2015 SENIOR DIGESTIVE
|
|
|
- Elfrieda Grant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2015 SENIOR DIGESTIVE EASY 2495 (easy) TH190/HIH705-1 Q: In reference to digestion, describe 2 main functions of the horse's mouth. A: Intake food, chew food, wet food with saliva 2496 (easy) TH93/HIH405-1,2 Q: What type of jaw movement is necessary for a horse to grind its food? A: Lateral or side to side movement 2497 (easy) HIH705-1 Q: What is the technical name for chewing? A: Mastication 2498 (easy) HIH705-2 Q: What part of the digestive system is referred to as a blind pouch? A: Cecum 2499 (easy) HIH705-1/TH190/HS27 Q: What does mastication mean? A: Chewing 2500 (easy) HIH705-2 Q: What is the final part of the horse's digestive system? A: Rectum (also accept anus) 2501 (easy) HIH360-2 Q: The average 1000 pound horse can produce how much manure in one day? A: pounds (accept any number within this range) 2502 (easy) HIH710-1,705-1 Q: In which organ does the majority of digestion/absorption occur? A: Small intestine 2503 (easy) INT203-1/HIH705 Q: Of the following 3 organs, where does food stay the least amount of time in the digestive system: stomach, small intestine, or large intestine? A: Stomach 2504 (easy) HS27 Q: What do you call the process of preparing food for absorption? A: Digestion 2505 (easy) HS23 Q: How many compartments are in a horse's stomach? A: One
2 2506 (easy) HIH635-2 Q: How does the great length of the small intestine lead to many problems? A: Gets twisted or telescoped 2507 (easy) HS29 Q: How long does it take to completely empty a horse's stomach? A: 24 hours after eating 2508 (east) HS27 Q: What does prehension mean? A: Grasping of food 2509 (easy) HS27 Q: What do we call the grasping of food in order to get it into the mouth? A: Prehension 2510 (easy) HIH705/DET81 Q: The mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus are all parts of what system of the horse? A: Digestive system 2511 (easy) HIH705-1 Q: Saliva is produced by what gland? A: Salivary gland 2512 (easy) HIH705-1 Q: Why do you need to have knowledge of the horse's digestive system? A: So you know how to feed them correctly OR you know how to look for signs of colic (accept either) 2513 (easy) HIH705-1 Q: What is the purpose of the esophagus? A: Moves feed from the mouth/pharynx to the stomach 2514 (easy) HS31 Q: What is the name given to the waste matter of digestion? A: Manure or feces 2515 (easy) HIH710-1,705-1 Q: Where does digestion begin? A: In the mouth 2516 (easy) HIH705-1 Q: What is produced by the salivary glands? A: Saliva 2517 (easy) HIH705-1 Q: Which system of the horse is responsible for converting feed into a form that can be utilized by the body? A: Digestive
3 2518 (easy) HIH705-1/TH190 Q: What is the first part of the digestive system? A: Mouth 2519 (easy) HS31 Q: What does defecation mean? A: Pooping 2520 (easy) HIH705-1 Q: What is the horse's main structure for grasping food? A: Lips (also accept upper lip) 2521 (easy) HS27 Q: What stimulates the secretion of saliva in the horse? A: Chewing MEDIUM 2522 (medium) ES111 Q: Which takes more time to pass from the horse s stomach into the small intestine hay or water? A: Hay 2523 (medium) TH127 Q: What is the function of the horse's pancreas? A: Secretes insulin & enzymes 2524 (medium) HIH710-1 Q: Excess gas produced in the stomach can cause what? A: Rupture of the stomach & death 2525 (medium) TH606 DET6, 81, 118 Q: What is the name of the tract that consists of a musculo-membraneous tube that extends from the mouth to the anus? A: Digestive tract, Gastrointestinal tract or alimentary canal 2526 (medium) HIH742-3,4 Q: What are probiotics used for? A: To increase the population of beneficial micro-organisms in the digestive tract 2527 (medium) HS27 Q: Where do most of the fats get digested? A: Small intestine
