MS-MLPA is a specific and sensitive technique for detecting all chromosome 11p15.5 imprinting defects of BWS and SRS in a single-tube experiment
|
|
|
- Liliana Carson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (2008) 16, & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved /08 $ ARTICLE MS-MLPA is a specific and sensitive technique for detecting all chromosome 11p15.5 imprinting defects of BWS and SRS in a single-tube experiment Manuela Priolo*,1,4, Angela Sparago 2,4, Corrado Mammì 1, Flavia Cerrato 2, Carmelo Laganà 1 and Andrea Riccio 2,3 1 Operative Unit of Medical Genetics, Hospital of Reggio Calabria Az. Ospedaliera Bianchi-Melacrino-Morelli, V Petrara Reggio Calabria, Reggio Calabria, Italy; 2 Dipartimento di Scienze Ambientali, Seconda Università di Napoli, via Vivaldi 43, Caserta, Italy; 3 Institute of Genetics and Byophisics A. Bozzati Traverso, Naples, Italy Human chromosome 11p15.5 harbours a large cluster of imprinted genes. Different epigenetic defects at this locus have been associated with both Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) and Silver Russell syndrome (SRS). Multiple techniques (Southern blotting, COBRA and microsatellite analysis) have been used so far to detect various DNA methylation abnormalities, uniparental disomies and copy number variations, which are characteristics of these two diseases. We have now evaluated a methylation-specific multiplex-ligation-dependent probe amplification assay (MS-MLPA) for the molecular diagnosis of BWS and SRS. Seventy-three samples derived from BWS- and SRS-affected individuals and 20 controls were analysed by conventional tests and MS-MLPA in blind. All cases that were found positive with conventional methods were also identified by MS-MLPA. These included cases with paternal UPD11, hyper- or hypomethylation at the Imprinting Centre 1 or Imprinting Centre 2 and rare 11p15.5 duplications. In summary, this MS-MLPA assay can detect both copy number variations and methylation defects of the 11p15.5 critical region within one single experiment and represents an easy, low cost and reliable system for the molecular diagnostics of BWS and SRS. (2008) 16, ; doi: /sj.ejhg ; published online 23 January 2008 Keywords: MS-MLPA; Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome; Silver Russell syndrome; 11p15.5 Introduction Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic mechanism causing the expression of a minority of genes to be monoallelic and dependent on its gametic origin. 1 Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) (MIM ) is a developmental disorder characterized by the occurrence of variably combined overgrowth, macroglossia, abdominal wall *Correspondence: Dr M Priolo, Operative Unit of Medical Genetics, Hospital of Reggio Calabria Az. Ospedaliera Bianchi-Melacrino-Morelli, Via Malacrino, V Petrara Reggio, Reggio Calabria 89100, Italy. Tel: þ ; Fax: þ ; prioloma@libero.it 4 These authors have contributed equally to this work. Received 5 September 2007; revised 30 October 2007; accepted 11 December 2007; published online 23 January 2008 defects and increased incidence of embryonal tumours caused by defective expression of imprinted genes located on chromosome 11p Silver Russell syndrome (SRS; OMIM ) is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous disorder characterized by severe pre- and postnatal growth defect, variable facial dysmorphisms, limb or facial asymmetry and developmental delay. Although maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 7 has been reported in B10% of SRS patients, molecular defects at 11p15.5 have been recently described as a major genetic disturbance in SRS, indicating that the dysregulation of 11p15.5 imprinted genes may cause both growthenhanced and growth-restricted phenotypes. 3,4 Both BWS and SRS include mostly sporadic and a minority of familial cases.
2 566 MS-MLPA for detecting 11p15.5 defects A 1 Mb cluster of imprinted genes is present at chromosome 11p15.5. The cluster is functionally divided into two domains that are autonomously controlled by separate Imprinting Control Regions or Imprinting Centres (IC1 and IC2). These are CpG-rich regions that work under different mechanisms, but share as a common feature to be differentially methylated on the maternally and paternally derived chromosomes (differentially methylated regions (DMRs)). The distal IC (IC1 or H19 DMR) is a methylationsensitive chromatin insulator controlling the imprinting of two genes, Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) and H19. 1,5 IGF2 is a paternally expressed fetal growth factor gene with an important role in cancer development, while H19 is a maternally expressed non-coding RNA with possible tumoursuppressor functions. By binding to the multi-zinc-finger protein CTCF, IC1 prevents the activation of IGF2 and allows that of H19 by downstream enhancers on the maternal chromosome. Conversely, DNA methylation on the paternal chromosome prevents CTCF binding at IC1 and allows the enhancer-mediated activation of IGF2, being the H19 promoter hypermethylated and silenced. The proximal IC (IC2 or KvDMR1) includes the promoter of the non-coding KCNQ1OT1 gene that is antisense transcribed with respect to the protein-coding gene KCNQ1. The IC2 sequence itself and/or the KCNQ1OT1 transcript mediate the silencing of several genes of the region including the growth inhibitor CDKN1C. 1,6,7 A great number of BWS and SRS cases show molecular abnormalities in the 11p15.5 imprinted gene cluster. In the BWS, the most common defects are uniparental paternal disomy (UPD) at 11p15.5 loci, gain of methylation at IC1 and loss of methylation at IC2. 2,8 All these anomalies result in excess of the genes expressed from the paternal chromosome and defect of the genes expressed from the maternal chromosome. Inherited deletions of the ICs have been reported in a small number of patients with BWS. 9,10 Almost 35% of SRS patients display IC1 hypomethylation or 11p15.5 maternal duplications. These defects result in the downregulation of IGF2 and activation of H19. 4,11,12 Conventional molecular testing for the IC1/IC2 methylation abnormalities, 11p15 UPD and copy number variations in BWS and SRS consisted of multiple and time-consuming Southern blotting and microsatellite assays. 2,3,8 We evaluated MS-MLPA for the diagnosis of both BWS and SRS, and challenged it with previously routine tests. Materials and methods Patients We collected DNAs from perypheral blood leukocytes of 73 patients with clinical diagnosis of BWS or SRS. All the genetic analyses were performed after the informed consent had been obtained from the parents of the patients. The experimental plan was approved by the ethical committee of the Second University of Naples. Methylation analysis by conventional methods Analysis of IC1 and IC2 methylation by Southern blotting or COBRA and detection of 11p15.5 UPD/copy number variations by microsatellite analysis were performed as described previously. 9,13 All the SRS patients have been previously excluded for maternal UPD7 by microsatellite analysis. MS-MLPA analysis The MS-MLPA probe mixture (ME030BWS/SRS) was purchased from the manufacturer (MRC-Holland, Amsterdam/ NL). This mix contains 45 probes, 27 of which are specific for the BWS/SRS region in 11p of the 11p15 probes are methylation-specific since they contain an HhaI recognition site. In particular, seven probes (five of which are methylation-specific) cover the H19 gene and its differentially methylated 5 0 region located inside IC1 (H19DMR). Four probes (three methylation-sensitive) cover the IGF2 gene and its DMR0 region. A further 14 probes (six methylation-sensitive) hybridize to the KCNQ1 gene, including the IC2 region (KvDMR). Finally, two probes (both methylation-insensitive) recognize CDKN1C (Figure 1a). We used a total of 200 ng of genomic DNA extracted from peripheral blood by the salting-out procedure. 10 mmol/l Tris-EDTA (ph 8.0) was added to DNA if dilution was necessary. After 16 h of hybridization at 601C, samples were equally split into two aliquots. The first aliquot underwent ligation only, whereas the second one underwent ligation followed by enzymatic digestion with HhaI (a restriction enzyme recognizing only unmethylated DNA) and PCR amplification using universal primers. In the latter case, amplification products were obtained and detected by capillary electrophoresis only if the CpG included in the HhaI site was methylated. Ligation, enzymatic digestion, and PCR amplification were performed according to the manufacturer s instructions. All samples were run in duplicate and at least two normal samples were analysed in each MS-MLPA experiment, as controls. PCR products (1 ml) were mixed with 0.4 ml of internal size standard (500LIZ Genescan; Applied Biosystems) and 9 ml of deionized formamide, and injected into an ABI-3130 genetic analyzer (Applied Biosystems) equipped with a 36 cm, four capillaries array using POP7 as polymer. The samples were injected for 20 s at 1.5 kv and run for a total time of 1200 s at 15 kv. Data analysis The reliability and normal values for the probes of this MS- MLPA kit were determined by testing 20 normal control DNA samples. A spreadsheet was developed in Microsoftt Excel to process the sample data efficiently. The estimation of allelic copy number was performed by comparing the quantified PCR products of the probes in each undigested sample with those in other samples. Data were normalized by dividing the peak area of each probe by the average peak
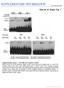
