Eco-friendly modules for management of fruit fly, B. cucurbitae infesting sponge gourd
|
|
|
- Horace Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2018; 6(2): P-ISSN: E-ISSN: IJCS 2018; 6(2): IJCS Received: Accepted: AM Bharadiya JB Bhut MV Variya Correspondence AM Bharadiya Eco-friendly modules for management of fruit fly, B. cucurbitae infesting sponge gourd AM Bharadiya, JB Bhut and MV Variya Abstract The experiment on Eco-friendly modules for management of fruit fly, B. cucurbitae infesting sponge gourd was carried out during consecutive two years kharif and at Agronomy Farm, Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh. The four eco-friendly modules were evaluated against the fruit fly, B. cucurbitae infesting sponge gourd for two years. The module-3 [destruction of infested fruits during each picking + poison 50 l/ha (jaggery 50 g/l + abamectin 1.9% EC %) + application of Azadirechtin 0.003% at 15 days interval starting from flower ]and module-2[destruction of infested fruits during each picking + poison 50 l/ha (jaggery 50 g/l + abamectin 1.9% EC %)] were found most effective and economic and were statistically at par with each other. In the module-3 significantly minimum fruit infestation per cent with maximum yield increased per cent and net return Rs /ha was recorded. While in module-2, per cent fruit infestation with per cent yield increased and Rs /ha net return was recorded. Keywords: eco-friendly module, management, fruit fly, Bactrocera cucurbitae, sponge gourd Introduction Cucurbits, a common name given to a number of vegetable crops belonging to botanical family cucurbitaceae which mostly possess trailing habit, are extensively grown all over the tropical and sub-tropical countries and include the largest number of summer and rainy season vegetables. Among the cucurbitaceous vegetables, sponge gourd (L. cylindrica) has its own importance as a human food. Sponge gourd is known by different names such as loofah, vegetable sponge, bath sponge or dish cloth gourd and Gujarati farmers called it Galaka. In Gujarat and gourd vegetables are cultivated in area of 0.61 and 1.66 lakh ha with production of 9.27 and m tones respectively (DOAC, 2012) [6]. Such an important crop is found to be attacked by various insect pests during its different growth stages. These include melon fruit fly (Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coq.)), aphids (Aphis gossypii Glower), white fly (Bemisia tabaci Gennadius), leaf miner (Liriomyza trifolii Burgess), jassid (Amrasca biguttula biguttula Ishida) and pumpkin beetles (Raphidopalpa foveicollis Lucas) that causes varying degrees of damage to the crop. Among these, melon fruit fly is a serious pest and was first described by Coquillett (1899) as Dacus cucurbitae on cucurbit from Hawaii. Later on, it was reported from different parts of the world, viz.; Australia, Mayanmar, China, East Africa, Taiwan, Hawaii, Malaysia, Nepal, Pakistan, Phillippines and Sri Lanka (Narayanan and Batra, 1960) [11]. In, the incidence of the melon fly was first reported by Lefroy (1907) [8] on cucurbits. Melon fruit fly, B. cucurbitae damages over 81 plant species, but plants belonging to the family cucurbitaceae are most preferred hosts (Allwood et al., 1999) [1]. Depending on the environmental conditions and susceptibility of the crop species, the extent of losses varies between 30 to 100 per cent (Pareek and Kavadia, 1994; Dhillon et al., 2005; Shooker et al., 2006) [12, 5, 15, 13]. This pest is reported to cause 80 per cent infestation in cucumber and bottle gourd, 60 per cent in bitter gourd and 50 per cent in sponge gourd (Gupta and Verma, 1992) [7]. For controlling this pest, spray schedules of synthetic insecticides are mostly calendar based with little consideration of detrimental effects like the problems of toxic pesticides residue in fruits, development of insecticidal resistance in pest, disruption of natural balance, biomagnifications and high cost of pesticides involved. In sponge gourd eco-system, it is time, the scientific information for devising and formulating eco-friendly measures against this pest. Hence, the present investigation was carried on eco-friendly module for management of fruit fly, Bactrocera cucurbitae on sponge gourd. ~ 3522 ~
2 Materials and Methods It is necessary to evaluate the various components of integrated pest management (IPM) individually as well as in combination for framing IPM strategy of a pest. For the effective and economical management of fruit fly, B. cucurbitae, various eco-friendly modules were evaluated to find out their bio efficacy against fruit fly infesting sponge gourd. Experiments were conducted during two consecutive year kharif and kharif. All the recommended agronomical practices were followed to raise good crop. The experimental details are given below: 1. Objective: Eco-friendly modules for management of fruit fly, B. cucurbitae 2. Location and Agro climatic Zone: Instructional Farm, JAU, Junagadh South Saurashtra Agro climatic Zone 3. Season and Year: Kharif and Kharif 4. Crop and Variety: Crop: Sponge gourd; Variety: Pusa Chickni 5. s (treatment) Details: Five different modules as under 1 (M1): Mass trapping of adult fruit fly using cue lure traps (Sawaj fruit fly 30/ha + destruction of infested fruits during each picking 2 (M2): Destruction of infested fruits during each picking + poison 50 l/ha (jaggery 50 g/l + abamectin 1.9% EC %) 3 (M3): M2 + application of Azadirechtin 0.003% at 15 days interval starting from flower 4 (M4): M2 + application of NSKE 5% at 15 days interval starting from flower 5 (M5): Control (water spray) 6. Experimental Design: Randomized block design 7. Replication: Four 8. Plot size: 8.0 m x 5.0 m 9. Spacing: 2.0 m x 1.0 m (row to row and plant to plant) Method for recording observations Adequate distance between two plots was maintained. The sponge gourd plot allotted to module-1 was kept 50 m away from the rest of the modules. The poison bait was prepared by mixing jaggery 50 g per cent (1.3 ml) in a litre of water. The spot application of poison bait was made with the help of broom. Total 50 litre of poison bait required for one hectare application. The first application of poison bait, Azadirechtin 0.003% and NSKE 5% was made at the time of flower and subsequent three applications were made at 15 days intervals. The observations on number of infested fruits and healthy fruits from five randomly selected and tagged plants as well as number of maggots per infested fruits were recorded during fruit picking at 4 to 5 days intervals and continue still last picking (maturity of crop). The fruits which were premature and dropped due to infestation of fruit fly were also considered in the observations. With a view to evaluate the effect of different eco-friendly modules on the yield of sponge gourd, the fruit yield per plot was recorded from each module and per cent increase in yield over control as well as net cost benefit ratio (NCBR) was also calculated. Results and Discussion Fruit infestation The fruit infestation due to fruit fly, B. cucurbitae showed significant difference among the modules. Significantly the lowest per cent fruit infestation was found in module-3; however, it was statistically at par with the fruit infestation per cent in module-2 and per cent in module-4. The fruit fly infestation per cent recorded in module-1 was significantly superior over module-5 (control) but was significantly inferior to module-3, module-2 and module-4. The significantly maximum fruit infestation per cent was recorded in module-5 (control) during first year (kharif ) of experimentation (Table 1). The data given in Table 1 revealed that more or less similar trend of efficacy of different modules against fruit fly was observed in second year of experimentation (kharif ). Significantly the lowest per cent fruit infestation was found in module-3; however, it was statistically at par with the fruit infestation per cent in module-2 and per cent in module-4. The fruit fly infestation per cent recorded in module-1 was significantly superior over module- 5 (control) but was significantly inferior to module-3, module-2 and module-4. The significantly maximum fruit infestation per cent was recorded in module-5 (control). Average of two years (pooled) data on fruit infestation recorded in the different eco-friendly modules are presented in Table 1. The data revealed that significantly the lowest per cent fruit infestation was found in module-3; however, it was statistically at par with the fruit infestation per cent in module-2. The fruit fly infestation per cent recorded in module-4 and per cent in module-1 was significantly superior over module-5 (control) but was significantly inferior to module-3 and module-2. The significantly maximum fruit infestation per cent was recorded in module-5 (control). Maggot population The data presented in Table 1 on maggot population in infested fruits due to fruit fly showed significant difference among the modules. Significantly the lowest 2.66 maggots per fruit were found in module-3 and it was statistically at par with module-2 in which 3.68 maggots per fruit was recorded. The maggot population in the -4 and module-1 was recorded as 4.21 and 4.48 maggots per fruit, respectively and was significantly lower over module-5 (control). The maximum maggot population 6.47 was recorded in module-5 (control) during kharif. The data presented in Table 1 on maggot population in infested fruits due to fruit fly showed that more or less similar trend of efficacy of different modules was observed in second year of experimentation (kharif ). Significantly the lowest 2.85 maggots per fruit were found in module-3 and it was statistically at par with module-2 in which 3.62 maggots ~ 3523 ~
3 per fruit was recorded. The maggot population in the module- 4 and module-1 was recorded as 4.38 and maggots per fruit, respectively and was significantly lower over module-5 (control). The maximum maggot population 6.82 was recorded in module-5 (control) during kharif. The pooled data of two different years ( and ) are given in Table 1 on maggot population in different modules. The data revealed that the maggot population 2.75 per fruit recorded in module-3 was significantly lower over all the modules applied. The maggot population per fruit 3.65 and 4.30 was recorded in module-2 and module-4 which was significantly superior over module-5 (control) but was inferior to module-3. However, the maggot population per fruit 4.68 was recorded in module-1 was significantly superior over module-5 (control) but was inferior to module-3 and module- 2 and was statistically at par with module-4. The maximum maggot population 6.64 was recorded in module-5 (control). From the above results, it can be concluded that module-3 was found relatively effective against fruit fly, B. cucurbitae infesting sponge gourd by recording significantly minimum fruit infestation and harbour lower number of pests per fruit. Further, it was found that module-2 was found comparatively effective against fruit fly by recording lower fruit infestation as well as lower number of pests per fruit over rest of the modules. In contrast to this, module-4 and module-1 has no any effect on incidence of fruit fly as they recorded higher amount of fruit infestation to per cent by the fruit fly and also having higher population of maggots per fruit (Table 1). Yield The yield of sponge gourd fruits during kharif in different modules was recorded significantly higher over control (Table 2). The sponge gourd yield 6213 kg/h (43.23% increased over module-5) was received from module-3 treated crop was significantly highest and was at par with the yield 5900 kg/ha (36.02% increased over module-5) from module-2 and 5375 kg/ha (23.92% increased over module-5) from module-4. The sponge gourd yield 5225 kg/ha (20.46% increased over module-5) received from module-1 was significantly higher over module-5 (control) but was lower than yield from module-3, module-2 and module-4. The minimum yield 4338 kg/ha was received from module-5 (control) which