Unit 9 CONTRACEPTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES
|
|
|
- Amos Freeman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 9 CONTRACEPTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Become aware of the magnitude of teen age sexual activity and pregnancy and some of the social and economic effects. 2. Learn about the various means of contraception, their efficiency, and dangers. 3. Learn how the various means of contraception prevent the production of children. 4. Learn some of the reasons that the most rapidly growing (developing) nations do not use contraceptives to the extent they are used in developed countries. Introduction Most animals are limited in the number of offspring they reproduce that in turn live to reproductive age. Various factors including predators, food availability, and disease limit their reproductive capacity. For most of human history, human reproduction was also limited or controlled by these same factors. Now, at least in developed nations, these factors have been largely eliminated. Also the need for large families to assure a work force and guarantee care of the elderly has changed as the majority of people moved from farm to city and various social systems have been established for the care of the elderly. Now many individuals wish to restrict their family size. In the past sexually activity often resulted in offspring. The fact that there is still a problem in unwanted pregnancies is illustrated in Figure 9-1 taken from The ZPG Reporter, Jan/Feb, It shows that the United States has a much higher rate of pregnancies and abortions in the year age group than many other industrial nations. These statistics are not unexpected when the increase in percent of teens having sex by age 18 is observed (Fig. 9-2). Adverse results of teen pregnancy include: 1) 70% of teen mothers drop out of high school; 2) teen mothers have more children; and 3) teen mothers depend more on public 108
2 Figure 9-1. Percent of unintended pregnancies (excluding miscarriages) to teens years which end in abortion and live births. assistance than teens who don t have children. More recently health professionals have become concerned with the prevalence of oral sex in teens. Figures 9-3, 9-4, 9-5, and 9-6 show the result of questioners give in 2002, and show the comparisons between males and females or different ages and virgins and sexually experienced. Just over half of teens aged 15-19, 54% girls and 55% boys, say they have had oral sex (fig. 9-3). Figure 9-4 shows that experience with oral sex increases with age; less than 45% of the year teens reported having oral sex as compared to over 70% of the aged Figures 9-5 and 9-6 show that sexually experienced males and females are more likely the have participated in oral sex than non-experienced. Figured 9-7 and 9-8 indicate the reasons for having had oral sex given by virgin boys and virgin girls respectively. A little more that 35% indicated it is a method of avoiding STDs. A study by the Kaiser Family Foundation found that 26% of sexually active year olds believed that one can not get HIV from oral sex and another 15% didn t know if HIV could be contacted by oral sex. Scientist have documented that Herpes, Syphilis, Gonorrhea, Chlamydia, Genital warts, and HIV can be transmitted through oral sex, even though the incidence is lower than with vaginal sex. American society has been historically averse to dealing with issues about reproductive health and sexuality as compared to other countries. In recent years, methods have been developed, which permit frequent sexually activity without the risk of offspring. In this unit we will discuss some of the methods, their efficiency, and risks. 109
3 Figure 9-2. Percent of teens having sex by age 18. Taken from ZPG Reporter, Jan/Feb Figure 9-3. Percent of teens (aged 15-19) who report having received or performed oral sex. From Science Says: Teens and Oral Sex Number 17, Sept. 2005, 110
4 Figure 9-4. Difference by age in the percent of teens who report having given or received oral sex. From Science Says: Teens and Oral Sex Number 17, Sept. 2005, Figure 9-5. Percent of virgin and sexually experienced teens who have received or performed oral sex, by gender. From Science Says: Teens and Oral Sex Number 17, Sept. 2005, 111
5 Figure 9-6. Percent of virgin and sexually experienced teens who have had oral sex (given or received), by age. From Science Says: Teens and Oral Sex Number 17, Sept. 2005, Figure 9-7. Proportion of virgin boys who have had oral sex, by main reason for postponing sexual intercourse. From Science Says: Teens and Oral Sex Number 17, Sept. 2005, 112
6 Figure 9-8. Portion of virgin girls who have had oral sex, by main reason for postponing sexual intercourse. From Science Says: Teens and Oral Sex Number 17, Sept. 2005, Contraception means against taking in this case the taking of a child. Prevention of pregnancy can be placed in three categories: 1) prevention of egg and sperm meeting in the female reproductive tract (fertilization is prevented); 2) prevention of implantation of the zygote, actually the embryo; and 3) preventing the release of mature eggs or sperm from the gonad. Table 9-1 lists the various methods, their effectiveness, and their risks. Table 9-1. Common birth-control methods. Name Effectiveness Method Risk Prevention of sperm and egg meeting Abstinence 100% Refrain from sex None Rhythm method 70% Abstinence 5-8 days None around time of ovulation Coitus interruptus 75% Withdraw penis prior to ejaculation None if ignore emotional stress Male condom 85% Fits over penis; traps None sperm; prevents STDs Female condom 85% Inserted with applicator; None outer rings holds condom in place; blocks sperm; prevents STDs Diaphragm (with 90% Inserted in vagina, covers None jelly) cervix; must be fitted Cervical cap 85% Latex cup held by suction over cervix; disposable; delivers spermicide Cervical cancer? 113
7 Jelly, creams, and foams 75% Inserted before intercourse; kills sperm Vaginal sponge 75% Small piece of foam is impregnated with spermicide jelly; place over cervix; effective immediately & for up to 24 hours Douch 70% Clean vagina after intercourse Prevention of implantation IUD, Intrauterine 90+% Plastic coil inserted into Device uterus by MD; some have progesterone in stem RU486 95% Requires taking two pills about 3 days apart; prescription Morning after pill 85% Take synthetic progesterone 72 hrs and 84 hrs after unprotected sex None None None Can cause PID Can cause excess bleeding Prevention of release of egg or sperm from gonad or from reproductive system Birth control pill Almost 100% Synthetic estrogen and progesterone stops FSH and LH Blood clots in smokers Norplant 90+% Insert progesterone releasing device under the skin; good for up to 5 years Depo-Provera 99% 4 injections of synthetic progesterone per year Gossypol?? Pill for men; disables testicular cells; not available in the U.S.???? none Breast cancer? Sterility in some Vasectomy 100% Cut and tie vas deferens Difficult to reverse Tubal ligation 100% Cut and tie oviducts Difficult to reverse Some new methods or modifications of older methods include: 1) Lea s Contraceptive is a modified diaphragm-like device in one size. It is available as an over-the-counter product in Germany, and was approved by the U.S. FDA in March It should remain in place at least 8 hours after intercourse, but be worn no longer than 48 hours before removing to wash. Pregnancy rates were 15% as compared with percent for standard diaphragm with spermicide. 2) Fem Cap is a modified cervical cap with a strap to aid in removal. It is available in some European countries and was approved for use in the U.S. in March, Found to be somewhat less effective than the standard cap, about 23% pregnancy. 3) Jadelle is a system of two Silastic rods that release levonorgestrel; it is undergoing registration in Europe. Duration of action is 5 years. 4) Implanon is a single implant system that releases etonogestrel; it is 114
