 5 Electromyography: Surface, needle conventional and single fiber - Level 1-2 Conventional
3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 5 Electromyography: Surface, needle conventional and single fiber - Level 1-2 Conventional
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction (BBD) Naida Kalloo, MD Pediatric Urology Children s National
 Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction (BBD) Naida Kalloo, MD Pediatric Urology Children s National What is Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction? Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and bowel movement disorders Majority
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction (BBD) Naida Kalloo, MD Pediatric Urology Children s National What is Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction? Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and bowel movement disorders Majority
Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests
 Defecatory Dysfunction Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests JMAJ 46(9): 373 377, 2003 Masatoshi OYA, Masashi UENO, and Tetsuichiro MUTO Department of
Defecatory Dysfunction Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests JMAJ 46(9): 373 377, 2003 Masatoshi OYA, Masashi UENO, and Tetsuichiro MUTO Department of
Original Articles. 198 Medicina Interna REVISTA DA SOCIEDADE PORTUGUESA DE MEDICINA INTERNA
 Original Articles Lumbosacral radiculopathy. The sensitivity of electromyographical studies compared to imaging techniques and clinical findings L. Negrão*, J. M. Santos**, J. Gonçalves***, L. Cunha****
Original Articles Lumbosacral radiculopathy. The sensitivity of electromyographical studies compared to imaging techniques and clinical findings L. Negrão*, J. M. Santos**, J. Gonçalves***, L. Cunha****
NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS
 NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS Introduction The pelvic floor is highly complex structure made up of skeletal and striated muscle, support and suspensory ligaments, fascial coverings and an intricate
NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS Introduction The pelvic floor is highly complex structure made up of skeletal and striated muscle, support and suspensory ligaments, fascial coverings and an intricate
Faecal Incontinence: Obstetric Causality
 Faecal Incontinence: Obstetric Causality A thesis submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Doctor of Medicine in the Faculty of Medical and Human Sciences 211 Kirsty Ruth Cattle School
Faecal Incontinence: Obstetric Causality A thesis submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Doctor of Medicine in the Faculty of Medical and Human Sciences 211 Kirsty Ruth Cattle School
Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D.
 Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Contrast the types of motility in the small intestine. 2. Describe the neural circuits that mediate peristalsis.
Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Contrast the types of motility in the small intestine. 2. Describe the neural circuits that mediate peristalsis.
10/15/2012. Pelvic Pain and Dysfunction
 Pain and Holly Bommersbach PT, MPT Angela De La Cruz PT, MPT Pain which occurs in the perineal and/or anal areas Pain in the lower abdomen, low back and/or pelvic girdle Pain may often affect other areas,
Pain and Holly Bommersbach PT, MPT Angela De La Cruz PT, MPT Pain which occurs in the perineal and/or anal areas Pain in the lower abdomen, low back and/or pelvic girdle Pain may often affect other areas,
2. List the 8 pelvic spaces: list one procedure or dissection which involves entering that space.
 Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
Computer method for the analysis of evoked
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 417-428 Computer method for the analysis of evoked motor unit potentials 2. Duchenne, limb-girdle, facioscapulohumeral and myotonic muscular
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 417-428 Computer method for the analysis of evoked motor unit potentials 2. Duchenne, limb-girdle, facioscapulohumeral and myotonic muscular
Parameters to quantify. shape of individual MUPs jiggle fullness recruitment (early, reduced) dynamic changes with time (fatigue) 2 normal motor units
 2 normal motor units STÅLBERG Reinnervated motor unit Myopathy STÅLBERG STÅLBERG Muscle membrane function - spontaneous Muscle fibre characteristics; diameter MU organisation number of fibres grouping
2 normal motor units STÅLBERG Reinnervated motor unit Myopathy STÅLBERG STÅLBERG Muscle membrane function - spontaneous Muscle fibre characteristics; diameter MU organisation number of fibres grouping
Incidence of Colorectal Cancers- Australia. Anterior Resection 5/23/2018. What spurs us to investigate?
