The nutrient formulas used for parenteral nutrition are
|
|
|
- Lionel Thomas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CASE REPORT Possible Incompatibility between Amino Acids and Copper in Solutions for Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition Maxime Thibault INTRODUCTION The nutrient formulas used for parenteral nutrition are highly complex admixtures of multiple solutions, infused by the IV route to patients who are unable to receive nutrition by mouth or by the enteral route. The administered products contain macronutrients (amino acids, dextrose, and lipids), electrolytes (sodium, potassium, calcium, phosphate, magnesium, chloride, and acetate), micronutrients (vitamins, trace elements), and water. The solution for parenteral administration can be prepared as a 2-in-1 solution, with lipids being infused separately from the other components, or as a 3-in-1 admixture, in which all components are mixed together. 1 The complexity of these solutions poses a significant risk of incompatibility between components. The most widely known incompatibility involving components of parenteral nutrition solutions is precipitation of calcium phosphate. In 1994, the US Food and Drug Administration published a safety communication describing cases of incompatibility between calcium and phosphate in parenteral nutrition solutions, in which infusion of the solutions resulted in death (2 patients) or respiratory distress (2 patients). 2 Measures taken to prevent adverse events related to incompatibilities include the use of filters during infusion, specifically 0.22-µm filters for 2-in-1 solutions and 1.2-µm filters for 3-in-1 admixtures. For compounded parenteral nutrition solutions, components should be added in the same order every time, and contact between incompatible solutions should be minimized. 3 Specifically, phosphates should be added at the beginning of the mixing sequence, and calcium gluconate should be added last, such that the calcium is added when the volume of the solution being compounded is at its maximum. 1 The solubility of calcium phosphate should be evaluated for all parenteral nutrition orders, using validated solubility curves specific to the brand of amino acids used. 2 Pharmacists preparing and validating parenteral nutrition orders should always inspect bags for visually detectable precipitates before releasing them for infusion. 1 Unfortunately, the measures described above do not always prevent incompatibilities in parenteral nutrition solutions. This report describes visual observation of precipitates in 3 different parenteral nutrition solutions. CASES All parenteral nutrition solutions administered within the study hospital are prepared in the pharmacy in a laminar flow hood located in a clean room, in conformity with USP Chapter <797> guidelines. 4 All orders for parenteral nutrition are compounded daily, using a Baxa ExactaMix 2400 automated compounder (Baxa, Markham, Ontario; precision of delivery 0.01 ml). Each order is entered into a computer program, which validates all parameters related to the solution, including solubility of calcium phosphate. The mixing order of the components is in keeping with recommendations to avoid precipitation of calcium phosphate, and all bags are inspected visually before delivery. Two-in-one solutions are used exclusively, with lipids administered into the IV tubing via a Y-site connector placed beyond the 0.22-µm filter. All 2-in-1 bags are protected from light during infusion. 5 On a single day, the pharmacy was notified of 3 separate cases of a yellow brown substance accumulating on the 0.22-µm filter during administration of parenteral nutrition solutions. Visual examination of the filters showed an apparently solid brown substance suspended in the yellow 2-in-1 solution (Figure 1). The composition of each solution is presented in Table 1, and the corresponding prescriptions are shown in Table 2. A possible compatibility issue was suspected. The calcium and phosphate concentrations were within acceptable limits for the amino acid concentrations, so calcium 160 C J H P Vol. 67, No. 2 March April 2014 J C P H Vol. 67, n o 2 mars avril 2014
2 Table 1. Volumes of Components Used to Prepare Parenteral Nutrition Solutions that Exhibited Precipitate Solution; Volume of Component (ml) Component Solution 1 Solution 2 Solution 3 Pediatric amino acids 10% (Primene)* Dextrose 70%* Sterile water* Sodium chloride, 4 mmol/ml Sodium acetate, 4 mmol/ml Potassium acetate, 4 mmol/ml Calcium gluconate, mmol/ml Sodium glycerophosphate, mmol/ml Magnesium sulphate, 200 mg/ml Pediatric multivitamin (Multi-12/K1 Pediatric) Ranitidine, 25 mg/ml Copper, 100 µg/ml Iodine, 25 µg/ml Selenium, 10 µg/ml Zinc, 1 mg/ml Heparin, 100 units/ml Iron dextran, 1 mg/ml *Manufacturer: Baxter Corporation, Mississauga, Ontario. Manufacturer: Pharmaceutical Partners of Canada, Richmond Hill, Ontario. Manufacturer: Sandoz, Boucherville, Quebec. Manufacturer: Fresenius Kabi, Bad Homburg, Germany. Manufacturer: B-Braun Medical, Allentown, Pennsylvania. Table 2. Prescribed Composition of Parenteral Nutrition Solutions that Exhibited Precipitate Prescribed Component Solution 1 Solution 2 Solution 3 Child s weight* (kg) PN fluids prescribed, including lipids (ml/kg daily) Amino acids (g/kg daily) Dextrose (g/kg daily) Lipids (g/kg daily) Sodium (mmol/kg daily) Potassium (mmol/kg daily) Calcium (mmol/kg daily) Phosphate (mmol/kg daily) Magnesium (mmol/kg daily) % acetate (versus chloride) Multivitamins (ml/day) Ranitidine (mg/kg daily) Copper (µg/kg daily) Iodine (µg/kg daily) Selenium (µg/kg daily) Zinc (µg/kg daily) Heparin (units/ml) Iron (µg/kg daily) PN = parenteral nutrition. *As recorded on prescription. Not included in compounded solution; administered separately. C J H P Vol. 67, No. 2 March April 2014 J C P H Vol. 67, n o 2 mars avril
3 This single copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. Figure 1. Precipitate observed on a 0.22-µm filter used for administration of parenteral nutrition solution. phosphate precipitates were ruled out. Only 2 of the solutions contained iron, and only 2 contained heparin; therefore, these components were excluded as possible causes of the incompatibility. All 3 solutions contained the same brand of pediatric amino acids (Primene, Baxter Corporation, Mississauga, Ontario). All patients in the hospital were temporarily switched to a different brand of amino acids pending investigation of the issue. The precipitation problem did not recur after this switch. To determine the components responsible for the incompatibility, solution 1 was re-created in the pharmacy and infused in a mock clinical setting at the prescribed rate through a 0.22-µm filter. After the infusion was complete, the same substance was visible on the filter as was observed in the sentinel cases. Modified solutions were compounded and tested, one with a different brand of amino acids (Travasol Blend C, Baxter Corporation, Mississauga, Ontario), one without phosphate, one without multivitamins, and one without trace elements. The solutions without phosphate or multivitamins produced a precipitate similar to the case findings, but the solution with different amino acids and the solution without trace elements failed to produce the precipitate, which suggested possible contributions from these components (Figure 2). A subsequent series of identical solutions were prepared, with each solution excluding one of the trace elements (copper, iodine, selenium, or zinc.) All of these solutions produced the precipitate with filtering, except the solution devoid of copper (Micro Cu, Sandoz, Boucherville, Quebec). To investigate the role of admixture concentration in causing the precipitate, a more dilute solution was compounded, using the same quantity of additives, including all trace elements, and twice the amount of diluent. This solution failed to produce the precipitate when filtered (Figure 3). 