8 registered is some foreign countries. Duration of action is 3 years. 5) Contraceptive Patch is a small patch containing estrogen and progesterone similar to the Pill but contains enough of the hormones so that the blood level of users contains 60 % more of the hormones. A new patch is put on every week for three weeks and then no patch for the fourth week. It has not been in use long enough to know all the risks, but there are certain risks and one should only use the patch with a doctor s advise. Usually upon seeing a doctor, you are given 3 months supply to see how It suits you and then you should check with your doctor. 6) Copper-T intrauterine device (IUD) which can be used up to 5 days after unprotected intercourse to prevent pregnancy. More effective than Emergency Contraceptive Pills; it reduces the rate of pregnancy by 90%. Can be left in place for 3-10 years depending upon the type and countryspecific licensing. 7) Pill for men is in clinical trials. The pill uses synthetic hormones to lower the sperm count. The effect is temporary. 8) Reversible inhibition of sperm under guidance, RISUG, works by an Injection into the vas deference. The injection coats the walls of the vas deferens with a clear gel made of 60 mg of the copolymere styrene/ dnhydride with 120 ul of the solvent dimethyl sulfoxide. Within an hour, the drugs produce an electrical charge that nullifies the electrical charge of the sperm preventing them from penetrating the egg. The effect can be reversed by washing the vas deferens. Some see the use of RISUG as having the disadvantage of no longer necessitating the use of the male condom, which offers protection against some STDs. 9) Vaccinations for males are in the investigation stage. This immunocontraceptive works by preventing or slowing sperm production by an immune system response to the hormone FSH, which is vital to the maturation of sperm. Men regain their fertility as the effect wears off. However, in clinical trials the vaccine was shown to work on only 1/3 of the men. Figure 9-9 illustrates some of the contraceptive methods. With all these methods available, what types are used by the people in the United States? Table 9-2 shows the types being used and the percent use of each. The 1995 Family Growth Survey reports that female sterilization is still the most widely used method in U.S. at 27.37%. The pill runs a close second at 26.9%. These methods, with the exception of Gossypol, are all available to prevent pregnancy in U.S. women. Developing countries, where most population increase is occurring, do not have these methods available. In some cases religious and cultural beliefs prohibit the use of contraceptives, but it is the unavailability and ignorance of their use that prevents many women in these countries from using them. Family planning is being introduced in some of these nations, but to facilitate the desire to reduce family size, safer, more convenient methods are being developed. Research is being done on nasal spray contraceptives, transdermal patches (technique similar to smokers patch), biodegradable implants which work for 18 months and do not have to be removed. The Food and Drug Association has approved the morning-after pill for over the counter sales, but the female must show proof of being 18 years or older Taken within three days of sexual intercourse, the prescription pill prevents ovulation or, if that already has occurred, blocks implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterus. AMA suggests that 115
9 under the present conditions, a woman might not be able to get the pill in time to prevent a pregnancy. The morning-after pill is essentially a high-dose birth control pill. It is different from the RU486 abortion pill which acts by causing contractions to expel an embryo from the uterus; RU486 can be given up to seven weeks after the start of the last menstrual period. Figure 9-9. Showing various contraceptive methods including vasectomy (A), tubal ligation (B), diaphragm (C), IUD (D), cervical cap (E),and female condom (F). 116
10 Table 9-2. Contraceptives by percent use in the United States 1 Type Percent Female sterilization 27.6% Pill 26.9% Male condom 20.4% Male sterilization 10.9% Withdrawal 3.1% Injectable 3.0% Periodic abstinence 2.3% Diaphragm 1.9% Implant 1.4% IUD 0.8% Female condom 0.0% Other methods 1.6% 1 As this survey was taken in 1995, a more recent survey would show some differences due to the availability of morning after pill and RU486. A more recent survey taken in 2002 shows the following: Type Percent Pill 30.6% Female sterilization 27.0% Male condom 18.0% Male sterilization 9.2% 3 Month injections 5.3% Other mechanisms 9.9% 117
11 Unit 9 OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS OVER CONTRACEPTION 1. Which of the following methods employs prevention of implantation as a method of contraception? (A) Birth control pill (B) Depo-Provera C) RU486 (D) Diaphragm. 2. Which of the following methods has the lowest percent success? (A) Vasectomy (B) Birth control pill (C) Male condom (D) Tubal ligation. 3. Which of the following methods is best for preventing transmission of STDs? (A) Vasectomy (B) Diaphragm (C) Douche (D) Male condom (E) IUD 4. Which of the following methods has no known risk factors? (A) IUD (B) Male condom (C) Birth control pill (D) Cervical cap 5. If one is employing the rhythm method of birth control, he/she should refrain from unprotected sex for a period of (A) 2-4 days (B) 5-8 days (C) 7-14 days (D) days around the time of ovulation. 6. Which of following methods has not been approved for use in the U.S.? (A) RU486 (B) Gossypol (C) IUD (D) Norplant 7. The commonest form of contraception in the U.S. is (A) tubal ligation (B) Birth control pill (C) vasectomy (D) male condom. 8. It is necessary to enter the abdominal cavity to perform (A) tubal ligation (B) vasectomy (C) both A and B (D) neither A or B. 9. A doctor s assistance is required or suggested in all but one of these methods. Which one is not? (A) vasectomy (B) tubal ligation (C) implants (D) diaphragm (E) female condom. 10. Which of the following has the lowest percent of success? (A) Jellies, creams, and foams (B) Contraceptive sponge (C) Douche (D) Cervical cap. DISCUSSION QUESTIONS OVER CONTRACEPTION 1. What are some of the difficulties of using the rhythm method or family planning? 118
12 2. Which methods of contraception are also good methods for STD prevention? 3. List the methods of contraception that have the best chances of being successful. 4. Which methods could be considered as abortion methods? Explain. 5. Most texts suggest that the birth-control pill is taken daily? Is that correct? Explain. 6. Some men after having a vasectomy relate that they are no longer able to have an ejaculation. Explain the reason for this. 7. What happens to the released sperm or eggs in the case of a man with a vasectomy or a woman with tubal ligation? 8. Suggest reasons that a woman doesn t want a tubal ligation or a man a vasectomy. 9. What are some of the problems involved in the use of contraceptive methods in third world countries? 119
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that
 The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
Contraceptives. Kim Dawson October 2010
 Contraceptives Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: The about the different methods of birth control. How to use each method of birth control. Emergency contraception What are they?
