Bio 230 Lecture Notes: THE URINARY SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Ilene Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bio 230 Lecture Notes: THE URINARY SYSTEM NOTE: You must follow along in your text book or the powerpoint supplied while reading through these lecture notes. A picture is worth a thousand words. Urinary System : 2 kidneys, 2 Ureters, 1 bladder, 1 urethra INTRODUCTION : Major Functions of Kidneys: When blood sugar (glucose) levels are low, the liver converts amino acids into glucose for energy. Amino acids come from the breakdown of protein in the GI tract. The conversion of amino acids to glucose results in the production of the nitrogenous waste product, ammonia (NH3). Ammonia is extremely toxic to cells, so the liver converts NH3 to the less toxic nitrogenous waste product, urea. Measured in our blood in the lab test BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen). The URINARY SYSTEM removes urea and other metabolic waste products, toxins, excess water, and excess electrolytes (salts) from the bloodstream and eliminates them from the body in the form of urine. The process of eliminating metabolic wastes is called excretion. The KIDNEYS are the excretory organs of the urinary system. As the kidneys perform their excretory function, they also regulate blood volume and the chemical makeup of the blood. They continuously maintain the proper balance between water and salts in the blood and they help to maintain the blood ph at and help regulate blood pressure. Kidneys also release the hormone erythropoietin (EPO), which stimulates the bone marrow to produce more RBC s (erythropoesis). KIDNEYS: EXTERNAL ANATOMY (Follow along with your classroom models/worksheets) Kidneys are kidney bean-shaped and reddish in color. (due to high vascularity-receive 25% of resting cardiac output). The adult kidney weighs 1/3 pound, is 4-5 inches long, 2-3 in. wide and 1 in. thick. The kidneys are located along the posterior abdominal wall, lateral to the vertebral column. They are retroperitoneal, extending from the level of the T12 vertebra to the level of the L3 vertebra. The kidneys receive some protection from the lower part of the rib cage and are surrounded by adipose for additional protection. The right kidney is slightly lower than left kidney. WHY? The lateral surface of each kidney is convex. The medial surface is concave and has an indentation called the HILUM. The ureters, renal blood vessels, enter or exit the kidney at the hilum. RENAL CAPSULE outer protective membrane that is transparent and made of fibrous connective tissue. The renal capsule prevents infections in surrounding regions from spreading to the kidneys. It also protects the kidney from physical trauma. KIDNEY: INTERNAL ANATOMY A frontal section of the kidney reveals 3 distinct regions inside the renal capsule and they are the RENAL CORTEX, RENAL MEDULLA, & RENAL PELVIS. 1. RENAL CORTEX: the outer region just inside the renal capsule; light red in color and granular in appearance. 2. RENAL MEDULLA: deep to the cortex; a darker, reddish brown color. Arranged in cone-shaped regions called RENAL PYRAMIDS, which have a striated appearance. Each kidney has about
2 pyramids. Each pyramid tapers to an apex (papilla). The numerous tubules and ducts in the pyramids give it a striated appearance. (Be sure to see these striations on the models) Extensions of the RENAL CORTEX between the renal pyramids are called RENAL COLUMNS. Together, the RENAL CORTEX & MEDULLA form a RENAL LOBE. 3. RENAL PELVIS: where the urine is collected and sent to the ureter. Each pyramid drains its formed urine into its own minor calyx. Minor calyces join to form major calyces with join to form the renal pelvis. NEPHRONS: Nephrons are contained within the renal lobes. Each kidney contain over 1 million microscopic NEPHRONS. Nephrons are the functional units of the kidneys because nephrons carry out the processes that form urine. Parts of a Nephron: Vessels Tubules 1. glomerulus 1. Glomerular (Bowman s) capsule 2. afferents arteriole 2. Proximal convoluted tubule 3. efferent arteriole 3. Loop of Henle 4. peritubular capillary 4. Distal convoluted tubule 5. * vasa recta 5. Collecting duct * (only in jutamedullary nephron) Each nephron consists of a RENAL CORPUSCLE (where urine is filtered). The renal corpuscle consists of a cup-shaped structure called the GLOMERULAR (BOWMAN'S) CAPSULE and the capillary bed that it surrounds, called the GLOMERULUS. The renal corpuscle (Bowman s capsule + glomerulus) are located in the RENAL CORTEX. The pores of the GLOMERULUS (fenestrated capillary endothelium) and the filtration slits of the BOWMAN S CAPSULE filter the blood as it moves through the glomerulus. Water and many solutes (glucose, salts, urea, drugs, vitamins, amino acids) can pass through the pores & filtration slits, but large molecules like plasma proteins and the formed elements of the blood (RBC s & WBC s) cannot. The water and solutes that