162 C J H P Vol. 67, No. 2 March April 2014 Figure 2. Filter (0.22 µm) after infusion of parenteral solution prepared with a different brand of amino acids. Figure 3. Filter (0.22 µm) after infusion of diluted parenteral nutrition solution. The issue was reported to the manufacturer of the amino acid product. Each of the 3 parenteral nutrition solutions had been partially infused to the patient for whom it had been prescribed, but none of the patients reported symptoms or presented signs that could be attributed to infusion of the precipitate. No additional laboratory tests or imaging studies were performed because of the absence of clinical manifestations. It was hypothesized that the use of 0.22-µm filters prevented the precipitate from reaching the patients. DISCUSSION In test situations with variants of one of the solutions involved in the sentinel cases, no precipitate was observed when J C P H Vol. 67, no 2 mars avril 2014
4 a different amino acid preparation was used or when copper was omitted. On the basis of these results the observed problem was attributed to an incompatibility between the specific type of amino acids used in the original solutions and cupric sulphate. Compared with the alternative product that did not cause precipitation, the amino acid solution implicated in the 3 sentinel cases contained cysteine and had a lower ph. This type of amino acid solution is commonly used in neonatology, because the lower ph allows for better solubility of calcium phosphate and because cysteine has been described as a conditionally essential amino acid in this population. 6 It is possible that the incompatibility could be a result of these features of the amino acid solution. Testing excluded heparin, iron, multivitamins, phosphate, selenium, iodine, and zinc as direct causes of the incompatibility, because the precipitate was observed in solutions prepared without these components. Copper is an essential trace element that must be added to parenteral nutrition solutions, especially for patients receiving little or no nutrition by other means. Copper deficiency may lead to hematologic disturbances, bone abnormalities, and other problems, all of which have been observed in patients receiving copper-free parenteral nutrition. 7,8 Removing copper from the solution would therefore be inappropriate in this situation. In a previous study of trace element stability in parenteral nutrition solutions, Allwood and others 9 found that use of cysteine-containing amino acid solutions in conjunction with copper might be problematic. The study authors suggested 2 hypotheses to explain this type of precipitation 9 : a direct reaction between copper and cysteine resulting in precipitation of copper cysteinate or a reaction between hydrogen sulphide (produced by degradation of cysteine to cystine during thermal sterilization) and copper to produce a precipitate of copper sulphide. In another study, 10 solutions prepared with amino acids that did not contain cysteine did not exhibit this type of precipitate. Precipitation did not seem to occur in the diluted test solution, so concentration may be a factor in the observed reaction. The 3 parenteral nutrition solutions involved in the sentinel cases contained higher concentrations of copper and other trace elements than the hospital s usual formulations because they were destined for administration to patients who were in transition from parenteral to enteral or oral nutrition. It was clinically desirable for these patients to receive less water than usual via the parenteral route, but they received the full dose of copper, since it is common practice to provide the full recommended daily doses of trace elements up to discontinuation of parenteral nutrition. The most dilute solution exhibiting a precipitate in the sentinel cases provided 101 ml/kg of fluids and 20 µg/kg of copper daily. In comparison, premature infants in neonatology, where the implicated amino acid solution is commonly used, typically receive between 120 and 160 ml/kg of fluids daily. 11 In the study by Allwood and others, 9 precipitate was not observed in a parenteral nutrition solution prepared with cysteine-containing amino acids and a product containing less copper (Peditrace, Pharmacia and Upjohn Ltd; 54 µg/ml copper chloride or 20 µg/ml elemental copper). The copper concentration in this solution, calculated in terms of elemental copper, amounted to about 157 µg/l. The diluted parenteral nutrition solution that was tested in the current study would have provided 117 ml/kg of fluids per day and 20 µg/kg of copper per day, which corresponds to a copper concentration of about 170 µg/l. However, lack of visual observation of a precipitate does not rule out precipitation, because some precipitates cannot be detected visually. 12 Allwood and others 9 excluded precipitates from their test solution using a complex method that involved filtering the entire solution with a 0.45-µm filter and examining the filter for precipitates with X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy coupled to scanning electron microscopy. Following application of this methodology, no precipitate was found in their test solution. For certain incompatibilities, temperature may affect the likelihood of precipitation. Generally, an increase in temperature increases solubility. However, for calcium phosphate, an increase in temperature favours precipitation. This phenomenon was highlighted in a previous report, which described body heat causing precipitation of calcium phosphate after the solution had passed through an in-line 0.22-µm filter, ultimately resulting in occlusion of the catheter. 13 However, subsequent analysis indicated that the compounded solution exceeded calcium phosphate solubility curves, which may have contributed to the precipitation. 2 The effect of temperature was not explored in the 3 cases described here. It is possible that body heat affects the likelihood of precipitation, in which case the use of filters would not prevent adverse events. CONCLUSION This report has described a possible incompatibility between a cysteine-containing pediatric amino acid solution commonly used in neonatology and cupric sulphate in parenteral nutrition solutions. This incompatibility could potentially be avoided by limiting the copper concentration. Further investigations should aim to determine the exact mechanism by which the precipitate is formed and to provide more specific recommendations to avoid precipitation. Until better recommendations are available, it is considered prudent to limit the concentration of elemental copper to a maximum of 157 µg/l when using low-ph, cysteine-containing amino acid solutions. A 0.22-µm filter should always be used when infusing 2-in-1 solutions, and a 1.2-µm filter should always be used for 3-in-1 solutions. C J H P Vol. 67, No. 2 March April 2014 J C P H Vol. 67, n o 2 mars avril