4 2528 (medium) DET56 Q: What is the material leaving the stomach & entering the small intestine called? A: Chyme 2529 (medium) HIH710-2 Q: Where in the digestive tract are amino acids synthesized? A: Large intestine 2530 (medium) HIH705-1 Q: What organ of the horse secretes gastric juices? A: Stomach 2531 (medium) HIH710-2/ES112 Q: Hay is digested primarily in what part of the digestive system? A: Cecum 2532 (medium) HIH710,705-1 Q: How long is the horse's small intestine? A: feet (accept any number within this range) 2533 (medium) HIH710-1 Q: The salivary glands, pancreas & liver are accessory organs of what system? A: Digestive 2534 (medium) FCH395 Q: What is the name for chemical reactions occurring in the body? A: Metabolism 2535 (medium) HIH705-1 Q: Continued exposure of the lower part of the stomach to excessive gastric secretions can cause what? A: Gastric ulcers 2536 (medium) HIH705-1 Q: What does the enzyme pepsin do? A: Helps digest proteins 2537 (medium) HIH705-1 Q: Which enzyme helps digest proteins? A: Pepsin (also accept trypsin) 2538 (medium) HIH705-1 Q: What are 2 things that happen in the small colon? A: Any remaining water is removed; fecal balls are formed 2539 (medium) HIH705-1 Q: Why is the cecum sometimes called a blind pouch? A: Because feedstuffs both enter & exit at the top OR it only has one opening (accept either)
5 2540 (medium) CAHA52/HIH710-2 Q: The horse's small colon lies between what 2 other parts of the horse's digestive system? A: Large colon & rectum 2541 (medium) CAHA54 Q: What 2 organs deliver enzymes & products into the duodenum to assist in the digestive process? A: Pancreas & liver 2542 (medium) HIH710-2 Q: Your horse is experiencing recurrent mild colic. Your veterinarian is listening to the right side of your horse's abdomen for rumbling, gurgling noises. What specific part of the digestive tract is he listening to? A: Cecum 2543 (medium) HIH705-1 Q: What is the esophagus? A: A muscular tube that extends from the pharynx to the stomach 2544 (medium) TH192 Q: Why doesn't a horse need a gall bladder? A: Horses graze/eat many small meals, so there's no need for a gall bladder; bile is constantly secreted & therefore doesn t need to be stored; (a gall bladder allows bile to be stored so that large amounts can be released in response to eating a large meal) (only need to give one) 2545 (medium) HIH710-1 Q: What is the process by which fiber is digested? A: Fermentation 2546 (medium) HIH710-1/TH199 Q: The soluble carbohydrates are digested & absorbed in what part of the digestive system? A: Small intestine 2547 (medium) HIH710-2 Q: How long is the large colon? A: feet (accept any number within this range) 2548 (medium) TH201 Q: Where is the primary site of water absorption? A: Cecum 2549 (medium) HIH705-2,710-2 Q: Which part of the horse's large intestine has the largest capacity? A: Large colon 2550 (medium) TH127 Q: Insulin controls glucose levels in the horse's body. Where is it produced? A: Pancreas
6 2551 (medium) DET153 Q: What is the function of insulin? A: Controls blood sugar levels & the utilization of sugar in the body 2552 (medium) HIH 435a-1 Q: Why is the small intestine susceptible to displacement, telescoping, or twisting? A: Its long length & its loose attachment to the abdominal wall (mesentery) 2553 (medium) HIH705-2 Q: Where are the characteristic balls of feces formed? A: Small colon 2554 (medium) HS25 Q: The cecum lies between what 2 parts of the horse's digestive system? A: Small intestine (ileum) & large colon 2555 (medium) HIH710-2 Q: How long is the cecum? A: 4 feet 2556 (medium) HIH710-2 Q: What is the muscular tube inches in length which extends from the pharynx to the stomach? A: Esophagus 2557 (medium) HIH705-1/TH192 Q: What is the name of the dark green-yellow substance secreted by the liver? A: Bile 2558 (medium) HS28 Q: What does deglutition mean? A: Swallowing 2559 (medium) HS23 Q: Because the upper jaw is wider than the lower jaw, how does mastication occur? A: On one side of the jaw at a time (also accept in a circular motion) 2560 (medium) TH190 Q: Where is the small intestine located in the horse? A: Between stomach and cecum 2561 (medium) HS26 Q: Most farm animals have an organ that stores bile, but horses do not. What is this organ? A: Gall bladder 2562 (medium) HS28 Q: What is the technical name for swallowing? A: Deglutition