filter out of the blood and are collected inside the glomerular capsule space are called the filtrate. The glomerular (Bowman s) capsule opens into the renal tubule.. The first section of the renal tubule is called the PROXIMAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE, which lies in the renal cortex. Notice that the cells that line the proximal convoluted tubule have microvilli on their apical surface (fig. 27.6a in McKinley). These cells reabsorb water and other needed substances from the filtrate and return them to the bloodstream (via the peritubular capillaries). Remember- microvilli (increase surface area)=increase the efficiency of reabsorption. The proximal convoluted tubule straightens and becomes the DESCENDING LIMB OF THE LOOP OF HENLE, and then it makes a narrow U-turn called the LOOP OF HENLE. The loop turns back up toward the renal cortex as the ASCENDING LIMB OF THE LOOP OF HENLE. Nephrons are classified into 2 types based on the location of the loop of Henle: 1. CORTICAL NEPHRONS: the loop of Henle is mostly in the cortex and penetrates a little into the medulla. 2. JUXTAMEDULLARY NEPHRONS: the loop of Henle penetrates deeply into the medulla, and the glomerular capsule is closer to the medulla. juxta means next too 2
3 In the renal cortex, the ascending limb of the loop of Henle becomes twisted again as the DISTAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE. The distal convoluted tubules of several nephrons empty into a COLLECTING DUCT. The collecting ducts absorb more water from the filtrate if needed. ADH (Anti Diuretic Hormone) acts on the collecting ducts to increase water reabsorption. ADH released from the pituitary gland when the body is dry, the urine becomes more concentrated, hence the name anti diuretic. Collecting ducts empty into a MINOR CALYX, minor calyxes join to form MAJOR CALYXES, which delivers urine to the RENAL PELVIS, which transports the urine to the ureter of the kidney. The filtrate is processed as it passes through these parts of the nephron. Needed substances, such as water, glucose and electrolytes (salts), are returned to the bloodstream. After the filtrate is processed by the nephron, it is called URINE. Urine contains urea and other metabolic wastes, toxins, excess salts, & excess water, as well as drugs and excess vitamins. BLOOD SUPPLY OF THE KIDNEYS: While the body is at rest, the large left and right RENAL ARTERIES deliver about about 1.2 liters of blood through the kidneys every minute (25 % of resting cardiac output). The renal arteries are branches of the ABDOMINAL AORTA. After each renal artery enters a kidney, it branches into numerous small arteries, which carry the blood to the renal cortex (where the Renal Corpuscles reside). The blood flow through the kidney is: Renal arteryàsegmental arteriesàinterlobar arteriesàarcuate arteriesàinterlobular arteriesàafferent ARTERIOLES (one for each nephron). Each afferent arteriole, divides to form a capillary tuft called the GLOMERULUS. The glomerulus is surrounded by the glomerular capsule and is specialized for filtration of blood. The glomerular capillaries merge to form the EFFERENT ARTERIOLE, which leads away from the glomerular capsule. The efferent arteriole's diameter is smaller than the afferent arteriole. This raises the blood pressure in the glomerulus, which aids in forcing water and solutes into the glomerular capsule. Each efferent arteriole branches into a second capillary network called the PERITUBULAR CAPILLARIES. These capillaries cling closely to the PROXIMAL & DISTAL CONVOLUTED TUBULES of both cortical & juxtamedullary nephrons. The efferent arterioles of juxtamedullary nephrons also branch into the VASA RECTA, capillaries that surround the LOOP OF HENLE in the medulla. The peritubular capillaries and vasa recta are adapted for absorption. They absorb water and needed substances from the filtrate in the nephron, so that much of the water and solutes that the body requires are returned to the bloodstream rather than flushed out in the urine. Toxins and excess water and solutes remain in the filtrate and are eliminated as urine. The peritubular capillaries and vasa recta merge into venules àinterlobular veinàarcuate veinsàinterlobar veinsàthat join and which empty into the RENAL VEIN. (note no segmental veins as counterpart to arterial side) The RENAL VEIN of each kidney leaves the kidney through the hilum. The renal vein of each kidney returns freshly cleansed blood to the INFERIOR VENA CAVA. URETERS: The URETERS are slender tubes about in long that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Each ureter runs posterior to the parietal peritoneum (retroperitoneal) from the renal hilum to the level of the urinary bladder. At the urinary bladder, each ureter makes a medial turn toward the bladder and enters the posterior bladder wall at an oblique angle, which prevents backflow of urine from the bladder into the ureters. The inner lining of the ureter wall is MUCOSA that consists of transitional epithelium, that stretches as urine passes through. Mucus secreted by the mucosa protects the epithelial cells from coming into contact with the urine, which contains toxins and is slightly acidic. Beneath the mucosa is the MUSCULARIS, which is composed of smooth muscle arranged in circular and longitudinal layers. The muscularis creates 3