3 MS-MLPA for detecting 11p15.5 defects 567 Figure 1 The 11p15.5 imprinted gene cluster and the MS-MLPA probes. (a) Schematic diagram of the genomic structure of the 11p15.5 region covered by the MS-MLPA probes used in this study (not in scale). Methylation-sensitive probes are presented in black boxes, other probes are presented in clear boxes. The position of the Southern blotting probes is indicated by hatched boxes. Asterisks show the restriction sites analysed by COBRA. Larger open rectangles indicate the position and extension of the imprinted genes, thick black lines indicate the extension of the DMRs and striped vertical rectangles the CTCF target sites. (b) Extension of a paternal duplication as determined by MS-MLPA in a BWS case. All probes corresponding to the duplicated sequences and their locations are shown. Table 1 Molecular alterations of the BWS and SRS cases included in this study BWS (55) RSS (18) IC1 epigenetic defect Hypermethylation (6/55) Hypomethylation (5/18) IC2 epigenetic defect Hypomethylation (24/55) Hypermethylation (0/18) 11p15.5 paternal UPD (12/55) (0/18) 11p15.5 paternal duplication (1/55) (0/18) 11p15.5 maternal duplication (0/55) (1/18) Normal methylation (12/55) (12/18) area of the same sample and then by the average peak pattern of all the samples run in the same experiment. 14 Quantification of the methylation status of each analysed CpG was done by dividing the peak area of the relative methylation-sensitive probe by the combined peak areas of the nearest control probes lacking an HhaI site. The corrected peak height of each fragment in the digested sample was then divided by the corrected peak area of the corresponding fragment in the undigested sample. This number is referred as the methylation index. To simplify the interpretation of data, we calculated the mean methylation index obtained with all the KvDMR probes (7173-L6782, 7172-L6781, 6276-L5782 and 7171-L6780) and that obtained with all the H19DMR probes (6264- L577, 6265-L5771, 7177-L6786 and 6266-L5772) and indicated them as IC2 and IC1 methylation indices, respectively. Results A total of 55 DNA samples derived from individuals affected by BWS and 18 samples derived from individuals affected by SRS were analysed by Southern blotting or COBRA assays plus microsatellite analysis for the identification of 11p15. 5 defects. The results are summarized in Table 1. Out of 55 BWS patients, we found that 24 patients had IC2 hypomethylation (BWS-ICD2), 6 had IC1 hypermethylation (BWS-ICD1), 12 had paternal UPD at chromosome 11p15.5 (UPD11), 1 had paternal duplication of 11p15.5 and 12 had none of the previous defects. Among the 18 SRS patients tested, 7 displayed IC1 hypomethylation (SRS-ICD1), 1 had maternal duplication of 11p15.5 and 10 none of the previous defects. The same patients and 20 normal controls were blindtested by MS-MLPA. The analysis of the 20 control samples gave reproducible results with all the probes both for copy
4 568 MS-MLPA for detecting 11p15.5 defects number and methylation, with the exception of the probe N0213-L9402, which (as also reported by the manufacturer) resulted to be non informative for the methylation analysis, because of a frequent polymorphism affecting the HhaI site (rs ). In particular, none of the 20 control samples had peak ratios o0.75 or at two or more adjacent probes. The mean methylation indices for the normal samples were 0.52 (range ) for IC2 and 0.50 (range ) for IC1 (see Table 2). Standard deviation was 0.03 for both IC1 and IC2 methylation indices. IC2 methylation indices o0.46 were considered indicative of IC2 hypomethylation, IC1 methylation indices indicative of IC1 hypermethylation and IC1 methylation indices o0.44 indicative of IC1 hypomethylation. The results obtained with the two methylation-sensitive probes specific for the IGF2 DMR0 region were inconsistent in some probes, indicating variable methylation of these CpGs in different individuals, and were therefore not taken into consideration for statistical analysis. Table 2 summarizes the results obtained from the MS- MLPA analysis of the BWS and SRS patients. All the molecular defects of the BWS cohort identified with the conventional methods were detected also with the MS- MLPA assay. In particular, the 24 BWS-ICD2 samples showed IC2 methylation indices between 0.00 and 0.40 but IC1 methylation indices within normal range, the 6 BWS-ICD1 samples had IC1 methylation indices between 0.63 and 0.97 but IC2 methylation indices within the normal range and the 12 paternal UPD11 had IC2 methylation indices between 0.16 and 0.43 and IC1 methylation indices between 0.62 and Figure 2 shows Table 2 Summary of the MS-MLPA methylation indices in BWS and SRS IC2 MI range a IC1 MI range a Normal controls (20) Mean±SD 0.52± ±0.03 BWS IC2 hypomethylation (24/55) BWS IC1 hypermethylation (6/55) BWS paternal 11p15.5 UPD (12/55) BWS Normal methylation (10/55) SRS IC1 hypomethylation (7/18) SRS Normal methylation (10/18) a Anomalous methylation indices (MI) are outlined in bold. Standard deviations (SD) for both IC1 and IC2 methylation indices were calculated on 20 normal samples. Figure 2 MS-MLPA peak patterns obtained with normal controls and BWS and SRS cases with different molecular defects. (a) normal sample, ligation only reaction. (b) normal sample, digestion/ligation reaction. (c) BWS sample with IC2 hypomethylation, digestion/ligation reaction. (d) BWS sample with IC1 hypermethylation, digestion/ ligation reaction. (e) BWS sample with paternal UPD11, digestion/ ligation reaction. (f) SRS sample with IC1 hypomethylation digestion/ ligation reaction. Grey arrows refer to the methylation-sensivite probes recognizing IC1, black arrows refer to the methylation-sensitive probes recognizing IC2. Black stars indicate methylation control (0% methylated) probes. Black arrowheads indicate the hypomethylated CpGs detected by IC2 probes in BWS-ICD2 and UPD samples. Grey arrowheads refer to the hypermethylated CpGs detected by IC1 probes in BWS-ICD1 and UPD11 samples. Grey arrowheads in panel f refer to hypomethylated CpGs detected by IC1 probes in SRS samples. Little black stars in panels d and e on the first peak indicate the variable results obtained with the N0213-L9999 probe due to a sequence polymorphism.
5 MS-MLPA for detecting 11p15.5 defects 569 Figure 3 MS-MLPA peak patterns (partial view) obtained with normal controls or BWS patients with different degree of IC2 hypomethylation and IC1 hypermethylation. (a) normal sample, digestion/ligation reaction (b) BWS sample with 2% IC2 methylation, digestion/ligation reaction (IC2 methylation index ¼ 0) (c) BWS sample with 28% IC2 methylation, digestion/ligation reaction. (IC2 methylation index ¼ 0.16) (d) BWS sample with 44% IC2 methylation, digestion/ligation reaction (IC2 methylation index ¼ 0.38) (e) BWS sample with 98% IC1 methylation, digestion/ligation reaction (IC1 methylation index ¼ 0.97). (f) BWS sample with 75% IC1 methylation, digestion/ligation reaction (IC1 methylation index ¼ 0.70). DNA methylation levels were measured by PhosphorImager (Molecular Dynamics) quantification of COBRA bands, while methylation indices were calculated from the peak areas of the MS-MLPA as described in the Materials and methods section. Black arrowheads indicate the peaks corresponding to two IC2 CpGs (probes 7173-L6782 and L5782) with normal 50% methylation. White arrowheads indicate the peaks corresponding to the same CpGs in the BWS-ICD2 samples. Grey arrowheads refer to two IC1 CpGs (probes 6264-L577 and L5771); Black stars indicate the variable results obtained with the N0213-L9999 probe. an example of the typical peak patterns obtained with normal controls (Figure 2a and b), BWS-ICD2 (Figure 2c), BWS-ICD1 (Figure 2d) and BWS-UPD11 (Figure 2e) samples. IC2 hypomethylation was indicated by abnormally low peaks corresponding to the four methylation-sensitive probes that were specific for KvDMR1 (7173-L6782, L6781, 6276-L5782 and 7171-L6780), after HhaI digestion (see Figures 1a and 2c, black arrowheads). IC1 hypermethylation was indicated by abnormally high peaks corresponding to the four methylation-sensitive probes located inside the H19DMR (6264-L577, 6265-L5771, 7177-L6786 and 6266-L5772, see Figures 1a and 2d, grey arrowheads). Interestingly, the MS-MLPA also detected those cases that had limited hyper- or hypomethylation. For instance, a sample with 60 70% methylation at IC1, as measured by COBRA, showed an IC1 methylation index of 0.68 by MS- MLPA, while a sample with 30 40% methylation at IC2, as measured by COBRA, had an IC2 methylation index of 0.38 (Figure 3). In contrast, the 12 BWS samples in which no methylation defect had been identified with the conventional methods showed methylation indices within normal range with the MS-MLPA assay (Table 2). Hypomethylation at IC1 was demonstrated by Southern blotting or COBRA and clearly confirmed by MS-MLPA in seven cases of our SRS cohort (N ¼ 18). IC1 methylation indices were in the range of , while IC2 methylation indices were within normal range in these cases (Table 2). In contrast, the 10 SRS samples in which no methylation defect had been identified with the conventional methods showed both IC1 and IC2 methylation indices within the normal range with the MS-MLPA assay (Table 2). Figure 2f shows the typical peak pattern obtained with the SRS cases with IC1 hypomethylation. The methylation defect was indicated by abnormally low IC1-specific peaks (probes 6264-L577, 6265-L5771, 7177-L6786 and 6266-L5772, see Figures 1a and 2f, grey arrowheads). The chromosome 11p15.5 duplications identified by Southern blotting and microsatellite analyses in a BWS patient and an SRS patient were also detected by the MS- MLPA assay. In both cases, the peak area ratios for the 11p15.5 probes were in the ligation only reactions. In particular, the MLPA demonstrated that the BWS sample had only a partial duplication of the 11p15.5 region, as the probes centromeric to 3544-L2910 produced peak area ratios within the normal range (Figure 1b). Therefore, only the IC1 domain and the part of the IC2 domain telomeric to KvDMR1 appeared to be duplicated in this sample. For this BWS case, the ligation-digestion reaction demonstrated an IC1 methylation index of 0.70 and an IC2 methylation index of 0.48, indicating IC1 hypermethylation and normal IC2 methylation, as expected from a paternally inherited duplication of the IC1 domain. In the SRS sample, the ligation-only reaction showed a duplication covering all the analysed 11p15.5 region and the ligation-digestion reaction demonstrated an IC1 methylation index of 0.26 and an IC2 methylation index of 0.71, indicating IC2 hypermethylation/ic1 hypomethylation, as expected from a maternally transmitted duplication.