 Incidence of Colorectal Cancers- Australia 17,000 Colorectal cancers in 2018 20% of Colorectal cancers are in the Rectum 12.3% of all new cancers Anterior Resection Syndrome (ARS) Lisa Wilson. Colorectal
Incidence of Colorectal Cancers- Australia 17,000 Colorectal cancers in 2018 20% of Colorectal cancers are in the Rectum 12.3% of all new cancers Anterior Resection Syndrome (ARS) Lisa Wilson. Colorectal
Electromyography (EMG)
 Introduction In this laboratory, you will explore the electrical activity of skeletal muscle by recording an electromyogram (EMG) from a volunteer. You will examine the EMG of both voluntary and evoked
Introduction In this laboratory, you will explore the electrical activity of skeletal muscle by recording an electromyogram (EMG) from a volunteer. You will examine the EMG of both voluntary and evoked
EPISIOTOMY & PERINEAL TEARS Anatomy &Functionality May Dr. Annie Leong MBBS, FRANZCOG, CU
 EPISIOTOMY & PERINEAL TEARS Anatomy &Functionality May 2011 Dr. Annie Leong MBBS, FRANZCOG, CU Restore normal perineal anatomy Achieve good haemostasis Avoid infection and wound breakdown Avoid coital
EPISIOTOMY & PERINEAL TEARS Anatomy &Functionality May 2011 Dr. Annie Leong MBBS, FRANZCOG, CU Restore normal perineal anatomy Achieve good haemostasis Avoid infection and wound breakdown Avoid coital
SINGLE FIBER EMG AND MACRO EMG
 AANEM WORKSHOP SINGLE FIBER EMG AND MACRO EMG Erik V. Stålberg, MD, PhD AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF NEUROMUSCULAR & ELECTRODIAGNOSTIC MEDICINE Workshop handouts are prepared as background didactic material
AANEM WORKSHOP SINGLE FIBER EMG AND MACRO EMG Erik V. Stålberg, MD, PhD AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF NEUROMUSCULAR & ELECTRODIAGNOSTIC MEDICINE Workshop handouts are prepared as background didactic material
Force in the anal canal and anal continence
 Gut, 1967, 8, 354 Force in the anal canal and anal continence C. D. COLLINS, H. L. DUTHIE, T. SHELLEY, AND G. E. WHITTAKER From the University Department of Surgery, Royal Infirmary, Sheffield EDITORIAL
Gut, 1967, 8, 354 Force in the anal canal and anal continence C. D. COLLINS, H. L. DUTHIE, T. SHELLEY, AND G. E. WHITTAKER From the University Department of Surgery, Royal Infirmary, Sheffield EDITORIAL
ORIENTING TO BISECTED SPECIMENS ON THE PELVIS PRACTICAL
 ORIENTING TO BISECTED SPECIMENS ON THE PELVIS PRACTICAL The Pelvis is just about as complicated as head and neck and considerably more mysterious. You have to be able to visualize (imagine) the underlying
ORIENTING TO BISECTED SPECIMENS ON THE PELVIS PRACTICAL The Pelvis is just about as complicated as head and neck and considerably more mysterious. You have to be able to visualize (imagine) the underlying
-15. -Alaa Albandi. -Dr. Mohammad Almohtasib. 0 P a g e
 -15 -Alaa Albandi - -Dr. Mohammad Almohtasib 0 P a g e In this last lecture, we will talk about the sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal. Sigmoid colon It has a mesentery called pelvic mesocolon or sigmoidal
-15 -Alaa Albandi - -Dr. Mohammad Almohtasib 0 P a g e In this last lecture, we will talk about the sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal. Sigmoid colon It has a mesentery called pelvic mesocolon or sigmoidal
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATIONS: LOCALISATION AND GRADING
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATIONS: LOCALISATION AND GRADING Author : MARK LOWRIE Categories : Vets Date : June 16, 2014 MARK LOWRIE
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATIONS: LOCALISATION AND GRADING Author : MARK LOWRIE Categories : Vets Date : June 16, 2014 MARK LOWRIE
Perineum. done by : zaid al-ghnaneem
 Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
TYPES OF RECTAL PROLAPSE
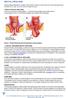 RECTAL PROLPASE Rectal prolapse describes a condition where either the lining or entire wall of the rectum becomes loose and falls into, or even out of, the rectum through the anus. TYPES OF RECTAL PROLAPSE
RECTAL PROLPASE Rectal prolapse describes a condition where either the lining or entire wall of the rectum becomes loose and falls into, or even out of, the rectum through the anus. TYPES OF RECTAL PROLAPSE
Regional curare for the reduction of the safety factor in human motor end-plates studied with single fibre electromyography
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 85-89 Regional curare for the reduction of the safety factor in human motor end-plates studied with single fibre electromyography HANS H. SCHILLER,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 85-89 Regional curare for the reduction of the safety factor in human motor end-plates studied with single fibre electromyography HANS H. SCHILLER,
Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Faecal Incontinence
 Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Faecal Incontinence Questions & Answers GLASGOW COLORECTAL CENTRE Ross Hall Hospital 221 Crookston Road Glasgow G52 3NQ e-mail: info@colorectalcentre.co.uk Ph: Main hospital
Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Faecal Incontinence Questions & Answers GLASGOW COLORECTAL CENTRE Ross Hall Hospital 221 Crookston Road Glasgow G52 3NQ e-mail: info@colorectalcentre.co.uk Ph: Main hospital
Steps in EMG analysis
 Steps in EMG analysis at rest - spontaneous activity fibs, psw, myotonia, complex rep discharges fasciculations, myokymia at slight voluntary contraction - MUP shape parameters, stability (jiggle), behaviour
Steps in EMG analysis at rest - spontaneous activity fibs, psw, myotonia, complex rep discharges fasciculations, myokymia at slight voluntary contraction - MUP shape parameters, stability (jiggle), behaviour
PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY. ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System
 PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System WHAT IS ANORECTAL MANOMETRY? Anorectal manometry is a test used to evaluate the function and coordination of the sphincter and pelvic
PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System WHAT IS ANORECTAL MANOMETRY? Anorectal manometry is a test used to evaluate the function and coordination of the sphincter and pelvic
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 2003, 48
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Surgical Strategy for Low Imperfora Anal Transplantation or Limited Pos Obatake, Masayuki; Yamashita, Hidek Norihisa; Nakagoe, Tohru Citation Acta medica
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Surgical Strategy for Low Imperfora Anal Transplantation or Limited Pos Obatake, Masayuki; Yamashita, Hidek Norihisa; Nakagoe, Tohru Citation Acta medica
Pelvic Prolapse. A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction
 Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
5 DIAGNOSIS. History taking
 5 DIAGNOSIS All of the photographs in Chapter 4 were taken in theatre before operation. This chapter deals with how one can recognize the type of fistula by history taking and examination. (Note that the
5 DIAGNOSIS All of the photographs in Chapter 4 were taken in theatre before operation. This chapter deals with how one can recognize the type of fistula by history taking and examination. (Note that the
A Case of Fecal Incontinence: Medical and Interventional Treatment Options
 A Case of Fecal Incontinence: Medical and Interventional Treatment Options HPI JP is a 69 year-old F with a 12-month history of FI. Her symptoms began after a colonoscopy She has been experiencing passive
A Case of Fecal Incontinence: Medical and Interventional Treatment Options HPI JP is a 69 year-old F with a 12-month history of FI. Her symptoms began after a colonoscopy She has been experiencing passive
A new concept for Biofeedback & Electrostimulation in Uro-Gynaecology using a specially designed probe : PERISIZE
 1 PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION A new concept for Biofeedback & Electrostimulation in Uro-Gynaecology using a specially designed probe : PERISIZE First - some reminders about the female pelvic floor The
1 PELVIC FLOOR REHABILITATION A new concept for Biofeedback & Electrostimulation in Uro-Gynaecology using a specially designed probe : PERISIZE First - some reminders about the female pelvic floor The
Novel Options for the Management of Fecal Incontinence
 Novel Options for the Management of Fecal Incontinence Arnold Wald, MD, MACG University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison WI ANORECTAL CONTINENCE MECHANISMS Reservoir Elements
Novel Options for the Management of Fecal Incontinence Arnold Wald, MD, MACG University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison WI ANORECTAL CONTINENCE MECHANISMS Reservoir Elements
Laparoscopic Ventral. Mesh Rectopexy (LVMR)
 Laparoscopic Ventral Mesh Rectopexy (LVMR) Questions & Answers GLASGOW COLORECTAL CENTRE Ross Hall Hospital 221 Crookston Road Glasgow G52 3NQ e-mail: info@colorectalcentre.co.uk Ph: Main hospital switchboard
Laparoscopic Ventral Mesh Rectopexy (LVMR) Questions & Answers GLASGOW COLORECTAL CENTRE Ross Hall Hospital 221 Crookston Road Glasgow G52 3NQ e-mail: info@colorectalcentre.co.uk Ph: Main hospital switchboard
Progress report. Anal continence. sphincter which is 15 to 5 mm in thickness and surrounds the craniad 2 to
 Gut, 1971, 12, 844-852 Progress report Anal continence Anal continence depends on an adaptable barrier formed at the ano-rectal junction and in the anal canal by a combination of forces. These are due