7 2563 (medium) HIH705-1 Q: What is the short, funnel-shaped tube between the mouth & esophagus? A: Pharynx 2564 (medium) HIH705-2 Q: What is the cecum? A: Large, sock-shaped pouch between small intestine & large colon 2565 (medium) HS28 Q: Why must food move through the pharynx quickly? A: So it won't enter the windpipe or be forced into nasal passage 2566 (medium) HIH705-1,710-1 Q: Food remains in the stomach for about how long before it starts passing into the small intestine? A: minutes (accept any number within this range) 2567 (medium) CAHA50/HIH705-1 Q: What is the pharynx? A: A short, funnel-shaped tube between the mouth & esophagus 2568 (medium) HIH710/HS31/TH194 Q: The rate of food passage from mouth to anus is how long? A: 1 ½ - 3 days OR hours (accept any number within this range) 2569 (medium) HIH705-1/TH219 Q: Name the primary site of protein digestion in the horse. A: Small intestine 2570 (medium) HIH705-1 Q: The stomach is what percent of the total capacity of the horse's digestive tract? A: 9-10% 2571 (medium) H3-35 Q: Commercial preparations of dried beneficial intestinal micro-organisms are called what? A: Probiotics 2572 (medium) TH401 Q: What body part should be examined closely in a horse that is quidding? A: Teeth or mouth 2573 (medium) CAHA55 Q: What causes the intestinal (gut) sounds that can be heard with a stethoscope pressed to the horse's abdomen? A: Movement of gas or fluids through the large intestine OR cecal activity (accept either) 2574 (medium) TH93 Q: What is referred to as a strong, sensitive, mobile organ of prehension? A: Upper lip (lips)
8 2575 (medium) HIH710-2 Q: What is the capacity of the small colon? A: 4 gallons 2576 (medium) HIH705-1,710-2 Q: What is the capacity of the stomach? A: 2-4 gallons/8-16 quarts (accept any number within this range) 2577 (medium) HIH705-1,710-2 Q: What is the capacity of the small intestine? A: 12 gallons/68 quarts HARD 2578 (hard) FCH294/DET93 Q: What is an enterolith? A: Intestinal stone or stone-like mass that forms around a foreign object in horse's intestines 2579 (hard) FCH393 Q. What is the name for the terminal portion of the small intestine? A. Ileum 2580 (hard) HIH705-2 Q: Fibrous feedstuffs are broken down into volatile fatty acids. What percent of the horse's energy needs do these acids provide? A: 80% 2581 (hard) HIH705-2 Q: Referring to the digestive system, what does VFA mean? A: Volatile fatty acid 2582 (hard) HIH705-1 Q: What are 2 functions of the pharynx? A: Food passage between mouth & esophagus; air passage between nostrils & trachea 2583 (hard) TH192 Q: What part of the large intestine serves as a microbacterial vat? A: Cecum 2584 (hard) HS25 Q: Sugar is absorbed in what form? A: Glucose OR in the forms of other simple sugars
9 2585 (hard) HIH705-2 Q: The large colon has the largest capacity of the horse's digestive system. What percent of total capacity is it? A: 40% 2586 (hard) HS31 Q: What is the diameter of the large colon? A: inches down to 3-4 inches (accept any number within this range) 2587 (hard) TH192 Q: 2 part question: How long is the large intestine & what is its' capacity? A: 25 feet long; 32 gallons capacity 2588 (hard) HS30 Q: What are the small projections in the small intestine called? A: Villi 2589 (hard) CAHA51 Q: What powerful, ring-like muscle closes the opening of the esophagus into the stomach? A: Sphincter (cardiac sphincter) 2590 (hard) DET154 Q: What is the general term for the bacteria and other microorganisms that normally reside in the large intestine? A: Intestinal Flora 2591 (hard) CAHA51/DET48 Q: What part of the stomach connects to the esophagus? A: Cardia 2592 (hard) HS23/DET209 Q: What is peristalsis? A: Wavelike movements of the esophagus that move food through the digestive tract 2593 (hard) HIH705-2,710-2 Q: 2 part question: What is the length & capacity of the cecum? A: 4 feet long; capacity quarts/4 gallons 2594 (hard) HS29 Q: What is the purpose of gastric lipase? A: Helps digest fats 2595 (hard) TH191/HS28 Q: Approximately how many gallons of saliva are produced & swallowed by the horse each day? A: 8-10 gallons (accept any number within this range) 2596 (hard) HIH710-2,705-2 Q: 2 part question: What is the length & capacity of the large colon? A: feet; capacity 86 quarts/20 gallons
