Biology 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reproductive Systems ANSWERS
|
|
|
- Brook Pierce
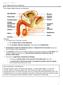
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bilgy 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reprductive Systems ANSWERS 1. What is the main excretry rgan? Kidneys 2. What are the functins f the kidney? helps maintain hmestasis thrugh regulatin f H 2O and ins 3. Ammnia, urea, uric acid and creatinine are knwn as nitrgenus wastes. 4. Hw are urea, uric acid, and creatinine frmed? Urea breakdwn f AA creates NH 3 (in the liver). NH 3 + CO 2 urea (less txic than NH 3) Uric acid = breakdwn f nucletides (can frm crystals) Creatinine= breakdwn f creatine phsphate synthesized by AA in liver high energy reserve mlecule fr muscles (like ATP) 5. Explain the 3 parts f a kidney : crtex, medulla, and pelvis. Renal crtex = uter regin (red because many capillaries) Renal medulla = inner area (striped because f tubules and bld vessels) Renal pelvis = innermst prtin where urine cllects befre leaving kidney 6. Explain the parts f a nephrn. It is the functinal unit f the kidney-- where filtratin takes place It cnsists f a renal crpuscle and a renal tubule (prximal cnvluted tubule, lp f henle, distal cnvluted tubule) It als cntains a glmerular capsule. 7. Explain the bld supply f the kidney (arund the nephrn). As bld flw cmes thrugh the kidney thrugh the renal artery, the artery branches several times and eventually results as an afferent arterile. The afferent arterile becmes the glmerular capillaries which make up the filtratin membrane (fenestrated capillaries). As bld exits the capillaries, it enters the efferent arteriles and frms anther series f capillaries. These tubules prvide a pathway fr sme f the filtrate t be reabsrbed 8. Knw the diagrams f the kidney 9. Knw the diagram f the nephrn and assciated bld supply 10. What are the functin and structure f the kidney, ureter, urethra, urinary bladder, renal crtex/medulla/pelvis, and nephrn 11. What is meant by water salt balance? Mre salts in bld = greater bld vlume = increased BP. Therefre, kidneys regulate bld pressure. Decrease salt = decrease bld vlume = decreased BP 12. What is meant by acid-base balance? kidneys mnitr and cntrl bld ph by excreting H + ins and by absrbing bicarbnate in HCO3 -. Urine has ph f 6 r lwer. 13. Explain the prcess f urine frmatin filtratin, selective reabsrptin, tubular secretin/excretin a. Filtratin = mvement frm bld t nephrn Bld enters the afferent arterile and then the glmerulus ú this increases BP int the glmerulus because capillaries are smaller than arteriles. ú increased BP frces water & small substances ut f the bld and int the Bwman s capsule (start f nephrn) ú fluid is nw called filtrate. ú The filtrate cntains: H 2O, glucse, AA, salts, nitrgenus wastes ú Larger mlecules remain in the nw thicker capillaries) ú they are taken away by the efferent arterile which is narrwer t keep pressure up in the glmerulus fr filtratin b. selective reabsrptin = mvement frm nephrn t bld (peritubular capillary netwrk PCN) - Occurs mainly in the prximal cnvluted tubule Cells cntain lts f prtein carriers and mitchndria fr active transprt micrvilli fr surface area fr absrptin - Glucse, AA, sme salts, little H 2O return t bld by active transprt (carrier prteins) Na + is actively reabsrbed and Cl - passively fllws - reabsrptin f salts increases smlarity f bld cmpared t filtrate water mves passively frm tubule int bld.
2 water mves ut fr 2 reasns: As slute is reabsrbed, water fllws by smsis (int PCN) Lp f Henle is in the renal medulla which is very salty (ECF full f NaCl and urea) water mves t establish equilibrium By end f descending lp, much water has been reabsrbed filtrate is very cncentrated (hypertnic t bld) The ascending (up) tubule f the Lp f Henle reabsrbs salt (e.g. NaCl) (permeable t salts nly NOT water) by the time filtrate reaches distal cnvluted tubule it is istnic t bld again c. tubular secretin = mvement frm bld t nephrn Occurs in distal cnvluted tubule by active transprt excess substances in bld enter the filtrate (i.e. Creatinine, drugs, penicillin, H + ) ph f bld is maintained by adjusting H + levels Nw int the Cllecting Duct sme urea slips ut and adds t slute cncentratin f renal medulla causes mre H 2O t diffuse ut f cllecting duct int renal medulla if ADH is present 14. Where des active transprt and diffusin ccur in the nephrn? Active = przimal tubule, ascending limb f lp f Henle, distal tubule, cllecting duct 15. What wuld happen if the glmerulus was damaged? salt and excess fluid can build up in the bdy 16. What is the rle f the hypthalamus and psterir pituitary in urine frmatin? Regulatin f urine frmatin by making and releases ADH 17. Where is the adrenal gland lcated? Hw des it affect