5 References 1. Mirtallo J, Canada T, Johnson D, Kumpf V, Petersen C, Sacks G, et al.; Task Force for the Revision of Safe Practices for Parenteral Nutrition. Safe practices for parenteral nutrition. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2004; 28(6):S Newton DW, Driscoll DF. Calcium and phosphate compatibility: revisited again. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2008;65(1): ASHP guidelines on the safe use of automated compounding devices for the preparation of parenteral nutrition admixtures. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2000;57(14): Curtis C, Sacks GS. Compounding parenteral nutrition: reducing the risks. Nutr Clin Pract. 2009;24(4): Lavoie PM, Lavoie JC, Watson C, Rouleau T, Chang BA, Chessex P. Inflammatory response in preterm infants is induced early in life by oxygen and modulated by total parenteral nutrition. Pediatr Res. 2010;68(3): Soghier LM, Brion LP. Cysteine, cystine or N-acetylcysteine supplementation in parenterally fed neonates. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;(4): CD Blackmer AB, Bailey E. Management of copper deficiency in cholestatic infants: review of the literature and a case series. Nutr Clin Pract. 2012;28(1): Shike M. Copper in parenteral nutrition. Gastroenterology. 2009;137(5 Suppl):S Allwood MC, Martin H, Greenwood M, Maunder M. Precipitation of trace elements in parenteral nutrition mixtures. Clin Nutr. 1998;17(5): Boddapati S, Yang K, Murty R. Intravenous solution compatibility and filter-retention characteristics of trace-element preparations. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1981;38(11): Corkins MR, Balint J; Pediatric nutrition support handbook. Silver Spring (MD): American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition; Melchore JA. Sound practices for consistent human visual inspection. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2011;12(1): Robinson LA, Wright BT. Central venous catheter occlusion caused by body-heat-mediated calcium phosphate precipitation. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1982;39(1): Maxime Thibault, BPharm, MSc, CNSC, is a Pharmacist with the Centre hospitalier universitaire Sainte-Justine, Montréal, Quebec. Competing interests: None declared. Address correspondence to: Maxime Thibault CHU Sainte-Justine 3175, chemin Côte-Sainte-Catherine Montréal QC H3T 1C5 maxime.thibault.hsj@ssss.gouv.qc.ca Advertisers Index Ad Page Prescribing Information Alveda Pharma / Corporate IFC Baxter / Corporate 99 Pfizer / Injectables 94 Pfizer / Injectables 96 Pharmaceutical Partners of Canada / Corporate OBC 164 C J H P Vol. 67, No. 2 March April 2014 J C P H Vol. 67, n o 2 mars avril 2014
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition
 Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
Risk Management in Parenteral Nutrition. J. Boullata
 Risk Management in Parenteral Nutrition J. Boullata Objectives Upon completion of this session, the participant will be able to: Describe safety issues with parenteral nutrition (PN) Present the PN-use
Risk Management in Parenteral Nutrition J. Boullata Objectives Upon completion of this session, the participant will be able to: Describe safety issues with parenteral nutrition (PN) Present the PN-use
Stability of micronutrients in PN what is known and what can be claimed? Prof. Mike.Allwood Pharmacy Consultant
 Stability of micronutrients in PN what is known and what can be claimed? Prof. Mike.Allwood Pharmacy Consultant Pharmaceutical interactions 1. Physical incompatibility = precipitation Caused by: Certain
Stability of micronutrients in PN what is known and what can be claimed? Prof. Mike.Allwood Pharmacy Consultant Pharmaceutical interactions 1. Physical incompatibility = precipitation Caused by: Certain
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 19 October 2011
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 October 2011 PEDIAVEN AP-HP G15, solution for infusion 1000 ml of solution in two chamber bag, B/4 (CIP code: 419
Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success
 Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success Mandy Corrigan, MPH, RD, CNSC Nutrition Support Clinician mandycorrigan1@gmail.com
Ensuring Safe Management of Parenteral Nutrition During Drug Shortages: Strategies and Protocols for Enabling Clinician Success Mandy Corrigan, MPH, RD, CNSC Nutrition Support Clinician mandycorrigan1@gmail.com
The Drug Shortage Crisis
 Objectives: The Drug Shortage Crisis Jay M. Mirtallo, MS, RPh, BCNSP, FASHP Director, MS in Health System Pharmacy Associate Professor of Clinical Pharmacy The Ohio State University, College of Pharmacy
Objectives: The Drug Shortage Crisis Jay M. Mirtallo, MS, RPh, BCNSP, FASHP Director, MS in Health System Pharmacy Associate Professor of Clinical Pharmacy The Ohio State University, College of Pharmacy
Solubility Study of Zinc and Phosphates in PN and IV Fluid. Rex Speerhas, RPh, BCNSP Nutrition Support Clinical Specialist
 Solubility Study of Zinc and Phosphates in PN and IV Fluid Rex Speerhas, RPh, BCNSP Nutrition Support Clinical Specialist What is that Brown Precipitate? What is that Brown Precipitate? Background Home
Solubility Study of Zinc and Phosphates in PN and IV Fluid Rex Speerhas, RPh, BCNSP Nutrition Support Clinical Specialist What is that Brown Precipitate? What is that Brown Precipitate? Background Home
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick Neonatal Pharmacist
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition. J. Eastwood (UK)
 ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 Pharmaceutical Session Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition J. Eastwood (UK) Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition
ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 Pharmaceutical Session Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition J. Eastwood (UK) Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention?
 Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
ASEPTIC DISPENSING TECHNIQUES/DRUG- NUTRIENT INTERACTIONS
 ASEPTIC DISPENSING TECHNIQUES/DRUG- NUTRIENT INTERACTIONS HARBANS KAUR DHILLON PRESIDENT OF PENSMA KUALA LUMPUR MALAYSIA PENSA 2007 University Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur ASEPTIC DISPENSING Ppn
ASEPTIC DISPENSING TECHNIQUES/DRUG- NUTRIENT INTERACTIONS HARBANS KAUR DHILLON PRESIDENT OF PENSMA KUALA LUMPUR MALAYSIA PENSA 2007 University Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur ASEPTIC DISPENSING Ppn
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
Review and comments on the 2014 recommendations for parenteral nutrition usage by ASPEN
 105 Review and comments on the 2014 recommendations for parenteral nutrition usage by ASPEN Submitted: August 10, 2015 Posted: August 31, 2015 Author: Luisito Llido, MD Clinical Nutrition Service, St.
105 Review and comments on the 2014 recommendations for parenteral nutrition usage by ASPEN Submitted: August 10, 2015 Posted: August 31, 2015 Author: Luisito Llido, MD Clinical Nutrition Service, St.