10 2597 (hard) CAHA51/DET224 Q: What is the opening of the stomach into the small intestine called? A: Pylorus 2598 (hard) CAHA51 Q: What do the bile duct & the pancreatic duct empty into? A: The duodenum 2599 (hard) TH191 Q: Besides water, what composes the saliva of a horse? A: Inorganic salts & proteins/enzymes 2600 (hard) HIH435-1 Q: What part of the horse functions similar to the rumen in cattle & sheep? A: Cecum 2601 (hard) HIH705-1/HS29 Q: What does hydrochloric acid do in the stomach? A: Helps with digestion OR mixes with the food & acidifies it so pepsin & gastric lipase can work 2602 (hard) CAHA51 Q: Where in the digestive system is hydrochloric acid secreted? A: Stomach lining 2603 (hard) HS29 Q: What does pancreatic amylase do? A: Digests starch 2604 (hard) TH191/HS28 Q: 2 part question: What makes up 99% of the saliva & what is the other 1%? A: 99% water & 1% inorganic salts & proteins/enzymes 2605 (hard) HS29 Q: Food does not leave the stomach until what happens? A: Stomach is 75% full 2606 (hard) TH194/HIH710-1 Q: When a horse is fed a balanced hay to grain ratio, it generally takes about how many hours for the ingested material to pass through the digestive tract & be passed out as fecal material? A: hours (1-1/2-3 days) (accept any number within this range) 2607 (hard) HIH710-1 Q: What percent of proteins in grain-based diets is digested to amino acids & absorbed from the small intestine? A: 50 70% 2608 (hard) HIH705-1,710-2 Q: Passage of feeds through the small intestine takes approximately how long? A: minutes (accept any number within this range)
11 2609 (hard) HIH705-1 Q: The angle at which the esophagus meets the stomach & the powerful spinchter at that junction makes it nearly impossible for feed to do what? A: Re-enter the esophagus once it's deposited in the stomach 2610 (hard) DET210 Q: Explain how the pharynx functions with the respiratory tract A: When horse isn t swallowing, it connects the nasal passages with the windpipe 2611 (hard) TH192/HS29 Q: Explain how bile is released in the horse's digestive system. A: Continuously secreted by the liver (into the bile duct which empties into the duodenum) 2612 (hard) TH196/HS29 Q: What does the enzyme trypsin do? A: Breaks down proteins (assists in the digestion of proteins) 2613 (hard) HS29 Q: Which enzyme assists in the digestion of fats? A: Lipase 2614 (hard) HS29 Q: Explain how insulin & glucagon act. A: Insulin - moves extra glucose from blood to storage in body; Glucagon - moves stored glucose back into the blood when needed 2615 (Hard) HS24 Q: 2 part question: A normal horse requires how many minutes to eat a pound of hay & how many minutes to eat a pound of grain? A: minutes to eat a pound of hay & 5-10 minutes to eat a pound of grain 2616 (hard) HIH710-1 Q: Describe a non-ruminant digestive system. A: Carbohydrates, proteins & fats are digested in foregut by enzymes & fiber is digested in hindgut by bacteria 2617 (hard) HIH710-1 Q: Describe a ruminant digestive system. A: Fiber is digested in the rumen, enzymatic digestion in foregut & relatively minimal digestion occurs in hindgut 2618 (hard) HIH710-1 Q: Digestively speaking, what is the horse categorized as? A: Non-ruminant herbivore 2619 (hard) FCH399 Q: Why can't a horse vomit? A: Blocking action of the soft palate OR angle at which esophagus meets stomach OR cardiac sphincter prevents food from re-entering esophagus (accept either)
12 2620 (hard) DET250 Q: What structure in the horse's mouth is forced up by the tongue during swallowing to keep food out of the nose? A: Soft palate 2621 (hard) CAHA51 Q: What muscle regulates the flow of stomach contents into the duodenum? A: Pyloric sphincter 2622 (hard) DET209 Q: What is the name for the wavelike muscular contractions that move food down the esophagus? A: Peristalsis 2623 (hard) TH204 Q: What is intestinal flora? A: Bacteria normally present in the intestine 2624 (hard) HIH710-2 Q: 2 part question: Where does the sound-generating action of digestion occur & where do you listen for it? A: Occurs in cecum. You should listen for it on right side of the horse's abdomen at junction of the hind leg & trunk BONUS 2625 (bonus) HS25 Q: What 3 things do intestinal movements do? A: Mix digested food with digestive secretions, enhance absorption, move material through intestines, expel the residue, assist in blood flow & lymph through vessels in intestinal wall 2626 (bonus) TH Q: What are 3 factors that may affect the rate of passage of ingesta through the gastrointestinal tract of the horse? A: Processing of food, level of intake/how much is eaten, frequency of feeding, exercise, individuality, time of watering, associative effects, ratio of hay to grain 2627 (bonus) TH /FCH4,5 Q: The gastrointestinal tract of the horse has many functions. Name 3. A: Ingestion, grinding/chewing, mixing, digestion, absorption, elimination of waste 2628 (bonus) HIH710-2 Q: Name 4 parts of the horse s hindgut. A: Cecum, large colon, small colon, rectum