urine frmatin? On tp f the kidneys, Regulates BP by adjusted bld vlume 18. Explain hw ADH regulates water in the urinary system Regulates reabsrptin f water by increased permeability f cllecting duct. S, mre water int bld ] increases BP 19. Explain hw Aldsterne regulates water in the urinary system Regulates BP by adjusted bld vlume. Increases Na + reabsrptin at distal cnvluted tubule this causes water t mve ut by smsis s bld vlume (BP) increases 20. What are the primary male reprductive parts and their functin? See male reprductive wrksheet key 21. Knw the diagram f the male reprductive system 22. Where are sperm made? Mature? Seminiferus tublules in testes is where sperm is made, matured in epididymis 23. Where is teststerne prduced? Interstitial cells in tests 24. What 3 glands release substances that make up semen/seminal fluid? Seminal vesicles, prstate gland, & Cwper s r Bulburethral gland What are the functins f seminal fluid? See Male Reprductive Wrksheet 25. Explain the prcess f spermatgenesis. Spermatgenesis is the prductin and maturatin f sperm cells. Where d sperm gain the ability t swim? Epididymis 26. What is the functin f teststerne? respnsible fr primary and secndary sex characteristics 27. Explain the cntrl f teststerne GnRH (frm Hypthalamus)= (gnadtrpic releasing hrmne) causes anterir pituitary t release LH and FSH LH (luteinizing hrmne) - stimulates interstitial cells (testes) t prduce teststerne 28. Explain the path f sperm thrugh the male reprductive system testes à epididymis à vas deferens à urethra à 29. What are the primary female reprductive parts and their functin? See Ntes 30. Knw the diagram f the female reprductive system 31. Where are cilia fund in the female reprductive system and what is their functin? Oviducts - tube is lined with cilia that create a current t carry the egg t uterus 32. Explain the path f an egg thrugh the female reprductive system fllicles have immarture eggs in varies à viducts à uterus 33. What are the functins f estrgen? T start primary and secndary sex characterisitcs
3 34. Explain the Menstrual cycle: uterine cycle and varian cycle. Als, explain the assciated hrmnal changes that ccur in each phase See wrksheets. 35. Explain the cntrl f hrmnes in the female reprductive system: gnadtrpic releasing hrmne, FSH, LH, estrgen, prgesterne, and the rle f the hypthalamus and pituitary gland. See wrksheets. 36. What 2 substances cause cntractin f the uterus? Oxytxin and estrgen 37. Cmpare and cntrast the rle f LH and FSH in the male and reprductive system. 38. What is HCG? What des it d? HCG = human chrinic gnadtrpin. HCG maintains the crpus luteum t prevent a drp in levels f estrgen & prgesterne. des 2 things: Shuts ff pituitary s n FSH r LH and Maintains endmetrium s crpus luteum n lnger neededè n menstruatin 39. Explain the rle f xytcin in pregnancy. Explain hw it is an example f psitive feedback. xytcin is a hrmne prduced by hypthalamus and stred in psterir pituitary. released in bld upn nervus stimulatin f hypthalamus. causes milk let-dwn by psitive feedback the mre the baby feeds mre xytcin mre milk prduced. stimulates cntractins f uterus during labur psitive feedback 40. What event marks the beginning f pregnancy? When the prductin f HCG 41. When des implantatin ccur? Abut 7 days after fertilzatin 42. Birth cntrl pills are a cmbinatin f estrgen + prgesterne 43. The tube that transprts urine frm the kidney t the urinary bladder is the a) Urethra c) Cllecting duct b) Ureter d) Prximal cnvluted tubule 44. The urinary bladder is useful because it a) Helps with defecatin b) Is a place where white cells attack bacteria c) Stres urine t prevent cnstant urinatin d) Transprts urine t the utside f the bdy 45. Nervus cntrl f urinatin invlves what mechanism(s)? a) The brain determines need fr urinatin frm an internal clck b) Stretch receptrs in the urinary bladder directly send impulses t the sphincters t cause urinatin c) Stretch receptrs in the urinary bladder send impulses t the spine causing a urinary reflex but the brain can delay the reflex d) Chemical receptrs in the bladder detect urine cncentratin and trigger a reflex actin 46. Which is NOT a functin f the urinary system? a) Mnitring and maintaining bld ph at abut 7.4 b) Regulating bld pressure by regulating salt balance in the bld c) Hrmne secretin t stimulate red bld cell prductin and regulate sdium in levels d) Prductin f water frm xygen and bicarbnate ins (HCO 3) 47. Excretin is a prcess in which is (are) remved frm the bdy a) Water c) Feces b) Salt d) Metablic wastes 48. Urea is a waste prduct in the metablism f a) Fats b) Glucse c) Minerals d) Prteins 49. The micrscpic anatmical unit f excretin fund in the kidney is the a) Nephrn b) Glmerular (Bwman s) capsule c) Glmerulus d) Alveli 50. In the diagram abve f the nephrn, which arrw represents the site f filtratin? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