Parenteral Nutrition
 Parenteral Nutrition Standard Operating Procedures Stony Brook University Hospital Pharmacy Department Authors and Contributors: Amanda Waldeck, PharmD, BCPS Nutrition Support Pharmacist Alfredo Viera
Parenteral Nutrition Standard Operating Procedures Stony Brook University Hospital Pharmacy Department Authors and Contributors: Amanda Waldeck, PharmD, BCPS Nutrition Support Pharmacist Alfredo Viera
Section 8.4 Special Dilutions
 Section 8.4 Special Dilutions Terminology: Diluent: Pediatric Compound Sterile Preparations (CSPs): Special Dilutions: Calculating Special Dilutions: Ratio-Proportion vs Dimensional Analysis Part A Calculating
Section 8.4 Special Dilutions Terminology: Diluent: Pediatric Compound Sterile Preparations (CSPs): Special Dilutions: Calculating Special Dilutions: Ratio-Proportion vs Dimensional Analysis Part A Calculating
What s In The Bag? 3-in-1 versus 2-in-1 PN
 What s In The Bag? 3-in-1 versus 2-in-1 PN Amber Verdell, PharmD, BCPS, BCNSP Assistant Professor, Pharmacy Practice West Coast University, Los Angeles, CA Disclosures I have no commercial relationships
What s In The Bag? 3-in-1 versus 2-in-1 PN Amber Verdell, PharmD, BCPS, BCNSP Assistant Professor, Pharmacy Practice West Coast University, Los Angeles, CA Disclosures I have no commercial relationships
Common Infusions for Neonatal Use
 Common Infusions for Neonatal Use Document Title and Reference : Common Infusions for Neonatal Use Main Author (s) Dr N B Soni Ratified by: LSC CEG Date Ratified: May 2016 Review Date: May 2018 Version:
Common Infusions for Neonatal Use Document Title and Reference : Common Infusions for Neonatal Use Main Author (s) Dr N B Soni Ratified by: LSC CEG Date Ratified: May 2016 Review Date: May 2018 Version:
DISCLOSURE. Learning Objectives. Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition
 Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
Controversies in Parenteral Nutrition Christopher Duggan, MD, MPH Center for Nutrition Center for Advanced Intestinal Rehabilitation (CAIR) Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Boston
Parenteral Nutrition. What is Parenteral Nutrition? Goals of Parenteral Nutrition
 Parenteral Nutrition Diamond Pharmacy Services What is Parenteral Nutrition? Intravenous feeding that provides a patient with fluids and essential nutrients during a time of gastrointestinal function disruption
Parenteral Nutrition Diamond Pharmacy Services What is Parenteral Nutrition? Intravenous feeding that provides a patient with fluids and essential nutrients during a time of gastrointestinal function disruption
Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients
 Fluid Dextrose Amino acid Lipid Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients (Calculated for normal organ function and normal caloric requirements) PN orders are due by 11 AM daily Newborn
Fluid Dextrose Amino acid Lipid Parenteral Nutrition Recommendations for Pediatric Patients (Calculated for normal organ function and normal caloric requirements) PN orders are due by 11 AM daily Newborn
Phosphoremia (mmol/l) Calcemia (mmol/l) Postnatal age (days) Postnatal age (days) Urinary Calcium (mg/kg/d) Phosphoremia (mmol/l)
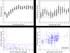 3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION. Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
ADULT ENTERAL NUTRITION PARENTERAL NUTRITION U.S. REGULATORY ENVIRONMENT THE INFANT FORMULA ACT OF The 1986 Amendments
 CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCTION... 1 STUDY GOALS AND OBJECTIVES... 1 REASONS FOR DOING THE STUDY... 1 SCOPE AND FORMAT... 1 METHODOLOGY AND INFORMATION SOURCES... 2 ANALYST CREDENTIALS... 2 RELATED BCC REPORTS...
CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCTION... 1 STUDY GOALS AND OBJECTIVES... 1 REASONS FOR DOING THE STUDY... 1 SCOPE AND FORMAT... 1 METHODOLOGY AND INFORMATION SOURCES... 2 ANALYST CREDENTIALS... 2 RELATED BCC REPORTS...
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT. Dr. Sarath Gopalan
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION - INDIAN CONTEXT Dr. Sarath Gopalan Senior Consultant in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi PN DELIVERY CENTRAL PERIPHERAL
Drug-Nutrition Interactions in Nutrition Support
 BAPEN Conference 2018 Harrogate Convention Centre Drug-Nutrition Interactions in Nutrition Support Joseph Boullata, PharmD, RPh, FASPEN, FACN Clinical Professor, Nutrition Sciences, Drexel University Pharmacy
BAPEN Conference 2018 Harrogate Convention Centre Drug-Nutrition Interactions in Nutrition Support Joseph Boullata, PharmD, RPh, FASPEN, FACN Clinical Professor, Nutrition Sciences, Drexel University Pharmacy
PRODUCT INFORMATION. DESCRIPTION Addaven is a concentrated trace element solution for infusion which is clear and colourless to slightly yellow.
 PRODUCT INFORMATION Addaven NAME OF MEDICINE Addaven is a concentrated trace element solution containing the following simple salts: chromic chloride hexahydrate (CAS No.:10060-12-5), cupric chloride dihydrate
PRODUCT INFORMATION Addaven NAME OF MEDICINE Addaven is a concentrated trace element solution containing the following simple salts: chromic chloride hexahydrate (CAS No.:10060-12-5), cupric chloride dihydrate
Vamin 18 EF QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 Title Page Information Dec. 2000 1 (7) Number Vamin 18 EF 121-01 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Vamin 18 g N/l electrolyte-free infusion fluid, solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000
Title Page Information Dec. 2000 1 (7) Number Vamin 18 EF 121-01 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Vamin 18 g N/l electrolyte-free infusion fluid, solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000
NOTE: The first appearance of terms in bold in the body of this document (except titles) are defined terms please refer to the Definitions section.