Gut, 1971, 12, 844-852 Progress report Anal continence Anal continence depends on an adaptable barrier formed at the ano-rectal junction and in the anal canal by a combination of forces. These are due
Lack of specificity in electrophysiological identification of lower sacral roots during selective dorsal rhizotomy
 J Neurosurg 86:28 33, 1997 Lack of specificity in electrophysiological identification of lower sacral roots during selective dorsal rhizotomy JEFFREY G. OJEMANN, M.D., T. S. PARK, M.D., ROBERT KOMANETSKY,
J Neurosurg 86:28 33, 1997 Lack of specificity in electrophysiological identification of lower sacral roots during selective dorsal rhizotomy JEFFREY G. OJEMANN, M.D., T. S. PARK, M.D., ROBERT KOMANETSKY,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging. Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague)
 Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging Workshop IUGA 2015 Nice Faculty: Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague) The use of translabial ultrasound
Pelvic Floor Ultrasound Imaging Workshop IUGA 2015 Nice Faculty: Prof HP Dietz (Sydney) A/Prof KL Shek (Sydney) Dr R Guzman Rojas (Santiago de Chile) Dr Kamil Svabik (Prague) The use of translabial ultrasound
Pathogenesis of Chronic Pelvic Pain
 Pathogenesis of Chronic Pelvic Pain Yong-Chul Kim Department of anesthesia and pain medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine 1 Overview Anatomy Nerve innervation CPP by pathology CPP by
Pathogenesis of Chronic Pelvic Pain Yong-Chul Kim Department of anesthesia and pain medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine 1 Overview Anatomy Nerve innervation CPP by pathology CPP by
An Analysis of Factors Associated with Increased Perineal Descent in Women
 Original Article Journal of the Korean Society of J Korean Soc Coloproctol 2012;28(4):195-200 http://dx.doi.org/10.3393/jksc.2012.28.4.195 pissn 2093-7822 eissn 2093-7830 An Analysis of Factors Associated
Original Article Journal of the Korean Society of J Korean Soc Coloproctol 2012;28(4):195-200 http://dx.doi.org/10.3393/jksc.2012.28.4.195 pissn 2093-7822 eissn 2093-7830 An Analysis of Factors Associated
Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injury- A guideline. Mr David Sim Ms Patricia McStay. Dr Martina Hogan Dept./Division Only: YES-IMWH Directorate Only: NO
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injury- A guideline Author: Dr Foteini Verani Designation: Specialist Doctor Speciality / Division: Obstetrics-IMWH Directorate: Acute Services
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injury- A guideline Author: Dr Foteini Verani Designation: Specialist Doctor Speciality / Division: Obstetrics-IMWH Directorate: Acute Services
Applied Anatomy and Physiology of the Pelvic Floor. Dr David Tarver Consultant Radiologist, Poole
 Applied Anatomy and Physiology of the Pelvic Floor Dr David Tarver Consultant Radiologist, Poole Pelvic Floor 1. Sacrospinous Ligament 2. Levator Ani A Puborectalis B. Pubococcygeus C. Iliococcygeus 3.
Applied Anatomy and Physiology of the Pelvic Floor Dr David Tarver Consultant Radiologist, Poole Pelvic Floor 1. Sacrospinous Ligament 2. Levator Ani A Puborectalis B. Pubococcygeus C. Iliococcygeus 3.
Inferior Pelvic Border
 Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy
 Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Neuropathic bladder and spinal dysraphism
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 176-180 Neuropathic bladder and spinal dysraphism MALGORZATA BORZYSKOWSKI AND B G R NEVILLE Evelina Children's Department, Guy's Hospital, London SUMMARY The
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 176-180 Neuropathic bladder and spinal dysraphism MALGORZATA BORZYSKOWSKI AND B G R NEVILLE Evelina Children's Department, Guy's Hospital, London SUMMARY The
Lumbar Plexus. Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Major nerves.. Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh
 Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Perineum. Dept. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying
 Perineum Dept. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying OUTLINE Subdivision The Layers Urogenital Diaphragm Main Structures inside Superficial & Deep Perineal Spaces Ischioanal Fossa Perineum A narrow region Urogenital
Perineum Dept. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying OUTLINE Subdivision The Layers Urogenital Diaphragm Main Structures inside Superficial & Deep Perineal Spaces Ischioanal Fossa Perineum A narrow region Urogenital
Operative Vaginal Delivery and Pelvic Floor Trauma. Anna Padoa, MD Urogynecology Service Dept of Ob & Gyn Assaf Harofe Medical Center
 + Operative Vaginal Delivery and Pelvic Floor Trauma Anna Padoa, MD Urogynecology Service Dept of Ob & Gyn Assaf Harofe Medical Center + Vaginal birth and the pelvic floor Mechanisms of injury Damage to