4 51. In the diagram, which arrw represents the site f tubular secretin? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) In the diagram, the lp f the nephrn (lp f Henle) is fund at which site? 53. In the diagram, hydrgen and ptassium ins, creatinine, and ammnia will be excreted at which site? 54. In the diagram, glucse, salt, and water will nrmally be reabsrbed at which site? 55. In the diagram, the highest cncentratin f slutes in the medulla wuld be fund at which site? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) In the diagram, the effect f the hrmne ADH will be at which site? 57. Which f the fllwing wuld be an indicatin f kidney failure? a) Urea in the urine b) Salts in the urine c) Uric acid in the urine d) Large amunt f prtein in the urine 58. Which f these is the crrect sequence f bld vessels abut the nephrn? a) Renal artery, capillary bed, afferent arterile, efferent arterile, renal vein b) Efferent arterile, glmerulus, venule, afferent arterile, cllecting duct c) Afferent arterile, glmerulus, efferent arterile, capillary bed, venule, renal vein d) Afferent arterile, glmerulus, capillary bed, efferent arterile, venule renal vein 59. What is the crrect rder an excreted water mlecule mves frm glmerulus t cllecting duct? a) Lp f nephrn glmerular capsule prximal cnvluted tubule distal cnvluted tubule b) Glmerular capsule prximal cnvluted tubule lp f nephrn distal cnvluted tubule c) Prximal cnvluted tubule glmerular capsule lp f nephrn distal cnvluted tubule d) Glmerular capsule prximal cnvluted tubule distal cnvluted tubule lp f nephrn 60. The capillaries are enclsed by the Bwman s capsule. a) Peritubular b) Glmerular c) Cllecting tubule d) Lp f Henle 61. The cncentratin f prtein in the bld is higher in pst-glmerular bld as cmpared with that in arterial bld because a) Prtein is digested in glmerular / Bwman s capsule b) The kidney manufactures prtein c) Reabsrptin f prtein ccurs d) As water passes int the capsule, the cncentratin f prtein in the bld will increase 62. Which f the fllwing is NOT ne f the three steps (prcesses) invlved in urine frmatin? a) Pressure filtratin c) Cuntercurrent mechanism b) Selective reabsrptin d) Tubular secretin 63. Selective reabsrptin ccurs in the f the nephrn. a) Glmerulus c) Prximal cnvluted tubule b) Distal cnvluted tubule d) Cllecting duct 64. Tubular secretin allws hydrgen ins, creatinine and penicillin t be excreted in the distal cnvluted tubule. Hw are these mlecules mved acrss? a) Fluid pressure similar t what happens in the glmerulus b) Passive diffusin 65. Glucse is fund in glmerular filtrate but NOT in the urine because a) The kidney stres glucse as glycgen b) Kidney cells require glucse because energy is needed fr active transprt c) Glucse is reabsrbed back int the bldstream d) Glucse is cnverted t amin acids in the kidney. c) Osmsis d) Active transprt 66. Nrmally, cncentratin f metablically imprtant substances, such as glucse, are a) High in glmerular filtrate but nly a trace in urine c) High in glmerular filtrate and urine b) Lw in glmerular filtrate but high in urine d) Lw in bth glmerular filtrate and urine 67. Nrmally, cncentratins f wastes, such as urea, are a) High in urine in cmparisn t plasma c) In trace amunts in urine but are high in bld b) High in the filtrate but lw in urine d) Nt in the filtrate but are a little in the urine 68. Which mechanism used t frm urine requires a high bld pressure? a) Glmerular filtratin c) Tubular secretin b) Selective reabsrptin d) Phagcytsis 69. Which f the fllwing is NOT true abut the cllecting ducts? a) They are fund within the medulla b) Fluid enters them frm the distal cnvluted tubule c) Water diffuses ut f them int the medulla d) The urine within them becmes hyptnic t the bld
5 70. Penicillin leaves the bld plasma thrugh tubular walls and nt thrugh the glmerulus. Therefre, penicillin is remved frm the bld by the prcess f a) Osmsis c) Tubular secretin b) Pressure filtratin d) Diffusin 71. Albumin is the large prtein mlecule fund in egg white and bld plasma. Table salt dissciates int sdium and chlride ins. Urea is assembled in the liver. In a healthy persn what is the fate f the majrity f these mlecules as they pass thrugh a nephrn? a) All 3 pass acrss t the glmerular capsule and are excreted in urine b) All 3 pass acrss t the glmerular capsule but the salt ins are mstly reabsrbed c) Albumin remains in the bld, salt ins and urea are passed acrss and excreted d) Albumin remains in the bld, salt ins pass acrss but are reabsrbed, and the urea is passed acrss and excreted 72. Hw can urine cntain a higher cncentratin f wastes (be hypertnic) than the bld? a) Urine cannt since the prcess is passive diffusin b) Reabsrptin f water in