13 2629 (bonus) HIH710-1 Q: Name 4 parts of the foregut. A: Mouth, esophagus, stomach & small intestine 2630 (bonus) HS31 Q: Name 3 things that make up feces. A: Waste matter of digestion, water, indigestible and/or undigested food, cells sloughed off intestinal walls, remains of digestive secretions 2631 (bonus) HIH705-1 Q: Explain how each of the following 4 parts of the horse is involved in the process of digestion --- Lips, incisor teeth, molars/premolars & tongue A: Lips pick up/sort loose feed Incisor Teeth bite off grasses Molars/Premolars chew the feed Tongue moves the feed into the mouth 2632 (bonus) HS25 Q: What are 3 sections of the digestive tract where impactions are most likely to occur? A: Cecum, small colon, & large colon 2633 (bonus) HIH705-1 Q: Name 3 things secreted by the stomach. A: Hydrochloric acid, pepsin, gastric lipase 2634 (bonus) HIH710-2,705 Q: Name the parts of the horse's foregut in correct order - starting from the mouth & including the 3 parts of the small intestine. A: Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, jejunum, ileum 2635 (bonus) HS24 Q: What are 3 substances that are secreted into the duodenum? A: Bile, trypsin, pancreatic lipase 2636 (bonus) TH190 Q: What are the 7 parts of the alimentary canal? A: Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum/anus 2637 (bonus) HIH701,705 Q: Name 3 mechanical factors in digestion. A: Chewing, swallowing, movements of stomach & intestines, defecation/pooping 2638 (bonus) HIH710-1 Q: Name 3 accessory organs of the digestive system. A: Teeth, tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver
14 2639 (bonus) CAHA51 Q: What are the 3 parts of the small intestine? A: Duodenum, jejunum, ileum 2640 (bonus) TH189/HS31/HIH705 Q: The important digestive action of the cecum & colon is due to the presence of bacteria & protozoa which do 3 things. Name these 3 things. A: Digest cellulose, synthesize B vitamins, synthesize amino acids
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body
 Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
Digestive System. What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning?
 Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
SNC4M The Digestive System
 SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Digestive System Anatomy
 Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by. broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells.
 Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells. Cells are then able to maintain homeostasis 6 main components
Purpose To reduce the size of large pieces of food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream and eventually into cells. Cells are then able to maintain homeostasis 6 main components
10/18/2017 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs 6/1/2015. The Wall of the Digestive Tract
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Ch41 Animal Nutrition
 Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
Digestion Introduction Lecture MMHS Science Chitraroff
 Digestion Introduction Lecture MMHS Science Chitraroff Digestion is the process that changes food into a form that is usable by your body. The Alimentary Canal The pathway of food from your mouth to your
Digestion Introduction Lecture MMHS Science Chitraroff Digestion is the process that changes food into a form that is usable by your body. The Alimentary Canal The pathway of food from your mouth to your
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! )
 POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! ) Life is organized in the following levels: Chemical Level, Cellular Level, Tissue Level, Organ Level, Organ System Level, and finally,
POGIL Activity on The Digestive System (Let s go Down the Hatch! ) Life is organized in the following levels: Chemical Level, Cellular Level, Tissue Level, Organ Level, Organ System Level, and finally,
* Produces various chemicals to break. down the food. * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes
 * * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
* * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM.