was significantly lower over yield from all the modules. The yield of sponge gourd fruits during kharif in different modules was recorded significantly higher over control. The sponge gourd yield 6288 kg/ha (46.22% increased over module-5) was received from module-3 treated crop was significantly highest and was at par with the yield 6038 kg/ha (40.41% increased over module-5) from module- 2. The sponge gourd yield 5463 kg/ha (27.03% increased over module-5) received from module-4 and 5375 kg/ha (25.00% increased over module-5) received from module-1 were at par with each other and was significantly higher over module-5 (control) but was lower than yield from module-3 and module -2. The minimum yield 4300 kg/ha was received from module-5 (control) which was significantly lower over yield from all the modules (Table 2). The pooled data given in Table 2 revealed that the sponge gourd yield 6250 kg/h (44.72% increased over module-5) was received from module-3 treated crop was significantly highest and was at par with the yield 5969 kg/ha (38.21% increased over module-5) from module-2. The sponge gourd yield 5419 kg/ha (25.47% increased over module-5) received from module-4 and 5300 kg/ha (22.72% increased over module-5) received from module-1 were at par with each other and was significantly higher over module-5 (control) but was lower than yield from module-3 and module-2. The minimum yield 4319 kg/ha was received from module-5 (control) which was significantly lower over yield from all the modules. Looking to the pooled data of two years (Table 1) on fruits yield of sponge gourd, it can be concluded that the module-3 and module-2 were found relatively effective against fruit fly infesting sponge gourd as they harvest significantly higher yield over rest of the modules. In contrast to this module-4 and module-1 has no any effect on incidence of fruit fly as they recorded significantly lower yield over module-3 and module-2. Economics of different eco-friendly modules The data on economics of the different eco-friendly modules applied against the melon fruit fly, B. cucurbitae was worked out along with net cost benefit ratio (NCBR) are present in Table 3. The data revealed that the gross income of Rs /ha was highest from the module-3 [destruction of infested fruits during each picking + poison 50 l/ha (jaggery 50 g/lit + abamectin 1.9% EC %) + Azadirechtin 0.003%], followed by Rs /ha from module-2 [destruction of infested fruits during each picking + poison 50 l/ha (jaggery 50g/lit + abamectin 1.9% EC %)]. Gross income of Rs /ha was obtained from module-4 [destruction of infested fruits during each picking + poison 50 l/ha (jaggery 50 g/lit + abamectin 1.9% EC %) + NSKE 5%] and Rs /ha from module-1 (mass trapping of adult fruit fly using cue lure 30/ha + destruction of infested fruits during each picking). Minimum gross income Rs /ha was received from control (module-5). The maximum net monitory benefit of Rs /ha was obtained from the module-3, followed by Rs /ha from module-2. The module-4 and module-1 gave relatively lower net monitory benefit of Rs /ha and Rs /ha, respectively. Looking to net cost benefit ratio (NCBR), module-2 stood first with 1:29.75 NCBR. The order of NCBR of rest of the module was module-4, 1:10.11, module-1, 1:5.45 and module-3, 1:5.05. The data given in Table 1, 2 and 3 clearly showed that the eco-friendly module-3 applied in sponge gourd was most effective and economic with the significantly lowest per cent fruit infestation, per cent higher yield (6250 kg/ha) and maximum Rs /ha net monitory return. The fruit infestation (17.16%), yield increased (38.21%) and net return Rs /ha from module-2 was statistically at par with module-3. The eco-friendly module-3 was consisted with destruction of infested fruits during each picking + poison 50 l/ha (jaggery 50 g/l + abamectin 1.9% EC %) + application of Azadirechtin 0.003% at 15 days interval starting from flower. However, module -2 was consisted with destruction of infested fruits during each ~ 3524 ~
4 picking + poison 50 l/ha (jaggery 50 g/l + abamectin 1.9% EC %). The fruit infestation, yield and economics were significantly higher in module-4 and module-1 over control (module-5) but significantly lower to module-3 and module-2. A very little work on eco-friendly modules against melon fruit fly, B. cucurbitae on sponge gourd has been done. However, very good amount of research work has been carried out on different cucurbit. It was reported that three applications of poison baits prepared from 50gm/l water and malathion 0.05 per cent (ICBR 1:15.67) or methyl parathion 0.05 per cent (ICBR 1:9..6) or DDVP 0.07 per cent (ICBR 1:8.69) at 15 days interval starting from blooming gave the effective and economical control of the melon fruit fly infesting bitter gourd (Anonymous, 1992) [2]. Further, Deshmukh and Patil (1996) [4] concluded that the fruit fly trap baited with methyl eugenol (3 ml/trap with 0.05% cent dichlorvos) was found the most effective and economical treatment against fruit flies (Dacus spp.) with the lowest percentage of fruit infestation. The area wide IPM program including male annihilations with male lures and attractants and protein bait sprays and traps was proved to be economically viable, environmentally sensitive, sustainable and had suppressed fruit flies (B. cucurbitae) below economic threshold with the minimum use of organo phosphate and carbamate insecticides (Wood et al., 2001 and Mau et al., 2003) [14, 10]. Mandal (2012) [9] reported that the average mean percentage of fruit damage was the lowest in package of treatment such as installation of sex pheromone traps and spinosad spray along with discarding of infested/damaged fruits at each harvesting. However, in present study ecofriendly module-3 consisting module-2 + application of Azadirechtin 0.003% at 15 days interval starting from flower and module-2 consisting destruction of infested fruits during each picking + poison 50 l/ha (jaggery 50 g/l + abamectin 1.9% EC %) were found effective against fruit fly, B. cucurbitae infesting sponge gourd and harbour lower number of pests per fruit. Table 1: Bio efficacy of different eco-friendly modules against fruit fly, B. cucurbitae infesting sponge gourd during two kharif season Per cent fruit infestation No. of maggots / damage fruit * * Pooled* ** ** Pooled** M1: Mass trapping of fruit fly using Cue lure 30/ha + destruction of infested fruits during each picking (22.08) (22.23) (22.15) 2.23 (4.48) 2.32 (4.88) 2.28 (4.68) M2: Destruction of infested fruits during each picking + poison 50 l/ha (jaggery 50 g/l + abamectin 1.9% EC %) (16.98) (17.34) (17.16) 2.04 (3.68) 2.03 (3.62) 2.04 (3.65) M3: M2 + application of Azadirechtin 0.003% at 15 days interval starting from flower (13.65) (14.56) (14.10) 1.78 (2.66) 1.83 (2.85) 1.80 (2.75) M4: M2 + application of NSKE 5% at 15 days interval starting from flower (19.54) (20.08) (19.81) 2.17 (4.21) 2.21 (4.38) 2.19 (4.30) M5: Control (water spray) (33.07) (33.91) (33.49) 2.64 (6.47) 2.71 (6.82) 2.67 (6.64) S.Em.± C.D. at 5 % C.V. % Y S.Em.± C.D. at 5 % NS NS YXT S.Em.± C.D. at 5 % NS NS Application of poison bait, neem oil 1% & NSKE 5% was made at 15 days interval starting from flower (total four applications) * Figures in the parentheses are retransformed values while outside are sine -1 (X + 0.5)/100 transformed value. ** Figures in the parentheses are retransformed values while outside square root (X + 0.5) transformed value M: Table 2: Effect of various eco-friendly modules on fruit yield of sponge gourd during two kharif season Fruit yield (kg/ha) Increased yield over control (%) Pooled Pooled M1: Mass trapping of fruit fly using Cue lure 30/ha + destruction of infested fruits during each picking M2: Destruction of infested fruits during each picking + poison 50 l/ha (jaggery 50 g/l + abamectin 1.9% EC %) M3: M2 + application of Azadirechtin 0.003% at 15 days interval starting from flower M4: M2 + application of NSKE 5% at 15 days interval starting from flower initiation stage M5: Control (water spray) S.Em.± C.D. at 5 % C.V. % Y S.Em.± C.D. at 5 % NS YXT S.Em.± C.D. at 5 % NS Application of poison bait, neem oil 1% & NSKE 5% was made at 15 days interval starting from flower (total four applications) M: ~ 3525 ~
5 Table 3: Economics of different eco-friendly module for the control of fruit fly, B. cucurbitae in sponge gourd during two kharif season M1: Mass trapping of fruit fly using Cue lure 30/ha + destruction of infested fruits during each picking M2: Destruction of infested fruits during each picking + poison 50 l/ha (jaggery 50 g/l + abamectin 1.9% EC %) M3: M2 + application of Azadirechtin 0.003% at 15 days interval starting from flower M4: M2 + application of NSKE 5% at 15 days interval starting from flower Cost of inputs (Rs.) Rs. 10/trap Rs. 20/lure Jaggory : Rs. 40/kg Abamectin : Rs. 5100/l M2 + Neem oil : Rs. 450/l Quantity of inputs (l/kg per ha) 30 traps 120 lure Jaggory : 2.5 kg Abamectin : l -- Neem oil : 10 l Total cost of inputs (Rs.) Cost of inputs + labourer charges (Rs./ha) Sponge gourd yield (kg/ha) Gross benefit (Rs./ha) Net benefit (Rs./ha) Net cost benefit ratio (NCBR) : : : 5.05 M : M5: Control (water spray) Application of poison bait, Azadirechtin 0.003% & NSKE 5% was made at 15 days interval starting from flower (total four applications) Labourer Rs. 200/ha/spray Quantity of water required for one 500 l/ha M: The price of sponge gourd Rs. 15/kg Quantity of water required for one application of poison 50 l/ha References 1. Allwood AJ, Chinajariyawong A, Drew RAI, Hamacek EL, Hancock DL, Hengsawad C et al. Host plant records for fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) in South-East Asia. The Raffles Bulletin of Zoology, Supplement. 1999; 7: Anonymous. Recommendations/Achievements made by the Entomology Discipline, GAU, S.K. Nagar, , Coquillette DW. A new Trypetid form Hawaii. Ent. News., 10: Deshmukh, RP, Patil RS. (1996). Comparative efficacy of baited and non-baited sprays of insecticides and chemical attractant against fruit flies infesting ridge gourd. J Maharashtra Agric. Univ. 1899; 21(3): Deshmukh RP, Patil RS. Comparative efficacy of baited and non-baited sprays of insecticides and chemical attractant against fruit flies infesting ridge gourd. J Maharashtra Agric. Univ. 1996; 21(3): Dhillon MK, Singh R, Naresh JS, Sharma HC. The melon fruit fly, Bactrocera cucurbitae: A review of its biology and management. J Insec. Sci. 2005; 5: DOAC. Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Directorate of Agriculture and Co-operation, Government of, New-Delhi, Gupta D, Verma AK. Population fluctuation of the fruit flies (Dacus cucurbitae Coq. and Dacus tau Walker) infesting cucurbitaceous crops. Advances in pl. sci. 1992; 5(2): Lefroy HM. Ento. Memo. Dept. Agril. (Ent. Ser.). 1907; 1: Mandal SK. Management of Bactrocera Cucurbitae Coq. through pheromone traps and bio-rational insecticides in bitter gourd. Annals Pl. Pro. Sci. 2012; 20(1): Mau RFL, Sugano JS, Jang EB. Farmer education and organization in the Hawaii area wide fruit fly pest management program. Recent Trends on Sterile Insect Technique and Area-wide Integrated Pest Management: Economic Feasibility, Control Projects, Farmer Organization and Dorsalis Complex Control Study, Research Institute of Subtropics, Okinawa, Japan, Naraanan ES, Batra HN. Fruit flies and their control. n Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi,, 1960, Pareek BL, Kavadia VS. Relative preference of fruit fly, Dacus cucurbitae Coquillet on different cucurbits. n J Ent. 1994; 56(1): Shooker P, Khayrattee F, Permalloo S. Use of maize as a trap crops for the control of melon fly, B. cucurbitae with GF-120. Bio-control and other control methods, (http// 14. Wood M. Forcing exotic, invasive insects into retreat: new IPM program targets Hawaii's fruit flies. Agricultural Research Washington. 2001; 49: Fide Dhillon et al., J Insec. Sci. 2005; 5:40. ~ 3526 ~
Volume 1 Issue 2 April-June,2012 DOSE OF CUE- LURE FOR SUPPRESSION OF MELON FLY POPULATION IN PUMPKIN CHAUDHARY*, F. K. AND PATEL, G. M.