the lp f Henle and cllecting ducts leaves behind a mre cncentrated urine c) All stages in the kidney invlve active transprt d) Urine can be hypertnic fr small mlecules if it is hyptnic fr an equal number f big mlecules 73. Which statement is NOT true abut ADH? a) It increases the permeability f the cllecting ducts b) ADH increases water reabsrptin 74. An increased amunt f ADH leads t a) An increased amunt f urine b) A decreased amunt f urine 75. The lp f Henle will shw a) Active release f sdium frm the descending limb b) Active release f sdium frm the ascending limb c) ADH decreases urine vlume d) It is secreted by the adrenal gland c) N change in the amunt f urine d) Kidney failure c) Passive release f sdium frm the ascending limb d) Water release frm the ascending limb 76. The structure which mnitrs bld pressure in the kidney is called the a) Juxtaglmerular apparatus c) Ascending tubule b) Glmerular (Bwman s) capsule d) Renal pelvis 77. Which structure will release renin? a) Glmerular (Bwman s) capsule c) Lp f the nephrn (lp f Henle) b) Prximal cnvluted tubule cells d) Juxtaglmerular apparatus 78. The physical principle upn which kidney dialysis is based is a) Active transprt b) Diffusin c) Heat transfer d) Pincytsis 79. If the bld is alkaline a) Mre hydrgen ins, sdium, and bicarbnate ins are excreted b) Less hydrgen ins and mre sdium and bicarbnate ins are reabsrbed c) Less hydrgen ins are excreted and less sdium and bicarbnate ins are reabsrbed d) The kidneys reabsrb increased amunts f water 80. Which f these characterizes the bld in the renal vein? a) High in CO 2 and high in urea b) High in CO 2 and lw in urea c) Lw in CO 2 and lw in urea d) Lw in CO 2 and high in urea 81. What d FSH, LH, teststerne, prgesterne, and estrgen have in cmmn? a) They ccur nly in the female c) All f them directly affect the uterine lining b) They ccur nly in the male d) All f them are necessary t sexual reprductin 82. The vas deferens a) Becmes erect c) Is surrunded by the prstate gland b) Carries sperm d) All f these 83. The uterus a) Is cnnected t bth the viducts and the vagina b) Is nt an endcrine gland 84. The prstate gland a) Is remved when a vasectmy is perfrmed b) Is nt needed t maintain the secndary sex characteristics c) Receives urine frm the bladder 85. Ovulatin ccurs a) As a result f hrmnal changes b) Always n day 14 c) Cntributes t the develpment f the placenta d) All f these d) All f these c) In pstmenpausal wmen d) As a result f implantatin 86. Pregnancy begins a) When an egg is fertilized b) When vulatin ccurs
6 c) Upn successful implantatin d) During the fllicular phase 87. Which gland is an endcrine gland? a) Seminal vesicles c) Cwper s gland b) Prstate gland d) Testes 88. In the human male, hrmnes frm the stimulate prductin f teststerne by secreting a) Testis; seminal fluid c) Pituitary gland; luteinizing hrmne b) Hypthalamus; trphic hrmnes d) Seminal vesicles; fllicle-stimulating hrmne 89. The fllicle-stimulating hrmne stimulates the a) Release f the egg cell frm the fllicle b) Develpment f a fllicle 90. Menstruatin begins in respnse t a) An increase in circulating estrgen levels b) A decrease in circulating prgesterne levels True/False c) Develpment f the endmetrium d) Beginning f the menstrual flw c) Rupture f the varian fllicle d) Changes in the bld s CO 2 level 91. The cells f the distal cnvluted tubules have numerus mitchndria and micrvilli t supprt active transprt T 92. Urine cntains substances that underwent pressure filtratin and substances that underwent tubular secretin T 93. Bld pressure may be assciated with filtratin while smtic pressure and active transprt may be assciated with reabsrptin T 94. In fertile, sexually mature males, the urethra smetimes carries sperm and smetimes carries urine T 95. Fertilizatin usually ccurs in the viduct T
Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Function
 Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Functin Chapter Outline Functins f the Urinary System Anatmy f the Urinary System Basic Renal Exchange Prcesses Reginal Specializatin f the Renal Tubules Excretin 18.1.
Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Functin Chapter Outline Functins f the Urinary System Anatmy f the Urinary System Basic Renal Exchange Prcesses Reginal Specializatin f the Renal Tubules Excretin 18.1.
The Excretory System. 4 The Excretory System.notebook. May 24, 2017
 4 The Excretry System.ntebk The Excretry System OSMOREGULATION (WATER BALANCE) Mst marine invertebrates are smcnfrmers, meaning the cncentratin f slutes in their bdy fluid is equal t that f their envirnment.
4 The Excretry System.ntebk The Excretry System OSMOREGULATION (WATER BALANCE) Mst marine invertebrates are smcnfrmers, meaning the cncentratin f slutes in their bdy fluid is equal t that f their envirnment.