 1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that
 PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
The digestive tract of the pig
 The digestive tract of the pig 2010-11-26 J.P. Rowan1, K.L. Durrance2, G.E. Combs3 and L.Z. Fisher4 1Extension Agent - Agriculture, 4-h, Suwannee County 2professor, Animal Science Department 3professor,
The digestive tract of the pig 2010-11-26 J.P. Rowan1, K.L. Durrance2, G.E. Combs3 and L.Z. Fisher4 1Extension Agent - Agriculture, 4-h, Suwannee County 2professor, Animal Science Department 3professor,
Harvesting energy from food. Digestion: A Closer Look. Where digestion begins. Salivary Glands 4/17/13. Or how food gets from
 Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
The horse's digestive system
 The horse's digestive system The horse is a nonruminant herbivore. Non-ruminant means that horses do not have multi-compartmented stomachs as cattle do. Instead, the horse has a simple stomach that works
The horse's digestive system The horse is a nonruminant herbivore. Non-ruminant means that horses do not have multi-compartmented stomachs as cattle do. Instead, the horse has a simple stomach that works
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
Nutrition, part 2. Because 1 part isn t enough!
 Nutrition, part 2 Because 1 part isn t enough! 4. Calories and Caloric Intake Calories per gram of our Macro and Micro nutrients Macro Carbohydrates: 4 cal/g Fats: 9 cal/g Proteins: 4 cal/g Micro Vitamins:
Nutrition, part 2 Because 1 part isn t enough! 4. Calories and Caloric Intake Calories per gram of our Macro and Micro nutrients Macro Carbohydrates: 4 cal/g Fats: 9 cal/g Proteins: 4 cal/g Micro Vitamins:
Nutrition. Why do humans need food? How do some animals get their food? ROUGHAGE NUTRIENTS. Animals make energy available using:
 Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Animal Nutrition. Chapter 41. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
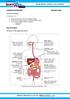 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Digestion. I. What is digestion? II. Enzymes involved in digestion
 Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes
 Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Digestive System. Physical and breakdown begins. : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic
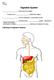 SBI 3C Digestive System : food enters the system Physical and breakdown begins : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic : Nutrients enter system, delivered to tissues of the body Elimination of Waste (
SBI 3C Digestive System : food enters the system Physical and breakdown begins : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic : Nutrients enter system, delivered to tissues of the body Elimination of Waste (
The Digestive System. Parts and Functions
 The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
Digestive System Lecture Notes Read Ch 14; review questions start on page 477 S/A # 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 26, 35
 The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
CHAPTER 22: THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Jayda Cortez Kimberly Navarro
 CHAPTER 22: THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jayda Cortez Kimberly Navarro Objectives - Describe the functions of the organs that make up the digestive system - Identify and describe the four stages of food processing
CHAPTER 22: THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jayda Cortez Kimberly Navarro Objectives - Describe the functions of the organs that make up the digestive system - Identify and describe the four stages of food processing
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Monday, October Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page.
 1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
Biology 12 Unit 5 Pretest
 Biology Unit 5 Pretest Name: Date: Block:. Chewing aids digestion by A. stimulating release of bile B. increasing surface area of food C. breaking up polymers into monomers D. stimulating water absorption.
Biology Unit 5 Pretest Name: Date: Block:. Chewing aids digestion by A. stimulating release of bile B. increasing surface area of food C. breaking up polymers into monomers D. stimulating water absorption.