 DOSE OF CUE- LURE FOR SUPPRESSION OF MELON FLY POPULATION IN PUMPKIN CHAUDHARY*, F. K. AND PATEL, G. M. KRUSHI VIGYAN KENDRA, SARDARKRUSHINAGAR DANTIWADA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY DEESA - 385 535 DIST.:
DOSE OF CUE- LURE FOR SUPPRESSION OF MELON FLY POPULATION IN PUMPKIN CHAUDHARY*, F. K. AND PATEL, G. M. KRUSHI VIGYAN KENDRA, SARDARKRUSHINAGAR DANTIWADA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY DEESA - 385 535 DIST.:
EFFICACY OF DIFFERENT BIO-PESTICIDES AGAINST SUCKING PESTS OF Bt COTTON PATEL, R. D.; *BHARPODA, T. M.; BORAD, P. K.; BHATT, N. A. AND MAHIDA, R. D.
 EFFICACY OF DIFFERENT BIO-PESTICIDES AGAINST SUCKING PESTS OF Bt COTTON PATEL, R. D.; *BHARPODA, T. M.; BORAD, P. K.; BHATT, N. A. AND MAHIDA, R. D. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURAL ENTOMOLOGY B. A. COLLEGE
EFFICACY OF DIFFERENT BIO-PESTICIDES AGAINST SUCKING PESTS OF Bt COTTON PATEL, R. D.; *BHARPODA, T. M.; BORAD, P. K.; BHATT, N. A. AND MAHIDA, R. D. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURAL ENTOMOLOGY B. A. COLLEGE
MANAGEMENT OF FRUIT FLY, BACTROCERACUCURBITAE (COQUILLETT) IN RIDGE GOURD THROUGH BOTANICALS AND NEWER INSECTICIDES
 International Journal of Botany and Research (IJBR) ISSN (P): 2277-4815; ISSN (E): 2319-4456 Vol. 8, Issue 2, Apr 2018, 21-26 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. MANAGEMENT OF FRUIT FLY, BACTROCERACUCURBITAE (COQUILLETT)
International Journal of Botany and Research (IJBR) ISSN (P): 2277-4815; ISSN (E): 2319-4456 Vol. 8, Issue 2, Apr 2018, 21-26 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. MANAGEMENT OF FRUIT FLY, BACTROCERACUCURBITAE (COQUILLETT)
Ecology and Sustainable Management of Major Bactrocera Fruit Flies in Goa, India
 Ecology and Sustainable Management of Major Bactrocera Fruit Flies in Goa, India V. R. Satarkar, S. V. Krishnamurthy, J.R. Faleiro, A. Verghese, R. Ramesh and J. Ashok Kumar Email: vved20@yahoo.co.in jrfaleiro@yahoo.co.in
Ecology and Sustainable Management of Major Bactrocera Fruit Flies in Goa, India V. R. Satarkar, S. V. Krishnamurthy, J.R. Faleiro, A. Verghese, R. Ramesh and J. Ashok Kumar Email: vved20@yahoo.co.in jrfaleiro@yahoo.co.in
FRUIT FLY OF CUCURBITS IN SEMI ARID REGION OF NORTH GUJARAT CHAUDHARY, F. K. *
 FRUIT FLY OF CUCURBITS IN SEMI ARID REGION OF NORTH GUJARAT CHAUDHARY, F. K. * KRUSHI VIGYAN KENDRA SARDARKRUSHINAGAR DANTIWADA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY DEESA-385 535, DI. BANASKANTHA (GUJARAT), INDIA *E-Mail:
FRUIT FLY OF CUCURBITS IN SEMI ARID REGION OF NORTH GUJARAT CHAUDHARY, F. K. * KRUSHI VIGYAN KENDRA SARDARKRUSHINAGAR DANTIWADA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY DEESA-385 535, DI. BANASKANTHA (GUJARAT), INDIA *E-Mail:
Population Dynamics of Three Species of Genus Bactrocera (Diptera: Tephritidae: Dacinae) in BARI, Chakwal (Punjab)
 Pakistan J. Zool., vol. 39(2), pp. 123-126, 2007. Population Dynamics of Three Species of Genus Bactrocera (Diptera: Tephritidae: Dacinae) in BARI, Chakwal (Punjab) KHALID MAHMOOD AND MISHKATULLAH Pakistan
Pakistan J. Zool., vol. 39(2), pp. 123-126, 2007. Population Dynamics of Three Species of Genus Bactrocera (Diptera: Tephritidae: Dacinae) in BARI, Chakwal (Punjab) KHALID MAHMOOD AND MISHKATULLAH Pakistan
Efficacy of Protein Bait Sprays in Controlling Melon Fruit Fly [Bactrocera Cucurbitae (Coquillett)] in Vegetable Agro-ecosystems
![Efficacy of Protein Bait Sprays in Controlling Melon Fruit Fly [Bactrocera Cucurbitae (Coquillett)] in Vegetable Agro-ecosystems Efficacy of Protein Bait Sprays in Controlling Melon Fruit Fly [Bactrocera Cucurbitae (Coquillett)] in Vegetable Agro-ecosystems](/thumbs/85/92068826.jpg) Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences: B. Life and Environmental Sciences 54 (2): 111 115 (2017) Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 2518-4261 (print), ISSN 2518-427X (online) Pakistan
Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences: B. Life and Environmental Sciences 54 (2): 111 115 (2017) Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 2518-4261 (print), ISSN 2518-427X (online) Pakistan
EFFICACY OF PROTEIN BAIT SPRAYS IN CONTROLLING FRUIT FLIES (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) INFESTING ANGLED LUFFA AND BITTER GOURD IN THAILAND
 THE RAFFLES BULLETIN OF ZOOLOGY 2003 51(1): 7-15 National University of Singapore EFFICACY OF PROTEIN BAIT SPRAYS IN CONTROLLING FRUIT FLIES (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) INFESTING ANGLED LUFFA AND BITTER GOURD
THE RAFFLES BULLETIN OF ZOOLOGY 2003 51(1): 7-15 National University of Singapore EFFICACY OF PROTEIN BAIT SPRAYS IN CONTROLLING FRUIT FLIES (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) INFESTING ANGLED LUFFA AND BITTER GOURD
Fruit Fly Surveillance in Nepal
 Agricultural and Biological Sciences Journal Vol. 1, No. 3, 2015, pp. 121-125 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/absj Fruit Fly Surveillance in Nepal D. R. Sharma 1, D. Adhikari 2, *, D. B. Tiwari 3 1 National
Agricultural and Biological Sciences Journal Vol. 1, No. 3, 2015, pp. 121-125 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/absj Fruit Fly Surveillance in Nepal D. R. Sharma 1, D. Adhikari 2, *, D. B. Tiwari 3 1 National
The Hawaii Fruit Fly Area-Wide Pest Management Program: Accomplishments and Future Directions
 Hawaii Proc. Hawaiian AWPM Accomplishments Entomol. Soc. (2007) and 39:99 104 Future Directions 99 The Hawaii Fruit Fly Area-Wide Pest Management Program: Accomplishments and Future Directions Roger I.