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 19. Excretry Prducts and Their Eliminatin Ammntelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste in the frm f ammnia.(fish) Uretelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste
POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 19. Excretry Prducts and Their Eliminatin Ammntelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste in the frm f ammnia.(fish) Uretelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste
Chapter 26: The Urinary System. An Overview of the Urinary System, p The Kidneys, p. 952
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System An Overview f the Urinary System, p. 952 Objective 1. Identify the cmpnents f the urinary system and describe the functins it perfrms. Figure 26-1 The urinary system has
Chapter 26: The Urinary System An Overview f the Urinary System, p. 952 Objective 1. Identify the cmpnents f the urinary system and describe the functins it perfrms. Figure 26-1 The urinary system has
Test 3 Study Guide: Photosynthesis, Respiration, and the Cell Membrane
 Name Blck Date Test 3 Study Guide: Phtsynthesis, Respiratin, and the Cell Membrane Test Dates: December 13 (1 st and 7 th blck) and 12 (6 th blck) SOL: BIO.2d, 3d-e Related Ntes Phtsynthesis Respiratin
Name Blck Date Test 3 Study Guide: Phtsynthesis, Respiratin, and the Cell Membrane Test Dates: December 13 (1 st and 7 th blck) and 12 (6 th blck) SOL: BIO.2d, 3d-e Related Ntes Phtsynthesis Respiratin
Endocrine glands secrete hormones that mediate slower, but longerlasting. Endocrine system functions more as a regulatory than a command system
 The Endcrine System 1 Tpics Types f cell signalling Fur types f cell signalling (majr) Fur types f hrmnes (majr) Types f hrmnes Hrmne receptrs Majr endcrine glands Majr hrmnes The hypthalamus and pituitary
The Endcrine System 1 Tpics Types f cell signalling Fur types f cell signalling (majr) Fur types f hrmnes (majr) Types f hrmnes Hrmne receptrs Majr endcrine glands Majr hrmnes The hypthalamus and pituitary
Human Reproductive System. Journal Why is it important to know and use the correct terminology of our bodies and its functions?
 Human Reprductive System Jurnal Why is it imprtant t knw and use the crrect terminlgy f ur bdies and its functins? Female Reprductin Cervix Neck r pening t the uterus. Strngest muscle in the bdy. Crpus
Human Reprductive System Jurnal Why is it imprtant t knw and use the crrect terminlgy f ur bdies and its functins? Female Reprductin Cervix Neck r pening t the uterus. Strngest muscle in the bdy. Crpus
Biology 30S Unit Test Review: Digestion
 Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES.! BIOL1040 University of Queensland
 CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES BIOL1040 University f Queensland BIOL1040 Cells t rganisms Lecture Ntes Cntents Mdule 1 Principles f Cell Functin... 2 Lecture 1: Membrane Structure and Functin 1... 2
CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES BIOL1040 University f Queensland BIOL1040 Cells t rganisms Lecture Ntes Cntents Mdule 1 Principles f Cell Functin... 2 Lecture 1: Membrane Structure and Functin 1... 2
Topic 12: Endocrine System. Function: Group of glands that produces regulatory chemicals ( )
 Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Testes The testes have 2 important functions: 1) They produce sperm (male gametes). 2) They produce male sex hormones, most importantly testosterone.
 Bilgy 12 Unit 3B The Reprductive System The Male Reprductive System Testes The testes have 2 imprtant functins: 1) They prduce sperm (male gametes). 2) They prduce male sex hrmnes, mst imprtantly teststerne.
Bilgy 12 Unit 3B The Reprductive System The Male Reprductive System Testes The testes have 2 imprtant functins: 1) They prduce sperm (male gametes). 2) They prduce male sex hrmnes, mst imprtantly teststerne.
1.&Glomerular/Pressure&Filtration&
 Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Function: Life at the Edge
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
Name: Date: Period: Notes: The Blood and Lymphatic System
 Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Science. Human Biology. New Jersey Quality Single Accountability Continuum (NJQSAC) Department: Course Title
 New Jersey Quality Single Accuntability Cntinuum (NJQSAC) Department: Curse Title Human Bilgy Textbk(s): Fundamentals f Anatmy and Physilgy Essential Questin(s): Cntent Unit 1, September 1. What are Anatmy
New Jersey Quality Single Accuntability Cntinuum (NJQSAC) Department: Curse Title Human Bilgy Textbk(s): Fundamentals f Anatmy and Physilgy Essential Questin(s): Cntent Unit 1, September 1. What are Anatmy
Topic 1: Cell Biology (Student) Essential Idea: Eukaryotes have a much more complex cell structure that prokaryotes.