6 570 MS-MLPA for detecting 11p15.5 defects In conclusion, the results obtained with this MS-MLPA assay demonstrate that this method is a specific and very sensitive method, as efficient as combined Southern blotting, COBRA and microsatellite analyses, for identifying methylation defects, UPD and copy number variations at chromosome 11p15.5. Discussion The molecular defects of BWS and SRS are very heterogenous. Many of these abnormalities consist of epigenetic or copy-number alterations inside the 11p15.5 imprinted gene cluster. The identification of these defects usually requires the use of multiple assays. We evaluated the MS- MLPA for the molecular diagnosis of BWS and SRS and challenged it with previous routinely used tests. The results obtained demonstrated that MS-MLPA is a sensitive and reliable tool for the identification of most of the molecular defects of BWS and SRS. Conventional techniques, such as the Southern blotting assay, require a large amount of genomic DNA and multiple hybridization experiments for the analysis of DNA methylation at multiple loci. Alternative methods, such as COBRA or methylation-specific PCR, are quite laborious to standardize and are not suitable for routine molecular diagnostics. In addition, these assays do not provide accurate information on copy number variations, which are better identified by microsatellite or FISH analyses. MS-MLPA, needs very little amount of DNA ( ng), is very rapid and provides information on copy number and methylation status of multiple loci in a single-tube experiment. 15 Most of the epigenetic defects of BWS and SRS occur sporadically and are present in the mosaic form in the affected individuals. 2,3 It is therefore important to use a sensitive diagnostic method to identify all the mosaic cases. We proved that the MS-MLPA assay described is not only very accurate but also extremely sensitive, concerning the detection of 11p15.5 defects. In fact, this method correctly identified also BWS cases with 60 70% IC1 methylation (methylation index 0.68) and BWS cases with 30 40% IC2 methylation (methylation index 0.38). A great advantage of MS-MLPA is that this method concomitantly determines both copy number and methylation level of the investigated loci. This is clearly demonstrated by the results we obtained on two cases with 11p15.5 duplication. While the ligation-only reaction demonstrated the copy number increase, the ligationdigestion reaction provided information on the parental origin of the duplicated region. The methylation indices of the DMRs indicated that the former case was a BWS sample with a paternally inherited 11p15.5 duplication and the latter was an SRS sample with maternal duplication of this chromosome region. These results were confirmed by the microsatellite analysis. Interestingly, the MS-MLPA results demonstrated that, in the BWS case, the duplication did not include KvDMR and the centromeric part of domain 2. As expected, the sample showed isolated IC1 hypermethylation. While revising this article, an independent group 16 reported on the use of MS-MLPA for the analysis of chromosome 11p5.5 defects obtaining similar results as ours and further confirming that MS-MLPA can be considered as a robust assay for the analysis of this region. Although we proved that MS-MLPA assay is very useful for the analysis of BWS and SRS, we believe that the method can be further improved in the future by modifying some of the probes. For instance, methylation-sensitive probes located in the more centromeric part of the H19DMR could be useful to detect the IC1 microdeletions present in a subset of the BWS patients. 9,13 On the other hand, the H19 DMR-specific probe (N0213-L9999) corresponding to a common SNP could be omitted. In conclusion, our experience with this large cohort of patients indicate that the MS-MLPA represents an easy, low cost and reliable system for the molecular diagnostics of BWS/SRS cases with either imprinting defects and duplications at chromosome 11p15. Paternal UPD11 can also be identified, although microsatellite testing should be offered to confirm these cases. Acknowledgements We thank all the patients and their families for their participation to the study. This work was supported by grants from MIUR PRIN 2005, Associazione Italiana Ricerca sul Cancro, Istituto Superiore di Sanità and Telethon, Italia Grant no. GGP04072 (to A.R.). FC was recipient of a fellowship from Società Italiana di Cancerologia and Fondazione Pezcoller. References 1 Edwards CA, Ferguson-Smith AC: Mechanisms regulating imprinted genes in clusters. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2007; 19: Weksberg R, Shuman C, Smith AC: Beckwith wiedemann syndrome. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 2005; 137: Smith AC, Choufani S, Ferreira JC, Weksberg A: Growth regulation, imprinted genes, and chromosome 11p15.5. Ped Research 2007; 61: 43R 47R. 4 Gicquel C, Rossignol S, Cabrol S et al: Epimutation of the telomeric imprinting center region on chromosome 11p15 in Silver Russell syndrome. Nat Genet 2005; 37: Hark AT, Schoenherr CJ, Katz DJ et al: CTCF mediates methylation-sensitive enhancer-blocking activity at the H19/Igf2 locus. Nature 2000; 405: Smilinich NJ, Day CD, Fitzpatrick GV et al: A maternally methylated CpG island in KvLQT1 is associated with an antisense paternal transcript and loss of imprinting in Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: Mancini-Dinardo D, Steele SJ, Levorse JM, Ingram RS, Tilghman SM: Elongation of the Kcnq1ot1 transcript is required for genomic imprinting of neighboring genes. Genes Dev 2006; 20:
7 MS-MLPA for detecting 11p15.5 defects Cooper WN, Luharia A, Evans GA et al: Molecular subtypes and phenotypic expression of Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 2005; 13: Sparago A, Cerrato F, Vernucci M et al: Microdeletions in the human H19 DMR result in loss of IGF2 imprinting and Beckwith Wiedemann. Nat Genet 2004; 36: Niemitz EL, DeBaun MR, Fallon J et al: Microdeletion of LIT1 in familial Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: Bliek J, Terhal P, van den Bogaard M-J et al: Hypomethylation of the H19 gene causes not only Silver Russell syndrome (SRS) but also isolated asymmetry or an SRS-like phenotype. Am J Hum Genet 2006; 78: Eggermann T, Meyer E, Schönherr N et al: Epigenetic mutations in 11p15 in Silve Russell syndrome are restricted to the telomeric imprinting domain. J Med Genet 2006; 46: Sparago A, Russo S, Cerrato F et al: Mechanisms causing imprinting defects in familial Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome with Wilms tumour. 2007; 16: Koolen DA, Nillesen WM, Versteeg MHA et al: Screening for subtelomeric rearrangements in 210 patients with unexplained mental retardation using multiplex ligation dependent probe amplification (MLPA). J Med Genet 2004; 41: Nygren AO, Ameziane N, Duarte HM et al: Methylation-specific MLPA (MS-MLPA): simultaneous detection of CpG methylation and copy number changes of up to 40 sequences. Nucleic Acis Res 2005; 16: e Scott RH, Douglas J, Baskcomb L et al: Methylation-specific MLPA (MS-MLPA) robustly detects and distinguishes 11p15 abnormalities associated with overgrowth and growth retardation. JMed Genet 2007: e-pub ahead of print 15 October 2007.