 TITLE PARENTERAL NUTRITION ADMINISTRATION AND MONITORING SCOPE Provincial: Acute Care APPROVAL AUTHORITY Clinical Operations Executive Committee SPONSOR Pharmacy Services, Nutrition Services, and Health
TITLE PARENTERAL NUTRITION ADMINISTRATION AND MONITORING SCOPE Provincial: Acute Care APPROVAL AUTHORITY Clinical Operations Executive Committee SPONSOR Pharmacy Services, Nutrition Services, and Health
Chromium and zinc contamination of parenteral nutrient solution components commonly used in infants and children
 Chromium and zinc contamination of parenteral nutrient solution components commonly used in infants and children EMILY B. HAK, MICHAEL C. STORM, AND RICHARD A. HELMS Abstract: Chromium and zinc contamination
Chromium and zinc contamination of parenteral nutrient solution components commonly used in infants and children EMILY B. HAK, MICHAEL C. STORM, AND RICHARD A. HELMS Abstract: Chromium and zinc contamination
U.S. AND GLOBAL MARKETS FOR ETHICAL NUTRITION IN HEALTHCARE
 U.S. AND GLOBAL MARKETS FOR ETHICAL NUTRITION IN HEALTHCARE FOD029E January 2015 Mary Anne Crandall Project Analyst ISBN: 1-62296-005-X BCC Research 49 Walnut Park, Building 2 Wellesley, MA 02481 USA 866-285-7215
U.S. AND GLOBAL MARKETS FOR ETHICAL NUTRITION IN HEALTHCARE FOD029E January 2015 Mary Anne Crandall Project Analyst ISBN: 1-62296-005-X BCC Research 49 Walnut Park, Building 2 Wellesley, MA 02481 USA 866-285-7215
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 19 March Date of the Marketing Authorisation (national procedure): 18 December 1997
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 March 2008 INTRALIPIDE 20 PER CENT, emulsion for infusion 100 ml in Excel container (PE/PP) (CIP: 355 096-5) 250
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 March 2008 INTRALIPIDE 20 PER CENT, emulsion for infusion 100 ml in Excel container (PE/PP) (CIP: 355 096-5) 250
Order Entry & Calculation Software
 Order Entry & Calculation Software COUNT ON ABACUS SOFTWARE FOR EASY TPN CALCULATION AND SAFE COMPOUNDING AT THE TOUCH OF A FINGER DESIGNED BY HOSPITAL PHARMACISTS, ABACUS promotes dose safety and reduces
Order Entry & Calculation Software COUNT ON ABACUS SOFTWARE FOR EASY TPN CALCULATION AND SAFE COMPOUNDING AT THE TOUCH OF A FINGER DESIGNED BY HOSPITAL PHARMACISTS, ABACUS promotes dose safety and reduces
THE AUTHOR OF THIS WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE: PARENTERAL NUTRITION (PN)
 WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? Alisha Mutch, Pharm.D., BCPS THE AUTHOR OF THIS PRESENTATION HAS NOTHING TO DISCLOSE. OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES Indicate when parenteral nutrition (PN) is warranted
WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? Alisha Mutch, Pharm.D., BCPS THE AUTHOR OF THIS PRESENTATION HAS NOTHING TO DISCLOSE. OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES Indicate when parenteral nutrition (PN) is warranted
Standards of Practice for Nutrition Support Pharmacists
 Standards Standards of Practice for Nutrition Support Pharmacists Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.) Task Force for Revision of Nutrition Support Pharmacist Standards: Carol Rollins, MS, PharmD, BCNSP Chair; Sharon
Standards Standards of Practice for Nutrition Support Pharmacists Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.) Task Force for Revision of Nutrition Support Pharmacist Standards: Carol Rollins, MS, PharmD, BCNSP Chair; Sharon
2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY 3. COMPOSITION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT ml of the solution for infusion contain:
 Title Page Information June 1999 1 (5) Aminoven infant 10% 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aminoven infant 10% 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only
Title Page Information June 1999 1 (5) Aminoven infant 10% 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aminoven infant 10% 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET
 1. PRODUCT NAME ADDAVEN (infusion, solution concentrate) NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each 10 ml ampoule of Addaven contains: Chromic chloride hexahydrate 53.33 µg
1. PRODUCT NAME ADDAVEN (infusion, solution concentrate) NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each 10 ml ampoule of Addaven contains: Chromic chloride hexahydrate 53.33 µg
Overview of the Parenteral Nutrition Process and use of PN in Long Term Care
 Disclosures The speaker is an employee of Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC Overview of the Parenteral Process and use of PN in Long Term Alyce Newton, MS, RDN, LDN, CNSC Medical Science Liaison Fresenius Kabi USA,
Disclosures The speaker is an employee of Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC Overview of the Parenteral Process and use of PN in Long Term Alyce Newton, MS, RDN, LDN, CNSC Medical Science Liaison Fresenius Kabi USA,
Package leaflet: Information for the user. multibic potassium-free solution for haemodialysis/haemofiltration
 Package leaflet: Information for the user multibic potassium-free solution for haemodialysis/haemofiltration Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains
Package leaflet: Information for the user multibic potassium-free solution for haemodialysis/haemofiltration Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition. in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT. Dzulfikar DLH. Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit
 The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY 3. COMPOSITION OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 Title Page Product Information May 2000 1 (6) Product Nephrotect 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Nephrotect 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only 3.
Title Page Product Information May 2000 1 (6) Product Nephrotect 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Nephrotect 2. PRESCRIPTION STATUS/RESTRICTION OF SALES TO PHARMACIES ONLY For sale in pharmacies only 3.
Parenteral Nutrition
 Approved by: Parenteral Nutrition Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual :
Approved by: Parenteral Nutrition Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual :
Vanessa Kumpf, PharmD, BCNSP Clinical Pharmacist Center for Human Nutri;on
 Vanessa Kumpf, PharmD, BCNSP Clinical Pharmacist Center for Human Nutri;on Learn what you can do to: Maximize TPN benefits Minimize TPN-related problems Learn how to monitor your therapy Learn how to read
Vanessa Kumpf, PharmD, BCNSP Clinical Pharmacist Center for Human Nutri;on Learn what you can do to: Maximize TPN benefits Minimize TPN-related problems Learn how to monitor your therapy Learn how to read
Prevention of Transcription Errors with Pediatric TPN Orders Using a Web Interface
 Prevention of Transcription Errors with Pediatric TPN Orders Using a Web Interface Organization Name: University of Maryland Type: Acute Care Hospital Medical Center Contact Person: Belinda Todjo, PharmD
Prevention of Transcription Errors with Pediatric TPN Orders Using a Web Interface Organization Name: University of Maryland Type: Acute Care Hospital Medical Center Contact Person: Belinda Todjo, PharmD
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION L-Leucine Ph. Eur 0.620% w/v L-Isoleucine
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Synthamin 14, 8.5% Amino Acid Intravenous Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION L-Leucine Ph. Eur 0.620% w/v L-Isoleucine
48 th Annual Meeting. A Review of Pharmacy Calculations for Pharmacy Technicians. Metric System of Measurement. Disclosure. Common Conversions
 48 th Annual Meeting A Review of Pharmacy Calculations for Pharmacy Technicians Nina Pavuluri, Ph.D. Navigating the Oceans of Opportunity Metric System of Measurement Base Unit Factor Name Symbol 1 (g,
48 th Annual Meeting A Review of Pharmacy Calculations for Pharmacy Technicians Nina Pavuluri, Ph.D. Navigating the Oceans of Opportunity Metric System of Measurement Base Unit Factor Name Symbol 1 (g,
Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ
 Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ Outline Refeeding Syndrome What is refeeding syndrome? What Electrolytes and minerals are involved? Who is at risk? How to manage
Prevention of Electrolyte Disorders Refeeding Syndrome พญ.น นทพร เต มพรเล ศ Outline Refeeding Syndrome What is refeeding syndrome? What Electrolytes and minerals are involved? Who is at risk? How to manage