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
In the list of organisms given below, those that reproduce by the asexual method are
 In the list f rganisms given belw, thse that reprduce by the asexual methd are Banana Dg Yeast Ameba (ii) and (iv) (i), (iii) and (iv) (i) and (iv) (ii), (iii) and (iv) Answer:(b) (i), (iii) and (iv) In
In the list f rganisms given belw, thse that reprduce by the asexual methd are Banana Dg Yeast Ameba (ii) and (iv) (i), (iii) and (iv) (i) and (iv) (ii), (iii) and (iv) Answer:(b) (i), (iii) and (iv) In
10.REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION
 10.REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION Ovarian functin is regulated thrugh the hypthalamic hypphyseal axis and, depending n the type f animal, envirnmental inputs r behaviural activities further regulate
10.REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION Ovarian functin is regulated thrugh the hypthalamic hypphyseal axis and, depending n the type f animal, envirnmental inputs r behaviural activities further regulate
The Digestive System. May 16, The Digestive System.notebook
 3 The Digestive System.ntebk The Digestive System THE BASIC CONCEPTS Animals btain energy by breaking fd mlecules int smaller pieces. The basic fuel mlecules are amin acids, lipids and carbhydrates. The
3 The Digestive System.ntebk The Digestive System THE BASIC CONCEPTS Animals btain energy by breaking fd mlecules int smaller pieces. The basic fuel mlecules are amin acids, lipids and carbhydrates. The
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
Intestinal Hormones Inhibit: Intestinal Hormones Promote:
 1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 3 INTESTINAL PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. INTESTINAL PHASE AND FEEDBACK SIGNALS a. Intr Net result f gastric phase is Digestin f prteins in the stmach
1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 3 INTESTINAL PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. INTESTINAL PHASE AND FEEDBACK SIGNALS a. Intr Net result f gastric phase is Digestin f prteins in the stmach
Cellular Neurophysiology Membrane Ionic Gradients Concentration gradients and diffusion Membrane transport:
 Cellular Neurphysilgy Membrane Inic Gradients Fluid-msaic mdel f plasma membrane: lipid bilayer separating intracellular and extracellular fluids Biplar phsphlipids Hydrphilic head grups and hydrphbic
Cellular Neurphysilgy Membrane Inic Gradients Fluid-msaic mdel f plasma membrane: lipid bilayer separating intracellular and extracellular fluids Biplar phsphlipids Hydrphilic head grups and hydrphbic
Module 2. Chapter 4 Anatomy of the Cell
 Mdule 2 Chapter 4 Anatmy f the Cell The Prkarytic and Eukarytic Cells Prkarytic cells and eukarytic cells Cmpsed f carbhydrates, prteins, nucleic acids, lipids Perfrm f chemical reactins Differences are
Mdule 2 Chapter 4 Anatmy f the Cell The Prkarytic and Eukarytic Cells Prkarytic cells and eukarytic cells Cmpsed f carbhydrates, prteins, nucleic acids, lipids Perfrm f chemical reactins Differences are
10. REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION
 10. REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION Ovarian functin is regulated thrugh the hypthalamic hypphyseal axis and, depending n the type f animal, envirnmental inputs r behaviural activities further
10. REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION Ovarian functin is regulated thrugh the hypthalamic hypphyseal axis and, depending n the type f animal, envirnmental inputs r behaviural activities further
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distribution
 Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distributin Where d drugs distribute? Drug distributin (and ptentially cncentratin) will depend n bld flw and the physichemical prperties f the chemical Lipid and water slubility
Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distributin Where d drugs distribute? Drug distributin (and ptentially cncentratin) will depend n bld flw and the physichemical prperties f the chemical Lipid and water slubility
Virginia Western Community College BIO 142 Human Anatomy and Physiology II
 Virginia Western Cmmunity Cllege BIO 142 Human Anatmy and Physilgy II Prerequisites BIO 141 r equivalent: an ENG 111 placement recmmendatin, c-enrllment in ENF 3/ENG 111, r successful cmpletin f all develpmental
Virginia Western Cmmunity Cllege BIO 142 Human Anatmy and Physilgy II Prerequisites BIO 141 r equivalent: an ENG 111 placement recmmendatin, c-enrllment in ENF 3/ENG 111, r successful cmpletin f all develpmental
Urine Alkalinization. Passawat Na Nakorn, MD. R 3 Emergency Medicine
 Urine Alkalinizatin Passawat Na Nakrn, MD. R 3 Emergency Medicine H + secretin HCO 3 - reabsrptin Mechanism Alkalinizatin f the urine increases urinary excretin f weak acids different frms f the acid have
Urine Alkalinizatin Passawat Na Nakrn, MD. R 3 Emergency Medicine H + secretin HCO 3 - reabsrptin Mechanism Alkalinizatin f the urine increases urinary excretin f weak acids different frms f the acid have
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
1A Human Biology Food, Digestion and Associated Body Systems
 1A Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Fd Fd is ne f the basic human needs and the digestive system enables the bdy t cnvert it int a frm
1A Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Fd Fd is ne f the basic human needs and the digestive system enables the bdy t cnvert it int a frm
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Fifth Year Biology. Excretion. Miss Rochford
 Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Chapter 13 The Urinary System
 Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
W9L17 The Yin and Yang of Human Defense
 W9L17 The Yin and Yang f Human Defense Learning utcmes: - The cncept f a micrbime as a part f us and its implicatins fr recgnitin f self - The micrbime trade-ffs f nutritinal benefit and infectin risk
W9L17 The Yin and Yang f Human Defense Learning utcmes: - The cncept f a micrbime as a part f us and its implicatins fr recgnitin f self - The micrbime trade-ffs f nutritinal benefit and infectin risk
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
Urinary System. Chapter 17 7/19/11. Introduction
 7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
Exercise Physiology CardioRespiratory Trimester 2. Exercise Physiology Cardiorespiratory Study Guide
 Exercise Physilgy CardiRespiratry Trimester 2 Cardivascular System Exercise Physilgy Cardirespiratry Study Guide 1. Be able t label the structures f the heart (chambers, vessels, valves) and the pattern
Exercise Physilgy CardiRespiratry Trimester 2 Cardivascular System Exercise Physilgy Cardirespiratry Study Guide 1. Be able t label the structures f the heart (chambers, vessels, valves) and the pattern
Chem 464 Biochemistry Third Hour Exam
 Name: Chem 464 Bichemistry Third Hur Exam Multiple chice (5 pints apiece): 1. Which f the fllwing statements cncerning fatty acids is crrect? A) One is the precursr f prstaglandins. B) Phsphatidic acid
Name: Chem 464 Bichemistry Third Hur Exam Multiple chice (5 pints apiece): 1. Which f the fllwing statements cncerning fatty acids is crrect? A) One is the precursr f prstaglandins. B) Phsphatidic acid
OHlympia: becoming the PRODIGY. A Special Thanks to Cary K for giving me the opportunity to do this!