Epigenetic mutations in 11p15 in Silver-Russell syndrome are restricted to the telomeric imprinting domain
 JMG Online First, published on October 19, 2005 as 10.1136/jmg.2005.038687 1 Epigenetic mutations in 11p15 in Silver-Russell syndrome are restricted to the telomeric imprinting domain Thomas Eggermann
JMG Online First, published on October 19, 2005 as 10.1136/jmg.2005.038687 1 Epigenetic mutations in 11p15 in Silver-Russell syndrome are restricted to the telomeric imprinting domain Thomas Eggermann
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names you wish listed) (A)-Testing
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names you wish listed) (A)-Testing
Epigenetics and Chromatin Remodeling
 Epigenetics and Chromatin Remodeling Bradford Coffee, PhD, FACMG Emory University Atlanta, GA Speaker Disclosure Information Grant/Research Support: none Salary/Consultant Fees: none Board/Committee/Advisory
Epigenetics and Chromatin Remodeling Bradford Coffee, PhD, FACMG Emory University Atlanta, GA Speaker Disclosure Information Grant/Research Support: none Salary/Consultant Fees: none Board/Committee/Advisory
2001 Oxford University Press Human Molecular Genetics, 2001, Vol. 10, No
 2001 Oxford University Press Human Molecular Genetics, 2001, Vol. 10, No. 26 2989 3000 Tumor development in the Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome is associated with a variety of constitutional molecular 11p15
2001 Oxford University Press Human Molecular Genetics, 2001, Vol. 10, No. 26 2989 3000 Tumor development in the Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome is associated with a variety of constitutional molecular 11p15
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 52; 22 July 2015
 SALSA MS-MLPA probemix ME028-B2 Prader-Willi/Angelman Lot B2-0413, lot B2-0811. As compared to version B1 (lot B1-0609), the control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME (PWS) and
SALSA MS-MLPA probemix ME028-B2 Prader-Willi/Angelman Lot B2-0413, lot B2-0811. As compared to version B1 (lot B1-0609), the control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME (PWS) and
PRADER WILLI/ANGELMAN
 SALSA MS-MLPA probemix ME028-B2 PRADER WILLI/ANGELMAN Lot B2-0811: As compared to version B1 (lot B1-0609, B1-1108), the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME
SALSA MS-MLPA probemix ME028-B2 PRADER WILLI/ANGELMAN Lot B2-0811: As compared to version B1 (lot B1-0609, B1-1108), the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME
Joanna Hillman Michael Higgins Lab Oncology for Scientists I 10/29/2015
 Joanna Hillman Michael Higgins Lab Oncology for Scientists I 10/29/2015 ! Define Epigenetics & Genomic Imprinting! Discovery! What is the imprint! Lifecycle of an Imprint DMRs and ICEs! 2 main mechanisms
Joanna Hillman Michael Higgins Lab Oncology for Scientists I 10/29/2015 ! Define Epigenetics & Genomic Imprinting! Discovery! What is the imprint! Lifecycle of an Imprint DMRs and ICEs! 2 main mechanisms
Aberrant genomic imprinting in chromosome 11p15-associated congenital growth disorders : consequences for DNA-diagnostics Bliek, H.J.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Aberrant genomic imprinting in chromosome 11p15-associated congenital growth disorders : consequences for DNA-diagnostics Bliek, H.J. Link to publication Citation
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Aberrant genomic imprinting in chromosome 11p15-associated congenital growth disorders : consequences for DNA-diagnostics Bliek, H.J. Link to publication Citation
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 08; 30 March 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P351-C1 / P352-D1 PKD1-PKD2 P351-C1 lot C1-0914: as compared to the previous version B2 lot B2-0511 one target probe has been removed and three reference probes have been replaced.
SALSA MLPA probemix P351-C1 / P352-D1 PKD1-PKD2 P351-C1 lot C1-0914: as compared to the previous version B2 lot B2-0511 one target probe has been removed and three reference probes have been replaced.
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 29; 31 July 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot 0813 and 0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are included. P082
SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot 0813 and 0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are included. P082
Russell-Silver syndrome (RSS)
 GENETIC DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY Russell-Silver syndrome (RSS) Background: Russell-Silver syndrome (RSS, OMIM 103280, 180860) is a growth disorder characterized by intrauterine and postnatal growth retardation,
GENETIC DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY Russell-Silver syndrome (RSS) Background: Russell-Silver syndrome (RSS, OMIM 103280, 180860) is a growth disorder characterized by intrauterine and postnatal growth retardation,
Epigenetic contribution to birth defects. David Amor 20 th June 2011
 Epigenetic contribution to birth defects David Amor 20 th June 2011 Genomic imprinting Genomic imprinting is the biological process whereby a gene or genomic domain is biochemically marked with information
Epigenetic contribution to birth defects David Amor 20 th June 2011 Genomic imprinting Genomic imprinting is the biological process whereby a gene or genomic domain is biochemically marked with information
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: imprinting in clusters revisited. Perspective. Eamonn R. Maher 1 and Wolf Reik 2 1
 Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: imprinting in clusters revisited Perspective SERIES on epigenetic regulation Eamonn R. Maher 1 and Wolf Reik 2 1 Section of Medical and Molecular Genetics, Department of Paediatrics
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: imprinting in clusters revisited Perspective SERIES on epigenetic regulation Eamonn R. Maher 1 and Wolf Reik 2 1 Section of Medical and Molecular Genetics, Department of Paediatrics
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 30; 06 June 2017
 SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0517, C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot B2-0813, B2-0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are
SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0517, C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot B2-0813, B2-0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are
SALSA MS-MLPA KIT ME011-A1 Mismatch Repair genes (MMR) Lot 0609, 0408, 0807, 0407
 SALSA MS-MLPA KIT ME011-A1 Mismatch Repair genes (MMR) Lot 0609, 0408, 0807, 0407 The Mismatch Repair (MMR) system is critical for the maintenance of genomic stability. MMR increases the fidelity of DNA
SALSA MS-MLPA KIT ME011-A1 Mismatch Repair genes (MMR) Lot 0609, 0408, 0807, 0407 The Mismatch Repair (MMR) system is critical for the maintenance of genomic stability. MMR increases the fidelity of DNA
Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3. Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented in our
 1 2 Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3 Mutations 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented
1 2 Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3 Mutations 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented
Imprinting. Joyce Ohm Cancer Genetics and Genomics CGP-L2-319 x8821
 Imprinting Joyce Ohm Cancer Genetics and Genomics CGP-L2-319 x8821 Learning Objectives 1. To understand the basic concepts of genomic imprinting Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon that causes
Imprinting Joyce Ohm Cancer Genetics and Genomics CGP-L2-319 x8821 Learning Objectives 1. To understand the basic concepts of genomic imprinting Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon that causes
Most severely affected will be the probe for exon 15. Please keep an eye on the D-fragments (especially the 96 nt fragment).
 SALSA MLPA probemix P343-C3 Autism-1 Lot C3-1016. As compared to version C2 (lot C2-0312) five reference probes have been replaced, one reference probe added and several lengths have been adjusted. Warning:
SALSA MLPA probemix P343-C3 Autism-1 Lot C3-1016. As compared to version C2 (lot C2-0312) five reference probes have been replaced, one reference probe added and several lengths have been adjusted. Warning:
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 08; 18 November 2016
 SALSA MLPA probemix P122-D1 NF1 AREA Lot D1-1016. As compared to lot C2-0312, four probes in the NF1 area and one reference probe have been removed, four reference probes have been replaced and several
SALSA MLPA probemix P122-D1 NF1 AREA Lot D1-1016. As compared to lot C2-0312, four probes in the NF1 area and one reference probe have been removed, four reference probes have been replaced and several
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 07; 26 November 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P266-B1 CLCNKB Lot B1-0415, B1-0911. As compared to version A1 (lot A1-0908), one target probe for CLCNKB (exon 11) has been replaced. In addition, one reference probe has been replaced
SALSA MLPA probemix P266-B1 CLCNKB Lot B1-0415, B1-0911. As compared to version A1 (lot A1-0908), one target probe for CLCNKB (exon 11) has been replaced. In addition, one reference probe has been replaced
SALSA MLPA probemix P372-B1 Microdeletion Syndromes 6 Lot B1-1016, B
 SALSA MLPA probemix P372-B1 Microdeletion Syndromes 6 Lot B1-1016, B1-0613. The purpose of the P372 probemix is to further investigate results found with the P245 Microdeletion Syndromes-1A probemix. The
SALSA MLPA probemix P372-B1 Microdeletion Syndromes 6 Lot B1-1016, B1-0613. The purpose of the P372 probemix is to further investigate results found with the P245 Microdeletion Syndromes-1A probemix. The
SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH
 SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH Lot 0510, 0909, 0408: Compared to lot 0107, extra control fragments have been added at 88, 96, 100 and 105 nt. The 274 nt probe gives a higher signal in lot 0510 compared to
SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH Lot 0510, 0909, 0408: Compared to lot 0107, extra control fragments have been added at 88, 96, 100 and 105 nt. The 274 nt probe gives a higher signal in lot 0510 compared to
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 12; 13 January 2017
 SALSA MLPA probemix P219-B3 PAX6 Lot B3-0915: Compared to version B2 (lot B2-1111) two reference probes have been replaced and one additional reference probe has been added. In addition, one flanking probe
SALSA MLPA probemix P219-B3 PAX6 Lot B3-0915: Compared to version B2 (lot B2-1111) two reference probes have been replaced and one additional reference probe has been added. In addition, one flanking probe
SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR
 SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR Lot B1-0215 and B1-0112. As compared to the previous A1 version (lot 0208), two mutation-specific probes for the EGFR mutations L858R and T709M as well as one additional
SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR Lot B1-0215 and B1-0112. As compared to the previous A1 version (lot 0208), two mutation-specific probes for the EGFR mutations L858R and T709M as well as one additional
SALSA MLPA KIT P060-B2 SMA
 SALSA MLPA KIT P6-B2 SMA Lot 111, 511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot 11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). Please note that, in contrast to the
SALSA MLPA KIT P6-B2 SMA Lot 111, 511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot 11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). Please note that, in contrast to the
Low frequency of imprinting defects in ICSI children born small for gestational age
 (29) 17, 22 29 & 29 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 118-4813/9 $32. ARTICLE www.nature.com/ejhg Low frequency of imprinting defects in ICSI children born small for gestational age Deniz
(29) 17, 22 29 & 29 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 118-4813/9 $32. ARTICLE www.nature.com/ejhg Low frequency of imprinting defects in ICSI children born small for gestational age Deniz
SALSA MLPA probemix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0716, D As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference probe has been replaced.