Contraceptives Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: The about the different methods of birth control. How to use each method of birth control. Emergency contraception What are they?
WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES?
 CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
Birth Control Options Chart
 Hormonal Methods Birth control pills also known as mini-pills 91-99% A daily pill containing hormones that stops you from ovulating. There are combination estrogen or progestin-only (mini-pill) options.
Hormonal Methods Birth control pills also known as mini-pills 91-99% A daily pill containing hormones that stops you from ovulating. There are combination estrogen or progestin-only (mini-pill) options.
100% Highly effective No cost No side effects
 effective? Advantages Disadvantages How do I get Cost Abstinence For some it can mean no sexual contact. For others it is no sexual intercourse or vaginal penetration. A permanent surgical procedure available
effective? Advantages Disadvantages How do I get Cost Abstinence For some it can mean no sexual contact. For others it is no sexual intercourse or vaginal penetration. A permanent surgical procedure available
Notes to Teacher continued Contraceptive Considerations
 Abstinence a conscious decision to refrain from sexual intercourse 100% pregnancy will not occur if close contact between the penis and vagina does not take place. The risk of a number of STDs, including
Abstinence a conscious decision to refrain from sexual intercourse 100% pregnancy will not occur if close contact between the penis and vagina does not take place. The risk of a number of STDs, including
1.Abstinence no sex (Abstinence only education has been proven ineffective in preventing unwanted pregnancies)
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs 1. Ovary Transplants 2. Freezing Eggs 3. Choosing Gender 4. The Male Pill, parts 1&2 5. Male Birth Control: RISUG 6. Birth Control. 1.Abstinence
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs 1. Ovary Transplants 2. Freezing Eggs 3. Choosing Gender 4. The Male Pill, parts 1&2 5. Male Birth Control: RISUG 6. Birth Control. 1.Abstinence
Contraception Effective Methods of Birth Control
 Contraception Effective Methods of Birth Control Abstinence Means choosing NOT to have sex It is the ONLY method that is 100% effective It is your right to be in control of your body and say NO What are
Contraception Effective Methods of Birth Control Abstinence Means choosing NOT to have sex It is the ONLY method that is 100% effective It is your right to be in control of your body and say NO What are
Power Point Use in EBPs. CAPP & PREP Learning Community May 15, 2018
 Power Point Use in EBPs CAPP & PREP Learning Community May 15, 2018 Objectives Best practices for power point use Why use power point for EBP delivery Examples: the Good, the Bad and the Ugly Recommendations
Power Point Use in EBPs CAPP & PREP Learning Community May 15, 2018 Objectives Best practices for power point use Why use power point for EBP delivery Examples: the Good, the Bad and the Ugly Recommendations
Birth Control Methods
 Birth Control Methods This guide provides useful information to help you and your partner consider pregnancy prevention options. Options are available through the CHS Pharmacy, Women s Health Clinic, and
Birth Control Methods This guide provides useful information to help you and your partner consider pregnancy prevention options. Options are available through the CHS Pharmacy, Women s Health Clinic, and
BIRTH CONTROL METHOD COMPARISON CHART
 BIRTH CONTROL METHOD COMPARISON CHART Abstinence 100% Yes Male latex condom 86%-95% Can increase to 98% by using with a contraceptive jelly Yes Highly effective No side effects, as with other methods No
BIRTH CONTROL METHOD COMPARISON CHART Abstinence 100% Yes Male latex condom 86%-95% Can increase to 98% by using with a contraceptive jelly Yes Highly effective No side effects, as with other methods No
Birth Control- an Overview. Keith Merritt, MD. Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy
 Birth Control- an Overview Keith Merritt, MD Basics Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy Even with perfect use, each method of birth control has a
Birth Control- an Overview Keith Merritt, MD Basics Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy Even with perfect use, each method of birth control has a
Chapter 7 Infertility, Contraception, and Abortion
 Chapter 7 Infertility, Contraception, and Abortion Infertility Incidence Affects about 10% to 15% of reproductive-age population Subfertility: prolonged time to conceive Sterility: inability to conceive
Chapter 7 Infertility, Contraception, and Abortion Infertility Incidence Affects about 10% to 15% of reproductive-age population Subfertility: prolonged time to conceive Sterility: inability to conceive
Information for Informed Consent for Insertion of a Mirena IUD
 Information for Informed Consent for Insertion of a Mirena IUD What is an IUD (intrauterine Device)? An intrauterine device (IUD) is a plastic device that is placed into your uterus to prevent pregnancy.
Information for Informed Consent for Insertion of a Mirena IUD What is an IUD (intrauterine Device)? An intrauterine device (IUD) is a plastic device that is placed into your uterus to prevent pregnancy.