 OHlympia: becming the PRODIGY A Special Thanks t Cary K fr giving me the pprtunity t d this! Prdigy defined by Webster is a nun described as a persn f unusual talent r marvelus talents, r anything that
OHlympia: becming the PRODIGY A Special Thanks t Cary K fr giving me the pprtunity t d this! Prdigy defined by Webster is a nun described as a persn f unusual talent r marvelus talents, r anything that
2. Ureters Composed of smooth muscle tissue ~25cm long Connects kidneys to bladder Undergoes peristaltic contraction to move urine to bladder
 Section 6: The Urinary System A) Organs of the Urinary system 1. Kidneys 2. Ureters 3. Bladder 4. Urethra 1. Kidneys Paired organs located on either side of vertebral column in upper part of abdominal
Section 6: The Urinary System A) Organs of the Urinary system 1. Kidneys 2. Ureters 3. Bladder 4. Urethra 1. Kidneys Paired organs located on either side of vertebral column in upper part of abdominal
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance 1. Osmoregulation (water balance) a. Most marine invertebrates are osmoconformers in which the concentration of solutes in their body fluid is equal to that of their environment.
Excretion and Water Balance 1. Osmoregulation (water balance) a. Most marine invertebrates are osmoconformers in which the concentration of solutes in their body fluid is equal to that of their environment.
Chapter 20 The Heart
 Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Topic 11: Nervous System
 Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
8. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION. Germinal cells, gonocytes. Indifferent stage INDIFFERENT STAGE
 8. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15% f the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is frmed in the sides f the embrynic tissue, ventral t the mesnephrs r
8. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15% f the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is frmed in the sides f the embrynic tissue, ventral t the mesnephrs r
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
b. Responses/Reflexes Food bulk stretches the fundus of stomach, activating mechanoreceptors GI peptides activate chemoreceptor s o o o
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 GASTRIC PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM a. Defined and Crrelatin with Shrt Reflexes Fund in walls f LUMEN Invlved in shrt reflexes
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 GASTRIC PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM a. Defined and Crrelatin with Shrt Reflexes Fund in walls f LUMEN Invlved in shrt reflexes
Refer to the figure below, a diagram of a renal tubule, to answer the following questions.
 1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Metabolism: Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Metablism: Oxidative Phsphrylatin Hand-ut fr the CBT versin April 2012 1. On average, hw much ATP is needed each day by ur bdy? 2. Which f the fllwing ccurs during cellular respiratin? Bisynthesis f glycgen
Metablism: Oxidative Phsphrylatin Hand-ut fr the CBT versin April 2012 1. On average, hw much ATP is needed each day by ur bdy? 2. Which f the fllwing ccurs during cellular respiratin? Bisynthesis f glycgen
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Proenza
 CV 03-20-17 08AM CVPR Overview-Anatmy - Prenza CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Prenza catherine.prenza@ucdenver.edu Recmmended Reading Lilly p 1-12 Other learning resurces: http://www.cvphysilgy.cm/
CV 03-20-17 08AM CVPR Overview-Anatmy - Prenza CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Prenza catherine.prenza@ucdenver.edu Recmmended Reading Lilly p 1-12 Other learning resurces: http://www.cvphysilgy.cm/
REVISION: PHOTOSYNTHESIS & CELLULAR RESPIRATION 18 JUNE 2014
 REVISION: PHOTOSYNTHESIS & CELLULAR RESPIRATION 18 JUNE 2014 Lessn Descriptin In this lessn, we revise: the prcess f phtsynthesis the prcesses invlved in cellular respiratin Summary Phtsynthesis (Slutins
REVISION: PHOTOSYNTHESIS & CELLULAR RESPIRATION 18 JUNE 2014 Lessn Descriptin In this lessn, we revise: the prcess f phtsynthesis the prcesses invlved in cellular respiratin Summary Phtsynthesis (Slutins
INFERTILITY DIAGNOSIS
 INFERTILITY Infertility is the inability t cnceive after 12 mnths f unprtected intercurse. There are multiple causes f infertility and a systematic way t evaluate the cnditin. Let s lk at sme f the causes.
INFERTILITY Infertility is the inability t cnceive after 12 mnths f unprtected intercurse. There are multiple causes f infertility and a systematic way t evaluate the cnditin. Let s lk at sme f the causes.
ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE. All Systems, GO! Lesson #3
 ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE All Systems, GO! Lessn #3 FOSS Califrnia, Grade 5, Living Systems, Investigatin 1, Part 3 CONTENT STANDARDS Dance Grade 5 2.1 Create, memrize
ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE All Systems, GO! Lessn #3 FOSS Califrnia, Grade 5, Living Systems, Investigatin 1, Part 3 CONTENT STANDARDS Dance Grade 5 2.1 Create, memrize
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Module 3. Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism. Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions Metabolism Two general types of metabolic reactions: o :
 Mdule 3 Chapter 5 Micrbial Metablism Catablic and Anablic Reactins Metablism Tw general types f metablic reactins: : : Recall frm Chapter 2: Energy can be when bnds Energy can be when bnds Catablism Purpse
Mdule 3 Chapter 5 Micrbial Metablism Catablic and Anablic Reactins Metablism Tw general types f metablic reactins: : : Recall frm Chapter 2: Energy can be when bnds Energy can be when bnds Catablism Purpse
Cairns Base Hospital Emergency Department Part 1 FACEM MCQs
 airns ase Hspital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 ncerning the cardiac actin ptential Phase 1 is due t rapid sdium influx Resting membrane ptential is typically -90mV Phase 2 results frm slw prlnged
airns ase Hspital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 ncerning the cardiac actin ptential Phase 1 is due t rapid sdium influx Resting membrane ptential is typically -90mV Phase 2 results frm slw prlnged
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Anemia. There are three types of Anemia that effect EB patients. They are Iron Deficiency, Chronic Inflammatory and Nutritional.
 Anemia Mst patients with Recessive Dystrphic Epidermlysis Bullsa are als Anemic. Anemia in EB is caused by many factrs and can becme very severe if nt treated. Anemia means nt having enugh red cells and
Anemia Mst patients with Recessive Dystrphic Epidermlysis Bullsa are als Anemic. Anemia in EB is caused by many factrs and can becme very severe if nt treated. Anemia means nt having enugh red cells and
Human Structure and Function LECTURE 1 ERIN HARRISON
 * Intrductin t Human Structure and Functin ULO1 = Structure ULO2 = Functin ULO3 = Applicatin f Knwledge TEXTBOOK: Dwnlad - Anatmical Landmarks - Directinal References - Sectinal Planes Structure = Anatmy
* Intrductin t Human Structure and Functin ULO1 = Structure ULO2 = Functin ULO3 = Applicatin f Knwledge TEXTBOOK: Dwnlad - Anatmical Landmarks - Directinal References - Sectinal Planes Structure = Anatmy
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System:
 Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variations on a Theme
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 13: Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme CONCEPTS: 13.1 Offspring acquire genes frm their parents by inheriting chrmsmes
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 13: Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme CONCEPTS: 13.1 Offspring acquire genes frm their parents by inheriting chrmsmes
Prokaryotic cells are placed in two taxonomic domains: o Bacteria o Archaea o
 AP Bilgy Ch. 4 Cellular Structure and Functin 4.1Cellular Level f Organizatin Cell Thery: Name Cell Size Large cells - Small cells EK 2.A.3b: Surface area- t- vlume ratis affect a bilgical system s ability
AP Bilgy Ch. 4 Cellular Structure and Functin 4.1Cellular Level f Organizatin Cell Thery: Name Cell Size Large cells - Small cells EK 2.A.3b: Surface area- t- vlume ratis affect a bilgical system s ability
1.6. Topic 1: Cell Biology (Teacher) Essential Idea: Cell division is essential but must be controlled. 1.6 Cell Division
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Chapter 12. Excretion and the Interaction of Systems
 Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Division
 The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
Chapter 14 Cell division: Continuity of Life means all life originates from other living things of the same type.
 Chapter 14 Cell divisin: 2.3 Cell Cntinuity Learning Objectives 2.3.1 2.3.8 The Cell Cycle, Mitsis, Meisis 1. Explain f the terms cell cntinuity and chrmsme. 2. Differentiate between "haplid" and "diplid"
Chapter 14 Cell divisin: 2.3 Cell Cntinuity Learning Objectives 2.3.1 2.3.8 The Cell Cycle, Mitsis, Meisis 1. Explain f the terms cell cntinuity and chrmsme. 2. Differentiate between "haplid" and "diplid"
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System
 Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
Mitosis and Meiosis Lecture Notes
 Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 Chapter 1: Intrductin 13 Anatmy and Physilgy I ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Anatmy (Greek a cutting up ) Physilgy (Greek relatinship t nature ) is always related t CORE PRINCIPLE IN A&P Structure and Functin
Chapter 1: Intrductin 13 Anatmy and Physilgy I ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Anatmy (Greek a cutting up ) Physilgy (Greek relatinship t nature ) is always related t CORE PRINCIPLE IN A&P Structure and Functin
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
mid ihsan (Physiology ) GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B **
 (Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
(Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
November 30, 2016 & URINE FORMATION
 & URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
& URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Functin Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane separates the living cell frm its surrundings. This thin barrier, 8 nm thick, cntrls traffic int and ut f the cell.
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Functin Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane separates the living cell frm its surrundings. This thin barrier, 8 nm thick, cntrls traffic int and ut f the cell.
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