 mix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0716, D2-0413. As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference has been replaced. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) is a distinct form of non insulin-dependent
mix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0716, D2-0413. As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference has been replaced. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) is a distinct form of non insulin-dependent
High resolution melting for methylation analysis
 High resolution melting for methylation analysis Helen White, PhD Senior Scientist National Genetics Reference Lab (Wessex) Why analyse methylation? Genomic imprinting In diploid organisms somatic cells
High resolution melting for methylation analysis Helen White, PhD Senior Scientist National Genetics Reference Lab (Wessex) Why analyse methylation? Genomic imprinting In diploid organisms somatic cells
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 14; 28 September 2016
 SALSA MLPA probemix P279-B3 CACNA1A Lot B3-0816. As compared to version B2 (lot B2-1012), one reference probe has been replaced and the length of several probes has been adjusted. Voltage-dependent calcium
SALSA MLPA probemix P279-B3 CACNA1A Lot B3-0816. As compared to version B2 (lot B2-1012), one reference probe has been replaced and the length of several probes has been adjusted. Voltage-dependent calcium
Product Description SALSA MS-MLPA Probemix ME028-C1 Prader-Willi/Angelman To be used with the MS-MLPA General Protocol.
 Product Description SALSA MS- Probemix ME028-C1 Prader-Willi/Angelman To be used with the MS-MLPA General Protocol. Version C1. For complete product history see page 9. Catalogue numbers: ME028-025R: SALSA
Product Description SALSA MS- Probemix ME028-C1 Prader-Willi/Angelman To be used with the MS-MLPA General Protocol. Version C1. For complete product history see page 9. Catalogue numbers: ME028-025R: SALSA
CHROMOSOMAL MICROARRAY (CGH+SNP)
 Chromosome imbalances are a significant cause of developmental delay, mental retardation, autism spectrum disorders, dysmorphic features and/or birth defects. The imbalance of genetic material may be due
Chromosome imbalances are a significant cause of developmental delay, mental retardation, autism spectrum disorders, dysmorphic features and/or birth defects. The imbalance of genetic material may be due
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 06; 23 December 2016
 SALSA MLPA probemix P417-B2 BAP1 Lot B2-1216. As compared to version B1 (lot B1-0215), two reference probes have been added and two target probes have a minor change in length. The BAP1 (BRCA1 associated
SALSA MLPA probemix P417-B2 BAP1 Lot B2-1216. As compared to version B1 (lot B1-0215), two reference probes have been added and two target probes have a minor change in length. The BAP1 (BRCA1 associated
Bisphenol A Exposure Disrupts Genomic Imprinting in the Mouse
 Bisphenol A Exposure Disrupts Genomic Imprinting in the Mouse Martha Susiarjo 1,2, Isaac Sasson 3, Clementina Mesaros 4, Marisa S. Bartolomei 1,2 * 1 Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, University
Bisphenol A Exposure Disrupts Genomic Imprinting in the Mouse Martha Susiarjo 1,2, Isaac Sasson 3, Clementina Mesaros 4, Marisa S. Bartolomei 1,2 * 1 Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, University
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 29;
 SALSA MLPA KIT P003-B1 MLH1/MSH2 Lot 1209, 0109. As compared to the previous lots 0307 and 1006, one MLH1 probe (exon 19) and four MSH2 probes have been replaced. In addition, one extra MSH2 exon 1 probe,
SALSA MLPA KIT P003-B1 MLH1/MSH2 Lot 1209, 0109. As compared to the previous lots 0307 and 1006, one MLH1 probe (exon 19) and four MSH2 probes have been replaced. In addition, one extra MSH2 exon 1 probe,
P323-B1 CDK4-HMGA2-MDM2
 SALSA MLPA probemix P323-B1 CDK4-HMGA2-MDM2 Lot B1-0714, B1-0711. As compared to previous test version (lot A1-0508), this probemix has been completely redesigned. Probes for HMGA2 and several other genes
SALSA MLPA probemix P323-B1 CDK4-HMGA2-MDM2 Lot B1-0714, B1-0711. As compared to previous test version (lot A1-0508), this probemix has been completely redesigned. Probes for HMGA2 and several other genes
SALSA MLPA probemix P169-C2 HIRSCHSPRUNG-1 Lot C As compared to version C1 (lot C1-0612), the length of one probe has been adjusted.
 mix P169-C2 HIRSCHSPRUNG-1 Lot C2-0915. As compared to version C1 (lot C1-0612), the length of one has been adjusted. Hirschsprung disease (HSCR), or aganglionic megacolon, is a congenital disorder characterised
mix P169-C2 HIRSCHSPRUNG-1 Lot C2-0915. As compared to version C1 (lot C1-0612), the length of one has been adjusted. Hirschsprung disease (HSCR), or aganglionic megacolon, is a congenital disorder characterised
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 19;
 SALSA MLPA probemix P6-B2 SMA Lot B2-712, B2-312, B2-111, B2-511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot B1-11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). SPINAL
SALSA MLPA probemix P6-B2 SMA Lot B2-712, B2-312, B2-111, B2-511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot B1-11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). SPINAL
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance.! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014
 Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Methylation reprogramming dynamics and defects in gametogenesis and embryogenesis: implications for reproductive medicine
 Univ.-Prof. Dr. Thomas Haaf Methylation reprogramming dynamics and defects in gametogenesis and embryogenesis: implications for reproductive medicine Epigenetics and DNA methylation Heritable change of
Univ.-Prof. Dr. Thomas Haaf Methylation reprogramming dynamics and defects in gametogenesis and embryogenesis: implications for reproductive medicine Epigenetics and DNA methylation Heritable change of
SALSA MLPA probemix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference probe has been replaced.
 mix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0413. As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference has been replaced. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) is a distinct form of non insulin-dependent diabetes
mix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0413. As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference has been replaced. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) is a distinct form of non insulin-dependent diabetes
An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice
 An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice Mei-Yi Wu 1 *, Ming Jiang 1, Xiaodong Zhai 2, Arthur L. Beaudet 2, Ray-Chang Wu 1 * 1 Department of
An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice Mei-Yi Wu 1 *, Ming Jiang 1, Xiaodong Zhai 2, Arthur L. Beaudet 2, Ray-Chang Wu 1 * 1 Department of
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 28; 4 January 2018
 SALSA MLPA probemix ME011-B3 Mismatch Repair genes Lot B3-1017 and B3-0715. As compared to the previous version B2 (lot B2-0614), one probe has a small change in length but no change in the sequence detected.
SALSA MLPA probemix ME011-B3 Mismatch Repair genes Lot B3-1017 and B3-0715. As compared to the previous version B2 (lot B2-0614), one probe has a small change in length but no change in the sequence detected.
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 23; 15 February 2018
 SALSA MLPA probemix P225-D2 PTEN Lot D2-0315. As compared to the previous version (lot D1-0613), one probe has a small change in length but no change in the sequence detected. PTEN is a tumour suppressor
SALSA MLPA probemix P225-D2 PTEN Lot D2-0315. As compared to the previous version (lot D1-0613), one probe has a small change in length but no change in the sequence detected. PTEN is a tumour suppressor
Constitutional and somatic methylation status of DMRH19 and KvDMR in Wilms tumor patients
 Genetics and Molecular Biology Online Ahead of Print Copyright 2012, Sociedade Brasileira de Genética. Printed in Brazil www.sbg.org.br Constitutional and somatic methylation status of DMRH19 and KvDMR
Genetics and Molecular Biology Online Ahead of Print Copyright 2012, Sociedade Brasileira de Genética. Printed in Brazil www.sbg.org.br Constitutional and somatic methylation status of DMRH19 and KvDMR
Chapter 14 Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome
 Chapter 14 Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome Michael DeBaun and Jennifer Horst Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) (OMIM 130650) is a disease of prenatal overgrowth, congenital malformations, and predisposition
Chapter 14 Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome Michael DeBaun and Jennifer Horst Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) (OMIM 130650) is a disease of prenatal overgrowth, congenital malformations, and predisposition
Chromosome-Wide Analysis of Parental Allele-Specific Chromatin and DNA Methylation
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Apr. 2011, p. 1757 1770 Vol. 31, No. 8 0270-7306/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/mcb.00961-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Chromosome-Wide
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Apr. 2011, p. 1757 1770 Vol. 31, No. 8 0270-7306/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/mcb.00961-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Chromosome-Wide
SALSA MLPA probemix P371-A1 Microdeletion Syndromes 5 Lot A1-0509
 mix P371-A1 Microdeletion Syndromes 5 Lot A1-0509 The purpose of the P371 mix is to further investigate results found with the P245 Microdeletion mix. The P245 mix provides a possibility to screen samples
mix P371-A1 Microdeletion Syndromes 5 Lot A1-0509 The purpose of the P371 mix is to further investigate results found with the P245 Microdeletion mix. The P245 mix provides a possibility to screen samples
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
MRC-Holland MLPA. Related SALSA MLPA probemixes P190 CHEK2: Breast cancer susceptibility, genes included: CHEK2, ATM, PTEN, TP53.