4 peristaltic contractions, similar to those in the GI tract. When the renal pelvis fills with urine, smooth muscle in the renal pelvis wall contracts rhythmically, sending urine into the ureter. Peristalsis propels the urine through the ureter to the urinary bladder. URINARY BLADDER: The URINARY BLADDER is a hollow muscular organ located in the pelvic cavity posterior to the pubic symphysis. Like the kidneys and ureters, the urinary bladder is retroperitoneal. In males the urinary bladder lies anterior to the rectum. In females the bladder is superior to the vagina and inferior to the uterus. Looking at your workshhet can you now understand why pregnant women have such bladder holding problems as the uterus get larger and larger! The function of the urinary bladder is the temporary storage of urine. Structures to find include the openings of the 2 ureters into the bladder and the urethra opening, which form the TRIGONE triangle. The inner wall of the urinary bladder consists of a MUCOSA made of transitional epithelium which is able to stretch a great deal. Mucus produced by the bladder mucosa helps protect the wall from urine. Beneath the mucosa is smooth muscle, arranged in circular and longitudinal layers. The smooth muscle in the wall allows the bladder to stretch a great deal. When empty, the bladder is 2-3 in long. Its walls are thick and its mucosa is thrown into folds called RUGAE (remember this term from the stomach?). When urine accumulates in the bladder, it expands and becomes pear-shaped as it rises upward in the pelvic cavity. The transitional epithelium and smooth muscle stretches and thins. This increases the internal volume of the bladder by decreasing the thickness of its wall. A moderately full bladder is about 5 in long and holds about 500 ml of urine. The average capacity of the bladder is ml. When the volume of urine in the bladder exceeds ml, stretch receptors in the bladder transmit nerve impulses to the brain, initiating the conscious desire to urinate. The constricted NECK of the bladder is where the Urethra leaves the bladder. Here is where the INTERNAL URETHRAL SPHINCTER is located. Smooth muscle, involuntary control. URETHRA: The URETHRA is a muscular tube that drains urine from the urinary bladder and conveys it out of the body. The INTERNAL URETHRAL SPHINCTER is an involuntary smooth muscle sphincter at the base of urinary bladder, Just distal to the bladder neck. The EXTERNAL URETHRAL SPHINCTER is a voluntary skeletal muscle sphincter in the UROGENITAL DIAPHRAGM. You control this one. The muscle toddlers learn to control when toilet training. THE FEMALE URETHRA: The urethra in females is short. It is only about about 1.5 inches lengthwise. The lining epithelium of the female urethra is psuedostratified columnar epithelium at its most promimal and then becomes stratified sqauamous epithelium. MALE URETHRA: The urethra in the male is longer than the urethra of females. The male urethra is 7 to 8 inches lengthwise (variable). The male urethra fuctions as a conduit for urine and semen. The male urethra is divided into three sections: prostatic urethra, membranous urethra, and spongy (penile) urethra. Make sure you can find these 3 regions. Histology of the Prostatic Urethra The first portion of the male urethra is the prostatic urethra. This portion of the urethra goes through the prostate gland. The prostatic urethra is lined by transitional epithelium. 4
5 Histology of the Membranous Urethra The second part of the male urethra is the membranous urethra. This is a short segment. where it passes through the urogenital diaphragm (external spinchter). The lining epithelium of the membranous urethra is psuedostratified columnar epithelium. Histology of the Spongy Urethra The third part of the urethra is the spongy urethra. The spongy urethra is also called the penile urethra. This is the longest section of the male urethra. It travels through the corpus spongiosum of the penis. The lining epithelium of the spongy urethra is psuedostratified columnar epithelium which then transitions to stratified squamous epithelium distally. Incontinence gatta go. Pregnant women don t forget your kegels! 5
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY
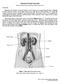 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden
 Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Urinary System. Chapter 17 7/19/11. Introduction
 7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
Waste. Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8. Urinary System. Urinary System. Nitrogenous Wastes. Nitrogenous Wastes 4/22/2016
 Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
1. The Fibrous Capsule covers the outside of the kidney. It is made of fat and fibers.
 Slide 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is the excretion of toxic metabolic waste through urine production. The kidneys filter blood plasma and as a result of filtering blood, the kidneys help
Slide 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is the excretion of toxic metabolic waste through urine production. The kidneys filter blood plasma and as a result of filtering blood, the kidneys help
Chapter 25: Urinary System
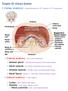 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Chapter 17: Urinary System
 Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
The Urinary System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Chapter 26. The Urinary System. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Filtration Reabsorption Secretion Concentration
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 25 For this lab you will use parts
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 25 For this lab you will use parts
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
URINARY SYSTEM. Urinary System
 URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily.
 1 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily. Next, the kidneys filter blood. As a result of filtering blood, the kidneys
1 2 The kidney has a number of functions. First is Urine Production. We ll discuss the specifics of this process momentarily. Next, the kidneys filter blood. As a result of filtering blood, the kidneys
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART
 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART 1 DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Urinary System Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body Regulates water, electrolyte, and ph
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART 1 DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Urinary System Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body Regulates water, electrolyte, and ph
Urinary System. Genitourinary System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 11. Overview 1/4/2013
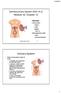 Genitourinary System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 11 Overview Urinary system Kidneys Ureter Bladder Nephron Male reproductive system Testes Accessory Structures Susie Turner, M.D. 71/3/13 Major homeostatic
Genitourinary System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 11 Overview Urinary system Kidneys Ureter Bladder Nephron Male reproductive system Testes Accessory Structures Susie Turner, M.D. 71/3/13 Major homeostatic
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Chapter 13 The Urinary System
 Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Urinary Anatomy. Lab 40. Kidneys. Nephrons. Renal Corpuscle
 Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
Histology / First stage The Urinary System: Introduction. Kidneys
 The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
The Urinary System PART A
 15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
Lesson 14.1: Learning the Key Terms
 209 Lesson 14.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. collecting duct 2. distal convoluted tubule 3. glomerulus 4. nephron 5. nephron loop
209 Lesson 14.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. collecting duct 2. distal convoluted tubule 3. glomerulus 4. nephron 5. nephron loop
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
The functional anatomy of the urinary system. Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic
 The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
The functional anatomy of the urinary system Human Anatomy Department Dr. Anastasia Bendelic Plan Development of the kidneys and their abnormalities Development of the urinary ways and their abnormalities
The Urinary System. Medical Assisting Third Edition. Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM
 AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra. The formation of urine is the function of the kidneys, and the rest of the system is responsible
URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra. The formation of urine is the function of the kidneys, and the rest of the system is responsible
The urinary system consists of:
 Urinary system The urinary system consists of: - Two kidneys: this organ extracts wastes from the blood, balance body fluids and form urine. - Two ureters: this tube conducts urine from the kidneys to
Urinary system The urinary system consists of: - Two kidneys: this organ extracts wastes from the blood, balance body fluids and form urine. - Two ureters: this tube conducts urine from the kidneys to
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a.
 I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
HISTOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Fifth Year Biology. Excretion. Miss Rochford
 Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT. 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys.
 Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys II. Nephron Unit and Urine Formation
 URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
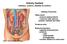 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology
 Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
Excretion and Waste Management. Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski
 Excretion and Waste Management Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski Lesson 1 Waste Products and Organs 2 3 Excretion Excretion: Process by which dissolved metabolic wastes are separated from body fluids and removed
Excretion and Waste Management Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski Lesson 1 Waste Products and Organs 2 3 Excretion Excretion: Process by which dissolved metabolic wastes are separated from body fluids and removed
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Urinary system. Lab-7
 Urinary system Lab-7 Excretion: processes that remove wastes and excess materials from the body Urinary system (kidneys): excretes nitrogenous wastes, excess solutes, and water The Kidneys Regulate Water
Urinary system Lab-7 Excretion: processes that remove wastes and excess materials from the body Urinary system (kidneys): excretes nitrogenous wastes, excess solutes, and water The Kidneys Regulate Water
2. Ureters Composed of smooth muscle tissue ~25cm long Connects kidneys to bladder Undergoes peristaltic contraction to move urine to bladder
 Section 6: The Urinary System A) Organs of the Urinary system 1. Kidneys 2. Ureters 3. Bladder 4. Urethra 1. Kidneys Paired organs located on either side of vertebral column in upper part of abdominal
Section 6: The Urinary System A) Organs of the Urinary system 1. Kidneys 2. Ureters 3. Bladder 4. Urethra 1. Kidneys Paired organs located on either side of vertebral column in upper part of abdominal
Urinary System. BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
4. VITA D- absorbs CALCIUM for healthy bones
 4. VITA D- absorbs CALCIUM for healthy bones The skin soaks in vita D from sun exposure 15-20 min or 30 min for darker complexions to synthesize vita D Kidneys metabolize vita D into CALCITROL Difference
4. VITA D- absorbs CALCIUM for healthy bones The skin soaks in vita D from sun exposure 15-20 min or 30 min for darker complexions to synthesize vita D Kidneys metabolize vita D into CALCITROL Difference
Pages Renal A&P Renal Blood Flow The Nephron Urine Formation Homeostatic Imbalances & Treatment
 CH. 25-URINARY SYSTEM Pages 960-994 Renal A&P Renal Blood Flow The Nephron Urine Formation Homeostatic Imbalances & Treatment 2009- First public case of water intoxication (hyponatremia); Jury awarded
CH. 25-URINARY SYSTEM Pages 960-994 Renal A&P Renal Blood Flow The Nephron Urine Formation Homeostatic Imbalances & Treatment 2009- First public case of water intoxication (hyponatremia); Jury awarded
Kidney, Kidney Bean..Which is. Which
 l AKA "The Urinary System" This is the system responsible for the removal of waste from blood. This waste is "cell waste" or "excretion" to distinguish it from "solid waste" or "feces". The principle organ
l AKA "The Urinary System" This is the system responsible for the removal of waste from blood. This waste is "cell waste" or "excretion" to distinguish it from "solid waste" or "feces". The principle organ
Question 1: Solution 1: Question 2: Question 3: Question 4: Class X The Excretory System Biology
 A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Bladder Schistosomes. Normally, urine is sterile. Presence of blood may indicate an infection.
 Bladder Schistosomes Normally, urine is sterile. Presence of blood may indicate an infection. 17.1 Introduction -Cells produce waste that can become toxic if they accumulate Functions the urinary system
Bladder Schistosomes Normally, urine is sterile. Presence of blood may indicate an infection. 17.1 Introduction -Cells produce waste that can become toxic if they accumulate Functions the urinary system
Urinary system. Aleš Hampl
 Urinary system Aleš Hampl Functions of urinary system 1. Regulating blood volume and pressure 2. Regulating plasma concentrations of sodium, potassium, chloride and other ions 3. Stabilising blood ph 4.
Urinary system Aleš Hampl Functions of urinary system 1. Regulating blood volume and pressure 2. Regulating plasma concentrations of sodium, potassium, chloride and other ions 3. Stabilising blood ph 4.
Chapter 32 Excretion
 Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Urinary System
 Urinary System What are the organs that comprise the urinary system? Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder Ureters Urethra Hepatic veins (cut) Esophagus (cut) Inferior vena cava Adrenal gland Aorta
Urinary System What are the organs that comprise the urinary system? Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder Ureters Urethra Hepatic veins (cut) Esophagus (cut) Inferior vena cava Adrenal gland Aorta
Urinary System Functions of the Urinary system (renal) A. B. C.
 Urinary System Functions of the Urinary system (renal) A. B. C. I. Overview of fluids A. Normal volumes 1. fluid intake a. = 1500 ml b. = 750 ml c. = 250 ml (remember ETS) d. total = 2500 ml/day 2. fluid
Urinary System Functions of the Urinary system (renal) A. B. C. I. Overview of fluids A. Normal volumes 1. fluid intake a. = 1500 ml b. = 750 ml c. = 250 ml (remember ETS) d. total = 2500 ml/day 2. fluid
Unit 15: The Urinary System
 Unit 15: The Urinary System I. Functions of the Urinary System A. Elimination of waste products 1. Nitrogenous wastes 2. Toxins 3. Drugs B. Regulate aspects of homeostasis 1. Water balance 2. Electrolytes
Unit 15: The Urinary System I. Functions of the Urinary System A. Elimination of waste products 1. Nitrogenous wastes 2. Toxins 3. Drugs B. Regulate aspects of homeostasis 1. Water balance 2. Electrolytes