Hawaii Proc. Hawaiian AWPM Accomplishments Entomol. Soc. (2007) and 39:99 104 Future Directions 99 The Hawaii Fruit Fly Area-Wide Pest Management Program: Accomplishments and Future Directions Roger I.
AField Evaluation of Compatibility of Pesticides against Major Pests of Paddy
 I J T AField Evaluation of Compatibility of Pesticides against Major Pests of Paddy Serials Publications B. N. Chaudhari, G. R. Shamkuwar and P. S. Neharkar ABSTRACT: Two insecticides and two fungicides
I J T AField Evaluation of Compatibility of Pesticides against Major Pests of Paddy Serials Publications B. N. Chaudhari, G. R. Shamkuwar and P. S. Neharkar ABSTRACT: Two insecticides and two fungicides
Curre nt Status of the Solanaceous Fruit Fly Control Project in Yonaguni Island. Abstract
 Curre nt Status of the Solanaceous Fruit Fly Control Project in Yonaguni Island Hiroyuki Kuba 1, Takashi Matsuyama 2, and Noriaki Mougi 2 1 Research Institute for Subtropics, 1 Asahimachi, Naha, Okinawa
Curre nt Status of the Solanaceous Fruit Fly Control Project in Yonaguni Island Hiroyuki Kuba 1, Takashi Matsuyama 2, and Noriaki Mougi 2 1 Research Institute for Subtropics, 1 Asahimachi, Naha, Okinawa
Bionomics of Fruit Fly, Bectrocera cucurbitae (Coquillet) on Cucumber under Laboratory Condition
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 03 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.703.297
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 03 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.703.297
Management of Coriander Wilt (Fusarium oxysporium) through Cultural Practices as Organic Amendments and Date of Sowing
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 896-900 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.108
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 896-900 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.108
Studies on the Eco-Friendly Insecticidal Management of Major Insect Pests of Cabbage under Agro-Climatic Conditions of Imphal, Manipur
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Yadav et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (6): 273-277 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5173 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5
Available online at www.ijpab.com Yadav et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (6): 273-277 (2017) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5173 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5
AGRES An International e. Journal (2018) Vol. 7, Issue 2: ISSN :
 BIOEFFICACY OF NEW INSECTICIDE MOLECULE CYANTRANILLPROLE 10.26 OD AGAINST PESTS OF POMEGRANATE LAD, R. H.; *WALUNJ, A. R.; POKHARKAR, D. S. AND PATIL, C. S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURAL ENTOMOLOGY MAHATMA
BIOEFFICACY OF NEW INSECTICIDE MOLECULE CYANTRANILLPROLE 10.26 OD AGAINST PESTS OF POMEGRANATE LAD, R. H.; *WALUNJ, A. R.; POKHARKAR, D. S. AND PATIL, C. S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURAL ENTOMOLOGY MAHATMA
Incidence of Podfly, Melanagromyza obtusa (MALLOCH) and its Influence on Weight Loss in Different Pigeonpea Genotypes
 Incidence of Podfly, Melanagromyza obtusa (MALLOCH) and its Influence on Weight Loss in Different Pigeonpea Genotypes *Revathi K, Sreekanth M**, Krishnayya P V and Srinivasa Rao V **Regional Agricultural
Incidence of Podfly, Melanagromyza obtusa (MALLOCH) and its Influence on Weight Loss in Different Pigeonpea Genotypes *Revathi K, Sreekanth M**, Krishnayya P V and Srinivasa Rao V **Regional Agricultural
Division of Entomology, Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology of Kashmir , INDIA 2
 NSave Nature to Survive QUARTERLY 9(3&4): 737-744, 2015 POPULATION BUILD UP OF FRUIT FLIES, BACTROCERA SPP. (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) IN RELATION TO HOST AVAILABILITY ASSOCIATED WITH CUCURBITS IN MID-HILL
NSave Nature to Survive QUARTERLY 9(3&4): 737-744, 2015 POPULATION BUILD UP OF FRUIT FLIES, BACTROCERA SPP. (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) IN RELATION TO HOST AVAILABILITY ASSOCIATED WITH CUCURBITS IN MID-HILL
MANAGEMENT OF Spodoptera litura Fabricius ON CABBAGE *RABARI, P. H., DODIA, D. A., PATEL, P. S. AND BARAD, C. S
 MANAGEMENT OF Spodoptera litura Fabricius ON CABBAGE *RABARI, P. H., DODIA, D. A., PATEL, P. S. AND BARAD, C. S DEPARTMENT OF ENTOMOLOGY C. P. COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE S. D. AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY, SARDARKRUSHINAGAR-385506
MANAGEMENT OF Spodoptera litura Fabricius ON CABBAGE *RABARI, P. H., DODIA, D. A., PATEL, P. S. AND BARAD, C. S DEPARTMENT OF ENTOMOLOGY C. P. COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE S. D. AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY, SARDARKRUSHINAGAR-385506
BIO-EFFICACY OF PROMISING BOTANICALS AGAINST INSECT INFESTING COWPEA. CV. CO 4
 Indian J. Agric. Res., 40 (4) : 262-266, 2006 BIO-EFFICACY OF PROMISING BOTANICALS AGAINST INSECT INFESTING COWPEA. CV. CO 4 J. Renugadevi, N. Natarajan, R. Rajasekaran and P. Srimathi Department of Seed
Indian J. Agric. Res., 40 (4) : 262-266, 2006 BIO-EFFICACY OF PROMISING BOTANICALS AGAINST INSECT INFESTING COWPEA. CV. CO 4 J. Renugadevi, N. Natarajan, R. Rajasekaran and P. Srimathi Department of Seed
Diversity and abundance of Dacinae fruit flies (Insecta: Diptera: Tephritidae) in Chini 2, Runchang and Sungai Bebar, Pahang, Peninsular Malaysia
 Journal of Science and Technology in the Tropics (200) 6: 7-2 7 Diversity and abundance of Dacinae fruit flies (Insecta: Diptera: Tephritidae) in Chini 2, Runchang and Sungai Bebar, Pahang, Peninsular
Journal of Science and Technology in the Tropics (200) 6: 7-2 7 Diversity and abundance of Dacinae fruit flies (Insecta: Diptera: Tephritidae) in Chini 2, Runchang and Sungai Bebar, Pahang, Peninsular
Full-text Available Online at
 JASEM ISSN 1119-8362 All rights reserved Full-text Available Online at www.bioline.org.br/ja J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manage. September, 21 Vol. 14 (3) 3-8 The Effect of Meteorological Factors on the Population
JASEM ISSN 1119-8362 All rights reserved Full-text Available Online at www.bioline.org.br/ja J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manage. September, 21 Vol. 14 (3) 3-8 The Effect of Meteorological Factors on the Population
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION Cabbage is an important cruciferous vegetable. Insect pests are one of the major biotic factors which contribute to major economic losses both quantitatively and qualitatively. These
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION Cabbage is an important cruciferous vegetable. Insect pests are one of the major biotic factors which contribute to major economic losses both quantitatively and qualitatively. These
Bio-efficacy of Clofentezine 50SC against two spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch on rose cv. First Red in polyhouse
 Bio-efficacy of Clofentezine 50SC against two spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch on rose cv. First Red in polyhouse V. SRIDHAR and B. JHANSI RANI Division of Entomology and Nematology, Indian
Bio-efficacy of Clofentezine 50SC against two spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch on rose cv. First Red in polyhouse V. SRIDHAR and B. JHANSI RANI Division of Entomology and Nematology, Indian
Combination of Garlic Extract and Some Organophosphate Insecticides in Controlling Thrips (Thrips palmi) Pest in Watermelon Management
 International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2011. 9, 1: 19-23 Combination of Garlic Extract and Some Organophosphate Insecticides in Controlling Thrips (Thrips palmi) Pest in W. Burubai*,
International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2011. 9, 1: 19-23 Combination of Garlic Extract and Some Organophosphate Insecticides in Controlling Thrips (Thrips palmi) Pest in W. Burubai*,
Effect of weather parameters on incidence of insect pests of cucumber in eastern Bihar
 Vol. Journal 20, No. of Agrometeorology 1 20 (1) : 57-61 (March 2018) SAHA et al 57 Effect of weather parameters on incidence of insect pests of cucumber in eastern Bihar TAMOGHNA SAHA 1, NITHYA CHANDRAN
Vol. Journal 20, No. of Agrometeorology 1 20 (1) : 57-61 (March 2018) SAHA et al 57 Effect of weather parameters on incidence of insect pests of cucumber in eastern Bihar TAMOGHNA SAHA 1, NITHYA CHANDRAN
Melon Fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) Genetic Sexing: All-male Sterile Fly Releases in Hawaii
 Melon Proc. Hawaiian Fly Genetic Entomol. Sexing: Soc. All-male (2007) 39:105 110 Sterile Releases in Hawaii 105 Melon Fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) Genetic Sexing: All-male Sterile Fly Releases in Hawaii
Melon Proc. Hawaiian Fly Genetic Entomol. Sexing: Soc. All-male (2007) 39:105 110 Sterile Releases in Hawaii 105 Melon Fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) Genetic Sexing: All-male Sterile Fly Releases in Hawaii
Area-wide integrated pest management of tephritid fruit flies using the sterile insect technique
 Area-wide integrated pest management of tephritid fruit flies using the sterile insect technique Rui Pereira, Jorge Hendrichs, Jesus Reyes and Marc Vreysen Insect Pest Control Section (Joint FAO/IAEA Division)
Area-wide integrated pest management of tephritid fruit flies using the sterile insect technique Rui Pereira, Jorge Hendrichs, Jesus Reyes and Marc Vreysen Insect Pest Control Section (Joint FAO/IAEA Division)
BIO-EFFICACY OF NEW COMBI-PRODUCT AGAINST COTTON BOLL WORMS
 BIO-EFFICACY OF NEW COMBI-PRODUCT AGAINST COTTON BOLL WORMS *Surpam A.N. 1, Neharkar P.S. 2, Shubhangi P. Bhasme 3, Kamdi S.R. 4 and Kadam B.S. 5 College of Agriculture, Sonapur, Gadchiroli, Dr. Panjabrao
BIO-EFFICACY OF NEW COMBI-PRODUCT AGAINST COTTON BOLL WORMS *Surpam A.N. 1, Neharkar P.S. 2, Shubhangi P. Bhasme 3, Kamdi S.R. 4 and Kadam B.S. 5 College of Agriculture, Sonapur, Gadchiroli, Dr. Panjabrao
Efficacy of various edible and non-edible oils against Sitophilus oryzae L. in sorghum
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PLANT PROTECTION VOLUME 8 ISSUE 2 OCTOBER, 2015 216-221 e ISSN-0976-6855 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in IJPP RESEARCH PAPER DOI : 10.15740/HAS/IJPP/8.2/216-221 Efficacy of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PLANT PROTECTION VOLUME 8 ISSUE 2 OCTOBER, 2015 216-221 e ISSN-0976-6855 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in IJPP RESEARCH PAPER DOI : 10.15740/HAS/IJPP/8.2/216-221 Efficacy of
Bio-efficacy of insecticides against mustard aphid (lipaphis erysimi Kalt.) on mustard (Brassica juncea L.)