 SALSA MLPA probemix P056-C1 TP53 Lot C1-0215 & lot C1-0214. As compared to version B1 (lot B1-1011) most of the reference and flanking probes have been replaced and several have been added. Furthermore,
SALSA MLPA probemix P056-C1 TP53 Lot C1-0215 & lot C1-0214. As compared to version B1 (lot B1-1011) most of the reference and flanking probes have been replaced and several have been added. Furthermore,
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 06; 07 August 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P323-B1 CDK4-HMGA2-MDM2 Lot B1-0711. As compared to version A1 (test version sent to test labs), this product has been completely redesigned. Probes for HMGA2 and several other genes
SALSA MLPA probemix P323-B1 CDK4-HMGA2-MDM2 Lot B1-0711. As compared to version A1 (test version sent to test labs), this product has been completely redesigned. Probes for HMGA2 and several other genes
Introduction. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 66: , 2000
 Am. J. Hum. Genet. 66:841 847, 2000 Relaxation of Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 Imprinting and Discordant Methylation at KvDMR1 in Two First Cousins Affected by Beckwith- Wiedemann and Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber
Am. J. Hum. Genet. 66:841 847, 2000 Relaxation of Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 Imprinting and Discordant Methylation at KvDMR1 in Two First Cousins Affected by Beckwith- Wiedemann and Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber
Epigenetic Regulation of Health and Disease Nutritional and environmental effects on epigenetic regulation
 Epigenetic Regulation of Health and Disease Nutritional and environmental effects on epigenetic regulation Robert FEIL Director of Research CNRS & University of Montpellier, Montpellier, France. E-mail:
Epigenetic Regulation of Health and Disease Nutritional and environmental effects on epigenetic regulation Robert FEIL Director of Research CNRS & University of Montpellier, Montpellier, France. E-mail:
Today. Genomic Imprinting & X-Inactivation
 Today 1. Quiz (~12 min) 2. Genomic imprinting in mammals 3. X-chromosome inactivation in mammals Note that readings on Dosage Compensation and Genomic Imprinting in Mammals are on our web site. Genomic
Today 1. Quiz (~12 min) 2. Genomic imprinting in mammals 3. X-chromosome inactivation in mammals Note that readings on Dosage Compensation and Genomic Imprinting in Mammals are on our web site. Genomic
Challenges of CGH array testing in children with developmental delay. Dr Sally Davies 17 th September 2014
 Challenges of CGH array testing in children with developmental delay Dr Sally Davies 17 th September 2014 CGH array What is CGH array? Understanding the test Benefits Results to expect Consent issues Ethical
Challenges of CGH array testing in children with developmental delay Dr Sally Davies 17 th September 2014 CGH array What is CGH array? Understanding the test Benefits Results to expect Consent issues Ethical
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 18; 09 September 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P090-A4 BRCA2 Lot A4-0715, A4-0714, A4-0314, A4-0813, A4-0712: Compared to lot A3-0710, the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). This product is identical to the
SALSA MLPA probemix P090-A4 BRCA2 Lot A4-0715, A4-0714, A4-0314, A4-0813, A4-0712: Compared to lot A3-0710, the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). This product is identical to the
MODULE NO.14: Y-Chromosome Testing
 SUBJECT Paper No. and Title Module No. and Title Module Tag FORENSIC SIENCE PAPER No.13: DNA Forensics MODULE No.21: Y-Chromosome Testing FSC_P13_M21 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcome 2. Introduction:
SUBJECT Paper No. and Title Module No. and Title Module Tag FORENSIC SIENCE PAPER No.13: DNA Forensics MODULE No.21: Y-Chromosome Testing FSC_P13_M21 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcome 2. Introduction:
Silver-Russell syndrome
 Silver-Russell syndrome Emma Wakeling Consultant in Clinical Genetics North West Thames Regional Genetic Centre (Kennedy-Galton Centre) London, UK Silver-Russell syndrome Clinical features Genetic heterogeneity
Silver-Russell syndrome Emma Wakeling Consultant in Clinical Genetics North West Thames Regional Genetic Centre (Kennedy-Galton Centre) London, UK Silver-Russell syndrome Clinical features Genetic heterogeneity
Monogenic Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia Disorders
 Frontiers in Diabetes 21 Monogenic Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia Disorders Bearbeitet von C.A. Stanley, D.D. De Léon 1. Auflage 2012. Buch. VIII, 196 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 8055 9943 6 Weitere Fachgebiete
Frontiers in Diabetes 21 Monogenic Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia Disorders Bearbeitet von C.A. Stanley, D.D. De Léon 1. Auflage 2012. Buch. VIII, 196 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 8055 9943 6 Weitere Fachgebiete
New: P077 BRCA2. This new probemix can be used to confirm results obtained with P045 BRCA2 probemix.
 SALSA MLPA KIT P045-B2 BRCA2/CHEK2 Lot 0410, 0609. As compared to version B1, four reference probes have been replaced and extra control fragments at 100 and 105 nt (X/Y specific) have been included. New:
SALSA MLPA KIT P045-B2 BRCA2/CHEK2 Lot 0410, 0609. As compared to version B1, four reference probes have been replaced and extra control fragments at 100 and 105 nt (X/Y specific) have been included. New:
SALSA MLPA probemix P185-C2 Intersex Lot C2-1015: As compared to the previous version C1 (lot C1-0611), the lengths of four probes have been adjusted.
 mix P185-C2 Intersex Lot C2-1015: As compared to the previous version C1 (lot C1-0611), the lengths of four s have been adjusted. The sex-determining region on chromosome Y (SRY) is the most important
mix P185-C2 Intersex Lot C2-1015: As compared to the previous version C1 (lot C1-0611), the lengths of four s have been adjusted. The sex-determining region on chromosome Y (SRY) is the most important
Epigenetics: Basic Principals and role in health and disease
 Epigenetics: Basic Principals and role in health and disease Cambridge Masterclass Workshop on Epigenetics in GI Health and Disease 3 rd September 2013 Matt Zilbauer Overview Basic principals of Epigenetics
Epigenetics: Basic Principals and role in health and disease Cambridge Masterclass Workshop on Epigenetics in GI Health and Disease 3 rd September 2013 Matt Zilbauer Overview Basic principals of Epigenetics
22q11.2 DELETION SYNDROME. Anna Mª Cueto González Clinical Geneticist Programa de Medicina Molecular y Genética Hospital Vall d Hebrón (Barcelona)
 22q11.2 DELETION SYNDROME Anna Mª Cueto González Clinical Geneticist Programa de Medicina Molecular y Genética Hospital Vall d Hebrón (Barcelona) Genomic disorders GENOMICS DISORDERS refers to those diseases
22q11.2 DELETION SYNDROME Anna Mª Cueto González Clinical Geneticist Programa de Medicina Molecular y Genética Hospital Vall d Hebrón (Barcelona) Genomic disorders GENOMICS DISORDERS refers to those diseases
Beta thalassemia major due to acquired uniparental disomy in a previously healthy adolescent
 Beta thalassemia major due to acquired uniparental disomy in a previously healthy adolescent Celeste Bento 1, Tabita M. Magalhães 1, Jelena D. Milosevic 2, Isabel M. Carreira 3 Kralovics 2 and M. Leticia
Beta thalassemia major due to acquired uniparental disomy in a previously healthy adolescent Celeste Bento 1, Tabita M. Magalhães 1, Jelena D. Milosevic 2, Isabel M. Carreira 3 Kralovics 2 and M. Leticia
SNP Array NOTE: THIS IS A SAMPLE REPORT AND MAY NOT REFLECT ACTUAL PATIENT DATA. FORMAT AND/OR CONTENT MAY BE UPDATED PERIODICALLY.