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Birth Control. Choosing the method that s right for you
 Birth Control Choosing the method that s right for you Contents Family planning services... 1 How to use this brochure... 2 Implant... 3 IUD/IUS... 5 Sterilization... 7 Depo-Provera : The shot...9 Pill/ring/patch...
Birth Control Choosing the method that s right for you Contents Family planning services... 1 How to use this brochure... 2 Implant... 3 IUD/IUS... 5 Sterilization... 7 Depo-Provera : The shot...9 Pill/ring/patch...
UNDERSTANDING. Permanent Birth Control for Men
 UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
Contraception. Objectives. Unintended Pregnancy. Unintended Pregnancy in the US. What s the Impact? 10/7/2014
 Contraception Tami Allen, RNC OB, MHA Robin Petersen, RN, MSN Perinatal Clinical Nurse Specialist Objectives Discuss the impact of unintended pregnancy in the United States Discuss the risks and benefits
Contraception Tami Allen, RNC OB, MHA Robin Petersen, RN, MSN Perinatal Clinical Nurse Specialist Objectives Discuss the impact of unintended pregnancy in the United States Discuss the risks and benefits
17. Preventing pregnancy
 17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
Lesson Plan Guidelines
 General Information Name: Daniel Hall Lesson Plan Guidelines Grade Level: 9 th Grade Pregnancy Prevention Primary Learning Outcome(s) (PLO) TSWBAT identify and describe various types of birth control methods
General Information Name: Daniel Hall Lesson Plan Guidelines Grade Level: 9 th Grade Pregnancy Prevention Primary Learning Outcome(s) (PLO) TSWBAT identify and describe various types of birth control methods
The Balanced Counseling Strategy Plus: A Toolkit for Family Planning Service Providers Working in High STI/HIV Prevalence Settings.
 The Balanced Counseling Strategy Plus: A Toolkit for Family Planning Service Providers Working in High STI/HIV Prevalence Settings Counseling Cards Checklist to be reasonably sure a woman is not pregnant
The Balanced Counseling Strategy Plus: A Toolkit for Family Planning Service Providers Working in High STI/HIV Prevalence Settings Counseling Cards Checklist to be reasonably sure a woman is not pregnant
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 22 Female Reproductive System 2 The Reproductive Cycle Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o The female reproductive
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 22 Female Reproductive System 2 The Reproductive Cycle Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o The female reproductive
Bio 3201 Unit 2 REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT. Cell Division MITOSIS (P )
 Bio 3201 Unit 2 REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT 31 Hours Cell Division MITOSIS (P. 460-469) 1. Describe mitosis in detail; Specifically describe, in detail, the events of interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis
Bio 3201 Unit 2 REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT 31 Hours Cell Division MITOSIS (P. 460-469) 1. Describe mitosis in detail; Specifically describe, in detail, the events of interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System
 Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Contraception. My Sexual Health: Objectives. Vocabulary. Standards Wisconsin Health Education Standards
 Contraception My Sexual Health: This lesson utilizes a game to review and explore the various forms of contraception. Abstinence is included as an option. Students will analyze scenarios to identify influences
Contraception My Sexual Health: This lesson utilizes a game to review and explore the various forms of contraception. Abstinence is included as an option. Students will analyze scenarios to identify influences
PREVENTING PREGNANCY: TALKING ABOUT AND USING CONTRACEPTION
 PREVENTING PREGNANCY: TALKING ABOUT AND USING CONTRACEPTION Lesson 11 DIFFERING ABILITIES LEARNER OUTCOME Identify and describe basic types of contraceptives; i.e., abstinence, condom, foam, birth control
PREVENTING PREGNANCY: TALKING ABOUT AND USING CONTRACEPTION Lesson 11 DIFFERING ABILITIES LEARNER OUTCOME Identify and describe basic types of contraceptives; i.e., abstinence, condom, foam, birth control
Sexual Q & A Game - Birth Control cards - From 5 to 100 Points
 Lesson Eight Sexual Q & A Game - Birth Control cards - From 5 to 100 Points Sexual Jeopardy Birth Control for 10 Points The only 100% effective method for preventing pregnancy and STIs Sexual Jeopardy
Lesson Eight Sexual Q & A Game - Birth Control cards - From 5 to 100 Points Sexual Jeopardy Birth Control for 10 Points The only 100% effective method for preventing pregnancy and STIs Sexual Jeopardy
A Teacher s Guide Sexually
 sue 3. Grades 9-12 : Issue 3. milk. ed every year. ow stopthesilence TeenZine ol, even once, can Grades 9-12 : Issue 3. men who don't use me pregnant. s. chlamydia.,ghest can among 15 to Contraceptives
sue 3. Grades 9-12 : Issue 3. milk. ed every year. ow stopthesilence TeenZine ol, even once, can Grades 9-12 : Issue 3. men who don't use me pregnant. s. chlamydia.,ghest can among 15 to Contraceptives
ANALYZING CONTRACEPTION OPTIONS
 ANALYZING CONTRACEPTION OPTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to identify and categorize the various forms of contraception and discuss influences on, and reasons why, students may
ANALYZING CONTRACEPTION OPTIONS LESSON INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lesson is to identify and categorize the various forms of contraception and discuss influences on, and reasons why, students may
Birth Control -- Especially for Teens
 AP112, June 2011 Birth Control -- Especially for Teens Making the decision whether to have sex can be difficult. You should make up your own mind when the time is right for you. If you are not ready for
AP112, June 2011 Birth Control -- Especially for Teens Making the decision whether to have sex can be difficult. You should make up your own mind when the time is right for you. If you are not ready for
CHAPTER 4 REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH POINTS TO REMEMBER
 CHAPTER 4 REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH POINTS TO REMEMBER Amniocentesis : Diagnostic technique to detect genetic disorder in the foetus. Infertility : Inability to produce children in spite of unprotected sexual
CHAPTER 4 REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH POINTS TO REMEMBER Amniocentesis : Diagnostic technique to detect genetic disorder in the foetus. Infertility : Inability to produce children in spite of unprotected sexual
Sexual Health: 101 Sexual Health 101
 Sexual Health 101 An IC student s guide to birth control, STD s, sexuality, and relationships. Healthy relationships can be tricky to find, but don t give up! There are many genuine, caring people out
Sexual Health 101 An IC student s guide to birth control, STD s, sexuality, and relationships. Healthy relationships can be tricky to find, but don t give up! There are many genuine, caring people out
HEALTH GRADE 11. THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618
 HEALTH GRADE 11 THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618 Board Approval Date: August 29, 2016 Michael Nitti Written by: Bud Kowal and EHS Staff Superintendent In accordance with The
HEALTH GRADE 11 THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618 Board Approval Date: August 29, 2016 Michael Nitti Written by: Bud Kowal and EHS Staff Superintendent In accordance with The
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Family Planning and Infertility
 Family Planning and Infertility Chapter 20 Objectives Discuss types of reversible contraception Natural methods Mechanical barrier methods Hormonal contraceptives Discuss types of permanent contraception
Family Planning and Infertility Chapter 20 Objectives Discuss types of reversible contraception Natural methods Mechanical barrier methods Hormonal contraceptives Discuss types of permanent contraception
Who s The Daddy? What You Should Know About OTC Contraception
 Who s The Daddy? What You Should Know About OTC Contraception By: Vona Broughton, BS Public Health & Kevin McCarthy, RPH This program has been brought to you by PharmCon PharmCon is accredited by the accreditation
Who s The Daddy? What You Should Know About OTC Contraception By: Vona Broughton, BS Public Health & Kevin McCarthy, RPH This program has been brought to you by PharmCon PharmCon is accredited by the accreditation
Contraception for Adolescents: What s New?