 2018; 6(2): 2704-2708 P-ISSN: 2349 8528 E-ISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2018; 6(2): 2704-2708 2018 IJCS Received: 09-01-2018 Accepted: 13-02-2018 SK Yadav Agriculture AND Technology, RB Singh MP Gautam Gajendra
2018; 6(2): 2704-2708 P-ISSN: 2349 8528 E-ISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2018; 6(2): 2704-2708 2018 IJCS Received: 09-01-2018 Accepted: 13-02-2018 SK Yadav Agriculture AND Technology, RB Singh MP Gautam Gajendra
Combining Ability Studies in Bitter Gourd (Momordica charantia L.) for Quantitative Characters
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 4471-4478 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.466
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 4471-4478 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.466
Successful Utilization of the Area-Wide Approach for the Management of Fruit Flies in Hawaii
 1 Successful Utilization of the Area-Wide Approach for the Management of Fruit Flies in Hawaii Roger I. Vargas 1, Ronald F. L. Mau 2, Lyle Wong 3, and Eric B. Jang 1 1 United States Department of Agriculture
1 Successful Utilization of the Area-Wide Approach for the Management of Fruit Flies in Hawaii Roger I. Vargas 1, Ronald F. L. Mau 2, Lyle Wong 3, and Eric B. Jang 1 1 United States Department of Agriculture
Potency of insecticidal combinations against bollworm complex of cotton
 2018; SP1: 1164-1168 E-ISSN: 2278-4136 P-ISSN: 2349-8234 JPP 2018; SP1: 1164-1168 V. K. Bhamare Department of Agricultural Entomology, Vasantrao Naik Marathwada Krishi Vidyapeeth, Parbhani (M.S.), India
2018; SP1: 1164-1168 E-ISSN: 2278-4136 P-ISSN: 2349-8234 JPP 2018; SP1: 1164-1168 V. K. Bhamare Department of Agricultural Entomology, Vasantrao Naik Marathwada Krishi Vidyapeeth, Parbhani (M.S.), India
EVALUATION OF NEW INSECTICIDES AND FUNGICIDES FOR COMPATIBILITY AND MANAGEMENT OF DEFOLIATORS AND LATE LEAF SPOT IN GROUNDNUT
 Volume-6, Issue-1, Jan-Mar-2016 Coden: IJPAJX-CAS-USA, Copyrights@2016 ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 28 th Oct-2015 Revised: 20 th Nov -2015 Accepted: 21 st Nov-2015 Research article EVALUATION OF NEW INSECTICIDES
Volume-6, Issue-1, Jan-Mar-2016 Coden: IJPAJX-CAS-USA, Copyrights@2016 ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 28 th Oct-2015 Revised: 20 th Nov -2015 Accepted: 21 st Nov-2015 Research article EVALUATION OF NEW INSECTICIDES
SEASONAL VARIATIONS OF MELON FLY, Bactrocera cucurbitae (COQUILLETT) (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) IN DIFFERENT AGRICULTURAL HABITATS OF BANGLADESH
 SEASONAL VARIATIONS OF MELON FLY, Bactrocera cucurbitae (COQUILLETT) (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) IN DIFFERENT AGRICULTURAL HABITATS OF BANGLADESH M. Abdul Alim 1, M. Aftab Hossain 2, Mahfuza Khan 2, Shakil
SEASONAL VARIATIONS OF MELON FLY, Bactrocera cucurbitae (COQUILLETT) (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) IN DIFFERENT AGRICULTURAL HABITATS OF BANGLADESH M. Abdul Alim 1, M. Aftab Hossain 2, Mahfuza Khan 2, Shakil
EFFECTIVENESS OF SOME INSECTICIDES AGAINST CABBAGE APHID, BREVICORYNE BRASSICAE (LINNAEUS) (APHIDIDAE: HOMOPTERA)
 Journal of Research (Science), Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan, Pakistan. Vol.13, No.2, December 2002, pp. 145-150 ISSN 1021-1012 EFFECTIVENESS OF SOME INSECTICIDES AGAINST CABBAGE APHID, BREVICORYNE
Journal of Research (Science), Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan, Pakistan. Vol.13, No.2, December 2002, pp. 145-150 ISSN 1021-1012 EFFECTIVENESS OF SOME INSECTICIDES AGAINST CABBAGE APHID, BREVICORYNE
The IPM based on mass trapping : Ceratitis capitata (Diptera, Tephritidae)?
 Regional Symposium on the Management of Fruit Flies in Near East Countries, 6 8 Nov. 2012, Hammamet, Tunisia The IPM based on mass trapping : is it an efficient method to control the Medfly Ceratitis capitata
Regional Symposium on the Management of Fruit Flies in Near East Countries, 6 8 Nov. 2012, Hammamet, Tunisia The IPM based on mass trapping : is it an efficient method to control the Medfly Ceratitis capitata
Biochemical Resistance Traits of Bitter Gourd against Fruit Fly Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) Infestation
 Journal of Agricultural Science; Vol. 9, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1916-9752 E-ISSN 1916-9760 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Biochemical Resistance Traits of Bitter Gourd against Fruit Fly
Journal of Agricultural Science; Vol. 9, No. 2; 2017 ISSN 1916-9752 E-ISSN 1916-9760 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Biochemical Resistance Traits of Bitter Gourd against Fruit Fly
The Mediterranean Fruit Fly in Central America
 The Mediterranean Fruit Fly in Central America P.V. Vail, I. Moore and D. Nadel Dr. Vail is Section Head, Joint FAO/IAEA Division of Atomic Energy in Food and Agriculture. Dr. Moore is Assistant to the
The Mediterranean Fruit Fly in Central America P.V. Vail, I. Moore and D. Nadel Dr. Vail is Section Head, Joint FAO/IAEA Division of Atomic Energy in Food and Agriculture. Dr. Moore is Assistant to the
whereas the fourth inhibitor was extracted and semi purified from cabbage (Brassica oleracae) in the Insect Physiology Laboratory of the Department of
 6. SUMMARY Due to long co-evolution of plants and herbivores a vast repertoire of unique bioactive compounds have appeared in plants, some of which have found use in medicines, drugs, antibiotics, insecticides,
6. SUMMARY Due to long co-evolution of plants and herbivores a vast repertoire of unique bioactive compounds have appeared in plants, some of which have found use in medicines, drugs, antibiotics, insecticides,
Management of Alternaria Leaf Blight of Bottle Gourd in Western Rajasthan, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 6 (2017) pp. 1272-1277 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.606.149
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 6 (2017) pp. 1272-1277 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.606.149
SEASONAL BIONOMICS OF MELON FRUIT FLY, BACTROCERA CUCURBITAE COQUILLETT ON BOTTLE GOURD IN LABORATORY CONDITION
 NSave Nature to Survive 8(1&2): 157-162, 2014 SEASONAL BIONOMICS OF MELON FRUIT FLY, BACTROCERA CUCURBITAE COQUILLETT ON BOTTLE GOURD IN LABORATORY CONDITION PARAMITA BHOWMIK*, LAISHRAM LAISHANA DEVI,
NSave Nature to Survive 8(1&2): 157-162, 2014 SEASONAL BIONOMICS OF MELON FRUIT FLY, BACTROCERA CUCURBITAE COQUILLETT ON BOTTLE GOURD IN LABORATORY CONDITION PARAMITA BHOWMIK*, LAISHRAM LAISHANA DEVI,
Demographic parameters and biotic factors of two Dacini species, Bactrocera cucurbitae and Dacus ciliatus, on Réunion Island
 Proceedings of 6th International Fruit Fly Symposium 6 10 May 2002, Stellenbosch, South Africa pp. 91 95 Demographic parameters and biotic factors of two Dacini species, Bactrocera cucurbitae and Dacus
Proceedings of 6th International Fruit Fly Symposium 6 10 May 2002, Stellenbosch, South Africa pp. 91 95 Demographic parameters and biotic factors of two Dacini species, Bactrocera cucurbitae and Dacus
Cotton Insect Control in Arizona
 Cotton Insect Control in Arizona Item Type Article Authors Watson, T. F.; Moore, Leon Publisher College of Agriculture, University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ) Journal Progressive Agriculture in Arizona Rights
Cotton Insect Control in Arizona Item Type Article Authors Watson, T. F.; Moore, Leon Publisher College of Agriculture, University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ) Journal Progressive Agriculture in Arizona Rights
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 1.393, ISSN: , Volume 2, Issue 2, March 2014
 MANAGEMENT OF INSECT PEST BY USING HERBAL PLANTS EXTRACTS DR. S.V.CHAUDHARI* *Associate Professor & Head, Dept. of Zoology, Arts, Science & Commerce College, Ahmednagar, University of Pune, Maharashtra
MANAGEMENT OF INSECT PEST BY USING HERBAL PLANTS EXTRACTS DR. S.V.CHAUDHARI* *Associate Professor & Head, Dept. of Zoology, Arts, Science & Commerce College, Ahmednagar, University of Pune, Maharashtra
INFLUENCE OF WEATHER PARAMETERS ON FRUIT FLY TRAP CATCHES INDHARWAD, KARNATAKA
 Pest Management in Horticultural Ecosystems, Vol. 12, NO.2 pp 143-151 (2006) INFLUENCE OF WEATHER PARAMETERS ON FRUIT FLY TRAP CATCHES INDHARWAD, KARNATAKA CH. RAVIKUMAR and SHASHIDHAR VIRAKTAMATH Department