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION. Dextrose Injection USP. (Concentrated Dextrose for Intravenous Administration) 50% (500 mg/ml) Fluid and Nutrient Replenisher
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Dextrose Injection USP (Concentrated Dextrose for Intravenous Administration) 50% (500 mg/ml) Fluid and Nutrient Replenisher Pfizer Canada Inc. 17300 Trans-Canada Highway Kirkland,
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Dextrose Injection USP (Concentrated Dextrose for Intravenous Administration) 50% (500 mg/ml) Fluid and Nutrient Replenisher Pfizer Canada Inc. 17300 Trans-Canada Highway Kirkland,
A STANDARD PROTOCOL for DERIVATION and ASSESSMENT of STABILITY. Part 4 Parenteral Nutrition
 A STANDARD PROTOCOL for DERIVATION and ASSESSMENT of STABILITY Part 4 Parenteral Nutrition 1 st Edition May 2016 NHS Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Committee 2016 This document has been produced on behalf
A STANDARD PROTOCOL for DERIVATION and ASSESSMENT of STABILITY Part 4 Parenteral Nutrition 1 st Edition May 2016 NHS Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Committee 2016 This document has been produced on behalf
STANDARD FORMULATED SUPPLEMENTARY SPORTS FOODS
 STANDARD 2.9.4 FORMULATED SUPPLEMENTARY SPORTS FOODS Purpose This Standard defines and regulates the composition and labelling of foods specially formulated to assist sports people in achieving specific
STANDARD 2.9.4 FORMULATED SUPPLEMENTARY SPORTS FOODS Purpose This Standard defines and regulates the composition and labelling of foods specially formulated to assist sports people in achieving specific
Preparing parenteral nutrition
 ar Layar NOTES Using failure mode and effects analysis to improve the safety of neonatal parenteral nutrition Preparing parenteral nutrition (PN) is a complex combination of high-risk activities. It is
ar Layar NOTES Using failure mode and effects analysis to improve the safety of neonatal parenteral nutrition Preparing parenteral nutrition (PN) is a complex combination of high-risk activities. It is
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018
 ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 Lipid Emulsions In Parenteral Nutrition The Abc Of Parenteral Lipid Emulsions P. Austin (UK) ESPEN Congress, Madrid, September 2018 The ABC of parenteral lipid emulsions Dr Peter
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 Lipid Emulsions In Parenteral Nutrition The Abc Of Parenteral Lipid Emulsions P. Austin (UK) ESPEN Congress, Madrid, September 2018 The ABC of parenteral lipid emulsions Dr Peter
Module 8: Practice Problems
 Module 8: Practice Problems 1. Convert a blood plasma level range of 5 to 20 µg/ml of tobramycin (Z = 467.52) to µmol/l. 5 µg/ml = 10.7 µmol/l 20 µg/ml = 42.8 µmol/l 2. A preparation contains in each milliliter,
Module 8: Practice Problems 1. Convert a blood plasma level range of 5 to 20 µg/ml of tobramycin (Z = 467.52) to µmol/l. 5 µg/ml = 10.7 µmol/l 20 µg/ml = 42.8 µmol/l 2. A preparation contains in each milliliter,
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH. TRAVASOL Amino Acid Injections WITH ELECTROLYTES. TRAVASOL Amino Acid Injections WITHOUT ELECTROLYTES
 1 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH TRAVASOL Amino Acid Injections WITH ELECTROLYTES TRAVASOL Amino Acid Injections WITHOUT ELECTROLYTES TRAVASOL AMINO ACID INJECTIONS AND DEXTROSE Intravenous Nutritive Supplements BAXTER
1 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH TRAVASOL Amino Acid Injections WITH ELECTROLYTES TRAVASOL Amino Acid Injections WITHOUT ELECTROLYTES TRAVASOL AMINO ACID INJECTIONS AND DEXTROSE Intravenous Nutritive Supplements BAXTER
PACKAGE INSERT CALCIUM GLUCONATE INJECTION, USP 10% Electrolyte Replenisher mosmol/ml 680 mosmol/l Ca meq/ml ph
 CALCIUM GLUCONATE INJECTION, USP 10% Electrolyte Replenisher 0.68 mosmol/ml 680 mosmol/l Ca ++ 0.465 meq/ml ph 6.0 8.2 DESCRIPTION Calcium Gluconate Injection, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic supersaturated
CALCIUM GLUCONATE INJECTION, USP 10% Electrolyte Replenisher 0.68 mosmol/ml 680 mosmol/l Ca ++ 0.465 meq/ml ph 6.0 8.2 DESCRIPTION Calcium Gluconate Injection, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic supersaturated
Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet
 1 Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1 Name of Guideline / Policy/ Procedure MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE PAEDIATRIC ASTHMA Purpose of Procedure/
1 Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1 Name of Guideline / Policy/ Procedure MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE PAEDIATRIC ASTHMA Purpose of Procedure/
Dextrose 5 normal saline and metronidazole compatible
 Search Dextrose 5 normal saline and metronidazole compatible Flagyl compatible with dextrose. Dextrose 5 %. Metronidazole.. Free download as. 6% in D5W or normal saline Compatible in water not NS 1 2 2
Search Dextrose 5 normal saline and metronidazole compatible Flagyl compatible with dextrose. Dextrose 5 %. Metronidazole.. Free download as. 6% in D5W or normal saline Compatible in water not NS 1 2 2
Aminosteril N-Hepa 8%, solution for infusion. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 Title Page Information Aminosteril N-Hepa 8% November 2001 1 (7) 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aminosteril N-Hepa 8%, solution for infusion. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000 ml solution
Title Page Information Aminosteril N-Hepa 8% November 2001 1 (7) 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Aminosteril N-Hepa 8%, solution for infusion. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1000 ml solution
D.K.M COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS) VELLORE-1 DEPARTMENT OF FOODS AND NUTRITION ESSENTIAL OF MICRO NUTRIENTS
 D.K.M COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS) VELLORE-1 DEPARTMENT OF FOODS AND NUTRITION ESSENTIAL OF MICRO NUTRIENTS Class: II M.Sc Subject Code: 15CPFN3A Unit - I (6 Marks Questions) 1. Write a note on performed
D.K.M COLLEGE FOR WOMEN (AUTONOMOUS) VELLORE-1 DEPARTMENT OF FOODS AND NUTRITION ESSENTIAL OF MICRO NUTRIENTS Class: II M.Sc Subject Code: 15CPFN3A Unit - I (6 Marks Questions) 1. Write a note on performed
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management
 Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
Short Bowel Syndrome: Medical management La Sindrome dell'intestino Corto in età pediatrica Brescia 18 marzo 2011 Jon A.Vanderhoof, M.D. Division of Pediatric GI Harvard Medical School Children s Hospital,
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants. Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital
 Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Nutrition JMRSO 2017 FOOD SCIENCE
 Nutrition JMRSO 2017 FOOD SCIENCE What is nutrition? Nutrition is the science that interprets the interaction of nutrients and other substances in food in relation to maintenance, growth, reproduction,
Nutrition JMRSO 2017 FOOD SCIENCE What is nutrition? Nutrition is the science that interprets the interaction of nutrients and other substances in food in relation to maintenance, growth, reproduction,
E.N : Tubal Feeding Systems ; Closed vs. Open
 E.N : Tubal Feeding Systems ; Closed vs. Open Dr:Enas Mogawer, MD Head Of Clinical Nutrition Department,AFSH Professor Of Internal Medicine Kasr El Aini Medical Consultant Of Clinical Nutrition And Obesity
E.N : Tubal Feeding Systems ; Closed vs. Open Dr:Enas Mogawer, MD Head Of Clinical Nutrition Department,AFSH Professor Of Internal Medicine Kasr El Aini Medical Consultant Of Clinical Nutrition And Obesity
11/4/10 SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP SAM: PREVENT MALNUTRITION 200. Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure
 Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Parenteral Micronutrient Recommendations and Laboratory Monitoring for Infants on Long Term Parenteral Nutrition (PN)
 Parenteral Micronutrient Recommendations and Laboratory Monitoring for nfants on Long Term Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Dosage Micronutrient Preterm Term Trace Elements (mcg/kg/day) (mcg/kg/day) 1 Chromium
Parenteral Micronutrient Recommendations and Laboratory Monitoring for nfants on Long Term Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Dosage Micronutrient Preterm Term Trace Elements (mcg/kg/day) (mcg/kg/day) 1 Chromium
Food for special medical purposes. phenylketonuria (PKU) Important notice: Suitable only for individuals with proven phenylketonuria.