+ Operative Vaginal Delivery and Pelvic Floor Trauma Anna Padoa, MD Urogynecology Service Dept of Ob & Gyn Assaf Harofe Medical Center + Vaginal birth and the pelvic floor Mechanisms of injury Damage to
stimulation with a magnetic coil. This approach has the great advantage of being relatively painless. We
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1989;52:767-772 Magnetic stimulation in the diagnosis of lumbosacral radiculopathy S CHOKROVERTY, R SACHDEO, J DILULLO, R C DUVOISIN From the Department
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1989;52:767-772 Magnetic stimulation in the diagnosis of lumbosacral radiculopathy S CHOKROVERTY, R SACHDEO, J DILULLO, R C DUVOISIN From the Department
CONSTIPATION. Atan Baas Sinuhaji
 CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve
 Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve Stefan De Wachter, MD, PhD, FEBU Professor of Urology University of Antwerpen, Belgium Chairman dept of Urology, UZA Disclosures Consultant speaker: Astellas, Medtronic,
Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve Stefan De Wachter, MD, PhD, FEBU Professor of Urology University of Antwerpen, Belgium Chairman dept of Urology, UZA Disclosures Consultant speaker: Astellas, Medtronic,
6/16/2016 IOM APPROACHES TO THE PUDENDAL NERVE TEAL TAYLOR, REEGT/REPT/CNIM EVOKES, LLC A SENSITIVE SUBJECT: I DON T WANT TO WEAR A DIAPER
 IOM APPROACHES TO THE PUDENDAL NERVE TEAL TAYLOR, REEGT/REPT/CNIM EVOKES, LLC A SENSITIVE SUBJECT: I DON T WANT TO WEAR A DIAPER In IOM we continuously work to protect the Sensory and Motor Function of
IOM APPROACHES TO THE PUDENDAL NERVE TEAL TAYLOR, REEGT/REPT/CNIM EVOKES, LLC A SENSITIVE SUBJECT: I DON T WANT TO WEAR A DIAPER In IOM we continuously work to protect the Sensory and Motor Function of
Childbirth Trauma & Its Complications 23/ Mr Stergios K. Doumouchtsis
 Mr Stergios K. Doumouchtsis Consultant Obstetrician Gynaecologist & Urogynaecologist Childbirth Trauma & Its Complications Over eighty per cent of women sustain some degree of perineal trauma during childbirth.
Mr Stergios K. Doumouchtsis Consultant Obstetrician Gynaecologist & Urogynaecologist Childbirth Trauma & Its Complications Over eighty per cent of women sustain some degree of perineal trauma during childbirth.
Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces
 Rationale Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces These guidelines are to provide the required information for designated registered nurses, health care assistants and bank support workers to perform
Rationale Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces These guidelines are to provide the required information for designated registered nurses, health care assistants and bank support workers to perform
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction. Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
OBSTETRICALLY-CAUSED ANAL SPHINCTER INJURY PREDICTION, MANAGEMENT, PREVENTION
 OBSTETRICALLY-CAUSED ANAL SPHINCTER INJURY PREDICTION, MANAGEMENT, PREVENTION COLM O HERLIHY, MD Professor and Chair University College Dublin Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology National Maternity
OBSTETRICALLY-CAUSED ANAL SPHINCTER INJURY PREDICTION, MANAGEMENT, PREVENTION COLM O HERLIHY, MD Professor and Chair University College Dublin Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology National Maternity
Fecal continence and the puborectal continence reflex
 Fecal continence and the puborectal continence reflex A study about whether the puborectal continence reflex is regulated by the same nerve pathway as the conscious contraction of the puborectal muscle
Fecal continence and the puborectal continence reflex A study about whether the puborectal continence reflex is regulated by the same nerve pathway as the conscious contraction of the puborectal muscle
Application of futility analysis to refine jitter recordings in myasthenia gravis
 Application of futility analysis to refine jitter recordings in myasthenia gravis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Application of futility analysis to refine jitter recordings in myasthenia gravis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
3/3/2016. International Standards for the Neurologic Classification of Spinal Cord Injury (ISNCSCI)
 International Standards for the Neurologic Classification of Spinal Cord Injury (ISNCSCI) American Spinal Injury Association International Spinal Cord Society Presented by Adam Stein, MD Chairman and Professor
International Standards for the Neurologic Classification of Spinal Cord Injury (ISNCSCI) American Spinal Injury Association International Spinal Cord Society Presented by Adam Stein, MD Chairman and Professor