Pest Management in Horticultural Ecosystems, Vol. 12, NO.2 pp 143-151 (2006) INFLUENCE OF WEATHER PARAMETERS ON FRUIT FLY TRAP CATCHES INDHARWAD, KARNATAKA CH. RAVIKUMAR and SHASHIDHAR VIRAKTAMATH Department
Name change of the invasive fruit fly and update on its pest status in South Africa
 Name change of the invasive fruit fly and update on its pest status in South Africa Fruit flies are the bane of many fruit growers existence, but in this case it s better the devil you know, than the one
Name change of the invasive fruit fly and update on its pest status in South Africa Fruit flies are the bane of many fruit growers existence, but in this case it s better the devil you know, than the one
The Threat of the Mediterranean Fruit Fly1 to American Agriculture and Efforts Being Made to Counter This Threat2 3
 Vol. XXII, No. 3, December, 1977 475 The Threat of the Mediterranean Fruit Fly1 to American Agriculture and Efforts Being Made to Counter This Threat2 3 Ernest J. Harris HAWAIIAN FRUIT FLIES LABORATORY,
Vol. XXII, No. 3, December, 1977 475 The Threat of the Mediterranean Fruit Fly1 to American Agriculture and Efforts Being Made to Counter This Threat2 3 Ernest J. Harris HAWAIIAN FRUIT FLIES LABORATORY,
Bio Efficacy of Botanical Insecticides against Defoliators Pests on Soybean
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 3 (2017) pp. 2196-2204 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.603.250
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 3 (2017) pp. 2196-2204 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.603.250
Efficacy of Biorational and eco-friendly control strategies in brinjal against Epilachna beetle, jassids and whiteflies
 2018; 6(4): 1581-1585 E-ISSN: 2320-7078 P-ISSN: 2349-6800 JEZS 2018; 6(4): 1581-1585 2018 JEZS Received: 20-05-2018 Accepted: 22-06-2018 JR Mallick S Dash HP Patnaik Efficacy of Biorational and eco-friendly
2018; 6(4): 1581-1585 E-ISSN: 2320-7078 P-ISSN: 2349-6800 JEZS 2018; 6(4): 1581-1585 2018 JEZS Received: 20-05-2018 Accepted: 22-06-2018 JR Mallick S Dash HP Patnaik Efficacy of Biorational and eco-friendly
The Changing Face of Agriculture: fruit flies, innovation and global trade
 The Changing Face of Agriculture: fruit flies, innovation and global trade Eric Jang, Fruit Fly Systems Applied Technologies (FFSATECH), Hilo, HI Dan Ryan, Horticulture Innovation Australia (HIA), Sydney,
The Changing Face of Agriculture: fruit flies, innovation and global trade Eric Jang, Fruit Fly Systems Applied Technologies (FFSATECH), Hilo, HI Dan Ryan, Horticulture Innovation Australia (HIA), Sydney,
Efficacy of Some New Insecticides against Diamond Back Moth (Plutella xylostella L.) on Cauliflower
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 1958-1963 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.218
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 1958-1963 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.218
Estimation of Genetic Divergence for Growth, Earliness and Yield Parameters in Cucumber (Cucumis Sativus L.)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 05 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.705.273
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 05 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.705.273
RESPONSE OF BIO FERTILIZERS IN CONJUNCTION WITH INORGANIC FERTILIZERS IN KHARIF PADDY
 RESPONSE OF BIO FERTILIZERS IN CONJUNCTION WITH INORGANIC FERTILIZERS IN KHARIF PADDY TANDEL, B. B., PATEL, D. D., THANKI, J. D., ARVADIA, M. K. AND JAT, R. A. NAVSARI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY NAVSARI-396
RESPONSE OF BIO FERTILIZERS IN CONJUNCTION WITH INORGANIC FERTILIZERS IN KHARIF PADDY TANDEL, B. B., PATEL, D. D., THANKI, J. D., ARVADIA, M. K. AND JAT, R. A. NAVSARI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY NAVSARI-396
Seasonal Incidence and Management of Red Spider Mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch. Infesting Rose
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 2723-2729 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.335
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 9 (2017) pp. 2723-2729 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.335
Evaluation of JH Biotech, Inc. Products under Egyptian environment
 1 Product Name: 5- Biorepel (Natural Insect Repellent) Supervisor: Dr. Mohamad Ibrahim Plant Protection Res. Institute, Sharkia Research Station. INTRODUCTION Evaluation of JH Biotech, Inc. Products under
1 Product Name: 5- Biorepel (Natural Insect Repellent) Supervisor: Dr. Mohamad Ibrahim Plant Protection Res. Institute, Sharkia Research Station. INTRODUCTION Evaluation of JH Biotech, Inc. Products under
Integrated Management of Turmeric Rhizome Rot Caused by Pythium aphanidermatum
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 5321-5327 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.508
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 11 (2017) pp. 5321-5327 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.611.508
EFFECTS OF ZINC AND BORON ON YIELD, NUTRIENT UPTAKE AND ECONOMICS OF MUSTARD (BRASSICA JUNCEA L.) IN MUSTARD-MAIZE CROPPING SEQUENCE
 Bangladesh J. Bot. 46(2): 817-821, 2017 (June) - Short communication EFFECTS OF ZINC AND BORON ON YIELD, NUTRIENT UPTAKE AND ECONOMICS OF MUSTARD (BRASSICA JUNCEA L.) IN MUSTARD-MAIZE CROPPING SEQUENCE
Bangladesh J. Bot. 46(2): 817-821, 2017 (June) - Short communication EFFECTS OF ZINC AND BORON ON YIELD, NUTRIENT UPTAKE AND ECONOMICS OF MUSTARD (BRASSICA JUNCEA L.) IN MUSTARD-MAIZE CROPPING SEQUENCE
Effect of Natural and Artificial Diets on the Life History Parameters of Melon Fruit Fly Bactrocera Cucurbitae (Coquillett)
 Effect of Natural and Artificial Diets on the Life History Parameters of Melon Fruit Fly Bactrocera Cucurbitae (Coquillett) ABRO ZAIN-UL-AABDIN 1*, NAHEED BALOCH 1, KHUHRO NIAZ HUSSAIN 2, SOOMRO QADEER
Effect of Natural and Artificial Diets on the Life History Parameters of Melon Fruit Fly Bactrocera Cucurbitae (Coquillett) ABRO ZAIN-UL-AABDIN 1*, NAHEED BALOCH 1, KHUHRO NIAZ HUSSAIN 2, SOOMRO QADEER
HETEROSIS FOR FODDER YIELD AND QUALITY TRAITS IN FORAGE SORGHUM
 Forage Res., 44 (1) : pp. 32-37 (2018) http://forageresearch.in HETEROSIS FOR FODDER YIELD AND QUALITY TRAITS IN FORAGE SORGHUM P. R. PATEL 1, R. M. CHOUHAN 1 AND S. K. JAIN*,2 1 Sardarkrushinagar Dantiwada
Forage Res., 44 (1) : pp. 32-37 (2018) http://forageresearch.in HETEROSIS FOR FODDER YIELD AND QUALITY TRAITS IN FORAGE SORGHUM P. R. PATEL 1, R. M. CHOUHAN 1 AND S. K. JAIN*,2 1 Sardarkrushinagar Dantiwada
DETERMINATION OF FRUIT FLIES (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) INFESTATION IN GUAVA, PEACH AND BITTER GOURD ORCHARDS IN KHYBER PAKHTUNKHWA.
 Sarhad J. Agric. Vol. 30, No. 2, 2014 DETERMINATION OF FRUIT FLIES (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) INFESTATION IN GUAVA, PEACH AND BITTER GOURD ORCHARDS IN KHYBER PAKHTUNKHWA. MUHAMMAD QASIM KAKAR 1, FARMAN ULLAH
Sarhad J. Agric. Vol. 30, No. 2, 2014 DETERMINATION OF FRUIT FLIES (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) INFESTATION IN GUAVA, PEACH AND BITTER GOURD ORCHARDS IN KHYBER PAKHTUNKHWA. MUHAMMAD QASIM KAKAR 1, FARMAN ULLAH
NAPPO Regional Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (RSPM)
 NAPPO Regional Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (RSPM) RSPM # 10 SURVEILLANCE FOR QUARANTINE FRUIT FLIES (IN A PORTION OF A GENERALLY INFESTED AREA) The Secretariat of the North American Plant Protection
NAPPO Regional Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (RSPM) RSPM # 10 SURVEILLANCE FOR QUARANTINE FRUIT FLIES (IN A PORTION OF A GENERALLY INFESTED AREA) The Secretariat of the North American Plant Protection
Journal of Insect Science: Vol. 12 Article 32
 Species diversity within a community of the curcurbit fruit flies Bactrocera cucurbitae, Dacus ciliatus, and Dacus demmerezi roosting in corn borders near cucurbit production areas of Reunion Island J.-P.
Species diversity within a community of the curcurbit fruit flies Bactrocera cucurbitae, Dacus ciliatus, and Dacus demmerezi roosting in corn borders near cucurbit production areas of Reunion Island J.-P.