Digestive System Notes. Biology - Mrs. Kaye
 Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Digestive System Notes Biology - Mrs. Kaye Digestion There are two kinds of digestion: Mechanical digestion - the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces to increase surface area for more enzyme
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes
 Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
>>> FOCUS. Context. Digestion. The human digestive system
 Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Modified Monogastric Digestive System
 Modified Monogastric Digestive System Digestive System of the Horse 8/7/2014 1 The Digestive Tract Horses and rabbits are modified monogastric herbivores. Horses are able to utilize large amounts of roughage
Modified Monogastric Digestive System Digestive System of the Horse 8/7/2014 1 The Digestive Tract Horses and rabbits are modified monogastric herbivores. Horses are able to utilize large amounts of roughage
Nutrition and Digestion
 Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food
 UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food Introduction to the Digestive System PART ONE Systems of the Body The Digestive System Also referred to as alimentary system, the gut, gastrointestinal
UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food Introduction to the Digestive System PART ONE Systems of the Body The Digestive System Also referred to as alimentary system, the gut, gastrointestinal
Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics
 Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 2 1 Introduction Some Ecology 3 Mr. Sun 4 2 Nuclear Fusion 5 Light energy from Sun radiates across
Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 2 1 Introduction Some Ecology 3 Mr. Sun 4 2 Nuclear Fusion 5 Light energy from Sun radiates across
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Digestive System Practice Test
 Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Rebel Biology - Nutrition. organisms need a variety of nutrients to perform life s activities. carbs, proteins. vitamins, water,
 Rebel Biology - Nutrition organisms need a variety of nutrients to perform life s activities the most important ones are fats, carbs, proteins vitamins, water, these either provide direct value(fats/carbs/proteins)
Rebel Biology - Nutrition organisms need a variety of nutrients to perform life s activities the most important ones are fats, carbs, proteins vitamins, water, these either provide direct value(fats/carbs/proteins)
Digestive System. Science 7 HMS 2015
 Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2015 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2015 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
Website: websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition
 Website: websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 2 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 3 Introduction Some Ecology 4 2 Mr. Sun 5 Nuclear Fusion 6 3
Website: websites.rcc.edu/halama Lecture 2 Digestive System &Nutrition 2 1 Lecture 3 1. Introduction 2. Digestive System 3. Nutrition Basics 3 Introduction Some Ecology 4 2 Mr. Sun 5 Nuclear Fusion 6 3
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
AF 1201 Digestive System. Dr. A.M.J.B. Adikari Dept. of Animal and Food Sciences
 AF 1201 Digestive System Dr. A.M.J.B. Adikari Dept. of Animal and Food Sciences Complex / Compound Stomach Large structure, located on the left side 4 parts Rumen, Reticulum, Omasum Abomasum Fore stomach
AF 1201 Digestive System Dr. A.M.J.B. Adikari Dept. of Animal and Food Sciences Complex / Compound Stomach Large structure, located on the left side 4 parts Rumen, Reticulum, Omasum Abomasum Fore stomach
Lesson 1. Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
The Human Digestive Tract
 The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
Full file at
 An. Dif. Page(s) Multiple Choice Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption c K 39 1. Another name for the digestive tract is the: a. urinary tract. b. exocrine system. c. gastrointestinal system. d. muscular
An. Dif. Page(s) Multiple Choice Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption c K 39 1. Another name for the digestive tract is the: a. urinary tract. b. exocrine system. c. gastrointestinal system. d. muscular
Digestive System. Part A Multiple Choice. 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin.
 Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
The Digestive System (11.1 and 11.2) Mar 27 9:53 AM. Section 11.1 The chemical Foundation of Digestion
 Chapter 11 The Digestive System (11.1 and 11.2) Biology 2201 Section 11.1 The chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms need food, and all foods contain nutrients. Nutrients are the substances that
Chapter 11 The Digestive System (11.1 and 11.2) Biology 2201 Section 11.1 The chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms need food, and all foods contain nutrients. Nutrients are the substances that
Primary Function. 1. Ingestion: food enters the system
 Digestive System Primary Function 1. Ingestion: food enters the system - Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins 2. Digestion: Further breakdown - Chemical/enzymatic 3. Absorption: Nutrients enter circulatory
Digestive System Primary Function 1. Ingestion: food enters the system - Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins 2. Digestion: Further breakdown - Chemical/enzymatic 3. Absorption: Nutrients enter circulatory
Anatomy & Physiology Digestive System
 Anatomy & Physiology Digestive System I. Nutrition A. chemical substance that is needed by the body for normal growth, maintenance & repair. Two categories 1. needed in large amounts. Carbohydrates, Lipids
Anatomy & Physiology Digestive System I. Nutrition A. chemical substance that is needed by the body for normal growth, maintenance & repair. Two categories 1. needed in large amounts. Carbohydrates, Lipids
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