 PKU Nutri 1 Energy Food for special medical purposes. For the dietary management of proven phenylketonuria (PKU) in infants from birth to 12 months and as a supplementary feed up to 3 years. An amino acid
PKU Nutri 1 Energy Food for special medical purposes. For the dietary management of proven phenylketonuria (PKU) in infants from birth to 12 months and as a supplementary feed up to 3 years. An amino acid
BROILER. Nutrition Specifications. An Aviagen Brand
 BROILER 708 Nutrition Specifications 2014 An Aviagen Brand Introduction Nutrition specifications for Ross 708 broilers are given in the following tables for a range of production and market situations
BROILER 708 Nutrition Specifications 2014 An Aviagen Brand Introduction Nutrition specifications for Ross 708 broilers are given in the following tables for a range of production and market situations
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION CONTRAINDICATIONS
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DEXTROSE INJECTION 20%, 30%, 40%, 50% and 70% safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DEXTROSE INJECTION 20%, 30%, 40%, 50% and 70% safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
COBIS Nutrition in Thermal Injuries PAEDIATRIC
 COBIS Nutrition in Thermal Injuries PAEDIATRIC 1 NUTRITIONAL MANAGEMENT OF PAEDIATRIC BURNS PATIENTS Aims of Nutritional Support in Burns To promote optimal wound healing To maintain lean body mass To
COBIS Nutrition in Thermal Injuries PAEDIATRIC 1 NUTRITIONAL MANAGEMENT OF PAEDIATRIC BURNS PATIENTS Aims of Nutritional Support in Burns To promote optimal wound healing To maintain lean body mass To
Product Information: EleCare (for Infants)
 1 of 5 Product Information: 2 of 5 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who cannot tolerate intact or hydrolyzed protein. EleCare is indicated for the dietary management
1 of 5 Product Information: 2 of 5 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who cannot tolerate intact or hydrolyzed protein. EleCare is indicated for the dietary management
Package leaflet: Information for the patient
 Package leaflet: Information for the patient KLORUR NATRIUMI Solution for injection 1000 mg / 10 ml (10 %) Solution for injection 85 mg / 10 ml (0.85 %) Solution for infusion 0.9% (Sodium chloride) Read
Package leaflet: Information for the patient KLORUR NATRIUMI Solution for injection 1000 mg / 10 ml (10 %) Solution for injection 85 mg / 10 ml (0.85 %) Solution for infusion 0.9% (Sodium chloride) Read
Pr Pascal BONNABRY Head of pharmacy
 Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Evaluating the risk of aseptic preparations Pr Pascal BONNABRY Head of pharmacy Etre les premiers pour HPE Live, Birmingham vous September 9, 2014 Facts Medication errors
Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Evaluating the risk of aseptic preparations Pr Pascal BONNABRY Head of pharmacy Etre les premiers pour HPE Live, Birmingham vous September 9, 2014 Facts Medication errors
Product Category: EleCare
 EleCare Product Category: EleCare EleCare (for Infants) Updated 4/28/2016 Product Information: EleCare (for Infants) 1 of 4 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who
EleCare Product Category: EleCare EleCare (for Infants) Updated 4/28/2016 Product Information: EleCare (for Infants) 1 of 4 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete amino acid-based formula for infants who
LIPOSYN III 30% Intravenous Fat Emulsion Pharmacy Bulk Package Not for Direct Infusion.