Effect of different application method of humic acid on nodulation and seed yield of soybean
 International Journal of Agricultural Sciences Volume 12 Issue 2 June, 2016 339-343 e ISSN 0976 5670 DOI:10.15740/HAS/IJAS/12.2/339-343 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in RESEARCH PAPER Effect of different
International Journal of Agricultural Sciences Volume 12 Issue 2 June, 2016 339-343 e ISSN 0976 5670 DOI:10.15740/HAS/IJAS/12.2/339-343 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in RESEARCH PAPER Effect of different
Studies on management of bitter gourd distortion mosaic virus using nonchemicals
 ORIGINAL PAPER Studies on management of bitter gourd distortion mosaic virus using nonchemicals Reeny Mary Zacharia. Sally K Mathew Abstract Bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) is the most important
ORIGINAL PAPER Studies on management of bitter gourd distortion mosaic virus using nonchemicals Reeny Mary Zacharia. Sally K Mathew Abstract Bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) is the most important
Pheromone Based Mating Disruption
 TM Thaumatotibia leucotreta Reg No: L10320, Act 36 of 1947 Pheromone Based Mating Disruption Pest specific Easy to apply Season long control Manufactured by Hinders chemical resistance Rain fast and no
TM Thaumatotibia leucotreta Reg No: L10320, Act 36 of 1947 Pheromone Based Mating Disruption Pest specific Easy to apply Season long control Manufactured by Hinders chemical resistance Rain fast and no
Yield and quality of cumin as influenced by FYM enriched micronutrients
 International J. Seed Spices 6(1), Jan 2016: 17-24 Abstract Yield and quality of cumin as influenced by FYM enriched micronutrients S. M. Patel, A. U. Amin, S. P. Patel and B. T. Patel Center for Research
International J. Seed Spices 6(1), Jan 2016: 17-24 Abstract Yield and quality of cumin as influenced by FYM enriched micronutrients S. M. Patel, A. U. Amin, S. P. Patel and B. T. Patel Center for Research
Comparative Toxicity of Certain Pesticides to Peach Fruit Fly, Bactrocera zonata Saunders (Diptera: Tephritidae) under Laboratory Conditions
 Plant Protect. Sci. Vol. 7,, No. 3: 5 Comparative Toxicity of Certain Pesticides to Peach Fruit Fly, Bactrocera zonata Saunders (Diptera: Tephritidae) under Laboratory Conditions Yahia Youssef Mosleh,
Plant Protect. Sci. Vol. 7,, No. 3: 5 Comparative Toxicity of Certain Pesticides to Peach Fruit Fly, Bactrocera zonata Saunders (Diptera: Tephritidae) under Laboratory Conditions Yahia Youssef Mosleh,
Evaluation of Assail for the Control of Early Season Cotton Aphids in Upland Cotton COOPERATIVE RESEARCH PROJECT 2001
 of Early Season Cotton Aphids in Upland Cotton COOPERATIVE RESEARCH PROJECT 2001 Donald J. Reid, Agronomist Texas A & M University-Commerce James S. Swart, Entomologist Texas Agricultural Extension Service
of Early Season Cotton Aphids in Upland Cotton COOPERATIVE RESEARCH PROJECT 2001 Donald J. Reid, Agronomist Texas A & M University-Commerce James S. Swart, Entomologist Texas Agricultural Extension Service
Bactrocera dorsalis : Current status JH VENTER NPPOZA MAY 2017
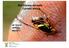 Bactrocera dorsalis : Current status JH VENTER NPPOZA MAY 2017 Photo: JH Venter National exotic fruit fly surveillance program Since 2006 Forms part of the Strategic plan of DAFF An early warning system
Bactrocera dorsalis : Current status JH VENTER NPPOZA MAY 2017 Photo: JH Venter National exotic fruit fly surveillance program Since 2006 Forms part of the Strategic plan of DAFF An early warning system
Progress. Agric. 18(2) : 93-97, 2007 ISSN
 Progress. Agric. 18(2) : 93-97, 2007 ISSN 1017-8139 EFFECTS OF GARLIC CLOVE, NEEM AND EUCALYPTUS LEAF EXTRACT ON MATING BEHAVIOUR, OVIPOSITION AND ADULT EMERGENCE OF PULSE BEETLE, Callosobruchus maculatus
Progress. Agric. 18(2) : 93-97, 2007 ISSN 1017-8139 EFFECTS OF GARLIC CLOVE, NEEM AND EUCALYPTUS LEAF EXTRACT ON MATING BEHAVIOUR, OVIPOSITION AND ADULT EMERGENCE OF PULSE BEETLE, Callosobruchus maculatus
EffectivenessofDifferentSpayTimingMethodsfortheControlofLepidopteronPestsinCotton
 Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: D Agriculture and Veterinary Volume 16 Issue 8 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: D Agriculture and Veterinary Volume 16 Issue 8 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Evaluation of modified waste brewer s yeast as a protein source for the control of the melon fly, Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett)
 Proceedings of 6th International Fruit Fly Symposium 6 10 May 2002, Stellenbosch, South Africa pp. 295 299 Evaluation of modified waste brewer s yeast as a protein source for the control of the melon fly,
Proceedings of 6th International Fruit Fly Symposium 6 10 May 2002, Stellenbosch, South Africa pp. 295 299 Evaluation of modified waste brewer s yeast as a protein source for the control of the melon fly,
Effect Of Bagging On Chemical Properties Of Mango (MangiferaindicaL.) CV. Alphonso
 International Journal of Horticultural & Crop Science Research. ISSN 2249-4243 Volume 6, Number 1 (2016), pp. 1-8 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Effect Of Bagging On Chemical
International Journal of Horticultural & Crop Science Research. ISSN 2249-4243 Volume 6, Number 1 (2016), pp. 1-8 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Effect Of Bagging On Chemical
EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL FOR HEALTH AND FOOD SAFETY
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL FOR HEALTH AND FOOD SAFETY Food and feed safety, innovation Pesticides and biocides COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT 1 Basic Substance diammonium phosphate SANTE/12351/2015
EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL FOR HEALTH AND FOOD SAFETY Food and feed safety, innovation Pesticides and biocides COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT 1 Basic Substance diammonium phosphate SANTE/12351/2015
Chemical Compatibility of Insecticides and Fungicides/ Bactericide on Cabbage aphid - Brevicoryne brassicae
 Chemical Compatibility of Insecticides and Fungicides/ Bactericide on Cabbage aphid - Brevicoryne brassicae V.Vidhyadhari 1, D. Sridevi 2, B. Pushpavathi 3 and T. Ramesh Babu 4 1,2,4 Department of Entomology,
Chemical Compatibility of Insecticides and Fungicides/ Bactericide on Cabbage aphid - Brevicoryne brassicae V.Vidhyadhari 1, D. Sridevi 2, B. Pushpavathi 3 and T. Ramesh Babu 4 1,2,4 Department of Entomology,
Relative efficacy of different insecticides against whitefly, Bemisia tabaci on tomato under field condition
 2017; 5(5): 728-732 E-ISSN: 2320-7078 P-ISSN: 2349-6800 JEZS 2017; 5(5): 728-732 2017 JEZS Received: 04-07-2017 Accepted: 05-08-2017 Sudeepa Kumari Jha Ph.D. (Ag.), Entomology, BAU Kanke, Ranchi, Jharkhand,
2017; 5(5): 728-732 E-ISSN: 2320-7078 P-ISSN: 2349-6800 JEZS 2017; 5(5): 728-732 2017 JEZS Received: 04-07-2017 Accepted: 05-08-2017 Sudeepa Kumari Jha Ph.D. (Ag.), Entomology, BAU Kanke, Ranchi, Jharkhand,
ORIENTATIONAL EFFECT OF AQUEOUS LEAF EXTRACT OF CITRUS AURANTIFOLIA ON HOUSEFLY, MUSCA DOMESTICA (DIPTERA:MUSCIDAE)
 Proceeding of the 2 nd International Conference on Agriculture and Forestry, Vol. 1, 2015, pp. 90-94 Copyright TIIKM ISSN: 2362 1036 online DOI: 10.17501/icoaf2015-1112 ORIENTATIONAL EFFECT OF AQUEOUS
Proceeding of the 2 nd International Conference on Agriculture and Forestry, Vol. 1, 2015, pp. 90-94 Copyright TIIKM ISSN: 2362 1036 online DOI: 10.17501/icoaf2015-1112 ORIENTATIONAL EFFECT OF AQUEOUS
ONGOING PROJECT REPORT YEAR 1/3 WTFRC Project # CH
 ONGOING PROJECT REPORT YEAR 1/3 WTFRC Project # CH-6-63 Project title: Cherry Fruit Fly Control Options PI: Timothy J. Smith Organization: WSU Extension, North Central Washington Address, phone, e-mail:
ONGOING PROJECT REPORT YEAR 1/3 WTFRC Project # CH-6-63 Project title: Cherry Fruit Fly Control Options PI: Timothy J. Smith Organization: WSU Extension, North Central Washington Address, phone, e-mail:
Review of Long-Term Containment Strategy for Exotic Fruit Flies in Torres Strait. Andrew Tomkins Chair
 Review of Long-Term Containment Strategy for Exotic Fruit Flies in Torres Strait Andrew Tomkins Chair The Torres Strait Zones protect biosecurity while enabling traditional movement of people and goods.
Review of Long-Term Containment Strategy for Exotic Fruit Flies in Torres Strait Andrew Tomkins Chair The Torres Strait Zones protect biosecurity while enabling traditional movement of people and goods.
ISPM No. 30 ESTABLISHMENT OF AREAS OF LOW PEST PREVALENCE FOR FRUIT FLIES (TEPHRITIDAE) (2008)
 Establishment of areas of low pest prevalence for fruit flies (Tephritidae) ISPM No. 30 ISPM No. 30 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES ISPM No. 30 ESTABLISHMENT OF AREAS OF LOW PEST PREVALENCE
Establishment of areas of low pest prevalence for fruit flies (Tephritidae) ISPM No. 30 ISPM No. 30 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES ISPM No. 30 ESTABLISHMENT OF AREAS OF LOW PEST PREVALENCE
Species composition of Dacine fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae: Dacinae: Dacini) associated with Cucurbits in Tripura, a North Eastern state of India
 2017; 5(3): 330-335 E-ISSN: 2320-7078 P-ISSN: 2349-6800 JEZS 2017; 5(3): 330-335 2017 JEZS Received: 20-03-2017 Accepted: 21-04-2017 N Nair Department of Entomology, Thangjam Bc Department of Entomology,
2017; 5(3): 330-335 E-ISSN: 2320-7078 P-ISSN: 2349-6800 JEZS 2017; 5(3): 330-335 2017 JEZS Received: 20-03-2017 Accepted: 21-04-2017 N Nair Department of Entomology, Thangjam Bc Department of Entomology,
Response of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium Levels on Linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.)
 Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 6 Special issue [3] 2017: 475-479 2017 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808
Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 6 Special issue [3] 2017: 475-479 2017 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808
Additions to the Fruit Fly Fauna (Diptera: Tephritidae: Dacinae) of Bangladesh, with a Key to the Species
 Additions Proceedings to of the the fruit Hawaiian fly fauna Entomological of Bangladesh Society (2014) 46:31 40 31 Additions to the Fruit Fly Fauna (Diptera: Tephritidae: Dacinae) of Bangladesh, with
Additions Proceedings to of the the fruit Hawaiian fly fauna Entomological of Bangladesh Society (2014) 46:31 40 31 Additions to the Fruit Fly Fauna (Diptera: Tephritidae: Dacinae) of Bangladesh, with
Relationship between Population Fluctuation of Oriental Fruit Fly Bactrocera dorsalis Hendel and Abiotic Factors in Yezin, Myanmar
 Journal of Life Sciences 12 (218) 141-149 doi: 1.17265/1934-7391/218.3.4 D DAVID PUBLISHING Relationship between Population Fluctuation of Oriental Fruit Fly Bactrocera dorsalis Hendel and Abiotic Factors
Journal of Life Sciences 12 (218) 141-149 doi: 1.17265/1934-7391/218.3.4 D DAVID PUBLISHING Relationship between Population Fluctuation of Oriental Fruit Fly Bactrocera dorsalis Hendel and Abiotic Factors
Olive Fly (Bactrocera Oleae Gmelin) MANAGEMENT WITH NEW ALLOWED FORMULATIONS, SATISFYING THE OLIVE OIL QUALITY REQUIREMENTS
 International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES) ISSN (Online) 2319-183X, (Print) 2319-1821 Volume 2, Issue 5(May 213), PP.9-13 Olive Fly (Bactrocera Oleae Gmelin) MANAGEMENT WITH NEW
International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES) ISSN (Online) 2319-183X, (Print) 2319-1821 Volume 2, Issue 5(May 213), PP.9-13 Olive Fly (Bactrocera Oleae Gmelin) MANAGEMENT WITH NEW
Variability in Grain Physico-Chemical Composition in Different Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] Genotypes
![Variability in Grain Physico-Chemical Composition in Different Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] Genotypes Variability in Grain Physico-Chemical Composition in Different Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] Genotypes](/thumbs/89/100952835.jpg) International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 2610-2618 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.368
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 2610-2618 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.368
Identification of Sources of Resistance against turcicum leaf blight of maize
 2017; 5(5): 1664-1668 P-ISSN: 2349 8528 E-ISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2017; 5(5): 1664-1668 2017 IJCS Received: 16-07-2017 Accepted: 18-08-2017 Manu TG Gangadhara Naik B Murali R Nagaraja H Correspondence Manu
2017; 5(5): 1664-1668 P-ISSN: 2349 8528 E-ISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2017; 5(5): 1664-1668 2017 IJCS Received: 16-07-2017 Accepted: 18-08-2017 Manu TG Gangadhara Naik B Murali R Nagaraja H Correspondence Manu
PILOT APPLICATION OF STERILE INSECT TECHNIQUE FOR THE ORIENTAL FRUIT FLY, BACTROCERA PHJLIPPJNENSIS, IN NAOWAY ISLET
 PH992 PILOT APPLICATION OF STERILE INSECT TECHNIQUE FOR THE ORIENTAL FRUIT FLY, BACTROCERA PHJLIPPJNENSIS, IN NAOWAY ISLET E. C. MANOTO, S. S. RESILVA, G. B. OBRA, M. R. REYES Philippine Nuclear Research
PH992 PILOT APPLICATION OF STERILE INSECT TECHNIQUE FOR THE ORIENTAL FRUIT FLY, BACTROCERA PHJLIPPJNENSIS, IN NAOWAY ISLET E. C. MANOTO, S. S. RESILVA, G. B. OBRA, M. R. REYES Philippine Nuclear Research
Collaborators: Gration Rwegasira, Marc De Meyer, Massimiliano Virgilio and Richard Drew
 (a) Progress report (i) Contract number IAEA Technical contract Nr 16077/RO (ii) Title of the project Host utilization and genetic divergence among populations of Bactrocera invadens Drew Tsuruta and White
(a) Progress report (i) Contract number IAEA Technical contract Nr 16077/RO (ii) Title of the project Host utilization and genetic divergence among populations of Bactrocera invadens Drew Tsuruta and White
MANAGEMENT OF COLLAR ROT OF GROUNDNUT THROUGH SEED TREATMENT ABSTRACT
 MANAGEMENT OF COLLAR ROT OF GROUNDNUT THROUGH SEED TREATMENT K. B. RAKHOLIYA*, K. B. JADEJA AND A. M. PARAKHIA Department of plant pathology college of agriculture junagadh agricultural university junagadh
MANAGEMENT OF COLLAR ROT OF GROUNDNUT THROUGH SEED TREATMENT K. B. RAKHOLIYA*, K. B. JADEJA AND A. M. PARAKHIA Department of plant pathology college of agriculture junagadh agricultural university junagadh
Area-wide Integrated Management of Fruit Flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) Pest in Vegetables Cultivation
 Journal of Biological and Environmental Engineering Vol. 1, No. 2, 2016, pp. 10-16 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/jbee Area-wide Integrated Management of Fruit Flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) Pest in Vegetables
Journal of Biological and Environmental Engineering Vol. 1, No. 2, 2016, pp. 10-16 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/jbee Area-wide Integrated Management of Fruit Flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) Pest in Vegetables
Status and management of anthracnose of pomegranate in Karnataka State of India
 Status and management of anthracnose of pomegranate in Karnataka State of India Nargund V.B., Jayalakshmi K., Venagi V.I., Byadgi A.S., Patil R.V. in Melgarejo P. (ed.), Valero D. (ed.). II International
Status and management of anthracnose of pomegranate in Karnataka State of India Nargund V.B., Jayalakshmi K., Venagi V.I., Byadgi A.S., Patil R.V. in Melgarejo P. (ed.), Valero D. (ed.). II International
REFERENCES. mite on okra.
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PLANT PROTECTION VOLUME 9 ISSUE 2 OCTOBER, 2016 439-444 e ISSN-0976-6855 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in IJPP DOI : 10.15740/HAS/IJPP/9.2/439-444 RESEARCH PAPER Bio-efficacy
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PLANT PROTECTION VOLUME 9 ISSUE 2 OCTOBER, 2016 439-444 e ISSN-0976-6855 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in IJPP DOI : 10.15740/HAS/IJPP/9.2/439-444 RESEARCH PAPER Bio-efficacy
The fruit flies are the classical international
 Pakistan J. Zool., vol. 36(3), pp. 219-230, 2004. Identification of Pest Species in Oriental Fruit Fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae) Species Complex KHALID MAHMOOD Barani Agricultural
Pakistan J. Zool., vol. 36(3), pp. 219-230, 2004. Identification of Pest Species in Oriental Fruit Fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) (Diptera: Tephritidae) Species Complex KHALID MAHMOOD Barani Agricultural
Genetic Analysis for Earliness and Yield Components using Gynoecious and Monoecious Lines in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.)
 Research Article Genetic Analysis for Earliness and Yield Components using Gynoecious and Monoecious Lines in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) G. S. Jat 1 *, A. D. Munshi 1, T. K. Behera 1, A. K. Singh 2
Research Article Genetic Analysis for Earliness and Yield Components using Gynoecious and Monoecious Lines in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) G. S. Jat 1 *, A. D. Munshi 1, T. K. Behera 1, A. K. Singh 2
Influence of High-P-Chelated Micronutrients on Nutrient Uptake of Chickpea Under Vertisols
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TROPICAL AGRICULTURE ISSN : 0254-8755 available at http: www.serialsjournal.com Serials Publications Pvt. Ltd. Volume 35 Number 3 2017 Influence of High-P-Chelated Micronutrients
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TROPICAL AGRICULTURE ISSN : 0254-8755 available at http: www.serialsjournal.com Serials Publications Pvt. Ltd. Volume 35 Number 3 2017 Influence of High-P-Chelated Micronutrients
Effect of Field Plot Design on the Efficacy of Boom Sprayer
 Universal Journal of Agricultural Research 2(7): 236-241, 2014 DOI: 10.13189/ujar.2014.020702 http://www.hrpub.org Effect of Field Plot Design on the Efficacy of Boom Sprayer Khurram Yousaf 1, Muhammad
Universal Journal of Agricultural Research 2(7): 236-241, 2014 DOI: 10.13189/ujar.2014.020702 http://www.hrpub.org Effect of Field Plot Design on the Efficacy of Boom Sprayer Khurram Yousaf 1, Muhammad
DEVELOPMENT, EVALUATION, PRODUCTION AND APPLICATION OF ECO-FRIENDLY NEEM BASED PESTICIDES AN INDIAN EXPERIENCE
 DEVELOPMENT, EVALUATION, PRODUCTION AND APPLICATION OF ECO-FRIENDLY NEEM BASED PESTICIDES AN INDIAN EXPERIENCE S.P. Dhua and Y.P. Ramdev RENPAP/UNIDO India Agriculture based economy Important inputs for
DEVELOPMENT, EVALUATION, PRODUCTION AND APPLICATION OF ECO-FRIENDLY NEEM BASED PESTICIDES AN INDIAN EXPERIENCE S.P. Dhua and Y.P. Ramdev RENPAP/UNIDO India Agriculture based economy Important inputs for