 SAMPLE REPORT SNP Array NOTE: THIS IS A SAMPLE REPORT AND MAY NOT REFLECT ACTUAL PATIENT DATA. FORMAT AND/OR CONTENT MAY BE UPDATED PERIODICALLY. RESULTS SNP Array Copy Number Variations Result: GAIN,
SAMPLE REPORT SNP Array NOTE: THIS IS A SAMPLE REPORT AND MAY NOT REFLECT ACTUAL PATIENT DATA. FORMAT AND/OR CONTENT MAY BE UPDATED PERIODICALLY. RESULTS SNP Array Copy Number Variations Result: GAIN,
Imprinting diseases and IVF. Øjvind Lidegaard Dept. Obstetrics & Gynaecology Herlev University Hospital Copenhagen, Denmark
 Imprinting diseases and IVF Øjvind Lidegaard Dept. Obstetrics & Gynaecology Herlev University Hospital Copenhagen, Denmark Li/03 What is the difference between a mule and a hinny? Stallion Hingst Horse
Imprinting diseases and IVF Øjvind Lidegaard Dept. Obstetrics & Gynaecology Herlev University Hospital Copenhagen, Denmark Li/03 What is the difference between a mule and a hinny? Stallion Hingst Horse
IGF2/H19 hypomethylation in a patient with very low birthweight, preocious pubarche and insulin resistance
 Murphy et al. BMC Medical Genetics 2012, 13:42 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access IGF2/H19 hypomethylation in a patient with very low birthweight, preocious pubarche and insulin resistance Rinki Murphy 1*, Lourdes
Murphy et al. BMC Medical Genetics 2012, 13:42 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access IGF2/H19 hypomethylation in a patient with very low birthweight, preocious pubarche and insulin resistance Rinki Murphy 1*, Lourdes
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 05; 03 April 2019
 SALSA MLPA probemix ME012-A1 MGMT-IDH1-IDH2 Lot A1-1215. Glioblastoma, the most common malignant primary brain tumour, is characterised by aggressive behaviour and a poor survival. Hypermethylation in
SALSA MLPA probemix ME012-A1 MGMT-IDH1-IDH2 Lot A1-1215. Glioblastoma, the most common malignant primary brain tumour, is characterised by aggressive behaviour and a poor survival. Hypermethylation in
R.C.P.U. NEWSLETTER. Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome Carrie Crain, B.S.
 R.C.P.U. NEWSLETTER Editor: Heather J. Stalker, M.Sc. Director: Roberto T. Zori, M.D. R.C. Philips Research and Education Unit Vol. XIX No. 1 A statewide commitment to the problems of mental retardation
R.C.P.U. NEWSLETTER Editor: Heather J. Stalker, M.Sc. Director: Roberto T. Zori, M.D. R.C. Philips Research and Education Unit Vol. XIX No. 1 A statewide commitment to the problems of mental retardation
Fragile X Syndrome. Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype
 Fragile X Syndrome Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype A loss of function of the FMR-1 gene results in severe learning problems, intellectual disability
Fragile X Syndrome Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype A loss of function of the FMR-1 gene results in severe learning problems, intellectual disability
Differentially methylated regions in maternal and paternal uniparental disomy for chromosome 7
 Research Paper Epigenetics 9:3, 351 365; March 2014; 2014 Landes Bioscience Research Paper Differentially methylated regions in maternal and paternal uniparental disomy for chromosome 7 Katariina Hannula-Jouppi
Research Paper Epigenetics 9:3, 351 365; March 2014; 2014 Landes Bioscience Research Paper Differentially methylated regions in maternal and paternal uniparental disomy for chromosome 7 Katariina Hannula-Jouppi
SNP Array NOTE: THIS IS A SAMPLE REPORT AND MAY NOT REFLECT ACTUAL PATIENT DATA. FORMAT AND/OR CONTENT MAY BE UPDATED PERIODICALLY.
 SAMPLE REPORT SNP Array NOTE: THIS IS A SAMPLE REPORT AND MAY NOT REFLECT ACTUAL PATIENT DATA. FORMAT AND/OR CONTENT MAY BE UPDATED PERIODICALLY. RESULTS SNP Array Copy Number Variations Result: LOSS,
SAMPLE REPORT SNP Array NOTE: THIS IS A SAMPLE REPORT AND MAY NOT REFLECT ACTUAL PATIENT DATA. FORMAT AND/OR CONTENT MAY BE UPDATED PERIODICALLY. RESULTS SNP Array Copy Number Variations Result: LOSS,
The significance of genomic imprinting in assisted reproduction
 Gynaecological Clinic Rigshospitalet Copenhagen University The significance of genomic imprinting in assisted reproduction Øjvind Lidegaard Øjvind Gynaecological Lidegaard Clinic Rigshospitalet Copenhagen,
Gynaecological Clinic Rigshospitalet Copenhagen University The significance of genomic imprinting in assisted reproduction Øjvind Lidegaard Øjvind Gynaecological Lidegaard Clinic Rigshospitalet Copenhagen,
Sharan Goobie, MD, MSc, FRCPC
 Sharan Goobie, MD, MSc, FRCPC Chromosome testing in 2014 Presenter Disclosure: Sharan Goobie has no potential for conflict of interest with this presentation Objectives Review of standard genetic investigations
Sharan Goobie, MD, MSc, FRCPC Chromosome testing in 2014 Presenter Disclosure: Sharan Goobie has no potential for conflict of interest with this presentation Objectives Review of standard genetic investigations
Insulator and silencer sequences in the imprinted region of human chromosome 11p15.5
 Human Molecular Genetics, 2003, Vol. 12, No. 15 1927 1939 DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddg194 Insulator and silencer sequences in the imprinted region of human chromosome 11p15.5 Minjie Du 1, Linda G. Beatty 1, Wenjing
Human Molecular Genetics, 2003, Vol. 12, No. 15 1927 1939 DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddg194 Insulator and silencer sequences in the imprinted region of human chromosome 11p15.5 Minjie Du 1, Linda G. Beatty 1, Wenjing
Russell Silver syndrome due to paternal H19/IGF2 hypomethylation in a patient conceived using intracytoplasmic sperm injection
 Reproductive BioMedicine Online (2010) 20, 843 847 www.sciencedirect.com www.rbmonline.com CASE REPORT Russell Silver syndrome due to paternal H19/IGF2 hypomethylation in a patient conceived using intracytoplasmic
Reproductive BioMedicine Online (2010) 20, 843 847 www.sciencedirect.com www.rbmonline.com CASE REPORT Russell Silver syndrome due to paternal H19/IGF2 hypomethylation in a patient conceived using intracytoplasmic
QIAGEN Epigenetics Webinar
 QIAGEN Epigenetics Webinar Pyrosequencing A New Standard in Epigenetic and Genetic Analysis! Frank Fischinger, MS, MBA Sr. Technical Sales Scientist QIAGEN Inc. Profiling of DNA methylation in uniparental
QIAGEN Epigenetics Webinar Pyrosequencing A New Standard in Epigenetic and Genetic Analysis! Frank Fischinger, MS, MBA Sr. Technical Sales Scientist QIAGEN Inc. Profiling of DNA methylation in uniparental
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 08; 07 May 2015
 mix P185-C1 Intersex Lot C1-0611: As compared to the previous version B2 (lot B2-0311), s for CYP21A2 have been removed and s for the CXorf21 gene as well as additional s for NR0B1, NR5A1 and the Y chromosome
mix P185-C1 Intersex Lot C1-0611: As compared to the previous version B2 (lot B2-0311), s for CYP21A2 have been removed and s for the CXorf21 gene as well as additional s for NR0B1, NR5A1 and the Y chromosome
Schedule of Accreditation issued by United Kingdom Accreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK
 SW Thames Regional Genetics Laboratory, Jenner Wing, SGUL Cranmer Terrace London SW17 0RE Contact: Mr John Short Tel: +44 (0) 208 725 5332 Fax: +44 (0) 208 725 3440 E-Mail: swtrgl@stgeorges.nhs.uk Website:
SW Thames Regional Genetics Laboratory, Jenner Wing, SGUL Cranmer Terrace London SW17 0RE Contact: Mr John Short Tel: +44 (0) 208 725 5332 Fax: +44 (0) 208 725 3440 E-Mail: swtrgl@stgeorges.nhs.uk Website:
Association of In Vitro Fertilization with Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome and Epigenetic Alterations of LIT1 and H19
 Am. J. Hum. Genet. 72:156 160, 2003 Association of In Vitro Fertilization with Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome and Epigenetic Alterations of LIT1 and H19 Michael R. DeBaun, 1 Emily L. Niemitz, 2 and Andrew
Am. J. Hum. Genet. 72:156 160, 2003 Association of In Vitro Fertilization with Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome and Epigenetic Alterations of LIT1 and H19 Michael R. DeBaun, 1 Emily L. Niemitz, 2 and Andrew
SALSA MLPA probemix P360-A1 Y-Chromosome Microdeletions Lot A
 SALSA MLPA probemix P360-A1 Y-Chromosome Microdeletions Lot A1-1011. This SALSA MLPA probemix is for basic research and intended for experienced MLPA users only! This probemix enables you to quantify genes
SALSA MLPA probemix P360-A1 Y-Chromosome Microdeletions Lot A1-1011. This SALSA MLPA probemix is for basic research and intended for experienced MLPA users only! This probemix enables you to quantify genes
SAC review DNA methylation: a form of epigenetic control of gene expression
 The Obstetrician & Gynaecologist 10.1576/toag.12.1.037.27556 http://onlinetog.org 2010;12:37 42 SAC review SAC review DNA methylation: a form of epigenetic control of gene expression Authors Derek H K
The Obstetrician & Gynaecologist 10.1576/toag.12.1.037.27556 http://onlinetog.org 2010;12:37 42 SAC review SAC review DNA methylation: a form of epigenetic control of gene expression Authors Derek H K