 Contraception for Adolescents: What s New? US Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use Kathryn M. Curtis, PhD Division of Reproductive Health, CDC Expanding Our Experience and Expertise: Implementing
Contraception for Adolescents: What s New? US Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use Kathryn M. Curtis, PhD Division of Reproductive Health, CDC Expanding Our Experience and Expertise: Implementing
VASECTOMY INFORMATION AND CONSENT
 VASECTOMY INFORMATION AND CONSENT This information will help you understand more about the vasectomy: the indications for this procedure, the success and failure rates, the alternative forms of contraception,
VASECTOMY INFORMATION AND CONSENT This information will help you understand more about the vasectomy: the indications for this procedure, the success and failure rates, the alternative forms of contraception,
Transcervical Sterilization
 Q UESTIONS & ANSWERS A BOUT Transcervical Sterilization A New Choice in Permanent Birth Control Choosing a Birth Control Method Women and their partners now have more birth control choices than ever. How
Q UESTIONS & ANSWERS A BOUT Transcervical Sterilization A New Choice in Permanent Birth Control Choosing a Birth Control Method Women and their partners now have more birth control choices than ever. How
Reproductive Systems. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that s best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that s put
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that s best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that s put
Biology of fertility control. Higher Human Biology
 Biology of fertility control Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Compare fertile periods in females and males What is infertility? Infertility is the inability of a sexually active, non-contracepting
Biology of fertility control Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Compare fertile periods in females and males What is infertility? Infertility is the inability of a sexually active, non-contracepting
Human Reproduction. Human Reproductive System. Scrotum. Male Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Unintended Pregnancy is Common LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Distribution Of Contraception Use By Women In The Us. Unintended Pregnancy And Contraceptive Use
 3:45 4:30 pm Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraceptives and IUDs Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD: No financial
3:45 4:30 pm Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraceptives and IUDs Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD: No financial
16 East 40 th St, 2 nd Fl, New York, NY Ph fax
 Page 1 of 9 16 East 40 th St, 2 nd Fl, New York, NY 10016 Ph 212-679-2289 fax 212-679-2288 Please complete the following: Fertility Evaluation Name: Date of birth: Age: Partner s Name: Date of birth: Age:
Page 1 of 9 16 East 40 th St, 2 nd Fl, New York, NY 10016 Ph 212-679-2289 fax 212-679-2288 Please complete the following: Fertility Evaluation Name: Date of birth: Age: Partner s Name: Date of birth: Age:
Chapter 8: How do Organisms Reproduce? 1 What is the primary importance of DNA copying in reproduction? SOLUTION:
 Chapter 8: How do Organisms Reproduce? 1 What is the primary importance of DNA copying in reproduction? DNA copying in reproduction is important for maintenance of body designs and features. It is also
Chapter 8: How do Organisms Reproduce? 1 What is the primary importance of DNA copying in reproduction? DNA copying in reproduction is important for maintenance of body designs and features. It is also
LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraception. Distribution Of Contraception Use By Women In The Us. Unintended Pregnancy is Common
 4:15 5 pm Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraceptives and IUDs Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD: No financial
4:15 5 pm Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraceptives and IUDs Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD: No financial
Human Reproductive Anatomy The female anatomy first just the reproductive parts:
 Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
الحمد هلل رب العالمين والصالة والسالم علي محمد الصادق الوعد األمين اللهم أخرجنا من ظلمات الجهل والوهم إلى نور المعرفة والعلم..