 LIPOSYN III 30% Intravenous Fat Emulsion Pharmacy Bulk Package Not for Direct Infusion. R x only DESCRIPTION Liposyn III 30% (Intravenous Fat Emulsion) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic fat emulsion for intravenous
LIPOSYN III 30% Intravenous Fat Emulsion Pharmacy Bulk Package Not for Direct Infusion. R x only DESCRIPTION Liposyn III 30% (Intravenous Fat Emulsion) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic fat emulsion for intravenous
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT PRIMENE 10% 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each litre of the infusion solution contains: L-Isoleucine L-Leucine L-Valine
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT PRIMENE 10% 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each litre of the infusion solution contains: L-Isoleucine L-Leucine L-Valine
Product Information: Similac Special Care 24
 Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 1 of 5 A 24 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. Use under medical supervision. OptiGRO is our exclusive
Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 1 of 5 A 24 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. Use under medical supervision. OptiGRO is our exclusive
Broiler Nutrition Specifications
 Broiler Nutrition Specifications 2 Introduction 3 Table 1: Nutrition Specifications for As-Hatched Broilers - Target Live Weight
Broiler Nutrition Specifications 2 Introduction 3 Table 1: Nutrition Specifications for As-Hatched Broilers - Target Live Weight
Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition
 Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Audis Bethea, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor Therapeutics I December 5 & 9, 2003 Parenteral Nutrition Definition process of supplying nutrients via the intravenous route
Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Audis Bethea, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor Therapeutics I December 5 & 9, 2003 Parenteral Nutrition Definition process of supplying nutrients via the intravenous route
Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 High Protein
 Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 High Protein 1 of 5 A 24 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants who may need extra protein to help support
Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 High Protein 1 of 5 A 24 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants who may need extra protein to help support
PHARMACY DOSING AND ORDERING GUIDE
 PHARMACY DOSING AND ORDERING GUIDE FIRST AND ONLY APPROVED TREATMENT FOR PATIENTS WITH VOD WITH RENAL OR PULMONARY DYSFUNCTION POST HSCT VOD=veno-occlusive disease Indication Defitelio (defibrotide sodium)
PHARMACY DOSING AND ORDERING GUIDE FIRST AND ONLY APPROVED TREATMENT FOR PATIENTS WITH VOD WITH RENAL OR PULMONARY DYSFUNCTION POST HSCT VOD=veno-occlusive disease Indication Defitelio (defibrotide sodium)
ENDOTRACHEAL INTUBATION POLICY
 POLICY Indications: Ineffective ventilation with mask and t-piece, or mask and bag technique Inability to maintain a patent airway Need or anticipation of need for prolonged ventilation Need for endotracheal
POLICY Indications: Ineffective ventilation with mask and t-piece, or mask and bag technique Inability to maintain a patent airway Need or anticipation of need for prolonged ventilation Need for endotracheal
NHS Grampian Staff Guidance For The Management Of Hypomagnesaemia In Adults. Consultation Group: See Page 4. Review Date: June 2021
 NHS...... Grampian NHS Grampian Staff Guidance For The Management Of Hypomagnesaemia In Adults Co-ordinators: Consultation Group: Approver:. Senior Medicines Information Pharmacist See Page 4 Medicine
NHS...... Grampian NHS Grampian Staff Guidance For The Management Of Hypomagnesaemia In Adults Co-ordinators: Consultation Group: Approver:. Senior Medicines Information Pharmacist See Page 4 Medicine
codex alimentarius commission
 codex alimentarius commission FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION JOINT OFFICE: Viale delle Terme di Caracalla 00100 ROME Tel.: 39.06.57051 Telex: 625825-625853
codex alimentarius commission FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION JOINT OFFICE: Viale delle Terme di Caracalla 00100 ROME Tel.: 39.06.57051 Telex: 625825-625853
Re: Important changes to Fortisip Powder
 18 June 2014 Dear valued customer Nutricia Ltd 37 Banks Road, Mount Wellington Auckland, New Zealand PO Box 62 523 Greenlane, Auckland 1546 Tel: 0800 688 747 Re: Important changes to Fortisip Powder Nutricia
18 June 2014 Dear valued customer Nutricia Ltd 37 Banks Road, Mount Wellington Auckland, New Zealand PO Box 62 523 Greenlane, Auckland 1546 Tel: 0800 688 747 Re: Important changes to Fortisip Powder Nutricia
Ranger Gold. Parent Stock NUTRITION SPECIFICATIONS
 Ranger Gold Parent Stock NUTRITION SPECIFICATIONS Introduction This booklet contains the nutritional recommendations for Ranger Gold parent stock and is to be used with the Parent Stock Management Handbook
Ranger Gold Parent Stock NUTRITION SPECIFICATIONS Introduction This booklet contains the nutritional recommendations for Ranger Gold parent stock and is to be used with the Parent Stock Management Handbook
GUIDELINES FOR WEIGHT-BASED DOSING AND INFUSION
 GUIDELINES FOR WEIGHT-BASED DOSING AND INFUSION Includes Example dose calculation wheel Preparation and administration information for healthcare professionals Please see enclosed full Prescribing Information,
GUIDELINES FOR WEIGHT-BASED DOSING AND INFUSION Includes Example dose calculation wheel Preparation and administration information for healthcare professionals Please see enclosed full Prescribing Information,
APPENDIX 1 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SmPC Country: Lebanon Date of approval : 17/08/2011 Procedure : National APPENDIX 1 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1- NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT DECAN, concentrate for solution for infusion 2- QUALITATIVE
SmPC Country: Lebanon Date of approval : 17/08/2011 Procedure : National APPENDIX 1 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1- NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT DECAN, concentrate for solution for infusion 2- QUALITATIVE
INCOMPATIBILITY. Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève OF IV DRUGS : SOME CLINICAL HIGHLIGHTS. Dre Caroline Fonzo-Christe Pharmacie des HUG
 Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève INCOMPATIBILITY OF IV DRUGS : SOME CLINICAL HIGHLIGHTS Dre Caroline Fonzo-Christe Pharmacie des HUG Etre les premiers pour vous FACULTY DISCLOSURE 2 x No, nothing to disclose
Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève INCOMPATIBILITY OF IV DRUGS : SOME CLINICAL HIGHLIGHTS Dre Caroline Fonzo-Christe Pharmacie des HUG Etre les premiers pour vous FACULTY DISCLOSURE 2 x No, nothing to disclose
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION
 DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
Long term monitoring. Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital
 Long term monitoring Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital Patient 23 year old lady 1/4/14 Colectomy for UC 3-7/4/14 Ischaemic bowel 4 laparotomies Jejunostomy at 35 cm 23/5/14 Weight
Long term monitoring Dr Alison Culkin Research Dietitian St Mark s Hospital Patient 23 year old lady 1/4/14 Colectomy for UC 3-7/4/14 Ischaemic bowel 4 laparotomies Jejunostomy at 35 cm 23/5/14 Weight
Normosol -R and 5% Dextrose Injection MULTIPLE ELECTROLYTES AND 5% DEXTROSE INJECTION TYPE 1, USP For Replacing Acute Losses of Extracellular Fluid
 Normosol -R and 5% Dextrose Injection MULTIPLE ELECTROLYTES AND 5% DEXTROSE INJECTION TYPE 1, USP For Replacing Acute Losses of Extracellular Fluid R x only Flexible Plastic Container DESCRIPTION Normosol-R
Normosol -R and 5% Dextrose Injection MULTIPLE ELECTROLYTES AND 5% DEXTROSE INJECTION TYPE 1, USP For Replacing Acute Losses of Extracellular Fluid R x only Flexible Plastic Container DESCRIPTION Normosol-R
Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
Supplying Nutrients to Crops
 Supplying Nutrients to Crops What is Plant Nutrition? Plants need nutrients for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on
Supplying Nutrients to Crops What is Plant Nutrition? Plants need nutrients for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on
Product Information: Phenex -1
 Product Information: Phenex -1 1 of 5 For nutrition support of infants and toddlers with phenylketonuria (PKU). Phenylalanine-free Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine-free to allow greater intake
Product Information: Phenex -1 1 of 5 For nutrition support of infants and toddlers with phenylketonuria (PKU). Phenylalanine-free Use under medical supervision. Phenylalanine-free to allow greater intake