FACT SHEET 15. Epigenetics. What is imprinting of genes? Produced by the Centre for Genetics Education. Internet:
 Important points It is increasingly clear that translation of the genetic code into proteins is not the only way that our genes influence our growth, development and health and that changes in the genetic
Important points It is increasingly clear that translation of the genetic code into proteins is not the only way that our genes influence our growth, development and health and that changes in the genetic
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6. Questions & Answers
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the
Design and Setting: A longitudinal study. Participants: Sixty-two SRS and 227 non-srs subjects.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-Term Results of GH Treatment in Silver-Russell Syndrome (SRS): Do They Benefit the Same as Non-SRS Short-SGA? C. C. J. Smeets, G. R. J. Zandwijken, J. S. Renes, and A. C. S. Hokken-Koelega
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-Term Results of GH Treatment in Silver-Russell Syndrome (SRS): Do They Benefit the Same as Non-SRS Short-SGA? C. C. J. Smeets, G. R. J. Zandwijken, J. S. Renes, and A. C. S. Hokken-Koelega
Committee Paper SCAAC(05/09)01. ICSI guidance. Hannah Darby and Rachel Fowler
 Committee Paper Committee: Scientific and Clinical Advances Advisory Committee Meeting Date: 12 May 2009 Agenda Item: 4 Paper Number: SCAAC(05/09)01 Paper Title: ICSI guidance Author: Hannah Darby and
Committee Paper Committee: Scientific and Clinical Advances Advisory Committee Meeting Date: 12 May 2009 Agenda Item: 4 Paper Number: SCAAC(05/09)01 Paper Title: ICSI guidance Author: Hannah Darby and
BECKWITH-WIEDEMANN SYNDROME AND HEMIHYPERPLASIA
 10 BECKWITH-WIEDEMANN SYNDROME AND HEMIHYPERPLASIA ROSANNA WEKSBERG Division of Clinical and Metabolic Genetics, Department of Pediatrics, The Hospital for Sick Children University of Toronto, Toronto,
10 BECKWITH-WIEDEMANN SYNDROME AND HEMIHYPERPLASIA ROSANNA WEKSBERG Division of Clinical and Metabolic Genetics, Department of Pediatrics, The Hospital for Sick Children University of Toronto, Toronto,
Applications of Chromosomal Microarray Analysis (CMA) in pre- and postnatal Diagnostic: advantages, limitations and concerns
 Applications of Chromosomal Microarray Analysis (CMA) in pre- and postnatal Diagnostic: advantages, limitations and concerns جواد کریمزاد حق PhD of Medical Genetics آزمايشگاه پاتوبيولوژي و ژنتيك پارسه
Applications of Chromosomal Microarray Analysis (CMA) in pre- and postnatal Diagnostic: advantages, limitations and concerns جواد کریمزاد حق PhD of Medical Genetics آزمايشگاه پاتوبيولوژي و ژنتيك پارسه
4/8/2016. Objectives. Epigenetic Definitions. Gene Expression. More Questions. Epigentics. Questions to Consider
 Objectives Epigentics Lynda Britton, Ph.D., MLS(ASCP) CM Professor LSU Health Shreveport Discuss epigenetics and its role in cancer, imprinting and X chromosome inactivation. Describe the modifications/mechanisms
Objectives Epigentics Lynda Britton, Ph.D., MLS(ASCP) CM Professor LSU Health Shreveport Discuss epigenetics and its role in cancer, imprinting and X chromosome inactivation. Describe the modifications/mechanisms
Determination of Genomic Imbalances by Genome-wide Screening Approaches
 Overview Determination of Genomic Imbalances by Genome-wide Screening Approaches Károly Szuhai Introduction/Methodologies Applications/Results Conclusion Approaches Introduction/Methodologies Chromosome
Overview Determination of Genomic Imbalances by Genome-wide Screening Approaches Károly Szuhai Introduction/Methodologies Applications/Results Conclusion Approaches Introduction/Methodologies Chromosome
SALSA MLPA KIT P036-E1 HUMAN TELOMERE-3 Lot 0808: As compared to the previous version (P036-D2), the probes for 1p and 4q have been replaced.
 SALSA MLPA KIT P036-E1 HUMAN TELOMERE-3 Lot 0808: As compared to the previous version (P036-D2), the probes for 1p and 4q have been replaced. MENTAL RETARDATION is caused by aberrant copy numbers of subtelomeric
SALSA MLPA KIT P036-E1 HUMAN TELOMERE-3 Lot 0808: As compared to the previous version (P036-D2), the probes for 1p and 4q have been replaced. MENTAL RETARDATION is caused by aberrant copy numbers of subtelomeric
SALSA MLPA KIT P078-B1 Breast Tumour Lot 0210, 0109
 SALSA MLPA KIT P078-B1 Breast Tumour Lot 0210, 0109 This P078-B1 Breast Tumour probemix contains probes for several genes (including ERBB2, BIRC5, MYC, TOP2A, ESR1, MTDH, CCND1, CCNE1, EGFR and C11orf30)
SALSA MLPA KIT P078-B1 Breast Tumour Lot 0210, 0109 This P078-B1 Breast Tumour probemix contains probes for several genes (including ERBB2, BIRC5, MYC, TOP2A, ESR1, MTDH, CCND1, CCNE1, EGFR and C11orf30)
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 13;
 SALSA MLPA probemix P027-C1 Uveal Melanoma Lot C1-0211: A large number of probes have been replaced by other probes in the same chromosomal regions as compared to previous lots, and several reference probes
SALSA MLPA probemix P027-C1 Uveal Melanoma Lot C1-0211: A large number of probes have been replaced by other probes in the same chromosomal regions as compared to previous lots, and several reference probes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10495 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 3 4 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 5 6 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 7 8 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:10.1038/nature10495 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 3 4 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 5 6 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 7 8 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Epigenetic changes at the insulin-like growth factor II H19 locus in developing kidney is an early event in Wilms tumorigenesis
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 5367 5371, May 1997 Medical Sciences Epigenetic changes at the insulin-like growth factor II H19 locus in developing kidney is an early event in Wilms tumorigenesis
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 5367 5371, May 1997 Medical Sciences Epigenetic changes at the insulin-like growth factor II H19 locus in developing kidney is an early event in Wilms tumorigenesis
H19 Chromatin Insulator in Development and DiseaseEpigenetic Regulation of the
 Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Science and Technology 825 H19 Chromatin Insulator in Development and DiseaseEpigenetic Regulation of the BY CLAES HOLMGREN ACTA UNIVERSITATIS
Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Science and Technology 825 H19 Chromatin Insulator in Development and DiseaseEpigenetic Regulation of the BY CLAES HOLMGREN ACTA UNIVERSITATIS
Session 2: Biomarkers of epigenetic changes and their applicability to genetic toxicology
 Session 2: Biomarkers of epigenetic changes and their applicability to genetic toxicology Bhaskar Gollapudi, Ph.D The Dow Chemical Company Workshop: Genetic Toxicology: Opportunities to Integrate New Approaches
Session 2: Biomarkers of epigenetic changes and their applicability to genetic toxicology Bhaskar Gollapudi, Ph.D The Dow Chemical Company Workshop: Genetic Toxicology: Opportunities to Integrate New Approaches
OVERVIEW OF EPIGENETICS
 OVERVIEW OF EIENETICS Date: * Time: 9:00 am - 9:50 am * Room: Berryhill 103 Lecturer: Terry Magnuson 4312 MBRB trm4@med.unc.edu 843-6475 *lease consult the online schedule for this course for the definitive
OVERVIEW OF EIENETICS Date: * Time: 9:00 am - 9:50 am * Room: Berryhill 103 Lecturer: Terry Magnuson 4312 MBRB trm4@med.unc.edu 843-6475 *lease consult the online schedule for this course for the definitive
MMB (MGPG) Non traditional Inheritance Epigenetics. A.Turco
 MMB (MGPG) 2017 Non traditional Inheritance Epigenetics A.Turco NON TRADITIONAL INHERITANCE EXCEPTIONS TO MENDELISM - Genetic linkage (2 loci close to each other) - Complex or Multifactorial Disease (MFD)
MMB (MGPG) 2017 Non traditional Inheritance Epigenetics A.Turco NON TRADITIONAL INHERITANCE EXCEPTIONS TO MENDELISM - Genetic linkage (2 loci close to each other) - Complex or Multifactorial Disease (MFD)
Approach to Mental Retardation and Developmental Delay. SR Ghaffari MSc MD PhD
 Approach to Mental Retardation and Developmental Delay SR Ghaffari MSc MD PhD Introduction Objectives Definition of MR and DD Classification Epidemiology (prevalence, recurrence risk, ) Etiology Importance
Approach to Mental Retardation and Developmental Delay SR Ghaffari MSc MD PhD Introduction Objectives Definition of MR and DD Classification Epidemiology (prevalence, recurrence risk, ) Etiology Importance
Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development
 Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development 张戈 Method and material STAR ChIP seq (small-scale TELP-assisted rapid ChIP seq) 200 mouse embryonic stem cells PWK/PhJ
Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development 张戈 Method and material STAR ChIP seq (small-scale TELP-assisted rapid ChIP seq) 200 mouse embryonic stem cells PWK/PhJ