 الحمد هلل رب العالمين والصالة والسالم علي محمد الصادق الوعد األمين اللهم أخرجنا من ظلمات الجهل والوهم إلى نور المعرفة والعلم.. سيدنا 11/6/2013 1 Goals of Family Planning services : 1- Enable women and
الحمد هلل رب العالمين والصالة والسالم علي محمد الصادق الوعد األمين اللهم أخرجنا من ظلمات الجهل والوهم إلى نور المعرفة والعلم.. سيدنا 11/6/2013 1 Goals of Family Planning services : 1- Enable women and
Effective Contraception Utilization. Sarah Laiosa, DO Family Physician Contract Medical Director, EOCCO
 Effective Contraception Utilization Sarah Laiosa, DO Family Physician Contract Medical Director, EOCCO Disclosures Contract Medical Director, EOCCO Objectives Illustrate how to best address contraception
Effective Contraception Utilization Sarah Laiosa, DO Family Physician Contract Medical Director, EOCCO Disclosures Contract Medical Director, EOCCO Objectives Illustrate how to best address contraception
Family Planning د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد
 Family Planning د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد Objectives:- To know the different types of contraception To know the failure rate & mechansim of action of each type To explain
Family Planning د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد Objectives:- To know the different types of contraception To know the failure rate & mechansim of action of each type To explain
For more information: FMU Student Health Center Your personal physician
 CH. 20 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs For more information: www.plannedparenthood.org/health-info/birth-control FMU Student Health Center Your personal physician FMU's Student
CH. 20 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs For more information: www.plannedparenthood.org/health-info/birth-control FMU Student Health Center Your personal physician FMU's Student
Family Planning UNMET NEED. The Nurse Mildred Radio Talk Shows
 Family Planning UNMET NEED The Nurse Mildred Radio Talk Shows TOPIC 9: IUD/COIL Guests FP counsellor from MSU, RHU& UHMG Nurse Mildred Nurse Betty Objectives of the programme: To inform listeners about
Family Planning UNMET NEED The Nurse Mildred Radio Talk Shows TOPIC 9: IUD/COIL Guests FP counsellor from MSU, RHU& UHMG Nurse Mildred Nurse Betty Objectives of the programme: To inform listeners about
NON-HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HISTORY o Ebers Papyrus (1550 BC) o Pliny the Elder (23-79
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HISTORY o Ebers Papyrus (1550 BC) o Pliny the Elder (23-79
If you are sexually active, desire birth control or have other concerns, you should schedule a women s health h visit.
 If you are sexually active, desire birth control or have other concerns, you should schedule a women s health h visit. i Your appointment should not be made during your period. You should not have unprotected
If you are sexually active, desire birth control or have other concerns, you should schedule a women s health h visit. i Your appointment should not be made during your period. You should not have unprotected
POLICY & PROCEDURE DEFINITIONS: N/A POLICY:
 POLICY & PROCEDURE TITLE: Fertility Regulation Family Planning Scope/Purpose: To offer a wide range of approved methods for Family Planning services Division/Department: : All HealthPoint Clinics Policy/Procedure
POLICY & PROCEDURE TITLE: Fertility Regulation Family Planning Scope/Purpose: To offer a wide range of approved methods for Family Planning services Division/Department: : All HealthPoint Clinics Policy/Procedure
Our Moment of Truth 2013 Survey Women s Health Care Experiences & Perceptions: Spotlight on Family Planning & Contraception
 Our Moment of Truth 2013 Survey Women s Health Care Experiences & Perceptions: Spotlight on Family Planning & Contraception Thank you for taking part in this survey. We know your time is valuable. Through
Our Moment of Truth 2013 Survey Women s Health Care Experiences & Perceptions: Spotlight on Family Planning & Contraception Thank you for taking part in this survey. We know your time is valuable. Through
For more information: FMU Student Health Center Your personal physician
 CH. 20 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs For more information: www.plannedparenthood.org/health-info/birth-control FMU Student Health Center Your personal physician FMU's Student
CH. 20 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs For more information: www.plannedparenthood.org/health-info/birth-control FMU Student Health Center Your personal physician FMU's Student
Choices TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Choices TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE ABSTINENCE...1-2 OUTERCOURSE... 3 WITHDRAWAL... 4 CONDOMS: Male...5-7 CONDOMS: Female... 8 DUAL METHODS/FERTILITY AWARENESS METHODS... 9 BREASTFEEDING... 10 SPERMICIDES (Film,
Choices TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE ABSTINENCE...1-2 OUTERCOURSE... 3 WITHDRAWAL... 4 CONDOMS: Male...5-7 CONDOMS: Female... 8 DUAL METHODS/FERTILITY AWARENESS METHODS... 9 BREASTFEEDING... 10 SPERMICIDES (Film,
For more information: FMU Student Health Center Your personal physician
 CH. 20 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs For more information: www.plannedparenthood.org/health-info/birth-control FMU Student Health Center Your personal physician FMU's Student
CH. 20 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs For more information: www.plannedparenthood.org/health-info/birth-control FMU Student Health Center Your personal physician FMU's Student
Healthy Boys POWERFUL BOYS
 Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
LARC. sample. ask brook about. Are any of them right for me? How effective is it? How long does it last? long acting reversible contraception
 72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09 11:47 Page 1 Are any of them right for me? ask brook about LARC How effective is it? long acting reversible contraception How long does it last? 72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09
72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09 11:47 Page 1 Are any of them right for me? ask brook about LARC How effective is it? long acting reversible contraception How long does it last? 72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09
Emergency Contraception THE FACTS
 Emergency Contraception Quick Facts What is it? Emergency contraception is birth control that you use after you have had unprotected sex--if you didn t use birth control or your regular birth control failed.
Emergency Contraception Quick Facts What is it? Emergency contraception is birth control that you use after you have had unprotected sex--if you didn t use birth control or your regular birth control failed.
Vaginitis. Antibiotics Changes in hormone levels due to pregnancy, breastfeeding, or menopause Douching Spermicides Sexual intercourse Infection
 WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Vaginitis Vaginitis is an inflammation of a woman s vagina. It is one of the most common reasons why women see their health care providers.
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Vaginitis Vaginitis is an inflammation of a woman s vagina. It is one of the most common reasons why women see their health care providers.
Reproduction Notes. iii. LH stimulates the interstitial cells of testes to produce testosterone c. testes
 I. Asexual Reproduction a a single parent endows its offspring with a set of genes identical to its own (except for mutations) A. Forms 1. Budding a. a part of the parent's body grows and separates from
I. Asexual Reproduction a a single parent endows its offspring with a set of genes identical to its own (except for mutations) A. Forms 1. Budding a. a part of the parent's body grows and separates from
CONSENT TO STERILIZATION OPERATION (SURGICAL VASECTOMY)
 CONSENT TO STERILIZATION OPERATION (SURGICAL VASECTOMY) I (Patient s Name) have been given the following information: Explanation of Sterilization: Vasectomy is a minor surgical procedure that can be performed
CONSENT TO STERILIZATION OPERATION (SURGICAL VASECTOMY) I (Patient s Name) have been given the following information: Explanation of Sterilization: Vasectomy is a minor surgical procedure that can be performed
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system)
 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) Mirena does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) Mirena does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
 24 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 4 REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The method of directly injecting a sperm into ovum in Assisted Reproductive Technology is called: a. GIFT b. ZIFT
24 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 4 REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The method of directly injecting a sperm into ovum in Assisted Reproductive Technology is called: a. GIFT b. ZIFT
Study Guide. Biology 3101B. Science. Reproduction and Development. Adult Basic Education. Biology 2101A Biology 2101C Biology 3101A.
 Adult Basic Education Science Reproduction and Development Prerequisites: Biology 2101A Biology 2101C Biology 3101A Credit Value: 1 Text: Biology. Bullard, Chetty, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2003 Biology
Adult Basic Education Science Reproduction and Development Prerequisites: Biology 2101A Biology 2101C Biology 3101A Credit Value: 1 Text: Biology. Bullard, Chetty, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson, 2003 Biology
1. What is your date of birth? Month Day Year
 Participant ID # Today's Date 1. What is your date of birth? Month Day Year 2. How would you describe your race / ethnicity? African American / Black European American / White Hispanic Asian Native American
Participant ID # Today's Date 1. What is your date of birth? Month Day Year 2. How would you describe your race / ethnicity? African American / Black European American / White Hispanic Asian Native American
9p1 Identify the factors that contribute to positive relationships with others. 9p6 Describe the factors that lead to responsible sexual relationships
 Lesson Eight Title: Theme: Time: Materials: Wrapping up the Sexual Health Unit The 60 minutes * Sexuality Review-Quiz * Sexuality Review-Answer Sheet * Sexual Q & A -Laminated Game Cards * Sexual Q & A
Lesson Eight Title: Theme: Time: Materials: Wrapping up the Sexual Health Unit The 60 minutes * Sexuality Review-Quiz * Sexuality Review-Answer Sheet * Sexual Q & A -Laminated Game Cards * Sexual Q & A
The Science Behind Natural Family Planning
 The Science Behind Natural Family Planning Presented by Scott & Laura Schulze Pro-Life Symposium & Technology Symposium Saturday, September 20, 2008 Dayton Engineers Club Dayton, OH Definition of NFP Crash
The Science Behind Natural Family Planning Presented by Scott & Laura Schulze Pro-Life Symposium & Technology Symposium Saturday, September 20, 2008 Dayton Engineers Club Dayton, OH Definition of NFP Crash
Contraceptive Technology and Reproductive Health Series: Barrier Methods Post-test
 Contraceptive Technology and Reproductive Health Series: Barrier Methods Post-test Section I: Overview of Barrier Methods 1. The following are statements regarding all barrier methods. Please indicate
Contraceptive Technology and Reproductive Health Series: Barrier Methods Post-test Section I: Overview of Barrier Methods 1. The following are statements regarding all barrier methods. Please indicate
Types of Reproduction
 Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. It ensures continuity of life on earth. Nucleus of the cell contains DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid)
Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. It ensures continuity of life on earth. Nucleus of the cell contains DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid)
2/4/2011. What is your specialty? A. Family practice B. Internal medicine and subs C. OB/GYN D. Peds E. Surgery and subs
 Steve P. Buchanan D.O. FACOOG(Dist.) TOMA Mid Winter February 11, 2011 Dallas,TX Associate Professor OB/GYN UNTHSC/TCOM 1987- present Executive Vice President, American College of Osteopathic Obstetricians
Steve P. Buchanan D.O. FACOOG(Dist.) TOMA Mid Winter February 11, 2011 Dallas,TX Associate Professor OB/GYN UNTHSC/TCOM 1987- present Executive Vice President, American College of Osteopathic Obstetricians
The beginning of puberty is marked by the progressive increase in the production of sex hormones.
 Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Global Contraception
 Video Companion Guide Global Contraception Learning Objectives: By the end of the session, learners will be able to: Describe of all contraceptive methods. Develop a basic understanding of patient-centered
Video Companion Guide Global Contraception Learning Objectives: By the end of the session, learners will be able to: Describe of all contraceptive methods. Develop a basic understanding of patient-centered
Biology Homework Chapter 6: Continuity Through Reproduction Pages Answer the questions with complete thoughts!
 Name Biology Homework Chapter 6: Continuity Through Reproduction Pages 143-158 Answer the questions with complete thoughts! Per. * Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Reproduction, Read pages 143 to 146 PART A: Define
Name Biology Homework Chapter 6: Continuity Through Reproduction Pages 143-158 Answer the questions with complete thoughts! Per. * Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Reproduction, Read pages 143 to 146 PART A: Define
The reproductive system
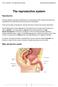 The reproductive system Reproduction All living organisms reproduce. Reproduction is the process by which organisms generate new individuals of the same kind ensuring continuation of the species. There
The reproductive system Reproduction All living organisms reproduce. Reproduction is the process by which organisms generate new individuals of the same kind ensuring continuation of the species. There
Special Parts: Gender. Why Have Sex?
 Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
Why Have Sex? Lots of animals clone themselves... 100% of their genes are passed on! Sex requires sharing, it s expensive (time, mate selection, special parts, prenuptial gifts...) So why do it? Special
Thinking about the fact that your bodies are maturing -
 Puberty Review Your bodies are rapidly changing, once puberty starts you are on your way to being an adult physically It takes your brain longer to mature, sometimes until age 25 or later Protecting your
Puberty Review Your bodies are rapidly changing, once puberty starts you are on your way to being an adult physically It takes your brain longer to mature, sometimes until age 25 or later Protecting your
CONTRACEPTION OLD FRIENDS, NEW TRENDS
 CONTRACEPTION OLD FRIENDS, NEW TRENDS AAP RECOMMENDATIONS 2014 1. Council about and ensure access to all contraceptive methods safe and appropriate describing most effective first. PEDIATRICS 134 (4)
CONTRACEPTION OLD FRIENDS, NEW TRENDS AAP RECOMMENDATIONS 2014 1. Council about and ensure access to all contraceptive methods safe and appropriate describing most effective first. PEDIATRICS 134 (4)
Taking Care of Your Sexual Health
 Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Intrauterine Insemination - FAQs Q. How Does Pregnancy Occur?
 Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Intrauterine Insemination - FAQs Q. How Does Pregnancy Occur? A. The female reproductive system involves the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix and vagina. The female hormones,
Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Intrauterine Insemination - FAQs Q. How Does Pregnancy Occur? A. The female reproductive system involves the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix and vagina. The female hormones,
What You Need to Know. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
 What You Need to Know Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) What You Need to Know About STIs What are STIs? Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are diseases that spread through sexual contact. If you
What You Need to Know Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) What You Need to Know About STIs What are STIs? Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are diseases that spread through sexual contact. If you
Family Planning Eligibility Program
 INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER REFERENCE M ODULE Family Planning Eligibility Program L I B R A R Y R E F E R E N C E N U M B E R : P R O M O D 0 0 0 5 3 P U B L I S H E D : N O V E M B E R 2
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER REFERENCE M ODULE Family Planning Eligibility Program L I B R A R Y R E F E R E N C E N U M B E R : P R O M O D 0 0 0 5 3 P U B L I S H E D : N O V E M B E R 2
F REQUENTLY A SKED Q UESTIONS. fallopian tube instead of the uterus), constant pelvic pain, and other problems.
 PID can be treated and cured with Pelvic antibiotics. If left untreated, PID can lead to serious problems like infertility (not being able to get pregnant), ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy in the Inflammatory
PID can be treated and cured with Pelvic antibiotics. If left untreated, PID can lead to serious problems like infertility (not being able to get pregnant), ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy in the Inflammatory
BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS. Patient Information Leaflet. Your Health. Our Priority. Microbiology Pathology Department.
 BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS Patient Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 Bacterial vaginosis What causes bacterial vaginosis? The cause of bacterial vaginosis sometimes called BV is not really
BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS Patient Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 5 Bacterial vaginosis What causes bacterial vaginosis? The cause of bacterial vaginosis sometimes called BV is not really
The reproductive system
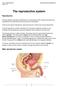 Unit 4. Reproduction (2016-17) Natural Science Department The reproductive system Reproduction All living organisms reproduce. Reproduction is the process by which organisms generate new individuals of
Unit 4. Reproduction (2016-17) Natural Science Department The reproductive system Reproduction All living organisms reproduce. Reproduction is the process by which organisms generate new individuals of
Questionnaire for Women
 Questionnaire for Women General Information Name Date Address Telephone Home _Work _ Cell Birth date Age _ Occupation Ethnic Background _ Height _ Weight _ Highest Education _ Partner s Name Marriage date
Questionnaire for Women General Information Name Date Address Telephone Home _Work _ Cell Birth date Age _ Occupation Ethnic Background _ Height _ Weight _ Highest Education _ Partner s Name Marriage date
Family Planning and Sexually Transmitted. Infections, including HIV
 Infections, including HIV Family Planning and Sexually Transmitted Introduction To protect themselves, people need correct information about sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including HIV. Women
Infections, including HIV Family Planning and Sexually Transmitted Introduction To protect themselves, people need correct information about sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including HIV. Women
Condoms: Condoms are thin latex caps that cover a man s penis during sex. If you are thinking about using condoms, think about this:
 Vocabulary words The Basics of Birth Control Methods STD Abstinence Penis Vagina Spermicide Birth Control Pills The Shot F O R Y O U R H E A L T H Have you ever heard your friends say: I cannot get pregnant
Vocabulary words The Basics of Birth Control Methods STD Abstinence Penis Vagina Spermicide Birth Control Pills The Shot F O R Y O U R H E A L T H Have you ever heard your friends say: I cannot get pregnant
Click to edit Master title style. Unintended Pregnancy: Prevalence. Unintended Pregnancy: Risk Groups. Unintended Pregnancy: Consequences 9/23/2015
 The Role of Childhood Violence, Self-esteem and Depressive Symptoms on Inconsistent Contraception Use among Young, Sexually Active Women Deborah B. Nelson, PhD Associate Professor Unintended Pregnancy:
The Role of Childhood Violence, Self-esteem and Depressive Symptoms on Inconsistent Contraception Use among Young, Sexually Active Women Deborah B. Nelson, PhD Associate Professor Unintended Pregnancy:
Score 1 for each correct part identified. [Max 8]
![Score 1 for each correct part identified. [Max 8] Score 1 for each correct part identified. [Max 8]](/thumbs/88/117203219.jpg) General Sexual knowledge Questionnaire This questionnaire looks at your understanding of sex and sex related topics. Some of the questions are quite difficult, and you are not expected to know all the
General Sexual knowledge Questionnaire This questionnaire looks at your understanding of sex and sex related topics. Some of the questions are quite difficult, and you are not expected to know all the
New Patient Medical History
 New Patient Medical History MR #: Initial Appointment Date: / / Name: Birth Date: / / Address: City: State: Zip: Best Phone # to reach you: ( ) Second contact #: ( ) Email Address: Occupation: Marital
New Patient Medical History MR #: Initial Appointment Date: / / Name: Birth Date: / / Address: City: State: Zip: Best Phone # to reach you: ( ) Second contact #: ( ) Email Address: Occupation: Marital
Preventive Care Coverage
 Preventive Care Coverage Benefits designed to protect your health BridgeSpanHealth.com Review Coverage» To find out if you re eligible for preventive coverage, call the Member Services number on the back
Preventive Care Coverage Benefits designed to protect your health BridgeSpanHealth.com Review Coverage» To find out if you re eligible for preventive coverage, call the Member Services number on the back
Web Activity: Simulation Structures of the Female Reproductive System
 differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
